Articles for week 47 2025
Detecting
the signature of helium reionization through 3HeII 3.46cm line-intensity
mapping
Link to the paper
Authors
- Benedetta Spina / Cristiano Porciani / Sarah E. I. Bosman /
Frederick B. Davies
- Enrico Garaldi / Ryan P. Keenan / Carlo Schimd
Summary
Helium reionization is the most recent phase change of the
intergalactic medium, yet its timing and main drivers remain uncertain.
Among the probes to trace its unfolding, the 3.46 cm hyperfine line of
singly-ionized helium opens the study of helium reionization to upcoming
radio surveys. We aim to evaluate the detectability of the 3.46,cm
signal with radio surveys and the possible constraints it can place on
helium reionization, in particular whether it can distinguish between
early and late helium reionization scenarios. Moreover, we perform a
comprehensive study of the advantages of single-dish vs. interferometric
setup. Using hydrodynamical simulations post-processed with radiative
transfer, we construct mock data cubes for two models of helium
reionization. We compute the power spectrum of the signal and forecast
the signal-to-noise ratio for SKA-1 MID, DSA-2000, and a PUMA-like
survey, in both observational setups. The two scenarios produce distinct
power spectra, but the faintness of the signal, largely caused by weak
coupling between the spin temperature and the kinetic temperature in
low-density regions of the IGM, combined with high instrumental noise,
makes detection very difficult within realistic integration times for
current surveys. A PUMA-like survey operating in single-dish mode could,
however, detect the 3.46 cm signal with an integrated signal-to-noise
ratio of a few in < 1000 h in both scenarios. Distinguishing helium
reionization scenarios with 3.46 cm line-intensity mapping therefore
remains challenging for current facilities. Our results, however,
indicate that next-generation, high-sensitivity surveys with optimized
observing strategies, especially when combined with complementary probes
of the IGM, could begin to place meaningful constraints on the timing
and morphology of helium reionization.
Multiphase
Astrophysics to Unveil the Virgo Environment (MAUVE)
Link to the paper
Authors
- Barbara Catinella / Luca Cortese / Jiayi Sun / Toby Brown
- Eric Emsellem / Amelia Fraser-McKelvie / Adam B. Watts / Amy
Attwater
- Andrew Battisti / Alessandro Boselli / Woorak Choi
/ Aeree Chung
- Elisabete da Cunha / Timothy A. Davis / Sara Ellison / Pavel
Jáchym
- Maria J. Jimenez-Donaire / Tutku Kolcu / Bumhyun Lee / James
McGregor
- Ian Roberts / Eva Schinnerer / Kristine Spekkens / Sabine
Thater
- David Thilker / Jesse van de Sande / Vicente Villanueva / Thomas G.
Williams
- Nikki Zabel
Summary
The Multiphase Astrophysics to Unveil the Virgo Environment (MAUVE)
project is a multi-facility programme exploring how dense environments
transform galaxies. Combining a VLT/MUSE P110 Large Programme and ALMA
observations of 40 late-type Virgo Cluster galaxies, MAUVE resolves star
formation, kinematics, and chemical enrichment within their molecular
gas discs. A key goal is to track the evolution of cold gas that
survives in the inner regions of satellites after entering the cluster,
and how it evolves across different infall stages. With its high spatial
resolution – probing down to the physical scales of giant molecular
cloud complexes – and multiphase synergy, MAUVE aims to offer a
time-resolved view of environmental quenching and set a new benchmark
for cluster galaxy studies.
Validation
of optical pathlength stability in a LISA test-bench demonstrator
Link to the paper
Authors
- Shivani Harer / Maxime Vincent / Hubert Halloin / Ouali Acef
- Nisrine Arab / Romain Arguel / Axel Arhancet / Damien Bachet
- Nathalie Besson / Sébastien Bize / Sara Bruhier / Christelle
Buy
- Michael Carle / Jean-Pierre Coulon / Nicoleta
Dinu-Jaeger / Mathieu Dupont
- Christophe Fabron / Rémi Granelli / David
Holleville / Dominique Huet
- Eric Kajfasz / Mickael Lacroix / Matthieu Laporte / Michel
Lintz
- Christophe Meessen / Mourad Merzougui / Alexis Mehlman / Marco
Nardello
- Laure Oudda / Benjamin Pointard / Pierre Prat / Emmanuelle
Rivière
- Jérôme Royon / Aurélia Secroun / Samuel Sube / Thomas
Zerguerras
- Julien Zoubian
Summary
The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) observatory is a future
L3 mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) to detect gravitational
waves, set to launch in 2035. The detector constellation will conduct
interferometry to picometer stability over an unprecedented arm length
of 2.5 million km. In this paper, we present the development and testing
results for the Zerodur interferometer (ZIFO), an optical demonstrator
built to validate critical technology for the test setup of the
interferometric core of LISA. Optical path length stability measurements
on the ZIFO demonstrate successful reduction of bench noise to maintain
the 10 pm/ specification across the 1 mHz to 1 Hz frequency band. We also identify
and characterize dominant noise sources from phasemeters and
correlations of beam tilt into the path length that were observed during
the test campaign.
specification across the 1 mHz to 1 Hz frequency band. We also identify
and characterize dominant noise sources from phasemeters and
correlations of beam tilt into the path length that were observed during
the test campaign.
A
search for cold molecular outflows in cosmic noon galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
- Ivanna Langan / Gergö Popping / Michele Ginolfi / Simon
Weng
- Francesco Valentino / Gareth Jones / Jan Scholtz
Summary
The flow of baryons in and out of galaxies is the primary driver for
galaxy evolution. In addition to depleting the gas reservoir of
galaxies, outflows also enrich their circumgalactic medium (CGM) with
processed gas – which can further impact the next stages of gas
accretion, resulting in the presence of molecular gas beyond the stellar
component of galaxies, out to CGM scales. Here, we aim to search for
cold molecular gas (MH2) in the CGM of typical main-sequence (MS)
star-forming galaxies (SFGs) at cosmic noon (zmed=1.3), where we expect
outflows to be particularly prominent. Using Band 3 CO(2-1) data from
the Atacama Large Millimeter and submillimeter Array (ALMA), we study
the spatial extent of the MH2 of a sample of 26 SFGs, via stacking
techniques. We compare this extent to that of the stacked stellar
emission of our sample traced by UltraVISTA Ks band data. We also search
for broad wings in the stacked spectrum which can be indicative of
ongoing outflows. Within the noise level of the observations, we find
that the total intrinsic MH2 of our sample spatially extends to scales
of ~12 kpc, similarly to the stellar emission (~13 kpc). We do not find
broad wings in the stacked spectrum that could hint at ongoing molecular
outflows, but we find a tentative minor excess of CO(2-1) emission at
negative velocities that might be indicative of outflows, where the
redshifted gas is optically thick. The absence of high-velocity
molecular gas suggests that molecular outflows traced by CO(2-1)
emission are weak in MS SFGs at cosmic noon. These weak outflows thus
fail to expel a significant amount of molecular gas to CGM scales, as
indicated by the absence of molecular emission extending beyond the
stellar emission region. This lack of CO emission at large radii could
also imply that the molecular gas does not survive at such
distances.
Deep
Learning Framework for Enhanced Neutrino Reconstruction of Single-line
Events in the ANTARES Telescope
Link to the paper
Authors
- A. Albert / S. Alves / M. André / M. Ardid
- S. Ardid / J.-J. Aubert / J. Aublin / B. Baret
- S. Basa / Y. Becherini / B. Belhorma / F.
Benfenati
- V. Bertin / S. Biagi / J. Boumaaza / M. Bouta
- M. C. Bouwhuis / H. Brânzaş / R. Bruijn / J. Brunner
- J. Busto / B. Caiffi / D. Calvo / S. Campion
- A. Capone / F. Carenini / J. Carr / V. Carretero
- T. Cartraud / S. Celli / L. Cerisy / M. Chabab
- R. Cherkaoui El Moursli / T. Chiarusi / M. Circella / J. A. B.
Coelho
- A. Coleiro / R. Coniglione / P. Coyle / A. Creusot
- A. F. Díaz / B. De Martino / C. Distefano / I. Di Palma
- C. Donzaud / D. Dornic / D. Drouhin / T. Eberl
- A. Eddymaoui / T. van Eeden / D. van Eijk / S. El Hedri
- N. El Khayati / A. Enzenhöfer / P. Fermani / G. Ferrara
- F. Filippini / L. Fusco / S. Gagliardini / J. García-Méndez
- C. Gatius Oliver / P. Gay / N. Geißelbrecht / H. Glotin
- R. Gozzini / R. Gracia Ruiz / K. Graf / C. Guidi
- L. Haegel / H. van Haren / A. J. Heijboer / Y. Hello
- L. Hennig / J. J. Hernández-Rey / J. Hößl / F. Huang
- G. Illuminati / B. Jisse-Jung / M. de Jong / P. de Jong
- M. Kadler / O. Kalekin / U. Katz / A. Kouchner
- I. Kreykenbohm / V. Kulikovskiy / R. Lahmann / M. Lamoureux
- A. Lazo / D. Lefèvre / E. Leonora / G. Levi
- S. Le Stum / S. Loucatos / J. Manczak / M.
Marcelin
- A. Margiotta / A. Marinelli / J. A. Martínez-Mora / P.
Migliozzi
- A. Moussa / R. Muller / S. Navas / E. Nezri
- B. Ó Fearraigh / E. Oukacha / A. M. Păun / G. E. Păvălaş
- S. Peña-Martínez / M. Perrin-Terrin / P. Piattelli / C. Poiré
- V. Popa / T. Pradier / N. Randazzo / D. Real
- G. Riccobene / A. Romanov / A. Sánchez Losa / A. Saina
- F. Salesa Greus / D. F. E. Samtleben / M. Sanguineti / P.
Sapienza
- F. Schüssler / J. Seneca / M. Spurio / Th. Stolarczyk
- M. Taiuti / Y. Tayalati / B. Vallage / G. Vannoye
- V. Van Elewyck / S. Viola / D. Vivolo / J. Wilms
- S. Zavatarelli / A. Zegarelli / J. D. Zornoza / J. Zúñiga
Summary
We present the 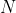 -fit algorithm designed to improve the
reconstruction of neutrino events detected by a single line of the
ANTARES underwater telescope, usually associated with low energy
neutrino events (
-fit algorithm designed to improve the
reconstruction of neutrino events detected by a single line of the
ANTARES underwater telescope, usually associated with low energy
neutrino events ( 100 GeV).
100 GeV). 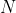 -Fit is a neural network model that
relies on deep learning and combines several advanced techniques in
machine learning –deep convolutional layers, mixture density output
layers, and transfer learning. This framework divides the reconstruction
process into two dedicated branches for each neutrino event topology
–tracks and showers– composed of sub-models for spatial estimation
–direction and position– and energy inference, which later on are
combined for event classification. Regarding the direction of
single-line events, the
-Fit is a neural network model that
relies on deep learning and combines several advanced techniques in
machine learning –deep convolutional layers, mixture density output
layers, and transfer learning. This framework divides the reconstruction
process into two dedicated branches for each neutrino event topology
–tracks and showers– composed of sub-models for spatial estimation
–direction and position– and energy inference, which later on are
combined for event classification. Regarding the direction of
single-line events, the 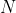 -Fit algorithm significantly refines the
estimation of the zenithal angle, and delivers reliable azimuthal angle
predictions that were previously unattainable with traditional
-Fit algorithm significantly refines the
estimation of the zenithal angle, and delivers reliable azimuthal angle
predictions that were previously unattainable with traditional  -fit methods. Improving on
energy estimation of single-line events is a tall order;
-fit methods. Improving on
energy estimation of single-line events is a tall order; 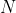 -Fit benefits from transfer learning to
efficiently integrate key characteristics, such as the estimation of the
closest distance from the event to the detector.
-Fit benefits from transfer learning to
efficiently integrate key characteristics, such as the estimation of the
closest distance from the event to the detector.  -Fit also takes advantage from transfer
learning in event topology classification by freezing convolutional
layers of the pretrained branches. Tests on Monte Carlo simulations and
data demonstrate a significant reduction in mean and median absolute
errors across all reconstructed parameters. The improvements achieved by
-Fit also takes advantage from transfer
learning in event topology classification by freezing convolutional
layers of the pretrained branches. Tests on Monte Carlo simulations and
data demonstrate a significant reduction in mean and median absolute
errors across all reconstructed parameters. The improvements achieved by
 -Fit highlight its potential for
advancing multimessenger astrophysics and enhancing our ability to probe
fundamental physics beyond the Standard Model using single-line events
from ANTARES data.
-Fit highlight its potential for
advancing multimessenger astrophysics and enhancing our ability to probe
fundamental physics beyond the Standard Model using single-line events
from ANTARES data.
Optical
gains measurement with a gain scheduling camera: On-sky demonstration
with PAPYRUS and perspectives
Link to the paper
Authors
- A. Striffling / C.-T. Héritier / R. J.-L Fétick /
O. Fauvarque
- J.-F Sauvage / A. Carlotti / B. Neichel T. Fusco
Summary
Reaching the high angular resolution and contrast level desired for
exoplanetary science requires us to equip large telescopes with extreme
adaptive optics (XAO) systems to compensate for the effect of the
atmospheric turbulence at a very fast rate. This calls for the
development of ultra-sensitive wavefront sensors (WFSs), such as Fourier
filtering wavefront sensors (FFWFSs), to be operated at low flux, as
well as an increase in the XAO loop frame rate. These sensors, which
constitute the baseline for current and future XAO systems, exhibit such
a high sensitivity at the expense of a non-linear behaviour that must be
properly calibrated and compensated for to deliver the required
performance. We aim to validate on-sky a recently proposed method that
associates the FFWFS with a focal plane detector, the gain scheduling
camera (GSC), to estimate in real time the first-order terms of the
sensor non-linearities, known as modal optical gains. We implemented a
GSC on the adaptive-optics (AO) bench PAPYRUS to be associated with the
existing pyramid wavefront sensor (PWFS). We compared experimental
results to expected results obtained with a high-fidelity numerical twin
of the AO system. We validated experimentally the method both in
laboratory and on-sky. We demonstrated the capability of the GSC to
accurately estimate the optical gains of the PWFS at 100 Hz,
corresponding to the current limit in speed imposed by PAPYRUS hardware,
but it could be applied at higher frequencies to enable frame-by-frame
optical gains tracking. The presented results exhibit good agreement on
the optical gains estimation with respect to numerical simulations
reproducing the experimental conditions tested. Our experimental results
validate the strategy of coupling a FFWFS with a focal-plane camera to
master the non-linearities of the sensor. This demonstrates its
attractiveness for future XAO application.
Link to the paper
Authors
- Lucie Leboulleux / Niyati Desai / Daniel Echeverri / Evangelia
Kleisioti
- Lorenzo Konig / Mathilde Malin / Elisabeth Matthews / Saavidra
Perera
- Schuyler Wolff / Elodie Choquet / Elsa Huby /
Garima Singh
Summary
Recognizing and addressing under-representation, exclusion, and
problematic behavior within astronomy and astrophysics is crucial. In
2019, a survey was conducted at the Spirit of Lyot conference to
evaluate the socio-demographics and well-being of the exoplanet and disk
imaging community. This paper presents the results of a second survey,
conducted at the 2022 Spirit of Lyot conference in Leiden, aiming to
improve the evaluation of the community, expand diversity-related
questions, and monitor the evolution of metrics since 2019. Sent to all
participants, the survey received 96 responses. It measures respondents’
visibility at conferences, recognition through publications and
projects, experiences of disrespect or inappropriate behaviors as
victims or witnesses, and identification as allies of minorities. These
aspects were analyzed with respect to job position, expatriation,
gender, belonging to another under-represented group (ethnicity,
disability, sexual orientation), and parenthood.
Estimating
differential pistons for the Extremely Large Telescope using focal plane
imaging and a residual network
Link to the paper
Authors
- P. Janin-Potiron / M. Gray /
B. Neichel / M. Dumont
- J.-F. Sauvage / C. T. Heritier / P.
Jouve / R. Fetick
- T. Fusco
Summary
As the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) approaches operational status,
optimising its imaging performance is critical. A differential piston,
arising from either the adaptive optics (AO) control loop,
thermomechanical effects, or other sources, significantly degrades the
image quality and is detrimental to the telescope’s overall performance.
In a numerical simulation set-up, we propose a method for estimating the
differential piston between the petals of the ELT’s M4 mirror using
images from a 2x2 Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor (SH-WFS), commonly
used in the ELT’s tomographic AO mode. We aim to identify the
limitations of this approach by evaluating its sensitivity to various
observing conditions and sources of noise. Using a deep learning model
based on a ResNet architecture, we trained a neural network (NN) on
simulated datasets to estimate the differential piston. We assessed the
robustness of the method under various conditions, including variations
in Strehl ratio, polychromaticity, and detector noise. The performance
was quantified using the root mean square error (RMSE) of the estimated
differential piston aberration. This method demonstrates the ability to
extract differential piston information from 2x2 SH-WFS images. Temporal
averaging of frames makes the differential piston signal emerge from the
turbulence-induced speckle field and leads to a significant improvement
in the RMSE calculation. As expected, better seeing conditions result in
improved accuracy. Polychromaticity only degrades the performance by
less than 5% compared to the monochromatic case. In a realistic
scenario, detector noise is not a limiting factor, as the primary
limitation rather arises from the need for sufficient speckle averaging.
The network was also shown to be applicable to input images other than
the 2x2 SH-WFS data.
ExoClock
Project IV: A homogeneous catalogue of 620 updated exoplanet
ephemerides
Link to the paper
Authors
- A. Kokori / A. Tsiaras / G. Pantelidou / A. Jones
- A. Siakas / B. Edwards / G. Tinetti / A. Wünsche
- Y. Jongen / F. Libotte / M. Correa / L. V. Mugnai
- A. Bocchieri / A. R. Capildeo / E. Poultourtzidis / C.
Sidiropoulos
- L. Bewersdorff / G. Lekkas / G. Grivas / R. A. Buckland
- S. R.-L. Futcher / P. Matassa / J.-P. Vignes / A. O. Kovacs
- M. Raetz / B. E. Martin / A. Popowicz / D. Gakis
- P. Batsela / V. Michalaki / A. Nastasi / C. Pereira
- A. Iliadou / F. Walter / N. I. Paschalis / K. Vats
- N. A-thano / R. Abraham / V. K. Agnihotri / M. Á. Álava-Amat
- R. Albanesi / T. Alderweireldt / J. Alonso-Santiago / D. Q.
Amat
- L. Andrade / V. Anzallo / J. Aragones / E. Arce-Mansego
- D. Arnot / R. A. Artola / C. Aumasson / M. Bachschmidt
- R. Barberá-Córdoba / J.-F. Barrois / P. R. Barroy / M. Bastoni
- V. Béjar / A. A. Belinski / A. Ben Lassoued / P. Bendjoya
- B. Benei / D. Bennett / K. Bernacki / G. O. Bernard
- L. Betti / G. Biesse / M. Billiani / P. Bosch-Cabot
- V. Boucher / R. C. Boufleur / D. Boulakos / P. J.-M.
Brandebourg
- S. M. Brincat / X. Bros / A. Brosio / S. Brouillard
- A.-M. Bruzzone / L. Cabona / C. Calamai / G. Calapai
- Y. Calatayud-Borràs / M. Caló / F. Campos / A. Carbognani
- F. Carretero / R. Casas / M. L. Castanheira / G. Catanzaro
- L. Cavaglioni / C.-M. Chang / M. Chella / W.-H. Chen
- P.-J. Chiu / R. Ciantini / J.-F. Coliac / J. Collins
- F. Conti / G. Conzo / W. R. Cooney, / L. N. Correa
- S. P. Cosentino / N. Crouzet / M. V. Crow / B. V.-H.-V.
da-Silva
- A. Damonte / D. Daniel / S. Dawes / L. de Almeida
- P. De Backer / A. de Melo / M. Deldem / D. Deligeorgopoulos
- Y. Delisle / F. Denjean / F. Dias / S. Diaz Lopez
- T. Dittadi / N. Dodd / S. Doman / G. Domènech-Rams
- T. G. Dooley / S. Drapkin-Junyent / F. Dubois / A. Dustor
- R. Dymock / T. Eenmäe / M. Emilio / E. Esparza-Borges
- J. Estevez / C. Falco / R. G. Farfán / P. Farissier
- G. Farrall / G. Fernandez Rodriguez / A. Ferretti / G. Ferrini
- L. Fini / J. Fiołka / G. Fleerackers / J. Flores-Martín
- follero / S. Foschino / L. Fossi / M. Fowler
- A. Frasca / E. Frigeni / I. Fukuda / A. Fukui
- G. Furlato / D. Gabellini / T. Gainey / P. Gajdoš
- D. Galán-Diéguez / P. Gamache / E. García Navarro / N. A.
Garcia
- A. García-Sánchez / A. Garmash / T. Gesser / A. Ginard
- I. Gkolias / E. Gomez / G. F. Gonçalves / J. González-Edo
- J. González-Rodríguez / G. Gruntz / B. Guillet / T. Guillot
- M. N. Günther / H. Hautecler / Y. Hayashi / E. Herrero
- K. Hills / H. S. Hodkinson / G. Holtkamp / G. R. Hunt
- N. Iannascoli / M. Iozzi / M. Irzyk / K. Isogai
- K. Johnson / P. Jóźwik-Wabik / A. E. Kaeouach / S. Kartal
- H. Kiiskinen / Ü. Kivila / U. Kolb / J. Korth
- D. Kustrin / S.-P. Lai / S. Lasota / F. Le Rhun
- Y. H. Lee / D. Lefoulon / F. Legrele / H. Leipold
- A. Liberti / T. Lien / Y.-H. Lin / F. Linsalata
- J. H. Livingston / C. Lopresti / S. Lora / E. R. Lorenz
- D. Madison / M. Mannucci / A. Marchini / A. Marino
- J.-C. Mario / E. Maris / J.-B. Marquette / N. A. Maslennikova
- A. E. McGregor / A. Mengoudis / P. Meni / M. Mesarč
- M. Michelagnoli / J. Michelet / J. Mieglitz / M. Mifsud
- M. Miller / S. A. Mills / E. Miny / S. Miquel Romero
- D. Molina / S. Montchaud / B. Monteleone / M. Monticelli
- N. Montigiani / M. Morales-Aimar / G. Morello / L. Moretti
- M. Mori / F. Mortari / M. Müller / D. Mura
- F. Murgas / N. Narita / A. Nath / R. Nicollerat
- V. Noce / P. Norridge / A. J. Norton / Y. Ogmen
- Z. Orbanic / J. Owen-Lloyd-Walters / E. P. Pace / E. Pakštienė
- A. F. Pala / E. Palle / C. Pantacchini / I. Parenti
- D. Patterson / E. Pavoni / A. W. Pereira / I. Peretto
- V. Perroud / S. W. Peterson / V. Pettina / M. Phillips
- J. Philpot / D. Pica / P. Pintr / J.-B. Pioppa
- T. J. Plunkett / T. G. Prado / A. Prasad / R. A.
Prestes
- A. Putz / F. Régembal / L. Ribe / D. F. Rocha
- J. Rodrigues / R. Roth / L. Rousselot / N. Rozand
- X. Rubia / N. Ruocco / M. Salisbury / T. Salomon
- L. Sassaro / J. E.-G. Savage / T. Savin / F. Scaggiante
- F.-X. Schmider / M. Serrau / I. D. Sharp / D. Shave-Wall
- A. F. Silva / V. Školník / A. Solmaz / A. Sonka
- M. Spiller / T. H. Sprecher / R. Stanga / M. Stefanini
- D. Stouraitis / M. Stratigou-Psarra / O. Suarez / D. Suys
- M. Szkudlarek / M. F. Talafha / A. N. Tarasenkov / G.
Tartalo-Montardit
- C. Titescu / A. Tomacelli / A. H. Triaud / S. Tsavdaridis
- K. Tsiganis / M. A. van der Grijp / S. Vanaverbeke /
j.-p. vergne
- J. Verheyden / J. Vilalta / P. Vuylsteke / P. Wagner
- D. Walliang / C. H. Wang / I. Weller / D. E. Wright
- K. O. Xenos / R. Yorke / O. Zamora / J. Zapata
- M. Zejmo / M. Zulian
Summary
The ExoClock project is an open platform aiming to monitor exoplanets
by integrating observations from space and ground based telescopes. This
study presents an updated catalogue of 620 exoplanet ephemerides,
integrating 30000 measurements from ground-based telescopes (the
ExoClock network), literature, and space telescopes (Kepler, K2 and
TESS). The updated catalogue includes 277 planets from TESS which
require special observing strategies due to their shallow transits or
bright host stars. This study demonstrates that data from larger
telescopes and the employment of new methodologies such as synchronous
observations with small telescopes, are capable of monitoring special
cases of planets. The new ephemerides show that 45% of the planets
required an update while the results show an improvement of one order of
magnitude in prediction uncertainty. The collective analysis also
enabled the identification of new planets showing TTVs, highlighting the
importance of extensive observing coverage. Developed in the context of
the ESA’s Ariel space mission, with the goal of delivering a catalogue
with reliable ephemerides to increase the mission efficiency, ExoClock’s
scope and service have grown well beyond the remit of Ariel. The
ExoClock project has been operating in the framework of open science,
and all tools and products are accessible to everyone within academia
and beyond, to support efficient scheduling of future exoplanet
observations, especially from larger telescopes where the pressure for
time allocation efficiency is higher (Ariel, JWST, VLT, ELT, Subaru
etc). The inclusion of diverse audiences in the process and the
collaborative mode not only foster democratisation of science but also
enhance the quality of the results.
Link to the paper
Authors
- F. Niederhofer / L. Cullinane / D. Massari / N. Bastian
- A. Bellini / F. Aguado-Agelet / S. Cassisi / D. Erkal
- M. Libralato / N. Kacharov / I. Cabrera-Ziri / E. Ceccarelli
- M.-R. L. Cioni / F. Dresbach / M. Häberle / S.
Martocchia
- S. Saracino
Summary
In this paper, we explore the kinematic properties of a sample of 19
young (<1 Gyr) and intermediate-age (1-2.5 Gyr) massive star clusters
within the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). We analyse the proper motions
of the clusters, which have been measured based on multi-epoch Hubble
Space Telescope (HST) observations. Additionally, we infer from the HST
data homogeneous and robust estimates for the distances, ages and
metallicities of the clusters. This collection of information, in
combination with literature line-of-sight velocities, allows us to
investigate the full 3D dynamics of our sample of clusters within the
frame of the LMC in a self-consistent way. While most young clusters
orbit the LMC close to the stellar disc plane, NGC 1850 (~100 Myr old)
depicts a peculiar case. Depending on the exact distance from the disc,
it follows either a highly inclined, retrograde orbit or an eccentric
orbit along the bar structure. The orbits of young clusters that formed
North of the LMC centre show signs that might be connected to the
resettling motion of the LMC bar structure. Based on the dynamic
properties in combination with the positions of the clusters in the
age-metallicity space, we find no clear-cut evidence for clusters in our
sample that could have been stripped from the Small Magellanic Cloud
(SMC) onto the LMC. We finally compare the kinematics of the
intermediate-age clusters with a suite of simple numerical simulations
of the Magellanic system to interpret the cluster motions. A possible
interaction history of the LMC with the SMC, where the SMC had two past
crossings of the LMC disc plane (about 300 and 900 Myr ago), in
combination with the recent SMC pericentre passage, can qualitatively
explain the observed kinematic structure of the clusters analysed in
this work.
Ice Giants
Pre-Decadal Survey Mission Study Report
Link to the paper
Authors
- M. Hofstadter / A. Simon / K. Reh / J. Elliott
- S. Atreya / D. Banfield / J. Fortney / A. Hayes
- M. Hedman / G. Hospodarsky / A. Masters / K. Mandt
- M. Showalter / K. Soderlund / D. Turini / E. Turtle
- P. Agrawal / T. Anderson / D. Atkinson / N. Arora
- C. Borden / M. Brennan / J. Cutts / H. Hwang
- M. Le / A. Petropoulos / S. Saikia / T. Spilker
- W. Smythe
Summary
The Ice Giants Study was commissioned by NASA to take a fresh look
(as of 2017) at science priorities and concepts for missions to the
Uranus and Neptune systems in preparation for the third Planetary
Science Decadal Survey. This study was led by a Science Definition Team
(SDT) and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) with participation from
Langley Research Center, Ames Research Center, The Aerospace
Corporation, Purdue University, and the European Space Agency. The SDT
was appointed by NASA and co-chaired by Mark Hofstadter (JPL) and Amy
Simon (Goddard Space Flight Center). The Study Manager was Kim Reh (JPL)
and the Study Lead was John Elliott (JPL). The study team assessed and
prioritized science objectives taking into account advances since the
last Decadal Survey, current and emerging technologies, mission
implementation techniques and celestial mechanics. This study examined a
wide range of mission architectures, flight elements, and instruments.
Six of the prioritized concepts were studied via JPL’s Team X process
and resulting cost estimates were subjected to independent assessment by
The Aerospace Corporation. Results presented herein show that high-value
flagship-class mission concepts to either Uranus or Neptune are
achievable within ground rule budgetary constraints.
Articles for week 46 2025
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): Identification of massive galaxy candidates at
the end of the Epoch of Reionisation
Link to the paper
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / R. Navarro-Carrera / K. I. Caputi / C. J. R.
McPartland
- J. R. Weaver / D. B. Sanders / G. Desprez / A. A. Tumborang
- A. Biviano / C. J. Conselice / Y. Fu / G. Girardi
- V. Le Brun / C. C. Lovell / G. Rodighiero / J.
Schaye
- R. G. Varadaraj / S. M. Wilkins / G. Zamorani / K. Jahnke
- D. Scott / M. Siudek / F. Shankar / J. G. Sorce
- F. Tarsitano / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese
- A. Cappi / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley
- M. Huertas-Company / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew
- M. Maturi / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. Bonici / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / T. Contini / A. R. Cooray / O.
Cucciati
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P.-A. Duc / M. Y. Elkhashab / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / F. Fontanot
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / J. Kim
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / C. J. A. P. Martins / L.
Maurin
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
Probing the presence and properties of massive galaxies at high
redshift is one of the most critical tests for galaxy formation models.
In this work, we search for galaxies with stellar masses M* >
10^10.25 Msun at z in [5,7], i.e., towards the end of the Epoch of
Reionisation, over a total of ~23 deg^2 in two of the Euclid Quick Data
Release (Q1) fields: the Euclid Deep Field North and Fornax (EDF-N and
EDF-F). In addition to the Euclid photometry, we incorporate Spitzer
Infrared Camera (IRAC) and ground-based optical data to perform spectral
energy distribution (SED) fitting, obtaining photometric redshifts and
derived physical parameters. After applying rigorous selection criteria,
we identify a conservative sample of 145 candidate massive galaxies with
M* > 10^10.25 Msun at z in [5,7], including 5 objects with M* >
10^11 Msun. This makes for a surface density of about 6.3 deg^-2 at z in
[5,7], which should be considered a lower limit because of the current
depth of the Euclid data (H_E < 24, 5 sigma in Q1). We find that the
inferred stellar masses are consistent with galaxy formation models with
standard star-formation efficiencies. These massive galaxies have colour
excess E(B-V) values up to 0.75, indicating significant dust attenuation
in some of them. In addition, half of the massive galaxies have best-fit
ages comparable to the age of the Universe at those redshifts, which
suggests that their progenitors were formed very early in cosmic time.
About 78% of the massive galaxies lie on the star-forming main sequence
(MS) in the SFR-M* plane, ~12% are found in the starburst region, and
10% in the transition zone between the MS and starbursts. We find no
significant evidence for outshining or AGN contamination that could
account for the elevated specific star-formation rates (sSFR) observed
in the ~12% of galaxies classified as starbursts.
:
From Galaxies to Gravitational Waves – Forecasting Stochastic
Gravitational Wave Background Anisotropies and Their
Cross-Correlation
Link to the paper
Authors
- K. Z. Yang / G. Cusin / V. Mandic / C. Scarlata
- J. Suresh / B. Altieri / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / H.
Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / E. Medinaceli / S.
Mei
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / A. Secroun
- E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / T. Castro
- J. García-Bellido / V. Scottez / M. Viel / P. Monaco
Summary
We estimate the amplitude and spatial anisotropy in the stochastic
gravitational wave background (SGWB) energy density due to compact
binary coalescence (CBC) events: binary black holes (BBH), binary
neutron stars (BNS), and black hole-neutron star (BHNS) mergers. Our
starting point is the Flagship Simulation Galaxy Catalogue developed by
the Euclid Consortium. For each galaxy in the Catalogue, we use the
simulated mass and starformation to constrain the galaxy’s
star-formation history, and predict its contribution to the
gravitational-wave energy density through CBC mergers. Combining such
contributions from all galaxies in the Catalogue results in a prediction
for the frequency spectrum and spatial anisotropy of the CBC SGWB. We
also compare this prediction to semi-analytical models of SGWB generated
by compact binaries. We identify a set of effective parameters that
capture the key features of these models, and we apply a Bayesian
framework to infer these parameters assuming an ideal scenario of cosmic
variance-limited search. This represents the first step toward
developing a comprehensive framework that will eventually enable the
correlation of SGWB anisotropy and galaxy data, potentially allowing us
to extract valuable astrophysical information from this new
observable.
PRIMA General
Observer Science Book Volume 2
Link to the paper
Authors
- A. Moullet / D. Burgarella / T. Kataria / H.
Beuther
- C. Battersby / M. Cheng / T. Essinger-Hileman / H. Inami
- E. Mills / T. Nagao / S. Unwin
Summary
This PRobe far-Infrared Mission for Astrophysics (PRIMA) mission
concept is a proposed mission to NASA’s Astrophysics Probe Explorer
(APEX) call. The concept features a cryogenically cooled 1.8 m diameter
telescope, and is designed to carry two science instruments covering the
24 to 264  m wavelength range: an imaging
polarimeter (PRIMAger) and a spectrometer (FIRESS). The majority of
PRIMA’s time (75%) will be open to observations proposed by the
community (General Observer science / GO), and all of data will be
publicly available for archival research (Guest Investigator science /
GI). Following up on the successful community engagement created by the
first volume of the GO PRIMA Science Book (arXiv:2310.20572), Volume 2
gathers 120 new and updated contributed science cases which could be
performed within the context of the PRIMA GO/GI program. This volume
reflects the strong development of the community interest, awareness and
involvement in PRIMA, and further develops how PRIMA’s unprecedented
capabilities can be leveraged for an impactful and innovative GO/GI
program covering most areas of astrophysics and over 90% of the
scientific questions and discovery areas in the Astro2020 decadal
survey.
m wavelength range: an imaging
polarimeter (PRIMAger) and a spectrometer (FIRESS). The majority of
PRIMA’s time (75%) will be open to observations proposed by the
community (General Observer science / GO), and all of data will be
publicly available for archival research (Guest Investigator science /
GI). Following up on the successful community engagement created by the
first volume of the GO PRIMA Science Book (arXiv:2310.20572), Volume 2
gathers 120 new and updated contributed science cases which could be
performed within the context of the PRIMA GO/GI program. This volume
reflects the strong development of the community interest, awareness and
involvement in PRIMA, and further develops how PRIMA’s unprecedented
capabilities can be leveraged for an impactful and innovative GO/GI
program covering most areas of astrophysics and over 90% of the
scientific questions and discovery areas in the Astro2020 decadal
survey.
Intra-night
optical polarization monitoring of blazars
Link to the paper
Authors
- Aristeidis Polychronakis / Ioannis Liodakis / Anastasia Glykopoulou
/ Dmitry Blinov
- Ivan Agudo / Svetlana G. Jorstad / Beatriz Agis-Gonzalez / Sara
Capecchiacci
- Alberto Floris / Sebastian Kielhmann / John A. Kypriotakis /
Dimitrios A. Langis
- Nikos Mandarakas / Karan Pal / Francisco J.
Aceituno / Giacomo Bonnoli
- Victor Casanova / Gabriel Emery / Juan Escudero Pedrosa / Jorge
Otero-Santos
- Daniel Morcuende / Alfredo Sota / Vilppu Piirola
Summary
Blazars are known for their extreme variability across the
electromagnetic spectrum. Variability at very short timescales can push
the boundaries between competing models offering us much needed
discriminating power. This is particularly true for polarization
variability that allows us to probe particle acceleration and
high-energy emission models in blazars. Here we present results from the
first pilot study of intra-night optical polarization monitoring
conducted using RoboPol at the Skinakas Observatory and supplemented by
observations from the Calar Alto, Perkins, and Sierra Nevada
observatories. Our results show that while variability patterns can
widely vary between sources, variability on timescales as short as
minutes is prevalent in blazar jets. The amplitude of variations are
typically small, a few percent for the polarization degree and less than
20 degrees for the polarization angle, pointing to a significant
contribution to the optical emission from a turbulent magnetic field
component, while the overall stability of the polarization angle over
time points to a preferred magnetic field orientation.
Large-Scale
Structure in COSMOS-Web: Tracing Galaxy Evolution in the Cosmic Web up
to  with the Largest
JWST Survey
with the Largest
JWST Survey
Link to the paper
Authors
- Hossein Hatamnia / Bahram Mobasher / Sina Taamoli / Jeyhan S.
Kartaltepe
- Caitlin M. Casey / Hollis B. Akins / Malte Brinch / Nima
Chartab
- Nicole E. Drakos / Andreas L. Faisst / Steven L. Finkelstein /
Maximilien Franco
- Finn Giddings / Ghassem Gozaliasl / Ali Hadi / Aryana Haghjoo
- Santosh Harish / Olivier Ilbert / Pascale L.
Jablonka / Shuowen Jin
- Ali Ahmad Khostovan / Anton M. Koekemoer / Ronaldo Laishram /
Daizhong Liu
- Matteo Maturi / Henry Joy McCracken / Crystal L. Martin / Lauro
Moscardini
- Diana Scognamiglio / Marko Shuntov / Greta Toni / Alexander de la
Vega
- John R. Weaver / Lilan Yang
Summary
We present a reconstruction of the large-scale structure using the
James Webb Space Telescope’s (JWST) COSMOS-Web program to trace
environmentally driven galaxy evolution up to  . We applied a
weighted kernel density estimation method to 160,000 galaxies with
robust photometric redshifts. We find that stellar mass has a positive
correlation with density at all redshifts, stronger for quiescent
galaxies (QGs) at
. We applied a
weighted kernel density estimation method to 160,000 galaxies with
robust photometric redshifts. We find that stellar mass has a positive
correlation with density at all redshifts, stronger for quiescent
galaxies (QGs) at  , while at
higher redshifts (
, while at
higher redshifts ( ) this trend is confined to extreme overdense
environments, consistent with early mass assembly in proto-clusters. The
star-formation rate (SFR) shows a negative trend with density for QGs at
) this trend is confined to extreme overdense
environments, consistent with early mass assembly in proto-clusters. The
star-formation rate (SFR) shows a negative trend with density for QGs at
 ,
reversing at
,
reversing at  , while
star-forming galaxies (SFGs) show a mild positive correlation up to
, while
star-forming galaxies (SFGs) show a mild positive correlation up to  . The specific SFR
remains nearly flat for SFGs and declines with density for QGs at
. The specific SFR
remains nearly flat for SFGs and declines with density for QGs at  .
Moreover, mass and environmental quenching efficiencies show that
mass-driven processes dominate at
.
Moreover, mass and environmental quenching efficiencies show that
mass-driven processes dominate at  , the two
processes act with comparable strength between
, the two
processes act with comparable strength between  , and environmental quenching becomes stronger for
low-mass galaxies (
, and environmental quenching becomes stronger for
low-mass galaxies ( ) at
) at  . These
findings reveal that large-scale structure drives galaxy evolution by
enhancing early mass assembly in dense regions and increasingly
suppressing star formation in low-mass systems at later times,
establishing the environmental role of the cosmic web across cosmic
history. COSMOS-Web, the largest JWST survey, provides accurate and deep
photometric redshifts, reaching 80% mass completeness at
. These
findings reveal that large-scale structure drives galaxy evolution by
enhancing early mass assembly in dense regions and increasingly
suppressing star formation in low-mass systems at later times,
establishing the environmental role of the cosmic web across cosmic
history. COSMOS-Web, the largest JWST survey, provides accurate and deep
photometric redshifts, reaching 80% mass completeness at  at
at  , enabling the first
view of how environments shaped galaxy evolution from the epoch of
reionization to the present day.
, enabling the first
view of how environments shaped galaxy evolution from the epoch of
reionization to the present day.
Radio Burst
from a Stellar Coronal Mass Ejection
Link to the paper
Authors
- J. R. Callingham / C. Tasse / R. Keers / R. D. Kavanagh
- H. Vedantham / P. Zarka / S. Bellotti / P. I. Cristofari
- S. Bloot / D. C. Konijn / M. J. Hardcastle / L.
Lamy
- E. K. Pass / B. J. S. Pope / H. Reid / H. J. A. Röttgering
- T. W. Shimwell / P. Zucca
Summary
Coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are massive expulsions of magnetised
plasma from a star, and are the largest contributors to space weather in
the Solar System. CMEs are theorized to play a key role in planetary
atmospheric erosion, especially for planets that are close to their host
star. However, such a conclusion remains controversial as there has not
been an unambiguous detection of a CME from a star outside of our Sun.
Previous stellar CME studies have only inferred the presence of a CME
through the detection of other types of stellar eruptive events. A
signature of a fast CME is a Type II radio burst, which is emitted from
the shock wave produced as the CME travels through the stellar corona
into interplanetary space. Here we report an analogue to a Type II burst
from the early M dwarf StKM 1-1262. The burst exhibits identical
frequency, time, and polarisation properties to fundamental plasma
emission from a solar Type II burst. We demonstrate the rate of such
events with similar radio luminosity from M dwarfs are
0.84$^{+1.94}_{-0.69}  ^{-3}$ per day per star. Our detection
implies that we are no longer restricted to extrapolating the solar CME
kinematics and rates to other stars, allowing us to establish the first
observational limits on the impact of CMEs on exoplanets.
^{-3}$ per day per star. Our detection
implies that we are no longer restricted to extrapolating the solar CME
kinematics and rates to other stars, allowing us to establish the first
observational limits on the impact of CMEs on exoplanets.
Euclid
preparation. Non-Gaussianity of 2-point statistics likelihood: Precise
analysis of the matter power spectrum distribution
Link to the paper
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / J. Bel / S. Gouyou Beauchamps / P.
Baratta
- L. Blot / C. Carbone / P.-S. Corasaniti / E. Sefusatti
- S. Escoffier / W. Gillard / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M.
Courtois
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / F. Rizzo
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca / M.
Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Conseil / S.
Contarini
- A. R. Cooray / S. Davini / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / L. Pagano / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P. Reimberg / P.-F. Rocci
- G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- L. C. Smith / J. G. Sorce / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- F. Vernizzi / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
We investigate the non-Gaussian features in the distribution of the
matter power spectrum multipoles. Using the COVMOS method, we generate
100,000 mock realisations of dark matter density fields in both real and
redshift space across multiple redshifts and cosmological models. We
derive an analytical framework linking the non-Gaussianity of the power
spectrum distribution to higher-order statistics of the density field,
including the trispectrum and pentaspectrum. We explore the effect of
redshift-space distortions, the geometry of the survey, the Fourier
binning, the integral constraint, and the shot noise on the skewness of
the distribution of the power spectrum measurements. Our results
demonstrate that the likelihood of the estimated matter power spectrum
deviates significantly from a Gaussian assumption on nonlinear scales,
particularly at low redshift. This departure is primarily driven by the
pentaspectrum contribution, which dominates over the trispectrum at
intermediate scales. We also examine the impact of the finiteness of the
survey geometry in the context of the Euclid mission and find that both
the shape of the survey and the integral constraint amplify the
skewness.
No
TiO detected in the hot Neptune-desert planet LTT-9779 b in reflected
light at high spectral resolution
Link to the paper
Authors
- Sophia R. Vaughan / Jayne L. Birkby / Natasha E. Batalha / Luke T.
Parker
- Haochuan Yu / Julia V. Seidel / Michael Radica / Jake Taylor
- Laura Kreidberg / Vivien Parmentier / Sergio Hoyer
/ James S. Jenkins
- Annabella Meech / Ricardo Ramírez Reyes / Lennart van Sluijs
Summary
LTT-9779 b is an inhabitant of the hot Neptune desert and one of only
a few planets with a measured high albedo. Characterising the atmosphere
of this world is the key to understanding what processes dominate in
creating the hot Neptune desert. We aim to characterise the reflected
light of LTT-9779 b at high spectral resolution to break the degeneracy
between clouds and atmospheric metallicity. This is key to interpreting
its mass loss history which may illuminate how it kept its place in the
desert. We use the high resolution cross-correlation spectroscopy
technique on four half-nights of ESPRESSO observations in 4-UT mode
(16.4-m effective mirror) to constrain the reflected light spectrum of
LTT-9779 b. We do not detect the reflected light spectrum of LTT-9779 b
despite these data having the expected sensitivity at the level 100 ppm.
Injection tests on the post-eclipse data indicate that TiO should have
been detected for a range of different equilibrium chemistry models.
Therefore this non-detection suggests TiO depletion in the western
hemisphere however, this conclusion is sensitive to temperature which
impacts the chemistry in the upper atmosphere and the reliability of the
line list. Additionally, we are able to constrain the top of the western
cloud deck to  bar
and the top of the eastern cloud deck
bar
and the top of the eastern cloud deck  bar,
which is consistent with the predicted altitude of MgSiO
bar,
which is consistent with the predicted altitude of MgSiO and Mg
and Mg SiO
SiO clouds from JWST NIRISS/SOSS. While we
do not detect the reflected light spectrum of LTT-9779 b, we have
verified that this technique can be used in practice to characterise the
high spectral resolution reflected light of exoplanets so long as their
spectra contain a sufficient number of deep spectral lines. Therefore
this technique may become an important cornerstone of exoplanet
characterisation with the ELT and beyond.
clouds from JWST NIRISS/SOSS. While we
do not detect the reflected light spectrum of LTT-9779 b, we have
verified that this technique can be used in practice to characterise the
high spectral resolution reflected light of exoplanets so long as their
spectra contain a sufficient number of deep spectral lines. Therefore
this technique may become an important cornerstone of exoplanet
characterisation with the ELT and beyond.
Link to the paper
Authors
- Longji Bing / Seb Oliver / Mengyuan Xiao / Guilaine
Lagache
- Sylvia Adscheid / Daizhong Liu / Benjamin Magnelli / Roberto
Neri
- Miroslava Dessauges-Zavadsky / Anton M. Koekemoer / Maximilien
Franco / Shuowen Jin
- Olivia R. Cooper / Andreas L. Faisst / Catilin M. Casey / Jeyhan S.
Kartaltepe
- Hollis Akins / Alexandre Beelen / David Elbaz /
Steven Gillman
- Santosh Harish / Arianna S. Long / Henry Joy McCracken / Pascal
Oesch
- Louise Paquereau / Nicolas Ponthieu / Jason Rhodes / Brant
Robertson
- David B. Sanders / Marko Shuntov / Stephen Wilkins
Summary
We present AC-2168, an almost NIRCam-dark, millimetre-bright galaxy
in the COSMOS field. The source was identified blindly in ALMA Band-4
continuum data and remains undetected in the COSMOS-Web DR1 NIRCam
catalogue. We spectroscopically confirm a redshift of  from [CII] 158
from [CII] 158  m and four tentatively detected CO lines
in NOEMA and ALMA data. SED fitting to near-IR to millimetre photometry
yields
m and four tentatively detected CO lines
in NOEMA and ALMA data. SED fitting to near-IR to millimetre photometry
yields  , an
SFR of
, an
SFR of  , heavy dust attenuation
, heavy dust attenuation  mag, and a
stellar mass
mag, and a
stellar mass  .
From the millimetre continuum and [CII] emission, we infer a warm ISM
with
.
From the millimetre continuum and [CII] emission, we infer a warm ISM
with  ,
,  and
and
 .
AC-2168 has a gas fraction (
.
AC-2168 has a gas fraction ( ) of
) of  , a short
depletion time of
, a short
depletion time of  , a
compact (
, a
compact ( )
dust-continuum size, and an SFR consistent with the star-forming main
sequence at its mass. These properties match expectations for
progenitors of massive quiescent galaxies at the peak of their assembly,
as implied by NIRSpec-based SFHs of
)
dust-continuum size, and an SFR consistent with the star-forming main
sequence at its mass. These properties match expectations for
progenitors of massive quiescent galaxies at the peak of their assembly,
as implied by NIRSpec-based SFHs of  systems. Using
the blind detection, we estimate a space density of
systems. Using
the blind detection, we estimate a space density of  for AC-2168-like NIRCam-dark galaxies at
for AC-2168-like NIRCam-dark galaxies at  ,
,  of the abundance
of massive quiescent galaxies at
of the abundance
of massive quiescent galaxies at  . No overdensity
of Ly
. No overdensity
of Ly emitters or Lyman-break galaxies is
found nearby, suggesting AC-2168 does not lie in a prominent
protocluster and highlighting the importance of unbiased blind surveys
for this population.
emitters or Lyman-break galaxies is
found nearby, suggesting AC-2168 does not lie in a prominent
protocluster and highlighting the importance of unbiased blind surveys
for this population.
HARPS-N,
TESS, and CHEOPS discover a transiting sub-Neptune and two outer
companions around the bright solar analogue HD 85426
Link to the paper
Authors
- F. Lienhard / A. Mortier / A. Collier Cameron / M. Cretignier
- L. Borsato / A. Anna John / J. A. Egger / M. Stalport
- T. G. Wilson / A. Deline / A. Fortier / D. W. Latham
- L. Malavolta / P. F. L. Maxted / S. G. Sousa / S. L. Grimm
- L. Buchhave / Y. Alibert / B. S. Lakeland / X. Dumusque
- J. Cabrera / L. Naponiello / A. C. M. Correia / F. Rescigno
- L. Fossati / A. Sozzetti / R. Alonso / T. Bárczy
- D. Barrado / S. C. C. Barros / W. Baumjohann / W. Benz
- N. Billot / A. Brandeker / C. Broeg / K. Collins
- Sz. Csizmadia / P. E. Cubillos / M. B. Davies / M.
Deleuil
- O. D. S. Demangeon / B.-O. Demory / A. Derekas / B. Edwards
- D. Ehrenreich / A. Erikson / M. Fridlund / D. Gandolfi
- K. Gazeas / M. Gillon / M. Güdel / M. N. Günther
- R. Haywood / A. Heitzmann / Ch. Helling / K. G. Isaak
- J. M. Jenkins / L. L. Kiss / J. Korth / K. W. F. Lam
- J. Laskar / A. Lecavelier des Etangs / A. Leleu / M. Lendl
- D. Magrin / A. F. Martínez Fiorenzano / B. Merín / C. Mordasini
- V. Nascimbeni / G. Olofsson / H. P. Osborn / R. Ottensamer
- I. Pagano / L. Palethorpe / E. Pallé / G. Peter
- D. Piazza / G. Piotto / D. Pollacco / D. Queloz
- R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando / H. Rauer / I. Ribas
- K. Rice / N. C. Santos / G. Scandariato / D. Ségransan
- A. E. Simon / A. M. S. Smith / S. Sulis / Gy. M.
Szabó
- S. Udry / S. Ulmer-Moll / V. Van Grootel / J. Venturini
- E. Villaver / N. A. Walton / T. Zingales
Summary
We provide a detailed characterisation of the planetary system
orbiting HD 85426 (TOI-1774). This bright G-type star ( : 0.99
: 0.99  ;
;
 : 1.13
: 1.13  ;
age: 7.4 Gyr; V mag: 8.25) hosts a transiting sub-Neptune, HD 85426 b,
with an orbital period of 16.71 days and a blackbody equilibrium
temperature of
;
age: 7.4 Gyr; V mag: 8.25) hosts a transiting sub-Neptune, HD 85426 b,
with an orbital period of 16.71 days and a blackbody equilibrium
temperature of  K.
By jointly analysing HARPS-N RVs, TESS, and CHEOPS photometric data and
using two different stellar activity mitigation techniques, we constrain
planet b’s mass to
K.
By jointly analysing HARPS-N RVs, TESS, and CHEOPS photometric data and
using two different stellar activity mitigation techniques, we constrain
planet b’s mass to 
 and $8.5^{+1.3}_{-1.4} $
and $8.5^{+1.3}_{-1.4} $  , depending on the mitigation technique. We
investigate the dependence of these results on the priors, data
selection, and inclusion of other Keplerians in the modelling. Using
this approach, we identify the presence of two non-transiting planetary
companions with minimum masses near 10
, depending on the mitigation technique. We
investigate the dependence of these results on the priors, data
selection, and inclusion of other Keplerians in the modelling. Using
this approach, we identify the presence of two non-transiting planetary
companions with minimum masses near 10  and orbital periods of 35.7 and 89 days. Additionally, we reject the
initial hypothesis that the 35.7-day periodic signal was due to stellar
activity. We also determine HD 85426 b’s radius to be
and orbital periods of 35.7 and 89 days. Additionally, we reject the
initial hypothesis that the 35.7-day periodic signal was due to stellar
activity. We also determine HD 85426 b’s radius to be 
 and compute a transmission spectroscopy metric in the range of 82 to
115, making this planet a highly valuable target for atmospheric
characterisation.
and compute a transmission spectroscopy metric in the range of 82 to
115, making this planet a highly valuable target for atmospheric
characterisation.
A
warm ultra-luminous infrared galaxy just 600 million years after the Big
Bang
Link to the paper
Authors
- T. J. L. C. Bakx / Laura Sommovigo / Yoichi Tamura / Renske
Smit
- Andrea Ferrara / Hiddo Algera / Susanne Aalto / Duncan Bossion
- Stefano Carniani / Clarke Esmerian / Masato Hagimoto / Takuya
Hashimoto
- Bunyo Hatsukade / Edo Ibar / Hanae Inami / Akio K. Inoue
- Kirsten Knudsen / Nicolas Laporte / Ken Mawatari /
Juan Molina
- Gunnar Nyman / Takashi Okamoto / Andrea Pallottini / W. M. C.
Sameera
- Hideki Umehata / Wouter Vlemmings / Naoki Yoshida
Summary
We present an Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA)
Band 9 continuum detection ( ) of MACS0416_Y1 that
confirms the suspected warm dust (91
) of MACS0416_Y1 that
confirms the suspected warm dust (91 K) of
this Lyman-Break Galaxy (LBG) at
K) of
this Lyman-Break Galaxy (LBG) at  with
with  M
M . A modified black-body fit to the ALMA Bands 3
through 9 data of MACS0416_Y1 finds an intrinsic infrared luminosity of
1.0
. A modified black-body fit to the ALMA Bands 3
through 9 data of MACS0416_Y1 finds an intrinsic infrared luminosity of
1.0 , placing this UV-selected LBG in the regime of
Ultra Luminous Infrared Galaxies (ULIRGs). Its luminous but modest dust
reservoir (1.4
, placing this UV-selected LBG in the regime of
Ultra Luminous Infrared Galaxies (ULIRGs). Its luminous but modest dust
reservoir (1.4 ) is co-spatial to regions with a UV-continuum
slope
) is co-spatial to regions with a UV-continuum
slope  as seen by James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
imaging. Although this implies some dust obscuration, the JWST
photometry implies less obscured star formation than seen in the
complete characterization by ALMA, implying some spatial separation of
dust and stars on scales below 200 pc, i.e., smaller than those probed
by JWST and ALMA. This source is an extreme example of dust-obscured
star formation contributing strongly to the cosmic build-up of stellar
mass, which can only be revealed through direct and comprehensive
observations in the (sub)mm regime.
as seen by James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
imaging. Although this implies some dust obscuration, the JWST
photometry implies less obscured star formation than seen in the
complete characterization by ALMA, implying some spatial separation of
dust and stars on scales below 200 pc, i.e., smaller than those probed
by JWST and ALMA. This source is an extreme example of dust-obscured
star formation contributing strongly to the cosmic build-up of stellar
mass, which can only be revealed through direct and comprehensive
observations in the (sub)mm regime.
First
results from the PanRadio GRB Collaboration: the 400-day afterglow of
GRB~230815A
Link to the paper
Authors
- James K. Leung / Gemma E. Anderson / Alexander J. van der Horst /
Claire Morley
- Benjamin Schneider / Fabio De Colle / Om Sharan
Salafia / Giancarlo Ghirlanda
- Sarah L. Chastain / Adelle J. Goodwin / Ashna Gulati / Lauren
Rhodes
- Stuart D. Ryder / Ashley A. Chrimes / Valerio D’Elia / Mathieu de
Bony de Lavergne
- Massimiliano De Pasquale / Antonio de Ugarte Postigo / Dieter H.
Hartmann / Benjamin P. Gompertz
- Andrew J. Levan / Tara Murphy / Gavin P. Rowell / Thomas D.
Russell
- Fabian Schüssler / Rhaana L. C. Starling / Nial R. Tanvir / Susanna
D. Vergani
- Ralph A. M. J. Wijers
Summary
We introduce the PanRadio Gamma-ray Burst (GRB) program carried out
on the Australia Telescope Compact Array: a systematic, multi-year,
radio survey of all southern GRB events, comprehensively following the
multi-frequency evolution of their afterglows from within an hour to
years post-burst. We present the results of the 400-day observing
campaign following the afterglow of long-duration (collapsar)
GRB~230815A, the first one detected through this program. Typically,
GRB~230815A would not otherwise receive traditional radio follow-up,
given it has no known redshift and lacks comprehensive multi-wavelength
follow-up due to its high line-of-sight extinction with  . We found its
early X-ray jet break at
. We found its
early X-ray jet break at  days post-burst
to be at odds with the evolution of the multi-frequency radio light
curves that were traced over an unusually long duration of
days post-burst
to be at odds with the evolution of the multi-frequency radio light
curves that were traced over an unusually long duration of  days. The radio light curves
approximately evolved (with minor deviations) according to the standard
self-similar expansion for a relativistic blast wave in a homogeneous
environment prior to jet break, showing no evidence for evolution in the
microphysical parameters describing the electron acceleration processes.
We reconcile these features by proposing a two-component jet: the early
X-ray break originates from a narrow component with a half-opening angle
days. The radio light curves
approximately evolved (with minor deviations) according to the standard
self-similar expansion for a relativistic blast wave in a homogeneous
environment prior to jet break, showing no evidence for evolution in the
microphysical parameters describing the electron acceleration processes.
We reconcile these features by proposing a two-component jet: the early
X-ray break originates from a narrow component with a half-opening angle
 , while the evolution of the radio afterglow stems
from a wider component with a half-opening angle
, while the evolution of the radio afterglow stems
from a wider component with a half-opening angle  . The PanRadio GRB program will establish a sample
of comprehensively followed GRBs, where a rigorous inspection of their
microphysical and dynamical parameters can be performed, thereby
revealing the diversity of features in their outflows and
environments.
. The PanRadio GRB program will establish a sample
of comprehensively followed GRBs, where a rigorous inspection of their
microphysical and dynamical parameters can be performed, thereby
revealing the diversity of features in their outflows and
environments.
Link to the paper
Authors
- Hakim Atek / John Chisholm / Vasily Kokorev / Ryan Endsley
- Richard Pan / Lukas Furtak / Iryna Chemerynska / Johan Richard
- Adélaïde Claeyssens / Pascal Oesch / Seiji Fujimoto / Rohan
Naidu
- Damien Korber / Daniel Schaerer / Jeremy Blaizot / Joki Rosdahl
- Angela Adamo / Yoshihisa Asada / Arghyadeep Basu / Benjamin
Beauchesne
- Danielle Berg / Rachel Bezanson / Rychard Bouwens / Gabriel
Brammer
- Miroslava Dessauges-Zavadsky / Amaël Ellien / Meriam Ezziati /
Qinyue Fei
- Ilias Goovaerts / Sylvain Heurtier / Tiger Yu-Yang
Hsiao / Michelle Jecmen
- Gourav Khullar / Jean-Paul Kneib / Ivo Labbé / Floriane
Leclercq
- Rui Marques-Chaves / Charlotte Mason / Kristen B. W. McQuinn /
Julian B. Muñoz
- Priyamvada Natarajan / Alberto Saldana-Lopez / Mabel G. Stephenson /
Maxime Trebitsch
- Marta Volonteri / Andrea Weibel / Adi Zitrin
Summary
We present an overview of the JWST GLIMPSE program, highlighting its
survey design, primary science goals, gravitational lensing models, and
first results. GLIMPSE provides ultra-deep JWST/NIRCam imaging across
seven broadband filters (F090W, F115W, F200W, F277W, F356W, F444W) and
two medium-band filters (F410M, F480M), with exposure times ranging from
20 to 40 hours per filter. This yields a 5 limiting magnitude of 30.9 AB (measured
in a 0.2 arcsec diameter aperture). The field is supported by extensive
ancillary data, including deep HST imaging from the Hubble Frontier
Fields program, VLT/MUSE spectroscopy, and deep JWST/NIRSpec
medium-resolution multi-object spectroscopy. Exploiting the strong
gravitational lensing of the galaxy cluster Abell S1063, GLIMPSE probes
intrinsic depths beyond 33 AB magnitudes and covers an effective
source-plane area of approximately 4.4 arcmin
limiting magnitude of 30.9 AB (measured
in a 0.2 arcsec diameter aperture). The field is supported by extensive
ancillary data, including deep HST imaging from the Hubble Frontier
Fields program, VLT/MUSE spectroscopy, and deep JWST/NIRSpec
medium-resolution multi-object spectroscopy. Exploiting the strong
gravitational lensing of the galaxy cluster Abell S1063, GLIMPSE probes
intrinsic depths beyond 33 AB magnitudes and covers an effective
source-plane area of approximately 4.4 arcmin at
at  . The program’s
central aim is to constrain the abundance of the faintest galaxies from
. The program’s
central aim is to constrain the abundance of the faintest galaxies from
 up to the highest
redshifts, providing crucial benchmarks for galaxy formation models,
which have so far been tested primarily on relatively bright systems. We
present an initial sample of
up to the highest
redshifts, providing crucial benchmarks for galaxy formation models,
which have so far been tested primarily on relatively bright systems. We
present an initial sample of  galaxy candidates
identified at
galaxy candidates
identified at  ,
with intrinsic UV magnitudes spanning
,
with intrinsic UV magnitudes spanning  =
$-$20 to $-
=
$-$20 to $- z$ active galactic nuclei. This paper accompanies
the first public data release, which includes reduced JWST and HST
mosaics, photometric catalogs, and gravitational lensing models.
z$ active galactic nuclei. This paper accompanies
the first public data release, which includes reduced JWST and HST
mosaics, photometric catalogs, and gravitational lensing models.
Search
for steady and flaring neutrino emission from cosmic sources using the
complete ANTARES dataset
Link to the paper
Authors
- ANTARES Collaboration / A. Albert / S. Alves / M. André
- M. Ardid / S. Ardid / J. J. Aubert / J. Aublin
- B. Baret / S. Basa / Y. Becherini / B.
Belhorma
- F. Benfenati / V. Bertin / S. Biagi / J. Boumaaza
- M. Bouta / M. C. Bouwhuis / H. Brânzaş / R. Bruijn
- J. Brunner / J. Busto / B. Caiffi / D. Calvo
- S. Campion / A. Capone / F. Carenini / J. Carr
- V. Carretero / T. Cartraud / S. Celli / L. Cerisy
- M. Chabab / R. Cherkaoui El Moursli / T. Chiarusi / M. Circella
- J. A. B. Coelho / A. Coleiro / R. Coniglione / P. Coyle
- A. Creusot / A. F. Díaz / B. De Martino / C. Distefano
- I. Di Palma / C. Donzaud / D. Dornic / D. Drouhin
- T. Eberl / A. Eddymaoui / T. van Eeden / D. van Eijk
- S. El Hedri / N. El Khayati / A. Enzenhöfer / P. Fermani
- G. Ferrara / F. Filippini / L. Fusco / S. Gagliardini
- J. García / C. Gatius Oliver / P. Gay / N. Geißelbrecht
- H. Glotin / R. Gozzini / R. Gracia Ruiz / K. Graf
- C. Guidi / L. Haegel / S. Hallmann / H. van Haren
- A. J. Heijboer / Y. Hello / L. Hennig / J. J. Hernández-Rey
- J. Hößl / F. Huang / G. Illuminati / B. Jisse-Jung
- M. de Jong / P. de Jong / M. Kadler / O. Kalekin
- U. Katz / A. Kouchner / I. Kreykenbohm / V. Kulikovskiy
- R. Lahmann / M. Lamoureux / A. Lazo / D. Lefèvre
- E. Leonora / G. Levi / S. Le Stum / S. Loucatos
- J. Manczak / M. Marcelin / A. Margiotta / A.
Marinelli
- J. A. Martínez-Mora / P. Migliozzi / A. Moussa / R. Muller
- S. Navas / E. Nezri / B. Ó Fearraigh / E.
Oukacha
- A. M. Păun / G. E. Păvălaş / S. Peña-Martínez / M.
Perrin-Terrin
- P. Piattelli / C. Poirè / V. Popa / T. Pradier
- N. Randazzo / D. Real / G. Riccobene / A. Romanov
- A. Sánchez Losa / A. Saina / F. Salesa Greus / D. F. E.
Samtleben
- M. Sanguineti / P. Sapienza / F. Schüssler / J. Seneca
- M. Spurio / Th. Stolarczyk / M. Taiuti / Y. Tayalati
- B. Vallage / G. Vannoye / V. Van Elewyck / S. Viola
- D. Vivolo / J. Wilms / S. Zavatarelli / A. Zegarelli
- J. D. Zornoza / J. Zúñiga
Summary
ANTARES, a neutrino detector located in the depths of the
Mediterranean Sea, operated successfully for over 15 years before being
decommissioned in 2022. The telescope offered an ideal vantage view of
the Southern Sky and benefited from optimal water properties for
enhanced angular resolution. This study makes use of data collected over
the entire operational period of ANTARES to search for sources of
high-energy cosmic neutrinos, considering both steady and flaring
emission scenarios. First, a time-integrated search for high-energy
neutrino clustering across the celestial sphere is conducted. The most
significant accumulation is found at coordinates  with a
post-trial p-value equal to 0.38. A dedicated search in the Galactic
Plane is also performed for extended sources, yielding no significant
excess. Additionally, a list of potential neutrino sources are
investigated. The blazar MG3 J225517+2409 is identified as the most
significant object, yet the excess remains compatible with background
fluctuations. A mild local excess of 2.4
with a
post-trial p-value equal to 0.38. A dedicated search in the Galactic
Plane is also performed for extended sources, yielding no significant
excess. Additionally, a list of potential neutrino sources are
investigated. The blazar MG3 J225517+2409 is identified as the most
significant object, yet the excess remains compatible with background
fluctuations. A mild local excess of 2.4 is found for the blazar TXS 0506+056.
The full sky is also examined for the presence of flaring neutrino
emissions. The most significant excess in this case corresponds to a
$$4-day flare from the direction
is found for the blazar TXS 0506+056.
The full sky is also examined for the presence of flaring neutrino
emissions. The most significant excess in this case corresponds to a
$$4-day flare from the direction  , with
a post-trial p-value of 0.30. Finally, the directions of sources
highlighted in IceCube’s time-dependent searches are investigated.
Temporal overlaps between ANTARES and IceCube flares are identified for
PKS 1502+106 and TXS 0506+056, with an estimated chance probability of
about 0.02%, making this observation particularly noteworthy.
, with
a post-trial p-value of 0.30. Finally, the directions of sources
highlighted in IceCube’s time-dependent searches are investigated.
Temporal overlaps between ANTARES and IceCube flares are identified for
PKS 1502+106 and TXS 0506+056, with an estimated chance probability of
about 0.02%, making this observation particularly noteworthy.
Articles for week 45 2025
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Searching for giant gravitational arcs in
galaxy clusters with mask region-based convolutional neural
networks
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / L. Bazzanini / G. Angora / P. Bergamini
- M. Meneghetti / P. Rosati / A. Acebron / C. Grillo
- M. Lombardi / R. Ratta / M. Fogliardi / G. Di Rosa
- D. Abriola / M. D’Addona / G. Granata / L. Leuzzi
- A. Mercurio / S. Schuldt / E. Vanzella / INAF–OAS
- Osservatorio di Astrofisica e Scienza dello Spazio di Bologna / via
Gobetti 93/3 / I-40129 Bologna / Italy
- C. Tortora / B. Altieri / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M.
Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan
- J. Hoar / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / R. Laureijs
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / W. G. Hartley / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- E. Aubourg / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / M. Bonici / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / B. Clément
- F. Cogato / S. Conseil / A. R. Cooray / O.
Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro
- P.-A. Duc / M. Y. Elkhashab / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / R.
Gavazzi
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / A. H. Gonzalez
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / S. Hemmati
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / J. Kim
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / C. J. R. McPartland / M.
Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / J. G. Sorce
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / D. Scott
Summary
Strong gravitational lensing (SL) by galaxy clusters is a powerful
probe of their inner mass distribution and a key test bed for
cosmological models. However, the detection of SL events in wide-field
surveys such as Euclid requires robust, automated methods capable of
handling the immense data volume generated. In this work, we present an
advanced deep learning (DL) framework based on mask region-based
convolutional neural networks (Mask R-CNNs), designed to autonomously
detect and segment bright, strongly-lensed arcs in Euclid’s multi-band
imaging of galaxy clusters. The model is trained on a realistic
simulated data set of cluster-scale SL events, constructed by injecting
mock background sources into Euclidised Hubble Space Telescope images of
10 massive lensing clusters, exploiting their high-precision mass models
constructed with extensive spectroscopic data. The network is trained
and validated on over 4500 simulated images, and tested on an
independent set of 500 simulations, as well as real Euclid Quick Data
Release (Q1) observations. The trained network achieves high performance
in identifying gravitational arcs in the test set, with a precision and
recall of 76% and 58%, respectively, processing 2’x2’ images in a
fraction of a second. When applied to a sample of visually confirmed
Euclid Q1 cluster-scale lenses, our model recovers 66% of gravitational
arcs above the area threshold used during training. While the model
shows promising results, limitations include the production of some
false positives and challenges in detecting smaller, fainter arcs. Our
results demonstrate the potential of advanced DL computer vision
techniques for efficient and scalable arc detection, enabling the
automated analysis of SL systems in current and future wide-field
surveys. The code, ARTEMIDE, is open source and will be available at
github.com/LBasz/ARTEMIDE.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / R. Hill / A. Abghari / D. Scott
- M. Bethermin / S. C. Chapman / D. L. Clements / S. Eales
- A. Enia / B. Jego / A. Parmar / P. Tanouri
- L. Wang / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / A. Costille / F.
Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Sauvage
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri
- L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / M.
Huertas-Company
- R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca / L.
Bisigello
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer / M. Bonici
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- Y. Charles / F. Cogato / S.
Conseil / A. R. Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P.-A. Duc / M. Y. Elkhashab / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- F. Fontanot / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / A. H. Gonzalez / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / S. Hemmati / C.
Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / J. Kim
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / C. J. A. P.
Martins
- L. Maurin / C. J. R. McPartland / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / J. G. Sorce / S. A. Stanford
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton
Summary
The first Euclid Quick Data Release contains millions of galaxies
with excellent optical and near-infrared (IR) coverage. To complement
this dataset, we investigate the average far-IR properties of
Euclid-selected main sequence (MS) galaxies using existing Herschel and
SCUBA-2 data. We use 17.6deg (2.4deg
(2.4deg ) of overlapping Herschel (SCUBA-2)
data, containing 2.6 million (240000) MS galaxies. We bin the Euclid
catalogue by stellar mass and photometric redshift and perform a
stacking analysis following SimStack, which takes into account galaxy
clustering and bin-to-bin correlations. We detect stacked far-IR flux
densities across a significant fraction of the bins. We fit modified
blackbody spectral energy distributions in each bin and derive mean dust
temperatures, dust masses, and star-formation rates (SFRs). We find
similar mean SFRs compared to the Euclid catalogue, and we show that the
average dust-to-stellar mass ratios decreased from z$$1 to the present
day. Average dust temperatures are largely independent of stellar mass
and are well-described by the function
) of overlapping Herschel (SCUBA-2)
data, containing 2.6 million (240000) MS galaxies. We bin the Euclid
catalogue by stellar mass and photometric redshift and perform a
stacking analysis following SimStack, which takes into account galaxy
clustering and bin-to-bin correlations. We detect stacked far-IR flux
densities across a significant fraction of the bins. We fit modified
blackbody spectral energy distributions in each bin and derive mean dust
temperatures, dust masses, and star-formation rates (SFRs). We find
similar mean SFRs compared to the Euclid catalogue, and we show that the
average dust-to-stellar mass ratios decreased from z$$1 to the present
day. Average dust temperatures are largely independent of stellar mass
and are well-described by the function  , where
, where  is the age of the Universe,
is the age of the Universe,  K,
K,
 K, and
K, and
 Gyr. We
argue that since the dust temperatures are converging to a non-zero
value below
Gyr. We
argue that since the dust temperatures are converging to a non-zero
value below  , the dust is now primarily
heated by the existing cooler and older stellar population, as opposed
to hot young stars in star-forming regions at higher redshift. We show
that since the dust temperatures are independent of stellar mass, the
correlation between dust temperature and SFR depends on stellar mass.
Lastly, we estimate the contribution of the Euclid catalogue to the
cosmic IR background (CIB), finding that it accounts for >60% of the
CIB at 250, 350, and 500
, the dust is now primarily
heated by the existing cooler and older stellar population, as opposed
to hot young stars in star-forming regions at higher redshift. We show
that since the dust temperatures are independent of stellar mass, the
correlation between dust temperature and SFR depends on stellar mass.
Lastly, we estimate the contribution of the Euclid catalogue to the
cosmic IR background (CIB), finding that it accounts for >60% of the
CIB at 250, 350, and 500 m. Forthcoming Euclid data will extend
these results to higher redshifts, lower stellar masses, and recover
more of the CIB.
m. Forthcoming Euclid data will extend
these results to higher redshifts, lower stellar masses, and recover
more of the CIB.
Significant
Evidence of an AGN Contribution in GHZ2 at z = 12.34
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Oscar A. Chavez Ortiz / Steven L. Finkelstein / Adele Plat / Maddie
Silcock
- Emma Curtis Lake / Ansh R. Gupta / Lorenzo Napolitano / Marco
Castellano
- Volker Bromm / Ikki Mitsuhashi / Stephane Charlot / Adriano
Fontana
- Jorge A. Zavala / Jacopo Chevallard / Denis
Burgarella / Michaela Hirschmann
- Tom Bakx / Alba Vidal-Garcia / Antonello Calabrò / Anna Feltre
Summary
GHZ2 is among the highest-redshift galaxies discovered to date,
exhibiting a spectrum rich with prominent emission lines in the
rest-frame ultraviolet (UV) and optical. These features raise critical
questions about the mechanism powering this nebular emission, in
particular the extremely strong C IV$λ$1548 emission (rest-frame EW  45 Angstrom). Here we aim to quantify
the AGN contribution within this system using the BEAGLE-AGN tool to
simultaneously fit the spectrum and photometry of GHZ2. We consider a
range of models with and without AGN components, allowing us to
disentangle the stellar and AGN contribution of GHZ2 for the first time.
We conclude that a partial contribution by an AGN is significantly
favored based on the Bayes factor comparison to models without an AGN
component, measuring an AGN contribution of 54
45 Angstrom). Here we aim to quantify
the AGN contribution within this system using the BEAGLE-AGN tool to
simultaneously fit the spectrum and photometry of GHZ2. We consider a
range of models with and without AGN components, allowing us to
disentangle the stellar and AGN contribution of GHZ2 for the first time.
We conclude that a partial contribution by an AGN is significantly
favored based on the Bayes factor comparison to models without an AGN
component, measuring an AGN contribution of 54 % and 26
% and 26 % for the C
IV$λ
% for the C
IV$λ![1548 and C III] 1548 and C III]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%201548%20and%20C%20III%5D) λ
λ L_{acc}
L_{acc} {10}
{10} {BH}
{BH} {}
{} ^{+0.04}{-0.04}$, for an Eddington ratio of
^{+0.04}{-0.04}$, for an Eddington ratio of
 = 0.5 (with a systematic uncertainty of
$
= 0.5 (with a systematic uncertainty of
$ ^{+0.02}_{-0.02}$, consistent with other high
redshift AGN systems. If the black hole interpretation is confirmed,
GHZ2 would represent the most distant black hole identified to date,
making it an ideal laboratory to study AGN growth and their role in
shaping high-redshift galactic evolution.
^{+0.02}_{-0.02}$, consistent with other high
redshift AGN systems. If the black hole interpretation is confirmed,
GHZ2 would represent the most distant black hole identified to date,
making it an ideal laboratory to study AGN growth and their role in
shaping high-redshift galactic evolution.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Spectroscopic unveiling of highly ionised lines
at z = 2.48-3.88
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / D. Vergani / S. Quai / F. Ricci
- Y. Fu / S. Serjeant / M. Salvato / W. Roster
- M. Mezcua / M. Siudek / A. Enia / G. Zamorani
- L. Bisigello / A. Feltre / S. Fotopoulou / T. Matamoro Zatarain
- L. Pozzetti / D. Scott / B. Laloux / J. G. Sorce
- P. A. C. Cunha / A. Viitanen / C. Saulder / E. Rossetti
- M. Moresco / V. Le Brun / E. Palazzi / M.
Talia
- Z. Mao / L. Nicastro / E. Maiorano / D. Vibert
- P.-Y. Chabaud / G. Daste /
F. Dufresne / T. Bedrine
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar
- H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- L. Moscardini / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- C. Surace / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H.
I. Teplitz
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / M.
Huertas-Company
- R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. Bonici
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- F. Cogato / S. Conseil / T. Contini / A. R.
Cooray
- O. Cucciati / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / M. Y. Elkhashab / Y. Fang
- A. Finoguenov / F. Fontanot / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / S. Hemmati / C.
Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / J. Kim
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- M. Magliocchetti / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci / C. J. A. P.
Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / M. Radovich
- G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / F. Shankar / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
This study explores a rare population of sources in a currently
uncharted region of spectroscopic redshift space in the Euclid Quick
Data Release (Q1), and is intended potentially to support upcoming
spectroscopic studies. Our goal is to identify and investigate a
population of sources characterised by highly ionised emission lines in
their spectra, which are indicative of active galactic nucleus activity,
extreme shock phenomena, or Wolf–Rayet stars. A comprehensive visual
inspection of spectra is conducted to ensure the reliability of the
sample, focusing on the simultaneous detection of both NeV and OII
emission-line measurements, a condition that restricts the Euclid
spectroscopic redshift range to z=2.48–3.88. To characterise this
population, we analysed the morpho-spectrophotometric properties of
their host galaxies. This allowed for a direct comparison with control
sources that exhibit similar OII properties and spectroscopic redshifts,
but not NeV lines. We identify sources solely based on spectroscopic
criteria in the redshift range beyond the Halpha regime. Encompassing 65
potential NeV candidates, the resulting sample delivers the first
systematic probe of these NeV candidate emitters at high redshift. We
found a good agreement, within 1 , between the spectral measurements
calculated using both direct integration and Gaussian fitting
methodologies. The NeV candidates exhibit colours similar to bright
QSOs, with only a few in the tail of very red quasars. We observed a
higher stellar mass content, a lower continuum around the 4000A break,
and a similar Sérsic index distribution compared to the control sample.
This unique sample paves the way for a wide range of scientific
investigations, which will be pursued in the forthcoming data
releases.
, between the spectral measurements
calculated using both direct integration and Gaussian fitting
methodologies. The NeV candidates exhibit colours similar to bright
QSOs, with only a few in the tail of very red quasars. We observed a
higher stellar mass content, a lower continuum around the 4000A break,
and a similar Sérsic index distribution compared to the control sample.
This unique sample paves the way for a wide range of scientific
investigations, which will be pursued in the forthcoming data
releases.
Euclid:
Quick Data Release (Q1)- The connection between galaxy close encounters
and radio activity
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Magliocchetti / A. La Marca / L. Bisigello / M. Bondi
- F. Ricci / S. Fotopoulou / L. Wang / R. Scaramella
- L. Pentericci / I. Prandoni / J. G. Sorce / H. J. A. Rottgering
- M. J. Hardcastle / J. Petley / F. La Franca / K. Rubinur
- Y. Toba / Y. Zhong / M. Mezcua / G. Zamorani
- F. Shankar / B. Altieri / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Canas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / A. Costille / F.
Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / P. Franzetti
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihanen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kummel / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespi / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / E. Zucca / M. Huertas-Company / V. Scottez
Summary
Using the large statistics provided by both Euclid and the LOFAR
surveys, we present the first large-scale study of the connection
between radio emission, its morphology, and the merging properties of
the hosts of radio sources up to z=2. By dividing the radio sample into
active galactic nuclei (AGN) and star-forming galaxies, we find that
radio-emitting AGN show a clear preference to reside within galaxies
undergoing a merging event. This is more significant for AGN that
present extended and/or complex radio emission: indeed, about half of
them are associated with merging systems, while only 15% are hosted by
an isolated galaxy. The observed trend is primarily driven by AGN
residing at z < 1, especially in the case of high - P144MHz >
10^24 W Hz-1 sr-1 - radio luminosities (60% in mergers versus 10%
isolated regardless of radio appearance). The situation is reversed in
the case of radio-emitting star-forming galaxies, which are
preferentially associated with isolated systems. This is more
significant as we move towards low radio-luminosity/star-formation
objects (P144MHz < 10^23 W Hz-1 sr-1) for which we find 40% in
isolated systems versus 20% in mergers. These values hold regardless of
redshift. We interpret the above result for AGN with their need to
accrete outer gas from local encounters in order to trigger (radio)
activity, especially in the case of extended radio emission such as
hot-spots and lobes. This is mostly observed at z < 1, since in the
local Universe galaxies are more gas deprived than their higher-redshift
counterparts. Internal gas reservoirs instead seem sufficient to trigger
star formation within the majority of galaxies, which indeed prefer to
be associated with isolated systems at all redshifts probed.
(abridged)
Dissecting
the Perseus-Pisces supercluster observed with CFHT-MegaCam:
Investigating environmental effects on galaxy morphology
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Mondelin / S. Codis / J-C. Cuillandre / C. Laigle
- A. Boselli / K. Kraljic / C. Stone
Summary
The discovery of the large-scale structure has transformed our view
of galaxy formation and evolution. Filaments of the cosmic web provide
key environments that channel the growth of structures. Guided by
predictions from cosmological simulations, we study the morphological
distribution of galaxies in the Perseus-Pisces Supercluster, a prominent
filamentary complex at 70 Mpc. We focus on how galaxy morphology and
structural disturbances relate to position within the filament network
and to proximity to dense nodes. Our sample is built from a
spectroscopic catalogue cross-matched with deep r-band CFHT/MegaCam
imaging from UNIONS and additional time, enabling the detection of
low-surface-brightness features and extended outer structures.
Morphologies are determined both visually and through structural
parameters extracted from surface-brightness profiles using AutoProf and
AstroPhot. The 3D filamentary skeleton of Perseus-Pisces is
reconstructed with the DisPerSE algorithm, providing distances from each
galaxy to the nearest filament and to group or cluster centres. The 3D
mapping reveals a network of interconnected sub-filaments converging
around the Pisces cluster, forming a complex, multi-branched structure
that likely shapes environmental effects on galaxy evolution. We observe
clear morphological and stellar-mass segregation: massive early-type
galaxies (E/S0) concentrate along filament spines and near dense nodes,
while late-type and irregular systems are more broadly dispersed. About
10-13% of galaxies show strong signs of gravitational interaction, with
stellar-halo asymmetries particularly common in filaments and groups.
These findings underline the dual influence of filamentary environments,
which both host evolved early-type systems and foster local tidal
interactions and pre-processing that modify galaxy morphology.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): Hunting for luminous z > 6 galaxies in the
Euclid Deep Fields – forecasts and first bright detections
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / N. Allen / P. A. Oesch / R. A. A. Bowler
- S. Toft / J. Matharu / J. R. Weaver / C. J. R. McPartland
- M. Shuntov / D. B. Sanders / B. Mobasher / H. J. McCracken
- H. Atek / E. Bañados / S. W. J. Barrow / S. Belladitta
- D. Carollo / M. Castellano / C. J. Conselice / P. R. M.
Eisenhardt
- Y. Harikane / G. Murphree / M. Stefanon / S. M. Wilkins
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- R. Bender / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / R. Maoli
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / M. Maturi / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. Bonici
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / T. Contini / A. R. Cooray / O.
Cucciati
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / M. Y. Elkhashab / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / F. Fontanot
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J.
Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / J. Kim / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu
- X. Lopez Lopez / J. Macias-Perez / M. Magliocchetti / F.
Mannucci
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / R. Pello / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar
- L. C. Smith / J. G. Sorce / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / D. Scott
Summary
The evolution of the rest-frame ultraviolet luminosity function (UV
LF) is a powerful probe of early star formation and stellar mass
build-up. At z > 6, its bright end (MUV < -21) remains poorly
constrained due to the small volumes of existing near-infrared (NIR)
space-based surveys. The Euclid Deep Fields (EDFs) will cover 53 deg^2
with NIR imaging down to 26.5 AB, increasing area by a factor of 100
over previous space-based surveys. They thus offer an unprecedented
opportunity to select bright z > 6 Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) and
constrain the UV LF’s bright end. With NIR coverage extending to 2um,
Euclid can detect galaxies out to z = 13. We present forecasts for the
number densities of z > 6 galaxies expected in the final EDF dataset.
Using synthetic photometry from spectral energy distribution (SED)
templates of z = 5–15 galaxies, z = 1–4 interlopers, and Milky Way MLT
dwarfs, we explore optimal selection methods for high-z LBGs. A
combination of S/N cuts with SED fitting (from optical to MIR) yields
the highest-fidelity sample, recovering >76% of input z > 6 LBGs
while keeping low-z contamination <10%. This excludes instrumental
artefacts, which will affect early Euclid releases. Auxiliary data are
critical: optical imaging from the Hyper Suprime-Cam and Vera C. Rubin
Observatory distinguishes genuine Lyman breaks, while Spitzer/IRAC data
help recover z > 10 sources. Based on empirical double power-law LF
models, we expect >100,000 LBGs at z = 6-12 and >100 at z > 12
in the final Euclid release. In contrast, steeper Schechter models
predict no z > 12 detections. We also present two ultra-luminous (MUV
< -23.5) candidates from the EDF-N Q1 dataset. If their redshifts are
confirmed, their magnitudes support a DPL LF model at z > 9,
highlighting Euclid’s power to constrain the UV LF’s bright end and
identify the most luminous early galaxies for follow-up.
Keck
Observatory as an HWO Testbed: validating wavefront sensing and control
schemes on a large segmented aperture in parallel with high-contrast
science
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Maïssa Salama / Rebecca Jensen-Clem / Mahawa Cissé / J. Kent
Wallace
- Mitchell Troy / Laurent Pueyo / Charlotte Guthery / Antonin
Bouchez
- Vincent Chambouleyron
Summary
Exoplanet direct imaging allows us to directly probe and characterize
an exoplanet’s atmosphere, searching for signs of life in its
atmospheric signatures. Directly imaging an Earth-like planet around a
Sun-like star requires reaching 10 contrast levels and
will be the goal of the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO). A key
technical barrier to reaching such deep contrasts is maintaining
wavefront stability on the order of tens of picometers, in particular in
the presence of a segmented primary mirror. Keck Observatory is the only
facility with all of the hardware components necessary for validating
HWO segment phasing strategies: a large segmented primary mirror,
capacitive edge sensors, deformable mirror, Zernike wavefront sensor
(ZWFS), and high contrast science instruments. Taking advantage of these
parallels, we are using Keck as a testbed for developing and validating
HWO wavefront sensing and control loop strategies, as well as
demonstrating the full system-level segment control architecture for
HWO, using existing infrastructure. Recently, we set the stage for this
work by using the ZWFS installed on the Keck II telescope to sense and
correct the primary mirror segment pistons in closed-loop in parallel
with science observations. This resulted in improved Strehl ratios on
the NIRC2 science camera (Salama et al. 2024a). We now aim to directly
address concerns related to control authority, actuator offload, and
loop stability - tasks which require Keck’s existing infrastructure, but
which do not require picometer wavefront stability. Moreover, successful
comparisons of observed and predicted performances will validate, on a
real operating observatory, the HWO error budget methodology and in
particular its approach to nested loops operating at multiple
timescales.
contrast levels and
will be the goal of the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO). A key
technical barrier to reaching such deep contrasts is maintaining
wavefront stability on the order of tens of picometers, in particular in
the presence of a segmented primary mirror. Keck Observatory is the only
facility with all of the hardware components necessary for validating
HWO segment phasing strategies: a large segmented primary mirror,
capacitive edge sensors, deformable mirror, Zernike wavefront sensor
(ZWFS), and high contrast science instruments. Taking advantage of these
parallels, we are using Keck as a testbed for developing and validating
HWO wavefront sensing and control loop strategies, as well as
demonstrating the full system-level segment control architecture for
HWO, using existing infrastructure. Recently, we set the stage for this
work by using the ZWFS installed on the Keck II telescope to sense and
correct the primary mirror segment pistons in closed-loop in parallel
with science observations. This resulted in improved Strehl ratios on
the NIRC2 science camera (Salama et al. 2024a). We now aim to directly
address concerns related to control authority, actuator offload, and
loop stability - tasks which require Keck’s existing infrastructure, but
which do not require picometer wavefront stability. Moreover, successful
comparisons of observed and predicted performances will validate, on a
real operating observatory, the HWO error budget methodology and in
particular its approach to nested loops operating at multiple
timescales.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Marko Shuntov / Olivier Ilbert / Claudia del P.
Lagos / Sune Toft
- Francesco Valentino / Wilfried Mercier / Hollis B.
Akins / Nguyen Binh
- Malte Brinch / Caitlin M. Casey / Maximilien Franco / Fabrizio
Gentile
- Ghassem Gozaliasl / Aryana Haghjoo / Santosh Harish / Michaela
Hirschmann
- Marc Huertas-Company / Shuowen Jin / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Anton M.
Koekemoer
- Clotilde Laigle / Joseph S. W. Lewis / Georgios E. Magdis / Henry
Joy McCracken
- Bahram Mobasher / Thibaud Moutard / Pascal A. Oesch / Louise
Paquereau
- Alvio Renzini / Michael R. Rich / David B. Sanders / Greta Toni
- Laurence Tresse / Andrea Weibel / John R. Weaver /
Lilan Yang
Summary
We study the stellar mass function (SMF) of quiescent and
star-forming galaxies and its dependence on morphology in 10 redshift
bins at  using the COSMOS2025 catalog built from
using the COSMOS2025 catalog built from  JWST imaging from COSMOS-Web. Galaxies are
selected by type using the
JWST imaging from COSMOS-Web. Galaxies are
selected by type using the  rest-frame color
diagram and classified morphologically by bulge-to-total light ratio
(
rest-frame color
diagram and classified morphologically by bulge-to-total light ratio
( ). The quiescent SMF shows
rapid early build-up, with the most massive systems (
). The quiescent SMF shows
rapid early build-up, with the most massive systems ( ) assembled by
) assembled by  and evolving little
since. The star-forming SMF evolves more slowly, following a
mass-evolution scenario where galaxies grow via star formation and
quench at the characteristic mass
and evolving little
since. The star-forming SMF evolves more slowly, following a
mass-evolution scenario where galaxies grow via star formation and
quench at the characteristic mass  .
Bulge systems (
.
Bulge systems ( ) dominate the
quiescent SMF at
) dominate the
quiescent SMF at  at all redshifts, while disks (
at all redshifts, while disks ( ) dominate at
) dominate at
 . However, most bulge-dominated galaxies are
star-forming, with their fraction increasing with redshift and
decreasing mass, consistent with being progenitors of quiescent bulges.
We find evidence for environmental quenching onset at
. However, most bulge-dominated galaxies are
star-forming, with their fraction increasing with redshift and
decreasing mass, consistent with being progenitors of quiescent bulges.
We find evidence for environmental quenching onset at  from the upturn in
the quiescent SMF at
from the upturn in
the quiescent SMF at  , contributed by disk-dominated galaxies
consistent with satellite quenching that retains disk morphologies.
Number densities of
, contributed by disk-dominated galaxies
consistent with satellite quenching that retains disk morphologies.
Number densities of  quiescent galaxies are lower than recent
literature by
quiescent galaxies are lower than recent
literature by  dex, but agree well
with simulations at
dex, but agree well
with simulations at  . At
. At  , simulations
increasingly underpredict observations. Finally, we build an empirical
model describing galaxy number density evolution by parametrizing
quenching rates, baryon conversion efficiency, and bulge formation. Our
model supports a scenario where star-forming galaxies grow central
bulges before quenching in massive halos.
, simulations
increasingly underpredict observations. Finally, we build an empirical
model describing galaxy number density evolution by parametrizing
quenching rates, baryon conversion efficiency, and bulge formation. Our
model supports a scenario where star-forming galaxies grow central
bulges before quenching in massive halos.
Euclid:
Quick Data Release (Q1) – Secondary nuclei in early-type galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Fabricius / R. Saglia / F. Balzer / L. R. Ecker
- J. Thomas / R. Bender / J. Gracia-Carpio / M. Magliocchetti
- O. Marggraf / A. Rawlings / J. G. Sorce / K. Voggel
- L. Wang / A. van der Wel / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / C. Dolding / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / H. J. A. Rottgering / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / J.
Skottfelt
- L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / M. Wetzstein
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca
- M. Huertas-Company / V. Scottez / D. Scott / M. Siudek
Summary
Massive early-type galaxies (ETGs) are believed to form primarily
through mergers of less massive progenitors, leaving behind numerous
traces of violent formation histories, such as stellar streams and
shells. A particularly striking signature of these mergers is the
formation of supermassive black hole (SMBH) binaries, which can create
depleted stellar cores through interactions with stars on radial orbits
- a process known as core scouring. The secondary SMBH in such systems
may still carry a dense stellar envelope and thereby remain observable
for some time as a secondary nucleus, while it is sinking towards the
shared gravitational potential of the merged galaxy. We leverage
Euclid’s Q1 Early Release data to systematically search for secondary
nuclei in ETGs. We present a preliminary sample of 666 candidate systems
distributed over 504 hosts (some of which contain multiple secondary
nuclei). The vast majority of these fall at separations of 3 kpc to 15
kpc, indicative of normal mergers. 44 fall at projected separations of
less than 2 kpc. We argue those candidates at very close angular
separations are unlikely to be a consequence of chance alignments. We
show that their stellar masses are mostly too large for them to be
globular clusters and that a significant subset are unresolved even at
Euclid’s spatial resolution, rendering them too small to be dwarf
galaxies. These may represent the highest-density nuclei of a previously
merged galaxy, currently sinking into the centre of the new, common
gravitational potential and thus likely to host a secondary SMBH. We
then demonstrate that convolutional neural networks offer a viable
avenue to detect multiple nuclei in the thirty-times larger sky coverage
of the future Euclid DR1. Finally, we argue that our method could detect
the remnants of a recoil event from two merged SMBHs.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / F. Gentile / E. Daddi / D. Elbaz
- A. Enia / B. Magnelli / J-B. Billand / P. Corcho-Caballero
- C. Cleland / G. De Lucia / C. D’Eugenio / M. Fossati
- M. Franco / C. Lobo / Y. Lyu / M. Magliocchetti
- G. A. Mamon / L. Quilley / J. G. Sorce / M. Tarrasse
- M. Bolzonella / F. Durret / L. Gabarra / S. Guo
- L. Pozzetti / S. Quai / F. Shankar / V. Sangalli
- M. Talia / M. Baes / H. Fu / M. Girardi
- J. Matthee / P. A. Oesch / D. Roberts / J. Schaye
- D. Scott / L. Spinoglio / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / R. Bender / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin
Vigo
- W. G. Hartley / M. Huertas-Company / J. Martín-Fleitas / S.
Matthew
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- H. Böhringer / M. Bonici / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / S.
Conseil
- T. Contini / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro
- P.-A. Duc / M. Y. Elkhashab / Y. Fang / A. Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / F. Fontanot / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / R.
Gavazzi
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / A. H. Gonzalez
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- J. Kim / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / M. Radovich
- G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford
- K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
(Abridged) The bimodality between star-forming discs and quiescent
spheroids requires the existence of two main processes: the galaxy
quenching and the morphological transformation. In this paper, we aim to
understand the link between these processes and their relation with the
stellar mass of galaxies and their local environment. Taking advantage
of the first data released by the Euclid Collaboration, covering more
than 60 deg2 with space-based imaging and photometry, we analyse a
mass-complete sample of nearly one million galaxies in the range
0.25<z<1 with  . We divide the sample into four sub-populations
of galaxies, based on their star-formation activity and morphology. We
then analyse the physical properties of these populations and their
relative abundances in the stellar mass vs. local density plane.
Together with confirming the passivity-density relation and the
morphology-density relation, we find that quiescent discy galaxies are
more abundant in the low-mass regime of high-density environment. At the
same time, star-forming bulge-dominated galaxies are more common in
field regions, preferentially at high masses. Building on these results
and interpreting them through comparison with simulations, we propose a
scenario where the evolution of galaxies in the field significantly
differs from that in higher-density environments. The morphological
transformation in the majority of field galaxies takes place before the
onset of quenching and is mainly driven by secular processes taking
place within the main sequence, leading to the formation of star-forming
bulge-dominated galaxies as intermediate-stage galaxies. Conversely,
quenching of star formation precedes morphological transformation for
most galaxies in higher-density environments. This causes the formation
of quiescent disc-dominated galaxies before their transition into
bulge-dominated ones.
. We divide the sample into four sub-populations
of galaxies, based on their star-formation activity and morphology. We
then analyse the physical properties of these populations and their
relative abundances in the stellar mass vs. local density plane.
Together with confirming the passivity-density relation and the
morphology-density relation, we find that quiescent discy galaxies are
more abundant in the low-mass regime of high-density environment. At the
same time, star-forming bulge-dominated galaxies are more common in
field regions, preferentially at high masses. Building on these results
and interpreting them through comparison with simulations, we propose a
scenario where the evolution of galaxies in the field significantly
differs from that in higher-density environments. The morphological
transformation in the majority of field galaxies takes place before the
onset of quenching and is mainly driven by secular processes taking
place within the main sequence, leading to the formation of star-forming
bulge-dominated galaxies as intermediate-stage galaxies. Conversely,
quenching of star formation precedes morphological transformation for
most galaxies in higher-density environments. This causes the formation
of quiescent disc-dominated galaxies before their transition into
bulge-dominated ones.
Electromagnetic
variability from circumbinary discs around binary black holes during
their post-decoupling epoch
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Raphaël Mignon-Risse / Peggy Varniere / Fabien
Casse
Summary
We present general-relativistic hydrodynamical simulations of
inviscid circumbinary discs (CBDs) around near equal-mass binary black
holes (BBH) in the binary-disc post-decoupling epoch. We use an
approximate BBH spacetime with a post-Newtonian inspiral motion
trajectory from  (separation of
(separation of  gravitational
radii) to
gravitational
radii) to  before merger. Initial data for the inspiral runs
are produced from circular-orbits runs covering the formation timescale
of the overdense {}lump{}, orbiting the CBD inner edge. The CBD
non-axisymmetries (spiral waves and lump) lead to non-negligible angular
momentum transport with effective viscosity
before merger. Initial data for the inspiral runs
are produced from circular-orbits runs covering the formation timescale
of the overdense {}lump{}, orbiting the CBD inner edge. The CBD
non-axisymmetries (spiral waves and lump) lead to non-negligible angular
momentum transport with effective viscosity  . We post-process these simulations with a
general-relativistic ray-tracing code to obtain synthetic observations
in thermal emission. We find the lump and its associated electromagnetic
(EM) modulation, already reported in the pre-decoupling epoch, to
survive post-decoupling up until the end of the simulation. For LISA
sources, our findings point to an active EM signature in UV during
optimal gravitational wave source localization. For PTA sources and
current BBH candidates detected through their optical periodicity: the
lump{ in a low-viscosity CBD is a possible, though not unique, origin}
for the observed periodicity.
. We post-process these simulations with a
general-relativistic ray-tracing code to obtain synthetic observations
in thermal emission. We find the lump and its associated electromagnetic
(EM) modulation, already reported in the pre-decoupling epoch, to
survive post-decoupling up until the end of the simulation. For LISA
sources, our findings point to an active EM signature in UV during
optimal gravitational wave source localization. For PTA sources and
current BBH candidates detected through their optical periodicity: the
lump{ in a low-viscosity CBD is a possible, though not unique, origin}
for the observed periodicity.
The
most distant optically polarised GRB afterglow: GRB 240419A at z =
5.178
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- R. Brivio / S. Covino / M. Ferro / A. Saccardi
- A. Martin-Carrillo / A. Kuwata / K. Toma / P. D’Avanzo
- Y.-D. Hu / L. Izzo / S. Kobayashi / T. Laskar
- G. Leloudas / D. B. Malesani / M. Pursiainen / S. Vergani
- K. Wiersema / S. Bloemen / S. Campana / V. D’Elia
- S. de Wet / M. de Pasquale / P. J. Groot / P. Jakobsson
- J. Mao / A. Melandri / G. Pugliese / A. Rossi
- R. Salvaterra / B. Schneider / N. R. Tanvir / J.
van Roestel
- P. M. Vreeswijk / T. Zafar
Summary
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are extremely bright phenomena powered by
relativistic jets arising from explosive events at cosmological
distances. The nature of the jet and the configuration of the local
magnetic fields are still unclear, with the distinction between
different models possibly provided by the detection of early-time
polarisation. Past observations do not agree on a universal scenario
describing early-time polarisation in GRB afterglows, and new studies
are necessary to investigate this open question. We present here the
discovery of GRB,240419A, its redshift determination of  , its early-time
optical polarimetry observations, and the multi-wavelength monitoring of
its afterglow. We analysed three epochs of polarimetric data to derive
the early-time evolution of the polarisation. The multi-wavelength light
curve from the X-rays to the near-infrared band was also investigated to
give a broader perspective on the whole event. We find a high level of
polarisation,
, its early-time
optical polarimetry observations, and the multi-wavelength monitoring of
its afterglow. We analysed three epochs of polarimetric data to derive
the early-time evolution of the polarisation. The multi-wavelength light
curve from the X-rays to the near-infrared band was also investigated to
give a broader perspective on the whole event. We find a high level of
polarisation,  ,%, at 1740~s after the GRB trigger, followed by a
slight decrease up to
,%, at 1740~s after the GRB trigger, followed by a
slight decrease up to  ,% at 3059~s. On the same timescale, the
polarisation position angle is nearly constant. The multi-band afterglow
at the time of the polarisation measurements is consistent with a
forward shock (FS), while the earlier evolution at
,% at 3059~s. On the same timescale, the
polarisation position angle is nearly constant. The multi-band afterglow
at the time of the polarisation measurements is consistent with a
forward shock (FS), while the earlier evolution at  s
can be associated with the interplay between the forward and the reverse
shocks or with energy injection. The detected polarised radiation when
the afterglow is FS-dominated and the stable position angle are
consistent with an ordered magnetic field plus a turbulent component
driven by large-scale magnetohydrodynamic instabilities. The lack of a
jet break in the light curve prevents a comparison of the polarisation
temporal evolution with theoretical expectations from magnetic fields
amplified by microscopic-scale turbulence, limiting …
s
can be associated with the interplay between the forward and the reverse
shocks or with energy injection. The detected polarised radiation when
the afterglow is FS-dominated and the stable position angle are
consistent with an ordered magnetic field plus a turbulent component
driven by large-scale magnetohydrodynamic instabilities. The lack of a
jet break in the light curve prevents a comparison of the polarisation
temporal evolution with theoretical expectations from magnetic fields
amplified by microscopic-scale turbulence, limiting …
Articles for week 44 2025
Gamma-Ray
Burst Polarimetry with the COMCUBE-S CubeSat Swarm
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Nathan Franel / Vincent Tatischeff / David Murphy / Alexey
Ulianov
- Caimin McKenna / Lorraine Hanlon / Prerna Baranwal / Christophe
Beigbeder
- Arnaud Claret / Ion Cojocari / Nicolas de Séréville / Nicolas
Dosme
- Eric Doumayrou / Mariya Georgieva / Clarisse Hamadache / Sally
Hankache
- Jimmy Jeglot / Mózsi Kiss / Beng-Yun Ky / Vincent Lafage
- Philippe Laurent / Christine Le Galliard / Joseph
Mangan / Aline Meuris
- Mark Pearce / Jean Peyré / Arjun Poitaya / Diana Renaud
- Arnaud Saussac / Varun Varun / Matias Vecchio / Colin Wade
Summary
COMCUBE-S (Compton Telescope CubeSat Swarm) is a proposed mission
aimed at understanding the radiation mechanisms of ultra-relativistic
jets from Gamma-Ray Bursts (GRBs). It consists of a swarm of 16U
CubeSats carrying a state-of-the-art Compton polarimeter and a BGO
spectrometer to perform timing, spectroscopic and polarimetric
measurements of the prompt emission from GRBs. The mission is currently
in a feasibility study phase (Phase A) with the European Space Agency to
prepare an in-orbit demonstration. Here, we present the simulation work
used to optimise the design and operational concept of the
microsatellite constellation, as well as estimate the mission
performance in terms of GRB detection rate and polarimetry. We used the
MEGAlib software to simulate the response function of the gamma-ray
instruments, together with a detailed model for the background particle
and radiation fluxes in low-Earth orbit. We also developed a synthetic
GRB population model to best estimate the detection rate. These
simulations show that COMCUBE-S will detect about 2 GRBs per day, which
is significantly higher than that of all past and current GRB missions.
Furthermore, simulated performance for linear polarisation measurements
shows that COMCUBE-S will be able to uniquely distinguish between
competing models of the GRB prompt emission, thereby shedding new light
on some of the most fundamental aspects of GRB physics.
BEBOP
VIII. SOPHIE radial velocities reveal an eccentric, circumbinary brown
dwarf
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Amaury H. M. J. Triaud / Thomas A. Baycroft / Neda Heidari /
Alexandre Santerne
- Aleyna Adamson / Isabelle Boisse / Gavin A. L.
Coleman / Alexandre C. M. Correia
- Yasmin T. Davis / Magali Deleuil / Guillaume
Hébrard / David V. Martin
- Pierre F. L. Maxted / Richard P. Nelson / Lalitha Sairam / Daniel
Sebastian
- Matthew R. Standing / Adam T. Stevenson / Amalie Stokholm / Mathilde
Timmermans
- Stéphane Udry
Summary
Circumbinary configurations offer a test of planet formation in an
altered environment, where the inner binary has perturbed a
protoplanetary disc. Comparisons of the physical and orbital parameters
between the circumbinary planet population and the population of
exoplanets orbiting single stars will reveal how these disc
perturbations affect the assembly of planets. Circumbinary exoplanets
detected thus far typically have masses  raising the question of whether high-mass
circumbinary planets are possible, and also whether population features
such as the brown dwarf desert would appear in circumbinary
configurations like for single star systems. Here, we report
observations taken with the SOPHIE high-resolution spectrograph. These
observations reveal an
raising the question of whether high-mass
circumbinary planets are possible, and also whether population features
such as the brown dwarf desert would appear in circumbinary
configurations like for single star systems. Here, we report
observations taken with the SOPHIE high-resolution spectrograph. These
observations reveal an  outer companion, on an eccentric (
outer companion, on an eccentric ( ),
),  orbit,
which we call BEBOP-4 (AB) b. Using dynamical arguments we constrain the
true mass
orbit,
which we call BEBOP-4 (AB) b. Using dynamical arguments we constrain the
true mass  . The
inner binary’s two eclipsing stellar components have masses
. The
inner binary’s two eclipsing stellar components have masses  , and
, and  . Their
orbital period is
. Their
orbital period is  , and their
eccentricity is
, and their
eccentricity is  . This system contains the
longest period binary surveyed by the BEBOP project. BEBOP-4b is
expected to be detectable using Gaia DR4 single epoch astrometric
measurements. Despite a large period ratio of
. This system contains the
longest period binary surveyed by the BEBOP project. BEBOP-4b is
expected to be detectable using Gaia DR4 single epoch astrometric
measurements. Despite a large period ratio of  , the
substantial eccentricities of both orbits mean that the outer orbit is
on the edge of orbital stability, and located in between two
destabilising secular resonances. Should the outer companion survive,
the BEBOP-4 system appears like a precursor to several post-common
envelope binaries exhibiting eclipse timing variations where very
massive circumbinary companions have been proposed.
, the
substantial eccentricities of both orbits mean that the outer orbit is
on the edge of orbital stability, and located in between two
destabilising secular resonances. Should the outer companion survive,
the BEBOP-4 system appears like a precursor to several post-common
envelope binaries exhibiting eclipse timing variations where very
massive circumbinary companions have been proposed.
Euclid:
Systematic uncertainties from the halo mass conversion on galaxy cluster
number count data analyses
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- T. Gayoux / P.-S. Corasaniti / T. R. G. Richardson / S. T. Kay
- A. M. C. Le Brun / L. Moscardini / L. Pizzuti / S. Borgani
- M. Costanzi / C. Giocoli / S. Grandis / A. Ragagnin
- J. Rhodes / I. Saez-Casares / M. Sereno / E. Sarpa
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Canas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Farrens / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- E. Keihanen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / E. Munari / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / P. Schneider / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca
- C. Burigana / M. Maturi / V. Scottez / M. Viel
Summary
The large catalogues of galaxy clusters expected from the Euclid
survey will enable cosmological analyses of cluster number counts that
require accurate cosmological model predictions. One possibility is to
use parametric fits calibrated against  -body simulations, that capture the
cosmological parameter dependence of the halo mass function. Several
studies have shown that this can be obtained through a calibration
against haloes with spherical masses defined at the virial overdensity.
In contrast, if different mass definitions are used for the HMF and the
scaling relation, a mapping between them is required. Here, we
investigate the impact of such a mapping on the cosmological parameter
constraints inferred from galaxy cluster number counts. Using synthetic
data from
-body simulations, that capture the
cosmological parameter dependence of the halo mass function. Several
studies have shown that this can be obtained through a calibration
against haloes with spherical masses defined at the virial overdensity.
In contrast, if different mass definitions are used for the HMF and the
scaling relation, a mapping between them is required. Here, we
investigate the impact of such a mapping on the cosmological parameter
constraints inferred from galaxy cluster number counts. Using synthetic
data from  -body simulations, we show that the
standard approach, which relies on assuming a concentration-mass
relation, can introduce significant systematic bias. In particular,
depending on the mass definition and the relation assumed, this can lead
to biased constraints at more than 2
-body simulations, we show that the
standard approach, which relies on assuming a concentration-mass
relation, can introduce significant systematic bias. In particular,
depending on the mass definition and the relation assumed, this can lead
to biased constraints at more than 2 level. In contrast, we find that in all
the cases we have considered, the mass conversion based on the halo
sparsity statistics result in a systematic bias smaller than the
statistical error.
level. In contrast, we find that in all
the cases we have considered, the mass conversion based on the halo
sparsity statistics result in a systematic bias smaller than the
statistical error.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / F. Antonini / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther
- S. Appert / S. K. Apple / K. Arai / C. Araújo-Álvarez
- A. Araya / M. C. Araya / M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda
- N. Aritomi / F. Armato / S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud
- M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson / K. G. Arun / G. Ashton
- Y. Aso / L. Asprea / M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo
- S. M. Aston / P. Astone / P. S. Aswathi / F. Attadio
- F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone / E. A. Avila
- S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae / S. Bagnasco
- L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka / A. M. Baker
- K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi / N. Baldicchi
- M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri
- B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral
- M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish / D. Barker
- N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone / B. Barr
- L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti
- M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri
- A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley
- A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale
- F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell
- D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara
- J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin
- B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / C. P. L. Berry
- D. Bersanetti / T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser
- D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare
- R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya / S. Bhaumik
- V. Biancalana / A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley
- A. Binetti / S. Bini / C. Binu / S. Biot
- O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi
- M.-A. Bizouard / S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg
- C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair / N. Bode / N. Boettner
- G. Boileau / M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A.
Bolliand
- L. D. Bonavena / R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla
- M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / A. Borchers
- S. Borhanian / V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov
- Y. Bothra / A. Boudon / L. Bourg / M. Boyle
- A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady / A. Branch
- M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant / A. Brillet
- M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks
- B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett
- G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant / Y. Bu
- F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik
- H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio
- D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies
- R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli
- C. Cahillane / A. Calafat / J. Calderón Bustillo / T. A.
Callister
- E. Calloni / S. R. Callos / G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon
- H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa / E. Capote
- G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara
- J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli
- G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos
- J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S.
Caudill
- M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja / G. Cella
- P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi
- A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka
Subrahmanya
- J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / K. Chang / S. Chao
- P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee / Debarati
Chatterjee
- Deep Chatterjee / M. Chaturvedi / S. Chaty / K. Chatziioannou
- A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen / H. Chen
- H. Y. Chen / S. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen
- H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung
- F. Chiadini / D. Chairamello / G. Chiarini / A. Chiba
- A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo / C. Chou
- S. Choudhary / N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani
- P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok
- F. Clara / J. A. Clark / T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater
- S. Clesse / F. Cleva / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo
- P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace / E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni
- C. G. Collette / J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo
- C. M. Compton / G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt
- I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado
- A. Corsi / R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux
- P. Couvares / D. M. Coward / R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo
- J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton / P. Cremonese / S. Crook
- R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen
- A. Cumming / E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição
- T. Dal Canton / S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo
- S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch
- L. P. Dartez / R. Das / A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo
- A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave / A. Davenport
- M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis / L. Davis
- M. C. Davis / P. Davis / E. J. Daw / M. Dax
- J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis
- F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre / W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny
- F. De Marco / G. Demasi / F. De Matteis / N. Demos
- T. Dent / A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri
- R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi / M. Desai / R. DeSalvo
- A. DeSimone / R. De Simone / A. Dhani / R. Dhurkunde
- R. Diab / M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron
- T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni
- T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha / J. Ding / S. Di Pace
- I. Di Palma / D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti
- A. Dmitriev / J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen
- E. Dohmen / A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza / L. D’Onofrio
- F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney / S. Doravari
- O. Dorosh / W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers
- L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne / D. D’Urso
- P. Dutta Roy / H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa
- W. E. East / M. Ebersold / T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls
- A. Effler / J. Eichholz / H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann
- M. Emma / K. Endo / R. Enficiaud / L. Errico
- R. Espinosa / M. Esposito / R. C. Essick / H. Estellés
- T. Etzel / M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing
- J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi / V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst
- A. M. Farah / B. Farr / W. M. Farr / G. Favaro
- M. Favata / M. Fays / M. Fazio / J. Feicht
- M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes
- T. Fernandes / D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira
- F. Fidecaro / P. Figura / A. Fiori / I. Fiori
- M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara
- R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming / E. Floden
- H. Fong / J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes / C. Foo
- B. Fornal / K. Franceschetti / F. Frappez / S. Frasca
- F. Frasconi / J. P. Freed / Z. Frei / A. Freise
- O. Freitas / R. Frey / W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel
- V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii
- T. Fujimori / P. Fulda / M. Fyffe / B. Gadre
- J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage / V. Galdi / R. Gamba
- A. Gamboa / S. Gamoji / D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly
- B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido / C. García-Quirós / J. W.
Gardner
- K. A. Gardner / S. Garg / J. Gargiulo / X. Garrido
- A. Garron / F. Garufi / P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra
- B. Gateley / F. Gautier / V. Gayathri / T. Gayer
- G. Gemme / A. Gennai / V. Gennari / J. George
- R. George / O. Gerberding / L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh
- Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh
- Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson
- C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer / F. Glotin
- J. Godfrey / R. V. Godley / P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel
- E. Goetz / J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov
- G. González / P. Goodarzi / S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones
- M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova
- A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados / M. Granata
- V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia / J. Graves
- C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco / A. C. Green
- L. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green / C. Greenberg
- A. M. Gretarsson / H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith / H. L. Griggs
- G. Grignani / C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald
- D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes
- H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / H. Guo / W. Guo
- Y. Guo / Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta
- S. K. Gupta / V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs
- N. Gutierrez / N. Guttman / F. Guzman / D. Haba
- M. Haberland / S. Haino / E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton
- G. Hammond / M. Haney / J. Hanks / C. Hanna
- M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen
- J. Hanson / S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison
- S. Harikumar / K. Haris / I. Harley-Trochimczyk / T. Harmark
- J. Harms / G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry / J. Hart
- B. Haskell / C. J. Haster / K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa
- K. Hayama / A. Heffernan / M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze
- J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann / F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell
- G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M. Hendry / I. S. Heng
- M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw / M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt
- J. Heynen / J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham / S. Hild
- S. Hill / Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata / C. Hirose
- D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan / N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows
- D. E. Holz / L. Honet / D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough
- S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy
- C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi / H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh
- C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu / W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu
- H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart
- B. Hughey / V. Hui / S. Husa / R. Huxford
- L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni / G. Iannone
- J. Iascau / K. Ide / R. Iden / A. Ierardi
- S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku / Y. Inoue / G. Iorio
- P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa
- M. Isi / K. S. Isleif / Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya
- B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot
- S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav / M. Jain / T. Jain
- A. L. James / K. Jani / J. Janquart / N. N. Janthalur
- S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume / W. Javed
- A. Jennings / M. Jensen / W. Jia / J. Jiang
- H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston
- R. Johnston / N. Johny / D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones
- R. Jones / H. E. Jose / P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi
- G. Joubert / J. Ju / L. Ju / K. Jung
- J. Junker / V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita
- I. Kaku / V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi
- N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel
- J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty / S. J. Kapadia / D. P.
Kapasi
- M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack / H. Kato / T. Kato
- E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman / R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe
- R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel / L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington
- F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key / R. Khadela
- S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan
- T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo
- N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim / K. Kim
- M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball
- K. Kimes / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko
- A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi
- S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama
- S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori
- A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko
- X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam
- T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel
- N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker / A. Królak / K. Kruska
- J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn / S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan
- Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar / Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar
- Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume / K. Kuns
- N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak
- K. Kwan / S. Kwon / G. Lacaille / D. Laghi
- A. H. Laity / E. Lalande / M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati
- M. Landry / B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang / J. Lange
- R. Langgin / B. Lantz / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen
- A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. Laxen
- C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci
- L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee
- J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee / R. Lee
- Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred
- J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître
- M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy
- M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin
- K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li
- X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos
- E. T. Lin / F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin
- C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / A. Liu / G. C. Liu
- Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L.
Lo
- J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou / L. T. London
- A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla / A. Lorenzo-Medina
- V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / E. Lotti
- T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto
- N. Low / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi / H. Lück
- D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier / R. Macas
- M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet
- K. Maeda / S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee
- E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi / P. Mahapatra
- M. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi / E. Majorana
- C. N. Makarem / N. Malagon / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis
- U. Mali / S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick
- A.-K. Malz / N. Man / M. Mancarella / V. Mandic
- V. Mangano / N. Manning / B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell
- M. Manske / M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli / C. Marinelli
- F. Marion / A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros
- S. Marsat / F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin
- B. B. Martinez / D. A. Martinez / M. Martinez / V. Martinez
- A. Martini / J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx
- L. Massaro / A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni
- T. Matcovich / M. Matiushechkina / L. Maurin / N. Mavalvala
- N. Maxwell / G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland
- S. McCormick / L. McCuller / S. McEachin / C. McElhenny
- G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver
- A. McLeod / I. McMahon / T. McRae / R. McTeague
- D. Meacher / B. N. Meagher / R. Mechum / Q. Meijer
- A. Melatos / C. S. Menoni / F. Mera / R. A. Mercer
- L. Mereni / K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou
- J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui / C. Messick / B. Mestichelli
- M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske / A. Miani
- H. Miao / C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton
- D. P. Mihaylov / S. J. Miller / M. Millhouse / E. Milotti
- V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov / E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir
- L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra
- C. Mishra / T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell
- S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov / K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman
- O. Miyakawa / S. Miyoki / A. Miyoko / G. Mo
- L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz
- M. Mondin / M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru
- A. More / S. More / C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno
- G. Moreno / A. Moreso Serra / S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki
- G. Morras / A. Moscatello / M. Mould / B. Mours
- C. M. Mow-Lowry / L. Muccillo / F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee
- Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma Mukherjee / Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip
Mukherjee
- N. Mukund / A. Mullavey / H. Mullock / J. Mundi
- C. L. Mungioli / M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / D. Nabari
- S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki
- K. Nakamura / H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze
- D. Nandi / V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia
- T. Narikawa / H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak
- L. Negri / A. Nela / C. Nelle / A. Nelson
- T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery / A. Neunzert / S. Ng
- L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino
- A. Nishizawa / S. Nissanke / W. Niu / F. Nocera
- J. Noller / M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak
- R. Nowicki / J. F. Nuño Siles / L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi
- J. Oberling / J. O’Dell / E. Oelker / M. Oertel
- G. Oganesyan / T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / F. Ohme
- R. Oliveri / R. Omer / B. O’Neal / M. Onishi
- K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly / M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy
- S. O’Shea / S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota
- D. J. Ottaway / A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen
- R. Ozaki / A. E. Pace / R. Pagano / M. A. Page
- A. Pai / L. Paiella / A. Pal / S. Pal
- M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma / C. Palomba
- P. Palud / H. Pan / J. Pan / K. C. Pan
- P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey / Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang
- F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone / B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther
- M. Panzeri / F. Paoletti / A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos
- E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini / G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis
- A. Parisi / B.-J. Park / J. Park / W. Parker
- G. Pascale / D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti
- L. Passenger / D. Passuello / O. Patane / A. V. Patel
- D. Pathak / A. Patra / B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson
- K. Paul / S. Paul / E. Payne / T. Pearce
- M. Pedraza / A. Pele / F. E. Peña Arellano / X. Peng
- Y. Peng / S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego
- Z. Pereira / C. Périgois / G. Perna / A. Perreca
- J. Perret / S. Perriès / J. W. Perry / D. Pesios
- S. Peters / S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer
- H. Pham / K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam
- M. Piarulli / L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot
- M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra
- V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo
- L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski
- M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi
- M. L. Planas / W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani
- E. Polini / J. Pomper / L. Pompili / J. Poon
- E. Porcelli / E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton
- J. Powell / G. S. Prabhu / M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan
- T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati / K. Prasai / R. Prasanna
- P. Prasia / G. Pratten / G. Principe / G. A. Prodi
- P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher
- J. Pullin / P. Puppo / M. Pürrer / H. Qi
- J. Qin / G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez
- N. Qutob / R. Rading / I. Rainho / S. Raja
- C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal
- M. Ramos Arevalo / A. Ramos-Buades / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom
- P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto / A. Ravichandran / A. Ray
- V. Raymond / M. Razzano / J. Read / T. Regimbau
- S. Reid / C. Reissel / D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini
- B. Revenu / A. Revilla Peña / R. Reyes / L. Ricca
- F. Ricci / M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. Rice
- J. W. Richardson / M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles
- H. K. Riley / S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson
- F. Robinet / M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland
- J. G. Rollins / A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero
- I. M. Romero-Shaw / J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke
- L. Rosa / T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska
- M. P. Ross / M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy
- S. Roy / D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama
- E. Ruiz Morales / K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki
- P. Saffarieh / S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha
- T. Sainrat / S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / Y. Sakai
- M. Sakellariadou / S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba
- L. Salconi / M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé
- S. U. Salunkhe / S. Salvador / A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar
- A. Sanchez / E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual
- J. R. Sanders / E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea
- T. R. Saravanan / N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / A. Sasli
- P. Sassi / B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato
- S. Sato / Yukino Sato / Yu Sato / O. Sauter
- R. L. Savage / T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah
- V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein
- M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel
- M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield / K. Schouteden / B. W.
Schulte
- B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi / J. Scott
- S. M. Scott / R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo
- Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers / N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta
- E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo / V. Sequino / M. Serra
- A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh
- L. Shao / A. K. Sharma / Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma
- Ritwik Sharma / S. Sharma Chaudhary / P. Shawhan / N. S.
Shcheblanov
- E. Sheridan / Z.-H. Shi / M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura
- H. Shinkai / S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker
- R. W. Short / S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider / H. Siegel
- N. Siemonsen / D. Sigg / L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri
- M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer / Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh
- D. Singh / M. K. Singh / N. Singh / S. Singh
- A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen
- D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J. Smetana / J. R. Smith
- L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith / S. Soares de Albuquerque
Filho
- M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I. Song / S. Soni
- V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani / F. Spada
- V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli / A. K. Srivastava
- F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer / N. Steinle
- J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas / P. Stevens
- S. P. Stevenson / M. StPierre / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk
- A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / Y. Sudo
- N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun
- L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton
- P. J. Sutton / K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels
- A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca
- H. Tagoshi / K. Takada / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi
- A. Takamori / S. Takano / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita
- I. Takimoto Schmiegelow / M. Takou-Ayaoh / C. Talbot / M.
Tamaki
- N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka
- S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao
- R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto / A. Taruya
- J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / D. Tellez / R. Tenorio
- H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M.
Thomas
- M. Thomas / P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu
- K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari
- Pawan Tiwari / Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari
- M. R. Todd / M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland
- A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura
- H. Tong / C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie
- I. Tosta e Melo / E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran
- A. Trapananti / R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor
- M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian
- A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang
- S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi
- C. Turski / H. Ubach / N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama
- R. P. Udall / T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim
- L. E. Uronen / T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch
- N. Vaidya / G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia
- M. Valentini / S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan
- M. van Dael / E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van
Den Broeck
- M. van der Sluys / A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra
- M. VanDyke / H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van
Hove
- J. Vanier / M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel
- M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez
- A. Vecchio / G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch
- S. Venikoudis / R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken
- D. Verkindt / B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen
- F. Vetrano / A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant
- A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva
Espinosa
- V. Villa-Ortega / E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret
- S. Vitale / H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis
- J. S. A. von Wrangel / W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P.
Vyatchanin
- J. Wack / L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner
- L. Wallace / E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang
- W. H. Wang / Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner
- M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai
- B. Weaver / S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert
- A. J. Weinstein / R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette
- J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens
- D. Wilken / A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams
- M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke
- M. Wils / L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood
- C. C. Wipf / G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe
- H. T. Wong / H. W. Y. Wong / I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong
- T. Wouters / J. L. Wright / M. Wright / B. Wu
- C. Wu / D. S. Wu / H. Wu / K. Wu
- Q. Wu / Y. Wu / Z. Wu / E. Wuchner
- D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu / Y. Xu / N. Yadav
- H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto / T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto
- R. Yamazaki / T. Yan / K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang
- Z. Yarbrough / J. Yebana / S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar
- X. Yin / J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan
- H. Yuzurihara / M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova
- J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin
- L. Zhang / N. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang
- C. Zhao / Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao
- Y. Zheng / H. Zhong / H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu
- Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman / L. Zimmermann / Y. Zlochower
- M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
We report the observation of gravitational waves from two binary
black hole coalescences during the fourth observing run of the
LIGO–Virgo–KAGRA detector network, GW241011 and GW241110. The sources of
these two signals are characterized by rapid and precisely measured
primary spins, non-negligible spin–orbit misalignment, and unequal mass
ratios between their constituent black holes. These properties are
characteristic of binaries in which the more massive object was itself
formed from a previous binary black hole merger, and suggest that the
sources of GW241011 and GW241110 may have formed in dense stellar
environments in which repeated mergers can take place. As the third
loudest gravitational-wave event published to date, with a median
network signal-to-noise ratio of  , GW241011 furthermore
yields stringent constraints on the Kerr nature of black holes, the
multipolar structure of gravitational-wave generation, and the existence
of ultralight bosons within the mass range
, GW241011 furthermore
yields stringent constraints on the Kerr nature of black holes, the
multipolar structure of gravitational-wave generation, and the existence
of ultralight bosons within the mass range  –
– eV.
eV.
Cosmological
and High Energy Physics implications from gravitational-wave background
searches in LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA’s O1-O4a runs
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea / M. Assiduo
- S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone / F. Attadio
- F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone / E. A. Avila
- S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae / S. Bagnasco
- L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka / A. M. Baker
- K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi / N. Baldicchi
- M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri
- B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral
- M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish / D. Barker
- N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone / B. Barr
- L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti
- M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri
- A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley
- A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale
- F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell
- D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara
- J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin
- B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / D. Bersanetti
- T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge
- G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare / R. Bhatt
- D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya / S. Bhaumik / V.
Biancalana
- A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti
- S. Bini / C. Binu / S. Biot / O. Birnholtz
- S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard
- S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair
- D. G. Blair / S. Blasi / N. Bode / N. Boettner
- G. Boileau / M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A.
Bolliand
- L. D. Bonavena / R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla
- M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / A. Borchers
- S. Borhanian / V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov
- Y. Bothra / A. Boudon / L. Bourg / T. D. Boybeyi
- M. Boyle / A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady
- A. Branch / M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant
- A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller
- A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti
- S. Brunett / G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant
- Y. Bu / F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko
- T. Bulik / H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk
- R. Buscicchio / D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer
- G. S. Cabourn Davies / R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L.
Cadonati
- G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / A. Calafat / T. A. Callister
- E. Calloni / S. R. Callos / G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon
- H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa / E. Capote
- G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara
- J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli
- G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos
- J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S.
Caudill
- M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja / G. Cella
- P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi
- A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka
Subrahmanya
- J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / K. Chang / S. Chao
- P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee / Debarati
Chatterjee
- Deep Chatterjee / M. Chaturvedi / S. Chaty / A. Chen
- A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen
- S. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng
- P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini
- G. Chiarini / A. Chiba / A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo
- A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary / N. Christensen
- S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar
- M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok / F. Clara / J. A. Clark
- T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater / S. Clesse / F. Cleva
- E. Coccia / E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace
- E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette / J. Collins
- S. Colloms / A. Colombo / C. M. Compton / G. Connolly
- L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi
- N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado / A. Corsi / R. Cottingham
- M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux / P. Couvares / D. M. Coward
- R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo / J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton
- P. Cremonese / S. Crook / R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia
- J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming / E. Cuoco
- M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton / S. Dal Pra
- G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio
- K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez / R. Das
- A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo / A. Daumas / N. Davari
- I. Dave / A. Davenport / M. Davier / T. F. Davies
- D. Davis / L. Davis / M. C. Davis / P. Davis
- E. J. Daw / M. Dax / J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan
- J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis / F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre
- W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny / F. De Marco / G. Demasi
- F. De Matteis / N. Demos / T. Dent / A. Depasse
- N. DePergola / R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi
- M. Desai / R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone / R. De Simone
- A. Dhani / R. Diab / M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare
- G. Dideron / T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo
- M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha / J. Ding
- S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma / D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo
- Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev / J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor
- N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen / A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza
- L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney
- S. Doravari / O. Dorosh / W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago
- J. C. Driggers / L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne
- D. D’Urso / P. Dutta Roy / H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer
- C. Eassa / M. Ebersold / T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls
- A. Effler / J. Eichholz / H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann
- M. Emma / K. Endo / R. Enficiaud / L. Errico
- R. Espinosa / M. Esposito / R. C. Essick / H. Estellés
- T. Etzel / M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing
- J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi / V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst
- A. M. Farah / B. Farr / W. M. Farr / G. Favaro
- M. Favata / M. Fays / M. Fazio / J. Feicht
- M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes
- T. Fernandes / D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira
- F. Fidecaro / P. Figura / A. Fiori / I. Fiori
- M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara
- R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming / E. Floden
- H. Fong / J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes / C. Foo
- B. Fornal / K. Franceschetti / F. Frappez / S. Frasca
- F. Frasconi / J. P. Freed / Z. Frei / A. Freise
- O. Freitas / R. Frey / W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel
- V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii
- T. Fujimori / T. Fujita / P. Fulda / M. Fyffe
- B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage / V. Galdi
- R. Gamba / A. Gamboa / S. Gamoji / D. Ganapathy
- A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido / C.
García-Quirós
- J. W. Gardner / K. A. Gardner / S. Garg / J. Gargiulo
- X. Garrido / A. Garron / F. Garufi / P. A. Garver
- C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier / V. Gayathri
- T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai / V. Gennari
- J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding / L. Gergely
- Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh
- Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina
- D. R. Gibson / C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer
- F. Glotin / J. Godfrey / R. V. Godley / P. Godwin
- A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez
- B. Goncharov / G. González / P. Goodarzi / S. Goode
- A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould
- K. Govorkova / A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados
- M. Granata / V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia
- J. Graves / C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco
- A. C. Green / L. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green
- C. Greenberg / A. M. Gretarsson / H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith
- H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani / C. Grimaud / H. Grote
- S. Grunewald / D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi
- A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / H. Guo
- W. Guo / Y. Guo / Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta
- N. C. Gupta / S. K. Gupta / V. Gupta / N. Gupte
- J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez / N. Guttman / F. Guzman
- D. Haba / M. Haberland / S. Haino / E. D. Hall
- E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond / M. Haney / J. Hanks
- C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman
- H. Hansen / J. Hanson / S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada
- A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar / K. Haris / I.
Harley-Trochimczyk
- T. Harmark / J. Harms / G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry
- J. Hart / B. Haskell / C. J. Haster / K. Haughian
- H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama / M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze
- J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann / F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell
- G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M. Hendry / I. S. Heng
- M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw / M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt
- J. Heynen / J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham / S. Hild
- S. Hill / Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata / C. Hirose
- D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan / N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows
- D. E. Holz / L. Honet / D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough
- S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy
- C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi / H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh
- C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu / W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu
- H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart
- B. Hughey / V. Hui / S. Husa / R. Huxford
- L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni / G. Iannone
- J. Iascau / K. Ide / R. Iden / A. Ierardi
- S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku / Y. Inoue / G. Iorio
- P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa
- M. Isi / K. S. Isleif / Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya
- B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot
- S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav / M. Jain / T. Jain
- A. L. James / K. Jani / J. Janquart / N. N. Janthalur
- S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume / W. Javed
- A. Jennings / M. Jensen / W. Jia / J. Jiang
- H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston
- R. Johnston / N. Johny / D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones
- R. Jones / H. E. Jose / P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi
- G. Joubert / J. Ju / L. Ju / K. Jung
- J. Junker / V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita
- I. Kaku / V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi
- N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel
- J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty / S. J. Kapadia / D. P.
Kapasi
- M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack / H. Kato / T. Kato
- E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman / R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe
- R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel / L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington
- F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key / R. Khadela
- S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan
- T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo
- N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim / K. Kim
- M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball
- K. Kimes / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko
- A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi
- S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama
- S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori
- A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko
- X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam
- T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel
- N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker / A. Królak / K. Kruska
- J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn / S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan
- Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar / Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar
- Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume / K. Kuns
- N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak
- K. Kwan / S. Kwon / G. Lacaille / D. Laghi
- A. H. Laity / E. Lalande / M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati
- M. Landry / B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang / J. Lange
- R. Langgin / B. Lantz / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen
- A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. Laxen
- C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci
- L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee
- J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee / R. Lee
- Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred
- J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître
- M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy
- M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin
- K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li
- X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos
- E. T. Lin / F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin
- C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / A. Liu / G. C. Liu
- Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L.
Lo
- J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou / L. T. London
- A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla / A. Lorenzo-Medina
- V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / E. Lotti
- T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto
- N. Low / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi / H. Lück
- D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier / R. Macas
- M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet
- K. Maeda / S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee
- E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh
- M. Maini / S. Majhi / E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem
- D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis / U. Mali / S. Maliakal
- A. Malik / L. Mallick / A.-K. Malz / N. Man
- M. Mancarella / V. Mandic / V. Mangano / B. Mannix
- G. L. Mansell / M. Manske / M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli
- C. Marinelli / F. Marion / A. Mariotti / A. S. Markosyan
- A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat / F. Martelli
- I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez / D. A. Martinez
- M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini / J. C. Martins
- D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro / A. Masserot
- M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich / M.
Matiushechkina
- L. Maurin / N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell / G. McCarrol
- R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick / L. McCuller
- S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn
- K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod / I. McMahon
- T. McRae / R. McTeague / D. Meacher / B. N. Meagher
- R. Mechum / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos / C. S. Menoni
- F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni / K. Merfeld
- E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui
- C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn
- A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao / C. Michel
- Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov / S. J. Miller
- M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov
- E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés
- C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra / C. Mishra / T. Mishra
- A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov
- K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa / S. Miyoki
- A. Miyoko / G. Mo / L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra
- S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / M. Mondin / M. Montani
- C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More / S. More
- C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno / A. Moreso Serra
- S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras / A. Moscatello
- M. Mould / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry / L. Muccillo
- F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma
Mukherjee
- Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip Mukherjee / N. Mukund / A. Mullavey
- H. Mullock / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli / M. Murakoshi
- P. G. Murray / D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar
- N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura / H. Nakano
- M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi / V. Napolano
- P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa / H. Narola
- L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak / L. Negri / A. Nela
- C. Nelle / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery
- A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols
- A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa / S. Nissanke
- W. Niu / F. Nocera / J. Noller / M. Norman
- C. North / J. Novak / R. Nowicki / J. F. Nuño Siles
- L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling / J. O’Dell
- E. Oelker / M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan / T. O’Hanlon
- M. Ohashi / F. Ohme / R. Oliveri / R. Omer
- B. O’Neal / M. Onishi / K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly
- M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / S. Oshino
- C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway / A. Ouzriat
- H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki / A. E. Pace
- R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai / L. Paiella
- A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi
- P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud / H. Pan
- J. Pan / K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey
- Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone
- B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri / F. Paoletti
- A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini
- G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis / A. Parisi / B.-J. Park
- J. Park / W. Parker / G. Pascale / D. Pascucci
- A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger / D. Passuello
- O. Patane / A. V. Patel / D. Pathak / A. Patra
- B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul / S. Paul
- E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza / A. Pele
- F. E. Peña Arellano / X. Peng / Y. Peng / S. Penn
- M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego / Z. Pereira / C. Périgois
- G. Perna / A. Perreca / J. Perret / S. Perriès
- J. W. Perry / D. Pesios / S. Peters / S. Petracca
- C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham / K. A. Pham
- K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli / L. Piccari
- O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot / M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni
- L. Pierini / G. Pierra / V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak
- M. Pillas / F. Pilo / L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto
- M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin
- A. Placidi / E. Placidi / M. L. Planas / W. Plastino
- C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani / E. Polini / J. Pomper
- L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli / E. K. Porter
- C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell / G. S. Prabhu
- M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati
- K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia / G. Pratten
- G. Principe / G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito
- A. C. Providence / A. Puecher / J. Pullin / P. Puppo
- M. Pürrer / H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner
- V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez / N. Qutob / R. Rading
- I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari
- K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / M. Ramos Arevalo / A.
Ramos-Buades
- S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani / A. Rase
- B. Ratto / A. Ravichandran / A. Ray / V. Raymond
- M. Razzano / J. Read / T. Regimbau / S. Reid
- C. Reissel / D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu
- A. Revilla Peña / R. Reyes / L. Ricca / F. Ricci
- M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. Rice / J. W. Richardson
- M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley
- S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet
- M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins
- A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw
- J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa
- T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross
- M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy
- D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales
- K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh
- S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat
- S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou
- S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi
- M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe
- S. Salvador / A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez
- E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders
- E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan
- N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / A. Sasli / P. Sassi
- B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato / S. Sato
- Yukino Sato / Yu Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage
- T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco
- D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski
- P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind
- R. M. S. Schofield / K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F.
Schutz
- E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott
- R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y.
Sekiguchi
- D. Sellers / N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo
- J. W. Seo / V. Sequino / M. Serra / A. Sevrin
- T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao
- A. K. Sharma / Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma
- S. Sharma Chaudhary / P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / E.
Sheridan
- Z.-H. Shi / M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai
- S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short
- S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider / H. Siegel / D. Sigg
- L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer
- Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh / D. Singh / N. Singh
- S. Singh / A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris
- B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J.
Smetana
- J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith
- S. Soares de Albuquerque Filho / M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I.
Song
- S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani
- F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli
- A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer
- N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas
- P. Stevens / M. StPierre / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk
- A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / Y. Sudo
- N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun
- L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton
- P. J. Sutton / K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels
- A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca
- H. Tagoshi / K. Takada / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi
- A. Takamori / S. Takano / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita
- I. Takimoto Schmiegelow / M. Takou-Ayaoh / C. Talbot / M.
Tamaki
- N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka
- S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao
- R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto / A. Taruya
- J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / D. Tellez / R. Tenorio
- H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M.
Thomas
- M. Thomas / P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu
- K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari
- Pawan Tiwari / Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari
- M. R. Todd / M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland
- A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura
- H. Tong / C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie
- I. Tosta e Melo / E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran
- A. Trapananti / R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor
- M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian
- A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang
- S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi
- C. Turski / H. Ubach / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall
- T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim / L. E. Uronen
- T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya
- G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia / M. Valentini
- S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan / M. van Dael
- E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / M.
van der Sluys
- A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra / M. VanDyke
- H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J.
Vanier
- M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro
- A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio
- G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis
- R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt
- B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets
- A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva Espinosa / V.
Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / S. Vitale
- H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel
- W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack
- L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner / L. Wallace
- E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang
- Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner / M. Was
- T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai / B. Weaver
- S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein
- R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette / J. T. Whelan
- B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens / D. Wilken
- A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams / M. J. Williams
- N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils
- L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf
- G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong
- I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters / J. L. Wright
- M. Wright / B. Wu / C. Wu / D. S. Wu
- H. Wu / K. Wu / Q. Wu / Y. Wu
- Z. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu
- Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto
- T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki / T. Yan
- K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough / J. Yebana
- S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin / J. Yokoyama
- T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara / M. Zanolin
- M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli
- M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / H. Zhang / L. Zhang
- N. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang / C. Zhao
- Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng
- H. Zhong / H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu
- A. B. Zimmerman / L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
We search for gravitational-wave background signals produced by
various early Universe processes in the Advanced LIGO O4a dataset,
combined with the data from the earlier O1, O2, and O3 (LIGO-Virgo)
runs. The absence of detectable signals enables powerful constraints on
fundamental physics. We derive gravitational-wave background energy
density upper limits from the O1-O4a data to constrain parameters
associated with various possible processes in the early Universe:
first-order phase transitions, cosmic strings, domain walls, stiff
equation of state, axion inflation, second-order scalar perturbations,
primordial black hole binaries, and parity violation. In our analyses,
the presence of an astrophysical background produced by compact (black
hole and neutron star) binary coalescences throughout the Universe is
also considered. We address the implications for various cosmological
and high energy physics models based on the obtained parameter
constraints. We conclude that LIGO-Virgo data already yield significant
constraints on numerous early Universe scenarios.
Direct
multi-model dark-matter search with gravitational-wave interferometers
using data from the first part of the fourth LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA observing
run
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea / M. Assiduo
- S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone / F. Attadio
- F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone / E. A. Avila
- S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae / S. Bagnasco
- L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka / A. M. Baker
- K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi / N. Baldicchi
- M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri
- B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral
- M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish / D. Barker
- N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone / B. Barr
- L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti
- M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri
- A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley
- A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale
- F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell
- D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara
- J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin
- B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / D. Bersanetti
- T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge
- G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare / R. Bhatt
- D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya / S. Bhaumik / V.
Biancalana
- A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti
- S. Bini / C. Binu / S. Biot / O. Birnholtz
- S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard
- S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair
- D. G. Blair / N. Bode / N. Boettner / G. Boileau
- M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A. Bolliand / L.
D. Bonavena
- R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla
- A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / A. Borchers / V. Boschi
- S. Bose / V. Bossilkov / Y. Bothra / A. Boudon
- L. Bourg / M. Boyle / A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia
- P. R. Brady / A. Branch / M. Branchesi / I. Braun
- T. Briant / A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill
- E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown
- M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett / G. Bruno / R. Bruntz
- J. Bryant / Y. Bu / F. Bucci / J. Buchanan
- O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik / H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno
- K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio / D. Buskulic / C. Buy
- R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies / R. Cabrita / V.
Cáceres-Barbosa
- L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / A. Calafat
- T. A. Callister / E. Calloni / S. R. Callos / G. Caneva Santoro
- K. C. Cannon / H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa
- E. Capote / G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani
- M. Carlassara / J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney
- M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo
- A. Casallas-Lagos / J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y.
Castro-Lucas
- S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja
- G. Cella / P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra
- W. Chaibi / A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty
- S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / K. Chang
- S. Chao / P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee
- Debarati Chatterjee / Deep Chatterjee / M. Chaturvedi / S.
Chaty
- A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen / H. Chen
- H. Y. Chen / S. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen
- H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung
- F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini / A. Chiba / A. Chincarini
- M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary
- N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag
- M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok / F. Clara
- J. A. Clark / T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater / S. Clesse
- F. Cleva / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon
- S. Colace / E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette
- J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo / C. M. Compton
- G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión
- S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado / A. Corsi
- R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux / P. Couvares
- D. M. Coward / R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo / J. D. E. Creighton
- T. D. Creighton / P. Cremonese / S. Crook / R. Crouch
- J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming
- E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton
- S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin
- S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez
- R. Das / A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo / A. Daumas
- N. Davari / I. Dave / A. Davenport / M. Davier
- T. F. Davies / D. Davis / L. Davis / M. C. Davis
- P. Davis / E. J. Daw / M. Dax / J. De Bolle
- M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis / F. De Lillo
- S. Della Torre / W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny / F. De Marco
- G. Demasi / F. De Matteis / N. Demos / T. Dent
- A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa
- C. De Rossi / M. Desai / R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone
- R. De Simone / A. Dhani / R. Diab / M. C. Díaz
- M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron / T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore
- C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha
- J. Ding / S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma / D. Di Piero
- F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev / J. P. Docherty
- Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen / A. Doke
- A. Domiciano De Souza / L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan / K. L.
Dooley
- T. Dooney / S. Doravari / O. Dorosh / W. J. D. Doyle
- M. Drago / J. C. Driggers / L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa
- P.-A. Duverne / D. D’Urso / P. Dutta Roy / H. Duval
- S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa / M. Ebersold / T. Eckhardt
- G. Eddolls / A. Effler / J. Eichholz / H. Einsle
- M. Eisenmann / M. Emma / K. Endo / R. Enficiaud
- L. Errico / R. Espinosa / M. Esposito / R. C. Essick
- H. Estellés / T. Etzel / M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva
- B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi / V. Fafone
- S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr / W. M. Farr
- G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays / M. Fazio
- J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi
- J. Fernandes / T. Fernandes / D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo
- T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura / A. Fiori
- I. Fiori / M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi
- V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming
- E. Floden / H. Fong / J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes
- C. Foo / B. Fornal / K. Franceschetti / F. Frappez
- S. Frasca / F. Frasconi / J. P. Freed / Z. Frei
- A. Freise / O. Freitas / R. Frey / W. Frischhertz
- P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia
- S. Fujii / T. Fujimori / P. Fulda / M. Fyffe
- B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage / V. Galdi
- R. Gamba / A. Gamboa / S. Gamoji / D. Ganapathy
- A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido / C.
García-Quirós
- J. W. Gardner / K. A. Gardner / S. Garg / J. Gargiulo
- X. Garrido / A. Garron / F. Garufi / P. A. Garver
- C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier / V. Gayathri
- T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai / V. Gennari
- J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding / L. Gergely
- Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh
- Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina
- D. R. Gibson / C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer
- F. Glotin / J. Godfrey / R. V. Godley / P. Godwin
- A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez
- B. Goncharov / G. González / P. Goodarzi / S. Goode
- A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould
- K. Govorkova / A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados
- M. Granata / V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia
- J. Graves / C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco
- A. C. Green / L. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green
- C. Greenberg / A. M. Gretarsson / H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith
- H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani / C. Grimaud / H. Grote
- S. Grunewald / D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi
- A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / H. Guo
- W. Guo / Y. Guo / Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta
- N. C. Gupta / S. K. Gupta / V. Gupta / N. Gupte
- J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez / N. Guttman / F. Guzman
- D. Haba / M. Haberland / S. Haino / E. D. Hall
- E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond / M. Haney / J. Hanks
- C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman
- H. Hansen / J. Hanson / S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada
- A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar / K. Haris / I.
Harley-Trochimczyk
- T. Harmark / J. Harms / G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry
- J. Hart / B. Haskell / C. J. Haster / K. Haughian
- H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama / M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze
- J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann / F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell
- G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M. Hendry / I. S. Heng
- M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw / M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt
- J. Heynen / J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham / S. Hild
- S. Hill / Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata / C. Hirose
- D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan / N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows
- D. E. Holz / L. Honet / D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough
- S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy
- C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi / H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh
- C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu / W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu
- H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart
- B. Hughey / V. Hui / S. Husa / R. Huxford
- L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni / G. Iannone
- J. Iascau / K. Ide / R. Iden / A. Ierardi
- S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku / Y. Inoue / G. Iorio
- P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa
- M. Isi / K. S. Isleif / Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya
- B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot
- S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav / M. Jain / T. Jain
- A. L. James / K. Jani / J. Janquart / N. N. Janthalur
- S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume / W. Javed
- A. Jennings / M. Jensen / W. Jia / J. Jiang
- H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston
- R. Johnston / N. Johny / D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones
- R. Jones / H. E. Jose / P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi
- G. Joubert / J. Ju / L. Ju / K. Jung
- J. Junker / V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita
- I. Kaku / V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi
- N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel
- J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty / S. J. Kapadia / D. P.
Kapasi
- M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack / H. Kato / T. Kato
- E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman / R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe
- R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel / L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington
- F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key / R. Khadela
- S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan
- T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo
- N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim / K. Kim
- M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball
- K. Kimes / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko
- A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi
- S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama
- S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori
- A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko
- X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam
- T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel
- N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker / A. Królak / K. Kruska
- J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn / S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan
- Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar / Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar
- Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume / K. Kuns
- N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak
- K. Kwan / S. Kwon / G. Lacaille / D. Laghi
- A. H. Laity / E. Lalande / M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati
- M. Landry / B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang / J. Lange
- R. Langgin / B. Lantz / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen
- A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. Laxen
- C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci
- L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee
- J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee / R. Lee
- Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred
- J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître
- M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy
- M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin
- K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li
- X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos
- E. T. Lin / F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin
- C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / A. Liu / G. C. Liu
- Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L.
Lo
- J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou / L. T. London
- A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla / A. Lorenzo-Medina
- V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / E. Lotti
- T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto
- N. Low / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi / H. Lück
- D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier / R. Macas
- M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet
- K. Maeda / S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee
- E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh
- M. Maini / S. Majhi / E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem
- D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis / U. Mali / S. Maliakal
- A. Malik / L. Mallick / A.-K. Malz / N. Man
- M. Mancarella / V. Mandic / V. Mangano / B. Mannix
- G. L. Mansell / M. Manske / M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli
- C. Marinelli / F. Marion / A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz
- E. Maros / S. Marsat / F. Martelli / I. W. Martin
- R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez / D. A. Martinez / M. Martinez
- V. Martinez / A. Martini / J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov
- E. J. Marx / L. Massaro / A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid
- S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich / M. Matiushechkina / L.
Maurin
- N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell / G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy
- D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick / L. McCuller / S. McEachin
- C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan
- J. McIver / A. McLeod / I. McMahon / T. McRae
- R. McTeague / D. Meacher / B. N. Meagher / R. Mechum
- Q. Meijer / A. Melatos / C. S. Menoni / F. Mera
- R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni / K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh
- J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui / C. Messick
- B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske
- A. Miani / H. Miao / C. Michel / Y. Michimura
- H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov / A. L. Miller / S. J. Miller
- M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov
- E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés
- C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra / C. Mishra / T. Mishra
- A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov
- K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa / S. Miyoki
- A. Miyoko / G. Mo / L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra
- S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / M. Mondin / M. Montani
- C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More / S. More
- C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno / A. Moreso Serra
- S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras / A. Moscatello
- M. Mould / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry / L. Muccillo
- F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma
Mukherjee
- Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip Mukherjee / N. Mukund / A. Mullavey
- H. Mullock / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli / M. Murakoshi
- P. G. Murray / D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar
- N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura / H. Nakano
- M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi / V. Napolano
- P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa / H. Narola
- L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak / L. Negri / A. Nela
- C. Nelle / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery
- A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols
- A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa / S. Nissanke
- W. Niu / F. Nocera / J. Noller / M. Norman
- C. North / J. Novak / R. Nowicki / J. F. Nuño Siles
- L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling / J. O’Dell
- E. Oelker / M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan / T. O’Hanlon
- M. Ohashi / F. Ohme / R. Oliveri / R. Omer
- B. O’Neal / M. Onishi / K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly
- M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / S. Oshino
- C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway / A. Ouzriat
- H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki / A. E. Pace
- R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai / L. Paiella
- A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi
- P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud / H. Pan
- J. Pan / K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey
- Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone
- B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri / F. Paoletti
- A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini
- G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis / A. Parisi / B.-J. Park
- J. Park / W. Parker / G. Pascale / D. Pascucci
- A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger / D. Passuello
- O. Patane / A. V. Patel / D. Pathak / A. Patra
- B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul / S. Paul
- E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza / A. Pele
- F. E. Peña Arellano / X. Peng / Y. Peng / S. Penn
- M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego / Z. Pereira / C. Périgois
- G. Perna / A. Perreca / J. Perret / S. Perriès
- J. W. Perry / D. Pesios / S. Peters / S. Petracca
- C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham / K. A. Pham
- K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli / L. Piccari
- O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot / M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni
- L. Pierini / G. Pierra / V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak
- M. Pillas / F. Pilo / L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto
- M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin
- A. Placidi / E. Placidi / M. L. Planas / W. Plastino
- C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani / E. Polini / J. Pomper
- L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli / E. K. Porter
- C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell / G. S. Prabhu
- M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati
- K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia / G. Pratten
- G. Principe / G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito
- A. C. Providence / A. Puecher / J. Pullin / P. Puppo
- M. Pürrer / H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner
- V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez / N. Qutob / R. Rading
- I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari
- K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / M. Ramos Arevalo / A.
Ramos-Buades
- S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto
- A. Ravichandran / A. Ray / V. Raymond / M. Razzano
- J. Read / T. Regimbau / S. Reid / C. Reissel
- D. H. Reitze / V. Rella / A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu
- A. Revilla Peña / R. Reyes / L. Ricca / F. Ricci
- M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. Rice / J. W. Richardson
- M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley
- S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet
- M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins
- A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw
- J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa
- T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross
- M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy
- D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales
- K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh
- S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat
- S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou
- S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi
- M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe
- S. Salvador / A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez
- E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders
- E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan
- N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / A. Sasli / P. Sassi
- B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato / S. Sato
- Yukino Sato / Yu Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage
- T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco
- D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski
- P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind
- R. M. S. Schofield / K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F.
Schutz
- E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott
- R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y.
Sekiguchi
- D. Sellers / N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo
- J. W. Seo / V. Sequino / M. Serra / A. Sevrin
- T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao
- A. K. Sharma / Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma
- S. Sharma Chaudhary / P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / E.
Sheridan
- Z.-H. Shi / M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai
- S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short
- S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider / H. Siegel / D. Sigg
- L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer
- Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh / D. Singh / N. Singh
- S. Singh / A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris
- B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J.
Smetana
- J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith
- S. Soares de Albuquerque Filho / M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I.
Song
- S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani
- F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli
- A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer
- N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas
- P. Stevens / M. StPierre / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk
- A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / Y. Sudo
- N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun
- L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton
- P. J. Sutton / K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels
- A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca
- H. Tagoshi / K. Takada / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi
- A. Takamori / S. Takano / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita
- I. Takimoto Schmiegelow / M. Takou-Ayaoh / C. Talbot / M.
Tamaki
- N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka
- S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao
- R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto / A. Taruya
- J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / D. Tellez / R. Tenorio
- H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M.
Thomas
- M. Thomas / P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu
- K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari
- Pawan Tiwari / Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari
- M. R. Todd / M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland
- A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura
- H. Tong / C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie
- I. Tosta e Melo / E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran
- A. Trapananti / R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor
- M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian
- A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang
- S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi
- C. Turski / H. Ubach / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall
- T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim / L. E. Uronen
- T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya
- G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia / M. Valentini
- S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan / M. van Dael
- E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / M.
van der Sluys
- A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra / M. VanDyke
- H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J.
Vanier
- M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro
- A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio
- G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis
- R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt
- B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets
- A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva Espinosa / V.
Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / S. Vitale
- H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel
- W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack
- L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner / L. Wallace
- E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang
- Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner / M. Was
- T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai / B. Weaver
- S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein
- R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette / J. T. Whelan
- B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens / D. Wilken
- A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams / M. J. Williams
- N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils
- L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf
- G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong
- I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters / J. L. Wright
- M. Wright / B. Wu / C. Wu / D. S. Wu
- H. Wu / K. Wu / Q. Wu / Y. Wu
- Z. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu
- Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto
- T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki / T. Yan
- K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough / J. Yebana
- S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin / J. Yokoyama
- T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara / M. Zanolin
- M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli
- M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / L. Zhang / N. Zhang
- R. Zhang / T. Zhang / C. Zhao / Yue Zhao
- Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng / H. Zhong
- H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman
- L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig / J. Shu
Summary
Gravitational-wave detectors can probe the existence of dark matter
with exquisite sensitivity. Here, we perform a search for three kinds of
dark matter – dilatons (spin-0), dark photons (spin-1) and tensor bosons
(spin-2) – using three independent methods on the first part of the most
recent data from the fourth observing run of LIGO–Virgo–KAGRA. Each form
of dark matter could have interacted with different standard-model
particles in the instruments, causing unique differential strains on the
interferometers. While we do not find any evidence for a signal, we
place the most stringent upper limits to-date on each of these models.
For scalars with masses between ![[4\times 10^{-14},1.5\times 10^{-13}] [4\times 10^{-14},1.5\times 10^{-13}]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5B4%5Ctimes%2010%5E%7B-14%7D%2C1.5%5Ctimes%2010%5E%7B-13%7D%5D) eV
that couple to photons or electrons, our constraints improve upon those
from the third observing run by one order of magnitude, with the
tightest limit of
eV
that couple to photons or electrons, our constraints improve upon those
from the third observing run by one order of magnitude, with the
tightest limit of  at a mass
of
at a mass
of  . For
vectors with masses between
. For
vectors with masses between ![[7\times 10^{-13},8.47\times 10^{-12}] [7\times 10^{-13},8.47\times 10^{-12}]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5B7%5Ctimes%2010%5E%7B-13%7D%2C8.47%5Ctimes%2010%5E%7B-12%7D%5D) eV
that couple to baryons, our constraints supersede those from MICROSCOPE
and Eöt-Wash by one to two orders of magnitude, reaching a minimum of
eV
that couple to baryons, our constraints supersede those from MICROSCOPE
and Eöt-Wash by one to two orders of magnitude, reaching a minimum of
 at a mass of
at a mass of  eV. For
tensors with masses of
eV. For
tensors with masses of ![[4\times 10^{-14},8.47\times 10^{-12}] [4\times 10^{-14},8.47\times 10^{-12}]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5B4%5Ctimes%2010%5E%7B-14%7D%2C8.47%5Ctimes%2010%5E%7B-12%7D%5D) eV
(the full mass range analyzed) that couple via a Yukawa interaction, our
constraints surpass those from fifth-force experiments by four to five
orders of magnitude, achieving a limit as low as
eV
(the full mass range analyzed) that couple via a Yukawa interaction, our
constraints surpass those from fifth-force experiments by four to five
orders of magnitude, achieving a limit as low as  at
at  eV. Our results show that gravitational-wave
interferometers have become frontiers for new physics and laboratories
for direct multi-model dark-matter detection.
eV. Our results show that gravitational-wave
interferometers have become frontiers for new physics and laboratories
for direct multi-model dark-matter detection.
Articles for week 43 2025
Comparing
the data reduction pipelines of FRIPON, DFN, WMPL, and AMOS: Geminids
Case Study
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- P. M. Shober / J. Vaubaillon / S. Anghel / H. A. R. Devillepoix
- F. Hlobik / P. Matlovič / J. Tóth / D. Vida
- E. K. Sansom / T. Jansen-Sturgeon / F. Colas / A. Malgoyre
- L. Kornoš / F. Ďuriš / V. Pazderová / S. Bouley
- B. Zanda / P. Vernazza
Summary
Methods. We processed a dataset of 584 Geminid fireballs observed by
FRIPON between 2016 and 2023. The single-station astrometric data is
converted into the Global Fireball Exchange (GFE) standard format for
uniform processing. We assess variations in trajectory, velocity,
radiant, and orbital element calculations across the pipelines and
compare them to previously published Geminid measurements. Results. The
radiant and velocity solutions provided by the four data reduction
pipelines are all within the range of previously published values.
However, there are some nuances. Particularly, the radiants estimated by
WMPL, DFN, and AMOS are nearly identical. Whereas FRIPON reports a
systematic shift in right ascension (-0.3 degrees), caused by improper
handling of the precession. Additionally, the FRIPON data reduction
pipeline also tends to overestimate the initial velocity (+0.3 km s-1)
due to the deceleration model used as the velocity solver. The FRIPON
velocity method relies on having a well-constrained deceleration
profile; however, for the Geminids, many are low-deceleration events,
leading to an overestimation of the initial velocity. On the other end
of the spectrum, the DFN tends to predict lower velocities, particularly
for poorly observed events. However, this velocity shift vanishes for
the DFN when we only consider Geminids with at least three observations
or more. The primary difference identified in the analysis concerns the
velocity uncertainties. Despite all four pipelines achieving similar
residuals between their trajectories and observations, their velocity
uncertainties vary systematically, with WMPL outputting the smallest
values, followed by AMOS, FRIPON, and DFN.
HOLISMOKES
XIX: SN 2025wny at  , the first strongly lensed
superluminous supernova
, the first strongly lensed
superluminous supernova
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Stefan Taubenberger / Ana Acebron / Raoul Cañameras / Ting-Wan
Chen
- Aymeric Galan / Claudio Grillo / Alejandra Melo / Stefan
Schuldt
- Allan G. Schweinfurth / Sherry H. Suyu / Greg Aldering / Amar
Aryan
- Yu-Hsing Lee / Elias Mamuzic / Martin Millon / Thomas M.
Reynolds
- Alexey V. Sergeyev / Ildar M. Asfandiyarov / Stéphane Basa /
Stéphane Blondin
- Otabek A. Burkhonov / Lise Christensen / Frederic Courbin / Shuhrat
A. Ehgamberdiev
- Tom L. Killestein / Seppo Mattila / Asadulla M. Shaymanov / Yiping
Shu
- Dong Xu / Sheng Yang / Daniel Gruen / Justin D. R. Pierel
- Christopher J. Storfer / Kim-Vy Tran / Kenneth C. Wong / Rosa L.
Becerra
- Damien Dornic / Jean-Grégoire Ducoin / Noémie Globus / Claudia P.
Gutiérrez
- Ji-an Jiang / Hanindyo Kuncarayakti / Diego López-Cámara / Peter
Lundqvist
- Francesco Magnani / Enrique Moreno Méndez / Benjamin
Schneider / Christian Vogl
Summary
We present imaging and spectroscopic observations of supernova SN
2025wny, associated with the lens candidate PS1 J0716+3821. Photometric
monitoring from the Lulin and Maidanak observatories confirms multiple
point-like images, consistent with SN 2025wny being strongly lensed by
two foreground galaxies. Optical spectroscopy of the brightest image
with the Nordic Optical Telescope and the University of Hawaii 88-inch
Telescope allows us to determine the redshift to be z_s = 2.008 +-
0.001, based on narrow absorption lines originating in the interstellar
medium of the supernova host galaxy. At this redshift, the spectra of SN
2025wny are consistent with those of superluminous supernovae of Type I.
We find a high ejecta temperature and depressed spectral lines compared
to other similar objects. We also measure, for the first time, the
redshift of the fainter of the two lens galaxies (the “perturber”) to be
z_p = 0.375 +- 0.001, fully consistent with the DESI spectroscopic
redshift of the main deflector at z_d = 0.3754. SN 2025wny thus
represents the first confirmed galaxy-scale strongly lensed supernova
with time delays likely in the range of days to weeks, as judged from
the image separations. This makes SN 2025wny suitable for cosmography,
offering a promising new system for independent measurements of the
Hubble constant. Following a tradition in the field of strongly-lensed
SNe, we give SN 2025wny the nickname SN Winny.
Very
High Precision Astrometry for Exoplanets and Dark Matter with the
Habitable Worlds Observatory
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Fabien Malbet / J. Amiaux / F. Ardellier-Desages / E. Doumayrou
- P.-A. Frugier / R. Goullioud / T. Greene / L. Labadie
- P.-O. Lagage / M. Lizzana / A. Léger / T. Lépine
- G. Mamon / J. Martignac / F. Pancher / T.
Pichon
- A. Roberge / S. Ronayette / H. Rousset / S. Soler
- A. Sozzetti / T. Tourette
Summary
Astrometry, one of the oldest branches of astronomy, has been
revolutionized by missions like Hipparcos and especially Gaia, which
mapped billions of stars with extraordinary precision. However,
challenges such as detecting Earth-like exoplanets in nearby habitable
zones and probing the influence of dark matter in galactic environments
require sub-microarcsecond accuracy. With a 6–8 meter large-aperture
telescope operating across at visible wavelengths, the Habitable Worlds
Observatory by NASA can combine astrometry and direct imaging to detect
rocky exoplanets within 10 parsecs and study their atmospheres. We
consider here the scientific requirements and present a concept for a
dedicated astrometric instrument on HWO. It is capable to produce
diffraction-limited images of large fields, achieving a point-spread
function (PSF) precision of 20 milliarcseconds. Equipped with a detector
calibration system, HWO can perform high precision astrometry, and,
detect and measure the orbit of Earth-mass planets in the habitable zone
of Nearby Solar-type stars. HWO can dramatically improve current
constraints on the self- interaction cross-section of heavy dark matter
particles (WIMPs) and on the masses of ultra-high dark matter particles,
through the study of stellar motions in galactic environments. The
visible channel of the instrument features a large CMOS-based focal
plane with stitched pixel arrays, enabling a large field of view. The
``Detector Calibration Unit’’ system uses interferometric laser fringes
to calibrate pixel positions. Using differential astrometry and pointed
observations with a stable telescope design enables extended integration
times, enhancing sensitivity to sub-microarcsecond precision for
detecting exoplanets and studying dark matter through stellar
motion.
Comission
Femmes et Astronomie de la SF2A : Women participation in french
astronomy 2025
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- N. Lagarde / R.-M. Ouazzani / J. Malzac / M. Clavel
- P. de Laverny / L. Leboulleux / I. Vauglin / C. Bot
- S. Brau-Nogué / L. Ciesla / E. Josselin / N.
Nesvadba
- O. Venot
Summary
The Commission Femmes et Astronomie of the French Astronomical
Society, has conducted a statistical study aimed at mapping the current
presence of women in French professional astronomy and establishing a
baseline for tracking its evolution over time. This study follows an
initial survey carried out in 2021, which covered eight astronomy and
astrophysics institutes (1,060 employees). This year, the scope was
expanded to 11 institutes, bringing together a total of 1,525 employees,
including PhD students, postdoctoral researchers, academics, as well as
technical and administrative staff, representing about 57% of the whole
French community. We examined how the proportion of women varies
according to career stage, level of responsibility, job security, and
income. The results are compared to the 2021-2022 survey and appear to
illustrate the well-known “leaky pipeline”, with one of the main
bottlenecks being access to permanent positions. The study shows that
the proportion of women consistently declines with increasing job
security, career seniority, qualification level, and salary.
Parametric
strong lensing model of the galaxy cluster Abell 2390 from Euclid and
MUSE observations
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- D. Abriola / M. Lombardi / C. Grillo / P. Bergamini
- P. Rosati / M. Meneghetti / A. Bolamperti / A. Acebron
- G. Granata / G. Angora / H. Atek / J. M. Diego
- G. Congedo / R. Gavazzi / Y. Kang / M. Montes
- T. T. Thai
Summary
We present a new high precision parametric strong lensing total mass
reconstruction of the Euclid Early Release Observations (ERO) galaxy
cluster Abell 2390, at redshift z = 0.231. We include in this analysis
35 multiple images from 13 background sources, of which 25 are
spectroscopically confirmed thanks to observations from the MUSE,
spanning a redshift range from z = 0.535 to z = 4.877. After fully
reanalysing the MUSE spectroscopy, we combine it with archival
spectroscopic catalogues allowing us to select 65 secure cluster
members. This sample is further complemented with 114 photometric member
galaxies, identified within the Euclid VIS and NISP imaging down to
magnitude H = 23. We also measure the stellar velocity dispersions for
22 cluster members, in order to calibrate the Faber-Jackson relation and
hence the scaling relations for the subhalo mass components. We test and
compare 11 total mass parametrisations of the galaxy cluster with
increasing complexity. To do so, we employ the new parametric strong
lensing modelling code Gravity.jl. Our best fit total mass
parametrisation is characterised by a single large scale halo, 179
subhalo components, and an external shear term. The reference model
yields a mean scatter between the model predicted and observed positions
of the multiple images of 0.32 arcseconds. We are able to quantify the
systematics arising from our modelling choices by taking advantage of
all the different explored total mass parametrisations. When our results
are compared with those from other lensing studies, we notice an overall
agreement in the reconstructed cluster total mass profile in the
outermost strong lensing regime: the discrepancy in the innermost region
of the cluster (few kiloparsec from the brightest cluster galaxy, where
few or no strong lensing features are observed) could possibly be
ascribed to the different data and modelling choices.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Minerva M. Sardaneta / Philippe Amram / Roberto
Rampazzo / Margarita Rosado
- Isaura Fuentes-Carrera / Soumavo Ghosh
Summary
Isolated galaxies are rare yet invaluable for studying secular
evolution, as their physical properties can remain largely unaffected by
external influences for several billion years, primarily shaped by
internal evolutionary processes. This study focuses on a representative
sample of nearly edge-on ( )
late-type galaxies selected from the Catalogue of Isolated Galaxies
(CIG). We analyse the H
)
late-type galaxies selected from the Catalogue of Isolated Galaxies
(CIG). We analyse the H kinematics derived from Fabry-Perot
data and integrate these findings with a comprehensive examination of
the UV, optical, and FIR properties of these galaxies to study their
dynamic evolutionary processes. We investigate the individual kinematics
by computing rotation curves and dynamical masses for each galaxy in the
sample. The accuracy of our kinematic results is confirmed through
comparisons with HI data and by applying the B- and K-band Tully-Fisher
relationships. Among the galaxies studied, we observed a rotational lag
along the
kinematics derived from Fabry-Perot
data and integrate these findings with a comprehensive examination of
the UV, optical, and FIR properties of these galaxies to study their
dynamic evolutionary processes. We investigate the individual kinematics
by computing rotation curves and dynamical masses for each galaxy in the
sample. The accuracy of our kinematic results is confirmed through
comparisons with HI data and by applying the B- and K-band Tully-Fisher
relationships. Among the galaxies studied, we observed a rotational lag
along the  -axis in half of the total sample (7 out
of 14 cases), with an average lag (
-axis in half of the total sample (7 out
of 14 cases), with an average lag ( ) consistent with previous research findings.
Notably, not all galaxies exhibiting measurable lag display
morphological extraplanar components, leading us to conclude that this
cannot serve as a definitive marker for the extraplanar Diffuse Ionized
Gas (eDIG) component. While we found no significant correlations between
rotation lag and overall galaxy properties, there seems to be a
potential correlation with tidal strength. Based on the kinematic
characteristics observed in our sample, we suggest that that the
extended disc gas likely originates from interactions with the
Circumgalactic Medium (CGM) rather than arising internally within the
galaxies themselves.
) consistent with previous research findings.
Notably, not all galaxies exhibiting measurable lag display
morphological extraplanar components, leading us to conclude that this
cannot serve as a definitive marker for the extraplanar Diffuse Ionized
Gas (eDIG) component. While we found no significant correlations between
rotation lag and overall galaxy properties, there seems to be a
potential correlation with tidal strength. Based on the kinematic
characteristics observed in our sample, we suggest that that the
extended disc gas likely originates from interactions with the
Circumgalactic Medium (CGM) rather than arising internally within the
galaxies themselves.
A
simple toy model for the electromagnetic variability of lump-dominated
circumbinary disks around binary black holes
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- R. Mignon-Risse / P. Varniere / F. Casse
Summary
The electromagnetic detection of circumbinary disks around pre-merger
binary black holes (BBHs) relies on theoretical predictions. These are
generally obtained through expensive numerical simulations, but simple
or fast toy models are lacking to unleash the potential of these
theoretical advances for observational purposes. We aim to present a
simple toy model to compute the electromagnetic variability of
circumbinary disks around circular-orbit BBHs at relativistic
separations, focusing on the impact of disk non-axisymmetries. We assume
that the disk is threaded by spiral arms and hosts a hotspot linked to
an overdense structure (the {}lump{}) preferably reported in binaries
close to equal mass. We build a simple temperature distribution, and
estimate its thermal emission, perceived by a distant observer, via a
ray-tracing code in a BBH approximate metric. We propose a toy model
reproducing the main lightcurve features and show it is consistent with
2D general-hydrodynamical simulations under the assumption of
compressional heating and expansional cooling except for purely
dynamical effects such as the binary-lump beat. The lightcurve exhibits
a main modulation at the lump’s period (i.e. a few times the orbital
period), due to relativistic Doppler effect, and a shorter one at the
orbital-like period, due to spiral arms or the beat. These are more
prominent in the optical/UV band for a total binary mass  ,
where the disk energy spectrum peaks. For
,
where the disk energy spectrum peaks. For  , a
, a  -amplitude lump modulation
is detectable with the Vera Rubin Observatory after six months of
observation, up to
-amplitude lump modulation
is detectable with the Vera Rubin Observatory after six months of
observation, up to  . We
proposed a new, simple toy model that can be used, for instance, to test
the compatibility of the periodicity of BBH candidate sources with a
circumbinary disk origin.
. We
proposed a new, simple toy model that can be used, for instance, to test
the compatibility of the periodicity of BBH candidate sources with a
circumbinary disk origin.
Euclid
preparation: The flat-sky approximation for the clustering of Euclid’s
photometric galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / W. L. Matthewson / R. Durrer / S. Camera
- I. Tutusaus / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / B. Morin / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese
- A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra
- W. G. Hartley / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / M. Maturi
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Blot
- M. Bonici / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Conseil / A. R.
Cooray
- S. Davini / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / M. Y. Elkhashab / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- C. M. Gutierrez / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / J. Kim / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / F. Lacasa / M. Lattanzi / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / A. Silvestri / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi / G. Verza / N. A. Walton
Summary
We compare the performance of the flat-sky approximation and Limber
approximation for the clustering analysis of the photometric galaxy
catalogue of Euclid. We study a 6 bin configuration representing the
first data release (DR1) and a 13 bin configuration representative of
the third and final data release (DR3). We find that the Limber
approximation is sufficiently accurate for the analysis of the wide bins
of DR1. Contrarily, the 13 bins of DR3 cannot be modelled accurately
with the Limber approximation. Instead, the flat-sky approximation is
accurate to below  in recovering the angular
power spectra of galaxy number counts in both cases and can be used to
simplify the computation of the full power spectrum in harmonic space
for the data analysis of DR3.
in recovering the angular
power spectra of galaxy number counts in both cases and can be used to
simplify the computation of the full power spectrum in harmonic space
for the data analysis of DR3.
Evidence
of Energy Injection in the Short and Distant GRB 250221A
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Camila Angulo-Valdez / Rosa L. Becerra / Ramandeep Gill / Noémie
Globus
- William H. Lee / Diego López-Cámara / Cassidy Mihalenko / Enrique
Moreno-Méndez
- Roberto Ricci / Karelle Siellez / Alan M. Watson / Muskan Yadav
- Yu-han Yang / Dalya Akl / Sarah Antier / Jean-Luc Atteia
- Stéphane Basa / Nathaniel R. Butler / Simone Dichiara / Damien
Dornic
- Jean-Grégoire Ducoin / Francis Fortin / Leonardo García-García / Kin
Ocelotl López
- Francesco Magnani / Brendan O’Connor / Margarita Pereyra / Ny Avo
Rakotondrainibe
- Fredd Sánchez-Álvarez / Benjamin Schneider /
Eleonora Troja / Antonio de Ugarte Postigo
Summary
We present the photometric and spectroscopic analysis of the
short-duration GRB 250221A ( s), using a data set from the optical facilities
COLIBRÍ, the Harlingten 50 cm Telescope, and the Very Large Telescope.
We complement these observations with data from the and the , as well as
radio observations from the Very Large Array. GRB 250221A is among the
few short GRBs with direct afterglow spectroscopy, which gives a secure
redshift determination of
s), using a data set from the optical facilities
COLIBRÍ, the Harlingten 50 cm Telescope, and the Very Large Telescope.
We complement these observations with data from the and the , as well as
radio observations from the Very Large Array. GRB 250221A is among the
few short GRBs with direct afterglow spectroscopy, which gives a secure
redshift determination of  and allows the
unambiguous identification of the host as a galaxy with a star-formation
rate of
and allows the
unambiguous identification of the host as a galaxy with a star-formation
rate of  . The X-ray
and optical light curves up to
. The X-ray
and optical light curves up to  ks (where
ks (where  refers to the GRB trigger time) are
well described by forward-shock synchrotron emission in the slow-cooling
regime within the standard fireball framework. However, at
refers to the GRB trigger time) are
well described by forward-shock synchrotron emission in the slow-cooling
regime within the standard fireball framework. However, at  days, both the
X-ray and optical bands exhibit an excess over the same interval, which
we interpret as evidence of energy injection into a jet with a
half-opening angle of
days, both the
X-ray and optical bands exhibit an excess over the same interval, which
we interpret as evidence of energy injection into a jet with a
half-opening angle of  through a refreshed shock powered by late central engine activity or a
radially stratified ejecta. The burst properties (duration, spectral
hardness, peak energy, and location in the Amati plane) all favour a
compact binary merger origin. However, our modelling of the afterglow
suggests a dense circumburst medium (
through a refreshed shock powered by late central engine activity or a
radially stratified ejecta. The burst properties (duration, spectral
hardness, peak energy, and location in the Amati plane) all favour a
compact binary merger origin. However, our modelling of the afterglow
suggests a dense circumburst medium ( cm
cm ), which is more typical
of a Collapsar environment. This tension over the classification of this
burst (short-hard vs. long-soft) as inferred from the prompt and
afterglow emissions makes GRB~250221A an unusual event and underscores
the limitations of duration-based classifications and the importance of
multi-wavelength, time-resolved follow-up observations.
), which is more typical
of a Collapsar environment. This tension over the classification of this
burst (short-hard vs. long-soft) as inferred from the prompt and
afterglow emissions makes GRB~250221A an unusual event and underscores
the limitations of duration-based classifications and the importance of
multi-wavelength, time-resolved follow-up observations.
Directional
Search for Persistent Gravitational Waves: Results from the First Part
of LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA’s Fourth Observing Run
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea / M. Assiduo
- S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone / F. Attadio
- F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone / E. A. Avila
- S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae / S. Bagnasco
- L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka / A. M. Baker
- K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi / N. Baldicchi
- M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri
- B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral
- M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish / D. Barker
- N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone / B. Barr
- L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti
- M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri
- A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley
- A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale
- F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell
- D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara
- J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin
- B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / D. Bersanetti
- T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge
- G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare / R. Bhatt
- D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya / S. Bhaumik / V.
Biancalana
- A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti
- S. Bini / C. Binu / S. Biot / O. Birnholtz
- S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard
- S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair
- D. G. Blair / N. Bode / N. Boettner / G. Boileau
- M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A. Bolliand / L.
D. Bonavena
- R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla
- A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / A. Borchers / S. Borhanian
- V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov / Y. Bothra
- A. Boudon / L. Bourg / M. Boyle / A. Bozzi
- C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady / A. Branch / M. Branchesi
- I. Braun / T. Briant / A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann
- P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown
- D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett / G. Bruno
- R. Bruntz / J. Bryant / Y. Bu / F. Bucci
- J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik / H. J. Bulten
- A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio / D. Buskulic
- C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies / R. Cabrita
- V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane
- A. Calafat / T. A. Callister / E. Calloni / S. R. Callos
- G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon / H. Cao / L. A. Capistran
- E. Capocasa / E. Capote / G. Capurri / G. Carapella
- F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara / J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson
- M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter
- G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos / J. Casanueva Diaz / C.
Casentini
- S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri
- A. Ceja / G. Cella / P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini
- N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi / A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty
- S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C. L. Chan / M.
Chan
- K. Chang / S. Chao / P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin
- C. Chatterjee / Debarati Chatterjee / Deep Chatterjee / M.
Chaturvedi
- S. Chaty / K. Chatziioannou / A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen
- D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen / S. Chen
- Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa
- H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini
- A. Chiba / A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo
- C. Chou / S. Choudhary / N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua
- G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi
- B. Cirok / F. Clara / J. A. Clark / T. A. Clarke
- P. Clearwater / S. Clesse / F. Cleva / E. Coccia
- E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace / E. Colangeli
- M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette / J. Collins / S. Colloms
- A. Colombo / C. M. Compton / G. Connolly / L. Conti
- T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish
- I. Coronado / A. Corsi / R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin
- A. Couineaux / P. Couvares / D. M. Coward / R. Coyne
- A. Cozzumbo / J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton / P.
Cremonese
- S. Crook / R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell
- T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming / E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato
- L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton / S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya
- B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann
- K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez / R. Das / A. Dasgupta
- V. Dattilo / A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave
- A. Davenport / M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis
- L. Davis / M. C. Davis / P. Davis / E. J. Daw
- M. Dax / J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix
- M. De Laurentis / F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre / W. Del Pozzo
- A. Demagny / F. De Marco / G. Demasi / F. De Matteis
- N. Demos / T. Dent / A. Depasse / N. DePergola
- R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi / M. Desai
- R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone / R. De Simone / A. Dhani
- R. Diab / M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron
- T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni
- T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha / J. Ding / S. Di Pace
- I. Di Palma / D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti
- A. Dmitriev / J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen
- E. Dohmen / A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza / L. D’Onofrio
- F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney / S. Doravari
- O. Dorosh / W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers
- L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne / D. D’Urso
- P. Dutta Roy / H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa
- M. Ebersold / T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / A. Effler
- J. Eichholz / H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann / M. Emma
- K. Endo / R. Enficiaud / L. Errico / R. Espinosa
- M. Esposito / R. C. Essick / H. Estellés / T. Etzel
- M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga
- F. Fabrizi / V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah
- B. Farr / W. M. Farr / G. Favaro / M. Favata
- M. Fays / M. Fazio / J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer
- R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes / T. Fernandes
- D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro
- P. Figura / A. Fiori / I. Fiori / M. Fishbach
- R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio
- S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming / E. Floden / H. Fong
- J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes / C. Foo / B. Fornal
- K. Franceschetti / F. Frappez / S. Frasca / F. Frasconi
- J. P. Freed / Z. Frei / A. Freise / O. Freitas
- R. Frey / W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov
- G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii / T. Fujimori
- P. Fulda / M. Fyffe / B. Gadre / J. R. Gair
- S. Galaudage / V. Galdi / R. Gamba / A. Gamboa
- S. Gamoji / D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa
- J. García-Bellido / C. García-Quirós / J. W. Gardner / K. A.
Gardner
- S. Garg / J. Gargiulo / X. Garrido / A. Garron
- F. Garufi / P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley
- F. Gautier / V. Gayathri / T. Gayer / G. Gemme
- A. Gennai / V. Gennari / J. George / R. George
- O. Gerberding / L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh
- Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh
- J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson / C. Gier
- S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey
- R. V. Godley / P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz
- J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov / G. González
- P. Goodarzi / S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin
- R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / A. Grado
- V. Graham / A. E. Granados / M. Granata / V. Granata
- S. Gras / P. Grassia / J. Graves / C. Gray
- R. Gray / G. Greco / A. C. Green / L. Green
- S. M. Green / S. R. Green / C. Greenberg / A. M. Gretarsson
- H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith / H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani
- C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald / D. Guerra
- D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati
- F. Gulminelli / H. Guo / W. Guo / Y. Guo
- Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta / S. K. Gupta
- V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez
- N. Guttman / F. Guzman / D. Haba / M. Haberland
- S. Haino / E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond
- M. Haney / J. Hanks / C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam
- O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen / J. Hanson
- S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar
- K. Haris / I. Harley-Trochimczyk / T. Harmark / J. Harms
- G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry / J. Hart / B. Haskell
- C. J. Haster / K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama
- M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze / J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann
- F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming / O.
Henderson-Sapir
- M. Hendry / I. S. Heng / M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw
- M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt / J. Heynen / J. Heyns
- S. Higginbotham / S. Hild / S. Hill / Y. Himemoto
- N. Hirata / C. Hirose / D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan
- N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows / D. E. Holz / L. Honet
- D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough / S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard
- E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi
- H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu
- W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang
- Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey / V. Hui
- S. Husa / R. Huxford / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo
- M. Ianni / G. Iannone / J. Iascau / K. Ide
- R. Iden / A. Ierardi / S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku
- Y. Inoue / G. Iorio / P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal
- J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa / M. Isi / K. S. Isleif
- Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet
- P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot / S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav
- M. Jain / T. Jain / A. L. James / K. Jani
- J. Janquart / N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski
- R. Jaume / W. Javed / A. Jennings / M. Jensen
- W. Jia / J. Jiang / H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns
- N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston / N. Johny
- D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones / R. Jones / H. E. Jose
- P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi / G. Joubert / J. Ju
- L. Ju / K. Jung / J. Junker / V. Juste
- H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita / I. Kaku / V. Kalogera
- M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy
- G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty
- S. J. Kapadia / D. P. Kapasi / M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack
- H. Kato / T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman
- R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel
- L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington / F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani
- J. S. Key / R. Khadela / S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar
- F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan / T. Khanam / M. Khursheed
- N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim
- J. C. Kim / K. Kim / M. H. Kim / S. Kim
- Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball / K. Kimes / M. Kinnear
- J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox
- N. Knust / K. Kobayashi / S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek
- K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama / S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou
- A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori / A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos
- L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko / X. Kou / A. Koushik
- N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam / T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak
- S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker
- A. Królak / K. Kruska / J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn
- S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan / Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar
- Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar
- J. Kume / K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi
- S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak / K. Kwan / S. Kwon
- G. Lacaille / D. Laghi / A. H. Laity / E. Lalande
- M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry / B. B. Lane
- R. N. Lang / J. Lange / R. Langgin / B. Lantz
- I. La Rosa / J. Larsen / A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky
- J. Lawrence / M. Laxen / C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini
- C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci / L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche
- H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee / J. Lee / K. Lee
- R.-K. Lee / R. Lee / Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee
- Y. Lee / I. N. Legred / J. Lehmann / L. Lehner
- M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître / M. Lenti / M. Leonardi
- M. Lequime / N. Leroy / M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre
- M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin / K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li
- K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li / X. Li / Y. Li
- Z. Li / A. Lihos / E. T. Lin / F. Lin
- L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin / C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker
- A. Liu / G. C. Liu / Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal
- J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L. Lo / J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G.
Loggins
- M. R. Loizou / L. T. London / A. Longo / D. Lopez
- M. Lopez Portilla / A. Lorenzo-Medina / V. Loriette / M.
Lormand
- G. Losurdo / E. Lotti / T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough
- H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto / N. Low / N. Lu
- L. Lucchesi / H. Lück / D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren
- A. W. Lussier / R. Macas / M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod
- I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet / K. Maeda / S. Maenaut
- S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee / E. Maggio / R. Maggiore
- M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi
- E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis
- U. Mali / S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick
- A.-K. Malz / N. Man / M. Mancarella / V. Mandic
- V. Mangano / B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell / M. Manske
- M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli / C. Marinelli / F. Marion
- A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat
- F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez
- D. A. Martinez / M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini
- J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro
- A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich
- M. Matiushechkina / L. Maurin / N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell
- G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick
- L. McCuller / S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee
- J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod
- I. McMahon / T. McRae / R. McTeague / D. Meacher
- B. N. Meagher / R. Mechum / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos
- C. S. Menoni / F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni
- K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt
- M. Merzougui / C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde
- F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao
- C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov
- S. J. Miller / M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti
- Y. Minenkov / E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola
- M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra / C. Mishra
- T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra
- V. P. Mitrofanov / K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa
- S. Miyoki / A. Miyoko / G. Mo / L. Mobilia
- S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / M. Mondin
- M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More
- S. More / C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno
- A. Moreso Serra / S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras
- A. Moscatello / M. Mould / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry
- L. Muccillo / F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee
- Soma Mukherjee / Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip Mukherjee / N.
Mukund
- A. Mullavey / H. Mullock / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli
- M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji
- A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura
- H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi
- V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa
- H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak / L. Negri
- A. Nela / C. Nelle / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson
- M. Nery / A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh
- S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa
- S. Nissanke / W. Niu / F. Nocera / J. Noller
- M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak / R. Nowicki
- J. F. Nuño Siles / L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling
- J. O’Dell / E. Oelker / M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan
- T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / F. Ohme / R. Oliveri
- R. Omer / B. O’Neal / M. Onishi / K. Oohara
- B. O’Reilly / M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea
- S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway
- A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki
- A. E. Pace / R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai
- L. Paiella / A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia
- M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud
- H. Pan / J. Pan / K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda
- Shiksha Pandey / Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale
- K. A. Pannone / B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri
- F. Paoletti / A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis
- L. Papalini / G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis / A. Parisi
- B.-J. Park / J. Park / W. Parker / G. Pascale
- D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger
- D. Passuello / O. Patane / A. V. Patel / D. Pathak
- A. Patra / B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul
- S. Paul / E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza
- A. Pele / F. E. Peña Arellano / X. Peng / Y. Peng
- S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego / Z. Pereira
- C. Périgois / G. Perna / A. Perreca / J. Perret
- S. Perriès / J. W. Perry / D. Pesios / S. Peters
- S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham
- K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli
- L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot / M. Piendibene
- F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra / V. Pierro
- M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo / L. Pinard
- I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello
- M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi / M. L. Planas
- W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani / E. Polini
- J. Pomper / L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli
- E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell
- G. S. Prabhu / M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier
- A. K. Prajapati / K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia
- G. Pratten / G. Principe / G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi
- P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher / J. Pullin
- P. Puppo / M. Pürrer / H. Qi / J. Qin
- G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez / N. Qutob
- R. Rading / I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan
- B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / M. Ramos
Arevalo
- A. Ramos-Buades / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani
- B. Ratto / A. Ravichandran / A. Ray / V. Raymond
- M. Razzano / J. Read / T. Regimbau / S. Reid
- C. Reissel / D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu
- A. Revilla Peña / R. Reyes / L. Ricca / F. Ricci
- M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. Rice / J. W. Richardson
- M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley
- S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet
- M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins
- A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw
- J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa
- T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross
- M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy
- D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales
- K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh
- S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat
- S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou
- S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi
- M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe
- S. Salvador / A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez
- E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders
- E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan
- N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / A. Sasli / P. Sassi
- B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato / S. Sato
- Yukino Sato / Yu Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage
- T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco
- D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski
- P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind
- R. M. S. Schofield / K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F.
Schutz
- E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott
- R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y.
Sekiguchi
- D. Sellers / N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo
- J. W. Seo / V. Sequino / M. Serra / A. Sevrin
- T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao
- A. K. Sharma / Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma
- S. Sharma Chaudhary / P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / E.
Sheridan
- Z.-H. Shi / M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai
- S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short
- S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider / H. Siegel / D. Sigg
- L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer
- Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh / D. Singh / N. Singh
- S. Singh / A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris
- B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J.
Smetana
- J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith
- S. Soares de Albuquerque Filho / M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I.
Song
- S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani
- F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli
- A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer
- N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas
- P. Stevens / M. StPierre / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk
- A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / Y. Sudo
- N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun
- L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton
- P. J. Sutton / K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels
- A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca
- H. Tagoshi / K. Takada / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi
- A. Takamori / S. Takano / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita
- I. Takimoto Schmiegelow / M. Takou-Ayaoh / C. Talbot / M.
Tamaki
- N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka
- S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao
- R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto / A. Taruya
- J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / D. Tellez / R. Tenorio
- H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M.
Thomas
- M. Thomas / P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu
- K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari
- Pawan Tiwari / Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari
- M. R. Todd / M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland
- A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura
- H. Tong / C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie
- I. Tosta e Melo / E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran
- A. Trapananti / R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor
- M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian
- A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang
- S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi
- C. Turski / H. Ubach / N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama
- R. P. Udall / T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim
- L. E. Uronen / T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch
- N. Vaidya / G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia
- M. Valentini / S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan
- M. van Dael / E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van
Den Broeck
- M. van der Sluys / A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra
- M. VanDyke / H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van
Hove
- J. Vanier / M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel
- M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez
- A. Vecchio / G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch
- S. Venikoudis / R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken
- D. Verkindt / B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen
- F. Vetrano / A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant
- A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva
Espinosa
- V. Villa-Ortega / E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret
- S. Vitale / H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis
- J. S. A. von Wrangel / W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P.
Vyatchanin
- J. Wack / L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner
- L. Wallace / E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang
- W. H. Wang / Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner
- M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai
- B. Weaver / S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert
- A. J. Weinstein / R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette
- J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens
- D. Wilken / A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams
- M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke
- M. Wils / L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood
- C. C. Wipf / G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe
- H. T. Wong / I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters
- J. L. Wright / M. Wright / B. Wu / C. Wu
- D. S. Wu / H. Wu / K. Wu / Q. Wu
- Y. Wu / Z. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki
- V. A. Xu / Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto
- K. Yamamoto / T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki
- T. Yan / K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough
- J. Yebana / S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin
- J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara
- M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri
- M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / L. Zhang
- N. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang / C. Zhao
- Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng
- H. Zhong / H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu
- A. B. Zimmerman / L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
The angular distribution of gravitational-wave power from persistent
sources may exhibit anisotropies arising from the large-scale structure
of the Universe. This motivates directional searches for astrophysical
and cosmological gravitational-wave backgrounds, as well as
continuous-wave emitters. We present results of such a search using data
from the first observing run through the first portion of the fourth
observing run of the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Collaborations. We apply
gravitational-wave radiometer techniques to generate skymaps and search
for both narrowband and broadband persistent gravitational-wave sources.
Additionally, we use spherical harmonic decomposition to probe spatially
extended sources. No evidence of persistent gravitational-wave signals
is found, and we set the most stringent constraints to date on such
emissions. For narrowband point sources, our sensitivity estimate to
effective strain amplitude lies in the range  across all sky and frequency range
across all sky and frequency range  Hz. For
targeted sources – Scorpius X-1, SN 1987A, the Galactic Center, Terzan
5, and NGC 6397 – we constrain the strain amplitude with best limits
ranging from
Hz. For
targeted sources – Scorpius X-1, SN 1987A, the Galactic Center, Terzan
5, and NGC 6397 – we constrain the strain amplitude with best limits
ranging from  to
to  . For persistent broadband sources, we constrain
the gravitational-wave flux
. For persistent broadband sources, we constrain
the gravitational-wave flux  , depending on the sky direction
, depending on the sky direction  and spectral index
and spectral index
 .
Finally, for extended sources, we place upper limits on the strain
angular power spectrum
.
Finally, for extended sources, we place upper limits on the strain
angular power spectrum  .
.
Articles for week 42 2025
The
GAPS programme at TNG XYZ. A sub-Neptune suitable for atmospheric
characterization in a multiplanet and mutually inclined system orbiting
the bright K dwarf TOI-5789 (HIP 99452)
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. S. Bonomo / L. Naponiello / A. Sozzetti / S. Benatti
- I. Carleo / K. Biazzo / P. E. Cubillos / M. Damasso
- C. Di Maio / C. Dorn / N. Hara / D. Polychroni
- M.-L. Steinmeyer / K. A. Collins / S. Desidera / X. Dumusque
- A. F. Lanza / B. S. Safonov / C. Stockdale / D. Turrini
- C. Ziegler / L. Affer / M. D’Arpa / V. Fardella
- A. Harutyunyan / V. Lorenzi / L. Malavolta / L. Mancini
- G. Mantovan / G. Micela / F. Murgas / D. Nardiello
- I. Pagano / E. Pallé / M. Pedani / M. Pinamonti
- M. Rainer / G. Scandariato / R. Spinelli / T. Zingales
Summary
Sub-Neptunes with planetary radii of  are the most common planets around solar-type
stars in short-period (
are the most common planets around solar-type
stars in short-period ( d) orbits. It is
still unclear, however, what their most likely composition is, that is
whether they are predominantly gas dwarfs or water worlds. The
sub-Neptunes orbiting bright host stars are very valuable because they
are suitable for atmospheric characterization, which can break the
well-known degeneracy in planet composition from the planet bulk
density, when combined with a precise and accurate mass measurement.
Here we report on the characterization of the sub-Neptune TOI-5789 c,
which transits in front of the bright (
d) orbits. It is
still unclear, however, what their most likely composition is, that is
whether they are predominantly gas dwarfs or water worlds. The
sub-Neptunes orbiting bright host stars are very valuable because they
are suitable for atmospheric characterization, which can break the
well-known degeneracy in planet composition from the planet bulk
density, when combined with a precise and accurate mass measurement.
Here we report on the characterization of the sub-Neptune TOI-5789 c,
which transits in front of the bright ( mag and
mag and  mag) and
magnetically inactive K1V dwarf HIP 99452 every 12.93 days, thanks to
TESS photometry and 141 high-precision radial velocities obtained with
the HARPS-N spectrograph. We find that its radius, mass, and bulk
density are
mag) and
magnetically inactive K1V dwarf HIP 99452 every 12.93 days, thanks to
TESS photometry and 141 high-precision radial velocities obtained with
the HARPS-N spectrograph. We find that its radius, mass, and bulk
density are  ,
,  , and
, and  g cm
g cm , and we show that
TOI-5789 c is a promising target for atmospheric characterization with
both JWST and, in the future, Ariel. By analyzing the HARPS-N radial
velocities with different tools, we also detect three additional
non-transiting planets, namely TOI-5789 b, d, and e, with orbital
periods and minimum masses of
, and we show that
TOI-5789 c is a promising target for atmospheric characterization with
both JWST and, in the future, Ariel. By analyzing the HARPS-N radial
velocities with different tools, we also detect three additional
non-transiting planets, namely TOI-5789 b, d, and e, with orbital
periods and minimum masses of  d,
d,  ,
,  d,
d,  , and
, and
 d,
d,  . The
mutual orbital inclination between planets b and c must be higher than
. The
mutual orbital inclination between planets b and c must be higher than
 deg, which points to a
dynamically hot system. Nevertheless, from sensitivity studies based on
both the HARPS-N and archival HIRES radial-velocity measurements, we can
exclude that such high mutual inclinations are due to the perturbation
by an outer gaseous giant planet.
deg, which points to a
dynamically hot system. Nevertheless, from sensitivity studies based on
both the HARPS-N and archival HIRES radial-velocity measurements, we can
exclude that such high mutual inclinations are due to the perturbation
by an outer gaseous giant planet.
Characterizing
planetary systems with SPIRou: questions about the magnetic cycle of 55
Cnc A and two new planets around B
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. Moutou / P. Petit / P. Charpentier / P. Cristofari
- C. Baruteau / P. Thébault / L. Arnold / E. Artigau
- A. Carmona / N. J. Cook / F. Debras / X. Delfosse
- J.-F. Donati / L. Malo / M. Ould-Elhkim
Summary
One of the first exoplanet hosts discovered thirty years ago, the
star 55 Cnc has been constantly observed ever since. It is now known to
host at least five planets with orbital periods ranging from 17 hours to
15 years. It is also one of the most extreme metal rich stars in the
neighbourhood and it has a low-mass secondary star. In this article, we
present data obtained at the Canada-France-Hawai’i Telescope with the
SPIRou spectropolarimeter on both components of the 55 Cnc stellar
system. We revisit the long-period radial-velocity signals of 55 Cnc A,
with a focus on the role of the magnetic cycle, and propose the
existence of a sixth planet candidate, whose period falls close to that
of the magnetic cycle, or half of it. The other massive outer planet has
a revised period of 13.15 years and a minimum mass of 3.8 MJup. Although
some uncertainty remains on these outer planets, the characterization of
the four inner planets is very robust through the combination of many
different data sets, and all signals are consistent in the nIR and
optical domains. In addition, the magnetic topology of the solar-type
primary component of the system is observed by SPIRou at the minimum of
its activity cycle, characterized by an amplitude ten times smaller than
observed during its maximum in 2017. For the low-mass component 55 Cnc
B, we report the discovery of two exoplanets in the system, with a
period of 6.799+-0.0014 and 33.75+-0.04 days and a minimum mass of
3.5+-0.8 and 5.3+-1.4 MEarth, respectively. The secondary magnetic field
is very weak and the current data set does not allow its precise
characterization, setting an upper limit of 10 G. The system 55 Cnc
stands out as the sixth binary system with planetary systems around both
components, and the first one with non equal-mass stellar
components.
Thermodynamic
and magnetic evolution of an eruptive C-class solar flare observed with
SST/TRIPPEL-SP
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. J. Díaz Baso / J. de la Cruz Rodríguez / H.-P. Doerr / M. van
Noort
- A. Prasad / A. Feller / D. Kiselman
Summary
Solar flares are complex phenomena driven by the release of magnetic
energy, but a large energy reservoir is not sufficient to determine
their eruptive potential; the magnetic topology and plasma dynamics play
a key role. We investigate the thermodynamic and magnetic properties of
the solar atmosphere during the rise, peak, and decay phases of a
C5.1-class flare and filament eruption in active region NOAA 12561 on
2016 July 7, to understand the origin and atmospheric response of this
event. High spatial and spectral resolution spectropolarimetric
observations of the chromospheric Ca II 8542A line and nearby
photospheric lines were obtained with the TRIPPEL-SP spectropolarimeter
at the Swedish 1-m Solar Telescope. Using non-local thermodynamic
equilibrium (NLTE) inversions and non-force-free field (NFFF) magnetic
extrapolations, we followed the event’s evolution from its precursor to
its decay. Before the flare, our analysis reveals a complex, sheared
magnetic topology with a high free energy content ( erg). In this precursor phase, we detected
persistent, localized heating (temperature increase of $
erg). In this precursor phase, we detected
persistent, localized heating (temperature increase of $ $10-20
km/s) deep in the atmosphere. This heating was co-spatial with a
bald-patch region, suggesting that low-altitude magnetic reconnection
could destabilize the filament of the region. The flare’s rise phase was
marked by the filament’s eruption, with a total speed larger than $$70
km/s, when combining inversions and plane-of-sky motions. Following the
eruption, the free energy decreased by $
$10-20
km/s) deep in the atmosphere. This heating was co-spatial with a
bald-patch region, suggesting that low-altitude magnetic reconnection
could destabilize the filament of the region. The flare’s rise phase was
marked by the filament’s eruption, with a total speed larger than $$70
km/s, when combining inversions and plane-of-sky motions. Following the
eruption, the free energy decreased by $ %$ as post-flare loops formed,
connecting the flare ribbons and channeling the released energy into the
lower atmosphere. The flare ribbons exhibited significant heating to
$$8500 K and downflows up to $$10 km/s, consistent with energy
deposition along reconnected loops.
%$ as post-flare loops formed,
connecting the flare ribbons and channeling the released energy into the
lower atmosphere. The flare ribbons exhibited significant heating to
$$8500 K and downflows up to $$10 km/s, consistent with energy
deposition along reconnected loops.
Evidence
for cloud-to-cloud variations in the ratio of polarized thermal dust
emission to starlight polarization
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Nidhi Mehandiratta / Georgia V. Panopoulou / Eirik Gjerløw / Vincent
Pelgrims
- Konstantinos Tassis / Dmitry Blinov / Brandon Hensley / John A.
Kypriotakis
- Siddharth Maharana / Nikos Mandarakas / Vasiliki
Pavlidou / Stephen B. Potter
- A. N. Ramaprakash / Raphael Skalidis / Namita Uppal
Summary
The correlation between optical starlight polarization and polarized
thermal dust emission can be used to infer intrinsic dust properties.
This correlation is quantified by the ratio Rp/p, which has been
measured to be 5.42 +/- 0.05 MJy sr^-1 at 353 GHz when averaged over
large areas of the sky. We investigate this correlation using newly
published stellar polarimetric data densely sampling a continuous sky
region of ~4 square degrees at intermediate Galactic latitude. We
combine RoboPol optical polarization measurements for 1,430 stars with
submillimeter data from the Planck satellite at 353 GHz. We perform
linear fits between the Planck (Qs, Us) and optical (qv, uv) Stokes
parameters, accounting for the differences in resolution between the two
datasets as well as the distribution of clouds along the line of sight.
We find that in this region of the sky the Rp/p value is 3.67 +/- 0.05
MJy sr^-1, indicating a significantly shallower slope than that found
previously using different stellar samples. We also find significant
differences in the fitted slopes when fitting the Qs-qv and Us-uv data
separately. We explore two explanations using mock data: miscalibration
of polarization angle and variations in Rp/p along the line of sight due
to multiple clouds. We show that the former can produce differences in
the correlations of Qs-qv and Us-uv, but large miscalibration angles
would be needed to reproduce the magnitude of the observed differences.
Our simulations favor the interpretation that Rp/p differs between the
two dominant clouds that overlap on the sky in this region. The
difference in Rp/p suggests that the two clouds may have distinct dust
polarimetric properties. With knowledge from the tomographic
decomposition of the stellar polarization, we find that one cloud
appears to dominate the correlation of Us-uv, while both clouds
contribute to the correlation of the Qs-qv data.
NIRPS
and TESS reveal a peculiar system around the M dwarf TOI-756: A
transiting sub-Neptune and a cold eccentric giant
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Léna Parc / François Bouchy / Neil J. Cook / Nolan Grieves
- Étienne Artigau / Alexandrine L’Heureux / René Doyon / Yuri S.
Messias
- Frédérique Baron / Susana C. C. Barros / Björn Benneke / Xavier
Bonfils
- Marta Bryan / Bruno L. Canto Martins / Ryan Cloutier / Nicolas B.
Cowan
- Daniel Brito de Freitas / Jose Renan De Medeiros / Xavier Delfosse /
Elisa Delgado-Mena
- Xavier Dumusque / David Ehrenreich / Pedro Figueira / Jonay I.
González Hernández
- David Lafrenière / Izan de Castro Leão / Christophe Lovis / Lison
Malo
- Claudio Melo / Lucile Mignon / Christoph Mordasini / Francesco
Pepe
- Rafael Rebolo / Jason Rowe / Nuno C. Santos / Damien Ségransan
- Alejandro Suárez Mascareño / Stéphane Udry / Diana Valencia / Gregg
Wade
- Manuel Abreu / José L. A. Aguiar / Khaled Al Moulla / Guillaume
Allain
- Romain Allart / Jose Manuel Almenara / Tomy Arial / Hugues
Auger
- Luc Bazinet / Nicolas Blind / David Bohlender / Isabelle
Boisse
- Anne Boucher / Vincent Bourrier / Sébastien Bovay / Pedro
Branco
- Christopher Broeg / Denis Brousseau / Alexandre Cabral / Charles
Cadieux
- Andres Carmona / Yann Carteret / Zalpha Challita /
David Charbonneau
- Bruno Chazelas / Catherine A. Clark / João Coelho / Marion
Cointepas
- Karen A. Collins / Kevin I. Collins / Uriel Conod / Eduardo
Cristo
- Ana Rita Costa Silva / Antoine Darveau-Bernier / Laurie Dauplaise /
Jean-Baptiste Delisle
- Roseane de Lima Gomes / João Faria / Dasaev O. Fontinele / Thierry
Forveille
- Yolanda G. C. Frensch / Jonathan Gagné / Frédéric Genest / Ludovic
Genolet
- João Gomes da Silva / Félix Gracia Témich / Nicole Gromek / Olivier
Hernandez
- Melissa J. Hobson / Jens H. Hoeijmakers / Norbert Hubin / Marziye
Jafariyazani
- Farbod Jahandar / Ray Jayawardhana / Hans-Ulrich Käufl / Dan
Kerley
- Johann Kolb / Vigneshwaran Krishnamurthy / Benjamin Kung / Pierrot
Lamontagne
- Pierre Larue / Henry Leath / Olivia Lim / Gaspare Lo Curto
- Allan M. Martins / Elisabeth C. Matthews / Jaymie Matthews /
Jean-Sébastien Mayer
- Stan Metchev / Lina Messamah / Leslie Moranta / Dany Mounzer
- Nicola Nari / Louise D. Nielsen / Ares Osborn / Mathieu Ouellet
- Jon Otegi / Luca Pasquini / Vera M. Passegger / Stefan
Pelletier
- Céline Peroux / Caroline Piaulet-Ghorayeb / Mykhaylo Plotnykov /
Emanuela Pompei
- Anne-Sophie Poulin-Girard / José Luis Rasilla / Vladimir Reshetov /
Jonathan Saint-Antoine
- Mirsad Sarajlic / Ivo Saviane / Robin Schnell / Alex Segovia
- Julia Seidel / Armin Silber / Peter Sinclair / Michael Sordet
- Danuta Sosnowska / Avidaan Srivastava / Atanas K. Stefanov / Márcio
A. Teixeira
- Simon Thibault / Philippe Vallée / Thomas Vandal / Valentina
Vaulato
- Joost P. Wardenier / Bachar Wehbe / Drew Weisserman / Ivan
Wevers
- François Wildi / Vincent Yariv / Gérard Zins
Summary
The Near InfraRed Planet Searcher (NIRPS) joined HARPS on the 3.6-m
ESO telescope at La Silla Observatory in April 2023, dedicating part of
its Guaranteed Time Observations (GTO) program to the radial velocity
follow-up of TESS planet candidates to confirm and characterize
transiting planets around M dwarfs. We report the first results of this
program with the characterization of the TOI-756 system, which consists
of TOI-756 b, a transiting sub-Neptune candidate detected by TESS, as
well as TOI-756 c, an additional non-transiting planet discovered by
NIRPS and HARPS. TOI-756 b is a 1.24-day period sub-Neptune with a
radius of 2.81  0.10
0.10  and a mass of
9.8
and a mass of
9.8
 . TOI-756 c is a
cold eccentric (e
. TOI-756 c is a
cold eccentric (e = 0.45
= 0.45  0.01) giant planet orbiting
with a period of 149.6 days around its star with a minimum mass of 4.05
0.01) giant planet orbiting
with a period of 149.6 days around its star with a minimum mass of 4.05
 0.11
0.11  .
Additionally, a linear trend of 146
.
Additionally, a linear trend of 146 is
visible in the radial velocities, hinting at a third component, possibly
in the planetary or brown dwarf regime. This system is unique in the
exoplanet landscape, standing as the first confirmed example of such a
planetary architecture around an M dwarf. With a density of 2.42
is
visible in the radial velocities, hinting at a third component, possibly
in the planetary or brown dwarf regime. This system is unique in the
exoplanet landscape, standing as the first confirmed example of such a
planetary architecture around an M dwarf. With a density of 2.42  0.49 g cm
0.49 g cm , the inner planet,
TOI-756 b, is a volatile-rich sub-Neptune. Assuming a pure H/He
envelope, we inferred an atmospheric mass fraction of 0.023 and a core
mass fraction of 0.27, which is well constrained by stellar refractory
abundances derived from NIRPS spectra. It falls within the still poorly
explored radius cliff and at the lower boundary of the Neptune desert,
making it a prime target for a future atmospheric characterization with
JWST to improve our understanding of this population.
, the inner planet,
TOI-756 b, is a volatile-rich sub-Neptune. Assuming a pure H/He
envelope, we inferred an atmospheric mass fraction of 0.023 and a core
mass fraction of 0.27, which is well constrained by stellar refractory
abundances derived from NIRPS spectra. It falls within the still poorly
explored radius cliff and at the lower boundary of the Neptune desert,
making it a prime target for a future atmospheric characterization with
JWST to improve our understanding of this population.
The
factors that influence protostellar multiplicity II. Gas temperature and
mass in Perseus with APEX
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- N. M. Murillo / C. M. Fuchs / D. Harsono / T.-H. Hsieh
- D. Johnstone / R. Mignon-Risse / M. V. Persson / N.
Sakai
Summary
Protostellar multiplicity is a common outcome of the star formation
process. To fully understand the formation and evolution of these
systems, the physical parameters of the molecular gas together with the
dust must be systematically characterized. Using observations of
molecular gas tracers, we characterize the physical properties of cloud
cores in the Perseus molecular cloud (average distance of 295 pc) at
envelope scales (5000-8000 AU). We used Atacama Pathfinder EXperiment
(APEX) and Nobeyama 45m Radio Observatory (NRO) observations of DCO , H
, H CO and c-C
CO and c-C H
H in several transitions to derive the
physical parameters of the gas toward 31 protostellar systems in
Perseus. Gas kinetic temperature was obtained from DCO
in several transitions to derive the
physical parameters of the gas toward 31 protostellar systems in
Perseus. Gas kinetic temperature was obtained from DCO , H
, H CO and c-C
CO and c-C H
H line ratios. Column densities and gas
masses were then calculated for each species and transition. Gas kinetic
temperature and gas masses were compared with bolometric luminosity,
envelope dust mass, and multiplicity to search for statistically
significant correlations. Gas kinetic temperature derived from DCO
line ratios. Column densities and gas
masses were then calculated for each species and transition. Gas kinetic
temperature and gas masses were compared with bolometric luminosity,
envelope dust mass, and multiplicity to search for statistically
significant correlations. Gas kinetic temperature derived from DCO , H
, H CO and c-C
CO and c-C H
H line ratios have average values of 14
K, 26 and 16 K, respectively, with a range of 10-26 K for DCO
line ratios have average values of 14
K, 26 and 16 K, respectively, with a range of 10-26 K for DCO and c-C
and c-C H
H . The gas kinetic temperature obtained
from H
. The gas kinetic temperature obtained
from H CO line ratios have a range of 13-82 K.
Column densities of all three molecular species are on the order of
10
CO line ratios have a range of 13-82 K.
Column densities of all three molecular species are on the order of
10 to 10
to 10 cm
cm , resulting in gas
masses of 10
, resulting in gas
masses of 10 to 10
to 10 M
M . Statistical
analysis of the physical parameters finds: i) similar envelope gas and
dust masses for single and binary protostellar systems; ii) multiple
(>2 components) protostellar systems tend to have slightly higher gas
and dust masses than binaries and single protostars; iii) a continuous
distribution of gas and dust masses is observed regardless of separation
between components in protostellar systems.
. Statistical
analysis of the physical parameters finds: i) similar envelope gas and
dust masses for single and binary protostellar systems; ii) multiple
(>2 components) protostellar systems tend to have slightly higher gas
and dust masses than binaries and single protostars; iii) a continuous
distribution of gas and dust masses is observed regardless of separation
between components in protostellar systems.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Nixon Hanna / Paul L. Schechter / Michael A. McDonald /
Marceau Limousin
Summary
For any elliptical potential with an external parallel shear, Witt
has proven that the gravitational center lies on a rectangular hyperbola
derived from the image positions of a single quadruply lensed object.
Moreover, it is predicted that for an isothermal elliptical potential
the source position both lies on Witt’s Hyperbola and coincides with the
center of Wynne’s Ellipse (fitted through the four images). Thus, by
fitting Witt’s Hyperbolae to several quartets of images - ten are known
in Abell 1689 - the points of intersection provide an estimate for the
center for the assumed isothermal elliptical potential. We introduce a
new figure of merit defined by the offset of the center of Wynne’s
Ellipse from Witt’s Hyperbola. This offset quantifies deviations from an
ideal elliptical isothermal potential and serves as a discriminant to
exclude poorly fitted quadruples and assign greater weight to
intersections of hyperbolae of better fitting systems. Applying the
method to 10 quads (after excluding 7 poorly fitted quads) in Abell
1689, we find the potential is centered within 11” of the BCG, X-ray
center, flexion-based center and the center found from a total strong
lensing analysis. The Wynne-Witt framework thus delivers a fast,
analytic, and self-consistency-checked estimator for centers in clusters
with multiple quads.
JWST
COSMOS-3D: Spectroscopic Census and Luminosity Function of [O III]
Emitters at 6.75<z<9.05 in COSMOS
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Romain A. Meyer / Feige Wang / Koki Kakiichi / Gabe Brammer
- Jackie Champagne / Katharina Jurk / Zihao Li / Zijian Li
- Marat Musin / Sindhu Satyavolu / Jan-Torge Schindler / Marko
Shuntov
- Yi Xu / Siwei Zou / Fuyan Bian / Caitlin Casey
- Eiichi Egami / Xiaohui Fan / Danyang Jiang / Nicolas
Laporte
- Weizhe Liu / Pascal Oesch / Lidia Tasca / Jinyi
Yang
- Zijian Zhang / Hollis Akins / Zheng Cai / Dave A. Coulter
- Jiamu Huang / Mingyu Li / Weizhe Liu / Yongming Liang
- Xiangyu Jin / Jeyhan Kartaltepe / Jasleen Matharu / Maria
Pudoka
- Wei-Leong Tee / Callum Witten / Haowen Zhang / Yongda Zhu
Summary
We present a spectroscopically-selected [OIII]+Hb emitters catalogue
at 6.75<z<9.05 and the resulting [OIII] 5008 ÅLuminosity Function
(LF) in the COSMOS field. We leverage the 0.3 deg covered to date by
COSMOS-3D using NIRCam/WFSS F444W (90% of the survey) to perform the
largest spectroscopic search for [OIII] emitters at 6.75<z<9.05.
We present our catalogue of 237 [OIII] emitters and their associated
completeness function. The inferred constraints on the [OIII] LF enable
us to characterise the knee of the [OIII] LF, resulting in improved
[OIII] LF constraints at z~7,8. Notably, we find evidence for an
accelerated decline of the [OIII] luminosity density between z~7 and
z~8, which could be expected if the metallicity of [OIII] emitters, as
well as the cosmic star-formation rate density, is declining at these
redshifts. We find that theoretical models that reproduce the z~7,8
[OIII] LF do not reproduce well the [OIII] equivalent width
distribution, pointing to potential challenges in the modelling of[OIII]
and other nebular lines in the early Universe. Finally, we provide the
first constraints on the cosmic variance of [OIII] emitters, estimating
at 15% the relative uncertainty for the z~7,8 [OIII] LF in the 0.3
deg
covered to date by
COSMOS-3D using NIRCam/WFSS F444W (90% of the survey) to perform the
largest spectroscopic search for [OIII] emitters at 6.75<z<9.05.
We present our catalogue of 237 [OIII] emitters and their associated
completeness function. The inferred constraints on the [OIII] LF enable
us to characterise the knee of the [OIII] LF, resulting in improved
[OIII] LF constraints at z~7,8. Notably, we find evidence for an
accelerated decline of the [OIII] luminosity density between z~7 and
z~8, which could be expected if the metallicity of [OIII] emitters, as
well as the cosmic star-formation rate density, is declining at these
redshifts. We find that theoretical models that reproduce the z~7,8
[OIII] LF do not reproduce well the [OIII] equivalent width
distribution, pointing to potential challenges in the modelling of[OIII]
and other nebular lines in the early Universe. Finally, we provide the
first constraints on the cosmic variance of [OIII] emitters, estimating
at 15% the relative uncertainty for the z~7,8 [OIII] LF in the 0.3
deg field. This estimate is in good
agreement with that inferred from clustering, and shows that the [OIII]
LF derived from smaller extragalactic legacy fields is strongly affected
by cosmic variance. Our results highlight the fundamental role that
wide-area JWST slitless surveys play to map the galaxy large-scale
structure down into the reionisation era, serving as a springboard for a
variety of science cases.
field. This estimate is in good
agreement with that inferred from clustering, and shows that the [OIII]
LF derived from smaller extragalactic legacy fields is strongly affected
by cosmic variance. Our results highlight the fundamental role that
wide-area JWST slitless surveys play to map the galaxy large-scale
structure down into the reionisation era, serving as a springboard for a
variety of science cases.
Euclid:
Exploring observational systematics in cluster cosmology – a
comprehensive analysis of cluster counts and clustering
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Fumagalli / M. Costanzi / T. Castro / A. Saro
- S. Borgani / M. Romanello / F. Marulli / E. Tsaprazi
- P. Monaco / B. Altieri / A. Amara / L. Amendola
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole
- M. Douspis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / R. J. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / J. J. Mohr / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / E. Munari / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / C. Rosset / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N.
Taylor
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca
- C. Burigana / L. Gabarra / M. Maturi / C. Porciani
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Viel
Summary
This study explores the impact of observational and modelling
systematic effects on cluster number counts and cluster clustering and
provides model prescriptions for their joint analysis, in the context of
the survey. Using 1000 -like cluster catalogues, we investigate the
effect of systematic uncertainties on cluster summary statistics and
their auto- and cross-covariance, and perform a likelihood analysis to
evaluate their impact on cosmological constraints, with a focus on the
matter density parameter  and on the
power spectrum amplitude
and on the
power spectrum amplitude  . Combining cluster
clustering with number counts significantly improves cosmological
constraints, with the figure of merit increasing by over 300% compared
to number counts alone. We confirm that the two probes are uncorrelated,
and the cosmological constraints derived from their combination are
almost insensitive to the cosmology dependence of the covariance. We
find that photometric redshift uncertainties broaden cosmological
posteriors by 20–30%, while secondary effects like redshift-space
distortions (RSDs) have a smaller impact on the posteriors – 5% for
clustering alone, 10% when combining probes – but can significantly bias
the constraints if neglected. We show that clustering data below
. Combining cluster
clustering with number counts significantly improves cosmological
constraints, with the figure of merit increasing by over 300% compared
to number counts alone. We confirm that the two probes are uncorrelated,
and the cosmological constraints derived from their combination are
almost insensitive to the cosmology dependence of the covariance. We
find that photometric redshift uncertainties broaden cosmological
posteriors by 20–30%, while secondary effects like redshift-space
distortions (RSDs) have a smaller impact on the posteriors – 5% for
clustering alone, 10% when combining probes – but can significantly bias
the constraints if neglected. We show that clustering data below  Mpc
provides additional constraining power, while scales larger than
acoustic oscillation scale add almost no information on
Mpc
provides additional constraining power, while scales larger than
acoustic oscillation scale add almost no information on  and
and  parameters. RSDs and
photo-
parameters. RSDs and
photo- uncertainties also influence the number
count covariance, with a significant impact, of about 15–20%, on the
parameter constraints.
uncertainties also influence the number
count covariance, with a significant impact, of about 15–20%, on the
parameter constraints.
An
Ultra-Short Period Super-Earth and Sub-Neptune Spanning the Radius
Valley Orbiting the Kinematic Thick Disk Star TOI-2345
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Yoshi Nike Emilia Eschen / Thomas G. Wilson / Andrea Bonfanti /
Carina M. Persson
- Sérgio G. Sousa / Monika Lendl / Alexis Heitzmann / Attila E.
Simon
- Göran Olofsson / Amadeo Castro-González / Jo Ann Egger / Luca
Fossati
- Alexander James Mustill / Hugh P. Osborn / Hugo G. Vivien / Yann
Alibert
- Roi Alonso / Tamas Bárczy / David Barrado / Susana C. C. Barros
- Wolfgang Baumjohann / Willy Benz / Nicolas Billot / Luca
Borsato
- Alexis Brandeker / Christopher Broeg / Maximilian Buder / Douglas A.
Caldwell
- Andrew Collier Cameron / Alexandre C. M. Correia / Szilard Csizmadia
/ Patricio E. Cubillos
- Melvyn B. Davies / Magali Deleuil / Adrien Deline /
Olivier D. S. Demangeon
- Brice-Olivier Demory / Aliz Derekas / Billy Edwards / David
Ehrenreich
- Anders Erikson / Jacopo Farinato / Andrea Fortier / Malcolm
Fridlund
- Davide Gandolfi / Kosmas Gazeas / Michaël Gillon / Robert Goeke
- Manuel Güdel / Maximilian N. Günther / Johann Hasiba / Ch.
Helling
- Kate G. Isaak / Jon M. Jenkins / Tatiana Keller / Laszlo L.
Kiss
- Daniel Kitzmann / Judith Korth / Kristine W. F. Lam / Jacques
Laskar
- Alain Lecavelier des Etangs / Adrien Leleu / Demetrio Magrin /
Pierre F. L. Maxted
- Bruno Merín / Christoph Mordasini / Valerio Nascimbeni / Roland
Ottensamer
- Isabella Pagano / Enric Pallé / Gisbert Peter / Daniele Piazza
- Giampaolo Piotto / Don Pollacco / Didier Queloz / Roberto
Ragazzoni
- Nicola Rando / Francesco Ratti / Heike Rauer / Ignasi Ribas
- Nuno C. Santos / Gaetano Scandariato / Damien Ségransan / Avi
Shporer
- Alexis M. S. Smith / Manu Stalport / Sophia Sulis /
Gyula M. Szabó
- Stéphane Udry / Solène Ulmer-Moll / Valérie Van Grootel / Julia
Venturini
- Eva Villaver / Nicholas A. Walton / David Watanabe / Sebastian
Wolf
- Carl Ziegler
Summary
A crucial chemical link between stars and their orbiting exoplanets
is thought to exist. If universal, this connection could affect the
formation and evolution of all planets. Therefore, this potential vital
link needs testing by characterising exoplanets around
chemically-diverse stars. We present the discovery of two planets
orbiting the metal-poor, kinematic thick-disk K-dwarf TOI-2345. TOI-2345
b is a super-Earth with a period of 1.05 days and TOI-2345 c is a
sub-Neptune with a period of 21 days. In addition to the target being
observed in 4 TESS sectors, we obtained 5 CHEOPS visits and 26 radial
velocities from HARPS. By conducting a joint analysis of all the data,
we find TOI-2345 b to have a radius of  R
R and a mass of
and a mass of  M
M ; and TOI-2345 c to
have a radius of
; and TOI-2345 c to
have a radius of  R
R and a mass of
and a mass of  M
M . To explore
chemical links between these planets and their host star, we model their
interior structures newly accounting for devolatised stellar abundances.
TOI-2345 adds to the limited sample of well characterised planetary
systems around thick disk stars. This system challenges theories of
formation and populations of planets around thick disk stars with its
Ultra-Short Period super-Earth and the wide period distribution of these
two planets spanning the radius valley.
. To explore
chemical links between these planets and their host star, we model their
interior structures newly accounting for devolatised stellar abundances.
TOI-2345 adds to the limited sample of well characterised planetary
systems around thick disk stars. This system challenges theories of
formation and populations of planets around thick disk stars with its
Ultra-Short Period super-Earth and the wide period distribution of these
two planets spanning the radius valley.
Articles for week 41 2025
Photometric
Redshift Estimation for Rubin Observatory Data Preview 1 with Redshift
Assessment Infrastructure Layers (RAIL)
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- T. Zhang / E. Charles / J. F. Crenshaw / S. J. Schmidt
- P. Adari / J. Gschwend / S. Mau / B. Andrews
- E. Aubourg / Y. Bains / K. Bechtol / A. Boucaud
- D. Boutigny / P. Burchat / J. Chevalier / J. Chiang
- H.-F. Chiang / D. Clowe / J. Cohen-Tanugi / C. Combet
- A. Connolly / S. Dagoret-Campagne / P. N. Daly / F. Daruich
- G. Daubard / J. De Vicente / H. Drass / K. Fanning
- E. Gawiser / M. Graham / L. P. Guy / Q. Hang
- P. Ingraham / O. Ilbert / M. Jarvis / M. J.
Jee
- T. Jenness / A. Johnson / C. Juramy-Gilles / S. M. Kahn
- J. B. Kalmbach / Y. Kang / A. Kannawadi / L. S. Kelvin
- S. Liang / O. Lynn / N. B. Lust / M. Lutfi
- A. Malz / R. Mandelbaum / S. Marshall / J. Meyers
- M. Migliore / M. Moniez / J. Neveu / J. A. Newman
- E. Nourbakhsh / D. Oldag / H. Park / S. Pelesky
- A. A. Plazas Malagón / B. Quint / M. Rahman / A. Rasmussen
- K. Reil / W. Roby / A. Roodman / C. Roucelle
- M. Salvato / B. Sánchez / D. Sanmartim / R. H. Schindler
- J. Scora / J. Sebag / N. Sedaghat / I. Sevilla-Noarbe
- R. Shirley / A. Shugart / R. Solomon / D. Taranu
- G. Thayer / L. Toribio San Cipriano / E. Urbach / Y. Utsumi
- W. van Reeven / A. von der Linden / C. W. Walter / W. M.
Wood-Vasey
- J. Zuntz / LSST Dark Energy Science Collaboration
Summary
We present the first systematic analysis of photometric redshifts
(photo-z) estimated from the Rubin Observatory Data Preview 1 (DP1) data
taken with the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) Commissioning
Camera. Employing the Redshift Assessment Infrastructure Layers (RAIL)
framework, we apply eight photo-z algorithms to the DP1 photometry,
using deep ugrizy coverage in the Extended Chandra Deep Field South
(ECDFS) field and griz data in the Rubin_SV_38_7 field. In the ECDFS
field, we construct a reference catalog from spectroscopic redshift
(spec-z), grism redshift (grism-z), and multiband photo-z for training
and validating photo-z. Performance metrics of the photo-z are evaluated
using spec-zs from ECDFS and Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument Data
Release 1 samples. Across the algorithms, we achieve per-galaxy photo-z
scatter of  and outlier fractions around 10% in the 6-band
data, with performance degrading at faint magnitudes and z>1.2. The
overall bias and scatter of our machine-learning based photo-zs satisfy
the LSST Y1 requirement. We also use our photo-z to infer the ensemble
redshift distribution n(z). We study the photo-z improvement by
including near-infrared photometry from the Euclid mission, and find
that Euclid photometry improves photo-z at z>1.2. Our results
validate the RAIL pipeline for Rubin photo-z production and demonstrate
promising initial performance.
and outlier fractions around 10% in the 6-band
data, with performance degrading at faint magnitudes and z>1.2. The
overall bias and scatter of our machine-learning based photo-zs satisfy
the LSST Y1 requirement. We also use our photo-z to infer the ensemble
redshift distribution n(z). We study the photo-z improvement by
including near-infrared photometry from the Euclid mission, and find
that Euclid photometry improves photo-z at z>1.2. Our results
validate the RAIL pipeline for Rubin photo-z production and demonstrate
promising initial performance.
Unveiling
the evolution of the CO excitation ladder through cross-correlation of
CONCERTO-like experiments and galaxy redshift surveys
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Mathilde Van Cuyck / Matthieu Bethermin / Guilaine
Lagache / Alexandre Beelen
Summary
Context: Rotational CO transitions, while acting as a foreground for
[C II] line-intensity mapping (LIM) experiments, trace the physical
conditions of cold gas in galaxies at lower redshifts. Studying these
transitions is also crucial for improving component-separation methods
as LIM sensitivity increases. Aims: Galaxy-evolution models have so far
predicted only the total CO LIM signal. We explore the potential of
cross-correlating millimeter-wave LIM data with spectroscopic galaxy
surveys to constrain individual CO-line contributions, measure the
CO-background spectral line energy distribution (SLED), and derive the
cosmic molecular gas density,  , up to
, up to  . Methods: We built 12
light cones of
. Methods: We built 12
light cones of  from the Simulated Infrared Extragalactic Sky (SIDES) simulation. By
analyzing cross-power spectra between different CO transitions and the
galaxy density field, we recovered the CO background SLED. Combining it
with bias-weighted line intensities yielded
from the Simulated Infrared Extragalactic Sky (SIDES) simulation. By
analyzing cross-power spectra between different CO transitions and the
galaxy density field, we recovered the CO background SLED. Combining it
with bias-weighted line intensities yielded  . We also assessed the detectability of the
CO(4–3) cross-power spectrum with a CONCERTO-like experiment. Results:
For a realistic spectroscopic depth, the CO background SLED is
accurately recovered up to
. We also assessed the detectability of the
CO(4–3) cross-power spectrum with a CONCERTO-like experiment. Results:
For a realistic spectroscopic depth, the CO background SLED is
accurately recovered up to  with
with  uncertainties.
Reconstructing
uncertainties.
Reconstructing  from millimeter LIM data requires an excitation correction relative to
CO(1–0). Interloper-induced variance does not prevent precise
from millimeter LIM data requires an excitation correction relative to
CO(1–0). Interloper-induced variance does not prevent precise  estimation. In the two-star-formation-mode SIDES model, starbursts
dominate the SLED at
estimation. In the two-star-formation-mode SIDES model, starbursts
dominate the SLED at  but do not bias
but do not bias  estimates from
estimates from  . However,
CONCERTO lacks the sensitivity to detect the CO
. However,
CONCERTO lacks the sensitivity to detect the CO galaxy cross-power on
relevant scales, even under ideal conditions.
galaxy cross-power on
relevant scales, even under ideal conditions.
The
evolution of the bar fraction and bar lengths in the last 12 billion
years
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Zoe A. Le Conte / Dimitri A. Gadotti / Leonardo Ferreira /
Christopher J. Conselice
- Camila de Sá-Freitas / Taehyun Kim / Justus Neumann / Francesca
Fragkoudi
- E. Athanassoula / Nathan J. Adams
Summary
We investigate the evolution of the bar fraction and length using an
extended JWST NIRCam imaging dataset of galaxies in the  redshift range. We assess the wavelength dependence of the bar fraction
in disc galaxies and bar length evolution by selecting a nearly
mass-complete CEERS disc sample and performing independent visual
classifications on the short (F200W) and long (F356W+F444W) wavelength
channels. A similar bar fraction is observed for both samples, and
combined we find a declining trend in the bar fraction:
redshift range. We assess the wavelength dependence of the bar fraction
in disc galaxies and bar length evolution by selecting a nearly
mass-complete CEERS disc sample and performing independent visual
classifications on the short (F200W) and long (F356W+F444W) wavelength
channels. A similar bar fraction is observed for both samples, and
combined we find a declining trend in the bar fraction:  at
at  ;
;
 at
at  ;
;
 at
at  .
This corroborates our previous work and other recent studies, suggesting
that dynamically cold and rotationally supported massive discs are
present at Cosmic Noon. No evolution in the F356W+F444W bar length is
measured from
.
This corroborates our previous work and other recent studies, suggesting
that dynamically cold and rotationally supported massive discs are
present at Cosmic Noon. No evolution in the F356W+F444W bar length is
measured from  to
to  , which has a mean of
3.6,kpc, but a slight increase of about 1,kpc towards
, which has a mean of
3.6,kpc, but a slight increase of about 1,kpc towards  is measured in the
F200W sample, which has a mean of 2.9,kpc. The bar sample is shorter in
the short-wavelength channel due to the better physical spatial
resolution; however, we also suggest that dust obscuration plays a role.
We find that the correlation between bar length and galaxy mass for
massive galaxies observed at
is measured in the
F200W sample, which has a mean of 2.9,kpc. The bar sample is shorter in
the short-wavelength channel due to the better physical spatial
resolution; however, we also suggest that dust obscuration plays a role.
We find that the correlation between bar length and galaxy mass for
massive galaxies observed at  is not seen at
is not seen at
 . By adding
samples of barred galaxies at
. By adding
samples of barred galaxies at  , we show that there
is a modest increase in the bar length (
, we show that there
is a modest increase in the bar length ( ,kpc) towards
,kpc) towards
 , but bars longer than
, but bars longer than  ,kpc are only
found at
,kpc are only
found at  . We show that bars
and discs grow in tandem, for the bar length normalised by disc size
does not evolve from
. We show that bars
and discs grow in tandem, for the bar length normalised by disc size
does not evolve from  to
to  . Not only is a
significant population of bars forming beyond
. Not only is a
significant population of bars forming beyond  , but our results also
show that some of these bars are as long and strong as the average bar
at
, but our results also
show that some of these bars are as long and strong as the average bar
at  .
.
Validation
of the DESI-DR1 3x2-pt analysis: scale cut and shear ratio tests
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- N. Emas / A. Porredon / C. Blake / J. DeRose
- J. Aguilar / S. Ahlen / D. Bianchi / D. Brooks
- F. J. Castander / T. Claybaugh / A. Cuceu / A. de la Macorra
- A. Dey / B. Dey / P. Doel / S. Ferraro
- J. E. Forero-Romero / C. Garcia-Quintero / E. Gaztañaga / S. Gontcho
A Gontcho
- G. Gutierrez / S. Heydenreich / K. Honscheid / D. Huterer
- M. Ishak / S. Joudaki / R. Joyce / E. Jullo
- S. Juneau / R. Kehoe / D. Kirkby / T. Kisner
- A. Kremin / A. Krolewski / O. Lahav / M. Landriau
- J. U. Lange / L. Le Guillou / A. Leauthaud / M. Manera
- R. Miquel / S. Nadathur / W. J. Percival / F. Prada
- G. Rossi / R. Ruggeri / E. Sanchez / C. Saulder
- A. Semenaite / H. Seo / J. Silber / D. Sprayberry
- Z. Sun / G. Tarlé / B. A. Weaver / R. H. Wechsler
- R. Zhou
Summary
Combined survey analyses of galaxy clustering and weak gravitational
lensing (3x2-pt studies) will allow new and accurate tests of the
standard cosmological model. However, careful validation is necessary to
ensure that these cosmological constraints are not biased by
uncertainties associated with the modelling of astrophysical or
systematic effects. In this study we validate the combined 3x2-pt
analysis of the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument Data Release 1
(DESI-DR1) spectroscopic galaxy clustering and overlapping weak lensing
datasets from the Kilo-Degree Survey (KiDS), the Dark Energy Survey
(DES), and the Hyper-Suprime-Cam Survey (HSC). By propagating the
modelling uncertainties associated with the non-linear matter power
spectrum, non-linear galaxy bias and baryon feedback, we design scale
cuts to ensure that measurements of the matter density and the amplitude
of the matter power spectrum are biased by less than 30% of the
statistical error. We also test the internal consistency of the data and
weak lensing systematics by performing new measurements of the lensing
shear ratio. We demonstrate that the DESI-DR1 shear ratios can be
successfully fit by the same model used to describe cosmic shear
correlations, and analyse the additional information that can be
extracted about the source redshift distributions and intrinsic
alignment parameters. This study serves as crucial preparation for the
upcoming cosmological parameter analysis of these datasets.
CURLING
– II. Improvement on the  Inference from
Pixelized Cluster Strong Lens Modeling
Inference from
Pixelized Cluster Strong Lens Modeling
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Yushan Xie / Huanyuan Shan / Yiping Shu / Nan Li
- Ji Yao / Ran Li / Xiaoyue Cao / Zizhao He
- Yin Li / Eric Jullo / Jean-Paul Kneib / Guoliang
Li
Summary
Strongly lensed supernovae (glSNe) provide a powerful, independent
method to measure the Hubble constant,  , through time delays
between their multiple images. The accuracy of this measurement depends
critically on both the precision of time delay estimation and the
robustness of lens modeling. In many current cluster-scale modeling
algorithms, all multiple images used for modeling are simplified as
point sources to reduce computational costs. In the first paper of the
CURLING program, we demonstrated that such a point-like approximation
can introduce significant uncertainties and biases in both magnification
reconstruction and cosmological inference. In this study, we explore how
such simplifications affect
, through time delays
between their multiple images. The accuracy of this measurement depends
critically on both the precision of time delay estimation and the
robustness of lens modeling. In many current cluster-scale modeling
algorithms, all multiple images used for modeling are simplified as
point sources to reduce computational costs. In the first paper of the
CURLING program, we demonstrated that such a point-like approximation
can introduce significant uncertainties and biases in both magnification
reconstruction and cosmological inference. In this study, we explore how
such simplifications affect  measurements from glSNe. We simulate
a lensed supernova at
measurements from glSNe. We simulate
a lensed supernova at  , lensed by a galaxy
cluster at
, lensed by a galaxy
cluster at  , assuming time
delays are measured from LSST-like light curves. The lens model is
constructed using JWST-like imaging data, utilizing both Lenstool and a
pixelated method developed in CURLING. Under a fiducial cosmology with
, assuming time
delays are measured from LSST-like light curves. The lens model is
constructed using JWST-like imaging data, utilizing both Lenstool and a
pixelated method developed in CURLING. Under a fiducial cosmology with
 , the
Lenstool model yields
, the
Lenstool model yields  , whereas the pixelated framework improves the
precision by over an order of magnitude,
, whereas the pixelated framework improves the
precision by over an order of magnitude,  . Our results indicate that in the next-generation
observations (e.g., JWST), uncertainties from lens modeling dominate the
error budget for
. Our results indicate that in the next-generation
observations (e.g., JWST), uncertainties from lens modeling dominate the
error budget for  inference, emphasizing the importance
of incorporating the extended surface brightness of multiple images to
fully leverage the potential of glSNe for cosmology.
inference, emphasizing the importance
of incorporating the extended surface brightness of multiple images to
fully leverage the potential of glSNe for cosmology.
Euclid
preparation. Cosmology Likelihood for Observables in Euclid (CLOE). 3.
Inference and Forecasts
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / G. Cañas-Herrera / L. W. K. Goh / L.
Blot
- M. Bonici / S. Camera / V. F. Cardone / P. Carrilho
- S. Casas / S. Davini / S. Di Domizio / S. Farrens
- S. Gouyou Beauchamps / S. Ilić / S. Joudaki / F. Keil
- A. M. C. Le Brun / M. Martinelli / C. Moretti / V. Pettorino
- A. Pezzotta / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sciotti
- K. Tanidis / I. Tutusaus / V. Ajani / M. Crocce
- A. Fumagalli / C. Giocoli / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- G. F. Lesci / D. Navarro Girones / A. Nouri-Zonoz / S. Pamuk
- A. Pourtsidou / M. Tsedrik / J. Bel / C. Carbone
- J. Claramunt Gonzalez / C. A. J. Duncan / M. Kilbinger / A.
Porredon
- D. Sapone / E. Sellentin / P. L. Taylor / N. Tessore
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / L. Amendola / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- R. Bender / A. Biviano / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / V. Capobianco / J. Carretero
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik
- K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- O. Lahav / R. Laureijs / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / A. Boucaud / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / P. Casenove / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / V. Scottez
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / R. E. Angulo / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / A. Balaguera-Antolinez / M.
Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / A. Cappi / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / S.
Conseil
- S. Contarini / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro
- A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira
- A. Finoguenov / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / R. Gavazzi / E.
Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- F. Lacasa / M. Lattanzi / J. Le Graet / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / A. Montoro / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- L. Pagano / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P. Reimberg / I. Risso / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / E. Sarpa / J. Schaye / A. Schneider
- M. Sereno / A. Silvestri / L. C. Smith / J. Stadel
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi / G. Verza / N. A. Walton
Summary
The Euclid mission aims to measure the positions, shapes, and
redshifts of over a billion galaxies to provide unprecedented
constraints on the nature of dark matter and dark energy. Achieving this
goal requires a continuous reassessment of the mission’s scientific
performance, particularly in terms of its ability to constrain
cosmological parameters, as our understanding of how to model
large-scale structure observables improves. In this study, we present
the first scientific forecasts using CLOE (Cosmology Likelihood for
Observables in Euclid), a dedicated Euclid cosmological pipeline
developed to support this endeavour. Using advanced Bayesian inference
techniques applied to synthetic Euclid-like data, we sample the
posterior distribution of cosmological and nuisance parameters across a
variety of cosmological models and Euclid primary probes: cosmic shear,
angular photometric galaxy clustering, galaxy-galaxy lensing, and
spectroscopic galaxy clustering. We validate the capability of CLOE to
produce reliable cosmological forecasts, showcasing Euclid’s potential
to achieve a figure of merit for the dark energy parameters  and
and  exceeding 400 when combining all
primary probes. Furthermore, we illustrate the behaviour of the
posterior probability distribution of the parameters of interest given
different priors and scale cuts. Finally, we emphasise the importance of
addressing computational challenges, proposing further exploration of
innovative data science techniques to efficiently navigate the Euclid
high-dimensional parameter space in upcoming cosmological data
releases.
exceeding 400 when combining all
primary probes. Furthermore, we illustrate the behaviour of the
posterior probability distribution of the parameters of interest given
different priors and scale cuts. Finally, we emphasise the importance of
addressing computational challenges, proposing further exploration of
innovative data science techniques to efficiently navigate the Euclid
high-dimensional parameter space in upcoming cosmological data
releases.
The
ExoGRAVITY survey: A K-band spectral library of giant exoplanet and
brown dwarf companions
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. Kammerer / T. O. Winterhalder / S. Lacour / T. Stolker
- G.-D. Marleau / W. O. Balmer / A. F. Moore / L. Piscarreta
- C. Toci / A. Mérand / M. Nowak / E. L. Rickman
- L. Pueyo / N. Pourré / E. Nasedkin / J. J. Wang
- G. Bourdarot / F. Eisenhauer / Th. Henning / R. Garcia Lopez
- E. F. van Dishoeck / T. Forveille / J. D. Monnier / R. Abuter
- A. Amorim / M. Benisty / J.-P. Berger / H. Beust
- S. Blunt / A. Boccaletti / M. Bonnefoy / H. Bonnet
- M. S. Bordoni / W. Brandner / F. Cantalloube / P. Caselli
- W. Ceva / B. Charnay / G. Chauvin / A. Chavez
- A. Chomez / E. Choquet / V. Christiaens / Y.
Clénet
- V. Coudé du Foresto / A. Cridland / R. Davies / R. Dembet
- J. Dexter / A. Drescher / G. Duvert / A. Eckart
- C. Fontanive / N. M. Förster Schreiber / P. Garcia / E. Gendron
- R. Genzel / S. Gillessen / J. H. Girard / S. Grant
- J. Hagelberg / X. Haubois / G. Heißel / S. Hinkley
- S. Hippler / M. Houllé / Z. Hubert / L. Jocou
- M. Keppler / P. Kervella / L. Kreidberg / N. T. Kurtovic
- A.-M. Lagrange / V. Lapeyrère / J.-B. Le Bouquin / D. Lutz
- A.-L. Maire / F. Mang / E. C. Matthews / P. Mollière
- C. Mordasini / D. Mouillet / T. Ott / G. P. P. L. Otten
- C. Paladini / T. Paumard / K. Perraut / G. Perrin
- O. Pfuhl / D. C. Ribeiro / Z. Rustamkulov / D. Ségransan
- J. Shangguan / T. Shimizu / M. Samland / D. Sing
- J. Stadler / O. Straub / C. Straubmeier / E. Sturm
- L. J. Tacconi / S. Udry / A. Vigan / F.
Vincent
- S. D. von Fellenberg / F. Widmann / J. Woillez / S. Yazici
- the GRAVITY Collaboration
Summary
Direct observations of exoplanet and brown dwarf companions with
near-infrared interferometry, first enabled by the dual-field mode of
VLTI/GRAVITY, provide unique measurements of the objects’ orbital
motions and atmospheric compositions. Here, we compile a homogeneous
library of all exoplanet and brown dwarf K-band spectra observed by
GRAVITY thus far. We re-reduced all the available GRAVITY dual-field
high-contrast data and, where companions are detected, extract their
~2.0-2.4  m K-band contrast spectra. We then
derived stellar model atmospheres for all employed flux references,
which we used to convert the companion contrast into companion flux
spectra. Solely from the resulting GRAVITY spectra, we extracted
spectral types, spectral indices, and bulk physical properties for all
companions. Finally, and with the help of age constraints from the
literature, we also derived isochronal masses for most companions using
evolutionary models. The resulting library contains R ~ 500 GRAVITY
spectra of 39 substellar companions from late M to late T spectral
types, including the entire L-T transition. Throughout this transition,
a shift from CO-dominated late M- and L-type dwarfs to CH4-dominated
T-type dwarfs can be observed in the K-band. The GRAVITY spectra alone
constrain the objects’ bolometric luminosity to typically within $$0.15
dex. The derived isochronal masses agree with dynamical masses from the
literature where available, except for HD 4113 c for which we confirm
its previously reported potential underluminosity. Medium-resolution
spectroscopy of substellar companions with GRAVITY provides insight into
the carbon chemistry and the cloudiness of these objects’ atmospheres.
It also constrains these objects’ bolometric luminosities which can
yield measurements of their formation entropy if combined with dynamical
masses, for instance from Gaia and GRAVITY astrometry.
m K-band contrast spectra. We then
derived stellar model atmospheres for all employed flux references,
which we used to convert the companion contrast into companion flux
spectra. Solely from the resulting GRAVITY spectra, we extracted
spectral types, spectral indices, and bulk physical properties for all
companions. Finally, and with the help of age constraints from the
literature, we also derived isochronal masses for most companions using
evolutionary models. The resulting library contains R ~ 500 GRAVITY
spectra of 39 substellar companions from late M to late T spectral
types, including the entire L-T transition. Throughout this transition,
a shift from CO-dominated late M- and L-type dwarfs to CH4-dominated
T-type dwarfs can be observed in the K-band. The GRAVITY spectra alone
constrain the objects’ bolometric luminosity to typically within $$0.15
dex. The derived isochronal masses agree with dynamical masses from the
literature where available, except for HD 4113 c for which we confirm
its previously reported potential underluminosity. Medium-resolution
spectroscopy of substellar companions with GRAVITY provides insight into
the carbon chemistry and the cloudiness of these objects’ atmospheres.
It also constrains these objects’ bolometric luminosities which can
yield measurements of their formation entropy if combined with dynamical
masses, for instance from Gaia and GRAVITY astrometry.
Euclid
preparation. Cosmology Likelihood for Observables in Euclid (CLOE). 5.
Extensions beyond the standard modelling of theoretical probes and
systematic effects
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / L. W. K. Goh / A. Nouri-Zonoz / S. Pamuk
- M. Ballardini / B. Bose / G. Cañas-Herrera / S. Casas
- G. Franco-Abellán / S. Ilić / F. Keil / M. Kunz
- A. M. C. Le Brun / F. Lepori / M. Martinelli / Z. Sakr
- F. Sorrenti / E. M. Teixeira / I. Tutusaus / L. Blot
- M. Bonici / C. Bonvin / S. Camera / V. F. Cardone
- P. Carrilho / S. Di Domizio / R. Durrer / S. Farrens
- S. Gouyou Beauchamps / S. Joudaki / C. Moretti / A. Pezzotta
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sciotti / K. Tanidis / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / D. Bagot
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / H. Dole / M. Douspis
- F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / T. Schrabback
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- A. Tsyganov / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani
- E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- M. Maturi / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- A. Balaguera-Antolinez / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A.
Blanchard
- H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Conseil / S.
Contarini
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / J. M. Diego
- P. Dimauro / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gruppuso / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / F. Lacasa / M. Lattanzi
- V. Le Brun / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / G. Leroy
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / L. Pagano
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / D. Potter
- A. Pourtsidou / S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- J. Schaye / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis / E. Sellentin
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi / G. Verza / N. A. Walton
Summary
Euclid is expected to establish new state-of-the-art constraints on
extensions beyond the standard LCDM cosmological model by measuring the
positions and shapes of billions of galaxies. Specifically, its goal is
to shed light on the nature of dark matter and dark energy. Achieving
this requires developing and validating advanced statistical tools and
theoretical prediction software capable of testing extensions of the
LCDM model. In this work, we describe how the Euclid likelihood
pipeline, Cosmology Likelihood for Observables in Euclid (CLOE), has
been extended to accommodate alternative cosmological models and to
refine the theoretical modelling of Euclid primary probes. In
particular, we detail modifications made to CLOE to incorporate the
magnification bias term into the spectroscopic two-point correlation
function of galaxy clustering. Additionally, we explain the adaptations
made to CLOE’s implementation of Euclid primary photometric probes to
account for massive neutrinos and modified gravity extensions. Finally,
we present the validation of these CLOE modifications through dedicated
forecasts on synthetic Euclid-like data by sampling the full posterior
distribution and comparing with the results of previous literature. In
conclusion, we have identified in this work several functionalities with
regards to beyond-LCDM modelling that could be further improved within
CLOE, and outline potential research directions to enhance pipeline
efficiency and flexibility through novel inference and machine learning
techniques.
Cosmology
Likelihood for Observables in (CLOE). 1. Theoretical recipe
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / V. F. Cardone / S. Joudaki / L. Blot
- M. Bonici / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / P. Carrilho
- S. Casas / S. Davini / S. Di Domizio / S. Farrens
- L. W. K. Goh / S. Gouyou Beauchamps / S. Ilić / F. Keil
- A. M. C. Le Brun / M. Martinelli / C. Moretti / V. Pettorino
- A. Pezzotta / A. G. Sánchez / Z. Sakr / D. Sciotti
- K. Tanidis / I. Tutusaus / V. Ajani / M. Crocce
- C. Giocoli / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / G. F. Lesci
- D. Navarro Girones / A. Nouri-Zonoz / S. Pamuk / M. Tsedrik
- J. Bel / C. Carbone / C. A. J. Duncan / M. Kilbinger
- F. Lacasa / M. Lattanzi / D. Sapone / E. Sellentin
- P. L. Taylor / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / L. Amendola
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / V. Capobianco
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / B. Gillis
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / P. Liebing / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / S.
Maurogordato
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / G. D. Racca / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / B. Sartoris
- R. Scaramella / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin
Vigo
- L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew
- M. Maturi / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / A. Balaguera-Antolinez / M. Bethermin / S.
Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / S. Contarini / A. R. Cooray / O.
Cucciati
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / A. Gruppuso / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E.
Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / G. Morgante
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- L. Pagano / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P. Reimberg / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / J. Schaye / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis
- A. Silvestri / L. C. Smith / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi
- G. Verza / N. A. Walton
Summary
As the statistical precision of cosmological measurements increases,
the accuracy of the theoretical description of these measurements needs
to increase correspondingly in order to infer the underlying cosmology
that governs the Universe. To this end, we have created the Cosmology
Likelihood for Observables in Euclid (CLOE), which is a novel
cosmological parameter inference pipeline developed within the Euclid
Consortium to translate measurements and covariances into cosmological
parameter constraints. In this first in a series of six papers, we
describe the theoretical recipe of this code for the Euclid primary
probes. These probes are composed of the photometric 3x2pt observables
of cosmic shear, galaxy-galaxy lensing, and galaxy clustering, along
with spectroscopic galaxy clustering. We provide this description in
both Fourier and configuration space for standard and extended summary
statistics, including the wide range of systematic uncertainties that
affect them. This includes systematic uncertainties such as intrinsic
galaxy alignments, baryonic feedback, photometric and spectroscopic
redshift uncertainties, shear calibration uncertainties, sample
impurities, photometric and spectroscopic galaxy biases, as well as
magnification bias. The theoretical descriptions are further able to
accommodate both Gaussian and non-Gaussian likelihoods and extended
cosmologies with non-zero curvature, massive neutrinos, evolving dark
energy, and simple forms of modified gravity. These theoretical
descriptions that underpin CLOE will form a crucial component in
revealing the true nature of the Universe with next-generation
cosmological surveys such as Euclid.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / M. Martinelli / A. Pezzotta / D. Sciotti
- L. Blot / M. Bonici / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. F. Cardone / P. Carrilho / S. Casas / S. Davini
- S. Di Domizio / S. Farrens / L. W. K. Goh / S. Gouyou
Beauchamps
- S. Ilić / S. Joudaki / F. Keil / A. M. C. Le Brun
- C. Moretti / V. Pettorino / A. G. Sánchez / Z. Sakr
- K. Tanidis / I. Tutusaus / V. Ajani / M. Crocce
- C. Giocoli / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / G. F. Lesci
- D. Navarro Girones / A. Nouri-Zonoz / S. Pamuk / M. Tsedrik
- J. Bel / C. Carbone / C. A. J. Duncan / M. Kilbinger
- F. Lacasa / M. Lattanzi / D. Sapone / E. Sellentin
- P. L. Taylor / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / L. Amendola
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / R. Bender
- A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / V. Capobianco / J. Carretero
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard
- B. Gillis / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / P. Liebing
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P.
Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / S.
Matthew
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi
- I. T. Andika / R. E. Angulo / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / A. Balaguera-Antolinez / M. Bethermin / A.
Blanchard
- H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / A. Cappi / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / S.
Conseil
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro
- A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / R.
Gavazzi
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- A. Gruppuso / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / P. Natoli
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / L. Pagano / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- A. Shulevski / A. Silvestri / L. C. Smith / J. Stadel
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton
Summary
The Euclid satellite will provide data on the clustering of galaxies
and on the distortion of their measured shapes, which can be used to
constrain and test the cosmological model. However, the increase in
precision places strong requirements on the accuracy of the theoretical
modelling for the observables and of the full analysis pipeline. In this
paper, we investigate the accuracy of the calculations performed by the
Cosmology Likelihood for Observables in Euclid (CLOE), a software able
to handle both the modelling of observables and their fit against
observational data for both the photometric and spectroscopic surveys of
Euclid, by comparing the output of CLOE with external codes used as
benchmark. We perform such a comparison on the quantities entering the
calculations of the observables, as well as on the final outputs of
these calculations. Our results highlight the high accuracy of CLOE when
comparing its calculation against external codes for Euclid observables
on an extended range of operative cases. In particular, all the summary
statistics of interest always differ less than  from the chosen
benchmark, and CLOE predictions are statistically compatible with
simulated data obtained from benchmark codes. The same holds for the
comparison of correlation function in configuration space for
spectroscopic and photometric observables.
from the chosen
benchmark, and CLOE predictions are statistically compatible with
simulated data obtained from benchmark codes. The same holds for the
comparison of correlation function in configuration space for
spectroscopic and photometric observables.
The CEERS
Photometric and Physical Parameter Catalog
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Isa G. Cox / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Micaela B. Bagley / Steven L.
Finkelstein
- Caitlin Rose / Ali Ahmad Khostovan / Katherine Chworowsky /
Olivier Ilbert
- Anton M. Koekemoer / Henry C. Ferguson / Pablo Arrabal Haro / Bren
E. Backhaus
- Mark Dickinson / Adriano Fontana / Yuchen Guo / Andrea Grazian
- Norman A. Grogin / Santosh Harish / Nimish P. Hathi / Benne W.
Holwerda
- Kartheik G. Iyer / Lisa J. Kewley / Allison Kirkpatrick / Dale D.
Kocevski
- Rebecca L. Larson / Jennifer M. Lotz / Ray A. Lucas / Fabio
Pacucci
- Casey Papovich / Laura Pentericci / Pablo G. Pérez-González / Nor
Pirzkal
- Swara Ravindranath / Rachel S. Somerville / Jonathan R. Trump /
Stephen M. Wilkins
- Guang Yang / L. Y. Aaron Yung
Summary
We present the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science Survey (CEERS)
catalog, including space-based photometry, photometric redshifts, and
physical parameters for more than 80,000 galaxies. The imaging used for
this catalog comes from the CEERS survey, which has NIRCam coverage over
~100 sq. arcmin of the Extended Groth Strip (EGS) in seven filters from
1.15 m to 4.44
m to 4.44 m. Alongside these data, we also include
ancillary HST imaging in seven filters from 0.435
m. Alongside these data, we also include
ancillary HST imaging in seven filters from 0.435 m to 1.6
m to 1.6 m. We used Source Extractor with hot and
cold detection settings to extract photometry. We derive photometric
redshifts using the spectral energy distribution (SED) modeling code,
LePHARE, and estimate their accuracy using spectroscopically confirmed
galaxies out to
m. We used Source Extractor with hot and
cold detection settings to extract photometry. We derive photometric
redshifts using the spectral energy distribution (SED) modeling code,
LePHARE, and estimate their accuracy using spectroscopically confirmed
galaxies out to  , with
, with  ranging from
0.035-0.073, depending strongly on galaxy magnitude and redshift. We
compute stellar masses, star formation rates, and E(B-V) using three
different SED fitting codes with different templates and assumptions
about the galaxy star formation histories. All of these measurements, as
well as the full mosaics in all filters, and redshift probability
distribution functions, are made available via the CEERS DR1.0 data
release.
ranging from
0.035-0.073, depending strongly on galaxy magnitude and redshift. We
compute stellar masses, star formation rates, and E(B-V) using three
different SED fitting codes with different templates and assumptions
about the galaxy star formation histories. All of these measurements, as
well as the full mosaics in all filters, and redshift probability
distribution functions, are made available via the CEERS DR1.0 data
release.
Euclid
preparation: Towards a DR1 application of higher-order weak lensing
statistics
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / S. Vinciguerra / F. Bouchè /
N. Martinet
- L. Castiblanco / C. Uhlemann / S. Pires / J. Harnois-Déraps
- C. Giocoli / M. Baldi / V. F. Cardone / A. Vadalà
- N. Dagoneau / L. Linke / E. Sellentin / P. L. Taylor
- J. C. Broxterman / S. Heydenreich / V. Tinnaneri Sreekanth / N.
Porqueres
- L. Porth / M. Gatti / D. Grandón / A. Barthelemy
- F. Bernardeau / A. Tersenov / H. Hoekstra / J.-L. Starck
- S. Cheng / P. A. Burger / I. Tereno / R. Scaramella
- B. Altieri / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre
- G. De Lucia / H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / O. Mansutti
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / F. Marulli / R. J. Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / A. Boucaud / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / J. A. Escartin Vigo
- L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / R. E. Angulo / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / E. Aubourg / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. Bonici / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / A. R. Cooray / G. Desprez / A.
Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / M. Y. Elkhashab
- Y. Fang / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- R. Gavazzi / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F.
Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava
- Y. Kang / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / J. Kim
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- T. I. Liaudat / J. Macias-Perez / M. Magliocchetti / F.
Mannucci
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / N. A. Walton
Summary
This is the second paper in the HOWLS (higher-order weak lensing
statistics) series exploring the usage of non-Gaussian statistics for
cosmology inference within . With respect to our first paper, we develop
a full tomographic analysis based on realistic photometric redshifts
which allows us to derive Fisher forecasts in the ( ,
,  ) plane for a -like data release 1
(DR1) setup. We find that the 5 higher-order statistics (HOSs) that
satisfy the Gaussian likelihood assumption of the Fisher formalism
(1-point probability distribution function, $$1-norm, peak counts,
Minkowski functionals, and Betti numbers) each outperform the shear
2-point correlation functions by a factor
) plane for a -like data release 1
(DR1) setup. We find that the 5 higher-order statistics (HOSs) that
satisfy the Gaussian likelihood assumption of the Fisher formalism
(1-point probability distribution function, $$1-norm, peak counts,
Minkowski functionals, and Betti numbers) each outperform the shear
2-point correlation functions by a factor  on the
on the  forecasts, with only marginal
improvement when used in combination with 2-point estimators, suggesting
that every HOS is able to retrieve both the non-Gaussian and Gaussian
information of the matter density field. The similar performance of the
different estimators is explained by a homogeneous use of multi-scale
and tomographic information, optimized to lower computational costs.
These results hold for the
forecasts, with only marginal
improvement when used in combination with 2-point estimators, suggesting
that every HOS is able to retrieve both the non-Gaussian and Gaussian
information of the matter density field. The similar performance of the
different estimators is explained by a homogeneous use of multi-scale
and tomographic information, optimized to lower computational costs.
These results hold for the  mass mapping techniques of the
pipeline: aperture mass, Kaiser–Squires, and Kaiser–Squires plus, and
are unaffected by the application of realistic star masks. Finally, we
explore the use of HOSs with the Bernardeau–Nishimichi–Taruya (BNT)
nulling scheme approach, finding promising results towards applying
physical scale cuts to HOSs.
mass mapping techniques of the
pipeline: aperture mass, Kaiser–Squires, and Kaiser–Squires plus, and
are unaffected by the application of realistic star masks. Finally, we
explore the use of HOSs with the Bernardeau–Nishimichi–Taruya (BNT)
nulling scheme approach, finding promising results towards applying
physical scale cuts to HOSs.
Euclid
preparation. Cosmology Likelihood for Observables in Euclid (CLOE). 6:
Impact of systematic uncertainties on the cosmological analysis
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / L. Blot / K. Tanidis / G. Cañas-Herrera
- P. Carrilho / M. Bonici / S. Camera / V. F. Cardone
- S. Casas / S. Davini / S. Di Domizio / S. Farrens
- L. W. K. Goh / S. Gouyou Beauchamps / S. Ilić / S. Joudaki
- F. Keil / A. M. C. Le Brun / M. Martinelli / C. Moretti
- V. Pettorino / A. Pezzotta / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sciotti / I. Tutusaus / V. Ajani / M. Crocce
- A. Fumagalli / C. Giocoli / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- G. F. Lesci / D. Navarro Girones / A. Nouri-Zonoz / S. Pamuk
- A. Pourtsidou / M. Tsedrik / J. Bel / C. Carbone
- C. A. J. Duncan / M. Kilbinger / D. Sapone / E. Sellentin
- P. L. Taylor / L. Amendola / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / V. Capobianco
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / H. Dole / M. Douspis
- F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / L. Moscardini / E. Munari
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / C. Rosset
- R. Saglia / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner / C.
Surace
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / E. A. Valentijn
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- A. Boucaud / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra
- J. García-Bellido / W. G. Hartley / R. Maoli / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- M. Maturi / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / M. Pöntinen
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- E. Aubourg / L. Bazzanini / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / O. Cucciati / G. Desprez / A.
Díaz-Sánchez
- J. M. Diego / M. Y. Elkhashab / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / R. Gavazzi / E.
Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gruppuso
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / J. Kim / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- M. Lattanzi / V. Le Brun / F. Lepori / G.
Leroy
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / J. Macias-Perez
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / C. J. A. P. Martins / L.
Maurin
- M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / A. Montoro
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / L. Pagano / D. Paoletti / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / R. Paviot / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / W. Roster / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / J. Schaye
- A. Schneider / L. C. Smith / J. G. Sorce / J. Stadel
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- F. Vernizzi / G. Verza / S. Vinciguerra / N. A.
Walton
Summary
Extracting cosmological information from the Euclid galaxy survey
will require modelling numerous systematic effects during the inference
process. This implies varying a large number of nuisance parameters,
which have to be marginalised over before reporting the constraints on
the cosmological parameters. This is a delicate process, especially with
such a large parameter space, which could result in biased cosmological
results. In this work, we study the impact of different choices for
modelling systematic effects and prior distribution of nuisance
parameters for the final Euclid Data Release, focusing on the 3$$2pt
analysis for photometric probes and the galaxy power spectrum multipoles
for the spectroscopic probes. We explore the effect of intrinsic
alignments, linear galaxy bias, magnification bias, multiplicative
cosmic shear bias and shifts in the redshift distribution for the
photometric probes, as well as the purity of the spectroscopic sample.
We find that intrinsic alignment modelling has the most severe impact
with a bias up to  on the Hubble constant
on the Hubble constant
 if neglected, followed by
mis-modelling of the redshift evolution of galaxy bias, yielding up to
if neglected, followed by
mis-modelling of the redshift evolution of galaxy bias, yielding up to
 on the parameter
on the parameter  .
Choosing a too optimistic prior for multiplicative bias can also result
in biases of the order of
.
Choosing a too optimistic prior for multiplicative bias can also result
in biases of the order of  on
on  . We also find that the precision on
the estimate of the purity of the spectroscopic sample will be an
important driver for the constraining power of the galaxy clustering
full-shape analysis. These results will help prioritise efforts to
improve the modelling and calibration of systematic effects in
Euclid.
. We also find that the precision on
the estimate of the purity of the spectroscopic sample will be an
important driver for the constraining power of the galaxy clustering
full-shape analysis. These results will help prioritise efforts to
improve the modelling and calibration of systematic effects in
Euclid.
Articles for week 40 2025
Edge-On
Disk Study (EODS) III: Molecular Stratification in the Flying Saucer
Disk
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Dutrey / O. Denis-Alpizar / S. Guilloteau / C. Foucher
- S. Gavino / D. Semenov / V. Pietu / E. Chapillon
- L. Testi / E. Dartois / E. DiFolco / K. Furuya
- U. Gorti / N. Grosso / Th. Henning / J. M.
Huré
- Á. Kóspál / F. Le Petit / L. Majumdar / R. Meshaka
- H. Nomura / N. T. Phuong / M. Ruaud / Y. W. Tang
- S. Wolf
Summary
Context: Investigating the vertical distribution of molecular content
in protoplanetary disks remains difficult in most disks mildly inclined
along the line of sight. In contrast, edge-on disks provide a direct
(tomographic) view of the 2D molecular brightness. Aims: We study the
radial and vertical molecular distribution as well as the gas
temperature and density by observing the Keplerian edge-on disk
surrounding the Flying Saucer, a Class II object located in Ophiuchus.
Methods: We use new and archival ALMA data to perform a tomography of
 CO,
CO,  CO, C
CO, C O, CN, HCN, CS, H
O, CN, HCN, CS, H CO, c-C
CO, c-C H
H , N
, N D
D , DCN and
, DCN and  CS. We analyze molecular
tomographies and model data using the radiative transfer code DiskFit.
Results: We directly measure the altitude above the mid-plane for each
observed species. For the first time, we unambiguously demonstrate the
presence of a common molecular layer and measure its thickness: most
molecules are located at the same altitude versus radius. Beyond CO, as
predicted by chemical models, the CN emission traces the upper boundary
of the molecular layer, whereas the deuterated species (DCN and N2D+)
resides below one scale-height. Our best fits from DiskFit show that
most observed transitions in the molecular layer are thermalized because
their excitation temperature is the same, around 17-20 K. Conclusions:
These long-integration observations clearly reveal a molecular layer
predominantly located around 1-2 scale height, at a temperature above
the CO freeze-out temperature. The deuterated molecules are closer to
the mid-plane and N2D+ may be a good proxy for the CO snowline. Some
molecules, such as CN and H2CO, are likely influenced by the disk
environment, at least beyond the mm dust disk radius. The direct
observation of the molecular stratification opens the door to detailed
chemical modeling in this disk which appears representative of T Tauri
disks.
CS. We analyze molecular
tomographies and model data using the radiative transfer code DiskFit.
Results: We directly measure the altitude above the mid-plane for each
observed species. For the first time, we unambiguously demonstrate the
presence of a common molecular layer and measure its thickness: most
molecules are located at the same altitude versus radius. Beyond CO, as
predicted by chemical models, the CN emission traces the upper boundary
of the molecular layer, whereas the deuterated species (DCN and N2D+)
resides below one scale-height. Our best fits from DiskFit show that
most observed transitions in the molecular layer are thermalized because
their excitation temperature is the same, around 17-20 K. Conclusions:
These long-integration observations clearly reveal a molecular layer
predominantly located around 1-2 scale height, at a temperature above
the CO freeze-out temperature. The deuterated molecules are closer to
the mid-plane and N2D+ may be a good proxy for the CO snowline. Some
molecules, such as CN and H2CO, are likely influenced by the disk
environment, at least beyond the mm dust disk radius. The direct
observation of the molecular stratification opens the door to detailed
chemical modeling in this disk which appears representative of T Tauri
disks.
Impact
of Cosmic Filaments on Galaxy Morphological Evolution and Predictions of
Early Cosmic Web Structure for Roman
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Farhanul Hasan / Haowen Zhang / Viraj Pandya / Marc Rafelski
- Joseph N. Burchett / Douglas Hellinger / Kalina V. Nedkova /
Ilias Goovaerts
- Nir Mandelker / Daisuke Nagai / Grecco A. Oyarzún / Joel R.
Primack
- Joanna Woo
Summary
We leverage the IllustrisTNG cosmological simulations to test how the
large-scale cosmic web shapes galaxy morphology and to forecast the
early cosmic web structure that the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
will reveal. In the hydrodynamic TNG50 and 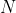 -body TNG50-Dark runs, we reconstruct
the cosmic web at redshifts
-body TNG50-Dark runs, we reconstruct
the cosmic web at redshifts  , 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 with
the Monte Carlo Physarum Machine density estimator and the DisPerSE
structure identification framework. We confirm that dark matter halos
start out predominantly prolate (elongated) and their shapes are aligned
with their nearest filaments; prolate galaxies retain strong
shape-alignment with their outer halos to later times. The fraction of
prolate galaxies and halos increases toward lower stellar mass, higher
redshift, and lower-density filaments. Oblate and spheroidal galaxies
show weaker trends with filament density, but spheroidal halos
preferentially reside in higher-density filaments. We also find that
higher-density filaments favor extended rotationally-supported disks,
whereas lower-density filaments more often host smaller
dispersion-supported systems. Then, generating mock galaxy samples from
TNG100 and TNG50, we predict the early cosmic web accessible to Roman.
We find that the spectroscopic emission-line depth planned for the
High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey (HLWAS) yields a highly incomplete galaxy
sample that does not accurately trace the
, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 with
the Monte Carlo Physarum Machine density estimator and the DisPerSE
structure identification framework. We confirm that dark matter halos
start out predominantly prolate (elongated) and their shapes are aligned
with their nearest filaments; prolate galaxies retain strong
shape-alignment with their outer halos to later times. The fraction of
prolate galaxies and halos increases toward lower stellar mass, higher
redshift, and lower-density filaments. Oblate and spheroidal galaxies
show weaker trends with filament density, but spheroidal halos
preferentially reside in higher-density filaments. We also find that
higher-density filaments favor extended rotationally-supported disks,
whereas lower-density filaments more often host smaller
dispersion-supported systems. Then, generating mock galaxy samples from
TNG100 and TNG50, we predict the early cosmic web accessible to Roman.
We find that the spectroscopic emission-line depth planned for the
High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey (HLWAS) yields a highly incomplete galaxy
sample that does not accurately trace the  cosmic web. A survey
cosmic web. A survey  deeper
over a few square degrees would enable a proper reconstruction and
reveal qualitatively correct filament-galaxy morphology relationships.
Nevertheless, the planned HLWAS Deep field should still identify most
galaxy overdensities; targeted deeper spectroscopy of these regions
would efficiently and adequately map the early filamentary
structure.
deeper
over a few square degrees would enable a proper reconstruction and
reveal qualitatively correct filament-galaxy morphology relationships.
Nevertheless, the planned HLWAS Deep field should still identify most
galaxy overdensities; targeted deeper spectroscopy of these regions
would efficiently and adequately map the early filamentary
structure.
Euclid:
Discovery of bright  Lyman-break
galaxies in UltraVISTA and Euclid COSMOS
Lyman-break
galaxies in UltraVISTA and Euclid COSMOS
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- R. G. Varadaraj / R. A. A. Bowler / M. J. Jarvis / J. R. Weaver
- E. Bañados / P. Holloway / K. I. Caputi / S. M. Wilkins
- D. Yang / B. Milvang-Jensen / L. Gabarra / P. A. Oesch
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar
- H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / J. Martín-Fleitas
- V. Scottez / M. Viel
Summary
We present a search for  Lyman-break
galaxies using the
Lyman-break
galaxies using the  near-infrared UltraVISTA survey in the COSMOS
field, reaching
near-infrared UltraVISTA survey in the COSMOS
field, reaching  depths in
depths in  of 26.2. We incorporate deep optical
and Spitzer imaging for a full spectral energy distribution (SED)
fitting analysis. We find 289 candidate galaxies at
of 26.2. We incorporate deep optical
and Spitzer imaging for a full spectral energy distribution (SED)
fitting analysis. We find 289 candidate galaxies at  covering
covering  , faint
enough to overlap with Hubble Space Telescope studies. We conduct a
separate selection by including complementary Euclid performance
verification imaging (reaching
, faint
enough to overlap with Hubble Space Telescope studies. We conduct a
separate selection by including complementary Euclid performance
verification imaging (reaching  depths of
depths of  ), yielding 140 galaxies
in
), yielding 140 galaxies
in  , with 38 sources unique to this sample. We
compute the rest-frame UV luminosity function (UV LF) from our samples,
extending below the knee (
, with 38 sources unique to this sample. We
compute the rest-frame UV luminosity function (UV LF) from our samples,
extending below the knee ( ). We find that the shape of the UV LF is
consistent with both a Schechter function and double-power law (DPL) at
the magnitudes probed by this sample, with a DPL preferred at
). We find that the shape of the UV LF is
consistent with both a Schechter function and double-power law (DPL) at
the magnitudes probed by this sample, with a DPL preferred at  when bright-end results are included. The
UltraVISTA+Euclid sample provides a clean measurement of the LF due to
the overlapping near-infrared filters identifying molecular absorption
features in the SEDs of ultra-cool dwarf interlopers, and additional
faint galaxies are recovered. A comparison with JWST LFs at
when bright-end results are included. The
UltraVISTA+Euclid sample provides a clean measurement of the LF due to
the overlapping near-infrared filters identifying molecular absorption
features in the SEDs of ultra-cool dwarf interlopers, and additional
faint galaxies are recovered. A comparison with JWST LFs at  suggests a gentle
evolution in the bright-end slope, although this is limited by a lack of
robust bright-end measurements at
suggests a gentle
evolution in the bright-end slope, although this is limited by a lack of
robust bright-end measurements at  . We forecast that in
the Euclid Deep Fields, the removal of contaminant ultra-cool dwarfs as
point sources will be possible at
. We forecast that in
the Euclid Deep Fields, the removal of contaminant ultra-cool dwarfs as
point sources will be possible at  . Finally, we present a high-equivalent-width
Lyman-
. Finally, we present a high-equivalent-width
Lyman- emitter candidate identified by
combining HSC, VISTA, and Euclid broadband photometry, highlighting the
synergistic power these instruments will have in the Euclid Auxiliary
Fields for identifying extreme sources in the Epoch of Reionisation.
emitter candidate identified by
combining HSC, VISTA, and Euclid broadband photometry, highlighting the
synergistic power these instruments will have in the Euclid Auxiliary
Fields for identifying extreme sources in the Epoch of Reionisation.
Serendipitous
Discovery of an Optically-Dark Ultra-Luminous Infrared Galaxy at  = 3.4
= 3.4
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- N. H. Hayatsu / Zhi-Yu Zhang / R. J. Ivison / Chao-Wei Tsai
- Ping Zhou / Katsuya Okoshi / Chentao Yang / Yuri Nishimura
- Kotaro Kohno / Nobunari Kashikawa / Masahiro Nagashima / Junfeng
Wang
- Denis Burgarella
Summary
Dusty, submillimeter-selected galaxies without optical counterparts
contribute a non-negligible fraction of the star formation in the early
universe. However, such a population is difficult to detect through
classical optical/UV-based surveys. We report the serendipitous
discovery of such an optically dark galaxy, behind the quadruply-lensed
 quasar, H1413+117,
offset to the north by 6. From
quasar, H1413+117,
offset to the north by 6. From  CO
CO  –3,
–3,  –5, and part of the
–5, and part of the  –12 transitions, which all
spatially coincide with a compact submillimeter continuum emission, we
determine an unambiguous spectroscopic redshift,
–12 transitions, which all
spatially coincide with a compact submillimeter continuum emission, we
determine an unambiguous spectroscopic redshift,  .
This galaxy has a molecular mass
.
This galaxy has a molecular mass  M
M and a black hole mass
and a black hole mass
 M
M , estimated from
, estimated from  CO
CO  –3 and archival {} X-ray
data (
–3 and archival {} X-ray
data ( ,erg,s
,erg,s ), respectively. We also
estimate a total infrared luminosity of
), respectively. We also
estimate a total infrared luminosity of  L
L and a stellar mass of
and a stellar mass of
 M
M , from spectral
energy distribution fitting. According to these simple mass estimations,
this gas-rich and X-ray bright galaxy might be in a transition phase
from starburst to quasar offering a unique case for studying
galaxy-black hole co-evolution under extremely dusty conditions.
, from spectral
energy distribution fitting. According to these simple mass estimations,
this gas-rich and X-ray bright galaxy might be in a transition phase
from starburst to quasar offering a unique case for studying
galaxy-black hole co-evolution under extremely dusty conditions.
Multi-modal
atmospheric characterization of  Pictoris b: Adding high-resolution
continuum spectra from GRAVITY
Pictoris b: Adding high-resolution
continuum spectra from GRAVITY
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Ravet / M. Bonnefoy / G. Chauvin / S. Lacour
- M. Nowak / B. Charnay / P. Tremblin / D. Homeier
- C. Morley / J. Fortney / A. Denis / S. Petrus
- P. Palma-Bifani / R. Landman / L. T. Parker / M. Houllé
- A. Chomez / K. Worthen / F. Kiefer / G.-D. Marleau
- Z. Zhang / J. L. Birkby / F. Millour / A.-M. Lagrange
- A. Vigan / G. P. P. L. Otten / J. Shangguan
Summary
We present the first VLTI/GRAVITY observations at R of
of  Pic b. These four high S/N ($$20)
K-band spectra conserve both the pseudo-continuum and molecular
absorption patterns. We analyze them with four self-consistent forward
model grids (Exo-REM, ATMO, BT-Settl, Sonora) exploring
Pic b. These four high S/N ($$20)
K-band spectra conserve both the pseudo-continuum and molecular
absorption patterns. We analyze them with four self-consistent forward
model grids (Exo-REM, ATMO, BT-Settl, Sonora) exploring  ,
log(g), metallicity, C/O, and
,
log(g), metallicity, C/O, and  CO/
CO/ CO ratio. We also
upgrade our forward modeling code to account for the data multi-modality
and combine the GRAVITY epochs with published 1-5
CO ratio. We also
upgrade our forward modeling code to account for the data multi-modality
and combine the GRAVITY epochs with published 1-5  m photometry, low- to medium-resolution
spectra (0.9-7
m photometry, low- to medium-resolution
spectra (0.9-7  m), and high-resolution echelle spectra
(2.1-5.2
m), and high-resolution echelle spectra
(2.1-5.2  m). Sonora and Exo-REM are statistically
preferred. Exo-REM yields
m). Sonora and Exo-REM are statistically
preferred. Exo-REM yields 
 K and log(g)
K and log(g)  dex from GRAVITY alone, and
dex from GRAVITY alone, and 
 K and log(g)
K and log(g)  dex when
including all datasets. Archival data significantly affect the retrieved
parameters. C/O remains solar (
dex when
including all datasets. Archival data significantly affect the retrieved
parameters. C/O remains solar ( ) while [M/H] reaches super-solar values
(0.50$
) while [M/H] reaches super-solar values
(0.50$ {12}
{12} {13}$CO) $
{13}$CO) $ $)
$)  , implying a heavy-element content of up to $
, implying a heavy-element content of up to $ $)
given the system age and dynamical mass measurements. Access to both
continuum and molecular lines at K-band significantly impacts the
metallicity, possibly owing to collision-induced absorption shaping the
continuum. Echelle spectra do not dominate the final fit with respect to
lower resolution data. Future multi-modal frameworks should include
weighting schemes reflecting bandwidth and central wavelength
coverage.
$)
given the system age and dynamical mass measurements. Access to both
continuum and molecular lines at K-band significantly impacts the
metallicity, possibly owing to collision-induced absorption shaping the
continuum. Echelle spectra do not dominate the final fit with respect to
lower resolution data. Future multi-modal frameworks should include
weighting schemes reflecting bandwidth and central wavelength
coverage.
SIGNALS
of Giant HII Regions: A Spatially Resolved Analysis of NGC 604
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Ray Garner / Robert C. Kennicutt / Laurent Drissen / Carmelle
Robert
- Laurie Rousseau-Nepton / Christophe Morisset / Philippe
Amram / R. Pierre Martin
- Emma Jarvis
Summary
Observing giant HII regions at fine spatial scales uncovers detailed
structures and reveals variations in ionization, abundance, and
dynamical properties of ionized gas and the effect of stellar feedback.
Using emission line data of M33 observed with SITELLE as part of the
Star-formation, Ionized Gas, and Nebular Abundances Legacy Survey
(SIGNALS), we present maps of the principal optical emission line ratios
for NGC 604, the most luminous HII region in M33. The excitation maps
align well with the H morphology and are clearly related to
the location of the central stellar cluster and secondary stellar
groups. The maps of ionization-sensitive line ratios show substantial
variations across the face of NGC 604. We demonstrate that these
variations are unlikely to be due to chemical inhomogeneities but are
primarily caused by changes in ionization, which in turn affect the
observed line ratios. We present the H
morphology and are clearly related to
the location of the central stellar cluster and secondary stellar
groups. The maps of ionization-sensitive line ratios show substantial
variations across the face of NGC 604. We demonstrate that these
variations are unlikely to be due to chemical inhomogeneities but are
primarily caused by changes in ionization, which in turn affect the
observed line ratios. We present the H kinematics of the region and connect it
to the excitation structure, showing how the dynamic motions influence
the spatial distribution of ionized gas. We note two distinct sources
identified in these excitation maps: a known supernova remnant and a
previously unknown planetary nebula. Such parsec-scale features
contribute only a small percentage to the overall light and would remain
undetected without the use of high-resolution spatial data. Throughout
the paper, we make comparisons to and raise concerns about
single-aperture and long-slit spectroscopic measurements of giant HII
regions, highlighting the limitations and potential inaccuracies of such
methods.
kinematics of the region and connect it
to the excitation structure, showing how the dynamic motions influence
the spatial distribution of ionized gas. We note two distinct sources
identified in these excitation maps: a known supernova remnant and a
previously unknown planetary nebula. Such parsec-scale features
contribute only a small percentage to the overall light and would remain
undetected without the use of high-resolution spatial data. Throughout
the paper, we make comparisons to and raise concerns about
single-aperture and long-slit spectroscopic measurements of giant HII
regions, highlighting the limitations and potential inaccuracies of such
methods.
Articles for week 39 2025
Constraints
on the Orbit of the Young Substellar Companion GQ Lup B from
High-Resolution Spectroscopy and VLTI/GRAVITY Astrometry
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Vidya Venkatesan / S. Blunt / J. J. Wang / S. Lacour
- G.-D. Marleau / G. A. L. Coleman / L. Guerrero / W. O. Balmer
- L. Pueyo / T. Stolker / J. Kammerer / N. Pourré
- M. Nowak / E. Rickman / A. Sivaramakrishnan / D. Sing
- K. Wagner / A.-M. Lagrange / R. Abuter / A. Amorim
- R. Asensio-Torres / J.-P. Berger / H. Beust / A. Boccaletti
- M. Bonnefoy / H. Bonnet / M. S. Bordoni / G. Bourdarot
- W. Brandner / F. Cantalloube / P. Caselli / B. Charnay
- G. Chauvin / A. Chavez / A. Chomez / E.
Choquet
- V. Christiaens / Y. Clénet / V. Coudé du Foresto / A. Cridland
- R. Davies / R. Dembet / J. Dexter / A. Drescher
- G. Duvert / A. Eckart / F. Eisenhauer / N. M. Förster Schreiber
- P. Garcia / R. Garcia Lopez / E. Gendron / R. Genzel
- S. Gillessen / J. H. Girard / S. Grant / X. Haubois
- G. Heißel / Th. Henning / S. Hinkley / S. Hippler
- M. Houllé / Z. Hubert / L. Jocou / M. Keppler
- P. Kervella / L. Kreidberg / N. T. Kurtovic / V. Lapeyrère
- J.-B. Le Bouquin / D. Lutz / A.-L. Maire / F. Mang
- A. Mérand / C. Mordasini / D. Mouillet / E. Nasedkin
- T. Ott / G. P. P. L. Otten / C. Paladini / T. Paumard
- K. Perraut / G. Perrin / S. Petrus / O. Pfuhl
- D. C. Ribeiro / Z. Rustamkulov / J. Shangguan / T. Shimizu
- A. Shields / J. Stadler / O. Straub / C. Straubmeier
- E. Sturm / L. J. Tacconi / A. Vigan / F.
Vincent
- S. D. von Fellenberg / F. Widmann / T. O. Winterhalder / J.
Woillez
- S. Yazici / the ExoGRAVITY Collaboration
Summary
Understanding the orbits of giant planets is critical for testing
planet formation models, particularly at wide separations greater than
10 au where traditional core accretion becomes inefficient. However,
constraining orbits at these separations has been challenging because of
sparse orbital coverage and degeneracies in the orbital parameters. We
use existing high-resolution spectroscopic measurements from CRIRES+ (R
~ 100000), astrometric data from SPHERE, NACO, and ALMA, and new
high-precision GRAVITY astrometry to refine the orbit of GQ Lup B, a ~30
M_J companion at ~100 au, in a system that also hosts a circumstellar
disk and a wide companion, GQ Lup C. Including radial velocity data
significantly improves orbital constraints by breaking the degeneracy
between inclination and eccentricity that affects astrometry-only fits
for long-period companions. This work is among the first to combine
high-precision astrometry with the companion’s relative radial velocity
to achieve improved orbital constraints. The eccentricity is refined
from e = 0.47 (+0.14, -0.16) with GRAVITY alone to e = 0.35 (+0.10,
-0.09) when RVs and GRAVITY data are combined. The orbit is misaligned
by 63 (+6, -14) deg relative to the circumstellar disk and 52 (+19, -24)
deg relative to the host star spin axis, and is more consistent (34 (+6,
-13) deg) with the inclination of the wide tertiary companion GQ Lup C
disk. These results support a formation scenario for GQ Lup B consistent
with cloud fragmentation and highlight the power of combining companion
RV constraints with interferometric astrometry to probe the dynamics and
formation of wide-orbit substellar companions.
DESI
Strong Lens Foundry III: Keck Spectroscopy for Strong Lenses Discovered
Using Residual Neural Networks
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Shrihan Agarwal / Xiaosheng Huang / William Sheu / Christopher J.
Storfer
- Marcos Tamargo-Arizmendi / Suchitoto Tabares-Tarquinio / D. J.
Schlegel / G. Aldering
- A. Bolton / A. Cikota / Arjun Dey / A. Filipp
- E. Jullo / K. J. Kwon / S. Perlmutter / Y. Shu
- E. Sukay / N. Suzuki / J. Aguilar / S. Ahlen
- S. BenZvi / D. Brooks / T. Claybaugh / P. Doel
- J. E. Forero-Romero / E. Gaztañaga / S. Gontcho A Gontcho / G.
Gutierrez
- K. Honscheid / M. Ishak / S. Juneau / R. Kehoe
- T. Kisner / S. E. Koposov / A. Lambert / M. Landriau
- L. Le Guillou / A. de la Macorra / A. Meisner / R. Miquel
- J. Moustakas / A. D. Myers / C. Poppett / F. Prada
- I. Pérez-Ràfols / G. Rossi / E. Sanchez / M. Schubnell
- D. Sprayberry / G. Tarlé / B. A. Weaver / H. Zou
Summary
We present spectroscopic data of strong lenses and their source
galaxies using the Keck Near-Infrared Echellette Spectrometer (NIRES)
and the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), providing redshifts
necessary for nearly all strong-lensing applications with these systems,
especially the extraction of physical parameters from lensing modeling.
These strong lenses were found in the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys using
Residual Neural Networks (ResNet) and followed up by our Hubble Space
Telescope program, with all systems displaying unambiguous lensed arcs.
With NIRES, we target eight lensed sources at redshifts difficult to
measure in the optical range and determine the source redshifts for six,
between  = 1.675 and 3.332. DESI observed one
of the remaining source redshifts, as well as an additional source
redshift within the six systems. The two systems with non-detections by
NIRES were observed for a considerably shorter 600s at high airmass.
Combining NIRES infrared spectroscopy with optical spectroscopy from our
DESI Strong Lensing Secondary Target Program, these results provide the
complete lens and source redshifts for six systems, a resource for
refining automated strong lens searches in future deep- and wide-field
imaging surveys and addressing a range of questions in astrophysics and
cosmology.
= 1.675 and 3.332. DESI observed one
of the remaining source redshifts, as well as an additional source
redshift within the six systems. The two systems with non-detections by
NIRES were observed for a considerably shorter 600s at high airmass.
Combining NIRES infrared spectroscopy with optical spectroscopy from our
DESI Strong Lensing Secondary Target Program, these results provide the
complete lens and source redshifts for six systems, a resource for
refining automated strong lens searches in future deep- and wide-field
imaging surveys and addressing a range of questions in astrophysics and
cosmology.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Pierre Larue / Xavier Delfosse / Andres Carmona / Nadège
Meunier
- Étienne Artigau / Stefano Bellotti / Paul Charpentier / Claire
Moutou
- Jean-François Donati / Isabelle Boisse / Thierry
Forveille / Luc Arnold
- Vincent Bourrier / Xavier Bonfils / Charles Cadieux / Antoine
Chomez
- Neil Cook / Pia Cortes Zuleta / Paul Cristofari / Rodrigo Diaz
- René Doyon / Salomé Grouffal / Nathan
Hara / Neida Heidari
- Guillaume Hébrard / Flavien Kiefer / Lucile Mignon / Alice
Maurel
- Julien Morin / Antoine Petit / Pascal Petit / Alexandre
Santerne
- Nuno Santos / Damien Segransan / Juan Serrano Bell / H. G.
Vivien
Summary
Context. In the search for exoplanets using radial velocities (RV),
stellar activity has become one of the main limiting factors for
detectability. Fortunately, activity-induced RV signals are
wavelength-dependent or chromatic, unlike planetary signals. This study
exploits the broad spectral coverage provided by the combined use of
SOPHIE and SPIRou velocimeters to investigate the chromatic nature of
the activity signal of the highly active M dwarf EV Lac. Aims. We aim to
understand the origin of the strong wavelength dependence (chromaticity)
observed in the RV signal of EV Lac by selecting spectral lines based on
physical properties. In particular, we explore the impact of starspots
by defining the contrast effect at the level of individual lines. The
Zeeman effect is also considered in this study. Methods. SPIRou and
SOPHIE spectra were reduced using the line-by-line (LBL) method. We
performed custom RV calculations, using groups of spectral lines
selected for their sensitivity to either the spot-to-photosphere
contrast or the Zeeman effect. The sensi- tivity of each line to the
spot is defined using a two-temperature model based on PHOENIX spectra,
while Landé factors were used to quantify Zeeman sensitivity. Results.
We find that the spectral lines are distributed in two distinct families
of contrasts, producing anti-correlated RV signals. This leads to a
partial cancellation of the total RV signal, especially at longer
wavelengths and provides a natural explanation for the strong
chromaticity observed in EV Lac. This sign-reversal effect is
demonstrated here, for the first time, on empirical data. Building on
this discovery, we propose a new approach to constraining spot
temperatures and to mitigating stellar activity. This will open up
promising avenues for improving activity corrections and enhancing the
detection of exoplanets around active M dwarfs.
Galaxy groups in
various evolutionary stages
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Kethelin Parra Ramos / C. Adami / N. Clerc / A.
Chu
- F. Durret / G. B. Lima Neto / I. Márquez / L. Paquereau
- F. Sarron / G. Soucail / P. Amram / Q. Moysan
- D. Russeil
Summary
The formation process of galaxy groups is not yet fully understood.
In particular, that of fossil groups (FGs) is still under debate. Due to
the relative rarity of FGs, large samples of such objects are still
missing. The present paper aims to analyse the properties of groups in
various evolutionary stages (FGs, “almost” FGs, and non-FGs), and to
increase the sample of FG candidates. We have spectroscopically observed
galaxies in four groups and ten candidate FGs detected in the Canada
France Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey. We searched for substructures by
applying the Serna-Gerbal dendrogram method to analyse the dynamical
structure of each group. By applying the FIREFLY software to the
continuum and PIPE_VIS to the emission lines, we derived the stellar
population properties in various regions for each group. A roughly
continuous variation in properties is found between a group that is
still building up (XCLASS 1330), a well-formed massive group
(MCG+00-27-023), a dynamically complex non-FG (NGC 4065), and a near-FG
(NGC 4104). We also optically confirm two FGs in the Canada France
Hawaii Telescope Legacy Survey, but their X-ray luminosity is still
unknown. We observe that the lower the mass of the substructure, the
more recent the stellar population in the considered groups. We also
show an apparent lack of high-mass substructures for low-metallicity
systems. These results are consistent with the generally adopted model
of energy transfer during interactions of the galaxies with the group
and cluster potential wells. Furthermore, the fossil status of a group
might be related to the large-scale environment. Therefore, studying the
positions of non-FGs, near-FGs, and FGs within the cosmic web can
provide insights into the process of how fossil systems come into being
in the Universe.
PRIMAger
General Observer programs: a { }-sr Infrared Survey and other General
Observer wide-field programs
}-sr Infrared Survey and other General
Observer wide-field programs
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Denis Burgarella / Matthieu Bethermin /
Alessandro Boselli / James Donnelan
- Charles Darren Dowell / Guilaine Lagache / Seb
Oliver / Herve Dole
Summary
The PRobe far-Infrared Mission for Astrophysics (PRIMA) is a
cryogenically-cooled, far-infrared (far-IR) observatory expected to
begin serving the astronomical community by early 2030. The mission
features two advanced instruments: PRIMAger and FIRESS. PRIMAger will
operate across the mid- to far-IR spectrum, covering wavelengths from
approximately 25 to 260  m. It will offer hyperspectral imaging
in medium resolution bands (R
m. It will offer hyperspectral imaging
in medium resolution bands (R  8, using a linear
variable filter) from 25 to 80
8, using a linear
variable filter) from 25 to 80  m, and broad band (R
m, and broad band (R  4) photometric and
polarimetric imaging in four bands spanning 80 to 260
4) photometric and
polarimetric imaging in four bands spanning 80 to 260  m. The capabilities of PRIMAger will
enable a broad range of unique scientific programs, accessible through
General Observer (GO) projects. In this paper, we present and define a
PRIMAger survey over 25% of the sky, called
m. The capabilities of PRIMAger will
enable a broad range of unique scientific programs, accessible through
General Observer (GO) projects. In this paper, we present and define a
PRIMAger survey over 25% of the sky, called  -IR survey. This survey would exploit
PRIMAger’s hyperspectral and polarimetric modes to collect data on about
8
-IR survey. This survey would exploit
PRIMAger’s hyperspectral and polarimetric modes to collect data on about
8  10
10 galaxies to z
galaxies to z  4. The R=8 spectral
resolution of the PRIMAger Hyperspectral Imaging (PHI) filters will
enable users to study the emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
(PAH). A large sample of galaxies will be observed with the polarimetric
bands of PRIMAger, allowing unique statistical information for galaxies
to be harvested for the first time.
4. The R=8 spectral
resolution of the PRIMAger Hyperspectral Imaging (PHI) filters will
enable users to study the emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
(PAH). A large sample of galaxies will be observed with the polarimetric
bands of PRIMAger, allowing unique statistical information for galaxies
to be harvested for the first time.
Challenges
of standard halo models in constraining galaxy properties from CIB
anisotropies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Athanasia Gkogkou / Guilaine Lagache / Matthieu
Béthermin / Abhishek Maniyar
Summary
The halo model, combined with halo occupation distribution (HOD)
prescriptions, is widely used to interpret cosmic infrared background
(CIB) anisotropies and connect star-forming galaxies to large-scale
structure. Recent implementations adopt more physical parameterizations,
but it remains unclear whether these models reliably recover
astrophysical quantities. We test whether current CIB halo models can
constrain the star formation efficiency,  , and the halo
mass where it peaks,
, and the halo
mass where it peaks,  , when
fitted to mock data. We examine whether discrepancies arise from
emission assumptions (the HOD ingredients) or from more fundamental
components, such as bias and matter clustering. Using the M21 CIB HOD
model within the halo framework, we fit mock CIB power spectra and star
formation rate density (SFRD) data from the SIDES-Uchuu simulation, then
repeat the analysis with a simplified simulation (SSU) matched to the
HOD assumptions. Comparing best-fit parameters to known inputs, we find
that although the M21 model fits the mock data well, it fails to recover
intrinsic parameters, especially
, when
fitted to mock data. We examine whether discrepancies arise from
emission assumptions (the HOD ingredients) or from more fundamental
components, such as bias and matter clustering. Using the M21 CIB HOD
model within the halo framework, we fit mock CIB power spectra and star
formation rate density (SFRD) data from the SIDES-Uchuu simulation, then
repeat the analysis with a simplified simulation (SSU) matched to the
HOD assumptions. Comparing best-fit parameters to known inputs, we find
that although the M21 model fits the mock data well, it fails to recover
intrinsic parameters, especially  , even when
applied to data generated with consistent assumptions. Emission-related
quantities (SFRD, emissivity) agree within 5%, but the two-halo term
shows a redshift- and scale-dependent offset exceeding 20%, likely due
to the linear treatment of halo bias and matter clustering. Scatter in
the SFR-halo mass relation and spectral energy distributions
significantly impacts shot noise (
, even when
applied to data generated with consistent assumptions. Emission-related
quantities (SFRD, emissivity) agree within 5%, but the two-halo term
shows a redshift- and scale-dependent offset exceeding 20%, likely due
to the linear treatment of halo bias and matter clustering. Scatter in
the SFR-halo mass relation and spectral energy distributions
significantly impacts shot noise ( ) but only
modestly (
) but only
modestly ( ) the clustered
signal. We conclude that robust recovery of physical parameters from CIB
clustering requires improved cosmological ingredients in halo models,
including scale-dependent halo bias and nonlinear matter power spectra,
alongside refined emission modeling.
) the clustered
signal. We conclude that robust recovery of physical parameters from CIB
clustering requires improved cosmological ingredients in halo models,
including scale-dependent halo bias and nonlinear matter power spectra,
alongside refined emission modeling.
WALLABY
Pilot Survey: the extensive interaction of NGC 4532 and DDO 137 with the
Virgo cluster
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- L. Staveley-Smith / K. Bekki / A. Boselli / L.
Cortese
- N. Deg / B.-Q. For / K. Lee-Waddell / T. O’Beirne
- M. E. Putman / C. Sinnott / J. Wang / T. Westmeier
- O. I. Wong / B. Catinella / H. Dénes / J. Rhee
- L. Shao / A. X. Shen / K. Spekkens
Summary
As part of the pilot survey of the Widefield ASKAP L-band Legacy
All-sky Survey (WALLABY), high-resolution neutral atomic hydrogen (HI)
observations of the dwarf galaxy pair NGC 4532/DDO 137 (WALLABY
J123424+062511) have revealed a huge (48 kpc) bridge of gas between the
two galaxies, as well as numerous arms and clouds which connect with the
even longer (0.5 Mpc) tail of gas previously discovered with the Arecibo
telescope. Our modelling suggests that a combination of ram pressure and
tidal forces are responsible for the nature of the system. Although the
pair lies well outside of the virial radius of the Virgo cluster, ram
pressure due to infall through an extensive envelope of hot gas around
the cluster is most likely responsible for the HI tail. Over a timescale
of 1 Gyr, the predicted electron density ( cm
cm ) and infall velocity
(880 km s
) and infall velocity
(880 km s ) are probably
sufficient to explain the extensive stripping from the common gaseous
envelope of NGC 4532/DDO 137. The ongoing tidal interaction with the
Virgo cluster appears to have prevented a rapid merger of the binary
pair, with the mutual tidal interaction between the galaxy pair being
responsible for raising gas from the outer parts of the galaxy potential
wells into the HI bridge and common envelope. The NGC 4532/DDO 137
system mirrors many of the physical features of the Magellanic System,
and may lead to a better understanding of that system, as well as
casting more light on the relative importance of interaction mechanisms
in the outskirts of dynamically young galaxy clusters such as Virgo.
) are probably
sufficient to explain the extensive stripping from the common gaseous
envelope of NGC 4532/DDO 137. The ongoing tidal interaction with the
Virgo cluster appears to have prevented a rapid merger of the binary
pair, with the mutual tidal interaction between the galaxy pair being
responsible for raising gas from the outer parts of the galaxy potential
wells into the HI bridge and common envelope. The NGC 4532/DDO 137
system mirrors many of the physical features of the Magellanic System,
and may lead to a better understanding of that system, as well as
casting more light on the relative importance of interaction mechanisms
in the outskirts of dynamically young galaxy clusters such as Virgo.
Dynamical
properties of oscillating, viscous, transonic accretion disks around
black holes
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Sanjit Debnath / Indranil Chattopadhyay / Raj Kishor Joshi /
Philippe Laurent
- Priyesh Kumar Tripathi / M. Saleem Khan
Summary
We investigate the time evolution of sub-Keplerian transonic
accretion flow onto a non-rotating black hole using axisymmetric viscous
hydrodynamic simulations. We simulate the accretion flow using boundary
values from semi-analytical analysis and set up three different models.
Two of the models do not predict accretion shocks from the semi-analytic
analysis, while one of them does. We also consider radiative cooling
along with viscosity in the simulation. Our two-dimensional simulation
deviated from the one-dimensional semi-analytical solution and admitted
shocks in all three models. Viscous dissipation tends to push the shock
front outward, and radiative cooling will push it in. Additionally,
gravity is attractive. Depending on the competing strengths of all three
processes, it may trigger shock oscillation. Different rates of
angular-momentum transport in various layers may trigger eddies, which
will enhance the shock oscillation. We show that any simple power law
cannot approximate these solutions. We find that hot and higher
angular-momentum flow requires higher viscosity to produce oscillatory
shocks. From the temporal variation of the luminosity, shock
oscillations generate QPOs in the range of sub-Hertz to a few Hertz
frequencies if a ten solar mass black hole is assumed.
JWST
Spectroscopy of GRB 250702B: An Extremely Rare and Exceptionally
Energetic Burst in a Dusty, Massive Galaxy at 
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Benjamin P. Gompertz / Andrew J. Levan / Tanmoy Laskar /
Benjamin Schneider
- Ashley A. Chrimes / Antonio Martin-Carrillo / Albert Sneppen / David
ONeill
- Daniele B. Malesani / Peter G. Jonker / Eric Burns / Gregory
Corcoran
- Laura Cotter / Antonio de Ugarte Postigo / Dimple / Rob A. J.
Eyles-Ferris
- L. Izzo / Pall Jakobsson / Gavin P. Lamb / Jesse T. Palmerio
- Giovanna Pugliese / Maria Edvige Ravasio / Andrea Saccardi / Ruben
Salvaterra
- Nikhil Sarin / Steve Schulze / Nial Tanvir / Makenzie E.
Wortley
Summary
We present follow-up observations of the day-long, repeating GRB
250702B with the Near Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) on board the James
Webb Space Telescope (JWST). Through the identification of narrow
hydrogen emission lines at a consistent redshift of  , we calibrate the distance scale, and therefore
the energetics, of this unique extragalactic transient. At this
distance, the resulting
, we calibrate the distance scale, and therefore
the energetics, of this unique extragalactic transient. At this
distance, the resulting  -ray energy release is at least
-ray energy release is at least  ,erg.
We find no evidence for ongoing transient emission at the GRB position,
and exclude any accompanying supernova with a luminosity comparable to
the Type Ic broad-line SN 2023lcr, though we are unable to constrain
fainter events. The inferred rate of such events, assuming at most one
in the lifetime of {}, suggests that such bursts are very rare, with
volumetric rates
,erg.
We find no evidence for ongoing transient emission at the GRB position,
and exclude any accompanying supernova with a luminosity comparable to
the Type Ic broad-line SN 2023lcr, though we are unable to constrain
fainter events. The inferred rate of such events, assuming at most one
in the lifetime of {}, suggests that such bursts are very rare, with
volumetric rates  times lower
than normal high luminosity long GRBs and
times lower
than normal high luminosity long GRBs and  times lower
than core collapse supernovae when corrected for beaming. Furthermore,
we find that the host galaxy is unique amongst GRB host galaxies, and
extremely rare in the general galaxy population, being extremely large,
dusty and with high stellar mass. The identification of such an exotic
GRB in such an unusual galaxy raises the possibility that the
environment was important in the progenitor channel for this event.
times lower
than core collapse supernovae when corrected for beaming. Furthermore,
we find that the host galaxy is unique amongst GRB host galaxies, and
extremely rare in the general galaxy population, being extremely large,
dusty and with high stellar mass. The identification of such an exotic
GRB in such an unusual galaxy raises the possibility that the
environment was important in the progenitor channel for this event.
Articles for week 38 2025
Euclid
preparation. Using mock Low Surface Brightness dwarf galaxies to probe
Wide Survey detection capabilities
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / M. Urbano / P.-A. Duc / M. Poulain
- A. A. Nucita / A. Venhola / O. Marchal / M. Kümmel
- H. Kong / F. Soldano / E. Romelli / M. Walmsley
- T. Saifollahi / K. Voggel / A. Lançon / F. R. Marleau
- E. Sola / L. K. Hunt / J. Junais / D. Carollo
- P. M. Sanchez-Alarcon / M. Baes / F. Buitrago / Michele
Cantiello
- J.-C. Cuillandre / H. Domínguez Sánchez / A. Ferré-Mateu / A.
Franco
- J. Gracia-Carpio / R. Habas / M. Hilker / E. Iodice
- J. H. Knapen / M. N. Le / D. Martínez-Delgado / O. Müller
- F. De Paolis / P. Papaderos / R. Ragusa / J. Román
- E. Saremi / V. Testa / B. Altieri / L. Amendola
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- R. Laureijs / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N.
Taylor
- H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / I. A. Zinchenko
- E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / M. Bonici / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / S.
Conseil
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- M. Y. Elkhashab / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- A. Finoguenov / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / J. Kim
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / J. G. Sorce
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
Local Universe dwarf galaxies are both cosmological and mass assembly
probes. Deep surveys have enabled the study of these objects down to the
low surface brightness (LSB) regime. In this paper, we estimate Euclid’s
dwarf detection capabilities as well as limits of its MERge processing
function (MER pipeline), responsible for producing the stacked mosaics
and final catalogues. To do this, we inject mock dwarf galaxies in a
real Euclid Wide Survey (EWS) field in the VIS band and compare the
input catalogue to the final MER catalogue. The mock dwarf galaxies are
generated with simple Sérsic models and structural parameters extracted
from observed dwarf galaxy property catalogues. To characterize the
detected dwarfs, we use the mean surface brightness inside the effective
radius SBe (in mag arcsec-2). The final MER catalogues achieve
completenesses of 91 % for SBe in [21, 24], and 54 % for SBe in [24,
28]. These numbers do not take into account possible contaminants,
including confusion with background galaxies at the location of the
dwarfs. After taking into account those effects, they become
respectively 86 % and 38 %. The MER pipeline performs a final local
background subtraction with small mesh size, leading to a flux loss for
galaxies with Re > 10”. By using the final MER mosaics and
reinjecting this local background, we obtain an image in which we
recover reliable photometric properties for objects under the arcminute
scale. This background-reinjected product is thus suitable for the study
of Local Universe dwarf galaxies. Euclid’s data reduction pipeline
serves as a test bed for other deep surveys, particularly regarding
background subtraction methods, a key issue in LSB science.
The
Broadband View of the Bare Seyfert PG 1426+015: Relativistic Reflection,
the Soft Excess and the Importance of Oxygen
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- D. J. Walton / A. Madathil-Pottayil / P. Kosec / J. Jiang
- J. Garcia / A. C. Fabian / C. Pinto / D. J. K.
Buisson
- M. L. Parker / W. N. Alston / C. S. Reynolds
Summary
We present results from a deep, coordinated  -
- +
+  observation of the
type 1 Seyfert PG 1426+015, a source of particular interest as the most
massive reverberation-mapped black hole to date (
observation of the
type 1 Seyfert PG 1426+015, a source of particular interest as the most
massive reverberation-mapped black hole to date (![\log [M_{\rm{BH}}/M_{\odot}] \log [M_{\rm{BH}}/M_{\odot}]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5Clog%20%5BM_%7B%5Crm%7BBH%7D%7D%2FM_%7B%5Codot%7D%5D) =
=  ). The high-resolution RGS data confirm the ‘bare’
nature of the source, showing no evidence for absorption beyond the
Galactic column, while the broadband spectrum unambiguously reveals the
presence of relativistic reflection from the innermost accretion disc
(in the form of a relativistically broadened iron emission and
associated Compton reflection hump) as well as confirming the presence
of the strong soft excess reported previously. We explore whether
relativistic reflection can successfully account for the soft excess
along with the higher-energy reflection features, utilizing the two
most-commonly used reflection codes (REFLIONX, XILLVER). Ultimately we
find that both models are able to successfully reproduce the soft
excess, though in the case of the XILLVER model this is contingent on
reducing the strength of the O VIII line included in the model, as
otherwise this feature prevents the model from reproducing the data. The
reflection models that successfully reproduce the broadband data imply a
relatively high density for the accretion disc of
). The high-resolution RGS data confirm the ‘bare’
nature of the source, showing no evidence for absorption beyond the
Galactic column, while the broadband spectrum unambiguously reveals the
presence of relativistic reflection from the innermost accretion disc
(in the form of a relativistically broadened iron emission and
associated Compton reflection hump) as well as confirming the presence
of the strong soft excess reported previously. We explore whether
relativistic reflection can successfully account for the soft excess
along with the higher-energy reflection features, utilizing the two
most-commonly used reflection codes (REFLIONX, XILLVER). Ultimately we
find that both models are able to successfully reproduce the soft
excess, though in the case of the XILLVER model this is contingent on
reducing the strength of the O VIII line included in the model, as
otherwise this feature prevents the model from reproducing the data. The
reflection models that successfully reproduce the broadband data imply a
relatively high density for the accretion disc of ![\log [n_{\rm{e}} / \rm{cm}^{-3}] \sim 18 \log [n_{\rm{e}} / \rm{cm}^{-3}] \sim 18](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5Clog%20%5Bn_%7B%5Crm%7Be%7D%7D%20%2F%20%5Crm%7Bcm%7D%5E%7B-3%7D%5D%20%5Csim%2018) ,
consistent with the loose anti-correlation seen from other AGN in the
,
consistent with the loose anti-correlation seen from other AGN in the
![\log [n_{\rm{e}} / \rm{cm}^{-3}] \log [n_{\rm{e}} / \rm{cm}^{-3}]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5Clog%20%5Bn_%7B%5Crm%7Be%7D%7D%20%2F%20%5Crm%7Bcm%7D%5E%7B-3%7D%5D) vs
vs ![\log[m_{\rm{BH}} \dot{m}^2] \log[m_{\rm{BH}} \dot{m}^2]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5Clog%5Bm_%7B%5Crm%7BBH%7D%7D%20%5Cdot%7Bm%7D%5E2%5D) plane, as well as a moderate-to-high black hole
spin of
plane, as well as a moderate-to-high black hole
spin of  .
This preliminary spin constraint is strongly dependent on the assumption
that the soft excess is dominated by relativistic reflection.
.
This preliminary spin constraint is strongly dependent on the assumption
that the soft excess is dominated by relativistic reflection.
Catastrophic
disruption of asteroid 2023 CX1 and implications for planetary
defense
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Auriane Egal / Denis Vida / François Colas / Brigitte Zanda
- Sylvain Bouley / Asma Steinhausser / Pierre
Vernazza / Ludovic Ferrière
- Jérôme Gattacceca / Mirel Birlan / Jérémie Vaubaillon / Karl
Antier
- Simon Anghel / Josselin Desmars / Kévin Baillié / Lucie Maquet
- Sébastien Bouquillon / Adrien Malgoyre / Simon Jeanne / Jiři
Borovička
- Pavel Spurný / Hadrien A. R. Devillepoix / Marco Micheli / Davide
Farnocchia
- Shantanu Naidu / Peter Brown / Paul Wiegert / Krisztián
Sárneczky
- András Pál / Nick Moskovitz / Theodore Kareta / Toni
Santana-Ros
- Alexis Le Pichon / Gilles Mazet-Roux / Julien Vergoz / Luke
McFadden
- Jelle Assink / Läslo Evers / Daniela Krietsch / Henner Busemann
- Colin Maden / Lisa Maria Eckart / Jean-Alix Barrat / Pavel
Povinec
- Ivan Sykora / Ivan Kontul’ / Oscar Marchhart / Martin
Martschini
- Silke Merchel / Alexander Wieser / Matthieu Gounelle / Sylvain
Pont
- Pierre Sans-Jofre / Sebastiaan de Vet / Ioannis Baziotis / Miroslav
Brož
- Michaël Marsset / Jérôme Vergne / Josef Hanuš / Maxime Devogèle
- Luca Conversi / Francisco Ocaña / Luca Buzzi / Dan Alin Nedelcu
- Adrian Sonka / Florent Losse / Philippe Dupouy / Korado
Korlević
- Dieter Husar / Jost Jahn / Damir Šegon / Mark McIntyre
- Ralf Neubert / Pierre Beck / Patrick Shober / Anthony Lagain
- Josep Maria Trigo-Rodriguez / Enrique Herrero / Jim Rowe / Andrew R.
D. Smedley
- Ashley King / Salma Sylla / Daniele Gardiol / Dario Barghini
- Hervé Lamy / Emmanuel Jehin / Detlef Koschny / Bjorn Poppe
- Andrés Jordán / Rene A. Mendez / Katherine Vieira / Hebe
Cremades
- Hasnaa Chennaoui Aoudjehane / Zouhair Benkhaldoun / Olivier
Hernandez / Darrel Robertson
- Peter Jenniskens
Summary
Mitigation of the threat from airbursting asteroids requires an
understanding of the potential risk they pose for the ground. How
asteroids release their kinetic energy in the atmosphere is not well
understood due to the rarity of significant impacts. Ordinary
chondrites, in particular L chondrites, represent a frequent type of
Earth-impacting asteroids. Here, we present the first comprehensive,
space-to-lab characterization of an L chondrite impact. Small asteroid
2023 CX1 was detected in space and predicted to impact over Normandy,
France, on 13 February 2023. Observations from multiple independent
sensors and reduction techniques revealed an unusual but potentially
high-risk fragmentation behavior. The nearly spherical 650  160 kg (72
160 kg (72  6 cm diameter) asteroid
catastrophically fragmented around 28 km altitude, releasing 98% of its
total energy in a concentrated region of the atmosphere. The resulting
shockwave was spherical, not cylindrical, and released more energy
closer to the ground. This type of fragmentation increases the risk of
significant damage at ground level. These results warrant consideration
for a planetary defense strategy for cases where a >3-4 MPa dynamic
pressure is expected, including planning for evacuation of areas beneath
anticipated disruption locations.
6 cm diameter) asteroid
catastrophically fragmented around 28 km altitude, releasing 98% of its
total energy in a concentrated region of the atmosphere. The resulting
shockwave was spherical, not cylindrical, and released more energy
closer to the ground. This type of fragmentation increases the risk of
significant damage at ground level. These results warrant consideration
for a planetary defense strategy for cases where a >3-4 MPa dynamic
pressure is expected, including planning for evacuation of areas beneath
anticipated disruption locations.
HerS-3:
An Exceptional Einstein Cross Reveals a Massive Dark Matter Halo
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- P. Cox / K. M. Butler / C. R. Keeton / L. Eid
- E. Borsato / T. J. L. C. Bakx / R. Neri / B. M. Jones
- P. Prajapati / A. J. Baker / S. Berta / A. Cooray
- E. M. Corsini / L. Marchetti / A. Omont / A.
Beelen
- R. Gavazzi / D. Ismail / R. J. Ivison / M.
Krips
- M. D. Lehnert / H. Messias / D. Riechers / C. Vlahakis
- A. Weiß / P. van der Werf / C. Yang
Summary
We present a study of HerS-3, a dusty star-forming galaxy at zspec =
3.0607, which is gravitationally amplified into an Einstein cross with a
fifth image of the background galaxy seen at the center of the cross.
Detailed 1-mm spectroscopy and imaging with NOEMA and ALMA resolve the
individual images and show that each of the five images display a series
of molecular lines that have similar central velocities, unambiguously
confirming that they have identical redshifts. The HST F110W image
reveals a foreground lensing group of four galaxies with a photometric
redshift zphot~1.0. Lens models that only include the four visible
galaxies are unable to reproduce the properties of HerS-3. By adding a
fifth massive component, lying south-east of the brightest galaxy of the
group, the source reconstruction is able to match the peak emission,
shape and orientation for each of the five images. The fact that no
galaxy is detected near that position indicates the presence of a
massive dark matter halo in the lensing galaxy group. In the source
plane, HerS-3 appears as an infrared luminous starburst galaxy seen
nearly edge-on. The serendipitous discovery of this exceptional Einstein
cross offers a potential laboratory for exploring at small spatial
scales a nuclear starburst at the peak of cosmic evolution and studying
the properties of a massive dark matter halo associated with the lensing
galaxy group.
Spatially
resolved broad line region in a quasar at z=4: Dynamical black hole mass
and prominent outflow
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- GRAVITY+ Collaboration / K. Abd El Dayem / N. Aimar / A. Berdeu
- J.-P. Berger / G. Bourdarot / P. Bourget / W. Brandner
- Y. Cao / C. Correia / S. Cuevas Cardona / R. Davies
- D. Defrère / A. Drescher / A. Eckart / F. Eisenhauer
- M. Fabricius / A. Farah / H. Feuchtgruber / N. M. Förster
Schreiber
- A. Foschi / P. Garcia / R. Garcia Lopez / R. Genzel
- S. Gillessen / T. Gomes / F. Gonté / V. Gopinath
- J. Graf / M. Hartl / X. Haubois / F. Haußmann
- L. C. Ho / S. Hönig / M. Houllé / S. Joharle
- C. Keiman / P. Kervella / J. Kolb / L. Kreidberg
- A. Labdon / S. Lacour / O. Lai / S. Lai
- R. Laugier / J.-B. Le Bouquin / J. Leftley / R. Li
- B. Lopez / D. Lutz / F. Mang / A. Mérand
- F. Millour / M. Montargès / N. More / N. Morujão
- H. Nowacki / M. Nowak / S. Oberti / C. Onken
- J. Osorno / T. Ott / T. Paumard / K. Perraut
- G. Perrin / R. Petrov / P.-O. Petrucci / N. Pourré
- S. Rabien / C. Rau / D. Ribeiro / S. Robbe-Dubois
- M. Sadun Bordoni / M. Salman / J. Sanchez-Bermudez / D.
Santos
- J. Sauter / M. Scialpi / J. Scigliuto / J. Shangguan
- P. Shchekaturov / T. Shimizu / F. Soulez / C. Straubmeier
- E. Sturm / M. Subroweit / C. Sykes / L. J. Tacconi
- H. Übler / G. Ulbricht / F. Vincent / R. Webster
- E. Wieprecht / J. Woillez / C. Wolf
Summary
We present the first near-infrared interferometric data of a QSO at
z=4. The K-band observations were performed with GRAVITY+ on the VLTI
using all 4 UTs, detecting a differential phase signal that traces the
spatially resolved kinematics for both the H and H
and H lines in the broad line region. We fit
the two lines simultaneously with an updated model that includes
distinct rotating and conical outflowing components. We find that more
than 80% of the HI line emission from the BLR originates in an outflow
with a velocity up to
lines in the broad line region. We fit
the two lines simultaneously with an updated model that includes
distinct rotating and conical outflowing components. We find that more
than 80% of the HI line emission from the BLR originates in an outflow
with a velocity up to  km s
km s . This is oriented so
that our line of sight is along an edge of the conical structure, which
produces the prominent blue wing on the line profile. A combination of
anisotropic line emission and mid-plane opacity lead to the single-sided
phase signal. The model is able to qualitatively match both the
outflowing CIV line profile and the systemic OI fluorescent emission.
The derived black hole mass of
. This is oriented so
that our line of sight is along an edge of the conical structure, which
produces the prominent blue wing on the line profile. A combination of
anisotropic line emission and mid-plane opacity lead to the single-sided
phase signal. The model is able to qualitatively match both the
outflowing CIV line profile and the systemic OI fluorescent emission.
The derived black hole mass of  M
M is the highest
redshift black hole mass measurement to date obtained directly from BLR
dynamics. It is an order of magnitude lower than that inferred from
various single epoch scaling relations, and implies that the accretion
is highly super-Eddington. With reference to recent simulations, the
data suggest that this QSO is emitting close to its radiative limit in a
regime where strong outflows are expected around a polar conical
region.
is the highest
redshift black hole mass measurement to date obtained directly from BLR
dynamics. It is an order of magnitude lower than that inferred from
various single epoch scaling relations, and implies that the accretion
is highly super-Eddington. With reference to recent simulations, the
data suggest that this QSO is emitting close to its radiative limit in a
regime where strong outflows are expected around a polar conical
region.
Transit
Timing Variations in HIP 41378: CHEOPS and TESS confirm a non-transiting
sixth planet in the system
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- P. Leonardi / L. Borsato / L. Pagliaro / D. Kubyshkina
- J. A. Egger / T. G. Wilson / A. Heitzmann / A. Brandeker
- M. N. Günther / V. Nascimbeni / A. Leleu / S. G. Sousa
- A. Bonfanti / G. Mantovan / G. Piotto / L. Fossati
- D. Nardiello / T. Zingales / V. Adibekyan / C. Pezzotti
- B. Akinsanmi / Y. Alibert / R. Alonso / T. Bárczy
- D. Barrado / S. C. C. Barros / W. Baumjohann / W. Benz
- N. Billot / C. Broeg / M. Buder / A. Collier Cameron
- C. Corral van Damme / A. C. M. Correia / Sz. Csizmadia / P. E.
Cubillos
- M. B. Davies / M. Deleuil / A. Deline / O. D. S.
Demangeon
- B.-O. Demory / A. Derekas / B. Edwards / D. Ehrenreich
- A. Erikson / J. Farinato / A. Fortier / M. Fridlund
- D. Gandolfi / K. Gazeas / M. Gillon / M. Güdel
- Ch. Helling / K. G. Isaak / L. L. Kiss / J. Korth
- K. W. F. Lam / J. Laskar / A. Lecavelier des Etangs / M. Lendl
- D. Magrin / P. F. L. Maxted / B. Merín / C. Mordasini
- G. Olofsson / R. Ottensamer / I. Pagano / E. Pallé
- G. Peter / D. Piazza / D. Pollacco / D. Queloz
- R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando / H. Rauer / I. Ribas
- N. C. Santos / G. Scandariato / D. Ségransan / A. E. Simon
- A. M. S. Smith / M. Stalport / S. Sulis / Gy. M.
Szabó
- S. Udry / B. Ulmer / S. Ulmer-Moll / V. Van Grootel
- J. Venturini / E. Villaver / N. A. Walton / S. Wolf
Summary
In multiple-planet systems, gravitational interactions of exoplanets
could lead to transit timing variations (TTVs), whose amplitude becomes
significantly enhanced when planets are in or near mean-motion
resonances (MMRs). In cases where both TTVs and radial velocity (RV)
measurements are available, combined analysis can break degeneracies and
provide robust planetary and system characterization, even detecting
non-transiting planets. In this context, HIP 41378 hosts five confirmed
transiting planets with periods ranging from 15 to over 542 days,
providing a unique dynamical laboratory for investigating wide
multi-planet systems analogous to the Solar System. In this study, we
present an intensive space-based photometric follow-up of HIP 41378,
combining 15 new CHEOPS observations with eight TESS sectors, alongside
data from K2, Spitzer, HST, and HARPS. We dynamically modeled the TTVs
and RV signals of the two inner sub-Neptunes via N-body integration.
These planets, HIP 41378 b ( = 15.57 days) and HIP
41378 c (
= 15.57 days) and HIP
41378 c ( = 31.71 days), are
close to (
= 31.71 days), are
close to ( %) a 2:1 period
commensurability. We report a clear detection of TTVs with amplitudes of
20 mins for planet b and greater than 3 hrs for planet c. We dynamically
confirm the planetary nature of HIP 41378 g, a non-transiting planet
with a period of about 64 days and a mass of about 7
%) a 2:1 period
commensurability. We report a clear detection of TTVs with amplitudes of
20 mins for planet b and greater than 3 hrs for planet c. We dynamically
confirm the planetary nature of HIP 41378 g, a non-transiting planet
with a period of about 64 days and a mass of about 7  , close to a
2:1 commensurability with planet c, suggesting a possible MMR chain in
the inner system. Our precise determination of the masses,
eccentricities, and radii of HIP 41378 b and c enabled us to investigate
their possible volatile-rich compositions. Finally, by leveraging on the
last TESS sectors we constrained the period of HIP 41378 d to three
possible aliases (
, close to a
2:1 commensurability with planet c, suggesting a possible MMR chain in
the inner system. Our precise determination of the masses,
eccentricities, and radii of HIP 41378 b and c enabled us to investigate
their possible volatile-rich compositions. Finally, by leveraging on the
last TESS sectors we constrained the period of HIP 41378 d to three
possible aliases ( 278, 371, and 1113
days) suggesting that the system could be placed in a double quasi
resonant chain, highlighting its complex dynamical architecture.
278, 371, and 1113
days) suggesting that the system could be placed in a double quasi
resonant chain, highlighting its complex dynamical architecture.
Thermal
Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect at the core of CL J1226.9+3332 revealed by
NOEMA
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Muñoz-Echeverría / J.-F. Macías-Pérez / R. Neri / E.
Pointecouteau
- R. Adam / P. Ade / H. Ajeddig / S. Amarantidis
- P. André / H. Aussel / A. Beelen / A. Benoît
- S. Berta / M. Béthermin / A. Bongiovanni / J. Bounmy
- O. Bourrion / M. Calvo / A. Catalano / D. Chérouvrier
- U. Chowdhury / M. De Petris / F.-X. Désert / S. Doyle
- E. F. C. Driessen / G. Ejlali / A. Ferragamo / A. Gómez
- J. Goupy / C. Hanser / S. Katsioli / F. Kéruzoré
- C. Kramer / B. Ladjelate / G. Lagache / S.
Leclercq
- J.-F. Lestrade / S. C. Madden / A. Maury / F. Mayet
- A. Monfardini / A. Moyer-Anin / I. Myserlis / A. Paliwal
- L. Perotto / G. Pisano / N. Ponthieu / V. Revéret
- A. J. Rigby / A. Ritacco / H. Roussel / F. Ruppin
- M. Sánchez-Portal / S. Savorgnano / K. Schuster / A. Sievers
- C. Tucker / R. Zylka / I. Bartalucci / J.-B. Melin
- G. W. Pratt
Summary
We present first detailed maps of the thermal Sunyaev-Zel’dovich
(tSZ) effect on a  cluster with the
NOrthern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA). The high sensitivity of
these observations enabled the effective identification and removal of
the millimetre-wave sources contaminating the tSZ signal, thus isolating
the influence of the hot electron gas of the cluster on the cosmic
microwave background radiation from other emissions. The tSZ observed
with success by NOEMA was modelled together with previous single-dish
observations (IRAM 30-metre, Green Bank Telescope, and Caltech
Sub-millimeter Observatory) to obtain the first core-to-outskirts (from
cluster with the
NOrthern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA). The high sensitivity of
these observations enabled the effective identification and removal of
the millimetre-wave sources contaminating the tSZ signal, thus isolating
the influence of the hot electron gas of the cluster on the cosmic
microwave background radiation from other emissions. The tSZ observed
with success by NOEMA was modelled together with previous single-dish
observations (IRAM 30-metre, Green Bank Telescope, and Caltech
Sub-millimeter Observatory) to obtain the first core-to-outskirts (from
 15 to
15 to  1500 kpc) pressure
profile reconstruction on such a high-redshift galaxy cluster. NOEMA
observations with a high angular resolution have shown that the pressure
profile is flat in the core of the cluster. These observations confirm
the disturbed nature of CL J1226.9+3332 and map for the first time the
distribution of its thermal gas at arcsecond scales in the environments
of the central cluster galaxy. Our results showcase the excellent
capabilities of NOEMA to complement and enhance the data provided by
other millimetre-wave instruments in resolving the core of high-redshift
clusters via tSZ emission.
1500 kpc) pressure
profile reconstruction on such a high-redshift galaxy cluster. NOEMA
observations with a high angular resolution have shown that the pressure
profile is flat in the core of the cluster. These observations confirm
the disturbed nature of CL J1226.9+3332 and map for the first time the
distribution of its thermal gas at arcsecond scales in the environments
of the central cluster galaxy. Our results showcase the excellent
capabilities of NOEMA to complement and enhance the data provided by
other millimetre-wave instruments in resolving the core of high-redshift
clusters via tSZ emission.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / S. Quai / L. Pozzetti / M. Talia
- C. Mancini / P. Cassata / L. Gabarra / V. Le
Brun
- M. Bolzonella / E. Rossetti / S. Kruk / B. R. Granett
- C. Scarlata / M. Moresco / G. Zamorani / D. Vergani
- X. Lopez Lopez / A. Enia / E. Daddi / V. Allevato
- I. A. Zinchenko / M. Magliocchetti / M. Siudek / L. Bisigello
- G. De Lucia / H. J. Dickinson / E. Lusso / M. Hirschmann
- A. Cimatti / L. Wang / J. G. Sorce / N. Aghanim
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / H. Dole / M. Douspis
- F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / D. Vibert / Y.
Wang
- J. Weller / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / M. Huertas-Company / J. Martín-Fleitas / S.
Matthew
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Conseil / T.
Contini
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- F. Fontanot / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
We introduce SpectraPyle, a versatile spectral stacking pipeline
developed for the Euclid mission’s NISP spectroscopic surveys, aimed at
extracting faint emission lines and spectral features from large galaxy
samples in the Wide and Deep Surveys. Designed for computational
efficiency and flexible configuration, SpectraPyle supports the
processing of extensive datasets critical to Euclid’s non-cosmological
science goals. We validate the pipeline using simulated spectra
processed to match Euclid’s expected final data quality. Stacking
enables robust recovery of key emission lines, including Halpha, Hbeta,
[O III], and [N II], below individual detection limits. However, the
measurement of galaxy properties such as star formation rate, dust
attenuation, and gas-phase metallicity are biased at stellar mass below
log10(M/Msol) ~ 9 due to the flux-limited nature of Euclid
spectroscopic samples, which cannot be overcome by stacking. The
SFR-stellar mass relation of the parent sample is recovered reliably
only in the Deep survey for log10(M/Msol) > 10, whereas the
metallicity-mass relation is recovered more accurately over a wider mass
range. These limitations are caused by the increased fraction of
redshift measurement errors at lower masses and fluxes. We examine the
impact of residual redshift contaminants that arises from misidentified
emission lines and noise spikes, on stacked spectra. Even after
stringent quality selections, low-level contamination (< 6%) has
minimal impact on line fluxes due to the systematically weaker emission
of contaminants. Percentile-based analysis of stacked spectra provides a
sensitive diagnostic for detecting contamination via coherent spurious
features at characteristic wavelengths. While our simulations include
most instrumental effects, real Euclid data will require further
refinement of contamination mitigation strategies.
Constraining
gamma-ray burst parameters with the first ultra-high energy neutrino
event KM3-230213A
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- KM3NeT Collaboration / O. Adriani / A. Albert / A. R. Alhebsi
- S. Alshalloudi / M. Alshamsi / S. Alves Garre / A. Ambrosone
- F. Ameli / M. Andre / L. Aphecetche / M. Ardid
- S. Ardid / J. Aublin / F. Badaracco / L. Bailly-Salins
- B. Baret / A. Bariego-Quintana / Y. Becherini / M. Bendahman
- F. Benfenati Gualandi / M. Benhassi / D. M. Benoit / Beňušová
- E. Berbee / E. Berti / V. Bertin / P. Betti
- S. Biagi / M. Boettcher / D. Bonanno / S. Bottai
- A. B. Bouasla / J. Boumaaza / M. Bouta / M. Bouwhuis
- C. Bozza / R. M. Bozza / H. Brânzaš / F. Bretaudeau
- M. Breuhaus / R. Bruijn / J. Brunner / R. Bruno
- E. Buis / R. Buompane / J. Busto / B. Caiffi
- D. Calvo / A. Capone / F. Carenini / V. Carretero
- T. Cartraud / P. Castaldi / V. Cecchini / S. Celli
- L. Cerisy / M. Chabab / A. Chen / S. Cherubini
- T. Chiarusi / M. Circella / R. Clark / R. Cocimano
- J. A. B. Coelho / A. Coleiro / A. Condorelli / R. Coniglione
- P. Coyle / A. Creusot / G. Cuttone / R. Dallier
- A. De Benedittis / G. De Wasseige / V. Decoene / P. Deguire
- I. Del Rosso / L. S. Di Mauro / I. Di Palma / A. F. Díaz
- D. Diego-Tortosa / C. Distefano / A. Domi / C. Donzaud
- D. Dornic / E. Drakopoulou / D. Drouhin / J.-G. Ducoin
- P. Duverne / R. Dvornický / T. Eberl / E. Eckerová
- A. Eddymaoui / T. van Eeden / M. Eff / D. van Eijk
- I. El Bojaddaini / S. El Hedri / S. El Mentawi / A. Enzenhöfer
- G. Ferrara / M. D. Filipović / F. Filippini / D. Franciotti
- L. A. Fusco / S. Gagliardini / T. Gal / J. García Méndez
- A. Garcia Soto / C. Gatius Oliver / N. Geißelbrecht / E. Genton
- H. Ghaddari / L. Gialanella / B. K. Gibson / E. Giorgio
- I. Goos / P. Goswami / S. R. Gozzini / R. Gracia
- B. Guillon / C. Haack / H. van Haren / A. Heijboer
- L. Hennig / J. J. Hernández-Rey / A. Idrissi / W. Idrissi
Ibnsalih
- G. Illuminati / R. Jaimes / O. Janik / D. Joly
- M. de Jong / P. de Jong / B. J. Jung / P. Kalaczyński
- J. Keegans / V. Kikvadze / G. Kistauri / C. Kopper
- A. Kouchner / Y. Y. Kovalev / L. Krupa / V. Kueviakoe
- V. Kulikovskiy / R. Kvatadze / M. Labalme / R. Lahmann
- M. Lamoureux / G. Larosa / C. Lastoria / J. Lazar
- A. Lazo / G. Lehaut / V. Lemaître / E. Leonora
- N. Lessing / G. Levi / M. Lindsey Clark / F. Longhitano
- S. Madarapu / F. Magnani / L. Malerba / F. Mamedov
- A. Manfreda / A. Manousakis / M. Marconi / A. Margiotta
- A. Marinelli / C. Markou / L. Martin / M.
Mastrodicasa
- S. Mastroianni / J. Mauro / K. C. K. Mehta / G. Miele
- P. Migliozzi / E. Migneco / M. L. Mitsou / C. M. Mollo
- L. Morales-Gallegos / N. Mori / A. Moussa / I. Mozun Mateo
- R. Muller / M. R. Musone / M. Musumeci / S. Navas
- A. Nayerhoda / C. A. Nicolau / B. Nkosi / B. Ó Fearraigh
- V. Oliviero / A. Orlando / E. Oukacha / L. Pacini
- D. Paesani / J. Palacios González / G. Papalashvili / P. Papini
- V. Parisi / A. Parmar / C. Pastore / A. M. Păun
- G. E. Păvălaš / S. Peña Martínez / M. Perrin-Terrin / V. Pestel
- M. Petropavlova / P. Piattelli / A. Plavin / C. Poirè
- V. Popa / T. Pradier / J. Prado / S. Pulvirenti
- C. A. Quiroz-Rangel / N. Randazzo / A. Ratnani / S. Razzaque
- I. C. Rea / D. Real / G. Riccobene / J. Robinson
- A. Romanov / E. Ros / A. Šaina / F. Salesa Greus
- D. F. E. Samtleben / A. Sánchez Losa / S. Sanfilippo / M.
Sanguineti
- D. Santonocito / P. Sapienza / M. Scaringella / M. Scarnera
- J. Schnabel / J. Schumann / J. Seneca / P. A. Sevle Myhr
- I. Sgura / R. Shanidze / Chengyu Shao / A. Sharma
- Y. Shitov / F. Šimkovic / A. Simonelli / A. Sinopoulou
- B. Spisso / M. Spurio / O. Starodubtsev / D. Stavropoulos
- I. Štekl / D. Stocco / M. Taiuti / G. Takadze
- Y. Tayalati / H. Thiersen / S. Thoudam / I. Tosta e Melo
- B. Trocmé / V. Tsourapis / E. Tzamariudaki / A. Ukleja
- A. Vacheret / V. Valsecchi / V. Van Elewyck / G. Vannoye
- E. Vannuccini / G. Vasileiadis / F. Vazquez de Sola / A. Veutro
- S. Viola / D. Vivolo / A. van Vliet / E. de Wolf
- I. Lhenry-Yvon / S. Zavatarelli / D. Zito / J. D. Zornoza
- J. Zúñiga
Summary
Context: The detection of the highest energy neutrino observed to
date by KM3NeT, with an estimated energy of 220 PeV, opens up new
possibilities for the study and identification of the astrophysical
sources responsible for a diffuse flux of such ultra-high-energy
neutrinos, among which gamma-ray bursts are longstanding candidates.
Aims: Based on the event KM3-230213A, we derive constraints on the
baryon loading and density of the surrounding environment in models of
blastwaves in long-duration gamma-ray bursts. Methods: We compute the
diffuse flux from gamma-ray burst blastwaves, either expanding in a
constant density interstellar medium or developing in a radially
decreasing density of a wind-like environment surrounding the gamma-ray
burst progenitor star, by taking into account the expected neutrino
spectra and luminosity function. We use a Poisson likelihood method to
constrain the blastwave model parameters by calculating the expected
number of neutrino events within the 90% confidence level energy range
of KM3-230213A and by using the joint exposure of KM3NeT/ARCA, IceCube
and Pierre Auger. Results: We constrain the baryon loading to be  at 90% confidence level, which is inversely
proportional to a varying interstellar medium particle density of
at 90% confidence level, which is inversely
proportional to a varying interstellar medium particle density of  cm
cm . In the wind-like
environment case, the baryon loading is
. In the wind-like
environment case, the baryon loading is  at 90% confidence level, which is proportional to
the sixth power of a varying density parameter of
at 90% confidence level, which is proportional to
the sixth power of a varying density parameter of  .
.
Articles for week 37 2025
YSES
2b is a background star: Differential astrometric M-dwarf measurements
in time
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Matthew Kenworthy / Tomas Stolker / Jens Kammerer / William
Balmer
- Arthur Vigan / Sylvestre Lacour / Gilles Otten /
Eric Mamajek
- Christian Ginski / Mathias Nowak / Steven Martos / Jason Wang
- Emily Rickman / Markus Janson / Alexander Bohn / Mariangela
Bonavita
Summary
We wish to confirm the nature of YSES 2b, a purportedly faint
companion of the young star YSES 2. We used on-sky observations from
SPHERE and GRAVITY to measure the astrometric position of 2b with
respect to the star YSES 2, and examined the competing hypotheses of (i)
a bound substellar companion versus (ii) a distant unrelated background
source with a non-zero proper motion. YSES 2b appears to be a late-type
M-dwarf star over 2 kiloparsecs behind the star YSES 2. It has a
transverse velocity of about 300 km/s and is located within one of the
spiral arms of the Galaxy. The main discriminant was multiple epochs of
GRAVITY astrometry that identified the sub-milliarcsecond parallactic
motion of the star.
A
four-planet system orbiting the old thick disk star TOI-1203
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- D. Gandolfi / A. Alnajjarine / L. M. Serrano / J. A. Egger
- K. W. F. Lam / J. Cabrera / A. P. Hatzes / M. Fridlund
- M. Garbaccio Gili / T. G. Wilson / W. D. Cochran / A. Brandeker
- E. Goffo / S. G. Sousa / G. Nowak / A. Heitzmann
- C. Hellier / J. Venturini / J. Livingston / A. Bonfanti
- O. Barragán / V. Adibekyan / E. Knudstrup / Y. Alibert
- S. Grziwa / C. Ziegler / L. Fossati / F. Murgas
- A. C. M. Correia / S. H. Albrecht / J. Laskar / E. W. Guenther
- S. J. A. J. Salmon / S. Redfield / N. Billot / H. J. Deeg
- L. Delrez / L. Palethorpe / V. Van Eylen / F. Rodler
- J. Alarcon / J. M. Jenkins / J. D. Twicken / A. W. Mann
- R. Alonso / J. Asquier / T. Bárczy / D. Barrado
- S. C. C. Barros / W. Baumjohann / W. Benz / L. Borsato
- C. Broeg / M. Buder / P. Chaturvedi / A. Collier Cameron
- Sz. Csizmadia / P. E. Cubillos / M. B. Davies / M.
Deleuil
- A. Deline / O. D. S. Demangeon / B.-O. Demory / A. Derekas
- B. Edwards / D. Ehrenreich / A. Erikson / A. Fortier
- K. Gazeas / M. Gillon / M. Güdel / M. N. Günther
- Ch. Helling / K. G. Isaak / L. L. Kiss / J. Korth
- N. Law / A. Lecavelier des Etangs / A. Leleu / M. Lendl
- P. Leonardi / D. Magrin / G. Mantovan / L. Marafatto
- P. F. L. Maxted / M. Mecina / B. Merín / C. Mordasini
- V. Nascimbeni / A. Nigioni / G. Olofsson / H. P. Osborn
- R. Ottensamer / I. Pagano / E. Pallé / C. M. Persson
- G. Peter / D. Piazza / G. Piotto / D. Pollacco
- D. Queloz / R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando / H. Rauer
- I. Ribas / G. R. Ricker / N. C. Santos / G. Scandariato
- S. Seager / D. Ségransan / A. E. Simon / A. M. S. Smith
- M. Stalport / S. Sulis / Gy. M. Szabó / S.
Udry
- S. Ulmer-Moll / V. Van Grootel / E. Villaver / N. A. Walton
- J. N. Winn / S. Wolf / T. Zingales
Summary
TOI-1203 is a bright (V=8.6) G3 V star known to host a transiting
warm sub-Neptune on a 25.5 d orbit. Here we report on an intensive
high-precision radial velocity and photometric follow-up campaign
carried out with the HARPS spectrograph and the CHEOPS space telescope.
We found that TOI-1203 has an enhancement of  elements relative to iron of [
elements relative to iron of [ /Fe]=
/Fe]= . With an
age of $$12.5 Gyr, TOI-1203 belongs to the old,
. With an
age of $$12.5 Gyr, TOI-1203 belongs to the old,  -element enhanced stellar population of
the galactic thick disk. We spectroscopically confirmed the planetary
nature of the 25.5 d sub-Neptune TOI-1203 d, measured its mass (
-element enhanced stellar population of
the galactic thick disk. We spectroscopically confirmed the planetary
nature of the 25.5 d sub-Neptune TOI-1203 d, measured its mass ( ) and refined its radius (
) and refined its radius ( ). We discovered the presence of an additional
transiting super-Earth on a 4.2 d orbit (TOI-1203 b) with a mass of
). We discovered the presence of an additional
transiting super-Earth on a 4.2 d orbit (TOI-1203 b) with a mass of  and
a radius of
and
a radius of  .
We also revealed the presence of two additional low-mass planets at 13.1
d and 204.6 d (TOI-1203 c and e), with minimum masses of
.
We also revealed the presence of two additional low-mass planets at 13.1
d and 204.6 d (TOI-1203 c and e), with minimum masses of  and
and  . We
found that the outer planet TOI-1203 e lies on an eccentric orbit with
. We
found that the outer planet TOI-1203 e lies on an eccentric orbit with
 . We performed a stability analysis of the system
confirming that there are configurations consistent with the observed
parameters that are dynamically stable over billion-year timescales.
While analyzing the HARPS time series, we discovered that the FWHM of
the HARPS cross-correlation function shows a significant long-period
signal ($$615 d) that has no counterpart in the radial velocity data or
in the remaining HARPS ancillary time series. We significantly detected
the same signal in the FWHM of the Th-Ar calibration lines used to
compute the nightly wavelength solution, and attributed this systematic
effect to a long-term variation of the HARPS instrumental profile.
. We performed a stability analysis of the system
confirming that there are configurations consistent with the observed
parameters that are dynamically stable over billion-year timescales.
While analyzing the HARPS time series, we discovered that the FWHM of
the HARPS cross-correlation function shows a significant long-period
signal ($$615 d) that has no counterpart in the radial velocity data or
in the remaining HARPS ancillary time series. We significantly detected
the same signal in the FWHM of the Th-Ar calibration lines used to
compute the nightly wavelength solution, and attributed this systematic
effect to a long-term variation of the HARPS instrumental profile.
A
comprehensive separation of dark matter and baryonic mass components in
galaxy clusters I: Mass constraints from Abell S1063
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Benjamin Beauchesne / Benjamin Clément / Marceau
Limousin / Belén Alcalde Pampliega
- Mathilde Jauzac / Anna Niemiec / Johan Richard / Guillaume
Mahler
- Jose M. Diego / Pascale Hibon / Anton M. Koekemoer / Thomas
Connor
- Jean-Paul Kneib / Andreas L. Faisst
Summary
In this two-part series, we present a multi-probe mass modelling
method for massive galaxy clusters, designed to disentangle the
contributions of individual mass components (Dark matter, intra-cluster
gas, stellar masses). In this first paper, we focus on recovering the
mass constraint datasets required for the modelling approach introduced
in the second paper. Specifically, we measure the light distribution,
stellar mass, and kinematics of the cluster members, the brightest
cluster galaxy (BCG), and the intra-cluster light (ICL) in Abell S1063.
To that end, we developed a new method to extract the light profiles of
the cluster members, BCG, and ICL, while accounting for contamination
from nearby foreground and background galaxies in (HST) imaging. We
obtained light profiles for  cluster members using a dual
Pseudo-Isothermal Elliptical (dPIE) model based on the HST F160W filter,
while the BCG & ICL is modelled as a single component using a
multi-Gaussian expansion. To estimate stellar masses and velocity
dispersions, we rely on multi-band HST photometry and integral field
spectroscopy, respectively. Stellar masses are derived using three
different spectral energy distribution (SED) models. We measure the
line-of-sight velocity dispersions of the cluster members at their
half-light radii, as determined from their light profiles, while for the
BCG & ICL components, we use elliptical annular apertures. Thanks to
these measurements, we will be able to constrain the cluster stellar
mass content, which is detailed in the second paper of the series. We
publicly release these measurements with intermediary data products.
cluster members using a dual
Pseudo-Isothermal Elliptical (dPIE) model based on the HST F160W filter,
while the BCG & ICL is modelled as a single component using a
multi-Gaussian expansion. To estimate stellar masses and velocity
dispersions, we rely on multi-band HST photometry and integral field
spectroscopy, respectively. Stellar masses are derived using three
different spectral energy distribution (SED) models. We measure the
line-of-sight velocity dispersions of the cluster members at their
half-light radii, as determined from their light profiles, while for the
BCG & ICL components, we use elliptical annular apertures. Thanks to
these measurements, we will be able to constrain the cluster stellar
mass content, which is detailed in the second paper of the series. We
publicly release these measurements with intermediary data products.
COSMOS-Web
galaxy groups: Evolution of red sequence and quiescent galaxy
fraction
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Greta Toni / Matteo Maturi / Gianluca Castignani / Lauro
Moscardini
- Ghassem Gozaliasl / Alexis Finoguenov / Sina Taamoli / B. Hollis
Akins
- C. Rafael Arango-Toro / M. Caitlin Casey / E. Nicole Drakos / L.
Andreas Faisst
- Carter Flayhart / Maximilien Franco / Fabrizio Gentile / Ali
Hadi
- Santosh Harish / Hossein Hatamnia / Olivier Ilbert
/ Shuowen Jin
- S. Jeyhan Kartaltepe / Ali Ahmad Khostovan / M. Anton Koekemoer /
Gavin Leroy
- E. Georgios Magdis / Henry Joy McCracken / Jed McKinney / Louise
Paquereau
- Jason Rhodes / R. Michael Rich / E. Brant Robertson / M. Rasha
Samir
- Diana Scognamiglio / Samaneh Shamyati / Marko Shuntov / A. Jorge
Zavala
Summary
We investigate the redshift and group richness dependence of the
quiescent fraction and red-sequence (RS) parameters in COSMOS galaxy
groups from z=0 to z=3.7. We analyzed the deep and well-characterized
sample of groups detected with AMICO in the COSMOS(-Web) field. Our
study of the quiescent galaxy population is based on a machine-learning
classification tool based on rest-frame magnitudes. The algorithm learns
from several traditional methods to estimate the probability of a galaxy
being quiescent, achieving high precision and recall. Starting from this
classification, we computed quiescent galaxy fractions within groups via
two methods: one based on the membership probabilities provided by
AMICO, which rely on an analytical model, and another using a
model-independent technique. We then detected the RS by estimating the
ridgeline position using photometric data, followed by sigma clipping to
remove outliers. This analysis was performed using both rest-frame and
observed-frame magnitudes with rest-frame matching. We compared the
results from both approaches and investigated the  and richness dependence of the RS
parameters. We found that the quiescent galaxy population in groups
builds up steadily from z=1.5-2 across all richnesses, with faster and
earlier growth in the richest groups. The first galaxies settle onto the
RS ridgeline by
and richness dependence of the RS
parameters. We found that the quiescent galaxy population in groups
builds up steadily from z=1.5-2 across all richnesses, with faster and
earlier growth in the richest groups. The first galaxies settle onto the
RS ridgeline by  , consistent with
current evolutionary scenarios. Notably, we reported a rare overdensity
of quiescent galaxies at z=3.4, potentially one of the most distant
early RSs observed. Extending our study to X-rays, we found that X-ray
faint groups have, on average, lower quiescent fractions than X-ray
bright ones, likely reflecting their typical location in filaments.
Leveraging the broad wavelength coverage of COSMOS2025, we traced RS
evolution over
, consistent with
current evolutionary scenarios. Notably, we reported a rare overdensity
of quiescent galaxies at z=3.4, potentially one of the most distant
early RSs observed. Extending our study to X-rays, we found that X-ray
faint groups have, on average, lower quiescent fractions than X-ray
bright ones, likely reflecting their typical location in filaments.
Leveraging the broad wavelength coverage of COSMOS2025, we traced RS
evolution over  Gyr, finding no
significant trends in either slope or scatter of the ridgeline.
Gyr, finding no
significant trends in either slope or scatter of the ridgeline.
A
comprehensive separation of dark matter and baryonic mass components in
galaxy clusters II: an overview of the mass distribution in Abell
S1063
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Benjamin Beauchesne / Benjamin Clément / Marceau
Limousin / Anna Niemiec
- Mathilde Jauzac / Belén Alcalde Pampliega / Johan Richard /
Guillaume Mahler
- Jose M. Diego / Pascale Hibon / Anton M. Koekemoer / Thomas
Connor
- Jean-Paul Kneib / Andreas L. Faisst
Summary
In the first paper of this series, we derived mass constraints on the
total mass and the baryonic components of the galaxy cluster Abell
S1063. The main focus was to recover stellar masses and kinematics for
cluster members, the brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) and the
intra-cluster light (ICL). In this second paper, we introduce a
multi-probe mass modelling approach that incorporates constraints on
both the total mass and the individual baryonic components. We obtain
comprehensive mass models of Abell S1063, in which the dark matter
distribution is disentangled from the baryonic mass at both cluster and
galaxy scales. The best-fitting mass model achieves an RMS of  on the
multiple image positions. The kinematic profiles of the BCG & ICL,
as well as the X-ray surface brightness of the intra-cluster gas, are
accurately reproduced within observational uncertainties. However, a
on the
multiple image positions. The kinematic profiles of the BCG & ICL,
as well as the X-ray surface brightness of the intra-cluster gas, are
accurately reproduced within observational uncertainties. However, a
 scatter is required for the cluster member line-of-sight dispersions.
This method yields the most complex parametric mass model with
consistency among almost all available mass constraints. We find a
scatter is required for the cluster member line-of-sight dispersions.
This method yields the most complex parametric mass model with
consistency among almost all available mass constraints. We find a  agreement between the
inferred stellar-to-subhalo mass relation and that predicted by
large-scale cosmological simulations. The ICL stellar mass derived from
our model is consistent with estimates from stellar population
modelling. We present the first multi-probe mass modelling method
capable of disentangling the dark matter from the baryonic mass
distributions in massive galaxy clusters. Its results, such as the
stellar-to-subhalo mass relation or the distribution of each mass
component, can be directly compared to hydrodynamical cosmological
simulations such as illustrisTNG.
agreement between the
inferred stellar-to-subhalo mass relation and that predicted by
large-scale cosmological simulations. The ICL stellar mass derived from
our model is consistent with estimates from stellar population
modelling. We present the first multi-probe mass modelling method
capable of disentangling the dark matter from the baryonic mass
distributions in massive galaxy clusters. Its results, such as the
stellar-to-subhalo mass relation or the distribution of each mass
component, can be directly compared to hydrodynamical cosmological
simulations such as illustrisTNG.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Annie Zavagno / Delphine Russeil /
Paolo Suin / Siju Zhang
- Ram Kesh Yadav / Miguel Figueira / Loris Berthelot
/ Doris Arzoumanian
- Manash Ranjan Samal / Vineet Rawat / Philippe André / Michael
Mattern
- Hong-Li Liu / Sarah Sadavoy / Parisa Nozari / Benoît Epinat
Summary
Recent results from the James Webb Space Telescope show that nearby
spiral galaxies are dominated by the presence of H I and H II bubbles
that strongly shape their surrounding medium. These bubbles result from
the feedback of high-mass stars at different stages of their life cycle.
However, early (pre-supernova) feedback from high-mass stars is still
poorly quantified. Recent results from numerical simulations suggest
that the impact of high-mass star early feedback (photoionization, wind)
on star formation properties is complex, time-dependent, and strongly
depends on physical conditions, including the magnetic field properties.
In our Galaxy, ionized (H II) regions observed in different evolution
stages show a high diversity of star formation in their associated
photo-dissociation regions (PDRs). However, the way in which the low- to
high-density interstellar medium evolves to this situation remains
elusive. Quantifying the impact of early feedback from high-mass stars
on star formation properties and star formation laws (star formation
rate, star formation efficiency versus gas surface density, Σgas) will
allow for a better understanding of the evolution of star formation laws
in external galaxies, the laws that are key ingredients of galaxy
evolution models. PRIMA, with its high sensitivity, large mapping
efficiency, and polarimetric capabilities, offers a unique opportunity
to address the way radiative feedback and magnetic field control star
formation in the Milky Way.
GW250114:
testing Hawking’s area law and the Kerr nature of black holes
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea / M. Assiduo
- S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone / F. Attadio
- F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone / E. A. Avila
- S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae / S. Bagnasco
- L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka / A. M. Baker
- K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi / N. Baldicchi
- M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri
- B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral
- M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish / D. Barker
- N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone / B. Barr
- L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti
- M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri
- A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley
- A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale
- F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell
- D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara
- J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin
- B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / C. P. L. Berry
- D. Bersanetti / T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser
- D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / S. Bhagwat
- R. Bhandare / R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya
- S. Bhaumik / V. Biancalana / A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko
- G. Billingsley / A. Binetti / S. Bini / C. Binu
- S. Biot / O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht
- M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard / S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn
- L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair / N. Bode
- N. Boettner / G. Boileau / M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke
- A. Bolliand / L. D. Bonavena / R. Bondarescu / F.
Bondu
- E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino / R. Bonnand
- A. Borchers / S. Borhanian / V. Boschi / S. Bose
- V. Bossilkov / Y. Bothra / A. Boudon / L. Bourg
- G. Bouyer / M. Boyle / A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia
- P. R. Brady / A. Branch / M. Branchesi / I. Braun
- T. Briant / A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill
- E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown
- M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett / G. Bruno / R. Bruntz
- J. Bryant / Y. Bu / F. Bucci / J. Buchanan
- O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik / H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno
- K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio / D. Buskulic / C. Buy
- R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies / R. Cabrita / V.
Cáceres-Barbosa
- L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / A. Calafat
- J. Calderón Bustillo / T. A. Callister / E. Calloni / S. R.
Callos
- M. Canepa / G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon / H. Cao
- L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa / E. Capote / G. Capurri
- G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara / J. B. Carlin
- T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo
- J. J. Carter / G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos / J. Casanueva
Diaz
- C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià
- R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja / G. Cella / P. Cerdá-Durán
- E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi / A. Chakraborty
- P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C.
L. Chan
- M. Chan / K. Chang / S. Chao / P. Charlton
- E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee / Debarati Chatterjee / Deep
Chatterjee
- M. Chaturvedi / S. Chaty / K. Chatziioannou / A. Chen
- A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen
- S. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng
- P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini
- D. Chiaramello / G. Chiarini / A. Chiba / A. Chincarini
- M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary
- N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag
- M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok / F. Clara
- J. A. Clark / T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater / S. Clesse
- F. Cleva / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon
- S. Colace / E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette
- J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo / C. M. Compton
- G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión
- S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado / A. Corsi
- R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux / P. Couvares
- D. M. Coward / R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo / J. D. E. Creighton
- T. D. Creighton / P. Cremonese / S. Crook / R. Crouch
- J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming
- E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton
- S. Dal Pra / T. Damour / G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo
- S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch
- L. P. Dartez / R. Das / A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo
- A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave / A. Davenport
- M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis / L. Davis
- M. C. Davis / P. Davis / E. J. Daw / M. Dax
- J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis
- F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre / W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny
- F. De Marco / G. Demasi / F. De Matteis / N. Demos
- T. Dent / A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri
- R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi / M. Desai / R. DeSalvo
- A. DeSimone / R. De Simone / A. Dhani / R. Diab
- M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron / T. Dietrich
- L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo
- D. Diksha / J. Ding / S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma
- D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev
- J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen
- A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza / L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan
- K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney / S. Doravari / O. Dorosh
- W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers / L. Dunn
- U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne / D. D’Urso / P. Dutta Roy
- H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa / M. Ebersold
- T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / A. Effler / J. Eichholz
- H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann / M. Emma / K. Endo
- R. Enficiaud / L. Errico / R. Espinosa / M. Esposito
- R. C. Essick / H. Estellés / T. Etzel / M. Evans
- T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi
- V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr
- W. M. Farr / G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays
- M. Fazio / J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti
- E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes / T. Fernandes / D. Fernando
- S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura
- E. Finch / A. Fiori / I. Fiori / M. Fishbach
- R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio
- S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming / E. Floden / H. Fong
- J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes / C. Foo / B. Fornal
- K. Franceschetti / F. Frappez / S. Frasca / F. Frasconi
- J. P. Freed / Z. Frei / A. Freise / O. Freitas
- R. Frey / W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov
- G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii / T. Fujimori
- P. Fulda / M. Fyffe / B. Gadre / J. R. Gair
- S. Galaudage / V. Galdi / R. Gamba / A. Gamboa
- S. Gamoji / D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa
- J. García-Bellido / C. García-Quirós / J. W. Gardner / K. A.
Gardner
- S. Garg / J. Gargiulo / X. Garrido / A. Garron
- F. Garufi / P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley
- F. Gautier / V. Gayathri / T. Gayer / G. Gemme
- A. Gennai / V. Gennari / J. George / R. George
- O. Gerberding / L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh
- Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh
- J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson / C. Gier
- S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey
- R. V. Godley / P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz
- J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov / G. González
- P. Goodarzi / S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin
- R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / A. Grado
- V. Graham / A. E. Granados / M. Granata / V. Granata
- S. Gras / P. Grassia / J. Graves / C. Gray
- R. Gray / G. Greco / A. C. Green / L. Green
- S. M. Green / S. R. Green / C. Greenberg / A. M. Gretarsson
- H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith / H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani
- C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald / D. Guerra
- D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati
- F. Gulminelli / H. Guo / W. Guo / Y. Guo
- Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta / S. K. Gupta
- V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez
- N. Guttman / F. Guzman / D. Haba / M. Haberland
- S. Haino / E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond
- M. Haney / J. Hanks / C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam
- O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen / J. Hanson
- S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar
- K. Haris / I. Harley-Trochimczyk / T. Harmark / J. Harms
- G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry / J. Hart / B. Haskell
- C. J. Haster / K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama
- M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze / J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann
- F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming / O.
Henderson-Sapir
- M. Hendry / I. S. Heng / M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw
- M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt / J. Heynen / J. Heyns
- S. Higginbotham / S. Hild / S. Hill / Y. Himemoto
- N. Hirata / C. Hirose / D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan
- N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows / D. E. Holz / L. Honet
- D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough / S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard
- E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi
- H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu
- W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang
- Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey / V. Hui
- S. Husa / R. Huxford / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo
- M. Ianni / G. Iannone / J. Iascau / K. Ide
- R. Iden / A. Ierardi / S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku
- Y. Inoue / G. Iorio / P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal
- J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa / M. Isi / T. Islam
- K. S. Isleif / Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer
- C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot / S. J. Jadhav
- S. P. Jadhav / M. Jain / T. Jain / A. L. James
- K. Jani / J. Janquart / N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba
- P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume / W. Javed / A. Jennings
- M. Jensen / W. Jia / J. Jiang / H.-B. Jin
- G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston
- N. Johny / D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones / R. Jones
- H. E. Jose / P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi / G. Joubert
- J. Ju / L. Ju / K. Jung / J. Junker
- V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita / I. Kaku
- V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda
- S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner
- S. A. KantiMahanty / S. J. Kapadia / D. P. Kapasi / M.
Karthikeyan
- M. Kasprzack / H. Kato / T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis
- W. Katzman / R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto
- D. Keitel / L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington / F. A. Kerkow
- R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key / R. Khadela / S. Khadka
- S. S. Khadkikar / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan / T. Khanam
- M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo
- C. Kim / J. C. Kim / K. Kim / M. H. Kim
- S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball / K. Kimes
- M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee
- E. J. Knox / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi / S. M. Koehlenbeck
- G. Koekoek / K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama / S. Koley
- P. Kolitsidou / A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori / A. K. H. Kong
- A. Kontos / L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko / X. Kou
- A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam / T. Koyama
- D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu
- S. Kroker / A. Królak / K. Kruska / J. Kubisz
- G. Kuehn / S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan / Achal Kumar
- Anil Kumar / Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar
- Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume / K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi
- S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak / K. Kwan
- S. Kwon / G. Lacaille / D. Laghi / A. H. Laity
- E. Lalande / M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry
- B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang / J. Lange / R. Langgin
- B. Lantz / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen / A. Lartaux-Vollard
- P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. Laxen / C. Lazarte
- A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci / L. Leali
- Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee / J. Lee
- K. Lee / R.-K. Lee / R. Lee / Sungho Lee
- Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred / J. Lehmann
- L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître / M. Lenti
- M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy / M. Lesovsky
- N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin / K. Leyde
- A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li / X. Li
- Y. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos / E. T. Lin
- F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin / C. Lindsay
- S. D. Linker / A. Liu / G. C. Liu / Jian Liu
- F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L. Lo / J.-P.
Locquet
- S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou / L. T. London / A. Longo
- D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla / M. Lorenzini / A. Lorenzo-Medina
- V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / E. Lotti
- T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto
- N. Low / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi / H. Lück
- D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier / R. Macas
- M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet
- K. Maeda / S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee
- E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh
- M. Maini / S. Majhi / E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem
- N. Malagon / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis / U. Mali
- S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick / A.-K. Malz
- N. Man / M. Mancarella / V. Mandic / V. Mangano
- N. Manning / B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell / M. Manske
- M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli / C. Marinelli / F. Marion
- A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat
- F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez
- D. A. Martinez / M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini
- J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro
- A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich
- M. Matiushechkina / L. Maurin / N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell
- G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick
- L. McCuller / S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee
- J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod
- I. McMahon / T. McRae / R. McTeague / D. Meacher
- B. N. Meagher / R. Mechum / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos
- C. S. Menoni / F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni
- K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt
- M. Merzougui / C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde
- F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao
- C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov
- S. J. Miller / M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti
- Y. Minenkov / E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola
- M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra / C. Mishra
- T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / K. Mitman
- S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov / K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman
- O. Miyakawa / S. Miyoki / A. Miyoko / G. Mo
- L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz
- M. Mondin / J. K. Monsalve / M. Montani / C. J. Moore
- D. Moraru / A. More / S. More / C. Moreno
- E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno / A. Moreso Serra / S. Morisaki
- Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras / A. Moscatello / M. Mould
- B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry / L. Muccillo / F. Muciaccia
- D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma Mukherjee / Subroto
Mukherjee
- Suvodip Mukherjee / N. Mukund / A. Mullavey / H. Mullock
- J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli / M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray
- D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan
- K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura / H. Nakano / M. Nakano
- D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi / V. Napolano / P. Narayan
- I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa / H. Narola / L. Naticchioni
- R. K. Nayak / L. Negri / A. Nela / C. Nelle
- A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery / A. Neunzert
- S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen
- Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa / S. Nissanke / W. Niu
- F. Nocera / J. Noller / M. Norman / C. North
- J. Novak / R. Nowicki / J. F. Nuño Siles / L. K. Nuttall
- K. Obayashi / J. Oberling / J. O’Dell / E. Oelker
- M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan / T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi
- F. Ohme / R. Oliveri / R. Omer / B. O’Neal
- M. Onishi / K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly / M. Orselli
- R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / S. Oshino / C. Osthelder
- I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway / A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier
- B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki / A. E. Pace / R. Pagano
- M. A. Page / A. Pai / L. Paiella / A. Pal
- S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma
- C. Palomba / P. Palud / H. Pan / J. Pan
- K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey / Swadha Pandey
- P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone / B. C. Pant
- F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri / F. Paoletti / A. Paolone
- A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini / G.
Papigkiotis
- A. Paquis / A. Parisi / B.-J. Park / J. Park
- W. Parker / G. Pascale / D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti
- R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger / D. Passuello / O. Patane
- A. V. Patel / D. Pathak / A. Patra / B. Patricelli
- B. G. Patterson / K. Paul / S. Paul / E. Payne
- T. Pearce / M. Pedraza / A. Pele / F. E. Peña Arellano
- X. Peng / Y. Peng / S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar
- A. Perego / Z. Pereira / C. Périgois / G. Perna
- A. Perreca / J. Perret / S. Perriès / J. W. Perry
- D. Pesios / S. Peters / S. Petracca / C. Petrillo
- H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham / K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon
- H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli / L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni
- M. Pichot / M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini
- G. Pierra / V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas
- F. Pilo / L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto
- B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi
- E. Placidi / M. L. Planas / W. Plastino / C. Plunkett
- R. Poggiani / E. Polini / J. Pomper / L. Pompili
- J. Poon / E. Porcelli / E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky
- R. Poulton / J. Powell / G. S. Prabhu / M. Pracchia
- B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati / V. Prasad
- K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia / G. Pratten
- G. Principe / G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito
- A. C. Providence / A. Puecher / J. Pullin / P. Puppo
- M. Pürrer / H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner
- V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez / N. Qutob / F. J. Raab
- R. Rading / I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan
- B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / M. Ramos
Arevalo
- A. Ramos-Buades / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani
- B. Ratto / A. Ravichandran / A. Ray / V. Raymond
- M. Razzano / J. Read / T. Regimbau / S. Reid
- C. Reissel / D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu
- A. Revilla Peña / R. Reyes / L. Ricca / F. Ricci
- M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. Rice / J. W. Richardson
- M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley
- S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet
- M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins
- A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw
- J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa
- T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross
- M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy
- D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales
- K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh
- S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat
- S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou
- S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi
- M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe
- S. Salvador / A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez
- E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders
- E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan
- N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / A. Sasli / P. Sassi
- B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato / S. Sato
- Yukino Sato / Yu Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage
- T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco
- D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski
- P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind
- R. M. S. Schofield / K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F.
Schutz
- E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott
- R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y.
Sekiguchi
- D. Sellers / N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo
- J. W. Seo / V. Sequino / M. Serra / A. Sevrin
- T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao
- A. K. Sharma / Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma
- S. Sharma Chaudhary / P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / E.
Sheridan
- Z.-H. Shi / M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai
- S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short
- S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider / H. Siegel / D. Sigg
- L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer
- Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh / D. Singh / N. Singh
- S. Singh / A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris
- B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J.
Smetana
- J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith
- S. Soares de Albuquerque Filho / M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I.
Song
- S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani
- F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli
- A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer
- N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas
- P. Stevens / S. Stevenson / M. StPierre / M. D. Strong
- A. Strunk / A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar
- Y. Sudo / N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan
- J. Sun / L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh
- B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton / K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki
- B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk
- M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi / K. Takada / H. Takahashi
- R. Takahashi / A. Takamori / S. Takano / H. Takeda
- K. Takeshita / I. Takimoto Schmiegelow / M. Takou-Ayaoh / C.
Talbot
- M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka
- S. J. Tanaka / S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner
- L. Tao / R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto
- A. Taruya / J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / D. Tellez
- R. Tenorio / S. A. Teukolsky / H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos
- M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M. Thomas / M. Thomas / P.
Thomas
- J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu / K. A. Thorne / K. S. Thorne
- E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari / Pawan Tiwari
- Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd
- M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland / A. E. Tolley
- T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura / H. Tong
- C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie / I. Tosta e Melo
- E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran / A. Trapananti
- R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor / M. Trevor
- M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian / A. Trovato
- L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang / S. Tsuchida
- L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi / C. Turski
- H. Ubach / N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall
- T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim / L. E. Uronen
- T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya
- G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia / M. Valentini
- S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan / M. van Dael
- E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / M.
van der Sluys
- A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra / M. VanDyke
- H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J.
Vanier
- M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro
- A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio
- G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis
- R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt
- B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets
- A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva Espinosa / V.
Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / S. Vitale
- H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel
- W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack
- L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner / R. M. Wald
- L. Wallace / E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang
- W. H. Wang / Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner
- M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai
- B. Weaver / S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert
- A. J. Weinstein / R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette
- J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens
- D. Wilken / A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams
- M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke
- M. Wils / L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood
- C. C. Wipf / G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe
- H. T. Wong / I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters
- J. L. Wright / M. Wright / B. Wu / C. Wu
- D. S. Wu / H. Wu / K. Wu / Q. Wu
- Y. Wu / Z. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki
- V. A. Xu / Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto
- K. Yamamoto / T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki
- T. Yan / K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough
- J. Yebana / S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin
- J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara
- M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri
- M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / L. Zhang
- N. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang / C. Zhao
- Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng
- H. Zhong / H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu
- A. B. Zimmerman / L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
The gravitational-wave signal GW250114 was observed by the two LIGO
detectors with a network matched-filter signal-to-noise ratio of 80. The
signal was emitted by the coalescence of two black holes with near-equal
masses  and
and
 , and
small spins
, and
small spins  (90% credibility) and negligible eccentricity
(90% credibility) and negligible eccentricity  .
Post-merger data excluding the peak region are consistent with the
dominant quadrupolar
.
Post-merger data excluding the peak region are consistent with the
dominant quadrupolar  mode of a Kerr black hole and its first overtone. We constrain the
modes’ frequencies to
mode of a Kerr black hole and its first overtone. We constrain the
modes’ frequencies to  of the Kerr
spectrum, providing a test of the remnant’s Kerr nature. We also examine
Hawking’s area law, also known as the second law of black hole
mechanics, which states that the total area of the black hole event
horizons cannot decrease with time. A range of analyses that exclude up
to 5 of the strongest merger cycles confirm that the remnant area is
larger than the sum of the initial areas to high credibility.
of the Kerr
spectrum, providing a test of the remnant’s Kerr nature. We also examine
Hawking’s area law, also known as the second law of black hole
mechanics, which states that the total area of the black hole event
horizons cannot decrease with time. A range of analyses that exclude up
to 5 of the strongest merger cycles confirm that the remnant area is
larger than the sum of the initial areas to high credibility.
Directed
searches for gravitational waves from ultralight vector boson clouds
around merger remnant and galactic black holes during the first part of
the fourth LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA observing run
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- K. G. Arun / G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea
- M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone
- F. Attadio / F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone
- E. A. Avila / S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae
- S. Bagnasco / L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka
- A. M. Baker / K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi
- N. Baldicchi / M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer
- S. Banagiri / B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste
- P. Baral / M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish
- D. Barker / N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone
- B. Barr / L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta
- A. M. Bartoletti / M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev
- R. Bassiri / A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi
- J. C. Bayley / A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan
- V. M. Bedakihale / F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli
- A. S. Bell / D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit
- I. Bentara / J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera
- F. Bergamin / B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz
- D. Bersanetti / T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser
- D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare
- R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya / S. Bhaumik
- V. Biancalana / A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley
- A. Binetti / S. Bini / C. Binu / S. Biot
- O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi
- M.-A. Bizouard / S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg
- C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair / N. Bode / N. Boettner
- G. Boileau / M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A.
Bolliand
- L. D. Bonavena / R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla
- M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / A. Borchers
- S. Borhanian / V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov
- Y. Bothra / A. Boudon / L. Bourg / M. Boyle
- A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady / A. Branch
- M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant / A. Brillet
- M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks
- B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett
- G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant / Y. Bu
- F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik
- H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio
- D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies
- R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli
- C. Cahillane / A. Calafat / T. A. Callister / E. Calloni
- S. R. Callos / M. Canepa / G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon
- H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa / E. Capote
- G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara
- J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli
- G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos
- J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S.
Caudill
- M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja / G. Cella
- P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi
- A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka
Subrahmanya
- J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / K. Chang / S. Chao
- P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee / Debarati
Chatterjee
- Deep Chatterjee / M. Chaturvedi / S. Chaty / A. Chen
- A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen
- S. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng
- P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini
- G. Chiarini / A. Chiba / A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo
- A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary / N. Christensen
- S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar
- M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok / F. Clara / J. A. Clark
- T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater / S. Clesse / F. Cleva
- E. Coccia / E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace
- E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette / J. Collins
- S. Colloms / A. Colombo / C. M. Compton / G. Connolly
- L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi
- N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado / A. Corsi / R. Cottingham
- M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux / P. Couvares / D. M. Coward
- R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo / J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton
- P. Cremonese / S. Crook / R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia
- J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming / E. Cuoco
- M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton / S. Dal Pra
- G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio
- K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez / R. Das
- A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo / A. Daumas / N. Davari
- I. Dave / A. Davenport / M. Davier / T. F. Davies
- D. Davis / L. Davis / M. C. Davis / P. Davis
- E. J. Daw / M. Dax / J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan
- J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis / F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre
- W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny / F. De Marco / G. Demasi
- F. De Matteis / N. Demos / T. Dent / A. Depasse
- N. DePergola / R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi
- M. Desai / R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone / R. De Simone
- A. Dhani / R. Diab / M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare
- G. Dideron / T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo
- M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha / J. Ding
- S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma / D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo
- Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev / J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor
- N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen / A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza
- L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney
- S. Doravari / O. Dorosh / W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago
- J. C. Driggers / L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne
- D. D’Urso / P. Dutta Roy / H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer
- C. Eassa / W. E. East / M. Ebersold / T. Eckhardt
- G. Eddolls / A. Effler / J. Eichholz / H. Einsle
- M. Eisenmann / M. Emma / K. Endo / R. Enficiaud
- L. Errico / R. Espinosa / M. Esposito / R. C. Essick
- H. Estellés / T. Etzel / M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva
- B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi / V. Fafone
- S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr / W. M. Farr
- G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays / M. Fazio
- J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi
- J. Fernandes / T. Fernandes / D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo
- T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura / A. Fiori
- I. Fiori / M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi
- V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming
- E. Floden / H. Fong / J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes
- C. Foo / B. Fornal / K. Franceschetti / F. Frappez
- S. Frasca / F. Frasconi / J. P. Freed / Z. Frei
- A. Freise / O. Freitas / R. Frey / W. Frischhertz
- P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia
- S. Fujii / T. Fujimori / P. Fulda / M. Fyffe
- B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage / V. Galdi
- R. Gamba / A. Gamboa / S. Gamoji / D. Ganapathy
- A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido / C.
García-Quirós
- J. W. Gardner / K. A. Gardner / S. Garg / J. Gargiulo
- X. Garrido / A. Garron / F. Garufi / P. A. Garver
- C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier / V. Gayathri
- T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai / V. Gennari
- J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding / L. Gergely
- Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh
- Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina
- D. R. Gibson / C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer
- F. Glotin / J. Godfrey / R. V. Godley / P. Godwin
- A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez
- B. Goncharov / G. González / P. Goodarzi / S. Goode
- A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould
- K. Govorkova / A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados
- M. Granata / V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia
- J. Graves / C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco
- A. C. Green / L. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green
- C. Greenberg / A. M. Gretarsson / H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith
- H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani / C. Grimaud / H. Grote
- S. Grunewald / D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi
- A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / H. Guo
- W. Guo / Y. Guo / Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta
- N. C. Gupta / S. K. Gupta / V. Gupta / N. Gupte
- J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez / N. Guttman / F. Guzman
- D. Haba / M. Haberland / S. Haino / E. D. Hall
- E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond / M. Haney / J. Hanks
- C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman
- H. Hansen / J. Hanson / S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada
- A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar / K. Haris / I.
Harley-Trochimczyk
- T. Harmark / J. Harms / G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry
- J. Hart / B. Haskell / C. J. Haster / K. Haughian
- H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama / M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze
- J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann / F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell
- G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M. Hendry / I. S. Heng
- M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw / M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt
- J. Heynen / J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham / S. Hild
- S. Hill / Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata / C. Hirose
- D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan / N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows
- D. E. Holz / L. Honet / D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough
- S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy
- C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi / H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh
- C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu / W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu
- H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart
- B. Hughey / V. Hui / S. Husa / R. Huxford
- L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni / G. Iannone
- J. Iascau / K. Ide / R. Iden / A. Ierardi
- S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku / Y. Inoue / G. Iorio
- P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa
- M. Isi / K. S. Isleif / Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya
- B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot
- S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav / M. Jain / T. Jain
- A. L. James / K. Jani / J. Janquart / N. N. Janthalur
- S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume / W. Javed
- A. Jennings / M. Jensen / W. Jia / J. Jiang
- H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston
- R. Johnston / N. Johny / D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones
- R. Jones / H. E. Jose / P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi
- G. Joubert / J. Ju / L. Ju / K. Jung
- J. Junker / V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita
- I. Kaku / V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi
- N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel
- J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty / S. J. Kapadia / D. P.
Kapasi
- M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack / H. Kato / T. Kato
- E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman / R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe
- R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel / L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington
- F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key / R. Khadela
- S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan
- T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo
- N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim / K. Kim
- M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball
- K. Kimes / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko
- A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi
- S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama
- S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori
- A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko
- X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam
- T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel
- N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker / A. Królak / K. Kruska
- J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn / S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan
- Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar / Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar
- Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume / K. Kuns
- N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak
- K. Kwan / S. Kwon / G. Lacaille / D. Laghi
- A. H. Laity / E. Lalande / M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati
- M. Landry / B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang / J. Lange
- R. Langgin / B. Lantz / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen
- A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. Laxen
- C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci
- L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee
- J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee / R. Lee
- Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred
- J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître
- M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy
- M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin
- K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li
- X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos
- E. T. Lin / F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin
- C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / A. Liu / G. C. Liu
- Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L.
Lo
- J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou / L. T. London
- A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla / A. Lorenzo-Medina
- V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / E. Lotti
- T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto
- N. Low / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi / H. Lück
- D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier / R. Macas
- M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet
- K. Maeda / S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee
- E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh
- M. Maini / S. Majhi / E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem
- D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis / U. Mali / S. Maliakal
- A. Malik / L. Mallick / A.-K. Malz / N. Man
- M. Mancarella / V. Mandic / V. Mangano / B. Mannix
- G. L. Mansell / M. Manske / M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli
- C. Marinelli / F. Marion / A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz
- E. Maros / S. Marsat / F. Martelli / I. W. Martin
- R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez / D. A. Martinez / M. Martinez
- V. Martinez / A. Martini / J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov
- E. J. Marx / L. Massaro / A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid
- S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich / M. Matiushechkina / L.
Maurin
- N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell / T. May / G. McCarrol
- R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick / L. McCuller
- S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn
- K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod / I. McMahon
- T. McRae / R. McTeague / D. Meacher / B. N. Meagher
- R. Mechum / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos / C. S. Menoni
- F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni / K. Merfeld
- E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui
- C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn
- A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao / C. Michel
- Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov / A. L. Miller
- S. J. Miller / M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti
- Y. Minenkov / E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola
- M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra / C. Mishra
- T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra
- V. P. Mitrofanov / K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa
- S. Miyoki / A. Miyoko / G. Mo / L. Mobilia
- S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / M. Mondin
- M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More
- S. More / C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno
- A. Moreso Serra / S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras
- A. Moscatello / M. Mould / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry
- L. Muccillo / F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee
- Soma Mukherjee / Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip Mukherjee / N.
Mukund
- A. Mullavey / H. Mullock / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli
- M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji
- A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura
- H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi
- V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa
- H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak / L. Negri
- A. Nela / C. Nelle / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson
- M. Nery / A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh
- S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa
- S. Nissanke / W. Niu / F. Nocera / J. Noller
- M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak / R. Nowicki
- J. F. Nuño Siles / L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling
- J. O’Dell / E. Oelker / M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan
- T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / F. Ohme / R. Oliveri
- R. Omer / B. O’Neal / M. Onishi / K. Oohara
- B. O’Reilly / M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea
- S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway
- A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki
- A. E. Pace / R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai
- L. Paiella / A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia
- M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud
- H. Pan / J. Pan / K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda
- Shiksha Pandey / Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale
- K. A. Pannone / B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri
- F. Paoletti / A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis
- L. Papalini / G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis / A. Parisi
- B.-J. Park / J. Park / W. Parker / G. Pascale
- D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger
- D. Passuello / O. Patane / A. V. Patel / D. Pathak
- A. Patra / B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul
- S. Paul / E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza
- A. Pele / F. E. Peña Arellano / X. Peng / Y. Peng
- S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego / Z. Pereira
- C. Périgois / G. Perna / A. Perreca / J. Perret
- S. Perriès / J. W. Perry / D. Pesios / S. Peters
- S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham
- K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli
- L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot / M. Piendibene
- F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra / V. Pierro
- M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo / L. Pinard
- I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello
- M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi / M. L. Planas
- W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani / E. Polini
- J. Pomper / L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli
- E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell
- G. S. Prabhu / M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier
- A. K. Prajapati / K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia
- G. Pratten / G. Principe / G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi
- P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher / J. Pullin
- P. Puppo / M. Pürrer / H. Qi / J. Qin
- G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez / N. Qutob
- R. Rading / I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan
- B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / M. Ramos
Arevalo
- A. Ramos-Buades / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani
- B. Ratto / A. Ravichandran / A. Ray / V. Raymond
- M. Razzano / J. Read / T. Regimbau / S. Reid
- C. Reissel / D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu
- A. Revilla Peña / R. Reyes / L. Ricca / F. Ricci
- M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. Rice / J. W. Richardson
- M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley
- S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet
- M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins
- A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw
- J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa
- T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross
- M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy
- D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales
- K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh
- S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat
- S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou
- S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi
- M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe
- S. Salvador / A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez
- E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders
- E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan
- N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / A. Sasli / P. Sassi
- B. Sassolas / R. Sato / S. Sato / Yukino Sato
- Yu Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage / T. Sawada
- H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl
- M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt
- S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield
- K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz
- M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott / R. M. Sedas
- T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers
- N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo
- V. Sequino / M. Serra / A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer
- U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao / A. K. Sharma
- Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma / S. Sharma
Chaudhary
- P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / E. Sheridan / Z.-H. Shi
- M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai / S. Shirke
- D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short / S.
ShyamSundar
- A. Sider / H. Siegel / N. Siemonsen / D. Sigg
- L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer
- Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh / D. Singh / N. Singh
- S. Singh / A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris
- B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J.
Smetana
- J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith
- S. Soares de Albuquerque Filho / M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I.
Song
- S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani
- F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli
- A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer
- N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas
- P. Stevens / M. StPierre / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk
- A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / Y. Sudo
- N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun
- L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton
- P. J. Sutton / K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels
- A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca
- H. Tagoshi / K. Takada / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi
- A. Takamori / S. Takano / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita
- I. Takimoto Schmiegelow / M. Takou-Ayaoh / C. Talbot / M.
Tamaki
- N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka
- S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao
- R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto / A. Taruya
- J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / D. Tellez / R. Tenorio
- H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M.
Thomas
- M. Thomas / P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu
- K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari
- Pawan Tiwari / Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari
- M. R. Todd / M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland
- A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura
- H. Tong / C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie
- I. Tosta e Melo / E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran
- A. Trapananti / R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor
- M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian
- A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang
- S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi
- C. Turski / H. Ubach / N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama
- R. P. Udall / T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim
- L. E. Uronen / T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch
- N. Vaidya / G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia
- M. Valentini / S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan
- M. van Dael / E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van
Den Broeck
- M. van der Sluys / A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra
- M. VanDyke / H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van
Hove
- J. Vanier / M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel
- M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez
- A. Vecchio / G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch
- S. Venikoudis / R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken
- D. Verkindt / B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen
- F. Vetrano / A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant
- A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva
Espinosa
- V. Villa-Ortega / E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret
- S. Vitale / H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis
- J. S. A. von Wrangel / W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P.
Vyatchanin
- J. Wack / L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner
- L. Wallace / E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang
- W. H. Wang / Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner
- M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai
- B. Weaver / S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert
- A. J. Weinstein / R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette
- J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens
- D. Wilken / A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams
- M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke
- M. Wils / L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood
- C. C. Wipf / G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe
- H. T. Wong / I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters
- J. L. Wright / M. Wright / B. Wu / C. Wu
- D. S. Wu / H. Wu / K. Wu / Q. Wu
- Y. Wu / Z. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki
- V. A. Xu / Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto
- K. Yamamoto / T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki
- T. Yan / K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough
- J. Yebana / S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin
- J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara
- M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri
- M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / L. Zhang
- N. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang / C. Zhao
- Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng
- H. Zhong / H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu
- A. B. Zimmerman / L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
We present the first directed searches for long-transient and
continuous gravitational waves from ultralight vector boson clouds
around known black holes (BHs). We use LIGO data from the first part of
the fourth LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA observing run. The searches target two
distinct types of BHs and use two new semicoherent methods: hidden
Markov model (HMM) tracking for the remnant BHs of the mergers
GW230814_230901 and GW231123_135430 (referred to as GW230814 and
GW231123 in this study), and a dedicated method using the Band Sampled
Data (BSD) framework for the galactic BH in the Cygnus X-1 binary
system. Without finding evidence of a signal from vector bosons in the
data, we estimate the mass range that can be constrained. For the HMM
searches targeting the remnants from GW231123 and GW230814, we disfavor
vector boson masses in the ranges ![[0.94, 1.08] [0.94, 1.08]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5B0.94%2C%201.08%5D) and
and ![[2.75, 3.28] \times 10^{-13} [2.75, 3.28] \times 10^{-13}](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5B2.75%2C%203.28%5D%20%5Ctimes%2010%5E%7B-13%7D) eV, respectively, at 30% confidence, assuming a
1% false alarm probability. Although these searches are only marginally
sensitive to signals from merger remnants at relatively large distances,
future observations are expected to yield more stringent constraints
with high confidence. For the BSD search targeting the BH in Cygnus X-1,
we exclude vector boson masses in the range
eV, respectively, at 30% confidence, assuming a
1% false alarm probability. Although these searches are only marginally
sensitive to signals from merger remnants at relatively large distances,
future observations are expected to yield more stringent constraints
with high confidence. For the BSD search targeting the BH in Cygnus X-1,
we exclude vector boson masses in the range ![[0.85, 1.59] \times 10^{-13} [0.85, 1.59] \times 10^{-13}](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5B0.85%2C%201.59%5D%20%5Ctimes%2010%5E%7B-13%7D) eV at 95% confidence, assuming an initial BH spin
larger than 0.5.
eV at 95% confidence, assuming an initial BH spin
larger than 0.5.
Discovery
and Analysis of Afterglows from Poorly Localised GRBs with the
Gravitational-wave Optical Transient Observer (GOTO) All-sky Survey
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Amit Kumar / B. P. Gompertz / B. Schneider / S.
Belkin
- M. E. Wortley / A. Saccardi / D. O’Neill / K. Ackley
- B. Rayson / A. de Ugarte Postigo / A. Gulati / D. Steeghs
- D. B. Malesani / J. R. Maund / M. J. Dyer / S. Giarratana
- M. Serino / Y. Julakanti / B. Kumar / D. Xu
- R. A. J. Eyles-Ferris / Z.-P. Zhu / B. Warwick / Y.-D. Hu
- I. Allen / G. Ramsay / R. L. C. Starling / J. Lyman
- K. Ulaczyk / B. Godson / D. K. Galloway / V. S. Dhillon
- P. O’Brien / K. Noysena / R. Kotak / R. P. Breton
- L. K. Nuttall / D. Pollacco / J. Casares / T. L. Killestein
- M. R. Kennedy / N. Habeeb / S. Moran / K. Wiersema
- I. Worssam / D. L. Coppejans / C. A. Phillips / A.
Martin-Carrillo
- N. S. Pankov / J. F. Agüí Fernández / M. A. Aloy / J. An
- G. E. Anderson / A. Bochenek / A. J. Castro-Tirado / X. Chen
- L. Cotter / R. Dastidar / M. De Pasquale / V. D’Elia
- Y. Fang / S. Y. Fu / J. P. U. Fynbo / D. H. Hartmann
- L. B. He / L. Izzo / S. Q. Jiang / Y. Kawakubo
- E. V. Klunko / A. J. Levan / X.-W. Liu / X. Liu
- G. Lombardi / E. Maiorano / J. T. Palmerio / D. A. Perley
- D. L. A. Pieterse / A. S. Pozanenko / G. Pugliese / A. Rossi
- B. Sbarufatti / S. Bijavara Seshashayana / N. R. Tanvir / C. C.
Thöne
- A. J. van der Horst / S. D. Vergani / A. A. Volnova / R. A. M. J.
Wijers
- J. L. Wise
Summary
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), particularly those detected by wide-field
instruments such as the Fermi/GBM, pose a challenge for optical
follow-up due to their large initial localisation regions, leaving many
GRBs without identified afterglows. The Gravitational-wave Optical
Transient Observer (GOTO), with its wide field of view, dual-site
coverage, and robotic rapid-response capability, bridges this gap by
rapidly identifying and localising afterglows from alerts issued by
space-based facilities including Fermi, SVOM, Swift, and the EP,
providing early optical positions for coordinated multi-wavelength
follow-up. In this paper, we present optical afterglow localisation and
multi-band follow-up of seven Fermi/GBM and MAXI/GSC triggered long GRBs
(240122A, 240225B, 240619A, 240910A, 240916A, 241002B, and 241228B)
discovered by GOTO in 2024. Spectroscopy for six GRBs (no spectroscopic
data for GRB 241002B) with VLT/X-shooter and GTC/OSIRIS yields precise
redshifts spanning $z-$3.16 and absorption-line diagnostics of host and
intervening systems. Radio detections for four events confirm the
presence of long-lived synchrotron emission. Prompt-emission analysis
with Fermi and MAXI data reveals a spectrally hard population, with two
bursts lying  above the Amati
relation. Although their optical afterglows resemble those of typical
long GRBs, the prompt spectra are consistently harder than the long-GRB
average. Consistent modelling of six GOTO-discovered GRB afterglows
yields jet half-opening angles of a few degrees and beaming-corrected
kinetic energies (
above the Amati
relation. Although their optical afterglows resemble those of typical
long GRBs, the prompt spectra are consistently harder than the long-GRB
average. Consistent modelling of six GOTO-discovered GRB afterglows
yields jet half-opening angles of a few degrees and beaming-corrected
kinetic energies ( ) erg, consistent with the canonical long-GRB
population. These findings suggest that optical discovery of poorly
localised GRBs may be subject to observational biases favouring luminous
events with high spectral peak energy, while also providing insight into
jet microphysics and central engine diversity.
) erg, consistent with the canonical long-GRB
population. These findings suggest that optical discovery of poorly
localised GRBs may be subject to observational biases favouring luminous
events with high spectral peak energy, while also providing insight into
jet microphysics and central engine diversity.
Euclid:
Methodology for derivation of IPC-corrected conversion gain of nonlinear
CMOS APS
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. Le Graet / A. Secroun / M. Tourneur-Silvain / W. Gillard
- N. Fourmanoit / S. Escoffier / E. Kajfasz / S. Kermiche
- B. Kubik / J. Zoubian / S. Andreon / M. Baldi
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat / S. Camera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva
- J. Dinis / M. Douspis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / M. Farina
- S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / R. Kohley / H. Kurki-Suonio
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Meneghetti / G. Meylan
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- R. Saglia / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
Summary
We introduce a fast method to measure the conversion gain in
Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductors (CMOS) Active Pixel Sensors
(APS), which accounts for nonlinearity and interpixel capacitance (IPC).
The standard ‘mean-variance’ method is biased because it assumes pixel
values depend linearly on signal, and existing methods to correct for
nonlinearity are still introducing significant biases. While current IPC
correction methods are prohibitively slow for a per-pixel application,
our new method uses separate measurements of the IPC kernel to make an
almost instantaneous calculation of gain. Validated using test data from
a flight detector from the ESA Euclid mission, the IPC correction
recovers the results of slower methods within 0.1% accuracy. Meanwhile
the nonlinearity correction ensures an estimation of the gain that is
independent of signal, correcting a bias of more than 2.5% on gain
estimation.
Cosmological
simulations of the same spiral galaxy: satellite properties, the role of
baryonic physics and star formation history in shaping dark matter
cores/cusps
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Nuñez-Castiñeyra / E. Nezri / P. Mollitor /
L. Michel-Dansac
- J. Devriendt / R. Teyssier
Summary
We investigate the role of baryonic physics in shaping the
population, structure, and internal dynamics of galactic subhalos using
the Mochima suite of cosmological zoom-in simulations. A refined method
is developed to identify bound subhalo material by isolating the local
gravitational potential and applying multi-criteria phase-space
selection. This approach enables a robust characterisation of subhalo
properties across five baryonic runs with varying prescriptions for star
formation, and supernova and protostellar feedback, as well as a dark
matter-only baseline. At the population level, we find that host halo
concentration, modulated by baryonic feedback, is a key predictor of
subhalo survival. Subhalos with more massive stellar components exhibit
deeper internal potentials and enhanced resilience to tidal disruption.
At the structural level, we identify a broad diversity in inner dark
matter profiles, consistent with observations of dwarf galaxies. We show
that this diversity correlates with both star formation history and
environmental interaction. In particular, galaxies that form most of
their stars early tend to retain steep cusps, while those with extended
or recent star formation exhibit oscillating inner slopes shaped by
bursty feedback and tidal perturbations. These findings suggest that the
so-called “diversity problem” may reflect the complex interplay between
feedback history and gravitational environment, rather than a breakdown
of cold dark matter predictions.
Cluster
Ages to Reconstruct the Milky Way Assembly (CARMA) IV. Chrono-dynamics
of seven old star clusters in the Large Magellanic Cloud and the
peculiar origin of NGC 1841
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- F. Niederhofer / D. Massari / F. Aguado-Agelet / S. Cassisi
- A. Bellini / V. Kozhurina-Platais / M. Libralato / N. Kacharov
- A. Mucciarelli / M. Monelli / N. Bastian / I. Cabrera-Ziri
- E. Ceccarelli / M.-R. L. Cioni / F. Dresbach / M. Häberle
- S. Martocchia / S. Saracino
Summary
In this study, we report conclusive evidence for an ancient star
cluster that has been accreted by the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). By
leveraging observations from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), we
investigate the chrono-dynamical structure of a sample of seven old star
clusters within the LMC in a self-consistent way. The multi-epoch nature
of the dataset allowed the determination of high-precision proper
motions for the clusters. Employing an isochrone-fitting methodology, we
additionally infer from the deep high-resolution HST data homogeneous
and robust estimates for their distances, ages and metallicities.
Supplementing these data with literature line-of-sight velocities, we
investigate the full 3-dimensional dynamics of the clusters within the
frame of the LMC. With respect to the other clusters in our sample, NGC
1841 depicts a peculiar case. Its position in the age-metallicity plane,
that makes it about 1 Gyr younger than the other metal-poor LMC
clusters, but also its dynamical properties with a radial orbit almost
perpendicular to the LMC disc plane, clearly advocates for a different
origin. We thus conclude that NGC 1841 has likely been accreted by the
LMC from a smaller galaxy. The other clusters in our sample show
disc-like kinematics, with the case of NGC 2210 being peculiar, based on
its inclined orbit. Their coherent age-metallicity relation closely
resembles that of Gaia-Sausage-Enceladus globular clusters, thus
suggesting a similar early evolution for the two dwarf galaxies. We do
not find clear-cut chrono-kinematic evidence that NGC 2005 has been
accreted by the LMC as suggested by a previous study based on its
chemical abundance pattern. Regardless of its nature, its very old age
illustrates that peculiar chemical evolutions already emerge at very
early times.
Euclid
preparation. Methodology for validating the Euclid Catalogue of Galaxy
Clusters using external data
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / J.-B. Melin / S. A. Stanford / A. Widmer
- P. Tarrío / J. G. Bartlett / T. Sadibekova / G. W. Pratt
- M. Arnaud / F. Pacaud / T. H. Reiprich / A. Biviano
- S. Bardelli / S. Borgani / P.-S. Corasaniti / S. Ettori
- A. Finoguenov / Z. Ghaffari / P. A. Giles / M. Girardi
- J. B. Golden-Marx / A. H. Gonzalez / M. Klein / G. F. Lesci
- M. Maturi / B. J. Maughan / L. Moscardini / M. Pierre
- M. Radovich / P. Rosati / J. G. Sorce / E. Tsaprazi
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / E. Munari / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno
- N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo
- L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- C. Benoist / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / S.
Conseil
- A. R. Cooray / M. Costanzi / O. Cucciati / S. Davini
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / R.
Gavazzi
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / S. Hemmati
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E.
Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / G. A. Mamon
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / A. Montoro / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / C. Murray / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- A. Schneider / M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
We present our methodology for identifying known clusters as
counterparts to objects in the Euclid Catalogue of Galaxy Clusters
(ECGC). Euclid is expected to detect a large number of
optically-selected galaxy clusters over the approximately 14000 square
degrees of its extragalactic sky survey. Extending out well beyond
redshift unity, the catalogue will contain many new high-redshift
clusters, while at lower redshifts a fraction of the clusters will have
been observed in other surveys. Identifying these known clusters as
counterparts to the Euclid-detected clusters is an important step in the
validation and construction of the ECGC to augment information with
external observables. We present a set of catalogues and meta-catalogues
of known clusters that we have assembled for this step, and we
illustrate their application and our methodology using the Dark Energy
Survey Year 1 RedMaPPer cluster catalogue in lieu of the future ECGC. In
the process of this work, we have constructed and deliver an updated
EC-RedMaPPer catalogue with multi-wavelength counterparts.
Euclid:
Early Release Observations – The star cluster systems of the Local Group
dwarf galaxies IC 10 and NGC 6822
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. M. Howell / A. M. N. Ferguson / S. S. Larsen / A. Lançon
- F. Annibali / J.-C. Cuillandre / L. K. Hunt / D.
Martínez-Delgado
- D. Massari / T. Saifollahi / K. Voggel / B. Altieri
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / G. P. Candini
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / I. A. Zinchenko / J. Martín-Fleitas / V. Scottez
Summary
Star clusters are valuable indicators of galaxy evolution, offering
insights into the buildup of stellar populations across cosmic time.
Understanding intrinsic star cluster populations of dwarf galaxies is
particularly important given their role in the hierarchical growth of
larger systems. Using Euclid Early Release Observation data, we study
star clusters in two star-forming dwarf irregulars in the Local Group,
NGC 6822 and IC 10 [ (1–4)
(1–4)
 ]. With Euclid, clusters are resolved into
individual stars across the main bodies and haloes of both galaxies.
Visual inspection of
]. With Euclid, clusters are resolved into
individual stars across the main bodies and haloes of both galaxies.
Visual inspection of  images uncovers 30 new cluster
candidates in NGC 6822 and 16 in IC 10, from compact to extended
clusters. We re-evaluate literature candidates, producing combined
catalogues of 52 (NGC 6822) and 71 (IC 10) clusters with
confidence-based classifications. We present homogeneous photometry in
images uncovers 30 new cluster
candidates in NGC 6822 and 16 in IC 10, from compact to extended
clusters. We re-evaluate literature candidates, producing combined
catalogues of 52 (NGC 6822) and 71 (IC 10) clusters with
confidence-based classifications. We present homogeneous photometry in
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , and archival UBVRI data, alongside
size measurements and properties from BAGPIPES SED fitting. Synthetic
cluster injection shows our sample is
, and archival UBVRI data, alongside
size measurements and properties from BAGPIPES SED fitting. Synthetic
cluster injection shows our sample is  % complete to
% complete to  for ages
for ages  Myr, and
to
Myr, and
to  for
for  Gyr. IC 10 has more
young clusters than NGC 6822, extending to higher masses, consistent
with its starburst nature. Both dwarfs host several old massive (
Gyr. IC 10 has more
young clusters than NGC 6822, extending to higher masses, consistent
with its starburst nature. Both dwarfs host several old massive ( ) clusters, including an exceptional
) clusters, including an exceptional  cluster in NGC 6822’s outskirts. In NGC 6822, we
identify a previously undetected, old, extended cluster (
cluster in NGC 6822’s outskirts. In NGC 6822, we
identify a previously undetected, old, extended cluster ( pc). Using well-defined criteria, we identify 11
candidate GCs in NGC 6822 and eight in IC 10. Both galaxies have high
specific frequencies (
pc). Using well-defined criteria, we identify 11
candidate GCs in NGC 6822 and eight in IC 10. Both galaxies have high
specific frequencies ( ) but remain consistent with known GC
scaling relations at low luminosity [abridged].
) but remain consistent with known GC
scaling relations at low luminosity [abridged].
Articles for week 36 2025
Synergy
between Roman and PRIMA imaging capabilities for large extragalactic
surveys
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Médéric Boquien / Laure Ciesla / Roman Amestoy /
Jason Glenn
- Carlotta Gruppioni / John-David Smith
Summary
The Roman Space Telescope will be instrumental for characterizing the
physical properties of galaxies and understanding their evolution across
time. However, a complete view of galaxy star formation activity will
only be possible with the addition of far-infrared observations that a
telescope such as PRobe far-Infrared Mission for Astrophysics (PRIMA)
will be able to provide. Indeed, PRIMA’s far-infrared camera will be
highly sensitive to dust emission, whereas Roman will probe the stellar
emission in rest-frame optical and ultraviolet of distant galaxies. Our
aim here is to evaluate the advantage of combining large PRIMA and Roman
extragalactic surveys to retrieve the physical properties of galaxies
and compare them with what we would obtain using either dataset
separately. To do so, we use the Code Investigating Galaxy Emission
photometric modeling code to generate a far-ultraviolet to a
far-infrared synthetic set of dusty star-forming galaxies at redshifts
from 1.5 to 2.5, simulating the observations from the main extragalactic
surveys of PRIMA and Roman. We find that the PRIMA + Roman observations
can reliably retrieve the star formation rate, stellar masses, and dust
luminosity.
Improved
characterization of the TOI-2141 system: a dense sub-Neptune with
non-transiting inner and outer companions
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- R. Luque / K. W. F. Lam / J. Cabrera / A. Bonfanti
- Y. N. E. Eschen / G. Olofsson / W. Benz / N. Billot
- A. Brandeker / A. C. M. Correia / L. Fossati / D. Gandolfi
- H. P. Osborn / C. Pezzotti / S. G. Sousa / T. G. Wilson
- S. Wolf / Y. Alibert / R. Alonso / J. Asquier
- T. Bárczy / D. Barrado / S. C. C. Barros / W. Baumjohann
- F. Biondi / L. Borsato / C. Broeg / A. Collier Cameron
- Sz. Csizmadia / P. E. Cubillos / M. B. Davies / M.
Deleuil
- A. Deline / O. D. S. Demangeon / B.-O. Demory / A. Derekas
- B. Edwards / J. A. Egger / D. Ehrenreich / A. Erikson
- A. Fortier / M. Fridlund / K. Gazeas / M. Gillon
- M. Güdel / M. N. Günther / A. Heitzmann / Ch. Helling
- K. G. Isaak / T. Keller / L. L. Kiss / J. Korth
- J. Laskar / A. Lecavelier des Etangs / A. Leleu / M. Lendl
- D. Magrin / G. Mantovan / P. F. L. Maxted / B. Merín
- C. Mordasini / V. Nascimbeni / R. Ottensamer / I. Pagano
- E. Pallé / G. Peter / D. Piazza / G. Piotto
- D. Pollacco / D. Queloz / R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando
- H. Rauer / I. Ribas / N. C. Santos / G. Scandariato
- D. Ségransan / A. E. Simon / A. M. S. Smith / M. Stalport
- S. Sulis / Gy. M. Szabó / S. Udry / B. Ulmer
- S. Ulmer-Moll / V. Van Grootel / J. Venturini / E. Villaver
- N. A. Walton / D. Wolter
Summary
We aim to refine the fundamental parameters of the TOI-2141 planetary
system, which includes a transiting sub-Neptune orbiting a Sun-like star
in a relatively long orbit of 18.26 days, by combining new photometric
and spectroscopic observations. We analyze new space-based photometry
from TESS and CHEOPS as well as 61 radial velocity measurements from
HARPS-N. We perform individual and joint photometric and RV analyses
using several modeling tools within a Bayesian model comparison
framework. We refine the radius and mass of the transiting planet
TOI-2141 b to 3.15  0.04
0.04  and 20.1
and 20.1  1.6
1.6  , respectively,
five and two times more precise than the previously reported values. Our
radial velocity analysis reveals two additional non-transiting
companions with orbital periods of 5.46 and 60.45 days. Despite the
innermost planet’s high geometric transit probability, we find no
evidence for transits in the photometric data. The bulk properties of
TOI-2141 b suggest a significant volatile envelope atop an Earth-like
core, with modeling indicating a hydrogen-rich atmosphere that may have
experienced mild photoevaporation over the system’s history. Planets b
and c must exhibit a modest mutual inclination of at least 2.4
degrees.
, respectively,
five and two times more precise than the previously reported values. Our
radial velocity analysis reveals two additional non-transiting
companions with orbital periods of 5.46 and 60.45 days. Despite the
innermost planet’s high geometric transit probability, we find no
evidence for transits in the photometric data. The bulk properties of
TOI-2141 b suggest a significant volatile envelope atop an Earth-like
core, with modeling indicating a hydrogen-rich atmosphere that may have
experienced mild photoevaporation over the system’s history. Planets b
and c must exhibit a modest mutual inclination of at least 2.4
degrees.
Need
for PRIMA to understand the nature and ISM physical conditions of
HST-dark galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Carlotta Gruppioni / Lee Armus / Matthieu Bethermin / Laura
Bisigello
- Denis Burgarella / Francesco Calura / Ivan
Delvecchio / Andrea Enia
- Andreas Faisst / Francesca Pozzi / Giulia Rodighiero / Alberto
Traina
- Livia Vallini
Summary
One of the main open issues in galaxy formation and evolution is the
early assembly of the most massive galaxies and their contribution to
the stellar mass and star formation rate densities at early epochs.
Massive red sources already in place at z > 2 to 3 have been found in
deep Spitzer-IRAC and ALMA surveys. They are often called optically and
near-IR dark, or HST-dark, being undetected even in the deepest HST
frames. The submillimeter (i.e., ALMA) detection of these sources
confirms their high-z dusty nature: they are massive (e.g., log(M*/Msun)
> 10) and dusty star-forming galaxies with estimated redshifts in the
2.5 to 7 range. They seem to lie mostly below the main sequence (MS) of
star-forming galaxies and show gas depletion times <1 Gyr. Imaging
with the PRIMA/PRIMAger instrument over the full 25 to 265 micron range
will allow us to characterize their still uncovered spectral energy
distributions between JWST and ALMA spectral windows, probing their dust
content and properties (e.g., temperature, mass), whereas spectroscopic
observations with FIRESS will be the key to investigate the nature of
their powering source (e.g., AGN or star formation) and to study the
physics of their ISM, by detecting and measuring fine structure lines in
the mid- and far-IR domain.
PRIMA:
PRIMAger, a far-infrared hyperspectral and polarimetric instrument
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Laure Ciesla / Charles Darren Dowell / Marc Sauvage
/ Denis Burgarella
- Jochem Baselmans / Matthieu Béthermin / Jeffrey T. Booth / Charles
M. Bradford
- Florent Canourgues / Ivan Charles / Anne Costille /
Thomas Essinger-Hileman
- Lorenza Ferrari / Johan Floriot / Marc Foote /
Jason Glenn
- Renaud Goullioud / Matt Griffin / Oliver Krause / Willem
Jellema
- Elizabeth Luthman / Laurent Martin / Margaret
Meixner / Tony Pamplona
- Klaus M. Pontoppidan / Alexandra Pope / Thomas Prouvé / Jennifer
Rocca
- Johannes Staguhn / Carole Tucker
Summary
The PRobe far-Infrared Mission for Astrophysics (PRIMA) is an
infrared observatory for the next decade, currently in Phase A, with a
1.8m telescope actively cooled to 4.5K. On board, an infrared camera,
PRIMAger, equipped with ultra-sensitive kinetic inductance detector
(KID) arrays, will provide observers with coverage of mid-infrared to
far-infrared wavelengths from 24 to 264 microns. PRIMAger will offer two
imaging modes: the Hyperspectral mode will cover the 24-84 microns
wavelength range with a spectral resolution R=8, while the Polarimetric
mode will provide polarimetric imaging in 4 broad bands, from 80 to 264
microns. These observational capabilities have been tailored to answer
fundamental astrophysical questions such as black hole and
star-formation co-evolution in galaxies, the evolution of small dust
grains over a wide range of redshifts, and the effects of interstellar
magnetic fields in various environments, as well as to open a vast
discovery space with versatile photometric and polarimetric
capabilities. PRIMAger is being developed by an international
collaboration bringing together French institutes (Laboratoire
d’Astrophysique de Marseille and CEA) through the center National
d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES, France), the Netherlands Institute for Space
Research (SRON, Netherlands), and the Cardiff University (UK) in Europe,
as well as the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and Goddard Space Flight
Center (GSFC) in the USA.
CONCERTO:
forward modeling of interferograms for calibration
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Lundgren / A. Beelen / G.
Lagache / F.-X. Desert
- A. Fasano / J. Macias-Perez / A. Monfardini / P. Ade
- M. Aravena / E. Barria / A. Benoit / M. Bethermin
- J. Bounmy / O. Bourrion / G. Bres / C. De Breuck
- M. Calvo / A. Catalano / C. Dubois / C. A Duran
- T. Fenouillet / J. Garcia / G.
Garde / J. Goupy
- C. Hoarau / W. Hu / J.-C. Lambert / F.
Levy-Bertrand
- J. Marpaud / R. Parra / G. Pisano / N. Ponthieu
- L. Prieur / D. Quinatoa / S. Roni / S. Roudier
- D. Tourres / C. Tucker / M. Van Cuyck
Summary
The CarbON [CII] line in post-rEionisation and ReionisaTiOn epoch
(CONCERTO) instrument is a low-resolution mapping Fourier-transform
spectrometer, based on lumped-element kinetic inductance detector
(LEKID) technology, operating at 130- 310 GHz. It was installed on the
12-meter APEX telescope in Chile in April 2021 and operated until
December 2022. CONCERTO’s main science goal is to constrain the [CII]
line fluctuations at high redshift. To reach that goal CONCERTO observed
1.4 deg2 in the COSMOS field. To ensure accurate calibration of the
data, we have developed a forward model capable of simulating both the
spectral response and the corresponding interferograms for each scan of
observation in the COSMOS field. We present the modeling approach that
enables us to reproduce the expected instrument outputs under controlled
input conditions and provides a framework for the different calibration
steps, including the absolute brightness calibration of the spectra. We
constructed a dedicated analysis pipeline to characterize the raw
interferometric data (interferograms) obtained under a broad range of
atmospheric conditions at APEX. Using the forward model, we measured the
interferogram alignment with the optical path difference (zero path
difference, ZPD) and the relative response of each KID (flatfield).
Together, these elements enable a robust characterization of the
instrument’s spectral brightness calibration.
Dust
stripping in cluster galaxies: a PRIMA perspective
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alessandro Boselli / Marc Sauvage / Laure
Ciesla
Summary
The evolution of galaxies in rich environments such as clusters and
groups can be significantly perturbed during their interaction with
nearby companions (tidal interactions) or with the hot intracluster
medium (ICM) trapped within the gravitational potential well of the
massive host halo (ram pressure stripping). Both gravitational
perturbations and the external pressure exerted by the hot ICM on the
galaxy ISM during its high velocity journey within the cluster are able
to remove most, if not all of it, producing extended tails of stripped
material. Along with the different gas phases (cold atomic and
molecular, ionised, hot), these perturbations can remove also dust, thus
contributing to the pollution of the ICM. Probe Infrared Mission for
Astrophysics (PRIMA) is offering a unique opportunity to observe this
dust component, a crucial ingredient in the energetic balance of the
stripped gas. We analyse how the two instruments onboard of PRIMA,
PRIMAger (in imaging and polarimetric mode) and far-IR enhanced survey
spectrometer (FIRESS), can be used to observe a selected sample of ram
pressure stripped tails detected at other frequencies (HI, CO, Halpha,
X-rays). These data can be used to determine the relative distribution
of the dust component with respect to that of the other gas phases,
derive its temperature, calculate different gas physical parameters
(electron density, photoelectric heating efficiency, gas metallicity),
and quantify the strength of the turbulent magnetic fields, all
fundamental parameters used to constrain the most recent hydrodynamic
simulations of gas stripping in clusters. The ultimate aim of this
research is that of understanding the fate of the cold stripped material
once mixed with the surrounding hot medium and study under which
condition it can collapse into giant molecular clouds (GMC) to form new
stars.
The
Far-Infrared Enhanced Survey Spectrometer (FIRESS) for PRIMA: Science
Drivers
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Klaus M. Pontoppidan / Alberto Bolatto / J D Smith / C. M.
- Bradford / Cara Battersby / Alexandra Pope / Tiffany Kataria
- Jason Glenn / Margaret Meixner / Lee Armus / Jochem Baselmans
- Edwin A. Bergin / Denis Burgurella / Laure Ciesla /
L. Ilsedore Cleeves
- Anna DiGiorgio / Carlotta Gruppioni / Thomas Henning / Brandon
Hensley
- Willem Jellema / Oliver Krause / Elisabeth Mills / Arielle
Moullet
- Marc Sauvage / Rachel Somerville / Johannes Staguhn / Steve
Unwin
Summary
We present the science drivers for the Far-Infrared Enhanced Survey
Spectrometer (FIRESS), one of two science instrument on the PRobe
Infrared Mission for Astrophysics (PRIMA). FIRESS is designed to meet
science objectives in the areas of the origins of planetary atmospheres,
the co-evolution of galaxies and supermassive black holes, and the
buildup of heavy elements in the Universe. In addition to these drivers,
FIRESS is envisioned as a versatile far-infrared spectrometer, capable
of addressing science questions in most areas of astrophysics and
planetary astronomy as part of a dominant General Observer (GO) program
with 2/3 of the current science cases using FIRESS. We summarize how the
instrument design choices and parameters enable the main science drivers
as well as a broad and vibrant GO program.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. Muñoz López / Davor Krajnović / B. Epinat / T.
Urrutia
- I. Pessa / T. Contini / T. Nanayakkara / J. Pharo
- T. S. Gonçalves / Tran Thi Thai / N. F. Bouché
Summary
We derive and analyse the star formation histories of 393
intermediate-redshift (0.1  z
z  0.9) galaxies with
stellar masses between $
0.9) galaxies with
stellar masses between $ ^{8}$ - 10
^{8}$ - 10 M
M . We probe a
cosmic time of approximately 6 Gyr and a range of environments, from
field (low-density systems) to rich groups (high-density systems). We
find that the galaxies’ stellar mean ages, metallicities, and star
formation rates (SFRs) follow similar trends to galaxies as those
characterising the nearby Universe. We modelled the derived SFRs,
quantifying and characterising the number of star-forming episodes
(SFEs). We found that more than 85
. We probe a
cosmic time of approximately 6 Gyr and a range of environments, from
field (low-density systems) to rich groups (high-density systems). We
find that the galaxies’ stellar mean ages, metallicities, and star
formation rates (SFRs) follow similar trends to galaxies as those
characterising the nearby Universe. We modelled the derived SFRs,
quantifying and characterising the number of star-forming episodes
(SFEs). We found that more than 85 of the galaxies have more
than one event of star formation, typically described with an
exponentially decaying SFR and subsequent Gaussian-like episode(s) of
star formation. We also observe that massive galaxies have fewer SFEs
than low-mass systems and that they form their stellar mass and reach
quiescence faster than lower mass galaxies. Moreover, the history of
mass assembly for the most massive galaxies in the sample can be
described with only one episode of star formation in the early Universe,
which we detected as an exponential decrease that was longer in duration
than subsequent SF events. This early event has typically been completed
by z$$3 and it accounts for a high fraction of the total stellar mass,
from $
of the galaxies have more
than one event of star formation, typically described with an
exponentially decaying SFR and subsequent Gaussian-like episode(s) of
star formation. We also observe that massive galaxies have fewer SFEs
than low-mass systems and that they form their stellar mass and reach
quiescence faster than lower mass galaxies. Moreover, the history of
mass assembly for the most massive galaxies in the sample can be
described with only one episode of star formation in the early Universe,
which we detected as an exponential decrease that was longer in duration
than subsequent SF events. This early event has typically been completed
by z$$3 and it accounts for a high fraction of the total stellar mass,
from $ %$ for low-mass galaxies to more than
50
%$ for low-mass galaxies to more than
50 for higher-mass galaxies. We
also analysed the dependence of stellar population parameters with the
various environments probed by the sample, finding no significant
correlations between different group environments; however, our field
galaxies are generally distinct from group galaxies in terms of the
mass, metallicity, stellar ages, and formation timescales. We discuss
possible biases in the sample selection and examine how representative
our galaxies are of the overall galaxy population.
for higher-mass galaxies. We
also analysed the dependence of stellar population parameters with the
various environments probed by the sample, finding no significant
correlations between different group environments; however, our field
galaxies are generally distinct from group galaxies in terms of the
mass, metallicity, stellar ages, and formation timescales. We discuss
possible biases in the sample selection and examine how representative
our galaxies are of the overall galaxy population.
A
milliarcsecond localization associates FRB 20190417A with a compact,
luminous persistent radio source and an extreme magneto-ionic
environment
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alexandra M. Moroianu / Shivani Bhandari / Maria R. Drout / Jason W.
T. Hessels
- Danté M. Hewitt / Franz Kirsten / Benito Marcote / Ziggy
Pleunis
- Mark P. Snelders / Navin Sridhar / Uwe Bach / Emmanuel K.
Bempong-Manful
- Vladislavs Bezrukovs / Richard Blaauw / Justin D. Bray / Salvatore
Buttaccio
- Shami Chatterjee / Alessandro Corongiu / Roman Feiler / Bryan M.
Gaensler
- Marcin P. Gawroński / Marcello Giroletti / Adaeze L. Ibik / Ramesh
Karuppusamy
- Mattias Lazda / Calvin Leung / Michael Lindqvist / Kiyoshi W.
Masui
- Daniele Michilli / Kenzie Nimmo / Omar S.
Ould-Boukattine / Ayush Pandhi
- Zsolt Paragi / Aaron B. Pearlman / Weronika Puchalska / Paul
Scholz
- Kaitlyn Shin / Jurjen J. Sluman / Matteo Trudu / David
Williams-Baldwin
- Jun Yang
Summary
We report the milliarcsecond localization of a high (1379 pc/cc)
dispersion measure (DM) repeating fast radio burst, FRB 20190417A.
Combining European VLBI Network detections of five repeat bursts, we
confirm the FRB’s host to be a low-metallicity, star-forming dwarf
galaxy at z = 0.12817, analogous to the hosts of FRBs 20121102A,
20190520B and 20240114A. We also show that FRB 20190417A is spatially
coincident with a compact, luminous persistent radio source (PRS).
Visibility-domain model fitting constrains the transverse physical size
of the PRS to < 23.1 pc and yields an integrated flux density of
191(39) microJy at 1.4 GHz. Though we do not find significant evidence
for DM evolution, FRB 20190417A exhibits a time-variable rotation
measure (RM) ranging between +3958(11) and +5061(24) rad/m2 over three
years. We find no evidence for intervening galaxy clusters in the FRB’s
line-of-sight and place a conservative lower limit on the rest-frame
host DM contribution of 1212.0 pc/cc (90% confidence) – the largest
known for any FRB so far. This system strengthens the emerging picture
of a rare subclass of repeating FRBs with large and variable RMs,
above-average host DMs, and luminous PRS counterparts in metal-poor
dwarf galaxies. We explore the role of these systems in the broader FRB
population, either as the youngest or most extreme FRB sources, or as a
distinct engine for FRB emission.
GWTC-4.0:
Constraints on the Cosmic Expansion Rate and Modified Gravitational-wave
Propagation
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- K. G. Arun / G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea
- M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone
- F. Attadio / F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone
- E. A. Avila / S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae
- S. Bagnasco / L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka
- A. M. Baker / K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi
- N. Baldicchi / M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer
- S. Banagiri / B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste
- P. Baral / M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish
- D. Barker / N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone
- B. Barr / L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta
- A. M. Bartoletti / M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev
- R. Bassiri / A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi
- J. C. Bayley / A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan
- V. M. Bedakihale / F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli
- A. S. Bell / D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit
- I. Bentara / J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera
- F. Bergamin / B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz
- C. P. L. Berry / D. Bersanetti / T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini
- J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins
- R. Bhandare / R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya
- S. Bhaumik / V. Biancalana / A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko
- M. Bilicki / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti / S. Bini
- C. Binu / S. Biot / O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu
- A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard / S. Blaber
- J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair
- N. Bode / N. Boettner / G. Boileau / M. Boldrini
- G. N. Bolingbroke / A. Bolliand / L. D. Bonavena /
R. Bondarescu
- F. Bondu / E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino
- R. Bonnand / A. Borchers / S. Borhanian / V. Boschi
- S. Bose / V. Bossilkov / Y. Bothra / A. Boudon
- L. Bourg / M. Boyle / A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia
- P. R. Brady / A. Branch / M. Branchesi / I. Braun
- T. Briant / A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill
- E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown
- M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett / G. Bruno / R. Bruntz
- J. Bryant / Y. Bu / F. Bucci / J. Buchanan
- O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik / H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno
- K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio / D. Buskulic / C. Buy
- R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies / R. Cabrita / V.
Cáceres-Barbosa
- L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / A. Calafat
- T. A. Callister / E. Calloni / S. R. Callos / M. Canepa
- G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon / H. Cao / L. A. Capistran
- E. Capocasa / E. Capote / G. Capurri / G. Carapella
- F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara / J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson
- M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter
- G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos / J. Casanueva Diaz / C.
Casentini
- S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri
- A. Ceja / G. Cella / P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini
- N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi / A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty
- S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C. L. Chan / M.
Chan
- K. Chang / S. Chao / P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin
- C. Chatterjee / Debarati Chatterjee / Deep Chatterjee / M.
Chaturvedi
- S. Chaty / K. Chatziioannou / A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen
- D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen / S. Chen
- Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa
- H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini
- A. Chiba / A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo
- C. Chou / S. Choudhary / N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua
- G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi
- B. Cirok / F. Clara / J. A. Clark / T. A. Clarke
- P. Clearwater / S. Clesse / F. Cleva / E. Coccia
- E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace / E. Colangeli
- M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette / J. Collins / S. Colloms
- A. Colombo / C. M. Compton / G. Connolly / L. Conti
- T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish
- I. Coronado / A. Corsi / R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin
- A. Couineaux / P. Couvares / D. M. Coward / R. Coyne
- A. Cozzumbo / J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton / P.
Cremonese
- S. Crook / R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell
- T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming / E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato
- L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton / S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya
- B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann
- K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez / R. Das / A. Dasgupta
- V. Dattilo / A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave
- A. Davenport / M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis
- L. Davis / M. C. Davis / P. Davis / E. J. Daw
- M. Dax / J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix
- M. De Laurentis / F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre / W. Del Pozzo
- A. Demagny / F. De Marco / G. Demasi / F. De Matteis
- N. Demos / T. Dent / A. Depasse / N. DePergola
- R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi / M. Desai
- R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone / R. De Simone / A. Dhani
- R. Diab / M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron
- T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni
- T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha / J. Ding / S. Di Pace
- I. Di Palma / D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti
- A. Dmitriev / J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen
- E. Dohmen / A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza / L. D’Onofrio
- F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney / S. Doravari
- O. Dorosh / W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers
- L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne / D. D’Urso
- P. Dutta Roy / H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa
- M. Ebersold / T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / A. Effler
- J. Eichholz / H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann / M. Emma
- K. Endo / R. Enficiaud / L. Errico / R. Espinosa
- M. Esposito / R. C. Essick / H. Estellés / T. Etzel
- M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga
- F. Fabrizi / V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah
- B. Farr / W. M. Farr / G. Favaro / M. Favata
- M. Fays / M. Fazio / J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer
- R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes / T. Fernandes
- D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro
- P. Figura / A. Fiori / I. Fiori / M. Fishbach
- R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio
- S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming / E. Floden / H. Fong
- J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes / C. Foo / B. Fornal
- K. Franceschetti / F. Frappez / S. Frasca / F. Frasconi
- J. P. Freed / Z. Frei / A. Freise / O. Freitas
- R. Frey / W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov
- G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii / T. Fujimori
- P. Fulda / M. Fyffe / B. Gadre / J. R. Gair
- S. Galaudage / V. Galdi / R. Gamba / A. Gamboa
- S. Gamoji / D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa
- J. García-Bellido / C. García-Quirós / J. W. Gardner / K. A.
Gardner
- S. Garg / J. Gargiulo / X. Garrido / A. Garron
- F. Garufi / P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley
- F. Gautier / V. Gayathri / T. Gayer / G. Gemme
- A. Gennai / V. Gennari / J. George / R. George
- O. Gerberding / L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh
- Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh
- J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson / C. Gier
- S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey
- R. V. Godley / P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz
- J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov / G. González
- P. Goodarzi / S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin
- R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / A. Grado
- V. Graham / A. E. Granados / M. Granata / V. Granata
- S. Gras / P. Grassia / J. Graves / C. Gray
- R. Gray / G. Greco / A. C. Green / L. Green
- S. M. Green / S. R. Green / C. Greenberg / A. M. Gretarsson
- H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith / H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani
- C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald / D. Guerra
- D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati
- F. Gulminelli / H. Guo / W. Guo / Y. Guo
- Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta / S. K. Gupta
- V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez
- N. Guttman / F. Guzman / D. Haba / M. Haberland
- S. Haino / E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond
- M. Haney / J. Hanks / C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam
- O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen / J. Hanson
- S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar
- K. Haris / I. Harley-Trochimczyk / T. Harmark / J. Harms
- G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry / J. Hart / B. Haskell
- C. J. Haster / K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama
- M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze / J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann
- F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming / O.
Henderson-Sapir
- M. Hendry / I. S. Heng / M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw
- M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt / J. Heynen / J. Heyns
- S. Higginbotham / S. Hild / S. Hill / Y. Himemoto
- N. Hirata / C. Hirose / D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan
- N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows / D. E. Holz / L. Honet
- D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough / S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard
- E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi
- H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu
- W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang
- Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey / V. Hui
- S. Husa / R. Huxford / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo
- M. Ianni / G. Iannone / J. Iascau / K. Ide
- R. Iden / A. Ierardi / S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku
- Y. Inoue / G. Iorio / P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal
- J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa / M. Isi / K. S. Isleif
- Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet
- P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot / S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav
- M. Jain / T. Jain / A. L. James / K. Jani
- J. Janquart / N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski
- R. Jaume / W. Javed / A. Jennings / M. Jensen
- W. Jia / J. Jiang / H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns
- N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston / N. Johny
- D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones / R. Jones / H. E. Jose
- P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi / G. Joubert / J. Ju
- L. Ju / K. Jung / J. Junker / V. Juste
- H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita / I. Kaku / V. Kalogera
- M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy
- G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty
- S. J. Kapadia / D. P. Kapasi / M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack
- H. Kato / T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman
- R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel
- L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington / F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani
- J. S. Key / R. Khadela / S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar
- F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan / T. Khanam / M. Khursheed
- N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim
- J. C. Kim / K. Kim / M. H. Kim / S. Kim
- Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball / K. Kimes / M. Kinnear
- J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox
- N. Knust / K. Kobayashi / S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek
- K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama / S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou
- A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori / A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos
- L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko / X. Kou / A. Koushik
- N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam / T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak
- S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker
- A. Królak / K. Kruska / J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn
- S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan / Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar
- Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar
- J. Kume / K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi
- S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak / K. Kwan / S. Kwon
- G. Lacaille / D. Laghi / A. H. Laity / E. Lalande
- M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry / B. B. Lane
- R. N. Lang / J. Lange / R. Langgin / B. Lantz
- I. La Rosa / J. Larsen / A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky
- J. Lawrence / M. Laxen / C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini
- C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci / L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche
- H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee / J. Lee / K. Lee
- R.-K. Lee / R. Lee / Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee
- Y. Lee / I. N. Legred / J. Lehmann / L. Lehner
- M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître / M. Lenti / M. Leonardi
- M. Lequime / N. Leroy / M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre
- M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin / K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li
- K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li / X. Li / Y. Li
- Z. Li / A. Lihos / E. T. Lin / F. Lin
- L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin / C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker
- A. Liu / G. C. Liu / Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal
- J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L. Lo / J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G.
Loggins
- M. R. Loizou / L. T. London / A. Longo / D. Lopez
- M. Lopez Portilla / M. Lorenzini / A. Lorenzo-Medina / V.
Loriette
- M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / E. Lotti / T. P. Lott
- J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto / N. Low
- N. Lu / L. Lucchesi / H. Lück / D. Lumaca
- A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier / R. Macas / M. MacInnis
- D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet / K. Maeda
- S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee / E. Maggio
- R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh / M. Maini
- S. Majhi / E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem / D. Malakar
- J. A. Malaquias-Reis / U. Mali / S. Maliakal / A. Malik
- L. Mallick / A.-K. Malz / N. Man / M. Mancarella
- V. Mandic / V. Mangano / B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell
- M. Manske / M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli / C. Marinelli
- F. Marion / A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros
- S. Marsat / F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin
- B. B. Martinez / D. A. Martinez / M. Martinez / V. Martinez
- A. Martini / J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx
- L. Massaro / A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni
- T. Matcovich / M. Matiushechkina / L. Maurin / N. Mavalvala
- N. Maxwell / G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland
- S. McCormick / L. McCuller / S. McEachin / C. McElhenny
- G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver
- A. McLeod / I. McMahon / T. McRae / R. McTeague
- D. Meacher / B. N. Meagher / R. Mechum / Q. Meijer
- A. Melatos / C. S. Menoni / F. Mera / R. A. Mercer
- L. Mereni / K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou
- J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui / C. Messick / B. Mestichelli
- M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske / A. Miani
- H. Miao / C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton
- D. P. Mihaylov / A. L. Miller / S. J. Miller / M. Millhouse
- E. Milotti / V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov / E. M. Minihan
- Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu
- A. Mishra / C. Mishra / T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell
- J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov / K. Mitsuhashi
- R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa / S. Miyoki / A. Miyoko
- G. Mo / L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite
- M. Molina-Ruiz / M. Mondin / M. Montani / C. J. Moore
- D. Moraru / A. More / S. More / C. Moreno
- E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno / A. Moreso Serra / S. Morisaki
- Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras / A. Moscatello / M. Mould
- B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry / L. Muccillo / F. Muciaccia
- D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma Mukherjee / Subroto
Mukherjee
- Suvodip Mukherjee / N. Mukund / A. Mullavey / H. Mullock
- J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli / M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray
- D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan
- K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura / H. Nakano / M. Nakano
- D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi / V. Napolano / P. Narayan
- I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa / H. Narola / L. Naticchioni
- R. K. Nayak / L. Negri / A. Nela / C. Nelle
- A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery / A. Neunzert
- S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen
- Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa / S. Nissanke / W. Niu
- F. Nocera / J. Noller / M. Norman / C. North
- J. Novak / R. Nowicki / J. F. Nuño Siles / L. K. Nuttall
- K. Obayashi / J. Oberling / J. O’Dell / E. Oelker
- M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan / T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi
- F. Ohme / R. Oliveri / R. Omer / B. O’Neal
- M. Onishi / K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly / M. Orselli
- R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / S. Oshino / C. Osthelder
- I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway / A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier
- B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki / A. E. Pace / R. Pagano
- M. A. Page / A. Pai / L. Paiella / A. Pal
- S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma
- C. Palomba / P. Palud / H. Pan / J. Pan
- K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey / Swadha Pandey
- P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone / B. C. Pant
- F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri / F. Paoletti / A. Paolone
- A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini / G.
Papigkiotis
- A. Paquis / A. Parisi / B.-J. Park / J. Park
- W. Parker / G. Pascale / D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti
- R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger / D. Passuello / O. Patane
- A. V. Patel / D. Pathak / A. Patra / B. Patricelli
- B. G. Patterson / K. Paul / S. Paul / E. Payne
- T. Pearce / M. Pedraza / A. Pele / F. E. Peña Arellano
- X. Peng / Y. Peng / S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar
- A. Perego / Z. Pereira / C. Périgois / G. Perna
- A. Perreca / J. Perret / S. Perriès / J. W. Perry
- D. Pesios / S. Peters / S. Petracca / C. Petrillo
- H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham / K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon
- H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli / L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni
- M. Pichot / M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini
- G. Pierra / V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas
- F. Pilo / L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto
- B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi
- E. Placidi / M. L. Planas / W. Plastino / C. Plunkett
- R. Poggiani / E. Polini / J. Pomper / L. Pompili
- J. Poon / E. Porcelli / E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky
- R. Poulton / J. Powell / G. S. Prabhu / M. Pracchia
- B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati / K. Prasai
- R. Prasanna / P. Prasia / G. Pratten / G. Principe
- G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence
- A. Puecher / J. Pullin / P. Puppo / M. Pürrer
- H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke
- P. J. Quinonez / N. Qutob / R. Rading / P. Raffai
- I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari
- K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / M. Ramos Arevalo / A.
Ramos-Buades
- S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto
- A. Ravichandran / A. Ray / V. Raymond / M. Razzano
- J. Read / T. Regimbau / S. Reid / C. Reissel
- D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu / A. Revilla Peña
- R. Reyes / L. Ricca / F. Ricci / M. Ricci
- A. Ricciardone / J. Rice / J. W. Richardson / M. L. Richardson
- A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley / S. Rinaldi
- J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet / M. Robinson
- A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins / R. Romano
- A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw / J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini
- T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa / T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose
- D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross / M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan
- S. K. Roy / S. Roy / D. Rozza / P. Ruggi
- N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales / K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev
- T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh / S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah
- S. Saha / T. Sainrat / S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai
- Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou / S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia
- F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi / M. Saleem / F. Salemi
- M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe / S. Salvador / A. Salvarese
- A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez / E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez
- N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders / E. M. Sänger / F.
Santoliquido
- F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan / N. Sarin / P. Sarkar
- A. Sasli / P. Sassi / B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash
- R. Sato / S. Sato / Yukino Sato / Yu Sato
- O. Sauter / R. L. Savage / T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant
- S. Sayah / V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel
- A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt
- R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield / K.
Schouteden
- B. W. Schulte / B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi
- J. Scott / S. M. Scott / R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu
- M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers / N. Sembo
- A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo / V. Sequino
- M. Serra / A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah
- M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao / A. K. Sharma / Preeti Sharma
- Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma / S. Sharma Chaudhary / P.
Shawhan
- N. S. Shcheblanov / E. Sheridan / Z.-H. Shi / M. Shikauchi
- R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai / S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker
- D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short / S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider
- H. Siegel / D. Sigg / L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri
- M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer / Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh
- D. Singh / N. Singh / S. Singh / A. M. Sintes
- V. Sipala / V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater
- T. J. Slaven-Blair / J. Smetana / J. R. Smith / L. Smith
- R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith / S. Soares de Albuquerque Filho / M.
Soares-Santos
- K. Somiya / I. Song / S. Soni / V. Sordini
- F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani / F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo
- A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli / A. K. Srivastava / F.
Stachurski
- C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer / N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner
- S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas / P. Stevens / S. P. Stevenson
- M. StPierre / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk / A. L. Stuver
- M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / Y. Sudo / N. Sueltmann
- L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun / L. Sun
- S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton
- K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx
- M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi
- K. Takada / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi / A. Takamori
- S. Takano / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita / I. Takimoto Schmiegelow
- M. Takou-Ayaoh / C. Talbot / M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini
- D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka / S. Tanioka
- D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao / R. D. Tapia
- E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto / A. Taruya / J. D. Tasson
- J. G. Tau / D. Tellez / R. Tenorio / H. Themann
- A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M. Thomas / M.
Thomas
- P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu / K. A. Thorne
- E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari / Pawan Tiwari
- Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd
- M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland / A. E. Tolley
- T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura / H. Tong
- C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie / I. Tosta e Melo
- E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran / A. Trapananti
- R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor / M. Trevor
- M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian / A. Trovato
- L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang / S. Tsuchida
- L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi / C. Turski
- H. Ubach / N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall
- T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim / L. E. Uronen
- T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya
- G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia / M. Valentini
- S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan / M. van Dael
- E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / M.
van der Sluys
- A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra / M. VanDyke
- H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J.
Vanier
- M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro
- A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio
- G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis
- R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt
- B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets
- A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva Espinosa / V.
Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / S. Vitale
- H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel
- W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack
- L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner / L. Wallace
- E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang
- Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner / M. Was
- T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai / B. Weaver
- S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein
- R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette / J. T. Whelan
- B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens / D. Wilken
- A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams / M. J. Williams
- N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils
- L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf
- G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong
- I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters / J. L. Wright
- M. Wright / B. Wu / C. Wu / D. S. Wu
- H. Wu / K. Wu / Q. Wu / Y. Wu
- Z. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu
- Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto
- T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki / T. Yan
- K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough / J. Yebana
- S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin / J. Yokoyama
- T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara / M. Zanolin
- M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli
- M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / L. Zhang / N. Zhang
- R. Zhang / T. Zhang / C. Zhao / Yue Zhao
- Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng / H. Zhong
- H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman
- L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
We analyze data from 142 of the 218 gravitational-wave (GW) sources
in the fourth LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Collaboration (LVK) Gravitational-Wave
Transient Catalog (GWTC-4.0) to estimate the Hubble constant  jointly with the population
properties of merging compact binaries. We measure the luminosity
distance and redshifted masses of GW sources directly; in contrast, we
infer GW source redshifts statistically through i) location of features
in the compact object mass spectrum and merger rate evolution, and ii)
identifying potential host galaxies in the GW localization volume.
Probing the relationship between source luminosity distances and
redshifts obtained in this way yields constraints on cosmological
parameters. We also constrain parameterized deviations from general
relativity which affect GW propagation, specifically those modifying the
dependence of a GW signal on the source luminosity distance. Assuming
our fiducial model for the source-frame mass distribution and using GW
candidates detected up to the end of the fourth observing run (O4a),
together with the GLADE+ all-sky galaxy catalog, we estimate
jointly with the population
properties of merging compact binaries. We measure the luminosity
distance and redshifted masses of GW sources directly; in contrast, we
infer GW source redshifts statistically through i) location of features
in the compact object mass spectrum and merger rate evolution, and ii)
identifying potential host galaxies in the GW localization volume.
Probing the relationship between source luminosity distances and
redshifts obtained in this way yields constraints on cosmological
parameters. We also constrain parameterized deviations from general
relativity which affect GW propagation, specifically those modifying the
dependence of a GW signal on the source luminosity distance. Assuming
our fiducial model for the source-frame mass distribution and using GW
candidates detected up to the end of the fourth observing run (O4a),
together with the GLADE+ all-sky galaxy catalog, we estimate  km s
km s Mpc
Mpc . This value is reported
as a median with 68.3% (90%) symmetric credible interval, and includes
combination with the
. This value is reported
as a median with 68.3% (90%) symmetric credible interval, and includes
combination with the  measurement from GW170817 and its
electromagnetic counterpart. Using a parametrization of modified GW
propagation in terms of the magnitude parameter
measurement from GW170817 and its
electromagnetic counterpart. Using a parametrization of modified GW
propagation in terms of the magnitude parameter  , we estimate
, we estimate  , where
, where  recovers the
behavior of general relativity.
recovers the
behavior of general relativity.
LOFAR
constraints on the repetition & environments of CHIME FRBs
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Pragya Chawla / Akshatha Gopinath / Ninisha Manaswini / Cees
Bassa
- Jason Hessels / Vlad Kondratiev / Daniele Michilli
/ Ziggy Pleunis
Summary
The behaviour of fast radio bursts (FRBs) at radio frequencies
<400 MHz is not well understood due to very few detections, with only
two known sources detected below 300 MHz. Characterising low-frequency
emission of FRBs is vital for understanding FRB emission mechanisms and
circumburst environments. We robustly characterise the 150 MHz activity
CHIME-detected FRB sources relative to their 600 MHz activity – using
their non-detection in 473 h of archival observations from the Low
Frequency Array (LOFAR) Tied-Array All-Sky Survey (LOTAAS), and 252 h of
LOFAR observations of 14 repeating FRB sources, the largest sub-300 MHz
targeted FRB campaign to date. In the LOTAAS data, we search for repeat
bursts from 33 CHIME/FRB repeaters, 10 candidate repeaters and 430
apparent non-repeaters. Their non-detection yields a population-level
constraint on the statistical spectral index  , indicating that FRB spectral indices are, on
average, flatter than known spectral indices from pulsars. From the
targeted campaign, we find that the prolific repeater FRB 20201124A
shows a positive
, indicating that FRB spectral indices are, on
average, flatter than known spectral indices from pulsars. From the
targeted campaign, we find that the prolific repeater FRB 20201124A
shows a positive  , implying
reduced low-frequency activity, unlike the typically negative
, implying
reduced low-frequency activity, unlike the typically negative  seen from FRBs at
higher frequency bands. We explore free-free absorption in the
circumburst environment as a cause of the non-detection at 150 MHz. The
non-detection of FRB 20201124A is consistent with either a very young
seen from FRBs at
higher frequency bands. We explore free-free absorption in the
circumburst environment as a cause of the non-detection at 150 MHz. The
non-detection of FRB 20201124A is consistent with either a very young
 yr old supernova
remnant, or a typical HII region. Our simulations indicate that LOFAR2.0
can detect 0.3-9 FRBs per week, and up to 4 FRBs at redshifts in the
range
yr old supernova
remnant, or a typical HII region. Our simulations indicate that LOFAR2.0
can detect 0.3-9 FRBs per week, and up to 4 FRBs at redshifts in the
range  . Such
detections will provide robust constraints on cosmological parameters
due to their clean environments. Our results guide future low-frequency
FRB searches by showing how even non-detections can place meaningful
constraints on the repetition rates and circumburst environments of
FRBs.
. Such
detections will provide robust constraints on cosmological parameters
due to their clean environments. Our results guide future low-frequency
FRB searches by showing how even non-detections can place meaningful
constraints on the repetition rates and circumburst environments of
FRBs.
The
HST-Hyperion Survey: Environmental Imprints on the Stellar-Mass Function
at z=2.5
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Derek Sikorski / Ben Forrest / Brian C. Lemaux / Lu Shen
- Finn Giddings / Roy Gal / Olga Cucciati / Emmet Golden-Marx
- Weida Hu / Denise Hung / Lori Lubin / Kaila Ronayne
- Ekta Shah / Sandro Bardelli / Devontae C. Baxter / Gayathri
Gururajan
- Laurence Tresse / Giovanni Zamorani / Joel Diamond
/ Lucia Guaita
- Nimish Hathi / Elena Zucca
Summary
Not all galaxies at Cosmic Noon evolve in the same way. It remains
unclear how the local environment – especially the extreme overdensities
of protoclusters – affects stellar mass assembly at high redshift. The
stellar mass function (SMF) encodes these processes; comparing SMFs
across environments reveals differences in evolutionary history. We
present the SMF of the Hyperion proto-supercluster at  , one of the
largest and most massive protostructures known. This dataset provides
the most statistically robust SMF of a single protostructure at
, one of the
largest and most massive protostructures known. This dataset provides
the most statistically robust SMF of a single protostructure at  . By comparing the SMF
of overdense peaks within Hyperion to the coeval field, we ask: how
early, and how strongly, does a dense environment favor massive
galaxies? Using COSMOS2020 photometry with ground-based and new HST
grism spectroscopy, we construct a 3D overdensity map that assigns
galaxies to peaks, outskirts, or the field. We perform 100 Monte Carlo
realizations to propagate redshift and mass uncertainties, and derive
SMFs normalized to the field. The peaks show a clear excess of massive
galaxies: number densities at
. By comparing the SMF
of overdense peaks within Hyperion to the coeval field, we ask: how
early, and how strongly, does a dense environment favor massive
galaxies? Using COSMOS2020 photometry with ground-based and new HST
grism spectroscopy, we construct a 3D overdensity map that assigns
galaxies to peaks, outskirts, or the field. We perform 100 Monte Carlo
realizations to propagate redshift and mass uncertainties, and derive
SMFs normalized to the field. The peaks show a clear excess of massive
galaxies: number densities at  are ~10x higher than the field, while those at
are ~10x higher than the field, while those at
 are enhanced by only ~3.5x. By contrast, the
outskirts and Hyperion as a whole mirror the field. Environmental
effects on stellar mass growth are thus evident by
are enhanced by only ~3.5x. By contrast, the
outskirts and Hyperion as a whole mirror the field. Environmental
effects on stellar mass growth are thus evident by  . The densest
regions already host galaxies with accelerated growth, while the global
SMF masks this signal. Protostructures therefore begin shaping the
high-mass end of the SMF well before cluster quenching, and may drive
the elevated star formation at Cosmic Noon.
. The densest
regions already host galaxies with accelerated growth, while the global
SMF masks this signal. Protostructures therefore begin shaping the
high-mass end of the SMF well before cluster quenching, and may drive
the elevated star formation at Cosmic Noon.
Understanding
the Evolution of Black Hole Accretion and Dust out to z=4 with a Deep
Imaging Extragalactic Survey with PRIMA
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Andreas L. Faisst / Chian-Chou Chen / Laure Ciesla
/ Carlotta Gruppioni
Summary
The cosmic evolution of obscured star formation, dust properties and
production mechanisms, and the prevalence of dust-obscured AGN out to
high redshifts are currently some of the hot topics in astrophysics.
While much progress has been made in the early days with Spitzer and
Herschel, these facilities have not reached the necessary depths to
observe the mid-IR light of high-redshift (z > 3) galaxies. Recently,
the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has filled in the blue side of the
rest-frame mid-IR. The Atacama Large (Sub)Millimeter Array (ALMA), on
the other hand, provides excellent sensitivity in the far-IR regime,
allowing the study of dust and gas properties at high redshifts. Filling
the wavelength gap between JWST and ALMA is crucial to progress our
understanding of early galaxy evolution - and this will be an important
goal in the next decades. The Probe far-IR Mission for Astrophysics
(PRIMA), with sensitive imaging and spectroscopic capabilities at
24-240 m and currently in Phase A study, will
achieve this and provide insights into early galaxy evolution, Black
Hole growth, and dust production mechanisms. Here we present PRIDES, a
possible deep and wide-area survey over 1.6 square-degrees of the COSMOS
field with PRIMA to study these science cases.
m and currently in Phase A study, will
achieve this and provide insights into early galaxy evolution, Black
Hole growth, and dust production mechanisms. Here we present PRIDES, a
possible deep and wide-area survey over 1.6 square-degrees of the COSMOS
field with PRIMA to study these science cases.
The
radial variation of the silicate-to-carbon ratio in M31 probed by
PRIMA
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Jérémy Chastenet / Ilse De Looze / Maarten Baes / Simone
Bianchi
- Viviana Casasola / Laure Ciesla / Stephen Eales /
Jacopo Fritz
- Frédéric Galliano / Suzanne C. Madden / Angelos Nersesian / Monica
Relaño
- Matthew W. L. Smith / Stefan van der Giessen / Emmanuel
Xilouris
Summary
The properties of interstellar dust grains are being scrutinized more
than ever before, with the advent of large facilities. Infrared emission
from dust grains is a powerful asset than can help constrain their
physical and chemical properties. Among these, the relative ratio of
carbon-rich to silicate-rich grains remains one that has not yet been
investigated thoroughly, due to the lack of dedicated instruments and
modeling limitations. In this paper, we quantify the modeling
degeneracies inherent to constraining the far-infrared (far-IR) slope of
the dust emission spectral energy distribution. Used as a proxy for the
silicate-to-carbon ratio, we find that recovering the far-IR slope is
affected by the estimate of the local radiation field, and the input
abundances of different grain species. We show that PRIMA’s
Hyperspectral Imaging will lead to better constrained local radiation
fields which will aid – together with PRIMA’s polarization capabilities
– to better constrain the silicate-to-carbon ratio in M31, and how it
spatially varies within the galaxy.
A
JWST/MIRI view of k Andromedae b: Refining its mass, age, and physical
parameters
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- N. Godoy / E. Choquet / E. Serabyn
/ M. Malin
- P. Tremblin / C. Danielski / P. O. Lagage / A. Boccaletti
- B. Charnay / M. E. Ressler
Summary
Context. kAndb is a substellar companion near the planet-brown dwarf
boundary, orbiting a B9IV star at 50-100 au. Estimates of its age and
mass vary, fueling a decade-long debate. Atmospheric parameters (Teff
1650-2050 K, log(g) 3.5-5.5) remain poorly constrained due to model
differences and heterogeneous datasets. Aims. We refine the
characterization of kAndb using mid-infrared data to capture its
bolometric emission. Combined with NIR measurements, we constrain Teff,
log(g), and radius to reduce uncertainties in age and mass. Methods. We
obtained JWST/MIRI coronagraphic data (F1065C, F1140C, F1550C) and
recalibrated NIR photometry with an updated ATLAS stellar model. MIRI
color-magnitude diagrams (CMDs) probe the likelihood of species (CH4,
NH3, silicates). We compared H and F1140C colors and magnitudes to
isochrones to constrain age and mass. We modeled the spectral energy
distribution with atmosphere models to refine Teff, radius, and log(g),
and to constrain age and mass using evolutionary models. Results. Cloudy
atmosphere models fit best, consistent with the L0/L2 spectral type and
position near silicate-atmosphere field objects in the MIRI CMD. We
derived an age of 47+-7 Myr and mass of 17.3+-1.8 MJup by weighted-mean
model combination. Modeling yielded Teff = 1791+-68 K and radius =
1.42+-0.06 RJup, improving precision by 30%. Log(g) = 4.35+-0.07 dex
represents a 70% improvement over the previous best value (4.75+-0.25).
Conclusions. The new mass places kAndb just above the deuterium-burning
limit. The age is 75% more precise and consistent with the Columba
association (42 Myr). The Teff suggests silicate clouds, requiring
spectroscopic confirmation. MIRI data were crucial to refining radius
and temperature, which led to stronger constraints on age and mass and
improving the overall characterization of kAndb.
The
Santa Cruz Extreme AO Lab (SEAL) 2.0: A reflective, multi-wavelength
rebuild
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Rebecca Jensen-Clem / Vincent Chambouleyron /
Prince Javier / Daren Dillon
- Emiel H. Por / Benjamin Calvin / Sylvain Cetre / Rodrigo Amezcua
Correa
- Tara Crowe / Jordan Diaz / Caleb Dobias / David Doelman
- Stephen Eikenberry / J. Fowler / Benjamin L. Gerard / Phil Hinz
- Renate Kupke / Ashai Moreno / Tiffany Nguyen / Maissa Salama
- Aditya R. Sengupta / Nour Skaf / Frans Snik
Summary
The Santa cruz Extreme Adaptive optics Lab (SEAL) is a
visible/near-infrared wavelength testbed designed to support technology
development for high contrast imaging on large, segmented, ground-based
telescopes. SEAL saw first light in 2021 as a transmissive,
visible-wavelength AO testbed. In this paper, we present four major
upgrades to SEAL: (1) the testbed has been rebuilt with custom off-axis
parabolic mirrors, enabling operation in both near-infrared and visible
wavelengths; (2) the suite of wavefront sensors now includes a
Shack-Hartmann, transmissive four-sided pyramid, vector-Zernike, and, in
the muirSEAL testbed, a photonic lantern; (3) the testbed includes a
vector-vortex coronagraph and will soon include a hybrid astrophotonic
coronagraph; (4) in addition to its original Keck-heritage RTC, SEAL now
includes two additional control software packages: Catkit, originally
developed for the HiCAT testbed at the Space Telescope Science
Institute, and the RTC Compute And Control for Adaptive Optics (CACAO),
originally designed for Subaru/SCExAO. We discuss the performance of the
testbed after the reflective rebuild and on-going technology development
work at SEAL.
Articles for week 35 2025
The
mid-infrared spectrum of  Pictoris b. First VLTI/MATISSE
interferometric observations of an exoplanet
Pictoris b. First VLTI/MATISSE
interferometric observations of an exoplanet
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Houllé / F. Millour / P. Berio / J. Scigliuto
- S. Lacour / B. Lopez / F. Allouche / J.-C. Augereau
- D. Blain / M. Bonnefoy / M. Carbillet / G. Chauvin
- J. Leftley / A. Matter / J. Milli / P. Mollière
- E. Nasedkin / M. Nowak / P. Palma-Bifani / É. Pantin
- P. Priolet / M. Ravet / J. Woillez / W. Balmer
- P. Boley / V. Gámez Rosas / J. H. Girard / X. Haubois
- S. Hinkley / M. Hogerheijde / W. Jaffe / J. Kammerer
- L. Kreidberg / O. Lai / S. Lagarde / A. Labdon
- J.-B. Le Bouquin / A. Meilland / A. Mérand / C. Paladini
- R. Petrov / E. Rickman / Th. Rivinius / S. Robbe-Dubois
- R. van Boekel / J. Varga / A. Vigan / J. J.
Wang
- G. Weigelt
Summary
Few spectra of directly-imaged exoplanets have been obtained in the
mid-infrared (> 3  m). This region is particularly rich in
molecular spectral signatures, whose measurements can help recover
atmospheric parameters and provide a better understanding of giant
planet formation and atmospheric dynamics. In the past years, exoplanet
interferometry with the VLTI/GRAVITY instrument has provided
medium-resolution spectra of a dozen substellar companions in the near
infrared. The 100-meter interferometric baselines allow for the stellar
and planetary signals to be efficiently disentangled at close angular
separations (< 0.3’’). We aim to extend this technique to the
mid-infrared using MATISSE, the VLTI’s mid-infrared
spectro-interferometer. We take advantage of the fringe tracking and
off-axis pointing capabilities recently brought by the GRA4MAT upgrade.
Using this new mode, we observed the giant planet
m). This region is particularly rich in
molecular spectral signatures, whose measurements can help recover
atmospheric parameters and provide a better understanding of giant
planet formation and atmospheric dynamics. In the past years, exoplanet
interferometry with the VLTI/GRAVITY instrument has provided
medium-resolution spectra of a dozen substellar companions in the near
infrared. The 100-meter interferometric baselines allow for the stellar
and planetary signals to be efficiently disentangled at close angular
separations (< 0.3’’). We aim to extend this technique to the
mid-infrared using MATISSE, the VLTI’s mid-infrared
spectro-interferometer. We take advantage of the fringe tracking and
off-axis pointing capabilities recently brought by the GRA4MAT upgrade.
Using this new mode, we observed the giant planet  Pictoris b in L and M bands (2.75-5
Pictoris b in L and M bands (2.75-5
 m) at a spectral resolution of 500. We
developed a method to correct chromatic dispersion and non-common paths
effects in the fringe phase and modelled the planet astrometry and
stellar contamination. We obtained a high-signal-to-noise spectrum of
m) at a spectral resolution of 500. We
developed a method to correct chromatic dispersion and non-common paths
effects in the fringe phase and modelled the planet astrometry and
stellar contamination. We obtained a high-signal-to-noise spectrum of
 Pictoris b, showing the planet
continuum in L (for the first time) and M bands, which contains broad
absorption features of H
Pictoris b, showing the planet
continuum in L (for the first time) and M bands, which contains broad
absorption features of H O and CO. In conjunction with a new
GRAVITY spectrum, we modelled it with the ForMoSA nested sampling tool
and the Exo-REM grid of atmospheric models, and found a solar
carbon-to-oxygen ratio in the planet atmosphere. This study opens the
way to the characterization of fainter and closer-in planets with
MATISSE, which could complement the JWST at angular separations too
close for it to obtain exoplanet spectra. Starting in 2025, the new
adaptive optics system brought by the GRAVITY+ upgrade will further
extend the detection limits of MATISSE.
O and CO. In conjunction with a new
GRAVITY spectrum, we modelled it with the ForMoSA nested sampling tool
and the Exo-REM grid of atmospheric models, and found a solar
carbon-to-oxygen ratio in the planet atmosphere. This study opens the
way to the characterization of fainter and closer-in planets with
MATISSE, which could complement the JWST at angular separations too
close for it to obtain exoplanet spectra. Starting in 2025, the new
adaptive optics system brought by the GRAVITY+ upgrade will further
extend the detection limits of MATISSE.
GWTC-4.0:
Updating the Gravitational-Wave Transient Catalog with Observations from
the First Part of the Fourth LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Observing Run
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- K. G. Arun / G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea
- M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone
- F. Attadio / F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone
- E. A. Avila / S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae
- S. Bagnasco / L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka
- A. M. Baker / K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi
- N. Baldicchi / M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer
- S. Banagiri / B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste
- P. Baral / M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish
- D. Barker / N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone
- B. Barr / L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta
- A. M. Bartoletti / M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev
- R. Bassiri / A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi
- J. C. Bayley / A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan
- V. M. Bedakihale / F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli
- A. S. Bell / D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit
- I. Bentara / J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera
- F. Bergamin / B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz
- C. P. L. Berry / D. Bersanetti / T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini
- J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins
- R. Bhandare / R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya
- S. Bhaumik / V. Biancalana / A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko
- G. Billingsley / A. Binetti / S. Bini / C. Binu
- S. Biot / O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht
- M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard / S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn
- L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair / N. Bode
- N. Boettner / G. Boileau / M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke
- A. Bolliand / L. D. Bonavena / R. Bondarescu / F.
Bondu
- E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino / R. Bonnand
- A. Borchers / S. Borhanian / V. Boschi / S. Bose
- V. Bossilkov / Y. Bothra / A. Boudon / L. Bourg
- M. Boyle / A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady
- A. Branch / M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant
- A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller
- A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti
- S. Brunett / G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant
- Y. Bu / F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko
- T. Bulik / H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk
- R. Buscicchio / D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer
- G. S. Cabourn Davies / R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L.
Cadonati
- G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / A. Calafat / T. A. Callister
- E. Calloni / S. R. Callos / M. Canepa / G. Caneva Santoro
- K. C. Cannon / H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa
- E. Capote / G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani
- M. Carlassara / J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney
- M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo
- A. Casallas-Lagos / J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y.
Castro-Lucas
- S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja
- G. Cella / P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra
- W. Chaibi / A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty
- S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / K. Chang
- S. Chao / P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee
- Debarati Chatterjee / Deep Chatterjee / M. Chaturvedi / S.
Chaty
- K. Chatziioannou / A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen
- H. Chen / H. Y. Chen / S. Chen / Yanbei Chen
- Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung
- S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini / A. Chiba
- A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo / C. Chou
- S. Choudhary / N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani
- P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok
- F. Clara / J. A. Clark / T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater
- S. Clesse / F. Cleva / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo
- P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace / E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni
- C. G. Collette / J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo
- C. M. Compton / G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt
- I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado
- A. Corsi / R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux
- P. Couvares / D. M. Coward / R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo
- J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton / P. Cremonese / S. Crook
- R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen
- A. Cumming / E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição
- T. Dal Canton / S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo
- S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch
- L. P. Dartez / R. Das / A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo
- A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave / A. Davenport
- M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis / L. Davis
- M. C. Davis / P. Davis / E. J. Daw / M. Dax
- J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis
- F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre / W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny
- F. De Marco / G. Demasi / F. De Matteis / N. Demos
- T. Dent / A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri
- R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi / M. Desai / R. DeSalvo
- A. DeSimone / R. De Simone / A. Dhani / R. Diab
- M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron / T. Dietrich
- L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo
- D. Diksha / J. Ding / S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma
- D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev
- J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen
- A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza / L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan
- K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney / S. Doravari / O. Dorosh
- W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers / L. Dunn
- U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne / D. D’Urso / P. Dutta Roy
- H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa / M. Ebersold
- T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / A. Effler / J. Eichholz
- H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann / M. Emma / K. Endo
- R. Enficiaud / L. Errico / R. Espinosa / M. Esposito
- R. C. Essick / H. Estellés / T. Etzel / M. Evans
- T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi
- V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr
- W. M. Farr / G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays
- M. Fazio / J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti
- E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes / T. Fernandes / D. Fernando
- S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura
- A. Fiori / I. Fiori / M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher
- R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer
- L. S. Fleming / E. Floden / H. Fong / J. A. Font
- F. Fontinele-Nunes / C. Foo / B. Fornal / K. Franceschetti
- F. Frappez / S. Frasca / F. Frasconi / J. P. Freed
- Z. Frei / A. Freise / O. Freitas / R. Frey
- W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé
- M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii / T. Fujimori / P. Fulda
- M. Fyffe / B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage
- V. Galdi / R. Gamba / A. Gamboa / S. Gamoji
- D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido
- C. García-Quirós / J. W. Gardner / K. A. Gardner / S. Garg
- J. Gargiulo / X. Garrido / A. Garron / F. Garufi
- P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier
- V. Gayathri / T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai
- V. Gennari / J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding
- L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh
- Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime
- K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson / C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis
- J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey / R. V. Godley
- P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb
- S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov / G. González / P. Goodarzi
- S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty
- D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / A. Grado / V. Graham
- A. E. Granados / M. Granata / V. Granata / S. Gras
- P. Grassia / J. Graves / C. Gray / R. Gray
- G. Greco / A. C. Green / L. Green / S. M. Green
- S. R. Green / C. Greenberg / A. M. Gretarsson / H. K. Griffin
- D. Griffith / H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani / C. Grimaud
- H. Grote / S. Grunewald / D. Guerra / D. Guetta
- G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli
- H. Guo / W. Guo / Y. Guo / Anuradha Gupta
- I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta / S. K. Gupta / V. Gupta
- N. Gupte / J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez / N. Guttman
- F. Guzman / D. Haba / M. Haberland / S. Haino
- E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond / M. Haney
- J. Hanks / C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela
- A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen / J. Hanson / S. Hanumasagar
- R. Harada / A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar / K. Haris
- I. Harley-Trochimczyk / T. Harmark / J. Harms / G. M. Harry
- I. W. Harry / J. Hart / B. Haskell / C. J. Haster
- K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama / M. C. Heintze
- J. Heinze / J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann / F. Hellman
- A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M.
Hendry
- I. S. Heng / M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw / M. Heurs
- A. L. Hewitt / J. Heynen / J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham
- S. Hild / S. Hill / Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata
- C. Hirose / D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan / N. A. Holland
- I. J. Hollows / D. E. Holz / L. Honet / D. J. Horton-Bailey
- J. Hough / S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell
- C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi / H.-F. Hsieh
- H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu / W.-F. Hsu
- Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang
- A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey / V. Hui / S. Husa
- R. Huxford / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni
- G. Iannone / J. Iascau / K. Ide / R. Iden
- A. Ierardi / S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku / Y. Inoue
- G. Iorio / P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin
- R. Ishikawa / M. Isi / K. S. Isleif / Y. Itoh
- M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet
- T. Jacquot / S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav / M. Jain
- T. Jain / A. L. James / K. Jani / J. Janquart
- N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume
- W. Javed / A. Jennings / M. Jensen / W. Jia
- J. Jiang / H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson
- M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston / N. Johny / D. H. Jones
- D. I. Jones / R. Jones / H. E. Jose / P. Joshi
- S. K. Joshi / G. Joubert / J. Ju / L. Ju
- K. Jung / J. Junker / V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz
- T. Kajita / I. Kaku / V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos
- M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang
- N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty / S. J.
Kapadia
- D. P. Kapasi / M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack / H. Kato
- T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman / R. Kaushik
- K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel / L. J. Kemperman
- J. Kennington / F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key
- R. Khadela / S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar / F. Y. Khalili
- F. Khan / T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid
- W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim
- K. Kim / M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim
- C. Kimball / K. Kimes / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel
- S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox / N. Knust
- K. Kobayashi / S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri
- K. Kokeyama / S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / A. E. Koloniari
- K. Komori / A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / L. M. Koponen
- M. Korobko / X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos
- M. Kovalam / T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff
- V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker / A. Królak
- K. Kruska / J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn / S. Kulkarni
- A. Kulur Ramamohan / Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar / Praveen Kumar
- Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume
- K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara
- K. Kwak / K. Kwan / S. Kwon / G. Lacaille
- D. Laghi / A. H. Laity / E. Lalande / M. Lalleman
- P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry / B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang
- J. Lange / R. Langgin / B. Lantz / I. La Rosa
- J. Larsen / A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence
- M. Laxen / C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro
- P. Leaci / L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee
- H. W. Lee / J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee
- R. Lee / Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee
- I. N. Legred / J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean
- A. Lemaître / M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime
- N. Leroy / M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier
- Y. Levin / K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li
- T. G. F. Li / X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li
- A. Lihos / E. T. Lin / F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin
- Y.-C. Lin / C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / A. Liu
- G. C. Liu / Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol
- R. K. L. Lo / J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou
- L. T. London / A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla
- M. Lorenzini / A. Lorenzo-Medina / V. Loriette / M. Lormand
- G. Losurdo / E. Lotti / T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough
- H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto / N. Low / N. Lu
- L. Lucchesi / H. Lück / D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren
- A. W. Lussier / R. Macas / M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod
- I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet / K. Maeda / S. Maenaut
- S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee / E. Maggio / R. Maggiore
- M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi
- E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis
- U. Mali / S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick
- A.-K. Malz / N. Man / M. Mancarella / V. Mandic
- V. Mangano / B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell / M. Manske
- M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli / C. Marinelli / F. Marion
- A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat
- F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez
- D. A. Martinez / M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini
- J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro
- A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich
- M. Matiushechkina / L. Maurin / N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell
- G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick
- L. McCuller / S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee
- J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod
- I. McMahon / T. McRae / R. McTeague / D. Meacher
- B. N. Meagher / R. Mechum / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos
- C. S. Menoni / F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni
- K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt
- M. Merzougui / C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde
- F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao
- C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov
- A. L. Miller / S. J. Miller / M. Millhouse / E. Milotti
- V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov / E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir
- L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra
- C. Mishra / T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell
- S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov / K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman
- O. Miyakawa / S. Miyoki / A. Miyoko / G. Mo
- L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz
- M. Mondin / M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru
- A. More / S. More / C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno
- G. Moreno / A. Moreso Serra / S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki
- G. Morras / A. Moscatello / M. Mould / B. Mours
- C. M. Mow-Lowry / L. Muccillo / F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee
- Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma Mukherjee / Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip
Mukherjee
- N. Mukund / A. Mullavey / H. Mullock / J. Mundi
- C. L. Mungioli / M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / D. Nabari
- S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki
- K. Nakamura / H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze
- D. Nandi / V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia
- T. Narikawa / H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak
- L. Negri / A. Nela / C. Nelle / A. Nelson
- T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery / A. Neunzert / S. Ng
- L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino
- A. Nishizawa / S. Nissanke / W. Niu / F. Nocera
- J. Noller / M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak
- R. Nowicki / J. F. Nuño Siles / L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi
- J. Oberling / J. O’Dell / E. Oelker / M. Oertel
- G. Oganesyan / T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / F. Ohme
- R. Oliveri / R. Omer / B. O’Neal / M. Onishi
- K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly / M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy
- S. O’Shea / S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota
- D. J. Ottaway / A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen
- R. Ozaki / A. E. Pace / R. Pagano / M. A. Page
- A. Pai / L. Paiella / A. Pal / S. Pal
- M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma / C. Palomba
- P. Palud / H. Pan / J. Pan / K. C. Pan
- P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey / Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang
- F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone / B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther
- M. Panzeri / F. Paoletti / A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos
- E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini / G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis
- A. Parisi / B.-J. Park / J. Park / W. Parker
- G. Pascale / D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti
- L. Passenger / D. Passuello / O. Patane / A. V. Patel
- D. Pathak / A. Patra / B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson
- K. Paul / S. Paul / E. Payne / T. Pearce
- M. Pedraza / A. Pele / F. E. Peña Arellano / X. Peng
- Y. Peng / S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego
- Z. Pereira / C. Périgois / G. Perna / A. Perreca
- J. Perret / S. Perriès / J. W. Perry / D. Pesios
- S. Peters / S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer
- H. Pham / K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam
- M. Piarulli / L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot
- M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra
- V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo
- L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski
- M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi
- M. L. Planas / W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani
- E. Polini / J. Pomper / L. Pompili / J. Poon
- E. Porcelli / E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton
- J. Powell / G. S. Prabhu / M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan
- T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati / K. Prasai / R. Prasanna
- P. Prasia / G. Pratten / G. Principe / G. A. Prodi
- P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher
- J. Pullin / P. Puppo / M. Pürrer / H. Qi
- J. Qin / G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez
- N. Qutob / R. Rading / I. Rainho / S. Raja
- C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal
- M. Ramos Arevalo / A. Ramos-Buades / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom
- P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto / A. Ravichandran / A. Ray
- V. Raymond / M. Razzano / J. Read / T. Regimbau
- S. Reid / C. Reissel / D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini
- B. Revenu / A. Revilla Peña / R. Reyes / L. Ricca
- F. Ricci / M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. Rice
- J. W. Richardson / M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles
- H. K. Riley / S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson
- F. Robinet / M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland
- J. G. Rollins / A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero
- I. M. Romero-Shaw / J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke
- L. Rosa / T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska
- M. P. Ross / M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy
- S. Roy / D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama
- E. Ruiz Morales / K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki
- P. Saffarieh / S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha
- T. Sainrat / S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / Y. Sakai
- M. Sakellariadou / S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba
- L. Salconi / M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé
- S. U. Salunkhe / S. Salvador / A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar
- A. Sanchez / E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual
- J. R. Sanders / E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea
- T. R. Saravanan / N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / A. Sasli
- P. Sassi / B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato
- S. Sato / Yukino Sato / Yu Sato / O. Sauter
- R. L. Savage / T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah
- V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein
- M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel
- M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield / K. Schouteden / B. W.
Schulte
- B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi / J. Scott
- S. M. Scott / R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo
- Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers / N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta
- E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo / V. Sequino / M. Serra
- A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh
- L. Shao / A. K. Sharma / Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma
- Ritwik Sharma / S. Sharma Chaudhary / P. Shawhan / N. S.
Shcheblanov
- E. Sheridan / Z.-H. Shi / M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura
- H. Shinkai / S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker
- R. W. Short / S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider / H. Siegel
- D. Sigg / L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds
- L. P. Singer / Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh / D. Singh
- N. Singh / S. Singh / A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala
- V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater / T. J.
Slaven-Blair
- J. Smetana / J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith
- W. J. Smith / S. Soares de Albuquerque Filho / M. Soares-Santos / K.
Somiya
- I. Song / S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino
- H. Sotani / F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer
- P. Spinicelli / A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark
- D. A. Steer / N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner
- N. Stergioulas / P. Stevens / M. StPierre / M. D. Strong
- A. Strunk / A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar
- Y. Sudo / N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan
- J. Sun / L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh
- B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton / K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki
- B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk
- M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi / K. Takada / H. Takahashi
- R. Takahashi / A. Takamori / S. Takano / H. Takeda
- K. Takeshita / I. Takimoto Schmiegelow / M. Takou-Ayaoh / C.
Talbot
- M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka
- S. J. Tanaka / S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner
- L. Tao / R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto
- A. Taruya / J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / D. Tellez
- R. Tenorio / H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos / M. P.
Thirugnanasambandam
- L. M. Thomas / M. Thomas / P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson
- S. R. Thondapu / K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane / J. Tissino
- A. Tiwari / Pawan Tiwari / Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari
- V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd / M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen
- K. Toland / A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini
- T. Tomura / H. Tong / C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné
- C. I. Torrie / I. Tosta e Melo / E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery
- K. Tran / A. Trapananti / R. Travaglini / F. Travasso
- G. Traylor / M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee
- G. Troian / A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau
- T. Tsang / S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada / K. Turbang
- M. Turconi / C. Turski / H. Ubach / N. Uchikata
- T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall / T. Uehara / K. Ueno
- V. Undheim / L. E. Uronen / T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello
- H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya / G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi
- J. Valencia / M. Valentini / S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero
- V. Valsan / M. van Dael / E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den
Brand
- C. Van Den Broeck / M. van der Sluys / A. Van de Walle / J. van
Dongen
- K. Vandra / M. VanDyke / H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van
Heijningen
- P. Van Hove / J. Vanier / M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky
- N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas / V. Varma
- A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio / G. Vedovato / J. Veitch
- P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis / R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier
- M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt / B. Verma / Y. Verma
- S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano / A. Veutro / A. Viceré
- S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha
- N. Villanueva Espinosa / V. Villa-Ortega / E. T. Vincent / J.-Y.
Vinet
- S. Viret / S. Vitale / H. Vocca / D. Voigt
- E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel / W. E. Vossius / L.
Vujeva
- S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack / L. E. Wade / M. Wade
- K. J. Wagner / L. Wallace / E. J. Wang / H. Wang
- J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang / Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar
- J. Warner / M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington
- D. Watarai / B. Weaver / S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt
- M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein / R. Weiss / L. Wen
- K. Wette / J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle
- E. G. Wickens / D. Wilken / A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams
- D. Williams / M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis
- B. Willke / M. Wils / L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn
- J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf / G. Woan / J. Woehler
- N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong / I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong
- T. Wouters / J. L. Wright / M. Wright / B. Wu
- C. Wu / D. S. Wu / H. Wu / K. Wu
- Q. Wu / Y. Wu / Z. Wu / E. Wuchner
- D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu / Y. Xu / N. Yadav
- H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto / T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto
- R. Yamazaki / T. Yan / K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang
- Z. Yarbrough / J. Yebana / S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar
- X. Yin / J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan
- H. Yuzurihara / M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova
- J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin
- L. Zhang / N. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang
- C. Zhao / Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao
- Y. Zheng / H. Zhong / H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu
- Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman / L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker
- J. Zweizig
Summary
Version 4.0 of the Gravitational-Wave Transient Catalog (GWTC-4.0)
adds new candidates detected by the LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
through the first part of the fourth observing run (O4a: 2023 May 24
15:00:00 to 2024 January 16 16:00:00 UTC) and a preceding engineering
run. In this new data, we find 128 new compact binary coalescence
candidates that are identified by at least one of our search algorithms
with a probability of astrophysical origin  and that are not vetoed during event validation.
We also provide detailed source property measurements for 86 of these
that have a false alarm rate
and that are not vetoed during event validation.
We also provide detailed source property measurements for 86 of these
that have a false alarm rate  . Based on the inferred component masses, these
new candidates are consistent with signals from binary black holes and
neutron star-black hole binaries (GW230518_125908 and GW230529_181500).
Median inferred component masses of binary black holes in the catalog
now range from
. Based on the inferred component masses, these
new candidates are consistent with signals from binary black holes and
neutron star-black hole binaries (GW230518_125908 and GW230529_181500).
Median inferred component masses of binary black holes in the catalog
now range from  (GW230627_015337) to
(GW230627_015337) to  (GW231123_135430), while GW231123_135430 was probably produced by the
most massive binary observed in the catalog. For the first time we have
discovered binary black hole signals with network signal-to-noise ratio
exceeding 30, GW230814_230901 and GW231226_01520, enabling high-fidelity
studies of the waveforms and astrophysical properties of these systems.
Combined with the 90 candidates included in GWTC-3.0, the catalog now
contains 218 candidates with
(GW231123_135430), while GW231123_135430 was probably produced by the
most massive binary observed in the catalog. For the first time we have
discovered binary black hole signals with network signal-to-noise ratio
exceeding 30, GW230814_230901 and GW231226_01520, enabling high-fidelity
studies of the waveforms and astrophysical properties of these systems.
Combined with the 90 candidates included in GWTC-3.0, the catalog now
contains 218 candidates with  and not otherwise vetoed, doubling the size of
the catalog and further opening our view of the gravitational-wave
Universe.
and not otherwise vetoed, doubling the size of
the catalog and further opening our view of the gravitational-wave
Universe.
GWTC-4.0:
Methods for Identifying and Characterizing Gravitational-wave
Transients
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / S. Adhicary
- D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari / V. K. Adkins
- S. Afroz / D. Agarwal / M. Agathos / M. Aghaei Abchouyeh
- O. D. Aguiar / S. Ahmadzadeh / L. Aiello / A. Ain
- P. Ajith / S. Akcay / T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi
- R. A. Alfaidi / A. Al-Jodah / C. Alléné / A. Allocca
- S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin / S. Alvarez-Lopez / O.
Amarasinghe
- A. Amato / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / T. Andrade
- M. Andrés-Carcasona / T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi
- J. M. Antelis / S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther
- S. Appert / S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya
- M. C. Araya / M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / L. Argianas
- N. Aritomi / F. Armato / S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud
- M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson / G. Ashton / Y. Aso
- M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone
- F. Attadio / F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone
- S. Babak / F. Badaracco / C. Badger / S. Bae
- S. Bagnasco / E. Bagui / L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai
- T. Baka / T. Baker / M. Ball / G. Ballardin
- S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri / B. Banerjee / D. Bankar
- T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish
- D. Barker / N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone
- B. Barr / L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta
- A. M. Bartoletti / M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / S. Basak
- A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri / A. Basti / D. E. Bates
- M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley / A. C. Baylor
- P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale / F. Beirnaert
- M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell / D. S. Bellie
- L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara / J. D. Bentley
- M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin / B. K. Berger
- S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / C. P. L. Berry / D. Bersanetti
- A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua
- N. Bevins / R. Bhandare / S. A. Bhat / R. Bhatt
- D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhaumik / S. Bhowmick / V. Biancalana
- A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti
- S. Bini / C. Binu / O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu
- A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard / S. Blaber
- J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair
- F. Bobba / N. Bode / G. Boileau / M. Boldrini
- G. N. Bolingbroke / A. Bolliand / L. D. Bonavena /
R. Bondarescu
- F. Bondu / E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino
- R. Bonnand / P. Booker / A. Borchers / S. Borhanian
- V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov / A. Boudon
- A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady / A. Branch
- M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant / A. Brillet
- M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks
- B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett
- G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant / Y. Bu
- F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik
- H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio
- D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies
- G. Cabras / R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati
- G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / A. Calafat / J. Calderón Bustillo
- T. A. Callister / E. Calloni / G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon
- H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa / E. Capote
- G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara
- J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli
- G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo / J. Casanueva Diaz
- C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià
- R. Cavalieri / G. Cella / P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini
- W. Chaibi / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka
Subrahmanya
- J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / R.-J. Chang / S. Chao
- E. L. Charlton / P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin / C.
Chatterjee
- Debarati Chatterjee / Deep Chatterjee / M. Chaturvedi / S.
Chaty
- K. Chatziioannou / C. Checchia / A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen
- D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen / S. Chen
- Y. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng
- P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini
- G. Chiarini / R. Chierici / A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo
- A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary / N. Christensen
- S. S. Y. Chua / P. Chugh / G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag
- M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / R. Ciolfi / F. Clara
- J. A. Clark / J. Clarke / T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater
- S. Clesse / S. M. Clyne / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo
- P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace / E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni
- C. G. Collette / J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo
- C. M. Compton / G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt
- I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / A. Corsi
- S. Cortese / R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux
- J.-P. Coulon / J.-F. Coupechoux / P. Couvares / D. M. Coward
- R. Coyne / K. Craig / J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton
- P. Cremonese / A. W. Criswell / S. Crook / R. Crouch
- J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming
- E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / P. Dabadie / L. V. Da Conceição
- T. Dal Canton / S. Dall’Osso / S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya
- B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann
- K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez / A. Dasgupta / S. Datta
- V. Dattilo / A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave
- A. Davenport / M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis
- L. Davis / M. C. Davis / P. Davis / M. Dax
- J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / U. Deka
- M. De Laurentis / S. Deléglise / F. De Lillo / D. Dell’Aquila
- F. Della Valle / W. Del Pozzo / F. De Marco / G. Demasi
- F. De Matteis / V. D’Emilio / N. Demos / T. Dent
- A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa
- C. De Rossi / M. Desai / R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone
- R. De Simone / A. Dhani / R. Diab / M. C. Díaz
- M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron / N. A. Didio / T. Dietrich
- L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo
- D. Diksha / A. Di Michele / J. Ding / S. Di Pace
- I. Di Palma / F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev
- Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen / D. Dominguez
- L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney
- S. Doravari / O. Dorosh / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers
- J.-G. Ducoin / L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / D. D’Urso
- H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa / M. Ebersold
- T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / B. Edelman / T. B. Edo
- O. Edy / A. Effler / J. Eichholz / H. Einsle
- M. Eisenmann / R. A. Eisenstein / A. Ejlli / M. Emma
- K. Endo / R. Enficiaud / A. J. Engl / L. Errico
- R. Espinosa / M. Esposito / R. C. Essick / H. Estellés
- T. Etzel / M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing
- J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi / F. Faedi / V. Fafone
- S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr / W. M. Farr
- G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays / M. Fazio
- J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi
- D. L. Ferguson / T. Fernandes / D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo
- I. Ferrante / T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura
- A. Fiori / I. Fiori / M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher
- R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer
- L. S. Fleming / E. Floden / H. Fong / J. A. Font
- C. Foo / B. Fornal / P. W. F. Forsyth / K. Franceschetti
- N. Franchini / S. Frasca / F. Frasconi / A. Frattale Mascioli
- Z. Frei / A. Freise / O. Freitas / R. Frey
- W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé
- M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii / T. Fujimori / P. Fulda
- M. Fyffe / B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage
- V. Galdi / H. Gallagher / B. Gallego / R. Gamba
- A. Gamboa / D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa
- J. García-Bellido / C. García Núñez / C. García-Quirós / J. W.
Gardner
- K. A. Gardner / J. Gargiulo / A. Garron / F. Garufi
- P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier
- V. Gayathri / T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai
- V. Gennari / J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding
- L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh
- Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime
- K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson / D. T. Gibson / C. Gier
- S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey
- P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb
- S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov / Y. Gong / G. González
- P. Goodarzi / S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin
- R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / S. Goyal
- B. Grace / A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados
- M. Granata / V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia
- A. Gray / C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco
- A. C. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green / A. M. Gretarsson
- E. M. Gretarsson / D. Griffith / W. L. Griffiths / H. L. Griggs
- G. Grignani / C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald
- D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes
- H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / A. M. Gunny / H. Guo
- W. Guo / Y. Guo / Anchal Gupta / Anuradha Gupta
- I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta / P. Gupta / S. K. Gupta
- T. Gupta / V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs
- N. Gutierrez / F. Guzman / D. Haba / M. Haberland
- S. Haino / E. D. Hall / R. Hamburg / E. Z. Hamilton
- G. Hammond / W.-B. Han / M. Haney / J. Hanks
- C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman
- H. Hansen / J. Hanson / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison
- S. Harikumar / K. Haris / T. Harmark / J. Harms
- G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry / J. Hart / B. Haskell
- C.-J. Haster / K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama
- R. Hayes / M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze / J. Heinzel
- H. Heitmann / A. Heffernan / F. Hellman / A. F.
Helmling-Cornell
- G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M. Hendry / I. S. Heng
- M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw / M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt
- J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham / S. Hild / S. Hill
- Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata / C. Hirose / S. Hochheim
- D. Hofman / N. A. Holland / D. E. Holz / L. Honet
- C. Hong / S. Hoshino / J. Hough / S. Hourihane
- N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh
- H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung / W.-F. Hsu
- Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang
- A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey / D. C. Y. Hui / V. Hui
- S. Husa / R. Huxford / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo
- M. Ianni / A. Ierardi / A. Iess / H. Imafuku
- K. Inayoshi / Y. Inoue / G. Iorio / P. Iosif
- M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa / M. Isi
- Y. Itoh / H. Iwanaga / M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer
- C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet / S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav
- T. Jain / A. L. James / P. A. James / R. Jamshidi
- A. Jan / K. Jani / J. Janquart / K. Janssens
- N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume
- W. Javed / A. Jennings / W. Jia / J. Jiang
- S. J. Jin / C. Johanson / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson
- N. K. Johnson-McDaniel / M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston / N.
Johny
- D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones / E. J. Jones / R. Jones
- S. Jose / P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi / J. Ju
- L. Ju / K. Jung / J. Junker / V. Juste
- H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita / I. Kaku / V. Kalogera
- M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy
- G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner / S. J. Kapadia
- D. P. Kapasi / S. Karat / R. Kashyap / M. Kasprzack
- W. Kastaun / T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman
- R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto / A. Kazemi
- D. Keitel / J. Kennington / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key
- R. Khadela / S. Khadka / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan
- I. Khan / T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid
- W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim
- K. Kim / M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim
- C. Kimball / M. Kinley-Hanlon / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel
- S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi
- P. Koch / S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri
- K. Kokeyama / S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / K. Komori
- A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / M. Korobko / R. V. Kossak
- X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam
- D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu
- A. Królak / K. Kruska / J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn
- S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan / A. Kumar / Praveen Kumar
- Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume
- K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara
- K. Kwak / K. Kwan / J. Kwok / G. Lacaille
- P. Lagabbe / D. Laghi / S. Lai / E. Lalande
- M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry / B. B. Lane
- R. N. Lang / J. Lange / R. Langgin / B. Lantz
- A. La Rana / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen / A. Lartaux-Vollard
- P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. N. Lawrence / M. Laxen
- C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci
- L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee
- J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee / R. Lee
- Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred
- J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lema{î
- M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy
- M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin
- K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li
- X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos
- C-Y. Lin / E. T. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin
- C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / T. B. Littenberg / A. Liu
- G. C. Liu / Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol
- R. K. L. Lo / J.-P. Locquet / M. R. Loizou / L. T. London
- A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla / A. Lorenzo-Medina
- V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / E. Lotti
- T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto
- N. Low / M. J. Lowry / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi
- H. Lück / D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier
- L.-T. Ma / S. Ma / R. Macas / A. Macedo
- M. MacInnis / R. R. Maciy / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan
- A. Macquet / D. Macri / K. Maeda / S. Maenaut
- S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee / E. Maggio / R. Maggiore
- M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi
- E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis
- U. Mali / S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick
- A. Malz / N. Man / V. Mandic / V. Mangano
- B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell / G. Mansingh / M. Manske
- M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli / F. Marchesoni / C. Marinelli
- D. Marín Pina / F. Marion / S. Márka / Z. Márka
- A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat
- F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez
- M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini / J. C. Martins
- D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro / A. Masserot
- M. Masso-Reid / M. Mastrodicasa / S. Mastrogiovanni / T.
Matcovich
- M. Matiushechkina / M. Matsuyama / N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell
- G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick
- L. McCuller / S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee
- J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod
- T. McRae / D. Meacher / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos
- M. Melching / S. Mellaerts / C. S. Menoni / F. Mera
- R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni / K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh
- J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui / C. Messenger
- C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn
- A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao / I. Michaloliakos
- C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / S. J. Miller
- M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov
- N. Mio / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés
- C.-A. Miritescu / A. K. Mishra / A. Mishra / C. Mishra
- T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra
- V. P. Mitrofanov / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa / S. Miyamoto
- S. Miyoki / G. Mo / L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra
- S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / C. Mondal / M. Mondin
- M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More
- S. More / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno / S. Morisaki
- Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras / A. Moscatello / M. Mould
- P. Mourier / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry / F. Muciaccia
- D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma Mukherjee / Subroto
Mukherjee
- Suvodip Mukherjee / N. Mukund / A. Mullavey / H. Mullock
- J. Munch / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli / Y. Murakami
- M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / S. Muusse / D. Nabari
- S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki
- K. Nakamura / H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze
- D. Nandi / V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia
- T. Narikawa / H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak
- A. Nela / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery
- A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols
- A. B. Nielsen / G. Nieradka / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa
- S. Nissanke / E. Nitoglia / W. Niu / F. Nocera
- M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak / J. F. Nuño Siles
- L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling / J. O’Dell
- M. Oertel / A. Offermans / G. Oganesyan / J. J. Oh
- K. Oh / T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / M. Ohkawa
- F. Ohme / R. Oliveri / R. Omer / B. O’Neal
- K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly / R. Oram / N. D. Ormsby
- M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / Y. Oshima
- S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway
- A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / A. E. Pace
- R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai / L. Paiella
- A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi
- P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud / J. Pan
- K. C. Pan / R. Panai / P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey
- Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone
- B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / F. Paoletti / A. Paolone
- A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini / G.
Papigkiotis
- A. Paquis / A. Parisi / B.-J. Park / J. Park
- W. Parker / G. Pascale / D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti
- R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger / D. Passuello / O. Patane
- D. Pathak / L. Pathak / A. Patra / B. Patricelli
- A. S. Patron / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul / S. Paul
- E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza / A. Pele
- F. E. Peña Arellano / S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego
- Z. Pereira / J. J. Perez / C. Périgois / G. Perna
- A. Perreca / J. Perret / S. Perriès / J. W. Perry
- D. Pesios / S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer
- H. Pham / K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam
- M. Piarulli / L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot
- M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra
- V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo
- L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski
- M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi
- M. L. Planas / W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani
- E. Polini / L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli
- E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell
- M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati
- K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia / G. Pratten
- G. Principe / M. Principe / G. A. Prodi / L. Prokhorov
- P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher
- J. Pullin / M. Punturo / P. Puppo / M. Pürrer
- H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke
- P. J. Quinonez / F. J. Raab / I. Rainho / S. Raja
- C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal
- A. Ramos-Buades / D. Rana / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom
- P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto / A. Ray / V. Raymond
- M. Razzano / J. Read / M. Recaman Payo / T. Regimbau
- L. Rei / S. Reid / D. H. Reitze / P. Relton
- A. I. Renzini / A. Renzini / B. Revenu / R. Reyes
- A. S. Rezaei / F. Ricci / M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone
- J. W. Richardson / M. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles
- H. K. Riley / S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson
- F. Robinet / M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland
- J. G. Rollins / A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero
- I. M. Romero-Shaw / J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke
- L. Rosa / T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska
- M. P. Ross / M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. Roy
- S. K. Roy / D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama
- E. Ruiz Morales / K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki
- J. Sadiq / P. Saffarieh / S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah
- S. Saha / T. Sainrat / S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai
- M. Sakellariadou / S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba
- L. Salconi / M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé
- S. U. Salunkhe / S. Salvador / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez
- E. J. Sanchez / J. H. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual
- J. R. Sanders / E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea
- T. R. Saravanan / N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / S. Sasaoka
- A. Sasli / P. Sassi / B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash
- R. Sato / Y. Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage
- T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco
- D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski
- P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind
- R. M. S. Schofield / K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F.
Schutz
- E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott
- R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y.
Sekiguchi
- D. Sellers / A. S. Sengupta / D. Sentenac / E. G. Seo
- J. W. Seo / V. Sequino / M. Serra / G. Servignat
- A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. S. Shahriar
- M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao / A. Sharma / A. K. Sharma
- P. Sharma / S. Sharma Chaudhary / M. R. Shaw / P. Shawhan
- N. S. Shcheblanov / Y. Shikano / M. Shikauchi / K. Shimode
- H. Shinkai / J. Shiota / S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker
- D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short / S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider
- H. Siegel / D. Sigg / L. Silenzi / M. Simmonds
- L. P. Singer / A. Singh / D. Singh / M. K. Singh
- N. Singh / S. Singh / A. Singha / A. M. Sintes
- V. Sipala / V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater
- T. J. Slaven-Blair / J. Smetana / J. R. Smith / L. Smith
- R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith / K. Somiya / I. Song
- K. Soni / S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino
- H. Sotani / A. Southgate / F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo
- A. P. Spencer / M. Spera / P. Spinicelli / C. A. Sprague
- A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / D. A. Steer / N. Steinle
- J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas / P. Stevens
- S. P. Stevenson / F. Stolzi / M. StPierre / G. Stratta
- M. D. Strong / A. Strunk / R. Sturani / A. L. Stuver
- M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman
- J. M. Sullivan / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun / L. Sun
- S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton
- T. Suzuki / Y. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx
- M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi
- S. C. Tait / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi / A. Takamori
- T. Takase / K. Takatani / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita
- C. Talbot / M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe
- K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka / T. Tanaka / D. Tang
- S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao
- R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / R. Tarafder / C. Taranto
- A. Taruya / J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / R. Tenorio
- H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M.
Thomas
- M. Thomas / P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu
- K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane / S. Tibrewal / J. Tissino
- A. Tiwari / P. Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari
- M. R. Todd / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland / A. E. Tolley
- T. Tomaru / K. Tomita / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura
- H. Tong / C. Tong-Yu / A. Toriyama / N. Toropov
- A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie / M. Toscani / I. Tosta e Melo
- E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / A. Trapananti / F. Travasso
- G. Traylor / C. Trejo / M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali
- A. Tripathee / G. Troian / A. Trovato / L. Trozzo
- R. J. Trudeau / T. T. L. Tsang / S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada
- K. Turbang / M. Turconi / C. Turski / H. Ubach
- N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall / T. Uehara
- M. Uematsu / S. Ueno / V. Undheim / T. Ushiba
- M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi
- G. Valdes / J. Valencia / A. F. Valentini / M. Valentini
- S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan / N. van Bakel
- M. van Beuzekom / M. van Dael / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den
Broeck
- D. C. Vander-Hyde / M. van der Sluys / A. Van de Walle / J. van
Dongen
- K. Vandra / H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van
Hove
- J. Vanier / M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / M. H. P. M. van Putten
- Z. Van Ranst / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas
- J. J. Varghese / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio
- G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis
- J. Venneberg / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt
- B. Verma / P. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen
- F. Vetrano / A. Veutro / A. M. Vibhute / A. Viceré
- S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha
- V. Villa-Ortega / E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret
- A. Virtuoso / S. Vitale / A. Vives / H. Vocca
- D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel / L. Vujeva
- S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack / L. E. Wade / M. Wade
- K. J. Wagner / A. Wajid / M. Walker / G. S. Wallace
- L. Wallace / E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang
- W. H. Wang / Y. F. Wang / Z. Wang / G. Waratkar
- J. Warner / M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington
- D. Watarai / K. E. Wayt / B. R. Weaver / B. Weaver
- C. R. Weaving / S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert
- A. J. Weinstein / R. Weiss / F. Wellmann / L. Wen
- P. Weßels / K. Wette / J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting
- C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens / J. B. Wildberger / D. Wilken
- D. J. Willadsen / K. Willetts / D. Williams / M. J. Williams
- N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils
- C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf / G. Woan
- J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong / I. C. F. Wong
- J. L. Wright / M. Wright / C. Wu / D. S. Wu
- H. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu
- Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto
- T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / S. Yamamura / R. Yamazaki
- T. Yan / F. W. Yang / F. Yang / K. Z. Yang
- Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough / H. Yasui / S.-W. Yeh
- A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin / J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa
- J. Yoo / H. Yu / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara
- A. Zadrożny / M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova
- J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin
- A. C. Zhang / L. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang
- Y. Zhang / C. Zhao / Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao
- Y. Zheng / H. Zhong / R. Zhou / X.-J. Zhu
- Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
The Gravitational-Wave Transient Catalog (GWTC) is a collection of
candidate gravitational-wave transient signals identified and
characterized by the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Collaboration. Producing the
contents of the GWTC from detector data requires complex analysis
methods. These comprise techniques to model the signal; identify the
transients in the data; evaluate the quality of the data and mitigate
possible instrumental issues; infer the parameters of each transient;
compare the data with the waveform models for compact binary
coalescences; and handle the large amount of results associated with all
these different analyses. In this paper, we describe the methods
employed to produce the catalog’s fourth release, GWTC-4.0, focusing on
the analysis of the first part of the fourth observing run of Advanced
LIGO, Advanced Virgo and KAGRA.
Unprecedentedly
bright X-ray flaring in Cygnus X-1 observed by INTEGRAL
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- P. Thalhammer / T. Bouchet / J. Rodriguez / F. Cangemi
- K. Pottschmidt / D. A. Green / L. Rhodes / C. Ferrigno
- M. A. Nowak / V. Grinberg / T. Siegert / P.
Laurent
- I. Kreykenbohm / M. Perucho / J. Tomsick / C. Sánchez-Fernández
- J. Wilms C. Sánchez-Fernández / J. Wilms
Summary
We study three extraordinarily bright X-ray flares originating from
Cyg X-1 seen on 2023 July 10 detected with INTEGRAL. The flares had a
duration on the order of only ten minutes each, and within seconds
reached a 1-100 keV peak luminosity of  erg/s. The associated INTEGRAL/IBIS count rate
was about ${}$10x higher than usual for the hard state. To our
knowledge, this is the first time that such strong flaring has been seen
in Cyg X-1, despite the more than 21 years of INTEGRAL monitoring, with
almost ${}$20 Ms of exposure, and the similarly deep monitoring with
RXTE/PCA that lasted from 1997 to 2012. The flares were seen in all
three X-ray and
erg/s. The associated INTEGRAL/IBIS count rate
was about ${}$10x higher than usual for the hard state. To our
knowledge, this is the first time that such strong flaring has been seen
in Cyg X-1, despite the more than 21 years of INTEGRAL monitoring, with
almost ${}$20 Ms of exposure, and the similarly deep monitoring with
RXTE/PCA that lasted from 1997 to 2012. The flares were seen in all
three X-ray and  -ray instruments of INTEGRAL. Radio
monitoring by the AMI Large Array with observations 6 h before and 40 h
after the X-ray flares did not detect a corresponding increase in radio
flux. The shape of the X-ray spectrum shows only marginal change during
the flares, i.e., photon index and cut-off energy are largely preserved.
The overall flaring behavior points toward a sudden and brief release of
energy, either due to the ejection of material in an unstable jet or due
to the interaction of the jet with the ambient clumpy stellar wind.
-ray instruments of INTEGRAL. Radio
monitoring by the AMI Large Array with observations 6 h before and 40 h
after the X-ray flares did not detect a corresponding increase in radio
flux. The shape of the X-ray spectrum shows only marginal change during
the flares, i.e., photon index and cut-off energy are largely preserved.
The overall flaring behavior points toward a sudden and brief release of
energy, either due to the ejection of material in an unstable jet or due
to the interaction of the jet with the ambient clumpy stellar wind.
A COSMOS: The dust content of massive
quiescent galaxies and its evolution with cosmic time
COSMOS: The dust content of massive
quiescent galaxies and its evolution with cosmic time
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Sylvia Adscheid / Benjamin Magnelli / Laure Ciesla
/ Daizhong Liu
- Eva Schinnerer / Frank Bertoldi
Summary
We study the dust content of massive ( ) quiescent galaxies (QGs) at redshifts
) quiescent galaxies (QGs) at redshifts  to place
constraints on the evolution of their cold interstellar medium (ISM) and
thereby obtain insights into the processes of galaxy quenching
throughout cosmic time. We used a robust sample of 458 colour-selected
QGs covered by the A
to place
constraints on the evolution of their cold interstellar medium (ISM) and
thereby obtain insights into the processes of galaxy quenching
throughout cosmic time. We used a robust sample of 458 colour-selected
QGs covered by the A COSMOS+A
COSMOS+A GOODSS database to perform a stacking
analysis in the
GOODSS database to perform a stacking
analysis in the  domain and measured their mean dust
masses from their stacked sub-millimetre luminosities. We used the
CIGALE spectral energy distribution fitting code to obtain star
formation histories and infer the time since quenching for all the QGs
in our sample. We used this information to gain insight into the time
evolution of the dust content after quenching. Most QGs in our sample
quenched around a redshift of
domain and measured their mean dust
masses from their stacked sub-millimetre luminosities. We used the
CIGALE spectral energy distribution fitting code to obtain star
formation histories and infer the time since quenching for all the QGs
in our sample. We used this information to gain insight into the time
evolution of the dust content after quenching. Most QGs in our sample
quenched around a redshift of  , following the
peak of cosmic star formation. The majority of QGs observed at
, following the
peak of cosmic star formation. The majority of QGs observed at  are recently quenched
(i.e. quenched for no longer than 500 Myr), whereas the majority of QGs
observed at
are recently quenched
(i.e. quenched for no longer than 500 Myr), whereas the majority of QGs
observed at  have already been
quenched for a significant amount of time (
have already been
quenched for a significant amount of time ( Gyr). This
implies that high-redshift galaxies (
Gyr). This
implies that high-redshift galaxies ( ) are ideal for
studying the mechanisms of quenching and its effects on the ISM, while
lower-redshift galaxies are more suitable for studying the long-term
effects of the QG environment on their ISM. We obtain upper limits on
the dust mass fraction of the QG population that indicate a lower dust
content than what was found by earlier stacking studies, and
significantly lower (by a factor of
) are ideal for
studying the mechanisms of quenching and its effects on the ISM, while
lower-redshift galaxies are more suitable for studying the long-term
effects of the QG environment on their ISM. We obtain upper limits on
the dust mass fraction of the QG population that indicate a lower dust
content than what was found by earlier stacking studies, and
significantly lower (by a factor of  ) than that of
normal star-forming galaxies. We also place constraints on the initial
gas fraction right after quenching. We find that within the first
) than that of
normal star-forming galaxies. We also place constraints on the initial
gas fraction right after quenching. We find that within the first  Myr after
quenching, QGs already lose on average
Myr after
quenching, QGs already lose on average  of their
cold ISM. Our findings support a gas consumption or removal scenario
acting on short timescales.
of their
cold ISM. Our findings support a gas consumption or removal scenario
acting on short timescales.
GWTC-4.0:
Population Properties of Merging Compact Binaries
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / D. Agarwal / M. Agathos
- M. Aghaei Abchouyeh / O. D. Aguiar / S. Ahmadzadeh / L. Aiello
- A. Ain / P. Ajith / T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi
- R. A. Alfaidi / A. Al-Jodah / C. Alléné / A. Allocca
- S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin / S. Alvarez-Lopez / O.
Amarasinghe
- A. Amato / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / T. Andrade
- M. Andrés-Carcasona / T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi
- J. M. Antelis / S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther
- S. Appert / S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya
- M. C. Araya / M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / L. Argianas
- N. Aritomi / F. Armato / S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud
- M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson / K. G. Arun / G. Ashton
- Y. Aso / M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston
- P. Astone / F. Attadio / F. Aubin / K. AultONeal
- G. Avallone / S. Babak / F. Badaracco / C. Badger
- S. Bae / S. Bagnasco / E. Bagui / L. Baiotti
- R. Bajpai / T. Baka / T. Baker / M. Ball
- G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri / B. Banerjee
- D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral / J. C. Barayoga
- B. C. Barish / D. Barker / N. Barman / P. Barneo
- F. Barone / B. Barr / L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia
- D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti / M. A. Barton / I. Bartos
- S. Basak / A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri / A. Basti
- D. E. Bates / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley
- A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale
- F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell
- D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / D. Beltran-Martinez / W. Benoit
- I. Bentara / J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera
- F. Bergamin / B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz
- C. P. L. Berry / D. Bersanetti / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser
- D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare
- R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhaumik / S. Bhowmick
- V. Biancalana / A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley
- A. Binetti / S. Bini / C. Binu / O. Birnholtz
- S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard
- S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair
- D. G. Blair / F. Bobba / N. Bode / G. Boileau
- M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A. Bolliand / L.
D. Bonavena
- R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla
- A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / P. Booker / A. Borchers
- S. Borhanian / V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov
- A. Boudon / A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady
- A. Branch / M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant
- A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller
- A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti
- S. Brunett / G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant
- Y. Bu / F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko
- T. Bulik / H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk
- R. Buscicchio / D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer
- G. S. Cabourn Davies / G. Cabras / R. Cabrita / V.
Cáceres-Barbosa
- L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / A. Calafat
- J. Calderón Bustillo / T. A. Callister / E. Calloni / M. Canepa
- G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon / H. Cao / L. A. Capistran
- E. Capocasa / E. Capote / G. Capurri / G. Carapella
- F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara / J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson
- M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter
- G. Carullo / J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y.
Castro-Lucas
- S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / G. Cella
- P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / W. Chaibi / P. Chakraborty
- S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C. L. Chan / M.
Chan
- R.-J. Chang / S. Chao / E. L. Charlton / P. Charlton
- E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee / Debarati Chatterjee / Deep
Chatterjee
- D. Chattopadhyay / M. Chaturvedi / S. Chaty / K. Chatziioannou
- C. Checchia / A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen
- H. Chen / H. Y. Chen / S. Chen / Y. Chen
- Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa
- H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini
- R. Chierici / A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo
- C. Chou / S. Choudhary / N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua
- P. Chugh / G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar
- M. Cifaldi / R. Ciolfi / F. Clara / J. A. Clark
- J. Clarke / T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater / S. Clesse
- S. M. Clyne / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon
- S. Colace / E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette
- J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo / C. M. Compton
- G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión
- S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / A. Corsi / S. Cortese
- R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux / J.-P. Coulon
- J.-F. Coupechoux / P. Couvares / D. M. Coward / R. Coyne
- K. Craig / J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton / P. Cremonese
- A. W. Criswell / S. Crook / R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia
- J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming / E. Cuoco
- M. Cusinato / P. Dabadie / L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton
- S. Dall’Osso / S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo
- S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch
- L. P. Dartez / A. Dasgupta / S. Datta / V. Dattilo
- A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave / A. Davenport
- M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis / L. Davis
- M. C. Davis / P. Davis / M. Dax / J. De Bolle
- M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis / S. Deléglise
- F. De Lillo / D. Dell’Aquila / F. Della Valle / W. Del Pozzo
- F. De Marco / G. Demasi / F. De Matteis / V. D’Emilio
- N. Demos / T. Dent / A. Depasse / N. DePergola
- R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi / M. Desai
- R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone / R. De Simone / A. Dhani
- R. Diab / M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron
- N. A. Didio / T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo
- M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha / A. Di Michele
- J. Ding / S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma / F. Di Renzo
- Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev / Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen
- E. Dohmen / D. Dominguez / L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan
- K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney / S. Doravari / O. Dorosh
- M. Drago / J. C. Driggers / J.-G. Ducoin / L. Dunn
- U. Dupletsa / D. D’Urso / H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer
- C. Eassa / M. Ebersold / T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls
- B. Edelman / T. B. Edo / O. Edy / A. Effler
- J. Eichholz / H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann / R. A. Eisenstein
- A. Ejlli / M. Emma / K. Endo / R. Enficiaud
- A. J. Engl / L. Errico / R. Espinosa / M. Esposito
- R. C. Essick / H. Estellés / T. Etzel / M. Evans
- T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi
- F. Faedi / V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah
- B. Farr / W. M. Farr / G. Favaro / M. Favata
- M. Fays / M. Fazio / J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer
- R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi / D. L. Ferguson / T. Fernandes
- A. Fernando / D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo / I. Ferrante
- T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura / A. Fiori
- I. Fiori / M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi
- V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming
- E. Floden / H. Fong / J. A. Font / C. Foo
- B. Fornal / P. W. F. Forsyth / K. Franceschetti / N. Franchini
- S. Frasca / F. Frasconi / A. Frattale Mascioli / Z. Frei
- A. Freise / O. Freitas / R. Frey / W. Frischhertz
- P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia
- S. Fujii / T. Fujimori / P. Fulda / M. Fyffe
- B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage / V. Galdi
- H. Gallagher / B. Gallego / R. Gamba / A. Gamboa
- D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido
- C. García Núñez / C. García-Quirós / J. W. Gardner / K. A.
Gardner
- J. Gargiulo / A. Garron / F. Garufi / P. A. Garver
- C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier / V. Gayathri
- T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai / V. Gennari
- J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding / L. Gergely
- Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh
- Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina
- D. R. Gibson / D. T. Gibson / C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis
- J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey / P. Godwin
- A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez
- B. Goncharov / Y. Gong / G. González / P. Goodarzi
- S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty
- D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / S. Goyal / B. Grace
- A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados / M. Granata
- V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia / A. Gray
- C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco / A. C. Green
- S. M. Green / S. R. Green / A. M. Gretarsson / E. M. Gretarsson
- D. Griffith / W. L. Griffiths / H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani
- C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald / D. Guerra
- D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati
- F. Gulminelli / A. M. Gunny / H. Guo / W. Guo
- Y. Guo / Anchal Gupta / Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta
- N. C. Gupta / P. Gupta / S. K. Gupta / T. Gupta
- V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez
- F. Guzman / D. Haba / M. Haberland / S. Haino
- E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond / W.-B. Han
- M. Haney / J. Hanks / C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam
- O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen / J. Hanson
- R. Harada / A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar / K. Haris
- T. Harmark / J. Harms / G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry
- J. Hart / B. Haskell / C.-J. Haster / K. Haughian
- H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama / R. Hayes / A. Heffernan
- M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze / J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann
- F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming / O.
Henderson-Sapir
- M. Hendry / I. S. Heng / M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw
- M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt / J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham
- S. Hild / S. Hill / Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata
- C. Hirose / S. Hochheim / D. Hofman / N. A. Holland
- D. E. Holz / L. Honet / C. Hong / S. Hoshino
- J. Hough / S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell
- C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh / H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh
- C. Hsiung / W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang
- Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey
- D. C. Y. Hui / V. Hui / S. Husa / R. Huxford
- L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni / A. Ierardi
- A. Iess / H. Imafuku / K. Inayoshi / Y. Inoue
- G. Iorio / P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin
- R. Ishikawa / M. Isi / Y. Itoh / H. Iwanaga
- M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet
- S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav / T. Jain / A. L. James
- P. A. James / R. Jamshidi / K. Jani / J. Janquart
- K. Janssens / N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski
- R. Jaume / W. Javed / A. Jennings / W. Jia
- J. Jiang / C. Johanson / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson
- M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston / N. Johny / D. H. Jones
- D. I. Jones / E. J. Jones / R. Jones / S. Jose
- P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi / J. Ju / L. Ju
- K. Jung / J. Junker / V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz
- T. Kajita / I. Kaku / V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos
- M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang
- N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner / S. J. Kapadia / D. P. Kapasi
- S. Karat / R. Kashyap / M. Kasprzack / W. Kastaun
- T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman / R. Kaushik
- K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto / A. Kazemi / A. Kedia
- D. Keitel / J. Kennington / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key
- R. Khadela / S. Khadka / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan
- I. Khan / T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid
- W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim
- K. Kim / M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim
- C. Kimball / M. Kinley-Hanlon / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel
- S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi
- P. Koch / S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri
- K. Kokeyama / S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / K. Komori
- A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / M. Korobko / R. V. Kossak
- X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam
- D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu
- A. Królak / K. Kruska / J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn
- S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan / A. Kumar / Praveen Kumar
- Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume
- K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara
- K. Kwak / K. Kwan / J. Kwok / G. Lacaille
- P. Lagabbe / D. Laghi / S. Lai / E. Lalande
- M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry / P. Landry
- B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang / J. Lange / R. Langgin
- B. Lantz / A. La Rana / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen
- A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. N. Lawrence
- M. Laxen / C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro
- P. Leaci / L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee
- H. W. Lee / J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee
- R. Lee / Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee
- I. N. Legred / J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean
- A. Lemaître / M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime
- N. Leroy / M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier
- Y. Levin / K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li
- T. G. F. Li / X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li
- A. Lihos / C-Y. Lin / E. T. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin
- Y.-C. Lin / C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / T. B. Littenberg
- A. Liu / G. C. Liu / Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal
- J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L. Lo / J.-P. Locquet / M. R. Loizou
- L. T. London / A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla
- M. Lorenzini / A. Lorenzo-Medina / V. Loriette / M. Lormand
- G. Losurdo / E. Lotti / T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough
- H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto / N. Low / M. J. Lowry
- N. Lu / L. Lucchesi / H. Lück / D. Lumaca
- A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier / L.-T. Ma / S. Ma
- R. Macas / A. Macedo / M. MacInnis / R. R. Maciy
- D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet / D. Macri
- K. Maeda / S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee
- E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh
- M. Maini / S. Majhi / E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem
- D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis / U. Mali / S. Maliakal
- A. Malik / L. Mallick / A. Malz / N. Man
- V. Mandic / V. Mangano / B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell
- G. Mansingh / M. Manske / M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli
- F. Marchesoni / C. Marinelli / D. Marín Pina / F. Marion
- S. Márka / Z. Márka / A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz
- E. Maros / S. Marsat / F. Martelli / I. W. Martin
- R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez / M. Martinez / V. Martinez
- A. Martini / J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx
- L. Massaro / A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid / M. Mastrodicasa
- S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich / M. Matiushechkina / M.
Matsuyama
- N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell / G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy
- D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick / L. McCuller / S. McEachin
- C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan
- J. McIver / A. McLeod / T. McRae / D. Meacher
- Q. Meijer / A. Melatos / S. Mellaerts / C. S. Menoni
- F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni / K. Merfeld
- E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui
- C. Messenger / C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde
- F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao
- I. Michaloliakos / C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton
- S. J. Miller / M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti
- Y. Minenkov / N. Mio / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola
- M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu / A. K. Mishra / A. Mishra
- C. Mishra / T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell
- S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa
- S. Miyamoto / S. Miyoki / G. Mo / L. Mobilia
- S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / C. Mondal
- M. Mondin / M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru
- A. More / S. More / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno
- S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras / A. Moscatello
- M. Mould / P. Mourier / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry
- F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma
Mukherjee
- Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip Mukherjee / N. Mukund / A. Mullavey
- H. Mullock / J. Munch / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli
- Y. Murakami / M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / S. Muusse
- D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan
- K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura / H. Nakano / M. Nakano
- D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi / V. Napolano / P. Narayan
- I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa / H. Narola / L. Naticchioni
- R. K. Nayak / A. Nela / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson
- M. Nery / A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh
- S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen / G. Nieradka / Y. Nishino
- A. Nishizawa / S. Nissanke / E. Nitoglia / W. Niu
- F. Nocera / M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak
- J. F. Nuño Siles / L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling
- J. O’Dell / M. Oertel / A. Offermans / G. Oganesyan
- J. J. Oh / K. Oh / T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi
- M. Ohkawa / F. Ohme / R. Oliveri / R. Omer
- B. O’Neal / K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly / N. D. Ormsby
- M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / Y. Oshima
- S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway
- A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / A. E. Pace
- R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai / L. Paiella
- A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi
- P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud / J. Pan
- K. C. Pan / R. Panai / P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey
- Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone
- B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / F. Paoletti / A. Paolone
- A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini / G.
Papigkiotis
- A. Paquis / A. Parisi / B.-J. Park / J. Park
- W. Parker / G. Pascale / D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti
- R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger / D. Passuello / O. Patane
- D. Pathak / L. Pathak / A. Patra / B. Patricelli
- A. S. Patron / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul / S. Paul
- E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza / A. Pele
- F. E. Peña Arellano / S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego
- Z. Pereira / J. J. Perez / C. Périgois / G. Perna
- A. Perreca / J. Perret / S. Perriès / J. W. Perry
- D. Pesios / S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer
- H. Pham / K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam
- M. Piarulli / L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot
- M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra
- V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo
- L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski
- M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi
- M. L. Planas / W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani
- E. Polini / L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli
- E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell
- M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati
- K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia / G. Pratten
- G. Principe / M. Principe / G. A. Prodi / L. Prokhorov
- P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher
- J. Pullin / M. Punturo / P. Puppo / M. Pürrer
- H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke
- P. J. Quinonez / I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan
- B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / A.
Ramos-Buades
- D. Rana / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani
- B. Ratto / A. Ray / V. Raymond / M. Razzano
- J. Read / M. Recaman Payo / T. Regimbau / L. Rei
- S. Reid / D. H. Reitze / P. Relton / A. I. Renzini
- B. Revenu / R. Reyes / A. S. Rezaei / F. Ricci
- M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. W. Richardson / M. Richardson
- A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley / S. Rinaldi
- J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet / M. Robinson
- A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins / A. E. Romano
- R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw / J. H. Romie
- S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa / T. J. Rosauer
- C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross / M. Rossello-Sastre
- S. Rowan / S. Roy / S. K. Roy / D. Rozza
- P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales / K. Ruiz-Rocha
- S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / J. Sadiq / P. Saffarieh
- S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat
- S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou / S. Sakon
- O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi / M. Saleem
- F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe / S. Salvador
- A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez / E. J. Sanchez / J. H. Sanchez
- L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders / E. M. Sänger
- F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan / N. Sarin
- P. Sarkar / S. Sasaoka / A. Sasli / P. Sassi
- B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato / Y. Sato
- O. Sauter / R. L. Savage / T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant
- S. Sayah / V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel
- A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt
- R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield / K.
Schouteden
- B. W. Schulte / B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi
- J. Scott / S. M. Scott / R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu
- M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers / A. S. Sengupta
- D. Sentenac / E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo / V. Sequino
- M. Serra / G. Servignat / A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer
- U. S. Shah / M. S. Shahriar / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao
- A. K. Sharma / P. Sharma / S. Sharma Chaudhary / M. R. Shaw
- P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / Y. Shikano / M. Shikauchi
- K. Shimode / H. Shinkai / J. Shiota / S. Shirke
- D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short / S.
ShyamSundar
- A. Sider / H. Siegel / D. Sigg / L. Silenzi
- M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer / A. Singh / D. Singh
- M. K. Singh / N. Singh / S. Singh / A. Singha
- A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen
- D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J. Smetana / J. R. Smith
- L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith / K. Somiya
- I. Song / K. Soni / S. Soni / V. Sordini
- F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani / A. Southgate / F. Spada
- V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / M. Spera / P. Spinicelli
- C. A. Sprague / A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / D. A. Steer
- N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas
- P. Stevens / S. P. Stevenson / F. Stolzi / M. StPierre
- G. Stratta / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk / R. Sturani
- A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / N. Sueltmann
- L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun / L. Sun
- S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton
- T. Suzuki / Y. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx
- M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi
- S. C. Tait / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi / A. Takamori
- T. Takase / K. Takatani / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita
- C. Talbot / M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe
- K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka / T. Tanaka / D. Tang
- S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao
- R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín / R. Tarafder / C. Taranto
- A. Taruya / J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / R. Tenorio
- H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M.
Thomas
- M. Thomas / P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu
- K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari
- P. Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd
- A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland / A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru
- K. Tomita / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura / H. Tong
- C. Tong-Yu / A. Toriyama / N. Toropov / A. Torres-Forné
- C. I. Torrie / M. Toscani / I. Tosta e Melo / E. Tournefier
- M. Trad Nery / A. Trapananti / F. Travasso / G. Traylor
- C. Trejo / M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee
- G. Troian / A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau
- T. T. L. Tsang / S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada / K. Turbang
- M. Turconi / C. Turski / H. Ubach / N. Uchikata
- T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall / T. Uehara / M. Uematsu
- S. Ueno / V. Undheim / T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello
- H. Vahlbruch / G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / G. Valdes
- J. Valencia / A. F. Valentini / M. Valentini / S. A.
Vallejo-Peña
- S. Vallero / V. Valsan / N. van Bakel / M. van Beuzekom
- M. van Dael / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / D. C.
Vander-Hyde
- M. van der Sluys / A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra
- H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J.
Vanier
- M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / M. H. P. M. van Putten / Z. Van
Ranst
- N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas / J. J. Varghese
- V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio / G. Vedovato
- J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis / J. Venneberg
- P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt / B. Verma
- P. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. M. Vibhute / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant
- A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / V. Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / A. Virtuoso
- S. Vitale / A. Vives / H. Vocca / D. Voigt
- E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel / L. Vujeva / S. P.
Vyatchanin
- J. Wack / L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner
- A. Wajid / M. Walker / G. S. Wallace / L. Wallace
- E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang
- Y. F. Wang / Z. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner
- M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai
- K. E. Wayt / B. R. Weaver / B. Weaver / C. R. Weaving
- S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein
- R. Weiss / F. Wellmann / L. Wen / P. Weßels
- K. Wette / J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle
- E. G. Wickens / J. B. Wildberger / D. Wilken / D. J. Willadsen
- K. Willetts / D. Williams / M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams
- J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils / C. W. Winborn
- J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf / G. Woan / J. Woehler
- N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong / I. C. F. Wong / J. L. Wright
- M. Wright / C. Wu / D. S. Wu / H. Wu
- T. Y. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu
- Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto
- T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / S. Yamamura / R. Yamazaki
- T. Yan / F. W. Yang / F. Yang / K. Z. Yang
- Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough / H. Yasui / S.-W. Yeh
- A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin / J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa
- J. Yoo / H. Yu / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara
- A. Zadrożny / M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova
- J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin
- A. C. Zhang / L. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang
- Y. Zhang / C. Zhao / Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao
- Y. Zheng / H. Zhong / R. Zhou / X.-J. Zhu
- Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
We detail the population properties of merging compact objects using
158 mergers from the cumulative Gravitational-Wave Transient Catalog
4.0, which includes three types of binary mergers: binary neutron star,
neutron star–black hole binary, and binary black hole mergers. We
resolve multiple over- and under-densities in the black hole mass
distribution: features persist at primary masses of  and
and  with a
possible third feature at
with a
possible third feature at  .
These are departures from an otherwise power-law-like continuum that
steepens above
.
These are departures from an otherwise power-law-like continuum that
steepens above  . Binary
black holes with primary masses near
. Binary
black holes with primary masses near  are more
likely to have less massive secondaries, with a mass ratio distribution
peaking at
are more
likely to have less massive secondaries, with a mass ratio distribution
peaking at  , potentially a signature of stable mass transfer
during binary evolution. Black hole spins are inferred to be
non-extremal, with 90% of black holes having
, potentially a signature of stable mass transfer
during binary evolution. Black hole spins are inferred to be
non-extremal, with 90% of black holes having  , and
preferentially aligned with binary orbits, implying many merging
binaries form in isolation. However, we find a significant fraction,
0.24-0.42, of binaries have negative effective inspiral spins,
suggesting many could be formed dynamically in gas-free environments. We
find evidence for correlation between effective inspiral spin and mass
ratio, though it is unclear if this is driven by variation in the mode
of the distribution or the width. (Abridged)
, and
preferentially aligned with binary orbits, implying many merging
binaries form in isolation. However, we find a significant fraction,
0.24-0.42, of binaries have negative effective inspiral spins,
suggesting many could be formed dynamically in gas-free environments. We
find evidence for correlation between effective inspiral spin and mass
ratio, though it is unclear if this is driven by variation in the mode
of the distribution or the width. (Abridged)
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Aditya R. Sengupta / Vincent Chambouleyron / Jordan
Diaz / Matthew DeMartino
- Rebecca Jensen-Clem / Benjamin L. Gerard / Michael J. Messerly /
Paul Pax
- Daren Dillon / Kevin Bundy / Maria Cuevas / Sylvain Cetre
- Bruce Macintosh / Caleb Dobias / Tara Crowe / Stephen S.
Eikenberry
- Rodrigo Amezcua-Correa / Stephanos Yerolatsitis
Summary
Photonic lanterns (PLs) are fiber-based waveguides that are capable
of focal-plane wavefront sensing while simultaneously directing light to
downstream science instruments. The optimal choice of wavefront
reconstruction algorithm has yet to be determined, and likely depends on
the particular observing scenario under consideration. Previous work in
simulation suggests that PLs can be used for nonlinear wavefront sensing
for several applications, including sensing the low-wind effect and
correcting large-amplitude aberrations. We present the design of
muirSEAL (miniature IR SEAL), a testbed designed to test PL wavefront
reconstruction over Zernike modes and segmented-mirror offsets. We
demonstrate throughput and linear wavefront reconstruction at multiple
f-numbers. We further present initial laboratory imaging of a new
photonic lantern fabricated at Lawrence Livermore National
Laboratory.
Euclid
preparation. LXXIV. Euclidised observations of Hubble Frontier Fields
and CLASH galaxy clusters
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / P. Bergamini / M. Meneghetti / G. Angora
- L. Bazzanini / P. Rosati / C. Grillo / M. Lombardi
- D. Abriola / A. Mercurio / F. Calura / G. Despali
- J. M. Diego / R. Gavazzi / P. Hudelot / L.
Leuzzi
- G. Mahler / E. Merlin / C. Scarlata / N. Aghanim
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / R. Bender
- A. Biviano / C. Bodendorf / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / H. Dole
- M. Douspis / F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Farrens
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / B. Garilli / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- I. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- R. Laureijs / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / S.
Maurogordato
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / G. Meylan
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / E. Munari / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / H. I. Teplitz
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella / A. Boucaud
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / N. Mauri / V. Scottez / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / V. Allevato
- S. Anselmi / M. Ballardini / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / S. Borgani / A. S. Borlaff / S. Bruton
- R. Cabanac / A. Calabro / A. Cappi / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / S. Contarini / T. Contini / A. R. Cooray
- O. Cucciati / B. De Caro / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- S. Di Domizio / A. G. Ferrari / I. Ferrero / F. Fornari
- L. Gabarra / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / G. Gozaliasl / A. Hall
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / M. Huertas-Company / A. Jimenez
Muñoz
- J. J. E. Kajava / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / C. C.
Kirkpatrick
- L. Legrand / G. Libet / A. Loureiro / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / S. Matthew / L. Maurin / R. B. Metcalf
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / Nicholas A. Walton
- J. Odier / L. Patrizii / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- V. Popa / C. Porciani / D. Potter / I. Risso
- P.-F. Rocci / M. Sahlén / A. Schneider / M. Sereno
- S. A. Stanford / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- D. Vergani / G. Verza
Summary
We present HST2EUCLID, a novel Python code to generate Euclid
realistic mock images in the  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  photometric
bands based on panchromatic Hubble Space Telescope observations. The
software was used to create a simulated database of Euclid images for
the 27 galaxy clusters observed during the Cluster Lensing And Supernova
survey with Hubble (CLASH) and the Hubble Frontier Fields (HFF) program.
Since the mock images were generated from real observations, they
incorporate, by construction, all the complexity of the observed galaxy
clusters. The simulated Euclid data of the galaxy cluster MACS
J0416.1$-$2403 were then used to explore the possibility of developing
strong lensing models based on the Euclid data. In this context,
complementary photometric or spectroscopic follow-up campaigns are
required to measure the redshifts of multiple images and cluster member
galaxies. By Euclidising six parallel blank fields obtained during the
HFF program, we provide an estimate of the number of galaxies detectable
in Euclid images per
photometric
bands based on panchromatic Hubble Space Telescope observations. The
software was used to create a simulated database of Euclid images for
the 27 galaxy clusters observed during the Cluster Lensing And Supernova
survey with Hubble (CLASH) and the Hubble Frontier Fields (HFF) program.
Since the mock images were generated from real observations, they
incorporate, by construction, all the complexity of the observed galaxy
clusters. The simulated Euclid data of the galaxy cluster MACS
J0416.1$-$2403 were then used to explore the possibility of developing
strong lensing models based on the Euclid data. In this context,
complementary photometric or spectroscopic follow-up campaigns are
required to measure the redshifts of multiple images and cluster member
galaxies. By Euclidising six parallel blank fields obtained during the
HFF program, we provide an estimate of the number of galaxies detectable
in Euclid images per  per
magnitude bin (number counts) and the distribution of the galaxy sizes.
Finally, we present a preview of the Chandra Deep Field South that will
be observed during the Euclid Deep Survey and two examples of
galaxy-scale strong lensing systems residing in regions of the sky
covered by the Euclid Wide Survey. The methodology developed in this
work lends itself to several additional applications, as simulated
Euclid fields based on HST (or JWST) imaging with extensive
spectroscopic information can be used to validate the feasibility of
legacy science cases or to train deep learning techniques in advance,
thus preparing for a timely exploitation of the Euclid Survey data.
per
magnitude bin (number counts) and the distribution of the galaxy sizes.
Finally, we present a preview of the Chandra Deep Field South that will
be observed during the Euclid Deep Survey and two examples of
galaxy-scale strong lensing systems residing in regions of the sky
covered by the Euclid Wide Survey. The methodology developed in this
work lends itself to several additional applications, as simulated
Euclid fields based on HST (or JWST) imaging with extensive
spectroscopic information can be used to validate the feasibility of
legacy science cases or to train deep learning techniques in advance,
thus preparing for a timely exploitation of the Euclid Survey data.
Exploring
the Capabilities of Astrophotonics for the Precise Alignment of
Segmented Telescopes
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Maria Cuevas / Aditya R. Sengupta / Vincent
Chambouleyron / Rebecca Jensen-Clem
- Daren Dillon / Sylvain Cetre / Maïssa Salama / Caleb Dobias
- Tara Crowe / Stephen Eikenberry / Rodrigo Amezcua-Correa / Stephanos
Yerolatsitis
Summary
The next generation of large telescopes for direct imaging of
exoplanets will require segmented primary mirrors. Over both long and
short timescales, these telescopes experience segment misalignments
which degrade the final science image. Adaptive optics (AO) systems can
be used to correct these aberrations in real time. AO systems require
wavefront sensors (WFSs) that measure the phase of the incoming light in
order to reconstruct optical aberrations. However, most WFSs used for
sensing atmospheric turbulence cannot correctly detect aberrations
induced by misalignments in segmented telescopes, as they show poor
sensitivity to phase discontinuities. We investigate the potential of
photonic lanterns (PLs), which are waveguides that allow for the
low-loss transmission from multi-mode to multiple single-mode optical
signals, for sensing segment misalignments at the focal plane. We assess
the ability of PLs to measure piston offsets in segmented mirrors
through both simulations and laboratory experiments. We simulate the
photonic lantern and demonstrate linear reconstruction on segment
pistons. Further, we train a neural network to reconstruct aberrations
outside of the linear regime. We experimentally validate reconstruction
of segment piston offsets on the Miniature Infrared SEAL (muirSEAL)
testbed, which includes a segmented deformable mirror, a PSF imaging
branch, and a PL. This work demonstrates the potential of the PL as a
compact WFS for future space- and ground-based segmented-mirror
telescopes.
Euclid:
A machine-learning search for dual and lensed AGN at sub-arcsec
separations
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- L. Ulivi / F. Mannucci / M. Scialpi / C. Marconcini
- G. Cresci / A. Marconi / A. Feltre / M. Ginolfi
- F. Ricci / D. Sluse / F. Belfiore / E. Bertola
- C. Bracci / E. Cataldi / M. Ceci / Q. D’Amato
- I. Lamperti / R. B. Metcalf / B. Moreschini / M. Perna
- G. Tozzi / G. Venturi / M. V. Zanchettin / Y. Fu
- M. Huertas-Company / N. E. P. Lines / M. Mezcua / M. Pöntinen
- K. Rojas / V. Scottez / M. Siudek / H. Teimoorinia
- I. T. Andika / J. A. Acevedo Barroso / B. Clément / F. Courbin
- R. Gavazzi / L. R. Ecker / B. C. Nagam / R.
Pearce-Casey
- S. Schuldt / S. H. Vincken / D. Stern / A. Chakraborty
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / A. A. Nucita
Summary
Cosmological models of hierarchical structure formation predict the
existence of a widespread population of dual accreting supermassive
black holes (SMBHs) on kpc-scale separations, corresponding to projected
distances < 0”.8 at redshifts higher than 0.5. However, close
companions to known active galactic nuclei (AGN) or quasars (QSOs) can
also be multiple images of the object itself, strongly lensed by a
foreground galaxy, as well as foreground stars in a chance
superposition. Thanks to its large sky coverage, sensitivity, and high
spatial resolution, Euclid offers a unique opportunity to obtain a
large, homogeneous sample of dual/lensed AGN candidates with sub-arcsec
projected separations. Here we present a machine learning approach, in
particular a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), to identify close
companions to known QSOs down to separations of $,$0”.15 comparable to
the Euclid VIS point spread function (PSF). We studied the effectiveness
of the CNN in identifying dual AGN and demonstrated that it outperforms
traditional techniques. Applying our CNN to a sample of $,$6000 QSOs
from the Q1 Euclid data release, we find a fraction of about 0.25% dual
AGN candidates with separation $,$0”.4 (corresponding to $$3 kpc at
z=1). Estimating the foreground contamination from stellar objects, we
find that most of the pair candidates with separation higher than 0”.5
are likely contaminants, while below this limit, contamination is
expected to be less than 20%. For objects at higher separation
(>0”.5, i.e. 4 kpc at z=1), we performed PSF subtraction and used
colour-colour diagrams to constrain their nature. We present a first set
of dual/lensed AGN candidates detected in the Q1 Euclid data, providing
a starting point for the analysis of future data releases.
Upper
Limits on the Isotropic Gravitational-Wave Background from the first
part of LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA’s fourth Observing Run
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea / M. Assiduo
- S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone / F. Attadio
- F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone / E. A. Avila
- S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae / S. Bagnasco
- L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka / A. M. Baker
- K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi / N. Baldicchi
- M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri
- B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral
- M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish / D. Barker
- N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone / B. Barr
- L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti
- M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri
- A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley
- A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale
- F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell
- D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara
- J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin
- B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / D. Bersanetti
- T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge
- G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare / R. Bhatt
- D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya / S. Bhaumik / V.
Biancalana
- A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti
- S. Bini / C. Binu / S. Biot / O. Birnholtz
- S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard
- S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair
- D. G. Blair / N. Bode / N. Boettner / G. Boileau
- M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A. Bolliand / L.
D. Bonavena
- R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla
- A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / A. Borchers / S. Borhanian
- V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov / Y. Bothra
- A. Boudon / L. Bourg / G. Bouyer / M. Boyle
- A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady / A. Branch
- M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant / A. Brillet
- M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks
- B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett
- G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant / Y. Bu
- F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik
- H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio
- D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies
- R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli
- C. Cahillane / A. Calafat / T. A. Callister / E. Calloni
- S. R. Callos / G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon / H. Cao
- L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa / E. Capote / G. Capurri
- G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara / J. B. Carlin
- T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo
- J. J. Carter / G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos / J. Casanueva
Diaz
- C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià
- R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja / G. Cella / P. Cerdá-Durán
- E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi / A. Chakraborty
- P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C.
L. Chan
- M. Chan / K. Chang / S. Chao / P. Charlton
- E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee / Debarati Chatterjee / Deep
Chatterjee
- M. Chaturvedi / S. Chaty / K. Chatziioannou / A. Chen
- A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen
- S. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng
- P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini
- G. Chiarini / A. Chiba / A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo
- A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary / N. Christensen
- S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar
- M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok / F. Clara / J. A. Clark
- T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater / S. Clesse / F. Cleva
- E. Coccia / E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace
- E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette / J. Collins
- S. Colloms / A. Colombo / C. M. Compton / G. Connolly
- L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi
- N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado / A. Corsi / R. Cottingham
- M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux / P. Couvares / D. M. Coward
- R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo / J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton
- P. Cremonese / S. Crook / R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia
- J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming / E. Cuoco
- M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton / S. Dal Pra
- G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio
- K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez / R. Das
- A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo / A. Daumas / N. Davari
- I. Dave / A. Davenport / M. Davier / T. F. Davies
- D. Davis / L. Davis / M. C. Davis / P. Davis
- E. J. Daw / M. Dax / J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan
- J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis / F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre
- W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny / F. De Marco / G. Demasi
- F. De Matteis / N. Demos / T. Dent / A. Depasse
- N. DePergola / R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi
- M. Desai / R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone / R. De Simone
- A. Dhani / R. Diab / M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare
- G. Dideron / T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo
- M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha / J. Ding
- S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma / D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo
- Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev / J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor
- N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen / A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza
- L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney
- S. Doravari / O. Dorosh / W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago
- J. C. Driggers / L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / D. D’Urso
- P. Dutta Roy / H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa
- M. Ebersold / T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / A. Effler
- J. Eichholz / H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann / M. Emma
- K. Endo / R. Enficiaud / L. Errico / R. Espinosa
- M. C. Espitia / M. Esposito / R. C. Essick / H. Estellés
- T. Etzel / M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing
- J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi / V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst
- A. M. Farah / B. Farr / W. M. Farr / G. Favaro
- M. Favata / M. Fays / M. Fazio / J. Feicht
- M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes
- T. Fernandes / D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira
- F. Fidecaro / P. Figura / A. Fiori / I. Fiori
- M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara
- R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming / E. Floden
- H. Fong / J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes / C. Foo
- B. Fornal / K. Franceschetti / F. Frappez / S. Frasca
- F. Frasconi / J. P. Freed / Z. Frei / A. Freise
- O. Freitas / R. Frey / W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel
- V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii
- T. Fujimori / P. Fulda / M. Fyffe / B. Gadre
- J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage / V. Galdi / R. Gamba
- A. Gamboa / S. Gamoji / D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly
- B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido / C. García-Quirós / J. W.
Gardner
- K. A. Gardner / S. Garg / J. Gargiulo / X. Garrido
- A. Garron / F. Garufi / P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra
- B. Gateley / F. Gautier / V. Gayathri / T. Gayer
- G. Gemme / A. Gennai / V. Gennari / J. George
- R. George / O. Gerberding / L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh
- Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh
- Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson
- C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer / F. Glotin
- J. Godfrey / R. V. Godley / P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel
- E. Goetz / J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov
- G. González / P. Goodarzi / S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones
- M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova
- A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados / M. Granata
- V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia / J. Graves
- C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco / A. C. Green
- L. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green / C. Greenberg
- A. M. Gretarsson / H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith / H. L. Griggs
- G. Grignani / C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald
- D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes
- H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / H. Guo / W. Guo
- Y. Guo / Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta
- S. K. Gupta / V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs
- N. Gutierrez / N. Guttman / F. Guzman / D. Haba
- M. Haberland / S. Haino / E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton
- G. Hammond / M. Haney / J. Hanks / C. Hanna
- M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen
- J. Hanson / S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison
- S. Harikumar / K. Haris / I. Harley-Trochimczyk / T. Harmark
- J. Harms / G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry / J. Hart
- B. Haskell / C. J. Haster / K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa
- K. Hayama / M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze / J. Heinzel
- H. Heitmann / F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming
- O. Henderson-Sapir / M. Hendry / I. S. Heng / M. H. Hennig
- C. Henshaw / M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt / J. Heynen
- J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham / S. Hild / S. Hill
- Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata / C. Hirose / D. Hofman
- B. E. Hogan / N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows / D. E. Holz
- L. Honet / D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough / S. Hourihane
- N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh
- P. Hsi / H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung
- S.-H. Hsu / W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang
- Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey
- V. Hui / S. Husa / R. Huxford / L. Iampieri
- G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni / G. Iannone / J. Iascau
- K. Ide / R. Iden / A. Ierardi / S. Ikeda
- H. Imafuku / Y. Inoue / G. Iorio / P. Iosif
- M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa / M. Isi
- K. S. Isleif / Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer
- C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot / S. J. Jadhav
- S. P. Jadhav / M. Jain / T. Jain / A. L. James
- K. Jani / J. Janquart / K. Janssens / N. N. Janthalur
- S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume / W. Javed
- A. Jennings / M. Jensen / W. Jia / J. Jiang
- H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston
- R. Johnston / N. Johny / D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones
- R. Jones / H. E. Jose / P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi
- G. Joubert / J. Ju / L. Ju / K. Jung
- J. Junker / V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita
- I. Kaku / V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi
- N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel
- J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty / S. J. Kapadia / D. P.
Kapasi
- M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack / H. Kato / T. Kato
- E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman / R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe
- R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel / L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington
- F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key / R. Khadela
- S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan
- T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo
- N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim / K. Kim
- M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball
- K. Kimes / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko
- A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi
- S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama
- S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori
- A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko
- X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam
- T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel
- N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker / A. Królak / K. Kruska
- J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn / S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan
- Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar / Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar
- Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume / K. Kuns
- N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak
- K. Kwan / S. Kwon / G. Lacaille / D. Laghi
- A. H. Laity / E. Lalande / M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati
- M. Landry / B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang / J. Lange
- R. Langgin / B. Lantz / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen
- A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. Laxen
- C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci
- L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee
- J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee / R. Lee
- Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred
- J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître
- M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy
- M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin
- K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li
- X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos
- E. T. Lin / F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin
- C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / A. Liu / G. C. Liu
- Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L.
Lo
- J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou / L. T. London
- A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla / M. Lorenzini
- A. Lorenzo-Medina / V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo
- E. Lotti / T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin
- C. O. Lousto / N. Low / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi
- H. Lück / D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier
- R. Macas / M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan
- A. Macquet / K. Maeda / S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare
- R. M. Magee / E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi
- M. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi / E. Majorana
- C. N. Makarem / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis / U. Mali
- S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick / A.-K. Malz
- N. Man / M. Mancarella / V. Mandic / V. Mangano
- B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell / M. Manske / M. Mantovani
- M. Mapelli / C. Marinelli / F. Marion / A. S. Markosyan
- A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat / F. Martelli
- I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez / D. A. Martinez
- M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini / J. C. Martins
- D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro / A. Masserot
- M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich / M.
Matiushechkina
- N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell / G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy
- D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick / L. McCuller / S. McEachin
- C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan
- J. McIver / A. McLeod / I. McMahon / T. McRae
- R. McTeague / D. Meacher / B. N. Meagher / R. Mechum
- Q. Meijer / A. Melatos / C. S. Menoni / F. Mera
- R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni / K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh
- J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui / C. Messick
- B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde / P. M. Meyers / F. Meylahn
- A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao / C. Michel
- Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov / S. J. Miller
- M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov
- E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés
- C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra / C. Mishra / T. Mishra
- A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov
- K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa / S. Miyoki
- A. Miyoko / G. Mo / L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra
- S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / M. Mondin / J. K. Monsalve
- M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More
- S. More / C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno
- A. Moreso Serra / S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras
- A. Moscatello / M. Mould / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry
- L. Muccillo / F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee
- Soma Mukherjee / Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip Mukherjee / N.
Mukund
- A. Mullavey / H. Mullock / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli
- M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji
- A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura
- H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi
- V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa
- H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak / L. Negri
- A. Nela / C. Nelle / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson
- M. Nery / A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh
- S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa
- S. Nissanke / W. Niu / F. Nocera / J. Noller
- M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak / R. Nowicki
- J. F. Nuño Siles / L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling
- J. O’Dell / E. Oelker / M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan
- T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / F. Ohme / R. Oliveri
- R. Omer / B. O’Neal / M. Onishi / K. Oohara
- B. O’Reilly / M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea
- S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway
- A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki
- A. E. Pace / R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai
- L. Paiella / A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia
- M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud
- H. Pan / J. Pan / K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda
- Shiksha Pandey / Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale
- K. A. Pannone / B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri
- F. Paoletti / A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis
- L. Papalini / G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis / A. Parisi
- B.-J. Park / J. Park / W. Parker / G. Pascale
- D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger
- D. Passuello / O. Patane / A. V. Patel / D. Pathak
- A. Patra / B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul
- S. Paul / E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza
- A. Pele / F. E. Peña Arellano / X. Peng / Y. Peng
- S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego / Z. Pereira
- C. Périgois / G. Perna / A. Perreca / J. Perret
- S. Perriès / J. W. Perry / D. Pesios / S. Peters
- S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham
- K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli
- L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot / M. Piendibene
- F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra / V. Pierro
- M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo / L. Pinard
- I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello
- M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi / M. L. Planas
- W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani / E. Polini
- J. Pomper / L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli
- E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell
- G. S. Prabhu / M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier
- A. K. Prajapati / K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia
- G. Pratten / G. Principe / G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi
- P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher / J. Pullin
- P. Puppo / M. Pürrer / H. Qi / J. Qin
- G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke / L. H. Quiceno / P. J. Quinonez
- N. Qutob / R. Rading / I. Rainho / S. Raja
- C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal
- M. Ramos Arevalo / A. Ramos-Buades / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom
- P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto / A. Ravichandran / A. Ray
- V. Raymond / M. Razzano / J. Read / T. Regimbau
- S. Reid / C. Reissel / D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini
- A. Renzini / B. Revenu / A. Revilla Peña / R. Reyes
- L. Ricca / F. Ricci / M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone
- J. Rice / J. W. Richardson / M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal
- K. Riles / H. K. Riley / S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer
- C. Robertson / F. Robinet / M. Robinson / A. Rocchi
- L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins / A. E. Romano / J. D. Romano
- R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw / J. H. Romie
- S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa / T. J. Rosauer
- C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross / M. Rossello-Sastre
- S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy / D. Rozza
- P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales / K. Ruiz-Rocha
- S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh / S. Safi-Harb
- M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat / S. Sajith Menon
- K. Sakai / Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou / S. Sakon
- O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi / M. Saleem
- F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe / S. Salvador
- A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez / E. J. Sanchez
- L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders / E. M. Sänger
- F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan / N. Sarin
- P. Sarkar / A. Sasli / P. Sassi / B. Sassolas
- B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato / S. Sato / Yukino Sato
- Yu Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage / T. Sawada
- H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl
- M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt
- S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield
- K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz
- M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott / R. M. Sedas
- T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers
- N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo
- V. Sequino / M. Serra / A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer
- U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao / A. K. Sharma
- Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma / S. Sharma
Chaudhary
- P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / E. Sheridan / Z.-H. Shi
- M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai / S. Shirke
- D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short / S.
ShyamSundar
- A. Sider / H. Siegel / D. Sigg / L. Silenzi
- L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer / Amitesh Singh
- Anika Singh / D. Singh / N. Singh / S. Singh
- A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen
- D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J. Smetana / J. R. Smith
- L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith / S. Soares de Albuquerque
Filho
- M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I. Song / S. Soni
- V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani / F. Spada
- V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli / A. K. Srivastava
- F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer / N. Steinle
- J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas / P. Stevens
- M. StPierre / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk / A. L. Stuver
- M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / Y. Sudo / N. Sueltmann
- L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun / L. Sun
- S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton
- K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx
- M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi
- K. Takada / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi / A. Takamori
- S. Takano / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita / I. Takimoto Schmiegelow
- M. Takou-Ayaoh / C. Talbot / M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini
- D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka / S. Tanioka
- D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao / R. D. Tapia
- E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto / A. Taruya / J. D. Tasson
- J. G. Tau / D. Tellez / R. Tenorio / H. Themann
- A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M. Thomas / M.
Thomas
- P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu / K. A. Thorne
- E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari / Pawan Tiwari
- Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd
- M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland / A. E. Tolley
- T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura / H. Tong
- C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie / I. Tosta e Melo
- E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran / A. Trapananti
- R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor / M. Trevor
- M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian / A. Trovato
- L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang / S. Tsuchida
- L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi / C. Turski
- H. Ubach / N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall
- T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim / L. E. Uronen
- T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya
- G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia / M. Valentini
- S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan / M. van Dael
- E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / M.
van der Sluys
- A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra / M. VanDyke
- H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J.
Vanier
- M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro
- A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio
- G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis
- R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt
- B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets
- A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva Espinosa / V.
Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / S. Vitale
- H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel
- W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack
- L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner / L. Wallace
- E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang
- Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner / M. Was
- T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai / B. Weaver
- S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein
- R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette / J. T. Whelan
- B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens / D. Wilken
- A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams / M. J. Williams
- N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils
- L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf
- G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong
- I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters / J. L. Wright
- M. Wright / B. Wu / C. Wu / D. S. Wu
- H. Wu / K. Wu / Q. Wu / T. Y. Wu
- Y. Wu / Z. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki
- V. A. Xu / Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto
- K. Yamamoto / T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki
- T. Yan / K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough
- J. Yebana / S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin
- J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara
- M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri
- M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / L. Zhang
- N. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang / C. Zhao
- Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng
- H. Zhong / H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu
- A. B. Zimmerman / L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
We present results from the search for an isotropic
gravitational-wave background using Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo
data from O1 through O4a, the first part of the fourth observing run.
This background is the accumulated signal from unresolved sources
throughout cosmic history and encodes information about the merger
history of compact binaries throughout the Universe, as well as exotic
physics and potentially primordial processes from the early cosmos. Our
cross-correlation analysis reveals no statistically significant
background signal, enabling us to constrain several theoretical
scenarios. For compact binary coalescences which approximately follow a
2/3 power-law spectrum, we constrain the fractional energy density to
 (95% cred.), a factor of 1.7 improvement over
previous results. Scale-invariant backgrounds are constrained to
(95% cred.), a factor of 1.7 improvement over
previous results. Scale-invariant backgrounds are constrained to  , representing a 2.1x sensitivity gain. We also
place new limits on gravity theories predicting non-standard
polarization modes and confirm that terrestrial magnetic noise sources
remain below detection threshold. Combining these spectral limits with
population models for GWTC-4, the latest gravitational-wave event
catalog, we find our constraints remain above predicted merger
backgrounds but are approaching detectability. The joint analysis
combining the background limits shown here with the GWTC-4 catalog
enables improved inference of the binary black hole merger rate
evolution across cosmic time. Employing GWTC-4 inference results and
standard modeling choices, we estimate that the total background arising
from compact binary coalescences is
, representing a 2.1x sensitivity gain. We also
place new limits on gravity theories predicting non-standard
polarization modes and confirm that terrestrial magnetic noise sources
remain below detection threshold. Combining these spectral limits with
population models for GWTC-4, the latest gravitational-wave event
catalog, we find our constraints remain above predicted merger
backgrounds but are approaching detectability. The joint analysis
combining the background limits shown here with the GWTC-4 catalog
enables improved inference of the binary black hole merger rate
evolution across cosmic time. Employing GWTC-4 inference results and
standard modeling choices, we estimate that the total background arising
from compact binary coalescences is  at 90% confidence, where the largest contribution
is due to binary black holes only,
at 90% confidence, where the largest contribution
is due to binary black holes only,  .
.
GWTC-4.0:
An Introduction to Version 4.0 of the Gravitational-Wave Transient
Catalog
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / S. Adhicary
- D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari / V. K. Adkins
- S. Afroz / D. Agarwal / M. Agathos / M. Aghaei Abchouyeh
- O. D. Aguiar / S. Ahmadzadeh / L. Aiello / A. Ain
- P. Ajith / S. Akcay / T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi
- R. A. Alfaidi / A. Al-Jodah / C. Alléné / A. Allocca
- S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin / S. Alvarez-Lopez / O.
Amarasinghe
- A. Amato / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / T. Andrade
- M. Andrés-Carcasona / T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi
- J. M. Antelis / S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther
- S. Appert / S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya
- M. C. Araya / M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / L. Argianas
- N. Aritomi / F. Armato / S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud
- M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson / G. Ashton / Y. Aso
- M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone
- F. Attadio / F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone
- S. Babak / F. Badaracco / C. Badger / S. Bae
- S. Bagnasco / E. Bagui / L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai
- T. Baka / T. Baker / M. Ball / G. Ballardin
- S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri / B. Banerjee / D. Bankar
- T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish
- D. Barker / N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone
- B. Barr / L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta
- A. M. Bartoletti / M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / S. Basak
- A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri / A. Basti / D. E. Bates
- M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley / A. C. Baylor
- P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale / F. Beirnaert
- M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell / D. S. Bellie
- L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara / J. D. Bentley
- M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin / B. K. Berger
- S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / C. P. L. Berry / D. Bersanetti
- A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua
- N. Bevins / R. Bhandare / S. A. Bhat / R. Bhatt
- D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhaumik / S. Bhowmick / V. Biancalana
- A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti
- S. Bini / C. Binu / O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu
- A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard / S. Blaber
- J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair
- F. Bobba / N. Bode / G. Boileau / M. Boldrini
- G. N. Bolingbroke / A. Bolliand / L. D. Bonavena /
R. Bondarescu
- F. Bondu / E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino
- R. Bonnand / P. Booker / A. Borchers / S. Borhanian
- V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov / A. Boudon
- A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady / A. Branch
- M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant / A. Brillet
- M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks
- B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett
- G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant / Y. Bu
- F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik
- H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio
- D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies
- G. Cabras / R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati
- G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / A. Calafat / J. Calderón Bustillo
- T. A. Callister / E. Calloni / M. Canepa / G. Caneva Santoro
- K. C. Cannon / H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa
- E. Capote / G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani
- M. Carlassara / J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney
- M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo
- J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S.
Caudill
- M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / G. Cella / P. Cerdá-Durán
- E. Cesarini / W. Chaibi / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty
- S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / R.-J.
Chang
- S. Chao / E. L. Charlton / P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin
- C. Chatterjee / Debarati Chatterjee / Deep Chatterjee / M.
Chaturvedi
- S. Chaty / K. Chatziioannou / C. Checchia / A. Chen
- A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen
- S. Chen / Y. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen
- H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung
- F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini / R. Chierici / A. Chincarini
- M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary
- N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua / P. Chugh / G. Ciani
- P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / R. Ciolfi
- F. Clara / J. A. Clark / J. Clarke / T. A. Clarke
- P. Clearwater / S. Clesse / S. M. Clyne / E. Coccia
- E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace / E. Colangeli
- M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette / J. Collins / S. Colloms
- A. Colombo / C. M. Compton / G. Connolly / L. Conti
- T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish
- A. Corsi / S. Cortese / R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin
- A. Couineaux / J.-P. Coulon / J.-F. Coupechoux / P. Couvares
- D. M. Coward / R. Coyne / K. Craig / J. D. E. Creighton
- T. D. Creighton / P. Cremonese / A. W. Criswell / S. Crook
- R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen
- A. Cumming / E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / P. Dabadie
- L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton / S. Dall’Osso / S. Dal Pra
- G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio
- K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez / A. Dasgupta
- S. Datta / V. Dattilo / A. Daumas / N. Davari
- I. Dave / A. Davenport / M. Davier / T. F. Davies
- D. Davis / L. Davis / M. C. Davis / P. Davis
- M. Dax / J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix
- U. Deka / M. De Laurentis / S. Deléglise / F. De Lillo
- D. Dell’Aquila / F. Della Valle / W. Del Pozzo / F. De Marco
- G. Demasi / F. De Matteis / V. D’Emilio / N. Demos
- A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa
- C. De Rossi / M. Desai / R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone
- R. De Simone / A. Dhani / R. Diab / M. C. Díaz
- M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron / N. A. Didio / T. Dietrich
- L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo
- D. Diksha / A. Di Michele / J. Ding / S. Di Pace
- I. Di Palma / F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev
- Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen / D. Dominguez
- L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney
- S. Doravari / O. Dorosh / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers
- J.-G. Ducoin / L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / D. D’Urso
- H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa / M. Ebersold
- T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / B. Edelman / T. B. Edo
- O. Edy / A. Effler / J. Eichholz / H. Einsle
- M. Eisenmann / R. A. Eisenstein / A. Ejlli / M. Emma
- K. Endo / R. Enficiaud / A. J. Engl / L. Errico
- R. Espinosa / M. Esposito / R. C. Essick / H. Estellés
- T. Etzel / M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing
- J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi / F. Faedi / V. Fafone
- S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr / W. M. Farr
- G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays / M. Fazio
- J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi
- D. L. Ferguson / T. Fernandes / D. Fernando / S. Ferraiuolo
- I. Ferrante / T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura
- A. Fiori / I. Fiori / M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher
- R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer
- L. S. Fleming / E. Floden / H. Fong / J. A. Font
- C. Foo / B. Fornal / P. W. F. Forsyth / K. Franceschetti
- N. Franchini / S. Frasca / F. Frasconi / A. Frattale Mascioli
- Z. Frei / A. Freise / O. Freitas / R. Frey
- W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé
- M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii / T. Fujimori / P. Fulda
- M. Fyffe / B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage
- V. Galdi / H. Gallagher / B. Gallego / R. Gamba
- A. Gamboa / D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa
- J. García-Bellido / C. García Núñez / C. García-Quirós / J. W.
Gardner
- K. A. Gardner / J. Gargiulo / A. Garron / F. Garufi
- P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier
- V. Gayathri / T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai
- V. Gennari / J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding
- L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh
- Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime
- K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson / D. T. Gibson / C. Gier
- S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey
- P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb
- S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov / Y. Gong / G. González
- P. Goodarzi / S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin
- R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / S. Goyal
- B. Grace / A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados
- M. Granata / V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia
- A. Gray / C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco
- A. C. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green / A. M. Gretarsson
- E. M. Gretarsson / D. Griffith / W. L. Griffiths / H. L. Griggs
- G. Grignani / C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald
- D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes
- H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / A. M. Gunny / H. Guo
- W. Guo / Y. Guo / Anchal Gupta / Anuradha Gupta
- I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta / P. Gupta / S. K. Gupta
- T. Gupta / V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs
- N. Gutierrez / F. Guzman / D. Haba / M. Haberland
- S. Haino / E. D. Hall / R. Hamburg / E. Z. Hamilton
- G. Hammond / W.-B. Han / M. Haney / J. Hanks
- C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman
- H. Hansen / J. Hanson / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison
- S. Harikumar / K. Haris / T. Harmark / J. Harms
- G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry / J. Hart / B. Haskell
- C.-J. Haster / K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama
- R. Hayes / M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze / J. Heinzel
- H. Heitmann / A. Heffernan / F. Hellman / A. F.
Helmling-Cornell
- G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M. Hendry / I. S. Heng
- M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw / M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt
- J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham / S. Hild / S. Hill
- Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata / C. Hirose / S. Hochheim
- D. Hofman / N. A. Holland / D. E. Holz / L. Honet
- C. Hong / S. Hoshino / J. Hough / S. Hourihane
- N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh
- H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung / W.-F. Hsu
- Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang
- A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey / D. C. Y. Hui / V. Hui
- S. Husa / R. Huxford / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo
- M. Ianni / A. Ierardi / A. Iess / H. Imafuku
- K. Inayoshi / Y. Inoue / G. Iorio / P. Iosif
- M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa / M. Isi
- Y. Itoh / H. Iwanaga / M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer
- C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet / S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav
- T. Jain / A. L. James / P. A. James / R. Jamshidi
- A. Jan / K. Jani / J. Janquart / K. Janssens
- N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume
- W. Javed / A. Jennings / W. Jia / J. Jiang
- S. J. Jin / C. Johanson / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson
- N. K. Johnson-McDaniel / M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston / N.
Johny
- D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones / E. J. Jones / R. Jones
- S. Jose / P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi / J. Ju
- L. Ju / K. Jung / J. Junker / V. Juste
- H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita / I. Kaku / V. Kalogera
- M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy
- G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner / S. J. Kapadia
- D. P. Kapasi / S. Karat / R. Kashyap / M. Kasprzack
- W. Kastaun / T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman
- R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto / A. Kazemi
- D. Keitel / J. Kennington / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key
- R. Khadela / S. Khadka / F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan
- I. Khan / T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid
- W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim
- K. Kim / M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim
- C. Kimball / M. Kinley-Hanlon / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel
- S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee / N. Knust / K. Kobayashi
- P. Koch / S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri
- K. Kokeyama / S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / K. Komori
- A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / M. Korobko / R. V. Kossak
- X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam
- D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu
- A. Królak / K. Kruska / J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn
- S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan / A. Kumar / Praveen Kumar
- Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume
- K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara
- K. Kwak / K. Kwan / J. Kwok / G. Lacaille
- P. Lagabbe / D. Laghi / S. Lai / E. Lalande
- M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry / B. B. Lane
- R. N. Lang / J. Lange / R. Langgin / B. Lantz
- A. La Rana / I. La Rosa / J. Larsen / A. Lartaux-Vollard
- P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. N. Lawrence / M. Laxen
- C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci
- L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee
- J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee / R. Lee
- Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred
- J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître
- M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy
- M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin
- K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li / T. G. F. Li
- X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos
- C-Y. Lin / E. T. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin
- C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / T. B. Littenberg / A. Liu
- G. C. Liu / Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol
- R. K. L. Lo / J.-P. Locquet / M. R. Loizou / L. T. London
- A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla / A. Lorenzo-Medina
- V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / E. Lotti
- T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto
- N. Low / M. J. Lowry / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi
- H. Lück / D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier
- L.-T. Ma / S. Ma / R. Macas / A. Macedo
- M. MacInnis / R. R. Maciy / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan
- A. Macquet / D. Macri / K. Maeda / S. Maenaut
- S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee / E. Maggio / R. Maggiore
- M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi
- E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis
- U. Mali / S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick
- A. Malz / N. Man / V. Mandic / V. Mangano
- B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell / G. Mansingh / M. Manske
- M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli / F. Marchesoni / C. Marinelli
- D. Marín Pina / F. Marion / S. Márka / Z. Márka
- A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat
- F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez
- M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini / J. C. Martins
- D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro / A. Masserot
- M. Masso-Reid / M. Mastrodicasa / S. Mastrogiovanni / T.
Matcovich
- M. Matiushechkina / M. Matsuyama / N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell
- G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick
- L. McCuller / S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee
- J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod
- T. McRae / D. Meacher / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos
- M. Melching / S. Mellaerts / C. S. Menoni / F. Mera
- R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni / K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh
- J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui / C. Messenger
- C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn
- A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao / I. Michaloliakos
- C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / S. J. Miller
- M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov
- N. Mio / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés
- C.-A. Miritescu / A. K. Mishra / A. Mishra / C. Mishra
- T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra
- V. P. Mitrofanov / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa / S. Miyamoto
- S. Miyoki / G. Mo / L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra
- S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / C. Mondal / M. Mondin
- M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More
- S. More / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno / S. Morisaki
- Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras / A. Moscatello / M. Mould
- P. Mourier / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry / F. Muciaccia
- D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma Mukherjee / Subroto
Mukherjee
- Suvodip Mukherjee / N. Mukund / A. Mullavey / H. Mullock
- J. Munch / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli / Y. Murakami
- M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / S. Muusse / D. Nabari
- S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki
- K. Nakamura / H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze
- D. Nandi / V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia
- T. Narikawa / H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak
- A. Nela / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery
- A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols
- A. B. Nielsen / G. Nieradka / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa
- S. Nissanke / E. Nitoglia / W. Niu / F. Nocera
- M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak / J. F. Nuño Siles
- L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling / J. O’Dell
- M. Oertel / A. Offermans / G. Oganesyan / J. J. Oh
- K. Oh / T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / M. Ohkawa
- F. Ohme / R. Oliveri / R. Omer / B. O’Neal
- K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly / R. Oram / N. D. Ormsby
- M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / Y. Oshima
- S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway
- A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / A. E. Pace
- R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai / L. Paiella
- A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi
- P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud / J. Pan
- K. C. Pan / R. Panai / P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey
- Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone
- B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / F. Paoletti / A. Paolone
- A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini / G.
Papigkiotis
- A. Paquis / A. Parisi / B.-J. Park / J. Park
- W. Parker / G. Pascale / D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti
- R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger / D. Passuello / O. Patane
- D. Pathak / L. Pathak / A. Patra / B. Patricelli
- A. S. Patron / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul / S. Paul
- E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza / A. Pele
- F. E. Peña Arellano / S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego
- Z. Pereira / J. J. Perez / C. Périgois / G. Perna
- A. Perreca / J. Perret / S. Perriès / J. W. Perry
- D. Pesios / S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer
- H. Pham / K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam
- M. Piarulli / L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot
- M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra
- V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo
- L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski
- M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi
- M. L. Planas / W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani
- E. Polini / L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli
- E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell
- M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati
- K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia / G. Pratten
- G. Principe / M. Principe / G. A. Prodi / L. Prokhorov
- P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher
- J. Pullin / M. Punturo / P. Puppo / M. Pürrer
- H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke
- P. J. Quinonez / F. J. Raab / I. Rainho / S. Raja
- C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal
- A. Ramos-Buades / D. Rana / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom
- P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto / A. Ray / V. Raymond
- M. Razzano / J. Read / M. Recaman Payo / T. Regimbau
- L. Rei / S. Reid / D. H. Reitze / P. Relton
- A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu / R. Reyes / A. S. Rezaei
- F. Ricci / M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. W. Richardson
- M. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley
- S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet
- M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins
- A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw
- J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa
- T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross
- M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. Roy / S. K. Roy
- D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales
- K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / J. Sadiq
- P. Saffarieh / S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha
- T. Sainrat / S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou
- S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi
- M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe
- S. Salvador / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez / E. J. Sanchez
- J. H. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders
- E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan
- N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / S. Sasaoka / A. Sasli
- P. Sassi / B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato
- Y. Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage / T. Sawada
- H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl
- M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt
- S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield
- K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz
- M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott / R. M. Sedas
- T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers
- A. S. Sengupta / D. Sentenac / E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo
- V. Sequino / M. Serra / G. Servignat / A. Sevrin
- T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. S. Shahriar / M. A. Shaikh
- L. Shao / A. Sharma / A. K. Sharma / P. Sharma
- S. Sharma Chaudhary / M. R. Shaw / P. Shawhan / N. S.
Shcheblanov
- Y. Shikano / M. Shikauchi / K. Shimode / H. Shinkai
- J. Shiota / S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker
- R. W. Short / S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider / H. Siegel
- D. Sigg / L. Silenzi / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer
- A. Singh / D. Singh / M. K. Singh / N. Singh
- S. Singh / A. Singha / A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala
- V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater / T. J.
Slaven-Blair
- J. Smetana / J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith
- W. J. Smith / K. Somiya / I. Song / K. Soni
- S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani
- A. Southgate / F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer
- M. Spera / P. Spinicelli / C. A. Sprague / A. K. Srivastava
- F. Stachurski / D. A. Steer / N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner
- S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas / P. Stevens / S. P. Stevenson
- F. Stolzi / M. StPierre / G. Stratta / M. D. Strong
- A. Strunk / R. Sturani / A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek
- S. Sudhagar / N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / J. M. Sullivan
- K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun / L. Sun / S. Sunil
- J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton / T. Suzuki
- Y. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk
- P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi / S. C. Tait
- H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi / A. Takamori / T. Takase
- K. Takatani / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita / C. Talbot
- M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka
- S. J. Tanaka / T. Tanaka / D. Tang / S. Tanioka
- D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao / R. D. Tapia
- E. N. Tapia San Martín / R. Tarafder / C. Taranto / A. Taruya
- J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau / R. Tenorio / H. Themann
- A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M. Thomas / M.
Thomas
- P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu / K. A. Thorne
- E. Thrane / S. Tibrewal / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari
- P. Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd
- A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland / A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru
- K. Tomita / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura / H. Tong
- C. Tong-Yu / A. Toriyama / N. Toropov / A. Torres-Forné
- C. I. Torrie / M. Toscani / I. Tosta e Melo / E. Tournefier
- M. Trad Nery / A. Trapananti / F. Travasso / G. Traylor
- C. Trejo / M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee
- G. Troian / A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau
- T. T. L. Tsang / S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada / K. Turbang
- M. Turconi / C. Turski / H. Ubach / N. Uchikata
- T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall / T. Uehara / M. Uematsu
- S. Ueno / V. Undheim / T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello
- H. Vahlbruch / G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / G. Valdes
- J. Valencia / A. F. Valentini / M. Valentini / S. A.
Vallejo-Peña
- S. Vallero / V. Valsan / N. van Bakel / M. van Beuzekom
- M. van Dael / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / D. C.
Vander-Hyde
- M. van der Sluys / A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra
- H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J.
Vanier
- M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / M. H. P. M. van Putten / Z. Van
Ranst
- N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas / J. J. Varghese
- V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio / G. Vedovato
- J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis / J. Venneberg
- P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt / B. Verma
- P. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. M. Vibhute / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant
- A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / V. Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / A. Virtuoso
- S. Vitale / A. Vives / H. Vocca / D. Voigt
- E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel / L. Vujeva / S. P.
Vyatchanin
- J. Wack / L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner
- A. Wajid / M. Walker / G. S. Wallace / L. Wallace
- E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang
- Y. F. Wang / Z. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner
- M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai
- K. E. Wayt / B. R. Weaver / B. Weaver / C. R. Weaving
- S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein
- R. Weiss / F. Wellmann / L. Wen / P. Weßels
- K. Wette / J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle
- E. G. Wickens / J. B. Wildberger / D. Wilken / D. J. Willadsen
- K. Willetts / D. Williams / M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams
- J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils / C. W. Winborn
- J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf / G. Woan / J. Woehler
- N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong / I. C. F. Wong / J. L. Wright
- M. Wright / C. Wu / D. S. Wu / H. Wu
- E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu / Y. Xu
- N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto / T. S. Yamamoto
- T. Yamamoto / S. Yamamura / R. Yamazaki / T. Yan
- F. W. Yang / F. Yang / K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang
- Z. Yarbrough / H. Yasui / S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar
- X. Yin / J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa / J. Yoo
- H. Yu / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara / A. Zadrożny
- M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri
- M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / A. C. Zhang
- L. Zhang / R. Zhang / T. Zhang / Y. Zhang
- C. Zhao / Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao / Y. Zheng
- H. Zhong / R. Zhou / X.-J. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu
- A. B. Zimmerman / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
The Gravitational-Wave Transient Catalog (GWTC) is a collection of
short-duration (transient) gravitational wave signals identified by the
LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Collaboration in gravitational-wave data produced by
the eponymous detectors. The catalog provides information about the
identified candidates, such as the arrival time and amplitude of the
signal and properties of the signal’s source as inferred from the
observational data. GWTC is the data release of this dataset and version
4.0 extends the catalog to include observations made during the first
part of the fourth LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA observing run up until 2024 January
31. This paper marks an introduction to a collection of articles related
to this version of the catalog, GWTC-4.0. The collection of articles
accompanying the catalog provides documentation of the methods used to
analyze the data, summaries of the catalog of events, observational
measurements drawn from the population, and detailed discussions of
selected candidates
A
direct black hole mass measurement in a Little Red Dot at the Epoch of
Reionization
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Ignas Juodžbalis / Cosimo Marconcini / Francesco D’Eugenio / Roberto
Maiolino
- Alessandro Marconi / Hannah Übler / Jan Scholtz / Xihan Ji
- Santiago Arribas / Jake S. Bennett / Volker Bromm / Andrew J.
Bunker
- Stefano Carniani / Stéphane Charlot / Giovanni Cresci / Pratika
Dayal
- Eiichi Egami / Andrew Fabian / Kohei Inayoshi / Yuki Isobe
- Lucy Ivey / Gareth C. Jones / Sophie Koudmani / Nicolas
Laporte
- Boyuan Liu / Jianwei Lyu / Giovanni Mazzolari / Stephanie Monty
- Eleonora Parlanti / Pablo G. Pérez-González / Michele Perna / Brant
Robertson
- Raffaella Schneider / Debora Sijacki / Sandro Tacchella / Alessandro
Trinca
- Rosa Valiante / Marta Volonteri / Joris Witstok / Saiyang Zhang
Summary
Recent discoveries of faint active galactic nuclei (AGN) at the
redshift frontier have revealed a plethora of broad emitters with
optically red continua, named Little Red Dots (LRDs), which comprise
15-30% of the high redshift broad line AGN population. Due to their
peculiar spectral properties and X-ray weakness, modeling LRDs with
standard AGN templates has proven challenging. In particular, the
validity of single-epoch virial mass estimates in determining the black
hole (BH) masses of LRDs has been called into question, with some models
claiming that masses might be overestimated by up to 2 orders of
magnitude, and other models claiming that LRDs may be entirely stellar
in nature. We report the direct, dynamical BH mass measurement in a
strongly lensed LRD at  . The combination
of lensing with deep spectroscopic data reveals a rotation curve that is
inconsistent with a nuclear star cluster, yet can be well explained by
Keplerian rotation around a point mass of 50 million Solar masses,
consistent with virial BH mass estimates from the Balmer lines. The
Keplerian rotation leaves little room for any stellar component in a
host galaxy, as we conservatively infer
. The combination
of lensing with deep spectroscopic data reveals a rotation curve that is
inconsistent with a nuclear star cluster, yet can be well explained by
Keplerian rotation around a point mass of 50 million Solar masses,
consistent with virial BH mass estimates from the Balmer lines. The
Keplerian rotation leaves little room for any stellar component in a
host galaxy, as we conservatively infer  . Such a ‘’naked’’ black hole, together with its
near-pristine environment, indicates that this LRD is a massive black
hole seed caught in its earliest accretion phase.
. Such a ‘’naked’’ black hole, together with its
near-pristine environment, indicates that this LRD is a massive black
hole seed caught in its earliest accretion phase.
Open
Data from LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA through the First Part of the Fourth
Observing Run
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya / M. C. Araya
- M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi / F. Armato
- S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- G. Ashton / Y. Aso / L. Asprea / M. Assiduo
- S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston / P. Astone / F. Attadio
- F. Aubin / K. AultONeal / G. Avallone / E. A. Avila
- S. Babak / C. Badger / S. Bae / S. Bagnasco
- L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka / A. M. Baker
- K. A. Baker / T. Baker / G. Baldi / N. Baldicchi
- M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri
- B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral
- M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga / B. C. Barish / D. Barker
- N. Barman / P. Barneo / F. Barone / B. Barr
- L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti
- M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri
- A. Basti / M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley
- A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale
- F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell
- D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi / W. Benoit / I. Bentara
- J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera / F. Bergamin
- B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi / M. Beroiz / C. P. L. Berry
- D. Bersanetti / T. Bertheas / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser
- D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare
- R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhattacharyya / S. Bhaumik
- V. Biancalana / A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley
- A. Binetti / S. Bini / C. Binu / S. Biot
- O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi
- M.-A. Bizouard / S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg
- C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair / N. Bode / N. Boettner
- G. Boileau / M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A.
Bolliand
- L. D. Bonavena / R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla
- M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / A. Borchers
- S. Borhanian / V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov
- Y. Bothra / A. Boudon / L. Bourg / M. Boyle
- A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady / A. Branch
- M. Branchesi / I. Braun / T. Briant / A. Brillet
- M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks
- B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett
- G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant / Y. Bu
- F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik
- H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio
- D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies
- R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli
- C. Cahillane / A. Calafat / T. A. Callister / E. Calloni
- S. R. Callos / M. Canepa / G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon
- H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa / E. Capote
- G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara
- J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli
- G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos
- J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S.
Caudill
- M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja / G. Cella
- P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi
- A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka
Subrahmanya
- J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / K. Chang / S. Chao
- P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee / Debarati
Chatterjee
- Deep Chatterjee / M. Chaturvedi / S. Chaty / K. Chatziioannou
- A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen / H. Chen
- H. Y. Chen / S. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen
- H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung
- F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini / A. Chiba / A. Chincarini
- M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary
- N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani / P. Ciecielag
- M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok / F. Clara
- J. A. Clark / T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater / S. Clesse
- F. Cleva / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo / P.-F. Cohadon
- S. Colace / E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette
- J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo / C. M. Compton
- G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt / I. Cordero-Carrión
- S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado / A. Corsi
- R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux / P. Couvares
- D. M. Coward / R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo / J. D. E. Creighton
- T. D. Creighton / P. Cremonese / S. Crook / R. Crouch
- J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen / A. Cumming
- E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição / T. Dal Canton
- S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin
- S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez
- R. Das / A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo / A. Daumas
- N. Davari / I. Dave / A. Davenport / M. Davier
- T. F. Davies / D. Davis / L. Davis / M. C. Davis
- P. Davis / E. J. Daw / M. Dax / J. De Bolle
- M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis / F. De Lillo
- S. Della Torre / W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny / F. De Marco
- G. Demasi / F. De Matteis / N. Demos / T. Dent
- A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri / R. De Rosa
- C. De Rossi / M. Desai / R. DeSalvo / A. DeSimone
- R. De Simone / A. Dhani / R. Diab / M. C. Díaz
- M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron / T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore
- C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha
- J. Ding / S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma / D. Di Piero
- F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev / J. P. Docherty
- Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen / A. Doke
- A. Domiciano De Souza / L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan / K. L.
Dooley
- T. Dooney / S. Doravari / O. Dorosh / W. J. D. Doyle
- M. Drago / J. C. Driggers / M. Dubois / L. Dunn
- U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne / D. D’Urso / P. Dutta Roy
- H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa / M. Ebersold
- T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / A. Effler / J. Eichholz
- H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann / M. Emma / K. Endo
- R. Enficiaud / L. Errico / R. Espinosa / M. Esposito
- R. C. Essick / H. Estellés / T. Etzel / M. Evans
- T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi
- V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr
- W. M. Farr / G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays
- M. Fazio / J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti
- E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes / T. Fernandes / D. Fernando
- S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura
- A. Fiori / I. Fiori / M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher
- R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer
- L. S. Fleming / E. Floden / H. Fong / J. A. Font
- F. Fontinele-Nunes / C. Foo / B. Fornal / K. Franceschetti
- F. Frappez / S. Frasca / F. Frasconi / J. P. Freed
- Z. Frei / A. Freise / O. Freitas / R. Frey
- W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé
- M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii / T. Fujimori / P. Fulda
- M. Fyffe / B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage
- V. Galdi / R. Gamba / A. Gamboa / S. Gamoji
- D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido
- C. García-Quirós / J. W. Gardner / K. A. Gardner / S. Garg
- J. Gargiulo / X. Garrido / A. Garron / F. Garufi
- P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier
- V. Gayathri / T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai
- V. Gennari / J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding
- L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh
- Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime
- K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson / C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis
- J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey / R. V. Godley
- P. Godwin / A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb
- S. Gomez Lopez / B. Goncharov / G. González / P. Goodarzi
- S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty
- D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / A. Grado / V. Graham
- A. E. Granados / M. Granata / V. Granata / S. Gras
- P. Grassia / J. Graves / C. Gray / R. Gray
- G. Greco / A. C. Green / L. Green / S. M. Green
- S. R. Green / C. Greenberg / A. M. Gretarsson / H. K. Griffin
- D. Griffith / H. L. Griggs / G. Grignani / C. Grimaud
- H. Grote / S. Grunewald / D. Guerra / D. Guetta
- G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes / H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli
- H. Guo / W. Guo / Y. Guo / Anuradha Gupta
- I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta / S. K. Gupta / V. Gupta
- N. Gupte / J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez / N. Guttman
- F. Guzman / D. Haba / M. Haberland / S. Haino
- E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond / M. Haney
- J. Hanks / C. Hanna / M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela
- A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen / J. Hanson / S. Hanumasagar
- R. Harada / A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar / K. Haris
- I. Harley-Trochimczyk / T. Harmark / J. Harms / G. M. Harry
- I. W. Harry / J. Hart / B. Haskell / C. J. Haster
- K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama / M. C. Heintze
- J. Heinze / J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann / F. Hellman
- A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M.
Hendry
- I. S. Heng / M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw / M. Heurs
- A. L. Hewitt / J. Heynen / J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham
- S. Hild / S. Hill / Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata
- C. Hirose / D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan / N. A. Holland
- I. J. Hollows / D. E. Holz / L. Honet / D. J. Horton-Bailey
- J. Hough / S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard / E. J. Howell
- C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi / H.-F. Hsieh
- H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu / W.-F. Hsu
- Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang / Y. T. Huang
- A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey / V. Hui / S. Husa
- R. Huxford / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni
- G. Iannone / J. Iascau / K. Ide / R. Iden
- A. Ierardi / S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku / Y. Inoue
- G. Iorio / P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin
- R. Ishikawa / M. Isi / K. S. Isleif / Y. Itoh
- M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet / P.-E. Jacquet
- T. Jacquot / S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav / M. Jain
- T. Jain / A. L. James / K. Jani / J. Janquart
- N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume
- W. Javed / A. Jennings / M. Jensen / W. Jia
- J. Jiang / H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson
- M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston / N. Johny / D. H. Jones
- D. I. Jones / R. Jones / H. E. Jose / P. Joshi
- S. K. Joshi / G. Joubert / J. Ju / L. Ju
- K. Jung / J. Junker / V. Juste / H. B. Kabagoz
- T. Kajita / I. Kaku / V. Kalogera / M. Kalomenopoulos
- M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang
- N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty / S. J.
Kapadia
- D. P. Kapasi / M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack / H. Kato
- T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman / R. Kaushik
- K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel / L. J. Kemperman
- J. Kennington / F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key
- R. Khadela / S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar / F. Y. Khalili
- F. Khan / T. Khanam / M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid
- W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim / J. C. Kim
- K. Kim / M. H. Kim / S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim
- C. Kimball / K. Kimes / M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel
- S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox / N. Knust
- K. Kobayashi / S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek / K. Kohri
- K. Kokeyama / S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou / A. E. Koloniari
- K. Komori / A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos / L. M. Koponen
- M. Korobko / X. Kou / A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos
- M. Kovalam / T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak / S. L. Kranzhoff
- V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker / A. Królak
- K. Kruska / J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn / S. Kulkarni
- A. Kulur Ramamohan / Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar / Praveen Kumar
- Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume
- K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / S. Kuwahara
- K. Kwak / K. Kwan / S. Kwon / G. Lacaille
- D. Laghi / A. H. Laity / E. Lalande / M. Lalleman
- P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry / B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang
- J. Lange / R. Langgin / B. Lantz / I. La Rosa
- J. Larsen / A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence
- M. Laxen / C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro
- P. Leaci / L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche / H. M. Lee
- H. W. Lee / J. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee
- R. Lee / Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee / Y. Lee
- I. N. Legred / J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean
- A. Lemaître / M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime
- N. Leroy / M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier
- Y. Levin / K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li
- T. G. F. Li / X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li
- A. Lihos / E. T. Lin / F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin
- Y.-C. Lin / C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / A. Liu
- G. C. Liu / Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol
- R. K. L. Lo / J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou
- L. T. London / A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla
- A. Lorenzo-Medina / V. Loriette / M. Lormand / G. Losurdo
- E. Lotti / T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough / H. A. Loughlin
- C. O. Lousto / N. Low / N. Lu / L. Lucchesi
- H. Lück / D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier
- R. Macas / M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod / I. A. O. MacMillan
- A. Macquet / K. Maeda / S. Maenaut / S. S. Magare
- R. M. Magee / E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi
- M. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi / E. Majorana
- C. N. Makarem / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis / U. Mali
- S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick / A.-K. Malz
- N. Man / M. Mancarella / V. Mandic / V. Mangano
- B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell / M. Manske / M. Mantovani
- M. Mapelli / C. Marinelli / F. Marion / A. S. Markosyan
- A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat / F. Martelli
- I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez / D. A. Martinez
- M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini / J. C. Martins
- D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro / A. Masserot
- M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich / M.
Matiushechkina
- L. Maurin / N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell / G. McCarrol
- R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick / L. McCuller
- S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn
- K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod / I. McMahon
- T. McRae / R. McTeague / D. Meacher / B. N. Meagher
- R. Mechum / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos / C. S. Menoni
- F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni / K. Merfeld
- E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt / M. Merzougui
- C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn
- A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao / C. Michel
- Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov / S. J. Miller
- M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov
- E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés
- C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra / C. Mishra / T. Mishra
- A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov
- K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa / S. Miyoki
- A. Miyoko / G. Mo / L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra
- S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / M. Mondin / M. Montani
- C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More / S. More
- C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno / A. Moreso Serra
- S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras / A. Moscatello
- M. Mould / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry / L. Muccillo
- F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma
Mukherjee
- Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip Mukherjee / N. Mukund / A. Mullavey
- H. Mullock / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli / M. Murakoshi
- P. G. Murray / D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji / A. Nagar
- N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura / H. Nakano
- M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi / V. Napolano
- P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa / H. Narola
- L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak / L. Negri / A. Nela
- C. Nelle / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery
- A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols
- A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa / S. Nissanke
- W. Niu / F. Nocera / J. Noller / M. Norman
- C. North / J. Novak / R. Nowicki / J. F. Nuño Siles
- L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling / J. O’Dell
- E. Oelker / M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan / T. O’Hanlon
- M. Ohashi / F. Ohme / R. Oliveri / R. Omer
- B. O’Neal / M. Onishi / K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly
- M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / S. Oshino
- C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway / A. Ouzriat
- H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki / A. E. Pace
- R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai / L. Paiella
- A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi
- P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud / H. Pan
- J. Pan / K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda / Shiksha Pandey
- Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone
- B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri / F. Paoletti
- A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini
- G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis / A. Parisi / B.-J. Park
- J. Park / W. Parker / G. Pascale / D. Pascucci
- A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger / D. Passuello
- O. Patane / A. V. Patel / D. Pathak / A. Patra
- B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul / S. Paul
- E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza / A. Pele
- F. E. Peña Arellano / X. Peng / Y. Peng / S. Penn
- M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego / Z. Pereira / C. Périgois
- G. Perna / A. Perreca / J. Perret / S. Perriès
- J. W. Perry / D. Pesios / S. Peters / S. Petracca
- C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham / K. A. Pham
- K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli / L. Piccari
- O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot / M. Piendibene / F. Piergiovanni
- L. Pierini / G. Pierra / V. Pierro / M. Pietrzak
- M. Pillas / F. Pilo / L. Pinard / I. M. Pinto
- M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello / M. D. Pitkin
- A. Placidi / E. Placidi / M. L. Planas / W. Plastino
- C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani / E. Polini / J. Pomper
- L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli / E. K. Porter
- C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell / G. S. Prabhu
- M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati
- K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia / G. Pratten
- G. Principe / G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi / P. Prosposito
- A. C. Providence / A. Puecher / J. Pullin / P. Puppo
- M. Pürrer / H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner
- V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez / N. Qutob / R. Rading
- I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari
- K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / M. Ramos Arevalo / A.
Ramos-Buades
- S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto
- A. Ravichandran / A. Ray / V. Raymond / M. Razzano
- J. Read / T. Regimbau / S. Reid / C. Reissel
- D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu / A. Revilla Peña
- R. Reyes / L. Ricca / F. Ricci / M. Ricci
- A. Ricciardone / J. Rice / J. W. Richardson / M. L. Richardson
- A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley / S. Rinaldi
- J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet / M. Robinson
- A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins / A. E. Romano
- R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw / J. H. Romie
- S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa / T. J. Rosauer
- C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross / M. Rossello-Sastre
- S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy / D. Rozza
- P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales / K. Ruiz-Rocha
- S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh / S. Safi-Harb
- M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat / S. Sajith Menon
- K. Sakai / Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou / S. Sakon
- O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi / M. Saleem
- F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe / S. Salvador
- A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez / E. J. Sanchez
- L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders / E. M. Sänger
- F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan / N. Sarin
- P. Sarkar / A. Sasli / P. Sassi / B. Sassolas
- B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato / S. Sato / Yukino Sato
- Yu Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage / T. Sawada
- H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl
- M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt
- S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield
- K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz
- M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott / R. M. Sedas
- T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers
- N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo
- V. Sequino / M. Serra / A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer
- U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao / A. K. Sharma
- Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma / S. Sharma
Chaudhary
- P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / E. Sheridan / Z.-H. Shi
- M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai / S. Shirke
- D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short / S.
ShyamSundar
- A. Sider / H. Siegel / D. Sigg / L. Silenzi
- L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer / Amitesh Singh
- Anika Singh / D. Singh / N. Singh / S. Singh
- A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen
- D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J. Smetana / J. R. Smith
- L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith / S. Soares de Albuquerque
Filho
- M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I. Song / S. Soni
- V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani / F. Spada
- V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli / A. K. Srivastava
- F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer / N. Steinle
- J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas / P. Stevens
- M. StPierre / M. D. Strong / A. Strunk / A. L. Stuver
- M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar / Y. Sudo / N. Sueltmann
- L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan / J. Sun / L. Sun
- S. Sunil / J. Suresh / B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton
- K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx
- M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi
- K. Takada / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi / A. Takamori
- S. Takano / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita / I. Takimoto Schmiegelow
- M. Takou-Ayaoh / C. Talbot / M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini
- D. Tanabe / K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka / S. Tanioka
- D. B. Tanner / W. Tanner / L. Tao / R. D. Tapia
- E. N. Tapia San Martín / C. Taranto / A. Taruya / J. D. Tasson
- J. G. Tau / D. Tellez / R. Tenorio / H. Themann
- A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M. Thomas / M.
Thomas
- P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu / K. A. Thorne
- E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari / Pawan Tiwari
- Praveer Tiwari / S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd
- M. Toffano / A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland / A. E. Tolley
- T. Tomaru / V. Tommasini / T. Tomura / H. Tong
- C. Tong-Yu / A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie / I. Tosta e Melo
- E. Tournefier / M. Trad Nery / K. Tran / A. Trapananti
- R. Travaglini / F. Travasso / G. Traylor / M. Trevor
- M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian / A. Trovato
- L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang / S. Tsuchida
- L. Tsukada / K. Turbang / M. Turconi / C. Turski
- H. Ubach / N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall
- T. Uehara / K. Ueno / V. Undheim / L. E. Uronen
- T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya
- G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia / M. Valentini
- S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan / M. van Dael
- E. Van den Bossche / J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / M.
van der Sluys
- A. Van de Walle / J. van Dongen / K. Vandra / M. VanDyke
- H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J.
Vanier
- M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro
- A. F. Vargas / V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio
- G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis
- R. C. Venterea / P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt
- B. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets
- A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva Espinosa / V.
Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / S. Vitale
- H. Vocca / D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel
- W. E. Vossius / L. Vujeva / S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack
- L. E. Wade / M. Wade / K. J. Wagner / L. Wallace
- E. J. Wang / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang
- Y. F. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner / M. Was
- T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai / B. Weaver
- S. A. Webster / N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein
- R. Weiss / L. Wen / K. Wette / J. T. Whelan
- B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens / D. Wilken
- A. T. Wilkin / B. M. Williams / D. Williams / M. J. Williams
- N. S. Williams / J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils
- L. Wilson / C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf
- G. Woan / J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong
- I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters / J. L. Wright
- M. Wright / B. Wu / C. Wu / D. S. Wu
- H. Wu / K. Wu / Q. Wu / Y. Wu
- Z. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu
- Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto
- T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki / T. Yan
- K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough / J. Yebana
- S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin / J. Yokoyama
- T. Yokozawa / S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara / M. Zanolin
- M. Zeeshan / T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli
- M. Zerrad / M. Zevin / L. Zhang / N. Zhang
- R. Zhang / T. Zhang / C. Zhao / Yue Zhao
- Yuhang Zhao / Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng / H. Zhong
- H. Zhou / H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman
- L. Zimmermann / M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA form a network of gravitational-wave
observatories. Data and analysis results from this network are made
publicly available through the Gravitational Wave Open Science Center.
This paper describes open data from this network, including the addition
of data from the first part of the fourth observing run (O4a) and
selected periods from the preceding engineering run, collected from May
2023 to January 2024. The public data set includes calibrated strain
time series for each instrument, data from additional channels used for
noise subtraction and detector characterization, and analysis data
products from version 4.0 of the Gravitational-Wave Transient
Catalog.
Articles for week 34 2025
Euclid
preparation. Establishing the quality of the 2D reconstruction of the
filaments of the cosmic web with DisPerSE using Euclid photometric
redshifts
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / N. Malavasi / F. Sarron / U. Kuchner
- C. Laigle / K. Kraljic / P. Jablonka / M. Balogh
- S. Bardelli / M. Bolzonella / J. Brinchmann / G. De Lucia
- F. Fontanot / C. Gouin / M. Hirschmann / Y. Kang
- M. Magliocchetti / T. Moutard / J. G. Sorce / M. Spinelli
- L. Wang / L. Xie / A. M. C. Le Brun / E. Tsaprazi
- O. Cucciati / G. Zamorani / M. De Petris / E. Bulbul
- R. van de Weygaert / N. Aghanim / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / A. M. Di Giorgio
- J. Dinis / H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- I. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- S. Ilić / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / S.
Maurogordato
- H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / S. Mourre
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L.
Gabarra
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / V. Scottez / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / V. Allevato / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / A.
Balaguera-Antolinez
- M. Ballardini / C. Benoist / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / R. Cabanac / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / A. Cappi / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Contarini / T. Contini
- A. R. Cooray / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / S. Hemmati
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / A. Jimenez
Muñoz
- J. J. E. Kajava / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / C. C.
Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi / S. Lee / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas / C. J. A. P.
Martins
- L. Maurin / R. B. Metcalf / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- V. Popa / D. Potter / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci
- M. Sahlén / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / M. Sereno / A. Silvestri / L. C. Smith
- S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / D. Vergani / G. Verza / N. A. Walton
Summary
Cosmic filaments are prominent structures of the matter distribution
of the Universe. Modern detection algorithms are an efficient way to
identify filaments in large-scale observational surveys of galaxies.
Many of these methods were originally designed to work with simulations
and/or well-sampled spectroscopic surveys. When spectroscopic redshifts
are not available, the filaments of the cosmic web can be detected in
projection using photometric redshifts in slices along the Line of
Sight, which enable the exploration of larger cosmic volumes. However,
this comes at the expense of a lower redshift precision. It is therefore
crucial to assess the differences between filaments extracted from exact
redshifts and from photometric redshifts for a specific survey. We apply
this analysis to capture the uncertainties and biases of filament
extractions introduced by using the photometric sample of the Euclid
Wide Survey. The question that we address in this work is how can we
compare two filament samples derived with redshifts of different
precisions in the Euclid Wide Survey context. We apply the cosmic web
detection algorithm DisPerSE, in the redshift range  , to the GAlaxy Evolution and Assembly (GAEA)
simulated galaxy sample which reproduces several characteristics of the
Euclid Wide Survey. We develop a method to compare skeletons derived
from photometric redshifts to those derived from true galaxy positions.
This method expands the commonly used measure of distance between
filaments to include geometrical (angles between filaments) and
astrophysical considerations (galaxy mass gradients and
connectivity-mass relations). We assess whether this approach
strengthens our ability to correctly identify filaments in very large
surveys such as the Euclid Wide Survey. [abridged]
, to the GAlaxy Evolution and Assembly (GAEA)
simulated galaxy sample which reproduces several characteristics of the
Euclid Wide Survey. We develop a method to compare skeletons derived
from photometric redshifts to those derived from true galaxy positions.
This method expands the commonly used measure of distance between
filaments to include geometrical (angles between filaments) and
astrophysical considerations (galaxy mass gradients and
connectivity-mass relations). We assess whether this approach
strengthens our ability to correctly identify filaments in very large
surveys such as the Euclid Wide Survey. [abridged]
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. Accard / M. Béthermin / M. Boquien / V.
Buat
- L. Vallini / F. Renaud / K. Kraljic / M. Aravena
- P. Cassata / E. da Cunha / P. Dam / I. de Looze
- M. Dessauges-Zavadsky / Y. Dubois / A. Faisst / Y. Fudamoto
- M. Ginolfi / C. Gruppioni / S. Han / R. Herrera-Camus
- H. Inami / A. M. Koekemoer / B. C. Lemaux / J. Li
- Y. Li / B. Mobasher / J. Molina / A. Nanni
- M. Palla / F. Pozzi / M. Relaño / M. Romano
- P. Sawant / J. Spilker / A. Tsujita / E. Veraldi
- V. Villanueva / W. Wang / S. K. Yi / G. Zamorani
Summary
Star formation governs galaxy evolution, shaping stellar mass
assembly and gas consumption across cosmic time. The Kennicutt-Schmidt
(KS) relation, linking star formation rate (SFR) and gas surface
densities, is fundamental to understand star formation regulation, yet
remains poorly constrained at  due to
observational limitations and uncertainties in locally calibrated gas
tracers. The [CII]
due to
observational limitations and uncertainties in locally calibrated gas
tracers. The [CII]  line has
recently emerged as a key probe of the cold ISM and star formation in
the early Universe. We investigate whether the resolved [CII]-SFR and KS
relations established at low redshift remain valid at
line has
recently emerged as a key probe of the cold ISM and star formation in
the early Universe. We investigate whether the resolved [CII]-SFR and KS
relations established at low redshift remain valid at  by
analysing 13 main-sequence galaxies from the ALPINE and CRISTAL surveys,
using multi-wavelength data (HST, JWST, ALMA) at
by
analysing 13 main-sequence galaxies from the ALPINE and CRISTAL surveys,
using multi-wavelength data (HST, JWST, ALMA) at  kpc resolution. We
perform pixel-by-pixel spectral energy distribution (SED) modelling with
CIGALE on resolution-homogenised images. We develop a statistical
framework to fit the [CII]-SFR relation that accounts for pixel
covariance and compare our results to classical fitting methods. We test
two [CII]-to-gas conversion prescriptions to assess their impact on
inferred gas surface densities and depletion times. We find a resolved
[CII]-SFR relation with a slope of
kpc resolution. We
perform pixel-by-pixel spectral energy distribution (SED) modelling with
CIGALE on resolution-homogenised images. We develop a statistical
framework to fit the [CII]-SFR relation that accounts for pixel
covariance and compare our results to classical fitting methods. We test
two [CII]-to-gas conversion prescriptions to assess their impact on
inferred gas surface densities and depletion times. We find a resolved
[CII]-SFR relation with a slope of  and
intrinsic scatter of
and
intrinsic scatter of  dex,
which is shallower and tighter than previous studies at
dex,
which is shallower and tighter than previous studies at  . The resolved KS
relation is highly sensitive to the [CII]-to-gas conversion factor:
using a fixed global
. The resolved KS
relation is highly sensitive to the [CII]-to-gas conversion factor:
using a fixed global ![α_{\rm [CII]} α_{\rm [CII]}](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%CE%B1_%7B%5Crm%20%5BCII%5D%7D) yields
depletion times of
yields
depletion times of  -
- Gyr, while a surface
brightness-dependent
Gyr, while a surface
brightness-dependent ![W_{\rm [CII]} W_{\rm [CII]}](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20W_%7B%5Crm%20%5BCII%5D%7D) , places
some galaxies with high gas density in the starburst regime (
, places
some galaxies with high gas density in the starburst regime ( Gyr). Future inputs
from both simulations and observations are required to better understand
how the [CII]-to-gas conversion factor depends on local ISM properties.
We need to break this fundamental limit to properly study the KS
relation at
Gyr). Future inputs
from both simulations and observations are required to better understand
how the [CII]-to-gas conversion factor depends on local ISM properties.
We need to break this fundamental limit to properly study the KS
relation at  .
.
The
radio flare and multi-wavelength afterglow of the short GRB 231117A:
energy injection from a violent shell collision
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- G. E. Anderson / G. P. Lamb / B. P. Gompertz / L. Rhodes
- A. Martin-Carrillo / A. J. van der Horst / A. Rowlinson / M. E.
Bell
- T.-W. Chen / H. M. Fausey / M. Ferro / P. J. Hancock
- S. R. Oates / S. Schulze / R. L. C. Starling / S. Yang
- K. Ackley / J. P. Anderson / A. Andersson / J. F. Agüí
Fernández
- R. Brivio / E. Burns / K. C. Chambers / T. de Boer
- V. D’Elia / M. De Pasquale / A. de Ugarte Postigo / Dimple
- R. Fender / M. D. Fulton / H. Gao / J. H. Gillanders
- D. A. Green / M. Gromadzki / A. Gulati / D. H. Hartmann
- M. E. Huber / N. P. M. Kuin / J. K. Leung / A. J. Levan
- C.-C. Lin / E. Magnier / D. B. Malesani / P. Minguez
- K. P. Mooley / T. Mukherjee / M. Nicholl / P. T. O’Brien
- G. Pugliese / A. Rossi / S. D. Ryder / B. Sbarufatti
- B. Schneider / F. Schüssler / S. J. Smartt / K. W.
Smith
- S. Srivastav / D. Steeghs / N. R. Tanvir / C. C. Thoene
- S. D. Vergani / R. J. Wainscoat / Z.-N. Wang / R. A. M. J.
Wijers
- D. Williams-Baldwin / I. Worssam / T. Zafar
Summary
We present the early radio detection and multi-wavelength modeling of
the short gamma-ray burst (GRB) 231117A at redshift  . The Australia
Telescope Compact Array automatically triggered a 9-hour observation of
GRB 231117A at 5.5 and 9 GHz following its detection by the Neil Gehrels
Swift Observatory just 1.3 hours post-burst. Splitting this observation
into 1-hour time bins, the early radio afterglow exhibited flaring,
scintillating and plateau phases. The scintillation allowed us to place
the earliest upper limit (
. The Australia
Telescope Compact Array automatically triggered a 9-hour observation of
GRB 231117A at 5.5 and 9 GHz following its detection by the Neil Gehrels
Swift Observatory just 1.3 hours post-burst. Splitting this observation
into 1-hour time bins, the early radio afterglow exhibited flaring,
scintillating and plateau phases. The scintillation allowed us to place
the earliest upper limit ( hours) on the size of
a GRB blast wave to date, constraining it to
hours) on the size of
a GRB blast wave to date, constraining it to  cm. Multi-wavelength modeling of the full
afterglow required a period of significant energy injection between
cm. Multi-wavelength modeling of the full
afterglow required a period of significant energy injection between  and
and  day. The energy injection was modeled
as a violent collision of two shells: a reverse shock passing through
the injection shell explains the early radio plateau, while an X-ray
flare is consistent with a shock passing through the leading impulsive
shell. Beyond 1 day, the blast wave evolves as a classic decelerating
forward shock with an electron distribution index of
day. The energy injection was modeled
as a violent collision of two shells: a reverse shock passing through
the injection shell explains the early radio plateau, while an X-ray
flare is consistent with a shock passing through the leading impulsive
shell. Beyond 1 day, the blast wave evolves as a classic decelerating
forward shock with an electron distribution index of  . Our
model also indicates a jet-break at
. Our
model also indicates a jet-break at  days, and a
half-opening angle of
days, and a
half-opening angle of  .
Following the period of injection, the total energy is
.
Following the period of injection, the total energy is  times the initial
impulsive energy, with a final collimation-corrected energy of
times the initial
impulsive energy, with a final collimation-corrected energy of  erg.
The minimum Lorentz factors this model requires are consistent with
constraints from the early radio measurements of
erg.
The minimum Lorentz factors this model requires are consistent with
constraints from the early radio measurements of  to
to  between
between  and
and  day. These results demonstrate the
importance of rapid and sensitive radio follow-up of GRBs for exploring
their central engines and outflow behaviour.
day. These results demonstrate the
importance of rapid and sensitive radio follow-up of GRBs for exploring
their central engines and outflow behaviour.
Adding
colour to the Zernike wavefront sensor: Advantages of including
multi-wavelength measurements for wavefront reconstruction
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Darcis / S. Y. Haffert / V. Chambouleyron / D.
S. Doelman
- P. J. de Visser / M. A. Kenworthy
Summary
To directly image Earth-like planets, contrast levels of 10^-8 -
10^-10 are required. The next generation of instruments will need
wavefront control below the nanometer level to achieve these goals. The
Zernike wavefront sensor (ZWFS) is a promising candidate thanks to its
sensitivity, which reaches the fundamental quantum information limits.
However, its highly non-linear response restricts its practical use
case. We aim to demonstrate the improvement in robustness of the ZWFS by
reconstructing the wavefront based on multi-wavelength measurements
facilitated by technologies such as the microwave kinetic inductance
detectors (MKIDs). We performed numerical simulations using an
accelerated multi-wavelength gradient descent reconstruction algorithm.
Three aspects are considered: dynamic range, photon noise sensitivity,
and phase unwrapping. We examined both the scalar and vector ZWFS.
Firstly, we find that using multiple wavelengths improves the dynamic
range of the scalar ZWFS. However, for the vector ZWFS, its already
extended range was not further increased. In addition, a
multi-wavelength reconstruction allowed us to take advantage of a
broader bandpass, which increases the number of available photons,
making the reconstruction more robust to photon noise. Finally,
multi-wavelength phase unwrapping enabled the measurement of large
discontinuities such as petal errors with a trade-off in noise
performance.
Spatial
variability of CH4 and C2H2 absorptions in Jupiter’s auroral regions
from Juno-UVS observations
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. Vinesse / B. Bonfond / B. Benmahi / A.
Moirano
- D. Grodent / T. K. Greathouse / V. Hue / G.
Sicorello
- L. A. Head / G. R. Gladstone / M. W. Davis
Summary
Color ratios derived from molecular hydrogen emissions provide
valuable diagnostics for the energy of precipitating electrons and the
structure of the auroral atmosphere. We aim to characterize the
horizontal and vertical variability of hydrocarbon absorption in
Jupiter’s auroral atmosphere using ultraviolet data from the Juno-UVS
spectrograph and to investigate potential departures from the expected
structure. We constructed color ratio maps sensitive to CH and C
and C H
H absorptions for perijoves (PJs) 6 and
10, two of Juno’s close approaches to Jupiter, by integrating auroral
H
absorptions for perijoves (PJs) 6 and
10, two of Juno’s close approaches to Jupiter, by integrating auroral
H emission over hydrocarbon-sensitive
spectral intervals. For CH
emission over hydrocarbon-sensitive
spectral intervals. For CH , we redefined the absorbed spectral
band, replacing the traditionally used 125-130 nm interval with 135-140
nm, in order to mitigate higher-order calibration issues. In regions of
intense auroral brightness, we developed a correction method to account
for spectral distortion due to detector non-linearities at high fluxes.
CH
, we redefined the absorbed spectral
band, replacing the traditionally used 125-130 nm interval with 135-140
nm, in order to mitigate higher-order calibration issues. In regions of
intense auroral brightness, we developed a correction method to account
for spectral distortion due to detector non-linearities at high fluxes.
CH and C
and C H
H absorptions generally follow the
expected vertical distribution, with the CH
absorptions generally follow the
expected vertical distribution, with the CH density extending to higher altitudes
than C
density extending to higher altitudes
than C H
H . However, several localized regions
show unexpected spatial distribution of the absorption. In PJ6, such
anomalies are attributed to instrumental non-linearities. After
correction, the CR distributions become consistent with standard
hydrocarbon vertical distributions. In PJ10, however, some anomalous
patterns persist despite correction. Spectral modeling indicates that
these can be explained by modifying the relative abundances of CH
. However, several localized regions
show unexpected spatial distribution of the absorption. In PJ6, such
anomalies are attributed to instrumental non-linearities. After
correction, the CR distributions become consistent with standard
hydrocarbon vertical distributions. In PJ10, however, some anomalous
patterns persist despite correction. Spectral modeling indicates that
these can be explained by modifying the relative abundances of CH and C
and C H
H , suggesting horizontal compositional
variability and possible deviations in homopause altitude between
species. These findings underscore the importance of accounting for
local atmospheric composition when interpreting ultraviolet auroral
spectra and retrieving electron energy distributions.
, suggesting horizontal compositional
variability and possible deviations in homopause altitude between
species. These findings underscore the importance of accounting for
local atmospheric composition when interpreting ultraviolet auroral
spectra and retrieving electron energy distributions.
Articles for week 33 2025
Studying
Exoplanets in the Radio from the Moon
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Jake D. Turner / Jack O. Burns / David Rapetti / Philippe Zarka
- Jean-Mathias Grießmeier / Judd Bowman / Gregg Hallinan / Joshua
Hibbard
- Johnny Dorigo Jones / Laurent Lamy / Corentin K.
Louis / Richard Lovelace
- Nivedita Mahesh / Ronald Polidan / Xiang Zhang
Summary
Exoplanets with and without a magnetic field are predicted to form,
behave, and evolve very differently. Therefore, there is great need to
directly constrain these fields to holistically understand the
properties of exoplanets including their potential habitability. This
goal aligns with the Astro2020 Decadal Survey recommendations. Observing
planetary auroral radio emissions is among the most promising detection
methods, but decades of searching have yet to yield a conclusive
detection, though promising hints are now emerging from ground-based
radio telescopes. However, these ground-based efforts are fundamentally
limited by Earth’s ionosphere, which blocks the low-frequency signals
(<10 MHz) expected from terrestrial and Neptune-like exoplanets. In
this white paper, we outline a strategy to overcome this barrier by
utilizing the unique environment of the Moon. We discuss how the
upcoming LuSEE-Night and ROLSES pathfinder missions will study our Solar
System’s planets as exoplanet analogs and place the first meaningful
upper limits on exoplanetary radio flux below 10 MHz. Furthermore, we
explore the revolutionary potential of the proposed future lunar arrays
FarView and FARSIDE. For example, FarView will be sensitive enough to
study the magnetic fields of a diverse set of exoplanets (super-Earths
to gas giants) and an order of magnitude more Jupiter-like planets than
ground-based telescopes, providing crucial tests for dynamo theory. Most
significantly, FARSIDE will be able to detect the magnetospheres of
nearby terrestrial exoplanets, offering a powerful synergy with
atmospheric characterization efforts by JWST and HWO to fully assess
their potential habitability. By opening this unexplored low-frequency
window, radio astronomy from the Moon is poised to transform the field
of exoplanet magnetospheric science. [Abridged]
Articles for week 32 2025
Worlds
Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of  Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and
Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits
Cen A. I. Observations, Orbital and
Physical Properties, and Exozodi Upper Limits
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Charles Beichman / Aniket Sanghi / Dimitri Mawet / Pierre
Kervella
- Kevin Wagner / Billy Quarles / Jack J. Lissauer / Max Sommer
- Mark Wyatt / Nicolas Godoy / William O. Balmer /
Laurent Pueyo
- Jorge Llop-Sayson / Jonathan Aguilar / Rachel Akeson / Ruslan
Belikov
- Anthony Boccaletti / Elodie Choquet / Edward
Fomalont / Thomas Henning
- Dean Hines / Renyu Hu / Pierre-Olivier Lagage / Jarron
Leisenring
- James Mang / Michael Ressler / Eugene Serabyn / Pascal Tremblin
- Marie Ygouf / Mantas Zilinskas
Summary
We report on coronagraphic observations of the nearest solar-type
star,  Cen A, using the MIRI instrument on the
James Webb Space Telescope. With three epochs of observation (August
2024, February 2025, and April 2025), we achieve a sensitivity
sufficient to detect
Cen A, using the MIRI instrument on the
James Webb Space Telescope. With three epochs of observation (August
2024, February 2025, and April 2025), we achieve a sensitivity
sufficient to detect  225-250 K (1-1.2
225-250 K (1-1.2  ) planets
between 1”-2” and exozodiacal dust emission at the level of $>
) planets
between 1”-2” and exozodiacal dust emission at the level of $> $ the brightness of our own zodiacal
cloud. The lack of exozodiacal dust emission sets an unprecedented limit
of a few times the brightness of our own zodiacal cloud
$ the brightness of our own zodiacal
cloud. The lack of exozodiacal dust emission sets an unprecedented limit
of a few times the brightness of our own zodiacal cloud a factor of $
a factor of $ _ν$(15.5
_ν$(15.5  m) = 3.5 mJy point source, called
m) = 3.5 mJy point source, called  , at a separation of 1.5” from
, at a separation of 1.5” from  Cen A. Because the August 2024 epoch
had only one successful observation at a single roll angle, it is not
possible to unambiguously confirm
Cen A. Because the August 2024 epoch
had only one successful observation at a single roll angle, it is not
possible to unambiguously confirm  as a bona fide planet. Our analysis
confirms that
as a bona fide planet. Our analysis
confirms that  is neither a background nor a
foreground object.
is neither a background nor a
foreground object.  is not recovered in the February and
April 2025 epochs. However, if
is not recovered in the February and
April 2025 epochs. However, if  is the counterpart of the object,
is the counterpart of the object,  , seen by the VLT/NEAR program in 2019,
we find that there is a 52% chance that the
, seen by the VLT/NEAR program in 2019,
we find that there is a 52% chance that the  candidate was missed in
both follow-up JWST/MIRI observations due to orbital motion.
Incorporating constraints from the non-detections, we obtain families of
dynamically stable orbits for
candidate was missed in
both follow-up JWST/MIRI observations due to orbital motion.
Incorporating constraints from the non-detections, we obtain families of
dynamically stable orbits for  with periods between
2-3 years. These suggest that the planet candidate is on an eccentric
(
with periods between
2-3 years. These suggest that the planet candidate is on an eccentric
( ) orbit
significantly inclined with respect to
) orbit
significantly inclined with respect to  Cen AB orbital plane (
Cen AB orbital plane ( , or
, or  ). Based on the photometry and orbital properties,
the planet candidate could have a temperature of 225 K, a radius of
$$1-1.1
). Based on the photometry and orbital properties,
the planet candidate could have a temperature of 225 K, a radius of
$$1-1.1  and a mass
between 90-150
and a mass
between 90-150  ,
consistent with RV limits.
,
consistent with RV limits.
Euclid:
Photometric redshift calibration with self-organising maps
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- W. Roster / A. H. Wright / H. Hildebrandt / R. Reischke
- O. Ilbert / W. d’Assignies D. / M. Manera / M.
Bolzonella
- D. C. Masters / S. Paltani / W. G. Hartley / Y. Kang
- H. Hoekstra / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero
- R. Casas / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M.
Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre
- G. De Lucia / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- P. Fosalba / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / B. Kubik
- H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant
/ S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- C. Rosset / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / C. Burigana
- L. Gabarra / C. Porciani / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
Summary
The Euclid survey aims to trace the evolution of cosmic structures up
to redshift 
 3 and beyond. Its success
depends critically on obtaining highly accurate mean redshifts for
ensembles of galaxies
3 and beyond. Its success
depends critically on obtaining highly accurate mean redshifts for
ensembles of galaxies  in all tomographic bins,
essential for deriving robust cosmological constraints. However,
photometric redshifts (photo-
in all tomographic bins,
essential for deriving robust cosmological constraints. However,
photometric redshifts (photo- s) suffer from systematic biases arising
from various sources of uncertainty. To address these challenges, we
utilised self-organising maps (SOMs) with mock samples resembling the
Euclid Wide Survey (EWS), to validate Euclid’s uncertainty requirement
of
s) suffer from systematic biases arising
from various sources of uncertainty. To address these challenges, we
utilised self-organising maps (SOMs) with mock samples resembling the
Euclid Wide Survey (EWS), to validate Euclid’s uncertainty requirement
of  per tomographic bin, assuming DR3-level data. We
observe that defining the redshift tomography using the mean
spectroscopic redshift (spec-
per tomographic bin, assuming DR3-level data. We
observe that defining the redshift tomography using the mean
spectroscopic redshift (spec- ) per SOM cell, results in none of the
ten tomographic redshift bins satisfying the requirement. In contrast,
the redshift tomography on the photo-
) per SOM cell, results in none of the
ten tomographic redshift bins satisfying the requirement. In contrast,
the redshift tomography on the photo- s of the EWS-like sample yields superior
results, with eight out of ten bins [
s of the EWS-like sample yields superior
results, with eight out of ten bins [ ]
meeting the Euclid requirement. To enhance the realism of our study, we
morph our calibration sample to mimic the C3R2 survey in incremental
steps. In this context, a maximum of six out of ten bins meet the
requirement, strongly advocating the adoption of a redshift tomography
defined by the photo-
]
meeting the Euclid requirement. To enhance the realism of our study, we
morph our calibration sample to mimic the C3R2 survey in incremental
steps. In this context, a maximum of six out of ten bins meet the
requirement, strongly advocating the adoption of a redshift tomography
defined by the photo- s of individual galaxies rather than the
commonly used mean spec-
s of individual galaxies rather than the
commonly used mean spec- of SOM cells. To examine the impact on
the expected biases for
of SOM cells. To examine the impact on
the expected biases for  ,
,  , and
, and  measured by Euclid,
we perform a Fisher forecast for cosmic shear only, based on our
redshift uncertainties. Here, we find that even under an evaluation of
the uncertainty where the impact of the redshift bias is substantial,
most absolute biases remain below 0.1
measured by Euclid,
we perform a Fisher forecast for cosmic shear only, based on our
redshift uncertainties. Here, we find that even under an evaluation of
the uncertainty where the impact of the redshift bias is substantial,
most absolute biases remain below 0.1 in the idealised scenario and below
0.3
in the idealised scenario and below
0.3 in the more realistic case.
in the more realistic case.
Worlds
Next Door: A Candidate Giant Planet Imaged in the Habitable Zone of  Cen A. II. Binary Star Modeling, Planet
and Exozodi Search, and Sensitivity Analysis
Cen A. II. Binary Star Modeling, Planet
and Exozodi Search, and Sensitivity Analysis
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Aniket Sanghi / Charles Beichman / Dimitri Mawet / William O.
Balmer
- Nicolas Godoy / Laurent Pueyo / Anthony Boccaletti
/ Max Sommer
- Alexis Bidot / Elodie Choquet / Pierre Kervella /
Pierre-Olivier Lagage
- Jarron Leisenring / Jorge Llop-Sayson / Michael Ressler / Kevin
Wagner
- Mark Wyatt
Summary
JWST observed our closest solar twin,  Cen A, with the MIRI coronagraph in
F1550C (15.5
Cen A, with the MIRI coronagraph in
F1550C (15.5  m) at three distinct epochs between
August 2024 and April 2025. For the first time with JWST, we demonstrate
the application of reference star differential imaging to simultaneously
subtract the coronagraphic image of a primary star and the point spread
function (PSF) of its binary companion to conduct a deep search for
exoplanets and dust emission. We achieve a typical 5
m) at three distinct epochs between
August 2024 and April 2025. For the first time with JWST, we demonstrate
the application of reference star differential imaging to simultaneously
subtract the coronagraphic image of a primary star and the point spread
function (PSF) of its binary companion to conduct a deep search for
exoplanets and dust emission. We achieve a typical 5 point source contrast sensitivity
between
point source contrast sensitivity
between 
 -
- at separations
at separations  1” and an
exozodiacal disk (coplanar with
1” and an
exozodiacal disk (coplanar with  Cen AB) sensitivity of $
Cen AB) sensitivity of $ $ the Solar System’s zodiacal cloud
around
$ the Solar System’s zodiacal cloud
around  Cen A. The latter is an extraordinary
limit, representing the deepest sensitivity to exozodiacal disks
achieved for any stellar system to date. Post-processing with the
PCA-KLIP algorithm reveals a point source, called
Cen A. The latter is an extraordinary
limit, representing the deepest sensitivity to exozodiacal disks
achieved for any stellar system to date. Post-processing with the
PCA-KLIP algorithm reveals a point source, called  , in August 2024, detected at S/N
, in August 2024, detected at S/N  4-6 (3.3-4.3
4-6 (3.3-4.3 ), a separation of $$1.5” (2 au), and
with a F1550C flux (contrast) of $
), a separation of $$1.5” (2 au), and
with a F1550C flux (contrast) of $ ^{-5}$).
Various tests conducted with the data show that
^{-5}$).
Various tests conducted with the data show that  is unlikely to be a detector or PSF
subtraction artifact and confirm that it is neither a background nor a
foreground object.
is unlikely to be a detector or PSF
subtraction artifact and confirm that it is neither a background nor a
foreground object.  is not re-detected in the two
follow-up observations (February and April 2025). If
is not re-detected in the two
follow-up observations (February and April 2025). If  is astrophysical in nature, the only
explanation is that it has moved to a region of poor sensitivity due to
orbital motion. We perform PSF injection-recovery tests and provide 2D
sensitivity maps for each epoch to enable orbital completeness
calculations. Additional observations are necessary to re-detect
candidate
is astrophysical in nature, the only
explanation is that it has moved to a region of poor sensitivity due to
orbital motion. We perform PSF injection-recovery tests and provide 2D
sensitivity maps for each epoch to enable orbital completeness
calculations. Additional observations are necessary to re-detect
candidate  and confirm its nature as a planet
orbiting our nearest solar-type neighbor.
and confirm its nature as a planet
orbiting our nearest solar-type neighbor.
Quantifying
thermal water dissociation in the dayside photosphere of WASP-121 b
using NIRPS
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Luc Bazinet / Romain Allart / Björn Benneke / Stefan Pelletier
- Joost P. Wardenier / Neil J. Cook / Thierry Forveille / Louise D.
Nielsen
- Khaled Al Moulla / Étienne Artigau / Frédérique Baron / Susana C. C.
Barros
- Xavier Bonfils / François Bouchy / Marta Bryan / Bruno L. Canto
Martins
- Ryan Cloutier / Nicolas B. Cowan / Daniel Brito de Freitas / Jose
Renan De Medeiros
- Xavier Delfosse / René Doyon / Xavier Dumusque / David
Ehrenreich
- Jonay I. González Hernández / David Lafrenière / Izan de Castro Leão
/ Christophe Lovis
- Lison Malo / Claudio Melo / Lucile Mignon / Christoph Mordasini
- Francesco Pepe / Rafael Rebolo / Jason Rowe / Nuno C. Santos
- Damien Ségransan / Alejandro Suárez Mascareño / Stéphane Udry /
Diana Valencia
- Gregg Wade / Manuel Abreu / José L. A. Aguiar / Guillaume
Allain
- Tomy Arial / Hugues Auger / Nicolas Blind / David Bohlender
- Anne Boucher / Vincent Bourrier / Sébastien Bovay / Christopher
Broeg
- Denis Brousseau / Alexandre Cabral / Charles Cadieux / Andres
Carmona
- Zalpha Challita / Bruno Chazelas / João Coelho /
Marion Cointepas
- Ana Rita Costa Silva / Louis-Philippe Coulombe / Eduardo Cristo /
Antoine Darveau-Bernier
- Laurie Dauplaise / Roseane de Lima Gomes / Dasaev O. Fontinele /
Yolanda G. C. Frensch
- Frédéric Genest / Ludovic Genolet / Félix Gracia Témich / Olivier
Hernandez
- H. Jens Hoeijmakers / Norbert Hubin / Ray Jayawardhana / Hans-Ulrich
Käufl
- Dan Kerley / Johann Kolb / Vigneshwaran Krishnamurthy / Benjamin
Kung
- Pierrot Lamontagne / Olivia Lim / Gaspare Lo Curto / José Luis
Rasilla
- Allan M. Martins / Jaymie Matthews / Jean-Sébastien Mayer / Yuri S.
Messias
- Stan Metchev / Dany Mounzer / Nicola Nari / Ares Osborn
- Mathieu Ouellet / Léna Parc / Luca Pasquini / Céline Peroux
- Caroline Piaulet-Ghorayeb / Emanuela Pompei / Anne-Sophie
Poulin-Girard / Vladimir Reshetov
- Jonathan Saint-Antoine / Mirsad Sarajlic / Robin Schnell / Alex
Segovia
- Julia Seidel / Armin Silber / Peter Sinclair / Michael Sordet
- Danuta Sosnowska / Avidaan Srivastava / Atanas K. Stefanov / Márcio
A. Teixeira
- Simon Thibault / Philippe Vallée / Thomas Vandal / Valentina
Vaulato
- Bachar Wehbe / Drew Weisserman / Ivan Wevers / François Wildi
- Vincent Yariv / Gérard Zins
Summary
The intense stellar irradiation of ultra-hot Jupiters results in some
of the most extreme atmospheric environments in the planetary regime. On
their daysides, temperatures can be sufficiently high for key
atmospheric constituents to thermally dissociate into simpler molecular
species and atoms. This dissociation drastically changes the atmospheric
opacities and, in turn, critically alters the temperature structure,
atmospheric dynamics, and day-night heat transport. To this date,
however, simultaneous detections of the dissociating species and their
thermally dissociation products in exoplanet atmospheres have remained
rare. Here we present the simultaneous detections of H O and its thermally dissociation
product OH on the dayside of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-121 b based on
high-resolution emission spectroscopy with the recently commissioned
Near InfraRed Planet Searcher (NIRPS). We retrieve a photospheric
abundance ratio of log
O and its thermally dissociation
product OH on the dayside of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-121 b based on
high-resolution emission spectroscopy with the recently commissioned
Near InfraRed Planet Searcher (NIRPS). We retrieve a photospheric
abundance ratio of log (OH/H
(OH/H O)
O)  indicating that there is about as much OH as H
indicating that there is about as much OH as H O at photospheric pressures, which
confirms predictions from chemical equilibrium models. We compare the
dissociation on WASP-121 b with other ultra-hot Jupiters and show that a
trend in agreement with equilibrium models arises. We also discuss an
apparent velocity shift of $4.79^{+0.93}_{-0.97}
O at photospheric pressures, which
confirms predictions from chemical equilibrium models. We compare the
dissociation on WASP-121 b with other ultra-hot Jupiters and show that a
trend in agreement with equilibrium models arises. We also discuss an
apparent velocity shift of $4.79^{+0.93}_{-0.97}  ^{-1}$ in the H
^{-1}$ in the H O signal, which is not reproduced by
current global circulation models. Finally, in addition to H
O signal, which is not reproduced by
current global circulation models. Finally, in addition to H O and OH, the NIRPS data reveal
evidence of Fe and Mg, from which we infer a Fe/Mg ratio consistent with
the solar and host star ratios. Our results demonstrate that NIRPS can
be an excellent instrument to obtain simultaneous measurements of
refractory and volatile molecular species, paving the way for many
future studies on the atmospheric composition, chemistry, and the
formation history of close-in exoplanets.
O and OH, the NIRPS data reveal
evidence of Fe and Mg, from which we infer a Fe/Mg ratio consistent with
the solar and host star ratios. Our results demonstrate that NIRPS can
be an excellent instrument to obtain simultaneous measurements of
refractory and volatile molecular species, paving the way for many
future studies on the atmospheric composition, chemistry, and the
formation history of close-in exoplanets.
The
ALMA-QUARKS Survey: III. Clump-to-core fragmentation and search for
high-mass starless cores
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Dongting Yang / Hong-Li Liu / Tie Liu / Xunchuan Liu
- Fengwei Xu / Sheng-Li Qin / Anandmayee Tej / Guido Garay
- Lei Zhu / Xiaofeng Mai / Wenyu Jiao / Siju Zhang
- Sami Dib / Amelia M. Stutz / Aina Palau / Patricio Sanhueza
- Annie Zavagno / A. Y. Yang / Xindi Tang / Mengyao
Tang
- Yichen Zhang / Pablo Garcia / Tianwei Zhang / Anindya Saha
- Shanghuo Li / Paul F. Goldsmith / Leonardo Bronfman / Chang Won
Lee
- Kotomi Taniguchi / Swagat Ranjan Das / Prasanta Gorai / Ariful
Hoque
- Li Chen / Zhiping Kou / Jianjun Zhou / Yankun Zhang
- L. Viktor Toth / Tapas Baug / Xianjin Shen / Chuanshou Li
- Jiahang Zou / Ankan Das / Hafiz Nazeer / L. K. Dewangan
- Jihye Hwang / James O. Chibueze
Summary
The Querying Underlying mechanisms of massive star formation with
ALMA-Resolved gas Kinematics and Structures (QUARKS) survey observed 139
infrared-bright (IR-bright) massive protoclusters at 1.3 mm wavelength
with ALMA. This study investigates clump-to-core fragmentation and
searches for candidate high-mass starless cores within IR-bright clumps
using combined ALMA 12-m (C-2) and Atacama Compact Array (ACA) 7-m data,
providing  1 arcsec (
1 arcsec ( at
3.7 kpc) resolution and
at
3.7 kpc) resolution and  continuum sensitivity (
continuum sensitivity ( at 30 K). We identified 1562 compact cores from
1.3 mm continuum emission using getsf. Observed linear core separations
(
at 30 K). We identified 1562 compact cores from
1.3 mm continuum emission using getsf. Observed linear core separations
( ) are
significantly less than the thermal Jeans length (
) are
significantly less than the thermal Jeans length ( ), with the
), with the  ratios peaking at
ratios peaking at  . This indicates
that thermal Jeans fragmentation has taken place within the IR-bright
protocluster clumps studied here. The observed low ratio of
. This indicates
that thermal Jeans fragmentation has taken place within the IR-bright
protocluster clumps studied here. The observed low ratio of  could be the result of evolving core separation
or hierarchical fragmentation. Based on associated signatures of star
formation (e.g., outflows and ionized gas), we classified cores into
three categories: 127 starless, 971 warm, and 464 evolved cores. Two
starless cores have mass exceeding 16
could be the result of evolving core separation
or hierarchical fragmentation. Based on associated signatures of star
formation (e.g., outflows and ionized gas), we classified cores into
three categories: 127 starless, 971 warm, and 464 evolved cores. Two
starless cores have mass exceeding 16 , and
represent high-mass candidates. The scarcity of such candidates suggests
that competitive accretion-type models could be more applicable than
turbulent core accretion-type models in high-mass star formation within
these IR-bright protocluster clumps.
, and
represent high-mass candidates. The scarcity of such candidates suggests
that competitive accretion-type models could be more applicable than
turbulent core accretion-type models in high-mass star formation within
these IR-bright protocluster clumps.
Physical
properties of galaxies and the UV Luminosity Function from  to
to  in COSMOS-Web
in COSMOS-Web
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Maximilien Franco / Caitlin M. Casey / Hollis B. Akins /
Olivier Ilbert
- Marko Shuntov / Steven L. Finkelstein / Louise Paquereau / Andreas
L. Faisst
- Anton M. Koekemoer / Michaela Hirschmann / Sebastiano Cantarella /
Nicole E. Drakos
- Stephen M. Wilkins / Henry Joy McCracken / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe /
Claudia Maraston
- Fatemeh Abedini / Mark J. Achenbach / Rafael C. Arango-Toro /
Fabrizio Gentile
- Ghassem Gozaliasl / Kohei Inayoshi / Darshan Kakkad / Atousa
Kalantari
- Ali Ahmad Khostovan / Vasily Kokorev / Erini Lambrides / Gavin
Leroy
- Richard Massey / Bahram Mobasher / Sophie L. Newman / Jason
Rhodes
- R. Michael Rich / Brant E. Robertson / David B. Sanders / Takumi S.
Tanaka
- Aswin P. Vijayan / John R. Weaver / Lilan Yang / Si-Yue Yu
Summary
We present measurements of the rest-frame ultraviolet luminosity
function (UVLF) in three redshift bins over  -14 from the JWST
COSMOS-Web survey. Our samples, selected using the dropout technique in
the HST/ACS F814W, JWST/NIRCam F115W, and F150W filters, contain a total
of 3099 galaxies spanning a wide luminosity range from faint (
-14 from the JWST
COSMOS-Web survey. Our samples, selected using the dropout technique in
the HST/ACS F814W, JWST/NIRCam F115W, and F150W filters, contain a total
of 3099 galaxies spanning a wide luminosity range from faint ( mag) to bright (
mag) to bright ( mag). The galaxies are undergoing rapid star
formation, with blue stellar populations. Surprisingly, their median UV
spectral slope
mag). The galaxies are undergoing rapid star
formation, with blue stellar populations. Surprisingly, their median UV
spectral slope  does not evolve at
does not evolve at  , suggesting minimal
dust, or physical separation of dust and star formation at early epochs.
The measured UVLF exhibits an excess at the bright-end (
, suggesting minimal
dust, or physical separation of dust and star formation at early epochs.
The measured UVLF exhibits an excess at the bright-end ( mag) compared to pre-JWST empirical results and theoretical predictions
of an evolving Schechter function, with the excess beginning at
mag) compared to pre-JWST empirical results and theoretical predictions
of an evolving Schechter function, with the excess beginning at  and becoming
increasingly prominent toward
and becoming
increasingly prominent toward  . Our analysis
suggests that reproducing the observed abundance of UV-bright galaxies
at high redshift requires a combination of physical processes, including
elevated star formation efficiencies, moderate levels of stochasticity
in galaxy luminosities, and minimal dust attenuation.
. Our analysis
suggests that reproducing the observed abundance of UV-bright galaxies
at high redshift requires a combination of physical processes, including
elevated star formation efficiencies, moderate levels of stochasticity
in galaxy luminosities, and minimal dust attenuation.
Articles for week 31 2025
Diving
into the planetary system of Proxima with NIRPS – Breaking the metre per
second barrier in the infrared
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alejandro Suárez Mascareño / Étienne Artigau / Lucile Mignon /
Xavier Delfosse
- Neil J. Cook / François Bouchy / René Doyon / Jonay I. González
Hernández
- Thomas Vandal / Izan de Castro Leão / Atanas K. Stefanov / João
Faria
- Charles Cadieux / Pierrot Lamontagne / Frédérique Baron / Susana C.
C. Barros
- Björn Benneke / Xavier Bonfils / Marta Bryan / Bruno L. Canto
Martins
- Ryan Cloutier / Nicolas B. Cowan / Daniel Brito de Freitas / Jose
Renan De Medeiros
- Elisa Delgado-Mena / Pedro Figueira / Xavier Dumusque / David
Ehrenreich
- David Lafrenière / Christophe Lovis / Lison Malo / Claudio Melo
- Christoph Mordasini / Francesco Pepe / Rafael Rebolo / Jason
Rowe
- Nuno C. Santos / Damien Ségransan / Stéphane Udry / Diana
Valencia
- Gregg Wade / Manuel Abreu / José L. A. Aguiar / Khaled Al
Moulla
- Guillaume Allain / Romain Allart / Tomy Arial / Hugues Auger
- Luc Bazinet / Nicolas Blind / David Bohlender / Isabelle
Boisse
- Anne Boucher / Vincent Bourrier / Sébastien Bovay / Christopher
Broeg
- Denis Brousseau / Alexandre Cabral / Andres Carmona / Yann
Carteret
- Zalpha Challita / Bruno Chazelas / João Coelho /
Marion Cointepas
- Uriel Conod / Eduardo Cristo / Ana Rita Costa Silva / Antoine
Darveau-Bernier
- Laurie Dauplaise / Jean-Baptiste Delisle / Roseane de Lima Gomes /
Thierry Forveille
- Yolanda G. C. Frensch / Félix Gracia Témich / Dasaev O. Fontinele /
Jonathan Gagné
- Frédéric Genest / Ludovic Genolet / João Gomes da Silva / Nolan
Grieves
- Olivier Hernandez / Melissa J. Hobson / H. Jens Hoeijmakers /
Norbert Hubin
- Farbod Jahandar / Ray Jayawardhana / Hans-Ulrich Käufl / Dan
Kerley
- Johann Kolb / Vigneshwaran Krishnamurthy / Benjamin Kung /
Alexandrine L’Heureux
- Pierre Larue / Henry Leath / Olivia Lim / Gaspare Lo Curto
- Allan M. Martins / Jaymie Matthews / Jean-Sébastien Mayer / Yuri S.
Messias
- Stan Metchev / Leslie Moranta / Dany Mounzer / Nicola Nari
- Louise D. Nielsen / Ares Osborn / Mathieu Ouellet / Jon Otegi
- Léna Parc / Luca Pasquini / Vera M. Passegger / Stefan
Pelletier
- Céline Peroux / Caroline Piaulet-Ghorayeb / Mykhaylo Plotnykov /
Emanuela Pompei
- Anne-Sophie Poulin-Girard / José Luis Rasilla / Vladimir Reshetov /
Jonathan Saint-Antoine
- Mirsad Sarajlic / Ivo Saviane / Robin Schnell / Alex Segovia
- Julia Seidel / Armin Silber / Peter Sinclair / Michael Sordet
- Danuta Sosnowska / Avidaan Srivastava / Márcio A. Teixeira / Simon
Thibault
- Philippe Vallée / Valentina Vaulato / Joost P. Wardenier / Bachar
Wehbe
- Drew Weisserman / Ivan Wevers / François Wildi / Vincent Yariv
- Gérard Zins
Summary
We obtained 420 high-resolution spectra of Proxima, over 159 nights,
using the Near Infra Red Planet Searcher (NIRPS). We derived 149 nightly
binned radial velocity measurements with a standard deviation of 1.69
m/s and a median uncertainty of 55 cm/s, and performed a joint analysis
combining radial velocities, spectroscopic activity indicators, and
ground-based photometry, to model the planetary and stellar signals
present in the data, applying multi-dimensional Gaussian process
regression to model the activity signals. We detect the radial velocity
signal of Proxima b in the NIRPS data. All planetary characteristics are
consistent with those previously derived using visible light
spectrographs. In addition, we find evidence of the presence of the
sub-Earth Proxima d in the NIRPS data. When combining the data with the
HARPS observations taken simultaneous to NIRPS, we obtain a tentative
detection of Proxima d and parameters consistent with those measured
with ESPRESSO. By combining the NIRPS data with simultaneously obtained
HARPS observations and archival data, we confirm the existence of
Proxima d, and demonstrate that its parameters are stable over time and
against change of instrument. We refine the planetary parameters of
Proxima b and d, and find inconclusive evidence of the signal attributed
to Proxima c (P = 1900 d) being present in the data. We measure Proxima
b and d to have minimum masses of 1.055  0.055 Me, and 0.260
0.055 Me, and 0.260  0.038 Me, respectively. Our
results show that, in the case of Proxima, NIRPS provides more precise
radial velocity data than HARPS, and a more significant detection of the
planetary signals. The standard deviation of the residuals of NIRPS
after the fit is 80 cm/s, showcasing the potential of NIRPS to measure
precise radial velocities in the near-infrared.
0.038 Me, respectively. Our
results show that, in the case of Proxima, NIRPS provides more precise
radial velocity data than HARPS, and a more significant detection of the
planetary signals. The standard deviation of the residuals of NIRPS
after the fit is 80 cm/s, showcasing the potential of NIRPS to measure
precise radial velocities in the near-infrared.
Blind
search for activity-sensitive lines in the near-infrared using HARPS and
NIRPS observations of Proxima and Gl 581
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- João Gomes da Silva / Elisa Delgado-Mena / Nuno C. Santos / Telmo
Monteiro
- Pierre Larue / Alejandro Suárez Mascareño / Xavier Delfosse / Lucile
Mignon
- Étienne Artigau / Nicola Nari / Manuel Abreu / José L. A.
Aguiar
- Khaled Al Moulla / Guillaume Allain / Romain Allart / Tomy
Arial
- Hugues Auger / Frédérique Baron / Susana C. C. Barros / Luc
Bazinet
- Björn Benneke / Nicolas Blind / David Bohlender / Isabelle
Boisse
- Xavier Bonfils / Anne Boucher / François Bouchy / Vincent
Bourrier
- Sébastien Bovay / Pedro Branco / Christopher Broeg / Denis
Brousseau
- Vincent Bruniquel / Marta Bryan / Alexandre Cabral / Charles
Cadieux
- Bruno L. Canto Martins / Andres Carmona / Yann Carteret /
Zalpha Challita
- Bruno Chazelas / Ryan Cloutier / João Coelho / Marion Cointepas
- Uriel Conod / Neil J. Cook / Ana Rita Costa Silva / Nicolas B.
Cowan
- Eduardo Cristo / Antoine Darveau-Bernier / Laurie Dauplaise /
Roseane de Lima Gomes
- José Renan De Medeiros / Jean-Baptiste Delisle / Dhvani Doshi / René
Doyon
- Xavier Dumusque / David Ehrenreich / Pedro Figueira / Dasaev O.
Fontinele
- Thierry Forveille / Yolanda G. C. Frensch / Jonathan Gagné /
Frédéric Genest
- Ludovic Genolet / Jonay I. González Hernández / Jennifer Glover /
Félix Gracia Témich
- Nolan Grieves / Nicole Gromek / Olivier Hernandez / Melissa J.
Hobson
- H. Jens Hoeijmakers / Norbert Hubin / Farbod Jahandar / Ray
Jayawardhana
- Hans-Ulrich Käufl / Dan Kerley / Johann Kolb / Vigneshwaran
Krishnamurthy
- Benjamin Kung / Alexandrine L’Heureux / David Lafrenière / Pierrot
Lamontagne
- Izan de Castro Leão / Henry Leath / Olivia Lim / Justin Lipper
- Gaspare Lo Curto / Christophe Lovis / Lison Malo / Allan M.
Martins
- Jaymie Matthews / Jean-Sébastien Mayer / Claudio Melo / Lina
Messamah
- Yuri S. Messias / Stan Metchev / Leslie Moranta / Christoph
Mordasini
- Dany Mounzer / Georgia Mraz / Louise D. Nielsen / Ares Osborn
- Jon Otegi / Mathieu Ouellet / Léna Parc / Luca Pasquini
- Vera M. Passegger / Stefan Pelletier / Francesco Pepe / Céline
Peroux
- Caroline Piaulet-Ghorayeb / Mykhaylo Plotnykov / Emanuela Pompei /
Anne-Sophie Poulin-Girard
- José Luis Rasilla / Rafael Rebolo / Vladimir Reshetov / Jason
Rowe
- Jonathan Saint-Antoine / Mirsad Sarajlic / Ivo Saviane / Robin
Schnell
- Alex Segovia / Damien Ségransan / Julia Seidel / Armin Silber
- Peter Sinclair / Michael Sordet / Danuta Sosnowska / Avidaan
Srivastava
- Atanas K. Stefanov / Márcio A. Teixeira / Simon Thibault / Stéphane
Udry
- Diana Valencia / Philippe Vallée / Thomas Vandal / Valentina
Vaulato
- Gregg Wade / Joost P. Wardenier / Bachar Wehbe / Drew
Weisserman
- Ivan Wevers / François Wildi / Vincent Yariv / Gérard Zins
Summary
Stellar activity variability is one of the main obstacles to the
detection of Earth-like planets using the RV method. The aim of this
work is to measure the effect of activity in the spectra of M dwarfs and
detect activity-sensitive lines in the NIR. We took advantage of the
simultaneous observations of HARPS and the newly commissioned NIRPS
spectrograph to carry out a blind search of the most activity-sensitive
spectral lines in the NIR using NIRPS spectra and known activity
indicators in the optical from HARPS as a reference. We analysed the
spectra of Proxima (M5.5V) and Gl 581 (M3V), two M dwarfs with different
activity levels and internal structures. Spectral lines were identified
for both stars and their profiles were fitted using different models. We
found hundreds of lines sensitive to activity for both stars; the
Proxima spectra were more affected. For Proxima, 32% of the identified
lines can be used to measure the rotation period of the star, while for
Gl 581 the numbers drops to 1%. The fraction of lines sensitive to
activity increases with increasing line depth. A list of 17 lines with
rotation period detection for both stars is provided. Stellar activity
is able to affect a significant number of spectral lines in the NIR, and
methods should be developed to mitigate those effects at the spectral
level. The line distortions detected here are expected to come mainly
from the flux effect due to temperature contrasts between active regions
and the quiet photosphere; however, we cannot rule out the possibility
that core-emission from chromospheric activity or Zeeman splitting are
also affecting some lines. The new line lists presented here can be used
to improve the RV extraction and the detection of RV variability due to
stellar activity signals, and to help false positive detection and the
modelling of activity variability, thereby enhancing exoplanet detection
in the NIR.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Francois Bouchy / Rene Doyon / Francesco Pepe / Claudio Melo
- Etienne Artigau / Lison Malo / Francois Wildi / Frederique
Baron
- Xavier Delfosse / Jose Renan De Medeiros / Rafael Rebolo / Nuno C.
Santos
- Gregg Wade / Romain Allart / Khaled Al Moulla / Nicolas Blind
- Charles Cadieux / Bruno L. Canto Martins / Neil J. Cook / Xavier
Dumusque
- Yolanda Frensch / Frederic Genest / Jonay I. Gonzalez Hernandez /
Nolan Grieves
- Gaspare Lo Curto / Christophe Lovis / Lucile Mignon / Louise D.
Nielsen
- Anne-Sophie Poulin-Girard / Jose Luis Rasilla / Vladimir Reshetov /
Danuta Sosnowska
- Michael Sordet / Jonathan Saint-Antoine / Alejandro Suarez Mascareno
/ Simon Thibault
- Philippe Vallee / Thomas Vandal / Manuel Abreu / Jose L. A.
Aguiar
- Guillaume Allain / Tomy Arial / Hugues Auger / Susana C. C.
Barros
- Luc Bazinet / Bjorn Benneke / Xavier Bonfils / Anne Boucher
- Vincent Bourrier / Sebastien Bovay / Christopher Broeg / Denis
Brousseau
- Vincent Bruniquel / Marta Bryan / Alexandre Cabral / Andres
Carmona
- Yann Carteret / Zalpha Challita / Bruno Chazelas /
Ryan Cloutier
- Joao Coelho / Marion Cointepas / Uriel Conod / Nicolas B. Cowan
- Eduardo Cristo / Joao Gomes da Silva / Laurie Dauplaise / Antoine
Darveau-Bernier
- Roseane de Lima Gomes / Daniel Brito de Freitas / Elisa Delgado-Mena
/ Jean-Baptiste Delisle
- David Ehrenreich / Joao Faria / Pedro Figueira / Dasaev O.
Fontinele
- Thierry Forveille / Jonathan Gagne / Ludovic Genolet / Felix Gracia
Temich
- Olivier Hernandez / Melissa J. Hobson / Jens Hoeijmakers / Norbert
Hubin
- Farbod Jahandar / Ray Jayawardhana / Hans-Ulrich Kauf / Dan
Kerley
- Johann Kolb / Vigneshwaran Krishnamurthy / David Lafreniere /
Pierrot Lamontagne
- Pierre Larue / Henry Leath / Alexandrine L Heureux / Izan de Castro
Leao
- Olivia Lim / Allan M. Martins / Jaymie Matthews / Jean-Sebastien
Mayer
- Yuri S. Messias / Stan Metchev / Leslie Moranta / Christoph
Mordasini
- Dany Mounzer / Nicola Nari / Ares Osborn / Mathieu Ouellet
- Jon Otegi / Lena Parc / Luca Pasquini / Vera M. Passegger
- Stefan Pelletier / Celine Peroux / Caroline Piaulet-Ghorayeb /
Mykhaylo Plotnykov
- Emanuela Pompei / Jason Rowe / Mirsad Sarajlic / Alex Segovia
- Julia Seidel / Damien Segransan / Robin Schnell / Ana Rita Costa
Silva
- Avidaan Srivastava / Valentina Vaulato / Atanas K. Stefanov / Marcio
A. Teixeira
- Stephane Udry / Joost P. Wardenier / Bachar Wehbe / Drew
Weisserman
- Vincent Yariv / Gerard Zins
Summary
The Near-InfraRed Planet Searcher (NIRPS) is a high-resolution,
high-stability near-infrared (NIR) spectrograph equipped with an AO
system. Installed on the ESO 3.6-m telescope, it was developed to enable
radial velocity (RV) measurements of low-mass exoplanets around M dwarfs
and to characterise exoplanet atmospheres in the NIR. This paper
provides a comprehensive design overview and characterisation of the
NIRPS instrument, reporting on its on-sky performance, and presenting
its GTO programme. The instrument started its operations on 1 Apr 2023
after intensive on-sky testing phases. The spectral range continuously
covers the Y, J, and H bands from 972.4 to 1919.6 nm. The thermal
control system maintains 1 mK stability over several months. The NIRPS
AO-assisted fibre link improves coupling efficiency and offers a unique
high-angular resolution capability with a fibre acceptance of only 0.4
arcsec. A high spectral resolving power of 90 000 and 75 000 is provided
in HA and HE modes, respectively. The overall throughput from the top of
the atmosphere to the detector peaks at 13 percent. The RV precision,
measured on the bright star Proxima with a known exoplanetary system, is
77 cm/s. NIRPS and HARPS can be used simultaneously, offering
unprecedented spectral coverage for spectroscopic characterisation and
stellar activity mitigation. Modal noise can be aptly mitigated by the
implementation of fibre stretchers and AO scanning mode. Initial results
confirm that NIRPS opens new possibilities for RV measurements, stellar
characterisation, and exoplanet atmosphere studies with high precision
and high spectral fidelity. NIRPS demonstrated stable RV precision at
the level of 1 m/s over several weeks. The instrument high throughput
offers a notable improvement over previous spectrographs, enhancing our
ability to detect small exoplanets.
NIRPS
detection of delayed atmospheric escape from the warm and misaligned
Saturn-mass exoplanet WASP-69b
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Romain Allart / Yann Carteret / Vincent Bourrier / Lucile
Mignon
- Frederique Baron / Charles Cadieux / Andres Carmona / Christophe
Lovis
- Hritam Chakraborty / Elisa Delgado-Mena / Etienne Artigau / Susana
C. C. Barros
- Bjorn Benneke / Xavier Bonfils / Francois Bouchy / Marta Bryan
- Bruno L. Canto Martins / Ryan Cloutier / Neil J. Cook / Nicolas B.
Cowan
- Xavier Delfosse / Rene Doyon / Xavier Dumusque / David
Ehrenreich
- Jonay I. Gonzalez Hernandez / David Lafreniere / Izan de Castro Leao
/ Lison Malo
- Claudio Melo / Christoph Mordasini / Francesco Pepe / Rafael
Rebolo
- Jose Renan De Medeiros / Jason Rowe / Nuno C. Santos / Damien
Segransan
- Alejandro Suarez Mascareno / Stephane Udry / Diana Valencia / Gregg
Wade
- Manuel Abreu / Jose L. A. Aguiar / Babatunde Akinsanmi / Guillaume
Allain
- Jose Manuel Almenara / Khaled Al Moulla / Tomy Arial / Hugues
Auger
- Luc Bazinet / Nicolas Blind / Anne Boucher / Christopher Broeg
- Denis Brousseau / Alexandre Cabral / Zalpha
Challita / Joao Coelho
- Marion Cointepas / Ana Rita Costa Silva / Eduardo Cristo / Antoine
Darveau-Bernier
- Laurie Dauplaise / Roseane de Lima Gomes / Daniel Brito de Freitas /
Dasaev O. Fontinele
- Thierry Forveille / Yolanda Frensch / Jonathan Gagne / Frederic
Genest
- Felix Gracia Temich / Nolan Grieves / Olivier Hernandez / Jens
Hoeijmakers
- Norbert Hubin / Farbod Jahandar / Ray Jayawardhana / Dan Kerley
- Johann Kolb / Vigneshwaran Krishnamurthy / Alexandrine L’Heureux /
Monika Lendl
- Olivia Lim / Gaspare Lo Curto / Jaymie Matthews / Allan M.
Martins
- Jean-Sebastien Mayer / Stan Metchev / Yuri S. Messias / Leslie
Moranta
- Dany Mounzer / Nicola Nari / Louise D. Nielsen / Ares Osborn
- Lena Parc / Luca Pasquini / Stefan Pelletier / Celine Peroux
- Caroline Piaulet / Mykhaylo Plotnykov / Emanuela Pompei /
Anne-Sophie Poulin-Girard
- Angelica Psaridi / Jose Luis Rasilla / Vladimir Reshetov / Jonathan
Saint-Antoine
- Jorge Sanz-Forcada / Julia Seidel / Ivo Saviane / Joao Gomes da
Silva
- Danuta Sosnowska / Avidaan Srivastava / Atanas K. Stefanov / Marcio
A. Teixeira
- Simon Thibault / Philippe Vallee / Thomas Vandal / Valentina
Vaulato
- Joost P. Wardenier / Bachar Wehbe / Drew Weisserman / Francois
Wildi
- Vincent Yariv / Gerard Zins
Summary
Near-infrared high-resolution echelle spectrographs unlock access to
fundamental properties of exoplanets, from their atmospheric escape and
composition to their orbital architecture, which can all be studied
simultaneously from transit observations. We present the first results
of the newly commissioned ESO near-infrared spectrograph, NIRPS, from
three transits of WASP-69b. We used the RM Revolutions technique to
better constrain the orbital architecture of the system. We extracted
the high-resolution helium absorption profile to study its spectral
shape and temporal variations. Then, we made 3D simulations from the EVE
code to fit the helium absorption time series. We measure a slightly
misaligned orbit for WASP-69b (psi of 28.7+/-5.7 deg). We confirm the
detection of helium with an average excess absorption of 3.17+/-0.05%.
The helium absorption is spectrally and temporally resolved, extends to
high altitudes and has a strong velocity shift up to -29.5+/-2.5 km/s 50
minutes after egress. EVE simulations put constraints on the mass loss
of 2.25 10^11 g/s and hint at reactive chemistry within the
cometary-like tail and interaction with the stellar winds that allow the
metastable helium to survive longer than expected. Our results suggest
that WASP-69b is undergoing a transformative phase in its history,
losing mass while evolving on a misaligned orbit. This work shows how
combining multiple observational tracers such as orbital architecture,
atmospheric escape, and composition, is critical to understand exoplanet
demographics and their formation and evolution. We demonstrate that
NIRPS can reach precisions similar to HARPS for RM studies, and the high
data quality of NIRPS leads to unprecedented atmospheric
characterization. The high stability of NIRPS combined with the large
GTO available for its consortium, enables in-depth studies of exoplanets
as well as large population surveys.
Different
arrival times of CM and CI-like bodies from the outer Solar System to
the asteroid belt
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Sarah E. Anderson / Pierre Vernazza / Miroslav
Brož
Summary
Understanding the provenance of CI and CM chondrites, the most
primitive materials in our meteorite collections, is critical for
shedding light on the Solar System’s early evolution and contextualizing
findings from recent sample return missions. Here we show that the
parent bodies of CM chondrites originate from the Saturn formation
region, whereas those of CI chondrites originate essentially from the
primordial trans-Uranian disk. Using Nbody simulations to investigate
the effect of giant planet growth and inward Type-I migration, along
with the current observed distribution of CM, CI, and comet-like P types
bodies in the asteroid belt, we demonstrate that CI- and CM-like bodies
must have been implanted at different times in the belt. In contrast, CI
and comet-like bodies were implanted at the same time. These different
implantation periods are imposed by the fact that the gas disk profile
entirely governs the radial distribution of bodies implanted by
aerodynamic drag in the asteroid belt. A preferred location coincides
with the inner edge of a gap opened by Jupiter. Saturn’s growth likely
drove the migration of CM-like bodies. In contrast, CI and comet-like
bodies were transported at a later stage during the outward migration of
Uranus and Neptune, driven by remaining planetesimals. Since CM
chondrites are chondrule-rich, it follows that chondrule formation
occurred mostly inward of the ice giants formation zone (under 10 au). A
byproduct of our simulations is that only CM-like, not CI-like, bodies
contributed to the water budget of the telluric planets.
Euclid:
Forecasts on  CDM consistency tests with growth rate
data
CDM consistency tests with growth rate
data
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- I. Ocampo / D. Sapone / S. Nesseris / G. Alestas
- J. García-Bellido / Z. Sakr / C. J. A. P. Martins / J. P.
Mimoso
- A. Carvalho / A. Da Silva / A. Blanchard / S. Casas
- S. Camera / M. Martinelli / V. Pettorino / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / F. Bernardeau
- A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / H. Degaudenzi
- S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / C. Rosset / R. Saglia / B. Sartoris
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri
- A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P.
Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / C. Burigana / L. Gabarra
- A. Pezzotta / V. Scottez / M. Viel
Summary
The large-scale structure (LSS) of the Universe is an important probe
for deviations from the canonical cosmological constant  and cold dark matter (
and cold dark matter ( CDM) model. A statistically significant
detection of any deviations would signify the presence of new physics or
the breakdown of any number of the underlying assumptions of the
standard cosmological model or possible systematic errors in the data.
In this paper, we quantify the ability of the LSS data products of the
spectroscopic survey of the Euclid mission, together with other
contemporary surveys, to improve the constraints on deviations from
CDM) model. A statistically significant
detection of any deviations would signify the presence of new physics or
the breakdown of any number of the underlying assumptions of the
standard cosmological model or possible systematic errors in the data.
In this paper, we quantify the ability of the LSS data products of the
spectroscopic survey of the Euclid mission, together with other
contemporary surveys, to improve the constraints on deviations from  CDM in the redshift range
CDM in the redshift range  . We
consider both currently available growth rate data and simulated data
with specifications from Euclid and external surveys, based on
. We
consider both currently available growth rate data and simulated data
with specifications from Euclid and external surveys, based on  CDM and a modified gravity (MoG) model
with an evolving Newton’s constant (denoted
CDM and a modified gravity (MoG) model
with an evolving Newton’s constant (denoted  CDM), and carry out a binning method and
a machine learning reconstruction, based on genetic algorithms (GAs), of
several LSS null tests. Using the forecast Euclid growth data from the
spectroscopic survey in the range
CDM), and carry out a binning method and
a machine learning reconstruction, based on genetic algorithms (GAs), of
several LSS null tests. Using the forecast Euclid growth data from the
spectroscopic survey in the range  , we find that in combination with external data
products (covering the range
, we find that in combination with external data
products (covering the range  ),
Euclid will be able to improve on current constraints of null tests of
the LSS on average by a factor of eight when using a binning method and
a factor of six when using the GAs. Our work highlights the need for
synergies between Euclid and other surveys, but also the usefulness of
statistical analyses, such as GAs, in order to disentangle any
degeneracies in the cosmological parameters. Both are necessary to
provide tight constraints over an extended redshift range and to probe
for deviations from the
),
Euclid will be able to improve on current constraints of null tests of
the LSS on average by a factor of eight when using a binning method and
a factor of six when using the GAs. Our work highlights the need for
synergies between Euclid and other surveys, but also the usefulness of
statistical analyses, such as GAs, in order to disentangle any
degeneracies in the cosmological parameters. Both are necessary to
provide tight constraints over an extended redshift range and to probe
for deviations from the  CDM model.
CDM model.
Articles for week 30 2025
Testing
the AGN unified model with simulated emission lines from the
circumgalactic medium (CGM)
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Shiwu Zhang / Zheng Cai / Aura Obreja / Fabrizio Arrigoni
Battaia
- Léo Michel-Dansac / Jérémy Blaizot / Donghui Quan /
Mingyu Li
Summary
The CGM around unobscured AGN has received much attention in recent
years. Comparatively, nebulae associated with obscured AGN are less
studied. Here, we simulate the Ly , H
, H , and HeII nebulae around the two types
of AGN at
, and HeII nebulae around the two types
of AGN at  with ten massive
systems from the FIRE simulations based on the unified model to show
their differences and to test if they can be used to constrain the AGN
model. We post-process the data with the CLOUDY and the Ly
with ten massive
systems from the FIRE simulations based on the unified model to show
their differences and to test if they can be used to constrain the AGN
model. We post-process the data with the CLOUDY and the Ly radiative transfer code, RASCAS.
Overall, we find that the Ly
radiative transfer code, RASCAS.
Overall, we find that the Ly nebulae around the unobscured AGN
(type-I nebulae) and obscured AGN (type-II nebulae) do not exhibit
significant differences in the luminosity, area, and HeII/Ly
nebulae around the unobscured AGN
(type-I nebulae) and obscured AGN (type-II nebulae) do not exhibit
significant differences in the luminosity, area, and HeII/Ly when the simulated cutout is set to the
halo virial radius. Whereas, the type-II nebulae exhibit less symmetric
morphologies, flatter surface brightness profiles, and larger emission
line widths (at
when the simulated cutout is set to the
halo virial radius. Whereas, the type-II nebulae exhibit less symmetric
morphologies, flatter surface brightness profiles, and larger emission
line widths (at  kpc) than those
of the type-I nebulae. These nebulae properties exhibit complicated
correlations with the AGN, indicating that nebulae observations can be
applied to constrain the AGN engine. However, independent observations
on nebulae in the mentioned emissions are insufficient to test the
unified model as a priori in observations is not possible to know the
direction and opening angle of the ionization cone. We prompt that the
joint observations of Ly
kpc) than those
of the type-I nebulae. These nebulae properties exhibit complicated
correlations with the AGN, indicating that nebulae observations can be
applied to constrain the AGN engine. However, independent observations
on nebulae in the mentioned emissions are insufficient to test the
unified model as a priori in observations is not possible to know the
direction and opening angle of the ionization cone. We prompt that the
joint observations of Ly nebulae and radio jets can help to
reveal the ionization cone to probe the unified model. Our calculations
suggest that this method requires
nebulae and radio jets can help to
reveal the ionization cone to probe the unified model. Our calculations
suggest that this method requires  type-II Ly
type-II Ly nebulae with current instruments to
reach a confidence level of
nebulae with current instruments to
reach a confidence level of  .
.
JWST
reveals a supernova following a gamma-ray burst at z  7.3
7.3
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. J. Levan / B. Schneider / E. Le Floc’h / G.
Brammer
- N. R. Tanvir / D. B. Malesani / A. Martin-Carrillo / A. Rossi
- A. Saccardi / A. Sneppen / S. D. Vergani / J. An
- J.-L. Atteia / F. E. Bauer / V. Buat / S.
Campana
- A. Chrimes / B. Cordier / L. Cotter / F. Daigne
- V. D’Elia / M. De Pasquale / A. de Ugarte Postigo / G. Corcoran
- R. A. J. Eyles-Ferris / H. Fausey / A. S. Fruchter / O. Godet
- B. P. Gompertz / D. Gotz / N. Habeeb / D. H. Hartmann
- L. Izzo / P. Jakobsson / T. Laskar / A. Melandri
- P. T. O’Brien / J. T. Palmerio / L. Piro / G. Pugliese
- Y. L. Qiu / B. C. Rayson / R. Salvaterra / S. Schanne
- A. L. Thakur / C. C. Thone / D. Watson / J. Y. Wei
- K. Wiersema / R. A. M. J. Wijers / L. P. Xin / D. Xu
- S. N. Zhang
Summary
The majority of energetic long-duration gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are
thought to arise from the collapse of massive stars, making them
powerful tracers of star formation across cosmic time. Evidence for this
origin comes from the presence of supernovae in the aftermath of the GRB
event, whose properties in turn link back to those of the collapsing
star. In principle, with GRBs we can study the properties of individual
stars in the distant universe. Here, we present JWST/NIRCAM observations
that detect both the host galaxy and likely supernova in the SVOM GRB
250314A with a spectroscopically measured redshift of z  7.3, deep in the era
of reionisation. The data are well described by a combination of faint
blue host, similar to many z
7.3, deep in the era
of reionisation. The data are well described by a combination of faint
blue host, similar to many z  7 galaxies, with a
supernova of similar luminosity to the proto-type GRB supernova, SN
1998bw. Although larger galaxy contributions cannot be robustly
excluded, given the evidence from the blue afterglow colours of low dust
extinction, supernovae much brighter than SN 1998bw can be. These
observations suggest that, despite disparate physical conditions, the
star that created GRB 250314A was similar to GRB progenitors in the
local universe.
7 galaxies, with a
supernova of similar luminosity to the proto-type GRB supernova, SN
1998bw. Although larger galaxy contributions cannot be robustly
excluded, given the evidence from the blue afterglow colours of low dust
extinction, supernovae much brighter than SN 1998bw can be. These
observations suggest that, despite disparate physical conditions, the
star that created GRB 250314A was similar to GRB progenitors in the
local universe.
Euclid
preparation: Expected constraints on initial conditions
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / F. Finelli / Y. Akrami / A. Andrews
- M. Ballardini / S. Casas / D. Karagiannis / Z. Sakr
- J. Valiviita / G. Alestas / N. Bartolo / J. R. Bermejo-Climent
- S. Nesseris / D. Paoletti / D. Sapone / I. Tutusaus
- A. Achúcarro / G. Cañas-Herrera / J. Jasche / G. Lavaux
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / L. Amendola
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / D. Bagot
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / S. Camera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / P. Fosalba
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. J.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / C. Rosset / R. Saglia / B. Sartoris
- M. Schirmer / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N.
Taylor
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / L. Valenziano / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes
Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese
- A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf
- A. A. Nucita / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / I. T. Andika / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / S. Avila / A. Balaguera-Antolinez / D.
Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- F. Cogato / S. Conseil / A. R. Cooray / S.
Davini
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / A. Gruppuso / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J.
Hjorth
- S. Joudaki / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi
- V. Le Brun / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M.
Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / L. Pagano / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P. Reimberg / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
The Euclid mission of the European Space Agency will deliver galaxy
and cosmic shear surveys, which will be used to constrain initial
conditions and statistics of primordial fluctuations. We present
highlights for the Euclid scientific capability to test initial
conditions beyond LCDM with the main probes, i.e. 3D galaxy clustering
from the spectroscopic survey, the tomographic approach to 3x2pt
statistics from photometric galaxy survey, and their combination. We
provide Fisher forecasts from the combination of Euclid spectroscopic
and photometric surveys for spatial curvature, running of the spectral
index of the power spectrum of curvature perturbations, isocurvature
perturbations, and primordial features. For the parameters of these
models we also provide the combination of Euclid forecasts (pessimistic
and optimistic) with current and future measurements of the cosmic
microwave background (CMB) anisotropies., i.e. Planck, the Simons
Observatory (SO), and CMB-S4. We provide Fisher forecasts for how the
power spectrum and bispectrum from the Euclid spectroscopic survey will
constrain the local, equilateral, and orthogonal shapes of primordial
non-Gaussianity. We also review how Bayesian field-level inference of
primordial non-Gaussianity can constrain local primordial
non-Gaussianity. We show how Euclid, with its unique combination of the
main probes, will provide the tightest constraints on low redshift to
date. By targeting a markedly different range in redshift and scale,
Euclid’s expected uncertainties are complementary to those obtained by
CMB primary anisotropy, returning the tightest combined constraints on
the physics of the early Universe.
GRB
241105A: A test case for GRB classification and rapid r-process
nucleosynthesis channels
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Dimple / B. P. Gompertz / A. J. Levan / D. B. Malesani
- T. Laskar / S. Bala / A. A. Chrimes / K. Heintz
- L. Izzo / G. P. Lamb / D. O’Neill / J. T. Palmerio
- A. Saccardi / G. E. Anderson / C. De Barra / Y. Huang
- A. Kumar / H. Li / S. McBreen / O. Mukherjee
- S. R. Oates / U. Pathak / Y. Qiu / O. J. Roberts
- R. Sonawane / P. Veres / K. Ackley / X. Han
- Y. Julakanti / J. Wang / P. D’Avanzo / A. Martin-Carrillo
- M. E. Ravasio / A. Rossi / N. R. Tanvir / J. P. Anderson
- M. Arabsalmani / S. Belkin / R. P. Breton / R. Brivio
- E. Burns / J. Casares / S. Campana / S. I. Chastain
- V. D’Elia / V. S. Dhillon / M. J. Dyer / J. P. U. Fynbo
- D. K. Galloway / A. Gulati / B. Godson / A. J. Goodwin
- M. Gromadzki / D. H. Hartmann / P. Jakobsson / T. L. Killestein
- R. Kotak / J. K. Leung / J. D. Lyman / A. Melandri
- S. Mattila / S. McGee / C. Morley / T. Mukherjee
- T. E. Muller-Bravo / K. Noysena / L. K. Nuttall / P. O’Brien
- M. De Pasquale / G. Pignata / D. Pollacco / G. Pugliese
- G. Ramsay / A. Sahu / R. Salvaterra / P. Schady
- B. Schneider / D. Steeghs / R. L. C. Starling / K.
Tsalapatas
- K. Ulaczyk / A. J. van der Horst / C. Wang / K. Wiersema
- I. Worssam / M. E. Wortley / S. Xiong / T. Zafar
Summary
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) offer a powerful window to probe the
progenitor systems responsible for the formation of heavy elements
through the rapid neutron capture (r-) process, thanks to their
exceptional luminosity, which allows them to be observed across vast
cosmic distances. GRB 241105A, observed at a redshift of z = 2.681,
features a short initial spike (1.5 s) and a prolonged weak emission
lasting about 64 s, positioning it as a candidate for a compact binary
merger and potentially marking it as the most distant merger-driven GRB
observed to date. However, the emerging ambiguity in GRB classification
necessitates further investigation into the burst’s true nature. Prompt
emission analyses, such as hardness ratio, spectral lag, and minimum
variability timescales, yield mixed classifications, while machine
learning-based clustering places GRB 241105A near both long-duration
mergers and collapsar GRBs. We conducted observations using the James
Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to search for a potential supernova
counterpart. Although no conclusive evidence was found for a supernova,
the host galaxy’s properties derived from the JWST observations suggest
active star formation with low metallicity, and a sub-kpc offset of the
afterglow from the host, which appears broadly consistent with a
collapsar origin. Nevertheless, a compact binary merger origin cannot be
ruled out, as the burst may plausibly arise from a fast progenitor
channel. This would have important implications for heavy element
enrichment in the early Universe.
MINERVA:
A NIRCam Medium Band and MIRI Imaging Survey to Unlock the Hidden Gems
of the Distant Universe
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Adam Muzzin / Katherine A. Suess / Danilo Marchesini / Luke
Robbins
- Chris J. Willott / Stacey Alberts / Jacqueline Antwi-Danso /
Yoshihisa Asada
- Gabriel Brammer / Sam E. Cutler / Kartheik G. Iyer / Ivo Labbe
- Nicholas S. Martis / Tim B. Miller / Ikki Mitsuhashi / Alexandra
Pope
- Anna Sajina / Ghassan T. E. Sarrouh / Monu Sharma / Mauro
Stefanon
- Katherine E. Whitaker / Roberto Abraham / Hakim Atek / Marusa
Bradac
- Samantha Berek / Rachel Bezanson / Westley Brown / Adam J.
Burgasser
- Nathalie Chicoine / Aidan P. Cloonan / Olivia R. Cooper / Pratika
Dayal
- Anna de Graaff / Guillaume Desprez / Robert Feldmann / Ben
Forrest
- Marijn Franx / Yoshinobu Fudamoto / Seiji Fujimoto / Lukas J.
Furtak
- Karl Glazebrook / Ilias Goovaerts / Jenny E. Greene
/ Naadiyah Jagga
- William W. H. Jarvis / Mariska Kriek / Gourav Khullar / Valentina La
Torre
- Joel Leja / Jamie Lin / Brian Lorenz / Daniel Lyon
- Vladan Markov / Michael V. Maseda / Ian McConachie / Maya
Merchant
- Rosa M. Merida / Lamiya Mowla / Katherine Myers / Rohan P.
Naidu
- Themiya Nanayakkara / Erica J. Nelson / Gael Noirot / Pascal A.
Oesch
- Kiyoaki C. Omori / Richard Pan / Natalia Porraz Barrera / Sedona H.
Price
- Swara Ravindranath / Marcin Sawicki / David J. Setton / Renske
Smit
- Visal Sok / Joshua S. Speagle / Edward N. Taylor / Vivian Yun Yan
Tan
- Roberta Tripodi / Arjen van der Wel / Edgar Perez Vidal / Bingjie
Wang
- John R. Weaver / Christina C. Williams / Sunna Withers / Kumail
Zaidi
Summary
We present an overview of the MINERVA survey, a 259.8 hour (prime)
and 127 hour (parallel) Cycle 4 treasury program on the James Webb Space
Telescope (JWST). MINERVA is obtaining 8 filter NIRCam medium band
imaging (F140M, F162M, F182M, F210M, F250M, F300M, F360M, F460M) and 2
filter MIRI imaging (F1280W, F1500W) in four of the five CANDELS
Extragalactic fields: UDS, COSMOS, AEGIS and GOODS-N. These fields were
previously observed in Cycle 1 with 7 - 9 NIRCam filters by the PRIMER,
CEERS and JADES programs. MINERVA reaches a 5 depth of 28.1 mag in F300M and covers
depth of 28.1 mag in F300M and covers
 542 arcmin
542 arcmin , increasing the area of existing JWST
medium-band coverage in at least 8 bands by
, increasing the area of existing JWST
medium-band coverage in at least 8 bands by  7
7 . The MIRI imaging
reaches a 5
. The MIRI imaging
reaches a 5 depth of 23.9 mag in F1280W and covers
depth of 23.9 mag in F1280W and covers
 275 arcmin
275 arcmin in at least 2 MIRI filters. When
combined with existing imaging, these data will provide a photometric
catalog with 20-26 JWST filters (depending on field) and 26-35 filters
total, including HST. This paper presents a detailed breakdown of the
filter coverage, exposure times, and field layout relative to previous
observations, as well as an overview of the primary science goals of the
project. These include uncovering the physics of enigmatic sources
hiding in current broadband catalogs, improving systematics on stellar
mass functions and number densities by factors of
in at least 2 MIRI filters. When
combined with existing imaging, these data will provide a photometric
catalog with 20-26 JWST filters (depending on field) and 26-35 filters
total, including HST. This paper presents a detailed breakdown of the
filter coverage, exposure times, and field layout relative to previous
observations, as well as an overview of the primary science goals of the
project. These include uncovering the physics of enigmatic sources
hiding in current broadband catalogs, improving systematics on stellar
mass functions and number densities by factors of  3, and resolved
mapping of stellar mass and star formation at 1
3, and resolved
mapping of stellar mass and star formation at 1  6. When
complete, MINERVA will become an integral part of the treasury deep
field imaging datasets, significantly improving population studies with
well-understood completeness, robust photometric redshifts, stellar
masses, and sizes, and facilitating spectroscopic follow up for decades
to come.
6. When
complete, MINERVA will become an integral part of the treasury deep
field imaging datasets, significantly improving population studies with
well-understood completeness, robust photometric redshifts, stellar
masses, and sizes, and facilitating spectroscopic follow up for decades
to come.
The
CHEOPS view of HD 95338b: refined transit parameters, and a search for
exomoons
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Sz. Kálmán / A. E. Simon / A. Deline / Sz. Csizmadia
- Gy. M. Szabó / D. Ehrenreich / T. G. Wilson / M. N. Günther
- A. Heitzmann / S. G. Sousa / M. Farnir / A. Bonfanti
- A. M. S. Smith / A. Pál / G. Scandariato / V. Adibekyan
- A. Brandeker / S. Charnoz / B. Akinsanmi / S. C. C. Barros
- X. Song / Y. Alibert / R. Alonso / T. Bárczy
- D. Barrado Navascues / W. Baumjohann / W. Benz / N. Billot
- F. Biondi / L. Borsato / C. Broeg / A. Collier Cameron
- C. Corral van Damme / A. C. M. Correia / P. E. Cubillos / M. B.
Davies
- M. Deleuil / O. D. S. Demangeon / B.-O. Demory / A.
Derekas
- B. Edwards / J. A. Egger / A. Erikson / A. Fortier
- L. Fossati / M. Fridlund / D. Gandolfi / K. Gazeas
- M. Gillon / M. Güdel / P. Guterman / J. Hasiba
- Ch. Helling / K. G. Isaak / L. L. Kiss / J. Korth
- K. W. F. Lam / J. Laskar / A. Lecavelier des Etangs / A. Leleu
- M. Lendl / D. Magrin / P. F. L. Maxted / B. Merín
- C. Mordasini / M. Munari / V. Nascimbeni / G. Olofsson
- R. Ottensamer / I. Pagano / E. Pallé / G. Peter
- D. Piazza / G. Piotto / D. Pollacco / D. Queloz
- R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando / H. Rauer / I. Ribas
- N. C. Santos / D. Ségransan / M. Stalport / S.
Sulis
- S. Udry / B. Ulmer / S. Ulmer-Moll / V. Van Grootel
- J. Venturini / E. Villaver / N. A. Walton / S. Wolf
- T. Zingales
Summary
Despite the ever-increasing number of known exoplanets, no
uncontested detections have been made of their satellites, known as
exomoons. The quest to find exomoons is at the forefront of exoplanetary
sciences. Certain space-born instruments are thought to be suitable for
this purpose. We show the progress made with the CHaracterizing
ExOPlanets Satellite (CHEOPS) in this field using the HD 95338 planetary
system. We present a novel methodology as an important step in the quest
to find exomoons. We utilize ground-based spectroscopic data in
combination with Gaia observations to obtain precise stellar parameters.
These are then used as input in the analysis of the planetary transits
observed by CHEOPS and the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS).
In addition, we search for the signs of satellites primarily in the form
of additional transits in the Hill sphere of the eccentric Neptune-sized
planet HD 95338b in a sequential approach based on four CHEOPS visits.
We also briefly explore the transit timing variations of the planet. We
present refined stellar and planetary parameters, narrowing down the
uncertainty on the planet-to-star radius ratio by a factor of  . We also pin down the ephemeris of HD
95338b. Using injection/retrieval tests, we show that a
. We also pin down the ephemeris of HD
95338b. Using injection/retrieval tests, we show that a  detection of an exomoon
would be possible at
detection of an exomoon
would be possible at  ~
~ with the
methodology presented here. We exclude the transit of an exomoon in the
system with
with the
methodology presented here. We exclude the transit of an exomoon in the
system with  ~
~ at the
at the  level. The algorithm used for
finding the transit-like event can be used as a baseline for other
similar targets, observed by CHEOPS or other missions.
level. The algorithm used for
finding the transit-like event can be used as a baseline for other
similar targets, observed by CHEOPS or other missions.
VLBI studies of
FLASH H I 21-cm absorbers – I
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. N. H. S. Aditya / Elaine M. Sadler / Raffaella Morganti / L. Y.
Petrov
- An Tao / Emily F. Kerrison / Elizabeth K. Mahony / Hyein Yoon
- Renzhi Su / Matthew Whiting / Vanessa A. Moss / Simon
Weng
Summary
We have conducted VLBA 1.4 GHz (L-band) continuum observations
towards twelve sources with HI 21-cm absorption detections at redshift
 in
the pilot surveys of FLASH, an ongoing survey with the ASKAP radio
telescope. 11 of the 12 targets are resolved in the VLBA observations.
Using the parsec scale radio images, we have classified the source
morphology and identified the radio core. Six of the twelve targets have
core-jet morphology, four have two-sided jet morphology, one has a
complex morphology, and one is unresolved. We describe a methodology to
test whether the emission from the core or the total emission detected
in the VLBA image has sufficient flux density to cause the entire HI
21-cm absorption, and we estimate limits on the gas covering factor and
velocity-integrated optical depth (VOD). We find that for seven of the
twelve sources, the core has sufficient flux density to cause all the HI
21-cm absorption detected in the ASKAP spectrum. For three other
targets, with projected sizes in the range
in
the pilot surveys of FLASH, an ongoing survey with the ASKAP radio
telescope. 11 of the 12 targets are resolved in the VLBA observations.
Using the parsec scale radio images, we have classified the source
morphology and identified the radio core. Six of the twelve targets have
core-jet morphology, four have two-sided jet morphology, one has a
complex morphology, and one is unresolved. We describe a methodology to
test whether the emission from the core or the total emission detected
in the VLBA image has sufficient flux density to cause the entire HI
21-cm absorption, and we estimate limits on the gas covering factor and
velocity-integrated optical depth (VOD). We find that for seven of the
twelve sources, the core has sufficient flux density to cause all the HI
21-cm absorption detected in the ASKAP spectrum. For three other
targets, with projected sizes in the range  ,
a large fraction of the entire emission in the VLBA map could be
occulted by the gas. For 0903+010 (NVSS J090331+010846), we estimate
that at least
,
a large fraction of the entire emission in the VLBA map could be
occulted by the gas. For 0903+010 (NVSS J090331+010846), we estimate
that at least  of the
peak absorption detected in the ASKAP spectrum could arise against the
emission detected in the VLBA image. For the target 0023+010 (NVSS
J002331+010114), we estimate an upper limit on the VOD of
of the
peak absorption detected in the ASKAP spectrum could arise against the
emission detected in the VLBA image. For the target 0023+010 (NVSS
J002331+010114), we estimate an upper limit on the VOD of  , the highest in our sample. For 0903+010 (NVSS
J090331+010846) we estimate a lower limit of
, the highest in our sample. For 0903+010 (NVSS
J090331+010846) we estimate a lower limit of  on the VOD. We find that the distribution of HI
21-cm VODs at
on the VOD. We find that the distribution of HI
21-cm VODs at  could increase by up to a factor of three after correction for the
covering factors using our VLBA measurements.
could increase by up to a factor of three after correction for the
covering factors using our VLBA measurements.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- D. Fernández-Arenas / L. Rousseau-Nepton / C. Robert / L.
Drissen
- R. P. Martin / P. Amram / B.
Epinat / Duarte Puertas
- R. Garner / G. Savard / S. Vicens-Mouret / É. Massé
Summary
NGC 4258 is a prime target for studying feedback in Low-Luminosity
Active Galactic Nuclei (LLAGNs) due to its proximity and comprehensive
multi-wavelength coverage. Using new Integral Field Spectroscopy (IFS)
data from SITELLE at the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope, we analysed the
galaxy’s nebular emission lines. Our study focused on spatially resolved
line ratios and Baldwin-Phillips-Terlevich diagrams, revealing that the
‘’anomalous spiral arms’’ exhibit intense interactions between the jet
and interstellar medium (ISM) extending up to 6 kpc with velocity
dispersions peak at 200-250 km/s in these regions, contrasting with
star-forming areas showing lower values around of 30-50 km/s. Analysis
of covering fractions indicates heightened AGN ionization cones aligned
with the radio jet, alongside evidence of shock quenching observed in
the lower “anomalous arc”. Conversely, jet-induced compression may
stimulate star formation in other areas. We derived a galaxy-wide star
formation rate of  decreasing to
decreasing to  within the
central
within the
central  . SITELLE’s broad field coverage elucidates the
galaxy’s structural details, confirming that low-power jets
significantly influence the host galaxy across parsec and kpc scales.
The velocity dispersion map reveals asymmetric or double-peaked emission
lines, tracing jet-disk interactions likely responsible for the
formation of anomalous arm features. Small-scale ionizing clusters were
detected in regions with disrupted gas flows, possibly formed through
tidal interactions or shock compression. NGC~4258 thus presents a
compelling case for studying LLAGN-driven feedback, illustrating how
optical IFS combined with multi-wavelength data clarifies the impact of
outflows and shocks on nearby spiral galaxies, providing insights into
how these processes shape star formation and ISM conditions.
. SITELLE’s broad field coverage elucidates the
galaxy’s structural details, confirming that low-power jets
significantly influence the host galaxy across parsec and kpc scales.
The velocity dispersion map reveals asymmetric or double-peaked emission
lines, tracing jet-disk interactions likely responsible for the
formation of anomalous arm features. Small-scale ionizing clusters were
detected in regions with disrupted gas flows, possibly formed through
tidal interactions or shock compression. NGC~4258 thus presents a
compelling case for studying LLAGN-driven feedback, illustrating how
optical IFS combined with multi-wavelength data clarifies the impact of
outflows and shocks on nearby spiral galaxies, providing insights into
how these processes shape star formation and ISM conditions.
SVOM
GRB 250314A at z  7.3: an exploding
star in the era of reionization
7.3: an exploding
star in the era of reionization
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- B. Cordier / J. Y. Wei / N. R. Tanvir / S. D. Vergani
- D. B. Malesani / J. P. U. Fynbo / A. de Ugarte Postigo / A.
Saccardi
- F. Daigne / J.-L. Atteia / O. Godet / D. Gotz
- Y. L. Qiu / S. Schanne / L. P. Xin / B. Zhang
- S. N. Zhang / A. J. Nayana / L. Piro / B.
Schneider
- A. J. Levan / A. L. Thakur / Z. P. Zhu / G. Corcoran
- N. A. Rakotondrainibe / V. D’Elia / D. Turpin / J. F. Agui
Fernandez
- M. A. Aloy / J. An / M. Bai / S. Basa
- M. G. Bernardini / A. Bochenek / R. Brivio / M. Brunet
- G. Bruni / S. B. Cenko / Q. Cheng / A. Chrimes
- L. Christensen / A. Claret / A. Coleiro / L. Cotter
- S. Crepaldi / J. S. Deng / Dimple / Y. W. Dong
- D. Dornic / P. A. E. Evans / R. A. J. Eyles-Ferris / H. Fausey
- M. Ferro / L. Galbany / M. Garnichey / G. Gianfagna
- B. P. Gompertz / H. Goto / N. Habeeb / P. Y. Han
- X. H. Han / D. H. Hartmann / K. E. Heintz / J. Y. Hu
- M. H. Huang / L. Izzo / P. Jakobsson / J. A. Kennea
- C. Lachaud / T. Laskar / D. Li / H. L. Li
- R. Z. Li / X. Liu / Y. Liu / G. Lombardi
- H. Louvin / P. Maggi / T. Maiolino / Q. Y. Mao
- A. Martin-Carrillo / K. Mercier / P. O’Brien / J. T. Palmerio
- P. Petitjean / D. L. A. Pieterse / F. Piron / G. Pugliese
- B. C. Rayson / T. Reynolds / F. Robinet / A. Rossi
- R. Salvaterra / C. C. Thone / B. Topcu / C. W. Wang
- J. Wang / Y. Wang / C. Wu / S. L. Xiong
- D. Xu / H. N. Yang / W. M. Yuan / Y. H. Zhang
- X. F. Zhang / S. J. Zheng
Summary
Most long Gamma-ray bursts originate from a rare type of massive
stellar explosion. Their afterglows, while rapidly fading, can be
initially extremely luminous at optical/near-infrared wavelengths,
making them detectable at large cosmological distances. Here we report
the detection and observations of GRB 250314A by the SVOM satellite and
the subsequent follow-up campaign with the near-infrared afterglow
discovery and the spectroscopic measurements of its redshift z  7.3 . This burst
happened when the Universe was only
7.3 . This burst
happened when the Universe was only  5% of its current age. We
discuss the signature of these rare events within the context of the
SVOM operating model, and the ways to optimize their identification with
adapted ground follow-up observation strategies.
5% of its current age. We
discuss the signature of these rare events within the context of the
SVOM operating model, and the ways to optimize their identification with
adapted ground follow-up observation strategies.
Testing
gravitational physics by combining DESI DR1 and weak lensing datasets
using the E_G estimator
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- S. J. Rauhut / C. Blake / U. Andrade / H. E. Noriega
- J. Aguilar / S. Ahlen / S. BenZvi / D. Bianchi
- D. Brooks / T. Claybaugh / A. Cuceu / A. de la Macorra
- J. DeRose / P. Doel / N. Emas / S. Ferraro
- J. E. Forero-Romero / C. Garcia-Quintero / E. Gaztañaga / G.
Gutierrez
- S. Heydenreich / K. Honscheid / C. Howlett / D. Huterer
- M. Ishak / S. Joudaki / R. Joyce / E. Jullo
- R. Kehoe / D. Kirkby / A. Kremin / A. Krolewski
- O. Lahav / A. Lambert / C. Lamman / M. Landriau
- J. U. Lange / L. Le Guillou / A. Leauthaud / M. Manera
- A. Meisner / R. Miquel / S. Nadathur / J. A. Newman
- G. Niz / N. Palanque-Delabrouille / W. J. Percival / A.
Porredon
- F. Prada / I. Pérez-Ràfols / G. Rossi / R. Ruggeri
- E. Sanchez / C. Saulder / D. Schlegel / A. Semenaite
- J. Silber / D. Sprayberry / Z. Sun / G. Tarlé
- B. A. Weaver / P. Zarrouk / R. Zhou / H. Zou
Summary
The action of gravitational physics across space-time creates
observable signatures in the behaviour of light and matter. We perform
combined-probe studies using data from the Baryon Oscillation
Spectroscopic Survey (BOSS) and Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument
survey Data Release 1 (DESI-DR1), in combination with three existing
weak lensing surveys, the Kilo-Degree Survey (KiDS), the Dark Energy
Survey (DES), and the Hyper Suprime-Cam Survey (HSC), to test and
constrain General Relativity (GR) in the context of the standard model
of cosmology (LCDM). We focus on measuring the gravitational estimator
statistic, E_G, which describes the relative amplitudes of weak
gravitational lensing and galaxy velocities induced by a common set of
overdensities. By comparing our amplitude measurements with their
predicted scale- and redshift-dependence within the GR+LCDM model, we
demonstrate that our results are consistent with the predictions of the
Planck cosmology. The redshift span of the DESI dataset allows us to
perform these E_G measurements at the highest redshifts achieved to
date, z ~ 1.
X-SHYNE:
X-Shooter spectra of young exoplanet analogs II. Presentation and
analysis of the full library
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Simon Petrus / Gaël Chauvin / Mickaël Bonnefoy / Pascal
Tremblin
- Caroline Morley / Benjamin Charnay / Genaro Suarez / Jonathan
Gagné
- Paulina Palma-Bifani / Allan Denis / Matthieu Ravet
/ Amelia Bayo
- Bruno Bézard / Beth Biller / Philippe Delorme / Jacqueline
Faherty
- Jayesh M. Goyal / Kielan Hoch / Kevin Hoy / James S Jenkins
- Anne-Marie Lagrange / Baptiste Lavie / Michael C. Liu / Elena
Manjavacas
- Gabriel-Dominique Marleau / Michael McElwain / Paul Mollière /
Christophe Mordasini
- Mark Phillips / Patricio Rojo / Zhoujian Zhang / Alice Zurlo
Summary
The X-SHYNE library is a homogeneous sample of 43 medium-resolution
(R=8000) infrared (0.3-2.5um) spectra of young (<500Myr), low-mass
(<20Mjup), and cold (Teff=600-2000K) isolated brown dwarfs and
wide-separation companions observed with the VLT/X-Shooter instrument.
To characterize our targets, we performed a global comparative analysis.
We first applied a semi-empirical approach. By refining their age and
bolometric luminosity, we derived key atmospheric and physical
properties, such as Teff, mass, surface gravity (g), and radius, using
the evolutionary model COND03. These results were then compared with the
results from a synthetic analysis based on three self-consistent
atmospheric models. To compare our spectra with these grids we used the
Bayesian inference code ForMoSA. We found similar Lbol estimates between
both approaches, but an underestimated Teff from the cloudy models,
likely due to a lack of absorbers that could dominate the J and H bands
of early L. We also observed a discrepancy in the log(g) estimates,
which are dispersed between 3.5 and 5.5 dex for mid-L objects. We
interpreted this as a bias caused by a range of rotational velocities
leading to cloud migration toward equatorial latitudes, combined with a
variety of viewing angles that result in different observed atmospheric
properties (cloud column densities, atmospheric pressures, etc.).
Finally, while providing robust estimates of [M/H] and C/O for
individual objects remains challenging, the X-SHYNE library globally
suggests solar values, which are consistent with a formation via stellar
formation mechanisms. This study highlights the strength of homogeneous
datasets in performing comparative analyses, reducing the impact of
systematics, and ensuring robust conclusions while avoiding
over-interpretation.
VERTICO
IX: Signatures of environmental processing of the gas in Virgo cluster
spiral galaxies through mapping of CO isotopologues
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Timothy A. Davis / Toby Brown / Maria J. Jimenez-Donaire / Christine
D. Wilson
- Dhruv Bisaria / Alessandro Boselli / Barbara
Catinella / Aeree Chung
- Luca Cortese / Sara Ellison / Bumhyun Lee / Ian D. Roberts
- Kristine Spekkens / Vicente Villanueva / Nikki Zabel
Summary
In this work we study CO isotopologue emission in the largest cluster
galaxy sample to date: 48 VERTICO spiral galaxies in Virgo. We show for
the first time in a significant sample that the physical conditions
within the molecular gas appear to change as a galaxy’s ISM is affected
by environmental processes. 13CO is detected across the sample, both
directly and via stacking, while C18O is detected in a smaller number of
systems. We use these data to study trends with global and radial galaxy
properties. We show that the CO/13CO line ratio changes systematically
with a variety of galaxy properties, including mean gas surface density,
HI-deficiency and galaxy morphology. 13CO/C18O line ratios vary
significantly, both radially and between galaxies, suggesting real
variations in abundances are present. Such abundance changes may be due
to star formation history differences, or speculatively even stellar
initial mass function variations. We present a model where the optical
depth of the molecular gas appears to change as a galaxy’s ISM is
affected by environmental processes. The molecular gas appears to become
more transparent as the molecular medium is stripped, and then more
opaque as the tightly bound remnant gas settles deep in the galaxy core.
This explains the variations we see, and also helps explain similar
observations in cluster early-type galaxies. Next generation simulations
and dedicated observations of additional isotopologues could thus
provide a powerful tool to help us understand the impact of environment
on the ISM, and thus the quenching of galaxies.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- L. R. Ivey / J. Scholtz / A. L. Danhaive / S. Koudmani
- G. C. Jones / R. Maiolino / M. Curti / F. D’Eugenio
- S. Tacchella / W. M. Baker / S. Arribas / S. Charlot
- D. Eisenstein / Z. Ji / M. Koller / N. Laporte
- D. Puskás / B. Robertson / D. Sijacki / J. A. A. Trussler
- C. Witten
Summary
A majority of JWST/NIRSpec/IFU studies at high redshifts to date have
focused on UV-bright or massive objects, while our understanding of
low-mass galaxies at early cosmic times remains limited. In this work,
we present NIRSpec/IFS high-resolution observations of two low-mass
( ), low-metallicity (
), low-metallicity (![[12 + \log(\text{O/H})] < 8 [12 + \log(\text{O/H})] < 8](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%5B12%20%2B%20%5Clog%28%5Ctext%7BO%2FH%7D%29%5D%20%3C%208) ) galaxies
at
) galaxies
at  , one of
which we identify as hosting a Type-II AGN. We measure flat strong-line
metallicity gradients, suggestive of ISM redistribution by outflows or
past merging, but also identify tension with the direct-
, one of
which we identify as hosting a Type-II AGN. We measure flat strong-line
metallicity gradients, suggestive of ISM redistribution by outflows or
past merging, but also identify tension with the direct- metallicity
gradient in one galaxy. We measure
metallicity
gradient in one galaxy. We measure  in both galaxies, consistent with observations of
lower rotational support at early cosmic times. We identify broad
kinematical components decoupled from galactic rotation with velocities
of
in both galaxies, consistent with observations of
lower rotational support at early cosmic times. We identify broad
kinematical components decoupled from galactic rotation with velocities
of  and argue these components trace outflows, for
which we infer outflow rates of
and argue these components trace outflows, for
which we infer outflow rates of  with
with  . We
compare our findings to results from the new large-volume AESOPICA
simulations, which fully incorporate different models of black hole
growth and AGN feedback. We find that our observational results of
. We
compare our findings to results from the new large-volume AESOPICA
simulations, which fully incorporate different models of black hole
growth and AGN feedback. We find that our observational results of  are consistent with the simulated dwarf AGN
population, hinting AGN-driven feedback may contribute to quenching both
in our systems and in a wider population of low-mass galaxies in the
early Universe. This novel study illustrates the necessity of deep IFU
observations to decompose the complex kinematics and morphology of
high-
are consistent with the simulated dwarf AGN
population, hinting AGN-driven feedback may contribute to quenching both
in our systems and in a wider population of low-mass galaxies in the
early Universe. This novel study illustrates the necessity of deep IFU
observations to decompose the complex kinematics and morphology of
high- galaxies, trace outflows, and constrain
the effect of feedback in the early Universe.
galaxies, trace outflows, and constrain
the effect of feedback in the early Universe.
Articles for week 29 2025
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alice Nucara / Alessio Traficante / Ugo Lebreuilly / Ngo-Duy
Tung
- Sergio Molinari / Patrick Hennebelle / Leonardo Testi / Ralf S.
Klessen
- Veli-Matti Pelkonen / Adam Avison / Milena Benedettini / Alessandro
Coletta
- Fabrizio De Angelis / Davide Elia / Gary A. Fuller / Bethany M.
Jones
- Seyma Mercimek / Chiara Mininni / Stefania Pezzuto / Thushara
Pillai
- Veronica Roccatagliata / Eugenio Schisano / Juan D. Soler /
Paolo Suin
- Claudia Toci / Daniel Walker
Summary
The physical mechanisms that regulate the collapse of high-mass
parsec-scale clumps and allow them to form clusters of new stars
represent a crucial aspect of star formation. To investigate these
mechanisms, we developed the Rosetta Stone project: an end-to-end
(simulations-observations) framework that is based on the systematic
production of realistic synthetic observations of clump fragmentation
and their comparison with real data. In this work, we compare ALMA 1.3mm
continuum dust emission observations from the SQUALO survey with a new
set of 24 radiative magnetohydrodynamical simulations of high-mass clump
fragmentation, post-processed using the CASA software to mimic the
observing strategy of SQUALO. The simulations were initialized combining
typical values of clump mass (500,1000 solar masses) and radius (~0.4pc)
with two levels of turbulence (Mach number of 7,10) and three levels of
magnetization (mass-to-flux ratio of ~3,10,100). Following the clump
evolution over time with two random seeds projected along three
orthogonal directions, we produced a collection of 732 synthetic fields.
The synthetic observations of clump fragmentation at ~7000AU revealed
between 2 and 14 fragments per field. Among the initial conditions of
the simulations, magnetic fields have the largest impact on the fragment
multiplicity at these scales. In advanced stages of clump evolution, a
lower number of fragments is preferentially associated with magnetized
clumps. Fragments identified at ~7000AU correspond to individual or
multiple sink particles in ~75% of the cases, suggesting that not all
fragments are actively forming stars. Both sinks and fragments accrete
mass throughout the whole clump evolution, favoring a scenario in which
fragments are not isolated from the environment. Our study demonstrates
the importance of synthetic observations in interpreting results from
interferometric observations.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. Carvajal-Bohorquez / L. Ciesla / N.
Laporte / M. Boquien
- V. Buat / O. Ilbert / G. Aufort /
M. Shuntov
- C. Witten / P. A. Oesch / A. Covelo-Paz
Summary
JWST highlighted an excess of UV-bright galaxies at z>10, with a
derived UVLF that exhibits a softer evolution than expected. In this
work, we aim at characterizing the burstiness level of high-redshift
galaxy SFHs and its evolution. We implement a stochastic SFH module in
CIGALE using power spectrum densities, to estimate the burstiness level
of star formation in galaxies at 6<z<12. We find that SFHs with a
high level of stochasticity better reproduce the SEDs of z>6
galaxies, while smoother assumptions introduce biases when applied to
galaxies with bursty star-formation activity. The assumed stochasticity
level of the SFH also affects the constraints on galaxies’ physical
properties, including the main sequence. Successively assuming different
levels of burstiness, we determined the best-suited SFH for each
6<z<12 galaxy in the JADES sample from a Bayes Factor analysis.
Galaxies are classified according to their level of burstiness, and the
corresponding physical properties are associated to them. For massive
galaxies (log Mstar/Msun> 8.8), the fraction of bursty galaxies
increases from 0.42+/-0.08 to 0.76+/-0.20 from z=6 to 12, respectively.
At all redshifts, only <20% of low-mass galaxies are classified as
bursty, due to their faintness resulting in low S/N. For bursty
galaxies, the log10(SFR10/SFR100) ratio, another indicator of bursty
star formation, does not evolve with redshift, but the fraction of
galaxies with high log10(SFR10/SFR100) slightly increases from
0.25+/-0.06 to 0.37+/-0.11 between z=6 and z=9. We include additional
constraints from observations on sigmaUV and SFE, finding a maximum of
0.72+/-0.02 mag and 0.06+/-0.01, for sigmaUV and SFE, respectively. This
confirms that neither alone is responsible for the weak evolution of the
UVLF at z>10. Our results add further evidence that a combination
with other mechanisms is likely responsible for the high-z UVLF.
The
Pedersen and Hall Conductances in the Jovian Polar Regions: New Maps
based on a Broadband Electron Energy Distribution
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- G. Sicorello / D. Grodent / B. Bonfond / J.-C. Gérard
- B. Benmahi / A. Salveter / A. Moirano / L. A.
Head
- J. Vinesse / T. Greathouse / G. R. Gladstone / M. Barthélémy
Summary
The ionospheric Pedersen and Hall conductances play an important role
in understanding the exchanges of angular momentum, energy and matter
between the magnetosphere and the ionosphere/thermosphere at Jupiter,
modifying the composition and temperature of the planet. In the high
latitude regions, these conductances are enhanced by the auroral
electron precipitation. The effect of a broadband precipitating electron
energy distribution, similar to the observed electron distributions
through particle measurements, on the conductance values is
investigated. The new values are compared to the ones obtained from
previous studies, notably when considering a mono-energetic
distribution. The broadband precipitating electron energy distribution
is modeled by a kappa distribution, which is used as an input in an
electron transport model that computes the density vertical profiles of
ionospheric ions. The vertical profiles of the Pedersen and Hall
conductivities are then evaluated assuming that the conductivities are
mostly governed by the densities of H3+ and CH5+. Finally, the Pedersen
and Hall conductances are computed by integrating the corresponding
conductivities over altitude. The Pedersen and Hall conductances are
globally higher when considering a broadband electron energy
distribution rather than a mono-energetic distribution. In addition, the
use of the direct outputs of an electron transport model rather than the
analytical expression presented in Hiraki and Tao (2008) as well as a
change in the electron collision cross-sections also have significant
impacts on the conductance values. Comparison between our results and
the ones deduced from the corotation enforcement theory suggests that
either a physical mechanism limits the field-aligned currents or the
auroral electrons precipitating in the atmosphere are also accelerated
by processes not associated with the field-aligned currents.
Very
bright, very blue, and very red: JWST CAPERS analysis of highly luminous
galaxies with extreme UV slopes at 
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Callum T. Donnan / Mark Dickinson / Anthony J. Taylor / Pablo
Arrabal Haro
- Steven L. Finkelstein / Thomas M. Stanton / Intae Jung / Casey
Papovich
- Hollis B. Akins / Anton M. Koekemoer / Derek J. McLeod / Lorenzo
Napolitano
- Ricardo O. Amorín / Ryan Begley / Denis Burgarella
/ Adam C. Carnall
- Caitlin M. Casey / Antonello Calabrò / Fergus Cullen / James S.
Dunlop
- Richard S. Ellis / Vital Fernández / Mauro Giavalisco / Michaela
Hirschmann
- Weida Hu / Garth Illingworth / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Dale D.
Kocevski
- Vasily Kokorev / Ho-Hin Leung / Ray A. Lucas / Alexa M. Morales
- Ross McLure / Laura Pentericci / Pablo G. Pérez-González / Rachel S.
Somerville
- Struan Stevenson / Jonathan R. Trump / L. Y. Aaron Yung / Jorge A.
Zavala
Summary
We present JWST/NIRSpec PRISM observations of three luminous ( ) galaxies at
) galaxies at  observed with the
CAPERS Cycle 3 program. These galaxies exhibit extreme UV slopes
compared to typical galaxies at
observed with the
CAPERS Cycle 3 program. These galaxies exhibit extreme UV slopes
compared to typical galaxies at  . Of the three sources,
two of them are a close pair (0.22 - arcsec) of blue galaxies at
. Of the three sources,
two of them are a close pair (0.22 - arcsec) of blue galaxies at  and
and
 with UV slopes of
with UV slopes of  and
and
 respectively, selected from PRIMER COSMOS NIRCam imaging. We perform
spectrophotometric modeling of the galaxies which suggests extremely
young stellar ages and a lack of dust attenuation. For the bluest
galaxy, its UV slope also suggests significant Lyman continuum escape.
In contrast, the third source (selected from CEERS NIRCam imaging) at
respectively, selected from PRIMER COSMOS NIRCam imaging. We perform
spectrophotometric modeling of the galaxies which suggests extremely
young stellar ages and a lack of dust attenuation. For the bluest
galaxy, its UV slope also suggests significant Lyman continuum escape.
In contrast, the third source (selected from CEERS NIRCam imaging) at
 exhibits a red UV slope with
exhibits a red UV slope with  . We
rule out the possibility of a strong nebular continuum due to the lack
of a Balmer jump and find no evidence to support the presence of active
galactic nucleus continuum due to a lack of strong UV emission lines and
no broad component to H
. We
rule out the possibility of a strong nebular continuum due to the lack
of a Balmer jump and find no evidence to support the presence of active
galactic nucleus continuum due to a lack of strong UV emission lines and
no broad component to H or H
or H . Instead, it is most likely that the
red UV slope is due to dust-reddening (
. Instead, it is most likely that the
red UV slope is due to dust-reddening ( ) implying a significant level of dust-obscured
star-formation only
) implying a significant level of dust-obscured
star-formation only  after the Big Bang. Under standard assumptions
for dust attenuation, EGS-25297 would be the most intrinsically
UV-luminous galaxy (
after the Big Bang. Under standard assumptions
for dust attenuation, EGS-25297 would be the most intrinsically
UV-luminous galaxy ( ) yet spectroscopically confirmed at
) yet spectroscopically confirmed at  . This work
highlights that luminous galaxies at
. This work
highlights that luminous galaxies at  have a
diversity of dust properties and that spectroscopy of these galaxies is
essential to fully understand star-formation at
have a
diversity of dust properties and that spectroscopy of these galaxies is
essential to fully understand star-formation at  .
.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Prathamesh Tamhane / William Waldron / Ming Sun / Silvia
Martocchia
- Claudia Maraston / Alessandro Boselli / William
Forman / Massimo Gaspari
- Juhi Tiwari / Megan Donahue / G. Mark Voit / Tim Edge
- Grant Tremblay / Daniel Thomas
Summary
We analyzed the deepest Hubble Space Telescope (HST) F275W
ultraviolet (UV) imaging of M87 to obtain the most robust constraints on
its star formation rate (SFR) and star formation history (SFH). After
removing the galaxy continuum and globular clusters, we detected an
excess of UV point sources near the center. By comparing their colors to
young stellar source (YSS) colors generated by stochastically simulated
star formation (SF) for various SFRs and SFHs, we ruled out their origin
as a UV-upturn population and identified them as YSS. We found an
extremely low SFR of  M
M yr
yr in M87, with evidence
of a weak starburst $$125 Myr ago that formed
in M87, with evidence
of a weak starburst $$125 Myr ago that formed  M
M of stars. Unlike
other cool-core clusters where SF is stronger and directly linked to
cooling gas, we found no spatial correlation between YSS and H
of stars. Unlike
other cool-core clusters where SF is stronger and directly linked to
cooling gas, we found no spatial correlation between YSS and H filaments. Comparing SF activity with
M87’s AGN outburst history suggests that recent AGN feedback events
($
filaments. Comparing SF activity with
M87’s AGN outburst history suggests that recent AGN feedback events
($ α$ filaments with similar lengths and widths,
though they are obscured by dust near the center. These filaments are
likely powered by metal-line emission from collisional ionization,
suggesting ongoing low-level precipitation of the intracluster medium.
Our results indicate that AGN feedback has quenched SF significantly in
M87 for at least 200 Myr, even though some precipitation persists.
Additionally, we identified a hotspot created by the counterjet, with
the spectral index also constrained.
α$ filaments with similar lengths and widths,
though they are obscured by dust near the center. These filaments are
likely powered by metal-line emission from collisional ionization,
suggesting ongoing low-level precipitation of the intracluster medium.
Our results indicate that AGN feedback has quenched SF significantly in
M87 for at least 200 Myr, even though some precipitation persists.
Additionally, we identified a hotspot created by the counterjet, with
the spectral index also constrained.
CHEX-MATE:
Cluster Multi-Probes in Three Dimensions (CLUMP-3D) II. Combined Gas and
Dark Matter Analysis from X-ray, SZE, and WL
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Adriana Gavidia / Junhan Kim / Jack Sayers / Mauro Sereno
- Loris Chappuis / Dominique Eckert / Keiichi Umetsu / Herve
Bourdin
- Federico De Luca / Stefano Ettori / Massimo Gaspari /
Raphael Gavazzi
- Scott Kay / Lorenzo Lovisari / Pasquale Mazzotta / Gabriel
Pratt
- Elena Rasia / Mariachiara Rossetti
Summary
Under the standard model of hierarchical structure formation, the
overall geometry of galaxy clusters is better described by a triaxial
ellipse than a sphere. As a result, applying spherically-symmetric
models can result in significant biases. These biases can be mitigated
by fitting a triaxial model, requiring deep multiprobe data and a set of
physically motivated models to describe them. Here we present a
multiprobe triaxial analysis methodology based on the data available for
galaxy clusters in the Cluster Heritage project with XMM-Newton - Mass
Assembly and Thermodynamics at Endpoint of structure formation
(CHEX-MATE), which includes X-ray data from XMM-Newton, SZ data from
Planck and ACT, and WL data from Subaru. This work builds on our
previous development of a gas-only X-ray and SZ triaxial fitting
formalism in Paper I. We apply our approach to the CHEX-MATE cluster
PSZ2 G313.33+61.13 (Abell 1689) and find that it is elongated along the
line of sight relative to the plane of sky by a factor of  . As a
result, the WL mass obtained from our triaxial fit,
. As a
result, the WL mass obtained from our triaxial fit,  , is significantly lower than the value of
, is significantly lower than the value of  obtained from a spherically-symmetric fit that
otherwise employs the same methodology. Our triaxial fit finds a
concentration of
obtained from a spherically-symmetric fit that
otherwise employs the same methodology. Our triaxial fit finds a
concentration of  , consistent
with the spherically-symmetric value of
, consistent
with the spherically-symmetric value of  , which suggests that the unexpectedly high
concentration in Abell 1689 is not due to triaxiality and orientation.
We also measure the non-thermal pressure fraction at radii between
0.18-1.37 Mpc, finding a minimum of approximately 20 per cent at
intermediate radii increasing to near 30 per cent at both the smallest
and largest radii, and with a typical measurement precision of $$5 per
cent.
, which suggests that the unexpectedly high
concentration in Abell 1689 is not due to triaxiality and orientation.
We also measure the non-thermal pressure fraction at radii between
0.18-1.37 Mpc, finding a minimum of approximately 20 per cent at
intermediate radii increasing to near 30 per cent at both the smallest
and largest radii, and with a typical measurement precision of $$5 per
cent.
Euclid VI. NISP-P optical
ghosts
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / K. Paterson / M. Schirmer / K. Okumura
- B. Venemans / K. Jahnke / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / R. da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / P. Franzetti / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / R. Kohley
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / P. Casenove / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. A. Nucita / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / V. Scottez / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca / M.
Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / A. Cappi / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / R. Chary / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S.
Davini
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. M. N. Ferguson / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- A. Montoro / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur
- K. Naidoo / P. Natoli / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- F. Passalacqua / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P. Reimberg / I. Risso
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / M. Sereno
- A. Shulevski / L. C. Smith / J. Stadel / K. Tanidis
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
The Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) onboard Euclid
includes several optical elements in its path, which introduce artefacts
into the data from non-nominal light paths. To ensure uncontaminated
source photometry, these artefacts must be accurately accounted for.
This paper focuses on two specific optical features in NISP’s
photometric data (NISP-P): ghosts caused by the telescope’s dichroic
beamsplitter, and the bandpass filters within the NISP fore-optics. Both
ghost types exhibit a characteristic morphology and are offset from the
originating stars. The offsets are well modelled using 2D polynomials,
with only stars brighter than approximately 10 magnitudes in each filter
producing significant ghost contributions. The masking radii for these
ghosts depend on both the source-star brightness and the filter
wavelength, ranging from 20 to 40 pixels. We present the final relations
and models used in the near-infrared (NIR) data pipeline to mask these
ghosts for Euclid’s Quick Data Release (Q1).
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Andrew J. Levan / Antonio Martin-Carrillo / Tanmoy Laskar / Rob A.
J. Eyles-Ferris
- Albert Sneppen / Maria Edvige Ravasio / Jillian C. Rastinejad / Joe
S. Bright
- Francesco Carotenuto / Ashley A. Chrimes / Gregory Corcoran /
Benjamin P. Gompertz
- Peter G. Jonker / Gavin P. Lamb / Daniele B. Malesani / Andrea
Saccardi
- Javier Sanchez Sierras / Benjamin Schneider / Steve
Schulze / Nial R. Tanvir
- Susana D. Vergani / Darach Watson / Jie An / Franz E. Bauer
- Sergio Campana / Laura Cotter / Joyce N. D. van Dalen / Valerio
D’Elia
- Massimiliano de Pasquale / Antonio de Ugarte Postigo / Dimple /
Dieter H. Hartmann
- Jens Hjorth / Luca Izzo / Pall Jakobsson / Amit Kumar
- Andrea Melandri / Paul O’Brien / Silvia Piranomonte / Giovanna
Pugliese
- Jonathan Quirola-Vasquez / Rhaana Starling / Gianpiero Tagliaferri /
Dong Xu
- Makenzie E. Wortley
Summary
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are singular outbursts of high-energy
radiation with durations typically lasting from milliseconds to minutes
and, in extreme cases, a few hours. They are attributed to the
catastrophic outcomes of stellar-scale events and, as such, are not
expected to recur. Here, we present observations of an exceptional
GRB,250702BDE which triggered the {} gamma-ray burst monitor on three
occasions over several hours, and which was detected in soft X-rays by
the a day before the  -ray triggers (EP250702a). We present
the discovery of an extremely red infrared counterpart of the event with
the VLT, as well as radio observations from MeerKAT. Hubble Space
Telescope observations pinpoint the source to a non-nuclear location in
a host galaxy with complex morphology, implying GRB 250702BDE is an
extragalactic event. The multi-wavelength counterpart is well described
with standard afterglow models at a relatively low redshift
-ray triggers (EP250702a). We present
the discovery of an extremely red infrared counterpart of the event with
the VLT, as well as radio observations from MeerKAT. Hubble Space
Telescope observations pinpoint the source to a non-nuclear location in
a host galaxy with complex morphology, implying GRB 250702BDE is an
extragalactic event. The multi-wavelength counterpart is well described
with standard afterglow models at a relatively low redshift  , but the
prompt emission does not readily fit within the expectations for either
collapsar or merger-driven GRBs. Indeed, a striking feature of the
multiple prompt outbursts is that the third occurs at an integer
multiple of the interval between the first two. Although not conclusive,
this could be indicative of periodicity in the progenitor system. We
discuss several possible scenarios to explain the exceptional properties
of the burst, which suggest that either a very unusual collapsar or the
tidal disruption of a white dwarf by an intermediate-mass black hole are
plausible explanations for this unprecedented GRB.
, but the
prompt emission does not readily fit within the expectations for either
collapsar or merger-driven GRBs. Indeed, a striking feature of the
multiple prompt outbursts is that the third occurs at an integer
multiple of the interval between the first two. Although not conclusive,
this could be indicative of periodicity in the progenitor system. We
discuss several possible scenarios to explain the exceptional properties
of the burst, which suggest that either a very unusual collapsar or the
tidal disruption of a white dwarf by an intermediate-mass black hole are
plausible explanations for this unprecedented GRB.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / B. Kubik / R. Barbier / J. Clemens
- S. Ferriol / A. Secroun / G. Smadja / W. Gillard
- N. Fourmanoit / A. Ealet / S. Conseil / J.
Zoubian
- R. Kohley / J.-C. Salvignol / L. Conversi / T. Maciaszek
- H. Cho / W. Holmes / M. Seiffert / A. Waczynski
- S. Wachter / K. Jahnke / F. Grupp / C. Bonoli
- L. Corcione / S. Dusini / E. Medinaceli / R. Laureijs
- G. D. Racca / A. Bonnefoi / M.
Carle / A. Costille
- F. Ducret / J-L. Gimenez / D. Le
Mignant / L. Martin
- L. Caillat / L. Valenziano / N. Auricchio / P. Battaglia
- A. Derosa / R. Farinelli / F. Cogato / G. Morgante
- M. Trifoglio / V. Capobianco / S. Ligori / E. Borsato
- C. Sirignano / L. Stanco / S. Ventura / R. Toledo-Moreo
- L. Patrizii / Y. Copin / R. Foltz / E. Prieto
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / S. Andreon / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / F. Bernardeau
- A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / R. da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole / M. Douspis
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / F. Faustini / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett
- A. Grazian / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar
- H. Hoekstra / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / P. Liebing / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / P. W. Morris / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio
- E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- G. Sirri / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- P. Casenove / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L.
Gabarra
- W. G. Hartley / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / Y.
Charles
- R. Chary / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. M. N. Ferguson / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / A. Montoro / C. Moretti / C. Murray
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / G. Setnikar / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / J. R. Weaver / L. Zalesky
Summary
The paper describes the objectives, design and findings of the
pre-launch ground characterisation campaigns of the Euclid infrared
detectors. The pixel properties, including baseline, bad pixels, quantum
efficiency, inter pixel capacitance, quantum efficiency, dark current,
readout noise, conversion gain, response nonlinearity, and image
persistence were measured and characterised for each pixel. We describe
in detail the test flow definition that allows us to derive the pixel
properties and we present the data acquisition and data quality check
software implemented for this purpose. We also outline the measurement
protocols of all the pixel properties presented and we provide a
comprehensive overview of the performance of the Euclid infrared
detectors as derived after tuning the operating parameters of the
detectors. The main conclusion of this work is that the performance of
the infrared detectors Euclid meets the requirements. Pixels classified
as non-functioning accounted for less than 0.2% of all science pixels.
IPC coupling is minimal and crosstalk between adjacent pixels is less
than 1% between adjacent pixels. 95% of the pixels show a QE greater
than 80% across the entire spectral range of the Euclid mission. The
conversion gain is approximately 0.52 ADU/e-, with a variation less than
1% between channels of the same detector. The reset noise is
approximately equal to 23 ADU after reference pixels correction. The
readout noise of a single frame is approximately 13  while the signal estimator
noise is measured at 7
while the signal estimator
noise is measured at 7  in photometric mode and 9
in photometric mode and 9
 in spectroscopic
acquisition mode. The deviation from linear response at signal levels up
to 80 k
in spectroscopic
acquisition mode. The deviation from linear response at signal levels up
to 80 k is less than 5% for 95% of
the pixels. Median persistence amplitudes are less than 0.3% of the
signal, though persistence exhibits significant spatial variation and
differences between detectors.
is less than 5% for 95% of
the pixels. Median persistence amplitudes are less than 0.3% of the
signal, though persistence exhibits significant spatial variation and
differences between detectors.
Euclid
preparation. Simulating thousands of Euclid spectroscopic skies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / P. Monaco / G. Parimbelli / M. Y.
Elkhashab
- J. Salvalaggio / T. Castro / M. D. Lepinzan / E. Sarpa
- E. Sefusatti / L. Stanco / L. Tornatore / G. E. Addison
- S. Bruton / C. Carbone / F. J. Castander / J. Carretero
- S. de la Torre / P. Fosalba / G. Lavaux / S. Lee
- K. Markovic / K. S. McCarthy / F. Passalacqua / W. J. Percival
- I. Risso / C. Scarlata / P. Tallada-Crespí / M. Viel
- Y. Wang / B. Altieri / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- F. Bernardeau / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- V. F. Cardone / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / F. Dubath / F. Ducret / C. A. J.
Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Farrens / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / E. Munari / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / F. Rizzo
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / J. Steinwagner / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / G. Fabbian / L.
Gabarra
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / S. Avila / A. Balaguera-Antolinez / P.
Bergamini
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / F. Cogato / S.
Conseil
- S. Contarini / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- A. Finoguenov / F. Fontanot / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / S. Hemmati / C.
Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / S. Joudaki / J. J. E. Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / V. Le Brun / J. Le
Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / C. Mancini
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Miluzio / A. Montoro / C. Moretti / G. Morgante
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- K. Paterson / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith
- J. G. Sorce / K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / F. Vernizzi / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
We present two extensive sets of 3500+1000 simulations of dark matter
haloes on the past light cone, and two corresponding sets of simulated
(`mock’) galaxy catalogues that represent the Euclid spectroscopic
sample. The simulations were produced with the latest version of the
PINOCCHIO code, and provide the largest, public set of simulated skies.
Mock galaxy catalogues were obtained by populating haloes with galaxies
using an halo occupation distribution (HOD) model extracted from the
Flagship galaxy catalogue provided by Euclid Collaboration. The Geppetto
set of 3500 simulated skies was obtained by tiling a 1.2 Gpc/h box to
cover a light-cone whose sky footprint is a circle of 30 deg radius, for
an area of 2763 deg and a minimum halo mass of
and a minimum halo mass of  Msun/h. The relatively small box size makes this set unfit for measuring
very large scales. The EuclidLargeBox set consists of 1000 simulations
of 3.38 Gpc/h, with the same mass resolution and a footprint that covers
half of the sky, excluding the Milky Way zone of avoidance. From this we
produced a set of 1000 EuclidLargeMocks on the 30 deg radius footprint,
whose comoving volume is fully contained in the simulation box. We
validated the two sets of catalogues by analysing number densities,
power spectra, and 2-point correlation functions, showing that the
Flagship spectroscopic catalogue is consistent with being one of the
realisations of the simulated sets, although we noticed small deviations
limited to the quadrupole at k>0.2 h/Mpc. We show cosmological
parameter inference from these catalogues and demonstrate that using one
realisation of EuclidLargeMocks in place of the Flagship mock produces
the same posteriors, to within the expected shift given by sample
variance. These simulated skies will be used for the galaxy clustering
analysis of Euclid’s Data Release 1 (DR1).
Msun/h. The relatively small box size makes this set unfit for measuring
very large scales. The EuclidLargeBox set consists of 1000 simulations
of 3.38 Gpc/h, with the same mass resolution and a footprint that covers
half of the sky, excluding the Milky Way zone of avoidance. From this we
produced a set of 1000 EuclidLargeMocks on the 30 deg radius footprint,
whose comoving volume is fully contained in the simulation box. We
validated the two sets of catalogues by analysing number densities,
power spectra, and 2-point correlation functions, showing that the
Flagship spectroscopic catalogue is consistent with being one of the
realisations of the simulated sets, although we noticed small deviations
limited to the quadrupole at k>0.2 h/Mpc. We show cosmological
parameter inference from these catalogues and demonstrate that using one
realisation of EuclidLargeMocks in place of the Flagship mock produces
the same posteriors, to within the expected shift given by sample
variance. These simulated skies will be used for the galaxy clustering
analysis of Euclid’s Data Release 1 (DR1).
Articles for week 28 2025
IXPE
Observations of the Blazar Mrk 501 in 2022: A Multiwavelength View
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- L. Lisalda / E. Gau / H. Krawczynski / F. Tavecchio
- I. Liodakis / A. Gokus / N. Rodriguez Cavero / M. Nowak
- M. Negro / R. Middei / M. Perri / S. Puccetti
- S. G. Jorstad / I. Agudo / A. P. Marscher / B. Agís-González
- A. V. Berdyugin / M. I. Bernardos / D. Blinov / G. Bonnoli
- G. A. Borman / I. G. Bourbah / C. Casadio / V. Casanova
- A. J. Castro-Tirado / E. Fernández-García / M. García-Comas / T. S.
Grishina
- P. Hakala / T. Hovatta / Y. D. Hu / C. Husillos
- J. Escudero / J. Jormanainen / F. José Aceituno / M. Kagitani
- S. Kiehlmann / E. Kontopodis / E. N. Kopatskaya / P. M. Kouch
- V. Kravtsov / A. Lähteenmäki / E. G. Larionova / E. Lindfors
- N. Mandarakas / A. Marchini / J. R. Masiero / D.
Mawet
- W. Max-Moerbeck / D. A. Morozova / I. Myserlis / K. Nilsson
- G. V. Panopoulou / T. J. Pearson / A. C. S. Readhead / R.
Reeves
- S. Romanopoulos / T. Sakanoi / Q. Salomé / S. S. Savchenko
- R. Skalidis / A. Sota / I. Syrjärinne / S. Tinyanont
- M. Tornikoski / Yu. V. Troitskaya / I. S. Troitskiy / A. A.
Vasilyev
- A. Vervelaki / A. V. Zhovtan / L. A. Antonelli / M. Bachetti
- L. Baldini / W. H. Baumgartner / R. Bellazzini / S. Bianchi
- S. D. Bongiorno / R. Bonino / A. Brez / N. Bucciantini
- F. Capitanio / S. Castellano / E. Cavazzuti / C. Chen
- S. Ciprini / E. Costa / A. De Rosa / E. Del Monte
- L. Di Gesu / N. Di Lalla / A. Di Marco / I. Donnarumma
- V. Doroshenko / M. Dovčiak / S. R. Ehlert / T. Enoto
- Y. Evangelista / S. Fabiani / R. Ferrazzoli / J. A. Garcia
- S. Gunji / M. Gurwell / K. Hayashida / J. Heyl
- W. Iwakiri / P. Kaaret / V. Karas / G. Keating
- F. Kislat / T. Kitaguchi / J. J. Kolodziejczak / F. La Monaca
- L. Latronico / S. Maldera / A. Manfreda / F. Marin
- A. Marinucci / H. L. Marshall / F. Massaro / G. Matt
- I. Mitsuishi / T. Mizuno / F. Muleri / C. Ng
- S. L. O’Dell / N. Omodei / C. Oppedisano / A. Papitto
- G. G. Pavlov / A. L. Peirson / M. Pesce-Rollins / P. Petrucci
- M. Pilia / A. Possenti / J. Poutanen / B. D. Ramsey
- J. Rankin / R. Rao / A. Ratheesh / O. J. Roberts
- R. W. Romani / C. Sgrò / P. Slane / P. Soffitta
- G. Spandre / D. A. Swartz / T. Tamagawa / R. Taverna
- Y. Tawara / A. F. Tennant / N. E. Thomas / F. Tombesi
- A. Trois / S. S. Tsygankov / R. Turolla / J. Vink
- M. C. Weisskopf / K. Wu / F. Xie / S. Zane
Summary
The blazar Markarian 501 (Mrk 501) was observed on three occasions
over a 4-month period between 2022 March and 2022 July with the Imaging
X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE). In this paper, we report for the
first time on the third IXPE observation, performed between 2022 July 9
and 12, during which IXPE detected a linear polarization degree of  per cent at a
polarization angle, measured east of north, of
per cent at a
polarization angle, measured east of north, of  within the 2-8 keV X-ray band. The X-ray
polarization angle and degree during this observation are consistent
with those obtained during the first two observations. The chromaticity
of the polarization across radio, optical, and X-ray bands is likewise
consistent with the result from the simultaneous campaigns during the
first two observations. Furthermore, we present two types of models to
explain the observed spectral energy distributions (SEDs) and
energy-resolved polarization: a synchrotron self-Compton model with an
anisotropic magnetic field probability distribution in the emitting
volume, as well as an energy-stratified shock model. Our results support
both the shock scenario as well as support that small levels of magnetic
field anisotropy can explain the observed polarization.
within the 2-8 keV X-ray band. The X-ray
polarization angle and degree during this observation are consistent
with those obtained during the first two observations. The chromaticity
of the polarization across radio, optical, and X-ray bands is likewise
consistent with the result from the simultaneous campaigns during the
first two observations. Furthermore, we present two types of models to
explain the observed spectral energy distributions (SEDs) and
energy-resolved polarization: a synchrotron self-Compton model with an
anisotropic magnetic field probability distribution in the emitting
volume, as well as an energy-stratified shock model. Our results support
both the shock scenario as well as support that small levels of magnetic
field anisotropy can explain the observed polarization.
A
comprehensive study on radial velocity signals using ESPRESSO: Pushing
precision to the 10 cm/s level
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- P. Figueira / J. P. Faria / A. M. Silva / A. Castro-González
- J. Gomes da Silva / S. G. Sousa / D. Bossini / M. R.
Zapatero-Osorio
- O. Balsalobre-Ruza / J. Lillo-Box / H. M. Tabernero / V.
Adibekyan
- R. Allart / S. Benatti / F. Bouchy / A. Cabral
- S. Cristiani / X. Dumusque / J. I. González-Hernández / N.
Hara
- G. Lo Curto / C. Lovis / A. Mehner / P. Molaro
- F. Pepe / N. C. Santos / D. Ségransan / D. Sosnowska
- R. Rebolo / A. Suárez Mascareño / A. Sozzetti / S. Udry
- B. Wehbe
Summary
We analyse ESPRESSO data for the stars HD10700, HD20794, HD102365,
and HD304636 acquired via its Guaranteed Time Observations (GTO)
programme. We characterise the stars’ radial velocity (RV) signals down
to a precision of 10 cm/s on timescales ranging from minutes to
planetary periods falling within the host’s habitable zone (HZ). We
study the RV signature of pulsation, granulation, and stellar activity,
inferring the potential presence of planets around these stars. Thus, we
outline the population of planets that while undetectable remain
compatible with the available data. A simple model of stellar pulsations
successfully reproduced the intra-night RV scatter of HD10700 down to a
few cm/s. For HD102365 and HD20794, an additional source of scatter at
the level of several 10 cm/s remains necessary to explain the data. A
kima analysis was used to evaluate the number of planets supported by
the nightly averaged time series of each of HD10700, HD102365, and
HD304636, under the assumption that a quasi-periodic Gaussian process
(GP) regression is able to model the activity signal. While a frequency
analysis of HD10700 RVs is able to identify a periodic signal at 20d,
when it is modelled along with the activity signal the signal is
formally non-significant. ESPRESSO data on their own do not provide
conclusive evidence for the existence of planets around these three
stars. ESPRESSO is shown to reach an on-sky RV precision of better than
10 cm/s on short timescales (<1h) and of 40 cm/s over 3.5 yr. A
subdivision of the datasets showcases a precision reaching 20-30 cm/s
over one year. These results impose stringent constraints on the impact
of granulation mechanisms on RV. In spite of no detections, our analysis
of HD10700 RVs demonstrates a sensitivity to planets with a mass of
1.7M for periods of
up to 100 d, and a mass of 2-5M
for periods of
up to 100 d, and a mass of 2-5M for the star’s
HZ. (abridged)
for the star’s
HZ. (abridged)
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Ugo Lebreuilly / Alessio Traficante / Alice Nucara / Ngo-Duy
Tung
- Patrick Hennebelle / Sergio Molinari / Ralf S. Klessen / Leonardo
Testi
- Veli-Matti Pelkonen / Milena Benedettini / Alessandro Coletta /
Davide Elia
- Chiara Mininni / Stefania Pezzuto / Juan D. Soler / Paolo
Suin
- Claudia Toci
Summary
Context. Star formation and, in particular, high-mass star formation
are key astrophysical processes that are far from being fully
understood. Unfortunately, progress in these fields is slow because
observations are hard to interpret as they cannot be directly compared
to numerical simulations. Synthetic observations are therefore necessary
to better constrain the models. Aims. With the Rosetta Stone project, we
aim to develop an end-to-end pipeline to compare star formation
simulations with observations as accurately as possible in order to
study the evolution from clumps scales to stars. Methods. Using the
adaptive mesh-refinement code RAMSES, we computed a first grid of model
of star-forming clumps to develop our pipeline and explore the impact of
the clump initial conditions on their evolution. The main purpose of
this set of simulations is to be converted into synthetic observations
to enable a direct comparison with real star-forming clumps observed
with Herschel and ALMA. Results. The Rosetta Stone simulations presented
here provide a catalog available for full post-processing and subsequent
comparison with observations (RS1). Among all the parameters explored
here, the strength of the magnetic field has the strongest influence on
the clump evolution (fragmentation, star formation, global collapse) at
both large and small scales. Numerical parameters such as the resolution
per Jeans length or the threshold for accretion onto sink particles
affects the formation of low-mass sinks. Finally, the widely used L/M
ratio is found to be a good indicator of the clump evolutionary state
regardless of its initial condition, but this could change when more
feedback processes (jets, HII regions) are included. Conclusions. We now
have a new suite of simulations of star-forming clumps that is available
for full post-processing and subsequent comparison with the
observations,
SLICE:
SPT-CL J0546-5345 – A prominent strong-lensing cluster at 
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Joseph F. V. Allingham / Adi Zitrin / Miriam Golubchik / Lukas J.
Furtak
- Matthew Bayliss / Catherine Cerny / Jose M. Diego / Alastair C.
Edge
- Raven Gassis / Michael D. Gladders / Mathilde Jauzac / David J.
Lagattuta
- Gavin Leroy / Marceau Limousin / Guillaume Mahler /
Ashish K. Meena
- Priyamvada Natarajan / Keren Sharon
Summary
Massive galaxy clusters act as prominent strong-lenses. Due to a
combination of observational biases, cluster evolution and lensing
efficiency, most of the known cluster lenses lie typically at  ,
with only a few prominent examples at higher redshifts. Here we report a
first strong-lensing analysis of the massive galaxy cluster SPT-CL
J0546-5345 at a redshift
,
with only a few prominent examples at higher redshifts. Here we report a
first strong-lensing analysis of the massive galaxy cluster SPT-CL
J0546-5345 at a redshift  . This cluster was
first detected through the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect, with a high
estimated mass for its redshift of
. This cluster was
first detected through the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect, with a high
estimated mass for its redshift of  . Using recent JWST/NIRCam and archival HST
imaging, we identify at least 10 secure and 6 candidate sets of multiply
imaged background galaxies, which we use to constrain the mass
distribution in the cluster. We derive effective Einstein radii of
. Using recent JWST/NIRCam and archival HST
imaging, we identify at least 10 secure and 6 candidate sets of multiply
imaged background galaxies, which we use to constrain the mass
distribution in the cluster. We derive effective Einstein radii of  for a
source at
for a
source at  , and
, and  for a
source at
for a
source at  . The total
projected mass within a
. The total
projected mass within a  kpc radius around the strong-lensing
region is
kpc radius around the strong-lensing
region is  . While our results rely on photometric redshifts
warranting spectroscopic follow-up, this central mass resembles that of
the Hubble Frontier Fields clusters - although SPT-CL J0546-5345 is
observed when the Universe was
. While our results rely on photometric redshifts
warranting spectroscopic follow-up, this central mass resembles that of
the Hubble Frontier Fields clusters - although SPT-CL J0546-5345 is
observed when the Universe was  Gyr younger.
Amongst the multiply-imaged sources, we identify a
hyperbolic-umbilic-like configuration, and, thanks to its point-like
morphology, a possible Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN). If confirmed
spectroscopically, it will add to just a handful of other quasars and
AGN known to be multiply lensed by galaxy clusters.
Gyr younger.
Amongst the multiply-imaged sources, we identify a
hyperbolic-umbilic-like configuration, and, thanks to its point-like
morphology, a possible Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN). If confirmed
spectroscopically, it will add to just a handful of other quasars and
AGN known to be multiply lensed by galaxy clusters.
A
portrait throughout perihelion of the NH -rich interstellar comet
2I/Borisov
-rich interstellar comet
2I/Borisov
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Sophie E. Deam / Michele T. Bannister / Cyrielle Opitom / Matthew M.
Knight
- Ryan Ridden-Harper / Darryl Z. Seligman / Alan Fitzsimmons / Aurélie
Guilbert-Lepoutre
- Emmanuel Jehin / Laurent Jorda / Michael Marsset /
Youssef Moulane
- Philippe Rousselot / Pierre Vernazza / Bin
Yang
Summary
The interstellar comet 2I/Borisov is the first interstellar object
where compositional characterisation was possible throughout its entire
perihelion passage. We report all 16 epochs of a comprehensive optical
observation campaign with ESO VLT’s integral field spectrograph MUSE,
spanning 126 days from 2019 November 14 to 2020 March 19. The spatial
dust emission of 2I/Borisov was predominantly smooth, with no seasonal
effect. A jet-like feature was consistently visible. The gas production
morphology of its coma was also smooth and similar for C , NH
, NH , and CN: symmetric around the
photocentre. The production rates of these species gently declined into
and beyond perihelion, until 2I’s outburst and splitting event in early
2020 March. C
, and CN: symmetric around the
photocentre. The production rates of these species gently declined into
and beyond perihelion, until 2I’s outburst and splitting event in early
2020 March. C , NH
, NH , and CN production rates all
increased, with NH
, and CN production rates all
increased, with NH being the most significant; the dust
emission also slightly reddened. 2I/Borisov is a carbon-depleted,
relatively NH
being the most significant; the dust
emission also slightly reddened. 2I/Borisov is a carbon-depleted,
relatively NH -rich comet when compared to those
comets yet measured in the Solar System.
-rich comet when compared to those
comets yet measured in the Solar System.
Spectral
analysis of two directly imaged benchmark L dwarf companions at the
stellar-substellar boundary
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- William Ceva / Elisabeth C. Matthews / Emily L. Rickman / Damien
Ségransan
- Arthur Vigan / Brendan P. Bowler / Thierry
Forveille / Kyle Franson
- Janis Hagelberg / Stéphane Udry
Summary
We used multiple epochs of high-contrast imaging spectrophotometric
observations to determine the atmospheric characteristics and thermal
evolution of two previously detected benchmark L dwarf companions, HD
112863 B and HD 206505 B. We analyzed IRDIS and IFS data from VLT/SPHERE
of each companion, both of which have dynamical masses near the
stellar-substellar boundary. We compared each companion with empirical
spectral standards, as well as constrained their physical properties
through atmospheric model fits. From these analyses, we estimate that HD
112863 B is spectral type  and that HD
206505 B is spectral type
and that HD
206505 B is spectral type  . Using the
BT-Settl atmospheric model grids, we find a bimodal solution for the
atmospheric model fit of HD 112863 B, such that
. Using the
BT-Settl atmospheric model grids, we find a bimodal solution for the
atmospheric model fit of HD 112863 B, such that  K or
K or  K
and
K
and  or
or  , while for HD 206505 B,
, while for HD 206505 B,  K and
K and  .
Comparing the bolometric luminosities of both companions with
evolutionary models imply that both companions are likely above the
hydrogen burning limit.
.
Comparing the bolometric luminosities of both companions with
evolutionary models imply that both companions are likely above the
hydrogen burning limit.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Callum Witten / Pascal A. Oesch / William McClymont / Romain A.
Meyer
- Yoshinobu Fudamoto / Debora Sijacki / Nicolas
Laporte / Jake S. Bennett
- Charlotte Simmonds / Emma Giovinazzo / A. Lola Danhaive /
Laure Ciesla
- Cristian Carvajal-Bohorquez / Maxime Trebitsch
Summary
Protoclusters represent the most extreme environments in the very
early Universe. They form from large-scale dark matter overdensities,
harbouring an overabundance of galaxies fed by large gas reservoirs.
Their early and accelerated evolution results in a distinct difference
in the properties of galaxies resident in protoclusters versus the
field, which is known to be in place by  . We utilise
JWST NIRCam observations of the A2744-z7p9OD protocluster at
. We utilise
JWST NIRCam observations of the A2744-z7p9OD protocluster at  to constrain the
properties of resident galaxies. We identify seven new protocluster
members, bringing the total number to 23 and the total stellar mass of
the protocluster to in excess of
to constrain the
properties of resident galaxies. We identify seven new protocluster
members, bringing the total number to 23 and the total stellar mass of
the protocluster to in excess of  . These galaxies are remarkably evolved just 650
Myr after the Big Bang, preferentially showing redder UV-slopes and
stronger Balmer breaks than is typical of field galaxies. We use the
PROSPECTOR spectral energy distribution fitting code to derive key
galaxy properties, finding distinct populations in the core versus the
outskirts of the protocluster. The core is largely composed of dusty,
massive galaxies which can be characterised as undergoing a synchronised
(mini)-quenched phase, while galaxies in the protocluster outskirts are
undergoing recent bursts of star formation. Finally, a strong
suppression of the continuum around the Ly
. These galaxies are remarkably evolved just 650
Myr after the Big Bang, preferentially showing redder UV-slopes and
stronger Balmer breaks than is typical of field galaxies. We use the
PROSPECTOR spectral energy distribution fitting code to derive key
galaxy properties, finding distinct populations in the core versus the
outskirts of the protocluster. The core is largely composed of dusty,
massive galaxies which can be characterised as undergoing a synchronised
(mini)-quenched phase, while galaxies in the protocluster outskirts are
undergoing recent bursts of star formation. Finally, a strong
suppression of the continuum around the Ly -break evidences extreme neutral
hydrogen column densities in many resident galaxies (
-break evidences extreme neutral
hydrogen column densities in many resident galaxies ( ).
The A2744-z7p9OD system is the most extreme, evolved overdensity yet
observed at
).
The A2744-z7p9OD system is the most extreme, evolved overdensity yet
observed at  , with higher stellar
masses, gas densities, and dust attenuation, revealing the intersection
of local environment and high-redshift galaxy formation at their
extremes.
, with higher stellar
masses, gas densities, and dust attenuation, revealing the intersection
of local environment and high-redshift galaxy formation at their
extremes.
Euclid:
Early Release Observations. A combined strong and weak lensing solution
for Abell 2390 beyond its virial radius
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. M. Diego / G. Congedo / R. Gavazzi / T.
Schrabback
- H. Atek / B. Jain / J. R. Weaver / Y. Kang
- W. G. Hartley / G. Mahler / N. Okabe / J. B. Golden-Marx
- M. Meneghetti / J. M. Palencia / M. Kluge / R. Laureijs
- T. Saifollahi / M. Schirmer / C. Stone / M. Jauzac
- D. Scott / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / G. P. Candini
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / C. J.
Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / J.-C. Cuillandre / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- P. Fosalba / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. J. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- J. J. Mohr / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- E. Munari / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella / C. Burigana
- L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Viel
Summary
Euclid is presently mapping the distribution of matter in the
Universe in detail via the weak lensing (WL) signature of billions of
distant galaxies. The WL signal is most prominent around galaxy
clusters, and can extend up to distances well beyond their virial
radius, thus constraining their total mass. Near the centre of clusters,
where contamination by member galaxies is an issue, the WL data can be
complemented with strong lensing (SL) data which can diminish the
uncertainty due to the mass-sheet degeneracy and provide high-resolution
information about the distribution of matter in the centre of clusters.
Here we present a joint SL and WL analysis of the Euclid Early Release
Observations of the cluster Abell 2390 at z=0.228. Thanks to Euclid’s
wide field of view of 0.5 deg$^$2, combined with its angular resolution
in the visible band of 0.”13 and sampling of 0.”1 per pixel, we
constrain the density profile in a wide range of radii, 30 kpc < r
< 2000 kpc, from the inner region near the brightest cluster galaxy
to beyond the virial radius of the cluster. We find consistency with
earlier X-ray results based on assumptions of hydrostatic equilibrium,
thus indirectly confirming the nearly relaxed state of this cluster. We
also find consistency with previous results based on weak lensing data
and ground-based observations of this cluster. From the combined SL+WL
profile, we derive the values of the viral mass  , and virial radius
, and virial radius  ), with
error bars representing one standard deviation. The profile is well
described by an NFW model with concentration c=6.5 and a small-scale
radius of 230 kpc in the 30,kpc
), with
error bars representing one standard deviation. The profile is well
described by an NFW model with concentration c=6.5 and a small-scale
radius of 230 kpc in the 30,kpc  2000,kpc
range that is best constrained by SL and WL data. Abell 2390 is the
first of many examples where Euclid data will play a crucial role in
providing masses for clusters.
2000,kpc
range that is best constrained by SL and WL data. Abell 2390 is the
first of many examples where Euclid data will play a crucial role in
providing masses for clusters.
Euclid:
Early Release Observations. Weak gravitational lensing analysis of Abell
2390
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- T. Schrabback / G. Congedo / R. Gavazzi / W. G.
Hartley
- H. Jansen / Y. Kang / F. Kleinebreil / H. Atek
- E. Bertin / J.-C. Cuillandre / J. M. Diego / S. Grandis
- H. Hoekstra / M. Kümmel / L. Linke / H. Miyatake
- N. Okabe / S. Paltani / M. Schefer / P. Simon
- F. Tarsitano / A. N. Taylor / J. R. Weaver / R. Bhatawdekar
- M. Montes / P. Rosati / S. Toft / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / L. Amendola / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- G. P. Candini / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M.
Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / H. Dole
- M. Douspis / F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Farrens
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan
- J. Hoar / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- R. Laureijs / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S.
Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. J. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- J. J. Mohr / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- C. Rosset / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella / C. Burigana / L. Gabarra
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / A. Pezzotta / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Viel / D. Scott
Summary
The Euclid space telescope of the European Space Agency (ESA) is
designed to provide sensitive and accurate measurements of weak
gravitational lensing distortions over wide areas on the sky. Here we
present a weak gravitational lensing analysis of early Euclid
observations obtained for the field around the massive galaxy cluster
Abell 2390 as part of the Euclid Early Release Observations programme.
We conduct galaxy shape measurements using three independent algorithms
(LensMC, KSB+, and SourceXtractor++). Incorporating multi-band
photometry from Euclid and Subaru/Suprime-Cam, we estimate photometric
redshifts to preferentially select background sources from tomographic
redshift bins, for which we calibrate the redshift distributions using
the self-organising map approach and data from the Cosmic Evolution
Survey (COSMOS). We quantify the residual cluster member contamination
and correct for it in bins of photometric redshift and magnitude using
their source density profiles, including corrections for source
obscuration and magnification. We reconstruct the cluster mass
distribution and jointly fit the tangential reduced shear profiles of
the different tomographic bins with spherical Navarro–Frenk–White
profile predictions to constrain the cluster mass, finding consistent
results for the three shape catalogues and good agreement with earlier
measurements. As an important validation test we compare these joint
constraints to mass measurements obtained individually for the different
tomographic bins, finding good consistency. More detailed constraints on
the cluster properties are presented in a companion paper that
additionally incorporates strong lensing measurements. Our analysis
provides a first demonstration of the outstanding capabilities of Euclid
for tomographic weak lensing measurements.
Finding Halos in the
Lyman- forest
forest
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Duarte Muñoz Santos / Matthew M. Pieri / Dylan Nelson /
Simon Weng
- Teng Hu / Manuel F. Ruiz-Herrera Bernal
Summary
It has been demonstrated that one can track down galaxies in
absorption ‘hidden’ in the Lyman- forest through the use of ‘strong,
blended Lyman-
forest through the use of ‘strong,
blended Lyman- ’ (or SBLA) absorption. Specifically a
series of publications studied SBLA absorption systems with Lyman-
’ (or SBLA) absorption. Specifically a
series of publications studied SBLA absorption systems with Lyman- flux transmission,
flux transmission,  on scales of 138 km s
on scales of 138 km s in the Sloan Digital
Sky Survey (SDSS). In order to better understand the connection between
halos and these SBLAs, we make use of several million synthetic
absorption spectra from the TNG50 cosmological simulation, at z=2 and
z=3. We explore spectra with SDSS-like resolution in order to understand
the nature of SBLAs as defined thus far, as well as with high resolution
(or ‘resolved’) spectra to generalise and optimise SBLAs as halo
finders. For the SDSS SBLAs, we find that up to 78% of these absorption
systems reside in hlaos, where the stronger the absorption and the lower
the redshift, the higher the probability. We also manage to recover a
mean halo mass of
in the Sloan Digital
Sky Survey (SDSS). In order to better understand the connection between
halos and these SBLAs, we make use of several million synthetic
absorption spectra from the TNG50 cosmological simulation, at z=2 and
z=3. We explore spectra with SDSS-like resolution in order to understand
the nature of SBLAs as defined thus far, as well as with high resolution
(or ‘resolved’) spectra to generalise and optimise SBLAs as halo
finders. For the SDSS SBLAs, we find that up to 78% of these absorption
systems reside in hlaos, where the stronger the absorption and the lower
the redshift, the higher the probability. We also manage to recover a
mean halo mass of  , in line with what is measured in observations.
For the resolved SBLAs, we expand on the previous definition and allow
the SBLA spectra size to vary between 54 km s
, in line with what is measured in observations.
For the resolved SBLAs, we expand on the previous definition and allow
the SBLA spectra size to vary between 54 km s and 483 km s
and 483 km s . We find that the
largest absorbers have the highest probability of finding halos. When
applying a hierarchical framework, where we allow the largest SBLAs to
consume the smaller ones, we find that the halo mass distributions for
each SBLA spectral size becomes narrower with respect to the
non-hierarchical case. We are also able to probe halo masses from
. We find that the
largest absorbers have the highest probability of finding halos. When
applying a hierarchical framework, where we allow the largest SBLAs to
consume the smaller ones, we find that the halo mass distributions for
each SBLA spectral size becomes narrower with respect to the
non-hierarchical case. We are also able to probe halo masses from  (for 100
km s
(for 100
km s SBLAs) to
SBLAs) to  (for 450
km s
(for 450
km s SBLAs). With these
results, we show that we are able to transform the Lyman-
SBLAs). With these
results, we show that we are able to transform the Lyman- forest into a powerful halo finding
machine for not only identifying CGM regions, but also estimating their
host halo masses.
forest into a powerful halo finding
machine for not only identifying CGM regions, but also estimating their
host halo masses.
Direct
imaging discovery of a young giant planet orbiting on Solar System
scales
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- T. Stolker / M. Samland / L. B. F. M. Waters / M. E. van den
Ancker
- W. O. Balmer / S. Lacour / M. L. Sitko / J. J. Wang
- M. Nowak / A.-L. Maire / J. Kammerer / G. P. P. L. Otten
- R. Abuter / A. Amorim / M. Benisty / J.-P. Berger
- H. Beust / S. Blunt / A. Boccaletti / M. Bonnefoy
- H. Bonnet / M. S. Bordoni / G. Bourdarot / W. Brandner
- F. Cantalloube / P. Caselli / B. Charnay / G. Chauvin
- A. Chavez / A. Chomez / E. Choquet / V.
Christiaens
- Y. Clénet / V. Coudé du Foresto / A. Cridland / R. Davies
- R. Dembet / J. Dexter / C. Dominik / A. Drescher
- G. Duvert / A. Eckart / F. Eisenhauer / N. M. Förster Schreiber
- P. Garcia / R. Garcia Lopez / T. Gardner / E. Gendron
- R. Genzel / S. Gillessen / J. H. Girard / S. Grant
- X. Haubois / G. Heißel / Th. Henning / S. Hinkley
- S. Hippler / M. Houllé / Z. Hubert / L. Jocou
- M. Keppler / P. Kervella / L. Kreidberg / N. T. Kurtovic
- A.-M. Lagrange / V. Lapeyrère / J.-B. Le Bouquin / D. Lutz
- F. Mang / G.-D. Marleau / A. Mérand / M. Min
- P. Mollière / J. D. Monnier / C. Mordasini / D. Mouillet
- E. Nasedkin / T. Ott / C. Paladini / T. Paumard
- K. Perraut / G. Perrin / O. Pfuhl / N. Pourré
- L. Pueyo / S. P. Quanz / D. C. Ribeiro / E. Rickman
- Z. Rustamkulov / J. Shangguan / T. Shimizu / D. Sing
- J. Stadler / O. Straub / C. Straubmeier / E. Sturm
- L. J. Tacconi / E. F. van Dishoeck / A. Vigan / F.
Vincent
- S. D. von Fellenberg / F. Widmann / T. O. Winterhalder / J.
Woillez
- S. Yazici
Summary
HD 135344 AB is a young visual binary system that is best known for
the protoplanetary disk around the secondary star. The circumstellar
environment of the A0-type primary star, on the other hand, is already
depleted. HD 135344 A is therefore an ideal target for the exploration
of recently formed giant planets because it is not obscured by dust. We
searched for and characterized substellar companions to HD 135344 A down
to separations of about 10 au. We observed HD 135344 A with VLT/SPHERE
in the  and
and  bands and obtained
bands and obtained  and
and  spectroscopy. In addition, we carried
out VLTI/GRAVITY observations for the further astrometric and
spectroscopic confirmation of a detected companion. We discovered a
close-in young giant planet, HD 135344 Ab, with a mass of about 10
spectroscopy. In addition, we carried
out VLTI/GRAVITY observations for the further astrometric and
spectroscopic confirmation of a detected companion. We discovered a
close-in young giant planet, HD 135344 Ab, with a mass of about 10  . The
multi-epoch astrometry confirms the bound nature based on common
parallax and common proper motion. This firmly rules out the scenario of
a non-stationary background star. The semi-major axis of the planetary
orbit is approximately 15-20 au, and the photometry is consistent with
that of a mid L-type object. The inferred atmospheric and bulk
parameters further confirm the young and planetary nature of the
companion. HD 135344 Ab is one of the youngest directly imaged planets
that has fully formed and orbits on Solar System scales. It is a
valuable target for studying the early evolution and atmosphere of a
giant planet that could have formed in the vicinity of the snowline.
. The
multi-epoch astrometry confirms the bound nature based on common
parallax and common proper motion. This firmly rules out the scenario of
a non-stationary background star. The semi-major axis of the planetary
orbit is approximately 15-20 au, and the photometry is consistent with
that of a mid L-type object. The inferred atmospheric and bulk
parameters further confirm the young and planetary nature of the
companion. HD 135344 Ab is one of the youngest directly imaged planets
that has fully formed and orbits on Solar System scales. It is a
valuable target for studying the early evolution and atmosphere of a
giant planet that could have formed in the vicinity of the snowline.
GW231123:
a Binary Black Hole Merger with Total Mass 190-265 
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley / C. Adamcewicz
- S. Adhicary / D. Adhikari / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari
- V. K. Adkins / S. Afroz / A. Agapito / D. Agarwal
- M. Agathos / N. Aggarwal / S. Aggarwal / O. D. Aguiar
- I.-L. Ahrend / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / W. Ali / S. Al-Kershi
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / W. Amar / O. Amarasinghe / A. Amato
- F. Amicucci / C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson
- W. G. Anderson / M. Andia / M. Ando / M. Andrés-Carcasona
- T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi / J. M. Antelis
- S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther / S. Appert
- S. K. Apple / K. Arai / C. Araujo Alvarez / A. Araya
- M. C. Araya / M. Arca Sedda / J. S. Areeda / N. Aritomi
- F. Armato / S. Armstrong / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti
- S. M. Aronson / K. G. Arun / G. Ashton / Y. Aso
- L. Asprea / M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo / S. M. Aston
- P. Astone / F. Attadio / F. Aubin / K. AultONeal
- G. Avallone / E. A. Avila / S. Babak / C. Badger
- S. Bae / S. Bagnasco / L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai
- T. Baka / A. M. Baker / K. A. Baker / T. Baker
- G. Baldi / N. Baldicchi / M. Ball / G. Ballardin
- S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri / B. Banerjee / D. Bankar
- T. M. Baptiste / P. Baral / M. Baratti / J. C. Barayoga
- B. C. Barish / D. Barker / N. Barman / P. Barneo
- F. Barone / B. Barr / L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia
- D. Barta / A. M. Bartoletti / M. A. Barton / I. Bartos
- A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri / A. Basti / M. Bawaj
- P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley / A. C. Baylor / P. A. Baynard
- M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale / F. Beirnaert / M. Bejger
- D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell / D. S. Bellie / L. Bellizzi
- W. Benoit / I. Bentara / J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala
- S. Bera / F. Bergamin / B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi
- M. Beroiz / C. P. L. Berry / D. Bersanetti / T. Bertheas
- A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser / D. Beveridge / G. Bevilacqua
- N. Bevins / R. Bhandare / R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee
- S. Bhattacharyya / S. Bhaumik / S. Bhagwat / V. Biancalana
- A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti
- S. Bini / C. Binu / S. Biot / O. Birnholtz
- S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht / M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard
- S. Blaber / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg / C. D. Blair
- D. G. Blair / N. Bode / N. Boettner / G. Boileau
- M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A. Bolliand / L.
D. Bonavena
- R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla / M. S. Bonilla
- A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / A. Borchers / S. Borhanian
- V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov / Y. Bothra
- A. Boudon / L. Bourg / M. Boyle / A. Bozzi
- C. Bradaschia / P. R. Brady / A. Branch / M. Branchesi
- I. Braun / T. Briant / A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann
- P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller / A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown
- D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti / S. Brunett / G. Bruno
- R. Bruntz / J. Bryant / Y. Bu / F. Bucci
- J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik / H. J. Bulten
- A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio / D. Buskulic
- C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies / R. Cabrita
- V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati / G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane
- A. Calafat / J. Calderón Bustillo / T. A. Callister / E.
Calloni
- S. R. Callos / M. Canepa / G. Caneva Santoro / K. C. Cannon
- H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa / E. Capote
- G. Capurri / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara
- J. B. Carlin / T. K. Carlson / M. F. Carney / M. Carpinelli
- G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter / G. Carullo / A. Casallas-Lagos
- J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y. Castro-Lucas / S.
Caudill
- M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / A. Ceja / G. Cella
- P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / N. Chabbra / W. Chaibi
- A. Chakraborty / P. Chakraborty / S. Chakraborty / S. Chalathadka
Subrahmanya
- J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / K. Chandra / K. Chang
- S. Chao / P. Charlton / E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee
- Debarati Chatterjee / Deep Chatterjee / M. Chaturvedi / S.
Chaty
- K. Chatziioannou / A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen / D. Chen
- H. Chen / H. Y. Chen / S. Chen / Yanbei Chen
- Yitian Chen / H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung
- S. Y. Cheung / F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini / A. Chiba
- A. Chincarini / M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo / C. Chou
- S. Choudhary / N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua / G. Ciani
- P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / B. Cirok
- F. Clara / J. A. Clark / T. A. Clarke / P. Clearwater
- S. Clesse / F. Cleva / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo
- P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace / E. Colangeli / M. Colleoni
- C. G. Collette / J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo
- C. M. Compton / G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt
- I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / I. Coronado
- A. Corsi / R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin / A. Couineaux
- P. Couvares / D. M. Coward / R. Coyne / A. Cozzumbo
- J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton / P. Cremonese / S. Crook
- R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen
- A. Cumming / E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / L. V. Da Conceição
- T. Dal Canton / S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya / B. D’Angelo
- S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann / K. E. Darroch
- L. P. Dartez / R. Das / A. Dasgupta / V. Dattilo
- A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave / A. Davenport
- M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis / L. Davis
- M. C. Davis / P. Davis / E. J. Daw / M. Dax
- J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis
- F. De Lillo / S. Della Torre / W. Del Pozzo / A. Demagny
- F. De Marco / G. Demasi / F. De Matteis / N. Demos
- T. Dent / A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri
- R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi / M. Desai / R. DeSalvo
- A. DeSimone / R. De Simone / A. Dhani / R. Diab
- M. C. Dí / M. Di Cesare / G. Dideron / T. Dietrich
- L. Di Fiore / C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo
- D. Diksha / J. Ding / S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma
- D. Di Piero / F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev
- J. P. Docherty / Z. Doctor / N. Doerksen / E. Dohmen
- A. Doke / A. Domiciano De Souza / L. D’Onofrio / F. Donovan
- K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney / S. Doravari / O. Dorosh
- W. J. D. Doyle / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers / L. Dunn
- U. Dupletsa / P.-A. Duverne / D. D’Urso / P. Dutta Roy
- H. Duval / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa / M. Ebersold
- T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / A. Effler / J. Eichholz
- H. Einsle / M. Eisenmann / M. Emma / K. Endo
- R. Enficiaud / L. Errico / R. Espinosa / M. Esposito
- R. C. Essick / H. Estellés / T. Etzel / M. Evans
- T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing / J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi
- V. Fafone / S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr
- W. M. Farr / G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays
- M. Fazio / J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti
- E. Fenyvesi / J. Fernandes / T. Fernandes / D. Fernando
- S. Ferraiuolo / T. A. Ferreira / F. Fidecaro / P. Figura
- A. Fiori / I. Fiori / R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi
- V. Fiumara / R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming
- E. Floden / H. Fong / J. A. Font / F. Fontinele-Nunes
- C. Foo / B. Fornal / K. Franceschetti / N. Franchini
- F. Frappez / S. Frasca / F. Frasconi / J. P. Freed
- Z. Frei / A. Freise / O. Freitas / R. Frey
- W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel / V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé
- M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii / T. Fujimori / P. Fulda
- M. Fyffe / B. Gadre / J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage
- V. Galdi / R. Gamba / A. Gamboa / S. Gamoji
- D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido
- C. García-Quirós / J. W. Gardner / K. A. Gardner / S. Garg
- J. Gargiulo / X. Garrido / A. Garron / F. Garufi
- P. A. Garver / C. Gasbarra / B. Gateley / F. Gautier
- V. Gayathri / T. Gayer / G. Gemme / A. Gennai
- V. Gennari / J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding
- L. Gergely / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh / Shrobana Ghosh
- Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina
- D. R. Gibson / C. Gier / S. Gkaitatzis / J. Glanzer
- F. Glotin / J. Godfrey / R. V. Godley / P. Godwin
- A. S. Goettel / E. Goetz / J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez
- B. Goncharov / G. González / P. Goodarzi / S. Goode
- M. Gosselin / R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova
- A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados / M. Granata
- V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia / J. Graves
- C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco / A. C. Green
- L. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green / C. Greenberg
- A. M. Gretarsson / H. K. Griffin / D. Griffith / H. L. Griggs
- G. Grignani / C. Grimaud / H. Grote / S. Grunewald
- D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes
- H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / H. Guo / W. Guo
- Y. Guo / Anuradha Gupta / I. Gupta / N. C. Gupta
- S. K. Gupta / V. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs
- N. Gutierrez / N. Guttman / F. Guzman / D. Haba
- M. Haberland / S. Haino / E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton
- G. Hammond / M. Haney / J. Hanks / C. Hanna
- M. D. Hannam / A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen / J. Hanson
- S. Hanumasagar / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison / S. Harikumar
- K. Haris / I. Harley-Trochimczyk / T. Harmark / J. Harms
- G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry / J. Hart / B. Haskell
- C. J. Haster / K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama
- M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze / J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann
- F. Hellman / A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming / O.
Henderson-Sapir
- M. Hendry / I. S. Heng / M. H. Hennig / C. Henshaw
- M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt / J. Heynen / J. Heyns
- S. Higginbotham / S. Hild / S. Hill / Y. Himemoto
- N. Hirata / C. Hirose / D. Hofman / B. E. Hogan
- N. A. Holland / I. J. Hollows / D. E. Holz / L. Honet
- D. J. Horton-Bailey / J. Hough / S. Hourihane / N. T. Howard
- E. J. Howell / C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh / P. Hsi
- H.-F. Hsieh / H.-Y. Hsieh / C. Hsiung / S.-H. Hsu
- W.-F. Hsu / Q. Hu / H. Y. Huang / Y. Huang
- Y. T. Huang / A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey / V. Hui
- S. Husa / R. Huxford / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo
- M. Ianni / G. Iannone / J. Iascau / K. Ide
- R. Iden / A. Ierardi / S. Ikeda / H. Imafuku
- Y. Inoue / G. Iorio / P. Iosif / M. H. Iqbal
- J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa / M. Isi / K. S. Isleif
- Y. Itoh / M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer / C. Jacquet
- P.-E. Jacquet / T. Jacquot / S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav
- M. Jain / T. Jain / A. L. James / K. Jani
- N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski / R. Jaume
- W. Javed / A. Jennings / M. Jensen / W. Jia
- J. Jiang / H.-B. Jin / G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson
- N. K. Johnson-McDaniel / M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston / N.
Johny
- D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones / R. Jones / H. E. Jose
- P. Joshi / S. K. Joshi / G. Joubert / J. Ju
- L. Ju / K. Jung / J. Junker / V. Juste
- H. B. Kabagoz / T. Kajita / I. Kaku / V. Kalogera
- M. Kalomenopoulos / M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda / S. Kandhasamy
- G. Kang / N. C. Kannachel / J. B. Kanner / S. A. KantiMahanty
- S. J. Kapadia / D. P. Kapasi / M. Karthikeyan / M. Kasprzack
- H. Kato / T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis / W. Katzman
- R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto / D. Keitel
- L. J. Kemperman / J. Kennington / F. A. Kerkow / R. Kesharwani
- J. S. Key / R. Khadela / S. Khadka / S. S. Khadkikar
- F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan / T. Khanam / M. Khursheed
- N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo / C. Kim
- J. C. Kim / K. Kim / M. H. Kim / S. Kim
- Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball / K. Kimes / M. Kinnear
- J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee / E. J. Knox
- N. Knust / K. Kobayashi / S. M. Koehlenbeck / G. Koekoek
- K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama / S. Koley / P. Kolitsidou
- A. E. Koloniari / K. Komori / A. K. H. Kong / A. Kontos
- L. M. Koponen / M. Korobko / X. Kou / A. Koushik
- N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam / T. Koyama / D. B. Kozak
- S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu / S. Kroker
- A. Królak / K. Kruska / J. Kubisz / G. Kuehn
- S. Kulkarni / A. Kulur Ramamohan / Achal Kumar / Anil Kumar
- Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar / Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar
- J. Kume / K. Kuns / N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi
- S. Kuwahara / K. Kwak / K. Kwan / S. Kwon
- G. Lacaille / D. Laghi / A. H. Laity / E. Lalande
- M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati / M. Landry / B. B. Lane
- R. N. Lang / J. Lange / R. Langgin / B. Lantz
- I. La Rosa / J. Larsen / A. Lartaux-Vollard / P. D. Lasky
- J. Lawrence / M. Laxen / C. Lazarte / A. Lazzarini
- C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci / L. Leali / Y. K. Lecoeuche
- H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee / J. Lee / K. Lee
- R.-K. Lee / R. Lee / Sungho Lee / Sunjae Lee
- Y. Lee / I. N. Legred / J. Lehmann / L. Lehner
- M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître / M. Lenti / M. Leonardi
- M. Lequime / N. Leroy / M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre
- M. Lethuillier / Y. Levin / K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li
- K. L. Li / X. Li / Y. Li / Z. Li
- A. Lihos / E. T. Lin / F. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin
- Y.-C. Lin / C. Lindsay / S. D. Linker / A. Liu
- G. C. Liu / Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol
- R. K. L. Lo / J.-P. Locquet / S. C. G. Loggins / M. R. Loizou
- L. T. London / A. Longo / D. Lopez / M. Lopez Portilla
- M. Lorenzini / A. Lorenzo-Medina / V. Loriette / M. Lormand
- G. Losurdo / E. Lotti / T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough
- H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto / N. Low / N. Lu
- L. Lucchesi / H. Lück / D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren
- A. W. Lussier / R. Macas / M. MacInnis / D. M. Macleod
- I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet / K. Maeda / S. Maenaut
- S. S. Magare / R. M. Magee / E. Maggio / R. Maggiore
- M. Magnozzi / M. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi
- E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem / D. Malakar / J. A. Malaquias-Reis
- U. Mali / S. Maliakal / A. Malik / L. Mallick
- A.-K. Malz / N. Man / M. Mancarella / V. Mandic
- V. Mangano / B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell / M. Manske
- M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli / C. Marinelli / F. Marion
- A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros / S. Marsat
- F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin / B. B. Martinez
- D. A. Martinez / M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini
- J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx / L. Massaro
- A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid / S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich
- M. Matiushechkina / L. Maurin / N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell
- G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy / D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick
- L. McCuller / S. McEachin / C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee
- J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan / J. McIver / A. McLeod
- I. McMahon / T. McRae / R. McTeague / D. Meacher
- B. N. Meagher / R. Mechum / Q. Meijer / A. Melatos
- C. S. Menoni / F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni
- K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt
- M. Merzougui / C. Messick / B. Mestichelli / M. Meyer-Conde
- F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske / A. Miani / H. Miao
- C. Michel / Y. Michimura / H. Middleton / D. P. Mihaylov
- S. J. Miller / M. Millhouse / E. Milotti / V. Milotti
- Y. Minenkov / E. M. Minihan / Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola
- M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu / A. Mishra / C. Mishra
- T. Mishra / A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra
- V. P. Mitrofanov / K. Mitsuhashi / R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa
- S. Miyoki / A. Miyoko / G. Mo / L. Mobilia
- S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite / M. Molina-Ruiz / M. Mondin
- M. Montani / C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More
- S. More / C. Moreno / E. A. Moreno / G. Moreno
- A. Moreso Serra / S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki / G. Morras
- A. Moscatello / M. Mould / B. Mours / C. M. Mow-Lowry
- L. Muccillo / F. Muciaccia / D. Mukherjee / Samanwaya Mukherjee
- Soma Mukherjee / Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip Mukherjee / N.
Mukund
- A. Mullavey / H. Mullock / J. Mundi / C. L. Mungioli
- M. Murakoshi / P. G. Murray / D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji
- A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. Nakagaki / K. Nakamura
- H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nanadoumgar-Lacroze / D. Nandi
- V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa
- H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak / L. Negri
- A. Nela / C. Nelle / A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson
- M. Nery / A. Neunzert / S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh
- S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa
- S. Nissanke / W. Niu / F. Nocera / J. Noller
- M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak / R. Nowicki
- J. F. Nu no Siles / L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling
- J. O’Dell / E. Oelker / M. Oertel / G. Oganesyan
- T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / F. Ohme / R. Oliveri
- R. Omer / B. O’Neal / M. Onishi / K. Oohara
- B. O’Reilly / M. Orselli / R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea
- S. Oshino / C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway
- A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / R. Ozaki
- A. E. Pace / R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai
- L. Paiella / A. Pal / S. Pal / M. A. Palaia
- M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma / C. Palomba / P. Palud
- H. Pan / J. Pan / K. C. Pan / P. K. Panda
- Shiksha Pandey / Swadha Pandey / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale
- K. A. Pannone / B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / M. Panzeri
- F. Paoletti / A. Paolone / A. Papadopoulos / E. E. Papalexakis
- L. Papalini / G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis / A. Parisi
- B.-J. Park / J. Park / W. Parker / G. Pascale
- D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti / L. Passenger
- D. Passuello / O. Patane / A. V. Patel / D. Pathak
- A. Patra / B. Patricelli / B. G. Patterson / K. Paul
- S. Paul / E. Payne / T. Pearce / M. Pedraza
- A. Pele / F. E. Pe na Arellano / X. Peng / Y. Peng
- S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego / Z. Pereira
- C. Périgois / G. Perna / A. Perreca / J. Perret
- S. Perriès / J. W. Perry / D. Pesios / S. Peters
- S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham
- K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli
- L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot / M. Piendibene
- F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra / V. Pierro
- M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo / L. Pinard
- I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello
- M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi / M. L. Planas
- W. Plastino / C. Plunkett / R. Poggiani / E. Polini
- J. Pomper / L. Pompili / J. Poon / E. Porcelli
- E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky / R. Poulton / J. Powell
- G. S. Prabhu / M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan / T. Pradier
- A. K. Prajapati / K. Prasai / R. Prasanna / P. Prasia
- G. Pratten / G. Principe / G. A. Prodi / P. Prosperi
- P. Prosposito / A. C. Providence / A. Puecher / J. Pullin
- P. Puppo / M. Pürrer / H. Qi / J. Qin
- G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke / P. J. Quinonez / N. Qutob
- R. Rading / I. Rainho / S. Raja / C. Rajan
- B. Rajbhandari / K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / M. Ramos
Arevalo
- A. Ramos-Buades / S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani
- B. Ratto / A. Ravichandran / A. Ray / V. Raymond
- M. Razzano / J. Read / T. Regimbau / S. Reid
- C. Reissel / D. H. Reitze / A. I. Renzini / B. Revenu
- A. Revilla Pe na / R. Reyes / L. Ricca / F. Ricci
- M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. Rice / J. W. Richardson
- M. L. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley
- S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet
- M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins
- A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw
- J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa
- T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross
- M. Rossello-Sastre / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy
- D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales
- K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / P. Saffarieh
- S. Safi-Harb / M. R. Sah / S. Saha / T. Sainrat
- S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / Y. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou
- S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi
- M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. U. Salunkhe
- S. Salvador / A. Salvarese / A. Samajdar / A. Sanchez
- E. J. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez / N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders
- E. M. Sänger / F. Santoliquido / F. Sarandrea / T. R. Saravanan
- N. Sarin / P. Sarkar / A. Sasli / P. Sassi
- B. Sassolas / B. S. Sathyaprakash / R. Sato / S. Sato
- Yukino Sato / Yu Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage
- T. Sawada / H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco
- D. Schaetzl / M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski
- P. Schmidt / S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind
- R. M. S. Schofield / K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F.
Schutz
- E. Schwartz / M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott
- R. M. Sedas / T. C. Seetharamu / M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y.
Sekiguchi
- D. Sellers / N. Sembo / A. S. Sengupta / E. G. Seo
- J. W. Seo / V. Sequino / M. Serra / A. Sevrin
- T. Shaffer / U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao
- A. K. Sharma / Preeti Sharma / Prianka Sharma / Ritwik Sharma
- S. Sharma Chaudhary / P. Shawhan / N. S. Shcheblanov / E.
Sheridan
- Z.-H. Shi / M. Shikauchi / R. Shimomura / H. Shinkai
- S. Shirke / D. H. Shoemaker / D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short
- S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider / H. Siegel / D. Sigg
- L. Silenzi / L. Silvestri / M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer
- Amitesh Singh / Anika Singh / D. Singh / N. Singh
- S. Singh / A. M. Sintes / V. Sipala / V. Skliris
- B. J. J. Slagmolen / D. A. Slater / T. J. Slaven-Blair / J.
Smetana
- J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith / W. J. Smith
- S. Soares de Albuquerque Filho / M. Soares-Santos / K. Somiya / I.
Song
- S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino / H. Sotani
- F. Spada / V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / P. Spinicelli
- A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski / C. J. Stark / D. A. Steer
- N. Steinle / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N. Stergioulas
- P. Stevens / S. P. Stevenson / M. StPierre / M. D. Strong
- A. Strunk / A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek / S. Sudhagar
- Y. Sudo / N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan
- J. Sun / L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh
- B. J. Sutton / P. J. Sutton / K. Suzuki / M. Suzuki
- S. Swain / B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx / M. J. Szczepańczyk
- P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi / K. Takada
- H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi / A. Takamori / S. Takano
- H. Takeda / K. Takeshita / I. Takimoto Schmiegelow / M.
Takou-Ayaoh
- C. Talbot / M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe
- K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka / S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner
- W. Tanner / L. Tao / R. D. Tapia / E. N. Tapia San Martín
- C. Taranto / A. Taruya / J. D. Tasson / J. G. Tau
- D. Tellez / R. Tenorio / H. Themann / A. Theodoropoulos
- M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M. Thomas / M. Thomas / P.
Thomas
- J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu / K. A. Thorne / E. Thrane
- J. Tissino / A. Tiwari / Pawan Tiwari / Praveer Tiwari
- S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd / M. Toffano
- A. M. Toivonen / K. Toland / A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru
- V. Tommasini / T. Tomura / H. Tong / C. Tong-Yu
- A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie / I. Tosta e Melo / E.
Tournefier
- M. Trad Nery / K. Tran / A. Trapananti / R. Travaglini
- F. Travasso / G. Traylor / M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali
- A. Tripathee / G. Troian / A. Trovato / L. Trozzo
- R. J. Trudeau / T. Tsang / S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada
- K. Turbang / M. Turconi / C. Turski / H. Ubach
- N. Uchikata / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall / T. Uehara
- K. Ueno / V. Undheim / L. E. Uronen / T. Ushiba
- M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya / G. Vajente
- A. Vajpeyi / J. Valencia / M. Valentini / S. A. Vallejo-Pe na
- S. Vallero / V. Valsan / M. van Dael / E. Van den Bossche
- J. F. J. van den Brand / C. Van Den Broeck / M. van der Sluys / A.
Van de Walle
- J. van Dongen / K. Vandra / M. VanDyke / H. van Haevermaet
- J. V. van Heijningen / P. Van Hove / J. Vanier / M. VanKeuren
- J. Vanosky / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas
- V. Varma / A. N. Vazquez / A. Vecchio / G. Vedovato
- J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis / R. C. Venterea
- P. Verdier / M. Vereecken / D. Verkindt / B. Verma
- Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano / A. Veutro
- A. Viceré / S. Vidyant / A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar
- A. Vilkha / N. Villanueva Espinosa / V. Villa-Ortega / E. T.
Vincent
- J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / S. Vitale / H. Vocca
- D. Voigt / E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel / W. E.
Vossius
- L. Vujeva / S. P. Vyatchanin / J. Wack / L. E. Wade
- M. Wade / K. J. Wagner / L. Wallace / E. J. Wang
- H. Wang / J. Z. Wang / W. H. Wang / Y. F. Wang
- G. Waratkar / J. Warner / M. Was / T. Washimi
- N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai / B. Weaver / S. A. Webster
- N. L. Weickhardt / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein / R. Weiss
- L. Wen / K. Wette / J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting
- C. Whittle / E. G. Wickens / D. Wilken / A. T. Wilkin
- B. M. Williams / D. Williams / M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams
- J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils / L. Wilson
- C. W. Winborn / J. Winterflood / C. C. Wipf / G. Woan
- J. Woehler / N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong / H. W. Y. Wong
- I. C. F. Wong / K. Wong / T. Wouters / J. L. Wright
- B. Wu / C. Wu / D. S. Wu / H. Wu
- K. Wu / Q. Wu / Y. Wu / Z. Wu
- E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu / Y. Xu
- N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto / T. S. Yamamoto
- T. Yamamoto / R. Yamazaki / T. Yan / K. Z. Yang
- Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough / J. Yebana / S.-W. Yeh
- A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin / J. Yokoyama / T. Yokozawa
- S. Yuan / H. Yuzurihara / M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan
- T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad
- M. Zevin / L. Zhang / N. Zhang / R. Zhang
- T. Zhang / C. Zhao / Yue Zhao / Yuhang Zhao
- Z.-C. Zhao / Y. Zheng / H. Zhong / H. Zhou
- H. O. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman / L. Zimmermann
- M. E. Zucker / J. Zweizig
Summary
On 2023 November 23 the two LIGO observatories both detected
GW231123, a gravitational-wave signal consistent with the merger of two
black holes with masses  and
and  (90% credible intervals), at luminosity distance
0.7-4.1 Gpc and redshift of
(90% credible intervals), at luminosity distance
0.7-4.1 Gpc and redshift of  , and a network signal-to-noise ratio of $$20.7.
Both black holes exhibit high spins,
, and a network signal-to-noise ratio of $$20.7.
Both black holes exhibit high spins,  and
and  respectively. A massive black hole remnant is
supported by an independent ringdown analysis. Some properties of
GW231123 are subject to large systematic uncertainties, as indicated by
differences in inferred parameters between signal models. The primary
black hole lies within or above the theorized mass gap where black holes
between 60-130
respectively. A massive black hole remnant is
supported by an independent ringdown analysis. Some properties of
GW231123 are subject to large systematic uncertainties, as indicated by
differences in inferred parameters between signal models. The primary
black hole lies within or above the theorized mass gap where black holes
between 60-130  should be rare due
to pair instability mechanisms, while the secondary spans the gap. The
observation of GW231123 therefore suggests the formation of black holes
from channels beyond standard stellar collapse, and that
intermediate-mass black holes of mass $$200
should be rare due
to pair instability mechanisms, while the secondary spans the gap. The
observation of GW231123 therefore suggests the formation of black holes
from channels beyond standard stellar collapse, and that
intermediate-mass black holes of mass $$200  form through
gravitational-wave driven mergers.
form through
gravitational-wave driven mergers.
Articles for week 27 2025
Detecting
and characterising the magnetic field of exoplanets
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Strugarek / S. V. Berdyugina / V. Bourrier / J. A. Caballero
- J. J. Chebly / R. Fares / A. Fludra / L. Fossati
- A. García Muñoz / L. Gkouvelis / C. Gourvès / J. L. Grenfell
- R. D. Kavanagh / K. G. Kislyakova / L. Lamy / A. F.
Lanza
- C. Moutou / D. Nandy / C. Neiner / A. Oklopčić
- A. Paul / V. Réville / D. Rodgers-Lee / E. L. Shkolnik
- J. D. Turner / A. A. Vidotto / F. Yang / P. Zarka
Summary
Magnetic fields play a crucial role in planetary evolution and
habitability. While the intrinsic magnetic fields of solar system
planets are relatively well understood, the magnetic properties of
exoplanets remain largely unconstrained, despite their potential
ubiquity. Detecting exoplanetary magnetic fields is essential to
advancing our understanding of planetary habitability beyond the solar
system. This paper focuses on two promising spectropolarimetric
techniques for detecting magnetic fields in hot exoplanets: direct
detection through polarization signatures in the He I 1083 nm triplet
and indirect detection via star-planet magnetic interactions manifesting
as stellar hot spots. The direct method is particularly suited to
close-in gas giants, leveraging the Hanle and Zeeman effects to detect
low-amplitude magnetic fields. The indirect method can apply to both
giant and low-mass planets by identifying magnetic connectivity-induced
features in the stellar atmosphere. Although the interpretation of
current detections remain tentative, upcoming high-resolution
spectropolarimetric capabilities in the UV and near-infrared,
particularly with future missions like HWO, promise to enable definitive
measurements of exoplanetary magnetic fields. These advancements will
open new avenues for probing the magnetic environments of exoplanets and
their implications for atmospheric retention and habitability.
Study
of the atmospheric effects of energetic particle precipitations on giant
planets with HWO
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J-Y. Chaufray / W. Dunn / L. N. Fletcher / L. Fossati
- M. Galand / L. Gkouvelis / C. M. Jackmann / L.
Lamy
- L. Roth
Summary
UV auroral emissions from giant planets are produced by
extra-atmospheric energetic particles interacting with an atmosphere.
They have been observed on Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus and should be
present on Neptune. Even if the mechanisms are similar, each planet is
unique due to its specific source of magnetospheric plasma and the
structure and dynamics of its magnetosphere. How these precipitations
modify atmospheric heating, dynamics and chemical balance at local and
global atmospheric scale is still poorly known, especially on Uranus and
Neptune, and critical to understanding the global
atmosphere-magnetosphere system of giant planets and exoplanets. In this
manucript we present how future observations by instruments, aboard
(HWO) will provide new information to better understand the origin and
the atmospheric effects of these precipitations. A major interest is for
the distant magnetospheres of Uranus and Neptune, never explored by an
orbital spacecraft whose UV auroral emissions remains at (Uranus) or
below (Neptune) the HST sensitivity. is one such UV instrument concept,
which will enable unprecedented high spectral resolution at fine spatial
scale not previously seen and polarimetric observations of the planetary
aurorae while , another UV instrument will image the full auroral
regions with a good spectral resolution.
DESI
DR2 reference mocks: clustering results from Uchuu-BGS and LRG
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- E. Fernández-García / F. Prada / A. Smith / J. DeRose
- A. J. Ross / S. Bailey / M. S. Wang / Z. Ding
- C. Guandalin / C. Lamman / R. Vaisakh / R. Kehoe
- J. Lasker / T. Ishiyama / S. M. Moore / S. Cole
- M. Siudek / A. Amalbert / A. Salcedo / A. Hearin
- B. Joachimi / A. Rocher / S. Saito / A. Krolewski
- Z. Slepian / Q. Li / K. S. Dawson / E. Jullo
- J. Aguilar / S. Ahlen / D. Bianchi / D. Brooks
- T. Claybaugh / A. de la Macorra / P. Doel / S. Ferraro
- A. Font-Ribera / J. E. Forero-Romero / S. Gontcho A Gontcho / G.
Gutierrez
- K. Honscheid / M. Ishak / R. Joyce / S. Juneau
- D. Kirkby / T. Kisner / A. Kremin / O. Lahav
- A. Lambert / M. Landriau / M. E. Levi / M. Manera
- R. Miquel / J. Moustakas / S. Nadathur / W. J. Percival
- I. Pérez-Ràfols / G. Rossi / E. Sanchez / D. Schlegel
- H. Seo / J. Silber / D. Sprayberry / G. Tarlé
- B. A. Weaver / P. Zarrouk / R. Zhou
Summary
The aim of this work is to construct mock galaxy catalogues that
accurately reproduce the redshift evolution of galaxy number density,
clustering statistics, and baryonic properties, such as stellar mass for
luminous red galaxies (LRGs) and absolute magnitude in the  -band for the bright galaxy sample
(BGS), based on the first three years of observations from the Dark
Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI). To achieve this, we applied the
subhalo abundance matching (SHAM) technique to the Uchuu
-band for the bright galaxy sample
(BGS), based on the first three years of observations from the Dark
Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI). To achieve this, we applied the
subhalo abundance matching (SHAM) technique to the Uchuu 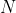 -body simulation, which follows the
evolution of 2.1 trillion particles within a volume of
-body simulation, which follows the
evolution of 2.1 trillion particles within a volume of  , assuming a Planck base-
, assuming a Planck base- CDM cosmology. Using SHAM, we populated
Uchuu subhalos with LRGs and BGS-BRIGHT (
CDM cosmology. Using SHAM, we populated
Uchuu subhalos with LRGs and BGS-BRIGHT ( ) galaxies up to
redshift
) galaxies up to
redshift  , assigning stellar
masses to LRGs and luminosities to BGS galaxies (up to
, assigning stellar
masses to LRGs and luminosities to BGS galaxies (up to  ).
Furthermore, we analyzed the clustering dependence on stellar mass and
luminosity for each tracer. Our results show that the Uchuu BGS-BRIGHT
and LRG mocks accurately reproduce the observed redshift evolution of
clustering, with better than 5% agreement for separations of
).
Furthermore, we analyzed the clustering dependence on stellar mass and
luminosity for each tracer. Our results show that the Uchuu BGS-BRIGHT
and LRG mocks accurately reproduce the observed redshift evolution of
clustering, with better than 5% agreement for separations of  and
below 10% for
and
below 10% for  . For
the Uchuu-LRG mock, we successfully captured the stellar mass dependence
of clustering, while for the Uchuu-BGS mock, we replicated the
clustering for various volume-limited subsamples. We also find good
agreement between the data and mocks in the dependence of large-scale
bias on luminosity for BGS-BRIGHT galaxies and on stellar mass for LRGs.
Altogether, these results equip DESI with robust tools for generating
high-fidelity lightcones for the remainder of the survey, thereby
enhancing our understanding of the galaxy–halo connection.
. For
the Uchuu-LRG mock, we successfully captured the stellar mass dependence
of clustering, while for the Uchuu-BGS mock, we replicated the
clustering for various volume-limited subsamples. We also find good
agreement between the data and mocks in the dependence of large-scale
bias on luminosity for BGS-BRIGHT galaxies and on stellar mass for LRGs.
Altogether, these results equip DESI with robust tools for generating
high-fidelity lightcones for the remainder of the survey, thereby
enhancing our understanding of the galaxy–halo connection.
Edge-On
Disk Study (EODS) II: Thermal Structure of the Flying Saucer Disk
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- S. Guilloteau / O. Denis-Alpizar / A. Dutrey / C. Foucher
- S. Gavino / D. Semenov / V. Piétu / E. Chapillon
- L. Testi / E. Dartois / E. di Folco / K. Furuya
- U. Gorti / N. Grosso / Th. Henning / J. M.
Huré
- A. Kospal / F. LePetit / L. Majumdar / H. Nomura
- N. T. Phuong / M. Ruaud / Y. W. Tang / S. Wolf
Summary
Context. The dust and gas temperature in proto-planetary disks play
critical roles in determining their chemical evolution and influencing
planet formation processes. Aims. We attempted an accurate measurement
of the dust and CO temperature profile in the edge-on disk of the Flying
Saucer. Methods. We used the unique properties of the Flying Saucer, its
edge-on geometry and its fortunate position in front of CO clouds with
different brightness temperatures to provide independent constraints on
the dust temperature. We compared it with the dust temperature derived
using the radiative transfer code DiskFit and the CO gas temperature.
Results. We find clear evidence for a substantial gas temperature
vertical gradient, with a cold (10 K) disk mid-plane and a warmer CO
layer where T(r) is 27 K at 100 au, dropping with exponent 0.3. Direct
evidence for CO depletion in the mid-plane, below about 1 scale height,
is also found. At this height, the gas temperature is 15-20 K,
consistent with the expected CO freeze out temperature. The dust disk
appears optically thin at 345 GHz, and exhibits moderate settling.
The
planetary-mass-limit VLT/SINFONI library: Spectral extraction and
atmospheric characterization via forward modeling
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- P. Palma-Bifani / M. Bonnefoy / G. Chauvin / P. Rojo
- P. Baudoz / B. Charnay / A. Denis / K. Hoch
- S. Petrus / M. Ravet / A. Simonnin / A. Vigan
Summary
We aim to deepen our understanding of the M-L transition on
planetary-mass companions and isolated brown dwarfs, and search for
evidence of possible differences between these two populations of
objects. To this end, we present a set of 21 VLT/SINFONI K-band
observations from five archival programs at a spectral resolution of
4000. We aim to measure atmospheric properties, such as temperature,
surface gravity, and metallicity, to understand the similarities and
differences between objects ranging from M5 to L5 in spectral type. We
extracted the spectra of these targets with the TExTRIS code.
Subsequently, we model them using ForMoSA, a Bayesian forward modeling
tool for spectral analysis, exploring four families of self-consistent
atmospheric models: ATMO, BT-Settl, Exo-REM, and Sonora. Here we present
the spectra of our targets and the derived parameters from the
atmospheric modeling. We observed a drop in effective temperature of
more than 500 K as a function of spectral type at the M/L transition,
likely related to limitations in the current atmospheric models. In
addition, we report carbon-to-oxygen ratio measurements for three
companions (2M 0103 AB b, AB Pic b, and CD-35 2722 b), which contribute
to the growing list of exoplanets for which this value has been
measured. In conclusion, the VLT/SINFONI Library highlights two key
points. First, there is a critical need to further investigate the
discrepancies among grids of spectra generated by self-consistent
models, as these models yield varying results and do not uniformly
explore the parameter space. Second, we do not observe apparent
discrepancies in the K-band spectra between companions and isolated
brown dwarfs, which potentially suggests that these super-Jupiter
objects formed through a similar process; however, this warrants further
investigation.
Measuring
the Suns radial velocity variability due to supergranulation over a
magnetic cycle
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Niamh K. O’Sullivan / Suzanne Aigrain / Michael Cretignier / Ben
Lakeland
- Baptiste Klein / Xavier Dumusque / Nadège Meunier / Sophia
Sulis
- Megan Bedell / Annelies Mortier / Andrew Collier Cameron / Heather
M. Cegla
Summary
In recent years supergranulation has emerged as one of the biggest
challenges for the detection of Earth-twins in radial velocity planet
searches. We used eight years of Sun-as-a-star radial velocity
observations from HARPS-N to measure the quiet-Sun’s granulation and
supergranulation properties of most of its 11-year activity cycle, after
correcting for the effects of magnetically active regions using two
independent methods. In both cases, we observe a clear, order of
magnitude variation in the time-scale of the supergranulation component,
which is largest at activity minimum and is strongly anti-correlated
with the relative Sunspot number. We also explored a range of
observational strategies which could be employed to characterise
supergranulation in stars other than the Sun, showing that a
comparatively long observing campaign of at least 23 nights is required,
but that up to 10 stars can be monitored simultaneously in the process.
We conclude by discussing plausible explanations for the
“supergranulation” cycle.
The
star HIP 41378 potentially misaligned with its cohort of long-period
planets
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- S. Grouffal / A. Santerne / V.
Bourrier / V. Kunovac
- C. Dressing / B. Akinsanmi / C. Armstrong / S. Baliwal
- O. Balsalobre-Ruza / S. C. C. Barros / D. Bayliss / I. J. M.
Crossfield
- O. Demangeon / X. Dumusque / S. Giacalone / C. K. Harada
- H. Isaacson / H. Kellermann / J. Lillo-Box / J. Llama
- A. Mortier / E. Palle / A. S. Rajpurohit / M. Rice
- N. C. Santos / J. V. Seidel / R. Sharma / S. G. Sousa
- L. Thomas / E. V. Turtelboom / S. Udry / P. J. Wheatley
Summary
The obliquity between the stellar spin axis and the planetary orbit,
detected via the Rossiter-McLaughlin (RM) effect, is a tracer of the
formation history of planetary systems. While obliquity measurements
have been extensively applied to hot Jupiters and short-period planets,
they remain rare for cold and long-period planets due to observational
challenges, particularly their long transit durations. We report the
detection of the RM effect for the 19-hour-long transit of HIP 41378 f,
a temperate giant planet on a 542-day orbit, observed through a
worldwide spectroscopic campaign. We measure a slight projected
obliquity of 21  8 degrees and a significant
3D spin-orbit angle of 52
8 degrees and a significant
3D spin-orbit angle of 52  6 degrees, based on the
measurement of the stellar rotation period. HIP 41378 f is part of a
5-transiting planetary system with planets close to mean motion
resonances. The observed misalignment likely reflects a primordial tilt
of the stellar spin axis relative to the protoplanetary disk, rather
than dynamical interactions. HIP 41378 f is the first non-eccentric
long-period (P>100 days) planet observed with the RM effect, opening
new constraints on planetary formation theories. This observation should
motivate the exploration of planetary obliquities across a longer range
of orbital distances through international collaboration.
6 degrees, based on the
measurement of the stellar rotation period. HIP 41378 f is part of a
5-transiting planetary system with planets close to mean motion
resonances. The observed misalignment likely reflects a primordial tilt
of the stellar spin axis relative to the protoplanetary disk, rather
than dynamical interactions. HIP 41378 f is the first non-eccentric
long-period (P>100 days) planet observed with the RM effect, opening
new constraints on planetary formation theories. This observation should
motivate the exploration of planetary obliquities across a longer range
of orbital distances through international collaboration.
Resolving
Individual Stars in Nearby Large Galaxies with the Habitable Worlds
Observatory
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Adam Smercina / Tara Fetherolf / Eric W. Koch / Silvia
Martocchia
- Chris Mihos / Benjamin F. Williams
Summary
The varied and dynamic evolutionary histories of galaxies give rise
to the stunning diversity in their properties that we observe in the
present-day universe. HST, and now JWST, have pioneered the study of
resolved individual stars in the Milky Way and other members of the
Local Group, uncovering the drivers of their morphological, star
formation, and chemical evolution. HWO will constitute a paradigm shift:
introducing the ability to panchromatically resolve the main bodies of
every galaxy in the Local Volume into their constituent stars. In this
science case, we summarize the breakthrough progress that HWO will
advance in the field of galaxy evolution through resolved stellar
populations. HWO will transform our understanding of galaxies in three
distance regimes: (1) in the nearest galaxies ($
 $50+ Mpc), providing access to the luminous
stellar populations in thousands of galaxies, enabling unprecedented
views of their morphology, stellar abundances, and dust content. The
principal technological requirement advanced by this science case is a
camera with a resolution of $$0.015’’ that is diffraction-limited, and
Nyquist-sampled (0.01’’ per pixel), to at least 550 nm
$50+ Mpc), providing access to the luminous
stellar populations in thousands of galaxies, enabling unprecedented
views of their morphology, stellar abundances, and dust content. The
principal technological requirement advanced by this science case is a
camera with a resolution of $$0.015’’ that is diffraction-limited, and
Nyquist-sampled (0.01’’ per pixel), to at least 550 nm  comparable to the High Definition
Imager from the LUVOIR concept.
comparable to the High Definition
Imager from the LUVOIR concept.
Unveiling
the nature and fate of the almost-dark cloud AGC 226178 through HI
mapping
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Yu-Zhu Sun / Hong-Xin Zhang / Elias Brinks / Rory Smith
- Fujia Li / Minsu Kim / Se-Heon Oh / Zesen Lin
- Jaebeom Kim / Weibin Sun / Tie Li / Patrick Côté
- Alessandro Boselli / Lijun Chen / Pierre-Alain Duc
/ Sanjaya Paudel
- Matthew A. Taylor / Kaixiang Wang / Enci Wang / Lanyue Zhang
- Yinghe Zhao
Summary
The origin of extragalactic, almost dark HI clouds with extreme
gas-to-stellar mass ratios remains poorly understood. We investigate the
nature and fate of the “almost dark” cloud AGC 226178, projected within
the Virgo cluster, with an HI-to-stellar mass ratio of ~1000. We present
deep single-dish HI mapping from the Five-hundred-meter Aperture
Spherical Telescope (FAST), complemented by high-resolution
interferometric data from the Very Large Array (VLA), as part of the
Atomic gas in Virgo Interacting Dwarf galaxies (AVID) project. These
observations provide the highest-quality HI analysis to date of such a
cloud, combining resolution and sensitivity. FAST data reveal a short,
low-velocity tail toward the dwarf galaxy VCC 2034, previously proposed
as a possible origin for AGC 226178. However, VCC 2034 shows a
line-of-sight asymmetric HI feature and cometary morphology indicating a
stripping event unrelated to AGC 226178. VLA data reveal a velocity
gradient across AGC 226178 and a clumpy internal structure. The velocity
dispersion exceeds the thermal linewidth, implying turbulence or
unresolved motions. The cloud cannot be gravitationally bound by atomic
gas alone. The resolved HI clumps follow standard HI mass-star formation
rate and mass-size relations, with those forming stars reaching surface
densities above the threshold for self-shielding. We conclude that AGC
226178 is a free-floating HI cloud of unknown origin. The system appears
to be in the process of disintegration. It is likely located well
outside the Virgo cluster, as the preservation of its extended HI
morphology within the cluster environment would otherwise require a
substantial reservoir of unseen molecular gas with a mass exceeding that
of the observed HI content. While confinement pressure from the hot
intracluster medium may aid its stability, it is unlikely to be the
dominant factor preventing its disruption.
Orbit
and atmosphere of HIP 99770 b through the eyes of VLTI/GRAVITY
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- T. O. Winterhalder / J. Kammerer / S. Lacour / A. Mérand
- M. Nowak / T. Stolker / W. O. Balmer / G.-D. Marleau
- R. Abuter / A. Amorim / R. Asensio-Torres / J.-P. Berger
- H. Beust / S. Blunt / M. Bonnefoy / H. Bonnet
- M. S. Bordoni / G. Bourdarot / W. Brandner / F. Cantalloube
- P. Caselli / B. Charnay / G. Chauvin / A. Chavez
- E. Choquet / V. Christiaens / Y. Clénet / V. Coudé
du Foresto
- A. Cridland / R. Davies / R. Dembet / J. Dexter
- A. Drescher / G. Duvert / A. Eckart / F. Eisenhauer
- N. M. Förster Schreiber / P. Garcia / R. Garcia Lopez / T.
Gardner
- E. Gendron / R. Genzel / S. Gillessen / J. H. Girard
- S. Grant / X. Haubois / G. Heißel / Th. Henning
- S. Hinkley / S. Hippler / M. Houllé / Z. Hubert
- L. Jocou / M. Keppler / P. Kervella / L. Kreidberg
- N. T. Kurtovic / A.-M. Lagrange / V. Lapeyrère / J.-B. Le
Bouquin
- D. Lutz / A.-L. Maire / F. Mang / P. Mollière
- C. Mordasini / D. Mouillet / E. Nasedkin / T. Ott
- G. P. P. L. Otten / C. Paladini / T. Paumard / K. Perraut
- G. Perrin / N. Pourré / L. Pueyo / D. C. Ribeiro
- E. Rickman / Z. Rustamkulov / J. Shangguan / T. Shimizu
- D. Sing / J. Stadler / O. Straub / C. Straubmeier
- E. Sturm / L. J. Tacconi / E. F. van Dishoeck / A.
Vigan
- F. Vincent / S. D. von Fellenberg / J. J. Wang / F. Widmann
- J. Woillez / S. Yazici / the GRAVITY Collaboration
Summary
Context: Inferring the likely formation channel of giant exoplanets
and brown dwarf companions from orbital and atmospheric observables
remains a formidable challenge. Further and more precise directly
measured dynamical masses of these companions are required to inform and
gauge formation, evolutionary, and atmospheric models. We present an
updated study of HIP 99770 b based on observations conducted with
VLTI/GRAVITY. Aims: Combining the new data with previous observations
from the literature, we characterise HIP 99770 b to better constrain its
orbit, dynamical mass, and atmospheric properties, as well as to shed
light on its likely formation channel. Methods: We ran a renewed orbit
fit to further constrain the dynamical mass of the companion and the
orbit solution. We also analysed the GRAVITY K-band spectrum, placing it
into context with literature data, and extracting magnitude, age,
spectral type, bulk properties and atmospheric characteristics of HIP
99770 b. Results: We detected the companion at a radial separation of
 from its host. The new orbit fit yields a dynamical mass of
from its host. The new orbit fit yields a dynamical mass of  and
an eccentricity of
and
an eccentricity of  . We also find that additional relative astrometry
epochs in the future will not enable further constraints on the
dynamical mass due to the dominating relative uncertainty on the
Hipparcos-Gaia proper motion anomaly. The publication of Gaia DR4 will
likely ease this predicament. We find that the companion is consistent
with spectral type L8 and exhibits a potential metal enrichment in its
atmosphere. Conclusions: These results do not yet allow for a definite
inference of the companion’s formation channel. Nevertheless, the new
constraints on its bulk properties and the additional GRAVITY spectrum
presented here will aid future efforts to determine the formation
history of HIP 99770 b.
. We also find that additional relative astrometry
epochs in the future will not enable further constraints on the
dynamical mass due to the dominating relative uncertainty on the
Hipparcos-Gaia proper motion anomaly. The publication of Gaia DR4 will
likely ease this predicament. We find that the companion is consistent
with spectral type L8 and exhibits a potential metal enrichment in its
atmosphere. Conclusions: These results do not yet allow for a definite
inference of the companion’s formation channel. Nevertheless, the new
constraints on its bulk properties and the additional GRAVITY spectrum
presented here will aid future efforts to determine the formation
history of HIP 99770 b.
GRB
240825A: Early Reverse Shock and Its Physical Implications
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Chao Wu / Yun Wang / Hua-Li Li / Li-Ping Xin
- Dong Xu / Benjamin Schneider / Antonio de Ugarte
Postigo / Gavin Lamb
- Andrea Reguitti / Andrea Saccardi / Xing Gao / Xing-Ling Li
- Qiu-Li Wang / Bing Zhang / Jian-Yan Wei / Shuang-Nan Zhang
- Frédéric Daigne / Jean-Luc Atteia / Maria-Grazia Bernardini /
Hong-bo Cai
- Arnaud Claret / Bertrand Cordier / Jin-Song Deng / Olivier
Godet
- Diego Götz / Xu-Hui Han / Zhe Kang / Guang-Wei Li
- Zhen-Wei Li / Cheng-Zhi Liu / Xiao-Meng Lu / You Lv
- Julian P Osborne / Jesse Palmerio / Yu-Lei Qiu / Stéphane
Schanne
- Damien Turpin / Susanna Diana Vergani / Jing Wang / Yu-Jie Xiao
- Wen-Jin Xie / Yang Xu / Zhu-Heng Yao / Pin-Pin Zhang
- Ruo-Son Zhang / Cheng-Wei Zhu / Riccardo Brivio / Stefano
Covino
- Paolo D’Avanzo / Matteo Ferro / Andrea Melandri / Andrea Rossi
- José Feliciano Agüí Fernández / Christina C. Thöne / Chun-Hai Bai /
Ali Esamdin
- Abdusamatjan Iskandar / Shahidin Yaqup / Yu Zhang / Tu-Hong
Zhong
- Shao-Yu Fu / Shuai-Qing Jiang / Xing Liu / Jie An
- Zi-Pei Zhu / Jia-Xin Cao / En-Wei Liang / Da-Bin Lin
- Xiang-Gao Wang / Guo-Wang Du / Xin-Zhong Er / Yuan Fang
- Xiao-Wei Liu / Christophe Adami / Michel Dennefeld
/ Emeric Le Floc’h
- Johan Peter Uldall Fynbo / Páll Jakobsson / Daniele Bjørn Malesani /
Zhi-Ping Jin
- Jia Ren / Hao Wang / Da-Ming Wei / Hao Zhou
- Sergio Campana / Shiho Kobayashi / Massimiliano De Pasquale
Summary
Early multiwavelength observations offer crucial insights into the
nature of the relativistic jets responsible for gamma-ray bursts and
their interaction with the surrounding medium.We present data of GRB
240825A from 17 space- and ground-based telescopes/instruments, covering
wavelengths from NIR/optical to X-ray and GeV, and spanning from the
prompt emission to the afterglow phase triggered by Swift and Fermi. The
early afterglow observations were carried out by SVOM/C-GFT, and
spectroscopic observations of the afterglow by GTC, VLT, and TNG
determined the redshift of the burst ( ) later.A
comprehensive analysis of the prompt emission spectrum observed by
Swift-BAT and Fermi-GBM/LAT reveals a rare and significant high-energy
cutoff at ~76 MeV. Assuming this cutoff is due to
) later.A
comprehensive analysis of the prompt emission spectrum observed by
Swift-BAT and Fermi-GBM/LAT reveals a rare and significant high-energy
cutoff at ~76 MeV. Assuming this cutoff is due to  absorption allows us to place
an upper limit on the initial Lorentz factor,
absorption allows us to place
an upper limit on the initial Lorentz factor,  . The
optical/NIR and GeV afterglow light curves be described by the standard
external shock model, with early-time emission dominated by a reverse
shock (RS) and a subsequent transition to forward shock (FS) emission.
Our afterglow modelling yields a consistent estimate of the initial
Lorentz factor (
. The
optical/NIR and GeV afterglow light curves be described by the standard
external shock model, with early-time emission dominated by a reverse
shock (RS) and a subsequent transition to forward shock (FS) emission.
Our afterglow modelling yields a consistent estimate of the initial
Lorentz factor ( ). Furthermore, the RS-to-FS magnetic field ratio
(
). Furthermore, the RS-to-FS magnetic field ratio
( ) indicates that the reverse shock region is
significantly more magnetized than the FS region. An
isotropic-equivalent kinetic energy of
) indicates that the reverse shock region is
significantly more magnetized than the FS region. An
isotropic-equivalent kinetic energy of  erg is derived, and the corresponding
erg is derived, and the corresponding  -ray radiation efficiency is estimated
to be
-ray radiation efficiency is estimated
to be  = 3.1%. On the other hand,
the standard afterglow model can not reproduce the X-ray light curve of
GRB 240825A, calling for improved models to characterize all
multiwavelength data.
= 3.1%. On the other hand,
the standard afterglow model can not reproduce the X-ray light curve of
GRB 240825A, calling for improved models to characterize all
multiwavelength data.
Earliest
Galaxy Evolution in the CANUCS+Technicolor fields: Galaxy Properties at
 seen with the
Full NIRCam Medium and Broad Band Filters
seen with the
Full NIRCam Medium and Broad Band Filters
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Yoshihisa Asada / Chris Willott / Adam Muzzin / Maruša Bradač
- Gabriel Brammer / Guillaume Desprez / Kartheik Iyer / Danilo
Marchesini
- Nicholas Martis / Gaël Noirot / Ghassan Sarrouh / Marcin
Sawicki
- Sunna Withers / Seiji Fujimoto / Giordano Felicioni / Ilias
Goovaerts
- Jon Judež / Naadiyah Jagga / Maya Merchant / Rosa Mérida
- Luke Robbins
Summary
We present a sample of  galaxies by exploiting one of the richest JWST
NIRCam imaging data, taken in the CANUCS survey in Cycle 1 and the
Technicolor (TEC) survey in Cycle 2. The combination of the CANUCS+TEC
provides multi-epoch, deep NIRCam images in all medium bands (MBs) and
broad bands (BBs) onboard NIRCam (22 filters in total), over
galaxies by exploiting one of the richest JWST
NIRCam imaging data, taken in the CANUCS survey in Cycle 1 and the
Technicolor (TEC) survey in Cycle 2. The combination of the CANUCS+TEC
provides multi-epoch, deep NIRCam images in all medium bands (MBs) and
broad bands (BBs) onboard NIRCam (22 filters in total), over  in three independent lines of sight. We select
high-
in three independent lines of sight. We select
high- galaxy candidates based on photometric
redshifts, and obtain eight candidates at
galaxy candidates based on photometric
redshifts, and obtain eight candidates at  , including a
very robust candidate at
, including a
very robust candidate at  . The
ultraviolet (UV) luminosity function (LF) from our sample is consistent
with previous JWST studies showing a scatter of
. The
ultraviolet (UV) luminosity function (LF) from our sample is consistent
with previous JWST studies showing a scatter of  dex across the
literature, marking the significance of the field-to-field variance in
interpreting galaxy abundance measurements at
dex across the
literature, marking the significance of the field-to-field variance in
interpreting galaxy abundance measurements at  . We find that the
UV LF moderately evolves at
. We find that the
UV LF moderately evolves at  , and the LF
normalization and the luminosity density decline by a factor of
, and the LF
normalization and the luminosity density decline by a factor of  from
from  to
to  , indicating less
steep evolution than
, indicating less
steep evolution than  . We highlight the
importance of MB filters, not only to minimize the contamination by
low-
. We highlight the
importance of MB filters, not only to minimize the contamination by
low- interlopers but also to maximize the
completeness. In particular, faint and less blue galaxies could be
missed when the sample is built solely on BB data. The contamination and
incompleteness of BB-only selected samples can bias our views of
earliest galaxy evolution at
interlopers but also to maximize the
completeness. In particular, faint and less blue galaxies could be
missed when the sample is built solely on BB data. The contamination and
incompleteness of BB-only selected samples can bias our views of
earliest galaxy evolution at  , including the UV
LF by
, including the UV
LF by  dex, the
size-magnitude relation by
dex, the
size-magnitude relation by  dex, and the UV
slope-magnitude relation by
dex, and the UV
slope-magnitude relation by  .
.
A
Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE). XIX.
The discovery of a spectacular 230 kpc Halpha tail following NGC 4569 in
the Virgo cluster
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Sun / H. Le / B. Epinat / A.
Boselli
- R. Luo / K. Hosogi / N. Pichette / W. Forman
- C. Sarazin / M. Fossati / H. Chen / E. Sarpa
- J. Braine / J. C. Cuillandre / S. Gwyn / G. Hensler
- S. Martocchia / B. Vollmer
Summary
Context. Galaxies fly inside galaxy clusters and ram pressure by the
ICM can remove a large amount of the ISM from the galaxy, and deposit
the gas in the ICM. The ISM decoupled from the host galaxy leaves a long
trail following the moving galaxy. Such long trails track the galaxy
motion and can be detected with sensitive data in Halpha. Aims. We study
the Halpha tail trailing NGC 4569 in the Virgo cluster. Methods. The
initial discovery was made with the deep Halpha imaging data with CFHT,
from the VESTIGE project. The follow-up spectroscopic observations were
made with APO/DIS, MMT/Binospec and CFHT/SITELLE. Results. Besides the
known 80 kpc Halpha tail downstream of NGC 4569, the deep Halpha imaging
data allow the Halpha tail detected to at least 230 kpc from the galaxy.
More importantly, the Halpha clumps implied from the imaging data are
confirmed with the spectroscopic data. The Halpha clumps show a smooth
radial velocity gradient across about 1300 km/s, eventually reaching the
velocity of the cluster. We build a simple model to explain the
deceleration of stripped clumps and constrain the age to about 0.9 Gyr.
Conclusions. This discovery, for the first time, demonstrates the full
deceleration process of the stripped ISM. This discovery also showcases
the potential with wide-field Halpha survey on galaxy clusters to
discover intracluster optical emission-line clouds originated from
cluster galaxies. These clouds provide kinematic tracers to the infall
history of cluster galaxies and the turbulence in the ICM. They are also
excellent multi-phase objects to study the relevant important physical
processes.
A
possible two-fold scenario for the disc-corona of the luminous AGN 1H
0419–577: a high-density disc or a warm corona
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Delphine Porquet / James N. Reeves / Valentina
Braito
Summary
[abridged] 1H 0419-577 is a highly-accreting, luminous BLS1 AGN. This
study aims to characterise its disc-corona system using, for the first
time, simultaneous XMM-Newton and NuSTAR observations, performed in May
and November 2018. We conducted high-resolution grating spectroscopy to
identify potential soft X-ray absorption and emission features. To
measure the hot corona temperatures from the spectral analysis above 3
keV, we also included data from a previous NuSTAR observation from June
2015. We characterised the disc-corona system properties by analysing
the broadband spectra and the SED from UV to hard X-rays. 1H 0419-577
was observed in a bare-like high-flux state at both epochs, with
negligible neutral and ionised absorption along its line of sight at
both Galactic and AGN rest-frames. However, several soft X-ray emission
lines were detected, notably a broad and intense OVII line indicating an
accretion disc origin at only a few tens of gravitational radii. The
broadband X-ray spectra revealed a prominent, absorption-free smooth
soft X-ray excess, a weak Fe Kalpha complex, and a lack of a Compton
hump. Fitting data above 3 keV yielded apparent moderate hot corona
temperatures of ~20-30 keV for the 2018 and 2015 observations, depending
on the model applied. The 2018 X-ray broadband spectra were well
reproduced by either a relativistic reflection model with a high-density
accretion disc (~10^18 cm^-2), or a hybrid model combining warm and hot
coronae with relativistic reflection. We performed the SED analysis for
the latter scenario, which indicated that both the hot and warm coronae
would have a small spatial extent. Both scenarios can successfully
reproduce the two 2018 observations of 1H 0419-577, but they imply very
different physical conditions, for example, in terms of disc density,
temperature and accretion power released in the hot corona and the
origin of the UV emission.
Articles for week 26 2025
Euclid:
Quick Data Release (Q1) – Watching ICM-selected galaxy clusters with
Euclid eyes – prospects of Euclid data in the context of large SZ and
X-ray based surveys
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Klein / K. George / J. J. Mohr / B. Altieri
- L. Amendola / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / F. Ducret / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / S.
Maurogordato
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- C. Rosset / H. J. A. Rottgering / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- D. Sapone / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / C. Burigana
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Viel
Summary
Galaxy clusters detected through their X-ray emission or
Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect (SZE), both produced by the intra-cluster
medium (ICM), are key probes in cosmological and astrophysical studies.
To maximise the scientific return of such surveys, complementary data
are required for cluster confirmation and redshift estimation. This is
typically provided by wide-field optical and infrared surveys, which are
increasingly challenged by ongoing and future ICM-selected samples. In
particular, at high redshifts ( ) probed by upcoming
SZE-selected samples, current large surveys may be insufficient for
reliable confirmation. Deep, high-resolution infrared surveys like
Euclid will thus be essential for confirming most high-redshift
clusters. We present an analysis of the first sizeable Euclid dataset
(Q1), overlapping with several ICM-selected cluster samples. We apply an
adaptation of the MCMF cluster confirmation tool to estimate key
properties, including redshift and richness, and to predict Euclid’s
capabilities for high-redshift cluster confirmation. We find promising
performance, particularly at high redshifts, while richness estimates at
low redshifts (
) probed by upcoming
SZE-selected samples, current large surveys may be insufficient for
reliable confirmation. Deep, high-resolution infrared surveys like
Euclid will thus be essential for confirming most high-redshift
clusters. We present an analysis of the first sizeable Euclid dataset
(Q1), overlapping with several ICM-selected cluster samples. We apply an
adaptation of the MCMF cluster confirmation tool to estimate key
properties, including redshift and richness, and to predict Euclid’s
capabilities for high-redshift cluster confirmation. We find promising
performance, particularly at high redshifts, while richness estimates at
low redshifts ( ) are currently
limited by Q1 data quality but should improve with future releases.
Using MCMF runs on random lines of sight, we predict that Euclid will
confirm clusters at
) are currently
limited by Q1 data quality but should improve with future releases.
Using MCMF runs on random lines of sight, we predict that Euclid will
confirm clusters at  as
effectively as current optical surveys at
as
effectively as current optical surveys at  , significantly
enhancing high-redshift confirmation. SZE-selected samples will thus
greatly benefit from Euclid overlap. Among five known high-
, significantly
enhancing high-redshift confirmation. SZE-selected samples will thus
greatly benefit from Euclid overlap. Among five known high- SZE clusters in Q1, we identify the
highest-redshift jellyfish galaxy candidate to date,
EUCLJ035330.86$-
SZE clusters in Q1, we identify the
highest-redshift jellyfish galaxy candidate to date,
EUCLJ035330.86$- -
- z=1.32
z=1.32 -
- z=1.46
z=1.46 -
- -$4845.
-$4845.
HOLISMOKES
XVIII: Detecting strongly lensed SNe Ia from time series of multi-band
LSST-like imaging data
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Satadru Bag / Raoul Canameras / Sherry H. Suyu /
Stefan Schuldt
- Stefan Taubenberger / Irham Taufik Andika / Alejandra Melo
Summary
Strong gravitationally lensed supernovae (LSNe), though rare, are
exceptionally valuable probes for cosmology and astrophysics. Upcoming
time-domain surveys like the Vera Rubin Observatory’s Legacy Survey of
Space and Time (LSST) offer a major opportunity to discover them in
large numbers. Early identification is crucial for timely follow-up
observations. We develop a deep learning pipeline to detect LSNe using
multi-band, multi-epoch image cutouts. Our model is based on a 2D
convolutional long short-term memory (ConvLSTM2D) architecture, designed
to capture both spatial and temporal correlations in time-series imaging
data. Predictions are made after each observation in the time series,
with accuracy improving as more data arrive. We train the model on
realistic simulations derived from Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC) data, which
closely matches LSST in depth and filters. This work focuses exclusively
on Type Ia supernovae (SNe Ia). LSNe Ia are injected onto HSC luminous
red galaxies (LRGs) at various phases of evolution to create positive
examples. Negative examples include variable sources from HSC Transient
Survey (including unclassified transients), and simulated unlensed SNe
Ia in LRG and spiral galaxies. Our multi-band model shows rapid
classification improvements during the initial few observations and
quickly reaches high detection efficiency: at a fixed false-positive
rate (FPR) of  , the true-positive
rate (TPR) reaches
, the true-positive
rate (TPR) reaches  by the
7th observation and exceeds
by the
7th observation and exceeds  by the
9th. Among the negative examples, SNe in LRGs remain the primary source
of FPR, as they can resemble their lensed counterparts under certain
conditions. The model detects quads more effectively than doubles and
performs better on systems with larger image separations. Although
trained and tested on HSC-like data, our approach applies to any
cadenced imaging survey, particularly LSST.
by the
9th. Among the negative examples, SNe in LRGs remain the primary source
of FPR, as they can resemble their lensed counterparts under certain
conditions. The model detects quads more effectively than doubles and
performs better on systems with larger image separations. Although
trained and tested on HSC-like data, our approach applies to any
cadenced imaging survey, particularly LSST.
A
Large Outburst, Coma Asymmetries, and the Color of Comet 243P/NEAT
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Michael S. P. Kelley / Silvia Protopapa / Dennis Bodewits / Aren N.
Heinze
- Youssef Moulane / Quanzhi Ye / Bryce Bolin / Simon
Conseil
- Tony L. Farnham / Lori Feaga / Xing Gao / Chih-Hao Hsia
- Emmanuel Jehin / Shrinivas R. Kulkarni / Russ R. Laher / Tim
Lister
- Frank J. Masci / Josiah Purdum / Bin Yang
Summary
Water ice is a fundamental building material of comets and other
bodies in the outer solar system. Yet, the properties of cometary water
ice are challenging to study, due to its volatility and the typical
distances at which comets are observed. Cometary outbursts, impulsive
mass-loss events that can liberate large amounts of material, offer
opportunities to directly observe and characterize cometary water ice.
We present a study of comet 243P/NEAT, instigated by a  mag outburst that occurred in December
2018. Optical images and a 251-day lightcurve were examined to
characterize the outburst and the comet’s quiescent activity. Variations
in the quiescent lightcurve appear to be dominated by coma asymmetries,
rather than changing activity levels as the comet approached and receded
from the Sun. Furthermore, the lightcurve shows evidence for 1 to 2
additional small outbursts (
mag outburst that occurred in December
2018. Optical images and a 251-day lightcurve were examined to
characterize the outburst and the comet’s quiescent activity. Variations
in the quiescent lightcurve appear to be dominated by coma asymmetries,
rather than changing activity levels as the comet approached and receded
from the Sun. Furthermore, the lightcurve shows evidence for 1 to 2
additional small outbursts ( mag) occurring in
September 2018. The large December 2018 outburst likely ejected water
ice grains, yet no signatures of ice were found in color photometry, a
color map, nor a near-infrared spectrum. We discuss possible dynamical
and thermal reasons for this non-detection. In this context, we examined
the comae of comets 103P/Hartley 2 and C/2013 US
mag) occurring in
September 2018. The large December 2018 outburst likely ejected water
ice grains, yet no signatures of ice were found in color photometry, a
color map, nor a near-infrared spectrum. We discuss possible dynamical
and thermal reasons for this non-detection. In this context, we examined
the comae of comets 103P/Hartley 2 and C/2013 US (Catalina), and show
that a one-to-one mapping between continuum color and the presence of
water ice cannot be supported. We also discuss possible causes for the
large outburst, and find that there is an apparent grouping in the
kinetic energy per mass estimates for the outbursts of 5 comets.
(Catalina), and show
that a one-to-one mapping between continuum color and the presence of
water ice cannot be supported. We also discuss possible causes for the
large outburst, and find that there is an apparent grouping in the
kinetic energy per mass estimates for the outbursts of 5 comets.
FRB
20250316A: A Brilliant and Nearby One-Off Fast Radio Burst Localized to
13 parsec Precision
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The CHIME/FRB Collaboration / : / Thomas C. Abbott / Daniel
Amouyal
- Shion E. Andrew / Kevin Bandura / Mohit Bhardwaj / Kalyani
Bhopi
- Yash Bhusare / Charanjot Brar / Alice Cai / Tomas Cassanelli
- Shami Chatterjee / Jean-François Cliche / Amanda M. Cook / Alice P.
Curtin
- Evan Davies-Velie / Matt Dobbs / Fengqiu Adam Dong / Yuxin Dong
- Gwendolyn Eadie / Tarraneh Eftekhari / Wen-fai Fong / Emmanuel
Fonseca
- B. M. Gaensler / Nina Gusinskaia / Jason W. T. Hessels / Danté M.
Hewitt
- Jeff Huang / Naman Jain / Ronniy. C. Joseph / Lordrick Kahinga
- Victoria M. Kaspi / Afrasiyab / Khan / Bikash Kharel
- Adam E. Lanman / Magnus L’Argent / Mattias Lazda / Calvin Leung
- Robert Main / Lluis Mas-Ribas / Kiyoshi W. Masui / Kyle
McGregor
- Ryan Mckinven / Juan Mena-Parra / Daniele Michilli
/ Nicole Mulyk
- Mason Ng / Kenzie Nimmo / Ayush Pandhi / Swarali Shivraj Patil
- Aaron B. Pearlman / Ue-Li Pen / Ziggy Pleunis / J. Xavier
Prochaska
- Masoud Rafiei-Ravandi / Scott M. Ransom / Gurman Sachdeva / Mawson
W. Sammons
- Ketan R. Sand / Paul Scholz / Vishwangi Shah / Kaitlyn Shin
- Seth R. Siegel / Sunil Simha / Kendrick Smith / Ingrid Stairs
- David C. Stenning / Haochen Wang / Thomas Boles / Ismaël
Cognard
- Tammo Jan Dijkema / Alexei V. Filippenko / Marcin P. Gawroński /
Wolfgang Herrmann
- Charles D. Kilpatrick / Franz Kirsten / Shawn Knabel / Omar S.
Ould-Boukattine
- Hadrien Paugnat / Weronika Puchalska / William Sheu / Aswin
Suresh
- Aaron Tohuvavohu / Tommaso Treu / WeiKang Zheng
Summary
Precise localizations of a small number of repeating fast radio
bursts (FRBs) using very long baseline interferometry (VLBI) have
enabled multiwavelength follow-up observations revealing diverse local
environments. However, the 2–3% of FRB sources that are observed to
repeat may not be representative of the full population. Here we use the
VLBI capabilities of the full CHIME Outriggers array for the first time
to localize a nearby (40 Mpc), bright (kJy), and apparently one-off FRB
source, FRB 20250316A, to its environment on 13-pc scales. We use
optical and radio observations to place deep constraints on associated
transient emission and the properties of its local environment. We place
a  upper limit of
upper limit of  on spatially coincident radio emission, a factor
of 100 lower than any known compact persistent radio source associated
with an FRB. Our KCWI observations allow us to characterize the gas
density, metallicity, nature of gas ionization, dust extinction and
star-formation rate through emission line fluxes. We leverage the
exceptional brightness and proximity of this source to place deep
constraints on the repetition of FRB 20250316A, and find it is
inconsistent with all well-studied repeaters given the non-detection of
bursts at lower spectral energies. We explore the implications of a
measured offset of 190
on spatially coincident radio emission, a factor
of 100 lower than any known compact persistent radio source associated
with an FRB. Our KCWI observations allow us to characterize the gas
density, metallicity, nature of gas ionization, dust extinction and
star-formation rate through emission line fluxes. We leverage the
exceptional brightness and proximity of this source to place deep
constraints on the repetition of FRB 20250316A, and find it is
inconsistent with all well-studied repeaters given the non-detection of
bursts at lower spectral energies. We explore the implications of a
measured offset of 190 pc from the center of
the nearest star-formation region, in the context of progenitor
channels. FRB 20250316A marks the beginning of an era of routine
localizations for one-off FRBs on tens of mas-scales, enabling
large-scale studies of their local environments.
pc from the center of
the nearest star-formation region, in the context of progenitor
channels. FRB 20250316A marks the beginning of an era of routine
localizations for one-off FRBs on tens of mas-scales, enabling
large-scale studies of their local environments.
The
KELT-7b atmospheric thermal-inversion conundrum revisited with CHEOPS,
TESS, and additional data
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Z. Garai / A. Krenn / P. E. Cubillos / G. Bruno
- A. M. S. Smith / T. G. Wilson / A. Brandeker / M. N. Günther
- A. Heitzmann / L. Carone / V. Singh / M. Lendl
- O. D. S. Demangeon / Y. Alibert / R. Alonso / J. Asquier
- T. Bárczy / D. Barrado / S. C. Barros / W. Baumjohann
- W. Benz / N. Billot / L. Borsato / C. Broeg
- A. Collier Cameron / A. C. M. Correia / Sz. Csizmadia / M. B.
Davies
- M. Deleuil / A. Deline / B.-O. Demory / A.
Derekas
- B. Edwards / J. A. Egger / D. Ehrenreich / A. Erikson
- J. Farinato / A. Fortier / L. Fossati / M. Fridlund
- D. Gandolfi / K. Gazeas / M. Gillon / M. Güdel
- Ch. Helling / K. G. Isaak / F. Kerschbaum / L. Kiss
- J. Korth / K. W. F. Lam / J. Laskar / A. Lecavelier des Etangs
- D. Magrin / P. F. L. Maxted / B. Merín / C. Mordasini
- V. Nascimbeni / G. Olofsson / R. Ottensamer / I. Pagano
- E. Pallé / G. Peter / D. Piazza / G. Piotto
- D. Pollacco / D. Queloz / R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando
- H. Rauer / I. Ribas / N. C. Santos / G. Scandariato
- D. Ségransan / A. E. Simon / S. G. Sousa / M. Stalport
- S. Sulis / M. Gy. Szabó / S. Udry / S.
Ulmer-Moll
- V. Van Grootel / J. Venturini / E. Villaver / N. A. Walton
- S. Wolf / D. Wolter / T. Zingales
Summary
Ultrahot Jupiters are predicted to show inverted temperature-pressure
(T-P) profiles in the presence of optical absorbers such as TiO and VO.
An inverted T-P profile of KELT-7b was recently detected, in line with
these predictions, but such diagnoses are known to be model-dependent.
We used CHEOPS, TESS, and literature data to characterize the atmosphere
of KELT-7b, reassess its T-P profile, measure its albedo, and search for
distortions in its CHEOPS transit light curve due to stellar rotation.
We jointly fitted CHEOPS and TESS data to measure the occultation depths
and modeled CHEOPS transits including gravity darkening. Emission and
transmission retrievals were performed, and the albedo was calculated in
the CHEOPS and TESS passbands. Thermochemical-equilibrium retrievals
yield a non-inverted T-P profile, while free-chemistry retrievals yield
an inverted profile with likely unphysical TiO/VO abundances. A 3D GCM
supports a TiO-driven inversion. We report a low geometric albedo of
 , consistent with inefficient heat redistribution
and supported by a GCM with magnetic drag. CHEOPS data provide no
constraint on the sky-projected orbital obliquity. Retrieval results
strongly depend on the chemical framework. Free-chemistry fits are
better but risk unphysical solutions for ultrahot Jupiters. We applied a
coherent stellar variability correction to CHEOPS and TESS data; future
observations would benefit from similar treatment.
, consistent with inefficient heat redistribution
and supported by a GCM with magnetic drag. CHEOPS data provide no
constraint on the sky-projected orbital obliquity. Retrieval results
strongly depend on the chemical framework. Free-chemistry fits are
better but risk unphysical solutions for ultrahot Jupiters. We applied a
coherent stellar variability correction to CHEOPS and TESS data; future
observations would benefit from similar treatment.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- B. I. Ciocan / N. F. Bouché / J. Fensch / W.
Mercier
- D. Krajnović / J. Richard / T. Contini / A. Jeanneau
Summary
[Abridged] We analyse the dark matter (DM) halo properties of 127
0.3<z<1.5 star-forming galaxies (SFGs) down to low stellar masses
(7<log(Mstar/Msun)<11), using data from the MUSE Hubble Ultra Deep
Field Survey and photometry from HST and JWST. We employ a 3D forward
modelling approach to analyse the morpho-kinematics of our sample,
enabling measurement of individual rotation curves out to 2-3 times the
effective radius. We perform a disk-halo decomposition with a 3D
parametric model that includes stellar, gas, and DM components, with
pressure support corrections. We validate our methodology on mock data
cubes generated from idealised disk simulations. We select the
best-fitting DM model among six density profiles, including the
Navarro-Frenk-White and the generalised alpha-beta-gamma profile of Di
Cintio et al. (2014, DC14). Our Bayesian analysis shows that DC14
performs as well as or better than the other profiles in >65% of the
sample. We find that the kinematically inferred stellar masses agree
with values from SED fitting. We find that 89% of galaxies have DM
fractions >50%. For 70% of SFGs, we infer a DM inner slope, gamma
< 0.5, indicating cored DM profiles, but no correlation is found
between gamma and star formation rate of the sample. The stellar- and
concentration-mass relations agree with theoretical expectations, but
with larger scatter. We confirm the anticorrelation between halo scale
radius and DM density. The halo scale radii and DM surface densities
increase with Mstar, while DM densities stay constant. We find tentative
evidence of an evolution of the DM density with z, which suggests that
the DM halos of intermediate-z systems are denser than those of local
galaxies. In contrast, the halo scale radii are z-invariant.
The
NIKA2 cosmological legacy survey at 2 mm: catalogs, colors, redshift
distributions, and implications for deep surveys
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Béthermin / G. Lagache / C. Carvajal-Bohorquez /
R. Adam
- P. Ade / H. Ajeddig / S. Amarantidis / P. André
- H. Aussel / A. Beelen / A. Benoît / S. Berta
- L. J. Bing / A. Bongiovanni / J. Bounmy / O. Bourrion
- M. Calvo / A. Catalano / D. Chérouvrier / M. De Petris
- F.-X. Désert / S. Doyle / E. F. C. Driessen / G. Ejlali
- A. Ferragamo / A. Gomez / J. Goupy / C. Hanser
- S. Katsioli / F. Kéruzoré / C. Kramer / B. Ladjelate
- S. Leclercq / J.-F. Lestrade / J. F. Macías-Pérez / S. C.
Madden
- A. Maury / F. Mayet / A. Monfardini / A. Moyer-Anin
- M. Muñoz-Echeverría / I. Myserlis / A. Paliwal / L. Perotto
- G. Pisano / N. Ponthieu / V. Revéret / A. J. Rigby
- A. Ritacco / H. Roussel / F. Ruppin / M. Sánchez-Portal
- S. Savorgnano / K. Schuster / A. Sievers / C. Tucker
- R. Zylka
Summary
Millimeter galaxy surveys are particularly effective in detecting
dusty star-forming galaxies at high redshift. While such observations
are typically conducted at ~1mm, studies suggest that 2mm may be better
suited for selecting sources at even higher redshifts. We use the
unprecedented 2mm data from the N2CLS, together with the SIDES
simulation, to study and interpret the statistical properties of
2mm-selected galaxies. We use the N2CLS robust sample at 2mm, which
contains 25 sources in the deep GOODS-N field and 90 sources in the wide
COSMOS. The sources are matched with the N2CLS 1.2mm sources, the
ancillary 850um sources, and redshift catalogs to study the colors and
redshift distributions. We also produce end-to-end simulations based on
SIDES and the observed N2CLS detector timelines to interpret the data.
We find a mean S2/S1.2 color of 0.215$ $0.004. We measure a mean redshift of
$0.004. We measure a mean redshift of  in GOODS-N,
which is marginally higher than expectations from SIDES (
in GOODS-N,
which is marginally higher than expectations from SIDES ( ) because of an
overdensity at
) because of an
overdensity at  , and
, and  in COSMOS,
which agrees with the
in COSMOS,
which agrees with the  predicted by
SIDES. We also show that the observed S2/S1.2 colors exhibit a weak
dependence with redshift but a large dispersion, which limits its
efficiency to select high-z sources. Finally, we studied the nine 2mm
sources not detected at 1.2mm, and found that two of them are
radiogalaxies, one is a z~2 galaxy, and the remaining six are compatible
with the expected number of spurious detections. The N2CLS survey shows
no evidence for any exotic 2mm-only galaxy population. Using SIDES, we
show that 2mm samples have a higher mean redshift compared to 1.2mm
because they miss z~2 dusty galaxies. Finally, we compare the N2CLS with
the ex-MORA survey and show that N2CLS is more efficient than
interferometric observations to build samples of high-z dusty
galaxies.
predicted by
SIDES. We also show that the observed S2/S1.2 colors exhibit a weak
dependence with redshift but a large dispersion, which limits its
efficiency to select high-z sources. Finally, we studied the nine 2mm
sources not detected at 1.2mm, and found that two of them are
radiogalaxies, one is a z~2 galaxy, and the remaining six are compatible
with the expected number of spurious detections. The N2CLS survey shows
no evidence for any exotic 2mm-only galaxy population. Using SIDES, we
show that 2mm samples have a higher mean redshift compared to 1.2mm
because they miss z~2 dusty galaxies. Finally, we compare the N2CLS with
the ex-MORA survey and show that N2CLS is more efficient than
interferometric observations to build samples of high-z dusty
galaxies.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Nikko J. Cleri / Grace M. Olivier / Bren E. Backhaus / Joel
Leja
- Casey Papovich / Jonathan R. Trump / Pablo Arrabal Haro /
Veronique Buat
- Denis Burgarella / Emilie Burnham / Antonello
Calabro / Jonathan H. Cohn
- Justin W. Cole / Kelcey Davis / Mark Dickinson / Steven L.
Finkelstein
- Ray Garner / Michaela Hirschmann / Weida Hu / Taylor A.
Hutchison
- Dale D. Kocevski / Anton M. Koekemoer / Rebecca L. Larson / Zach J.
Lewis
- Michael V. Maseda / Lise-Marie Seille / Raymond C. Simons
Summary
High-redshift observations from JWST indicate that optical strong
line ratios do not carry the same constraining power as they do at low
redshifts. Critically, this prevents a separation between stellar- and
black hole-driven ionizing radiation, thereby obscuring both active
galactic nuclei demographics and star formation rates. To investigate
this, we compute a large suite of photoionization models from Cloudy
powered by stellar populations and accreting black holes over a large
grid of ages, metallicities, initial mass functions, binarity,
ionization parameters, densities, and black hole masses. We use these
models to test three rest-frame optical strong line ratio diagnostics
which have been designed to separate ionizing sources at low redshifts:
the [NII]-BPT, VO87, and OHNO diagrams. We show that the position of a
model in these diagrams is strongly driven by the ionization parameter
(log U) and the gas-phase metallicity, often more so than the ionizing
spectrum itself; in particular, there is significant overlap between
stellar population and accreting black hole models at high log U and low
Z. We show that the OHNO diagram is especially susceptible to large
contamination of the AGN region defined at z=1 for stellar models with
high log U and low Z, consistent with many observed JWST spectra at high
redshift. We show that the optical line ratio diagnostics are most
sensitive to the shape of the <54 eV ionizing continuum, and that the
derived ionizing sources for a given set of optical strong line ratios
can be highly degenerate. Finally, we demonstrate that very high
ionization (>54 eV) emission lines that trace ionizing sources harder
than normal stellar populations help to break the degeneracies present
when using the strong line diagnostics alone, even in gas conditions
consistent with those at high redshifts.
A
systematic search for dormant galaxies at z~5-7 from the JWST NIRSpec
archive
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alba Covelo-Paz / Corentin Meuwly / Pascal A. Oesch / Callum
Witten
- Andrea Weibel / Cristian Carvajal-Bohorquez / Laure
Ciesla / Emma Giovinazzo
- Gabriel Brammer
Summary
JWST has revealed a population of “dormant” galaxies at z>5, which
have recently halted their star formation and are characterized by weak
emission lines and significant Balmer breaks. So far, only three such
galaxies have been published at z>5 with low stellar masses,  (so-called mini-quenched galaxies), and one
massive quiescent galaxy at z>5 with
(so-called mini-quenched galaxies), and one
massive quiescent galaxy at z>5 with  , without any such galaxy reported at intermediate
masses. Here, we present a systematic search for dormant galaxies at
5<z<7.4 which halted star formation at least 10 Myr before the
time of observation. To do this, we make use of all the publicly
available NIRSpec prism data in the DAWN JWST Archive and select
galaxies showing low Hα equivalent widths (
, without any such galaxy reported at intermediate
masses. Here, we present a systematic search for dormant galaxies at
5<z<7.4 which halted star formation at least 10 Myr before the
time of observation. To do this, we make use of all the publicly
available NIRSpec prism data in the DAWN JWST Archive and select
galaxies showing low Hα equivalent widths ( Å) and
strong Balmer breaks (
Å) and
strong Balmer breaks ( ). We find 14 dormant galaxies with stellar masses
ranging from
). We find 14 dormant galaxies with stellar masses
ranging from  , revealing an intermediate-mass population of
such galaxies. By construction, the 14 sources reported are located
about 1 dex below the star-forming main sequence. Their star formation
histories suggest that they halted star formation between 10 and 25 Myr
before the time of observation which, according to models, is comparable
with the timescales of internally regulated bursts driving a “breathing”
mode of star formation. Our results show that ~1% of the galaxies in the
DJA are in a dormant phase of their star formation histories and span a
wide stellar mass range. These galaxies can be empirically selected
using only their spectral features in NIRSpec prism data.
, revealing an intermediate-mass population of
such galaxies. By construction, the 14 sources reported are located
about 1 dex below the star-forming main sequence. Their star formation
histories suggest that they halted star formation between 10 and 25 Myr
before the time of observation which, according to models, is comparable
with the timescales of internally regulated bursts driving a “breathing”
mode of star formation. Our results show that ~1% of the galaxies in the
DJA are in a dormant phase of their star formation histories and span a
wide stellar mass range. These galaxies can be empirically selected
using only their spectral features in NIRSpec prism data.
Lensing
Without Borders: Measurements of galaxy-galaxy lensing and projected
galaxy clustering in DESI DR1
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- S. Heydenreich / A. Leauthaud / C. Blake / Z. Sun
- J. U. Lange / T. Zhang / M. DeMartino / A. J. Ross
- J. Aguilar / S. Ahlen / D. Bianchi / D. Brooks
- F. J. Castander / T. Claybaugh / A. Cuceu / A. de la Macorra
- J. DeRose / Arjun Dey / Biprateep Dey / P. Doel
- N. Emas / S. Ferraro / A. Font-Ribera / J. E. Forero-Romero
- C. Garcia-Quintero / E. Gaztañaga / S. Gontcho A Gontcho / G.
Gutierrez
- B. Hadzhiyska / K. Honscheid / D. Huterer / M. Ishak
- N. Jeffrey / S. Joudaki / E. Jullo / S. Juneau
- D. Kirkby / T. Kisner / A. Kremin / A. Krolewski
- O. Lahav / C. Lamman / M. Landriau / L. Le Guillou
- M. Manera / A. Meisner / R. Miquel / S. Nadathur
- N. Palanque-Delabrouille / W. J. Percival / A. Porredon / F.
Prada
- I. Pérez-Ràfols / G. Rossi / R. Ruggeri / E. Sanchez
- C. Saulder / D. Schlegel / A. Semenaite / J. Silber
- D. Sprayberry / G. Tarlé / B. A. Weaver / S. Yuan
- P. Zarrouk / R. Zhou / H. Zou
Summary
We present Galaxy-Galaxy Lensing measurements obtained by
cross-correlating spectroscopically observed galaxies from the first
data release of the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) with
source galaxies from the Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru Strategic Survey, the
Kilo-Degree Survey, the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, and the Dark Energy
Survey. Specifically, we measure the excess surface mass density  and tangential shear
and tangential shear  for the
Bright Galaxy Sample and Luminous Red Galaxies measured within the first
year of observations with DESI. To ensure robustness, we test the
measurements for systematic biases, finding no significant trends
related to the properties of the lens galaxies. We identify a
significant trend with the average redshift of source galaxies, however,
this trend vanishes once we apply shifts to the Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru
Strategic Survey redshift distributions that are also favored by their
fiducial cosmology analysis. Additionally, we compare the observed
scatter in the measurements with the theoretical covariance and find
excess scatter, driven primarily by small-scale measurements of
for the
Bright Galaxy Sample and Luminous Red Galaxies measured within the first
year of observations with DESI. To ensure robustness, we test the
measurements for systematic biases, finding no significant trends
related to the properties of the lens galaxies. We identify a
significant trend with the average redshift of source galaxies, however,
this trend vanishes once we apply shifts to the Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru
Strategic Survey redshift distributions that are also favored by their
fiducial cosmology analysis. Additionally, we compare the observed
scatter in the measurements with the theoretical covariance and find
excess scatter, driven primarily by small-scale measurements of  ; measurements on larger scales are consistent at
the
; measurements on larger scales are consistent at
the  level. We further present
the projected clustering measurements
level. We further present
the projected clustering measurements  of the galaxy samples in the the
first data release of DESI. These measurements, which will be made
publicly available, serve as a foundation for forthcoming cosmological
analyses.
of the galaxy samples in the the
first data release of DESI. These measurements, which will be made
publicly available, serve as a foundation for forthcoming cosmological
analyses.
NIKA2
Cosmological Legacy Survey: Blind detection of galaxy clusters in the
COSMOS field via the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- D. Chérouvrier / J. F. Macias-Perez / F. X. Désert / R. Adam
- P. Ade / H. Ajeddig / S. Amarantidis / P. André
- H. Aussel / R. Barrena / A. Beelen / A. Benoit
- S. Berta / M. Béthermin / A. Bongiovanni / J. Bounmy
- O. Bourrion / L.-J. Bing / M. Calvo / A. Catalano
- M. De Petris / S. Doyle / E. F. C. Driessen / G. Ejlali
- A. Ferragamo / M. Fernandez-Torreiro / A. Gomez / J. Goupy
- C. Hanser / S. Katsioli / F. Kéruzoré / C. Kramer
- B. Ladjelate / G. Lagache / S. Leclercq / J.-F.
Lestrade
- S. C. Madden / A. Maury / F. Mayet / J.-B. Melin
- A. Monfardini / A. Moyer-Anin / M. Mu noz-Echeverria / I.
Myserlis
- R. Neri / A. Paliwal / L. Perotto / G. Pisano
- E. Pointecouteau / N. Ponthieu / G. W. Pratt / V. Reveret
- A. J. Rigby / A. Ritacco / H. Roussel / F. Ruppin
- M. Sanchez-Portal / S. Savorgnano / K. Schuster / A. Sievers
- C. Tucker / R. Zylka
Summary
(Abridged) Clusters of galaxies, formed in the latest stages of
structure formation, are unique cosmological probes. With the advent of
large CMB surveys like those from the Planck satellite, the ACT and SPT
telescopes, we now have access to a large number of galaxy clusters
detected at millimeter wavelengths via the thermal Sunyaev-Zel’dovich
(tSZ) effect. Nevertheless, it is interesting to complement them with
high-angular-resolution (tens of arcseconds) observations to target the
lowest-mass and highest-redshift clusters. This is the case of
observations with the NIKA2 camera, which is installed on the IRAM 30–m
telescope in Pico Veleta, Spain. We used the existing 150 GHz (2 mm)
data from the NIKA2 Cosmological Legacy Survey (N2CLS) Large Program to
blindly search for galaxy clusters in the well-known COSMOS field,
across a 877 arcmin region centered on (R.A., Dec.)
region centered on (R.A., Dec.) = (10h00m28.81s,
+02d17m30.44s). We first developed a dedicated data reduction pipeline
to construct NIKA2 maps at 2 mm. We then used a matched-filter algorithm
to extract cluster candidates assuming a universal pressure profile to
model the expected cluster tSZ signal. We computed the purity and
completeness of the sample by applying the previous algorithm to
simulated maps of the sky signal in the COSMOS field. We find a total of
16 cluster candidates at S/N > 4, from which eight have either an
optical or X-ray cluster (or group of galaxies) counterpart. This is the
first blind detection of clusters of galaxies at mm wavelengths at 18”
angular resolution. From this analysis, we confirm that NIKA2 and the
IRAM 30–m telescope should be sensitive to low-mass clusters at
intermediate and high redshift, complementing current and planned large
tSZ-based cluster surveys.
= (10h00m28.81s,
+02d17m30.44s). We first developed a dedicated data reduction pipeline
to construct NIKA2 maps at 2 mm. We then used a matched-filter algorithm
to extract cluster candidates assuming a universal pressure profile to
model the expected cluster tSZ signal. We computed the purity and
completeness of the sample by applying the previous algorithm to
simulated maps of the sky signal in the COSMOS field. We find a total of
16 cluster candidates at S/N > 4, from which eight have either an
optical or X-ray cluster (or group of galaxies) counterpart. This is the
first blind detection of clusters of galaxies at mm wavelengths at 18”
angular resolution. From this analysis, we confirm that NIKA2 and the
IRAM 30–m telescope should be sensitive to low-mass clusters at
intermediate and high redshift, complementing current and planned large
tSZ-based cluster surveys.
Euclid
preparation. Full-shape modelling of 2-point and 3-point correlation
functions in real space
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / M. Guidi / A. Veropalumbo / A. Pugno
- M. Moresco / E. Sefusatti / C. Porciani / E. Branchini
- M.-A. Breton / B. Camacho Quevedo / M. Crocce / S. de la Torre
- V. Desjacques / A. Eggemeier / A. Farina / M.
Kärcher
- D. Linde / M. Marinucci / A. Moradinezhad Dizgah / C. Moretti
- K. Pardede / A. Pezzotta / E. Sarpa / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / D. Bagot
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- M. Brescia / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / B. Morin / L. Moscardini
- E. Munari / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P.
Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin
Vigo
- L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / M. Maturi
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. A. Nucita / M. Pöntinen
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / A.
Balaguera-Antolinez
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / S. Contarini / A. R. Cooray / O.
Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro
- A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira
- A. Finoguenov / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / C. M. Gutierrez / C.
Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / S. Joudaki / J. J. E. Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / L. Pagano / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P. Reimberg / P.-F. Rocci
- G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith
- J. G. Sorce / K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
We investigate the accuracy and range of validity of the perturbative
model for the 2-point (2PCF) and 3-point (3PCF) correlation functions in
real space in view of the forthcoming analysis of the Euclid mission
spectroscopic sample. We take advantage of clustering measurements from
four snapshots of the Flagship I N-body simulations at z = {0.9, 1.2,
1.5, 1.8}, which mimic the expected galaxy population in the ideal case
of absence of observational effects such as purity and completeness. For
the 3PCF we consider all available triangle configurations given a
minimal separation. First, we assess the model performance by fixing the
cosmological parameters and evaluating the goodness-of-fit provided by
the perturbative bias expansion in the joint analysis of the two
statistics, finding overall agreement with the data down to separations
of 20 Mpc/h. Subsequently, we build on the state-of-the-art and extend
the analysis to include the dependence on three cosmological parameters:
the amplitude of scalar perturbations As, the matter density ωcdm and
the Hubble parameter h. To achieve this goal, we develop an emulator
capable of generating fast and robust modelling predictions for the two
summary statistics, allowing efficient sampling of the joint likelihood
function. We therefore present the first joint full-shape analysis of
the real-space 2PCF and 3PCF, testing the consistency and constraining
power of the perturbative model across both probes, and assessing its
performance in a combined likelihood framework. We explore possible
systematic uncertainties induced by the perturbative model at small
scales finding an optimal scale cut of rmin = 30 Mpc/h for the 3PCF,
when imposing an additional limitation on nearly isosceles triangular
configurations included in the data vector. This work is part of a
Euclid Preparation series validating theoretical models for galaxy
clustering.
Euclid:
An emulator for baryonic effects on the matter bispectrum
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- P. A. Burger / G. Aricò / L. Linke / R. E. Angulo
- J. C. Broxterman / J. Schaye / M. Schaller / M. Zennaro
- A. Halder / L. Porth / S. Heydenreich / M. J. Hudson
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P.
Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / C. Burigana
- L. Gabarra / A. Pezzotta / V. Scottez / M. Viel
Summary
The Euclid mission and other next-generation large-scale structure
surveys will enable high-precision measurements of the cosmic matter
distribution. Understanding the impact of baryonic processes such as
star formation and AGN feedback on matter clustering is crucial to
ensure precise and unbiased cosmological inference. Most theoretical
models of baryonic effects to date focus on two-point statistics,
neglecting higher-order contributions. This work develops a fast and
accurate emulator for baryonic effects on the matter bispectrum, a key
non-Gaussian statistic in the nonlinear regime. We employ
high-resolution 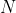 -body simulations from the BACCO suite
and apply a combination of cutting-edge techniques such as cosmology
scaling and baryonification to efficiently span a large cosmological and
astrophysical parameter space. A deep neural network is trained to
emulate baryonic effects on the matter bispectrum measured in
simulations, capturing modifications across various scales and redshifts
relevant to Euclid. We validate the emulator accuracy and robustness
using an analysis of mock data, employing predictions from the
state-of-the-art FLAMINGO hydrodynamical simulations. The emulator
reproduces baryonic suppression in the bispectrum to better than 2
-body simulations from the BACCO suite
and apply a combination of cutting-edge techniques such as cosmology
scaling and baryonification to efficiently span a large cosmological and
astrophysical parameter space. A deep neural network is trained to
emulate baryonic effects on the matter bispectrum measured in
simulations, capturing modifications across various scales and redshifts
relevant to Euclid. We validate the emulator accuracy and robustness
using an analysis of mock data, employing predictions from the
state-of-the-art FLAMINGO hydrodynamical simulations. The emulator
reproduces baryonic suppression in the bispectrum to better than 2 for the
for the  percentile across most
triangle configurations for
percentile across most
triangle configurations for ![k \in [0.01, 20]\,h^{-1}\mathrm{Mpc} k \in [0.01, 20]\,h^{-1}\mathrm{Mpc}](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20k%20%5Cin%20%5B0.01%2C%2020%5D%5C%2Ch%5E%7B-1%7D%5Cmathrm%7BMpc%7D) and
ensures consistency between cosmological posteriors inferred from
second- and third-order weak lensing statistics.
and
ensures consistency between cosmological posteriors inferred from
second- and third-order weak lensing statistics.
Articles for week 25 2025
BEBOP
VII. SOPHIE discovery of BEBOP-3b, a circumbinary giant planet on an
eccentric orbit
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Thomas A. Baycroft / Alexandre Santerne / Amaury H.
M. J. Triaud / Neda Heidari
- Daniel Sebastian / Yasmin T. Davis / Alexandre C. M. Correia /
Lalitha Sairam
- Alix V. Freckelton / Aleyna Adamson / Isabelle
Boisse / Gavin A. L. Coleman
- Georgina Dransfield / João Faria / Salomé Grouffal
/ Nathan Hara
- Guillaume Hébrard / Vedad Kunovac / David V. Martin / Pierre F. L.
Maxted
- Richard P. Nelson / Madison G. Scott / Owen J. Scutt / Matthew R.
Standing
Summary
Planetary systems orbiting close binaries are valuable testing
grounds for planet formation and migration models. More detections with
good mass measurements are needed. We present a new planet discovered
during the BEBOP survey for circumbinary exoplanets using radial
velocities. We use data taken with the SOPHIE spectrograph at the
Observatoire de Haute-Provence, and perform a spectroscopic analysis to
obtain high precision radial velocities. This planet is the first radial
velocity detection of a previously unknown circumbinary system. The
planet has a mass of 
 and orbits its host
binary in 550 days with an eccentricity of 0.25. Compared to most of the
previously known circumbinary planets, BEBOP-3b has a long period
(relative to the binary) and a high eccentricity. There also is a
candidate outer planet with a
and orbits its host
binary in 550 days with an eccentricity of 0.25. Compared to most of the
previously known circumbinary planets, BEBOP-3b has a long period
(relative to the binary) and a high eccentricity. There also is a
candidate outer planet with a  day orbital
period. We test the stability of potential further candidate signals
inside the orbit of BEBOP-3b, and demonstrate that there are stable
orbital solutions for planets near the instability region which is where
the Kepler circumbinary planets are located. We also use our data to
obtain independent dynamical masses for the two stellar components of
the eclipsing binary using High Resolution Cross-Correlation
Spectroscopy (HRCCS), and compare those results to a more traditional
approach, finding them compatible with one another.
day orbital
period. We test the stability of potential further candidate signals
inside the orbit of BEBOP-3b, and demonstrate that there are stable
orbital solutions for planets near the instability region which is where
the Kepler circumbinary planets are located. We also use our data to
obtain independent dynamical masses for the two stellar components of
the eclipsing binary using High Resolution Cross-Correlation
Spectroscopy (HRCCS), and compare those results to a more traditional
approach, finding them compatible with one another.
Euclid:
The potential of slitless infrared spectroscopy: A z=5.4 quasar and new
ultracool dwarfs
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- E. Bañados / V. Le Brun / S. Belladitta / I.
Momcheva
- D. Stern / J. Wolf / M. Ezziati / D. J. Mortlock
- A. Humphrey / R. L. Smart / S. L. Casewell / A. Pérez-Garrido
- B. Goldman / E. L. Martín / A. Mohandasan / C. Reylé
- C. Dominguez-Tagle / Y. Copin / E. Lusso / Y. Matsuoka
- K. McCarthy / F. Ricci / H.-W. Rix / H. J. A. Rottgering
- J.-T. Schindler / J. R. Weaver / A. Allaoui / T.
Bedrine
- M. Castellano / P.-Y. Chabaud / G.
Daste / F. Dufresne
- J. Gracia-Carpio / M. Kümmel / M. Moresco / M. Scodeggio
- C. Surace / D. Vibert / A.
Balestra / A. Bonnefoi
- A. Caillat / F. Cogato / A. Costille / S.
Dusini
- S. Ferriol / E. Franceschi / W. Gillard / K. Jahnke
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / E. Medinaceli / G.
Morgante
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / S. Pires / C. Sirignano
- I. T. Andika / H. Atek / D. Barrado / S. Bisogni
- C. J. Conselice / H. Dannerbauer / R. Decarli / H. Dole
- T. Dupuy / A. Feltre / S. Fotopoulou / B. Gillis
- X. Lopez Lopez / M. Onoue / G. Rodighiero / N. Sedighi
- F. Shankar / M. Siudek / L. Spinoglio / D. Vergani
- G. Vietri / F. Walter / G. Zamorani / M. R. Zapatero Osorio
- J.-Y. Zhang / M. Bethermin / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / L. Conversi
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / J.-G.
Cuby
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- C. Dolding / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- A. Ealet / M. Farina / F. Faustini / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / S. Galeotta / K. George / C. Giocoli
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes
- I. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / L. Moscardini
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / L. Gabarra / V. Scottez / M. Viel
- D. Scott
Summary
We demonstrate the potential of Euclid’s slitless spectroscopy to
discover high-redshift (z>5) quasars and their main photometric
contaminant, ultracool dwarfs. Sensitive infrared spectroscopy from
space is able to efficiently identify both populations, as demonstrated
by Euclid Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer Red Grism (NISP RGE)
spectra of the newly discovered z=5.404 quasar EUCL J181530.01+652054.0,
as well as several ultracool dwarfs in the Euclid Deep Field North and
the Euclid Early Release Observation field Abell 2764. The ultracool
dwarfs were identified by cross-correlating their spectra with
templates. The quasar was identified by its strong and broad CIII] and
MgII emission lines in the NISP RGE 1206-1892 nm spectrum, and confirmed
through optical spectroscopy from the Large Binocular Telescope. The
NISP Blue Grism (NISP BGE) 926-1366 nm spectrum confirms CIV and CIII]
emission. NISP RGE can find bright quasars at z~5.5 and z>7, redshift
ranges that are challenging for photometric selection due to
contamination from ultracool dwarfs. EUCL J181530.01+652054.0 is a
high-excitation, broad absorption line quasar detected at 144 MHz by the
LOw-Frequency Array (L144=4e25 W/Hz). The quasar has a bolometric
luminosity of 3e12 Lsun and is powered by a 3.4e9 Msun black hole. The
discovery of this bright quasar is noteworthy as fewer than one such
object was expected in the ~20 deg2 surveyed. This finding highlights
the potential and effectiveness of NISP spectroscopy in identifying
rare, luminous high-redshift quasars, previewing the census of these
sources that Euclid’s slitless spectroscopy will deliver over about
14,000 deg2 of the sky.
Testing
Light Unaffiliated Mass Clumps in MACS 0416 on galaxy and galaxy cluster
scales using JWST
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Marceau Limousin / Derek Perera / Gregor Rihtarsic
/ Liliya L. R. Williams
- Jori Liesenborgs
Summary
Light unaffiliated mass clumps (LUMCs), i.e. dark matter (DM)
components without any stellar counterparts, have been reported in
strong lensing mass reconstructions of MACS 0416, both on galaxy and
galaxy cluster scales. On galaxy cluster scale, the most recent
parametric study based on 303 multiple images features a LUMC, in the
south of the cluster. On galaxy scale, the most recent GRALE
non-parametric study based on 237 multiple images features two LUMCs, M1
and M2. Given the implications of these findings in the context of
structure formation and evolution, we test these features
parametrically, using LENSTOOL. First, we show that a mass model where
each large scale DM component introduced in the modelling is associated
with a stellar counterpart can reproduce the 303 multiple images,
removing the need for any cluster scale LUMC in . We then update the
GRALE model using the 303 multiple images, finding that one of the two
galaxy scale LUMC, M1, is no longer significant, while M2 remains. We
test M2 by explicitely including it in our parametric model. We find
that the inclusion of this LUMC does not improve the global RMS, but
mildly improves locally the RMS for one multiple image located close to
M2. Besides, the preferred mass for M2 corresponds to the lowest mass
allowed by the adopted prior. M2 is therefore not strongly favoured by a
parametric approach but it is not ruled out. We present a comparison of
parametric and non-parametric models in the M2 area. Both approaches
show very similar surface mass density at this location, with a 5-6 %
difference between the mass maps. The difference is that GRALE favors a
distinct mass substructure when LENSTOOL favors a more diffuse mass
distribution. We have been able to propose a parametric mass model
without including any LUMCs, providing further evidences for DM being
associated with light in clusters.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Suman Saha / James S. Jenkins / Vivien Parmentier / Sergio
Hoyer
- Magali Deleuil / Ian J. M. Crossfield / Pablo A.
Peña R. / Jose I. Vines
- R. Ramírez Reyes / Matías R. Díaz
Summary
Aims: In this work, we aim to confirm the high albedo of the
benchmark ultrahot Neptune LTT9779b using 20 secondary eclipse
measurements of the planet observed with CHEOPS. In addition, we perform
a search for variability in the reflected light intensity of the planet
as a function of time. Methods: First, we used the TESS follow-up data
of LTT9779b from three sectors (2, 29, and 69) to remodel the transit
signature and estimate an updated set of transit and ephemeris
parameters, which were directly used in the modeling of the secondary
eclipse lightcurves. This involved a critical noise-treatment algorithm,
including sophisticated techniques such as wavelet denoising and
Gaussian Process (GP) regression, to constrain noise levels from various
sources. In addition to using the officially released reduced aperture
photometry data from CHEOPS DRP, we also reduced the raw data using an
independent PSF photometry pipeline, known as PIPE, to verify the
robustness of our analysis. The extracted secondary eclipse lightcurves
were modeled using the PYCHEOPS package, where we have detrended the
background noise correlated with the spacecraft roll angle, originating
from the inhomogeneous and asymmetric shape of the CHEOPS point spread
function, using an N-order glint function. Results: Our independent
lightcurve analyses have resulted in consistent estimations of the
eclipse depths, with values of 89.9$
 $0.11. No significant eclipse depth variability is
detected down to a level of $$37 ppm. Conclusions: Our results confirm
that LTT9779b exhibits a strikingly high optical albedo, which
substantially reduces the internal energy budget of the planet compared
to more opaque…
$0.11. No significant eclipse depth variability is
detected down to a level of $$37 ppm. Conclusions: Our results confirm
that LTT9779b exhibits a strikingly high optical albedo, which
substantially reduces the internal energy budget of the planet compared
to more opaque…
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- G. Lagache / M. Xiao / A. Beelen /
S. Berta
- L. Ciesla / R. Neri / R. Pello /
R. Adam
- P. Ade / H. Ajeddig / S. Amarantidis / P. André
- H. Aussel / A. Benoît / M. Béthermin / L.-J. Bing
- A. Bongiovanni / J. Bounmy / O. Bourrion / M. Calvo
- A. Catalano / D. Chérouvrier / U. Chowdhury / M. De Petris
- F.-X. Désert / S. Doyle / E. F. C. Driessen / G. Ejlali
- A. Ferragamo / A. Gomez / J. Goupy / C. Hanser
- S. Katsioli / F. Kéruzoré / C. Kramer / B. Ladjelate
- S. Leclercq / J.-F. Lestrade / J. F. Macías-Pérez / S. C.
Madden
- A. Maury / F. Mayet / A. Monfardini / A. Moyer-Anin
- M. Muñoz-Echeverría / I. Myserlis / P. Oesch / A. Paliwal
- L. Perotto / G. Pisano / N. Ponthieu / V. Revéret
- A. J. Rigby / A. Ritacco / H. Roussel / F. Ruppin
- M. Sánchez-Portal / S. Savorgnano / K. Schuster / A. Sievers
- C. Tucker / R. Zylka
Summary
As part of the N2CLS Survey, we have identified a remarkable
overdensity of ten bright dusty star-forming galaxies at z$
 {}
{} {}
{} ^{11}$ M
^{11}$ M ) and highly
obscured (with a median A
) and highly
obscured (with a median A of 2.9), caught in a short-lived yet
extreme starburst phase at z$
of 2.9), caught in a short-lived yet
extreme starburst phase at z$ {}$ yr
{}$ yr ), efficient baryon to
stellar mass conversion ($ε{}>
), efficient baryon to
stellar mass conversion ($ε{}> _α$ emitters, and surpassing the cosmic average
star formation rate density for this epoch. Their properties suggest an
accelerated evolution that current models and simulations have
difficulty reproducing.
_α$ emitters, and surpassing the cosmic average
star formation rate density for this epoch. Their properties suggest an
accelerated evolution that current models and simulations have
difficulty reproducing.
Clumpiness
of galaxies revealed in the near-infrared with COSMOS-Web
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Wilfried Mercier / Boris Sindhu Kalita / Marko
Shuntov / Rafael C. Arango-Toro
- Olivier Ilbert / Laurence Tresse /
Yohan Dubois / Clotilde Laigle
- Hossein Hatamnia / Nicolas McMahon / Andreas Faisst / Isa Cox
- Maxime Trebitsch / Leo Michel-Dansac / Si-Yue Yu / Michaela
Hirschmann
- Marc Huertas-Company / Arianna Long / Anton Koekemoer / Grégoire
Aufort
- Joseph Lewis / Ghassem Gozaliasl / R. Michael Rich / Jason
Rhodes
- Henry Joy McCracken / Caitlin Casey / Jeyhan Kartaltepe / Brant
Robertson
- Maximilien Franco / Daizhong Liu / Hollis Akins / Natalie Allen
- Sune Toft
Summary
Clumps in the rest-frame UV emission of galaxies have been observed
for decades. Since the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST),
a large population is detected in the rest-frame near-infrared (NIR),
raising questions about their formation mechanism. We investigate the
presence and properties of NIR over-densities (hereafter substructures)
in star-forming and quiescent galaxies at 1 < z < 4 to understand
their link to the evolution of their host galaxy. We identify
substructures in JWST/NIRCam F277W and F444W residual images at a
rest-frame wavelength of 1 um. The fraction of galaxies with
substructures with M* > 10^9 Msun has been steadily decreasing with
cosmic time from 40% at z = 4 to 10% at z = 1. Clumps, the main small
substructures in the rest-frame NIR, are the most common type and are
much fainter (2% of the flux) than similar UV clumps in the literature.
Nearly all galaxies at the high-mass end of the main sequence (MS),
starburst, and green valley regions have substructures. However, we do
not find substructures in low-mass galaxies in the green valley and red
sequence. Although massive galaxies on the MS and in the green valley
have a 40% probability of hosting multiple clumps, the majority of
clumpy galaxies host only a single clump. The fraction of clumpy
galaxies in the rest-frame NIR is determined by the stellar mass and SFR
of the host galaxies. Its evolution with redshift is due to galaxies
moving towards lower SFRs at z < 2 and the build-up of low-mass
galaxies in the green valley and red sequence. Based on their spatial
distribution in edge-on galaxies, we infer that most of substructures
are produced in-situ via disk fragmentation. Galaxy mergers may still
play an important role at high stellar masses, especially at low
SFR.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Weibin Sun / Hong-Xin Zhang / Rory Smith / Elias Brinks
- Patrick Côté / Se-Heon Oh / Zesen Lin / Alessandro
Boselli
- Laura Ferrarese / Fujia Li / Yuzhu Sun / Lijun Chen
- Lanyue Zhang / Minsu Kim / Jaebeom Kim / Tie Li
- Bojun Tao / Matt Taylor / Pierre-Alain Duc / Ruben
Sánchez-Janssén
- Yinghe Zhao / Sanjaya Paudel / Eric W. Peng / Kaixiang Wang
- Stephen Gwyn / Matteo Fossati / Jean-Charles Cuillandre
Summary
Dwarf-dwarf galaxy mergers are among the least explored aspects of
dwarf galaxy pre-processing as they fall into clusters. We present the
first case study of a coalesced late-type dwarf major merger (VCC 479;
stellar mass  ) that
has undergone significant environmental influence, with the aim of
exploring dwarf galaxy evolution under the combined effects of galaxy
interactions and environmental processes, and understanding its
relevance to the diversity of dwarf galaxies in cluster environments.
Our analysis is based on VLA and FAST HI emission line mapping from the
Atomic gas in Virgo Interacting Dwarf galaxies (AVID) survey. We also
perform idealized hydrodynamical simulations of dwarf-dwarf mergers to
help interpret the observations. We identify symmetric stellar shell
structures in VCC 479, indicative of a coalesced major merger of dwarf
galaxies. The galaxy features a central starburst, initiated $$600 Myr
ago, embedded within an exponential disk quenched $
) that
has undergone significant environmental influence, with the aim of
exploring dwarf galaxy evolution under the combined effects of galaxy
interactions and environmental processes, and understanding its
relevance to the diversity of dwarf galaxies in cluster environments.
Our analysis is based on VLA and FAST HI emission line mapping from the
Atomic gas in Virgo Interacting Dwarf galaxies (AVID) survey. We also
perform idealized hydrodynamical simulations of dwarf-dwarf mergers to
help interpret the observations. We identify symmetric stellar shell
structures in VCC 479, indicative of a coalesced major merger of dwarf
galaxies. The galaxy features a central starburst, initiated $$600 Myr
ago, embedded within an exponential disk quenched $ $0.5% of the total stellar mass, and VCC 479’s
global star formation rate is 0.3 dex lower than typical dwarfs of
similar mass. The galaxy is highly HI deficient, with most HI gas
concentrated within the central 1 kpc and little extended HI envelope.
The misalignment of the HI velocity field with the stellar body is best
explained by merger-triggered gas inflow, as seen in our simulations.
Our analysis is consistent with a scenario that the majority of HI gas
of the progenitor galaxies was removed by the cluster environment prior
to the final coalescence. The merger concentrates the remaining gas
toward the galaxy center, triggering a central starburst. The combined
effect of environment stripping and galaxy merger has transformed VCC
479 into a blue-core dwarf undergoing morphological transition from a
late-type to an early-type galaxy.
$0.5% of the total stellar mass, and VCC 479’s
global star formation rate is 0.3 dex lower than typical dwarfs of
similar mass. The galaxy is highly HI deficient, with most HI gas
concentrated within the central 1 kpc and little extended HI envelope.
The misalignment of the HI velocity field with the stellar body is best
explained by merger-triggered gas inflow, as seen in our simulations.
Our analysis is consistent with a scenario that the majority of HI gas
of the progenitor galaxies was removed by the cluster environment prior
to the final coalescence. The merger concentrates the remaining gas
toward the galaxy center, triggering a central starburst. The combined
effect of environment stripping and galaxy merger has transformed VCC
479 into a blue-core dwarf undergoing morphological transition from a
late-type to an early-type galaxy.
Articles for week 24 2025
JWST
lens model for A370: A very low dark matter fraction for a brightest
cluster galaxy and lensing properties for the Dragon arc
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Jose M. Diego / Fengwu Sun / Jose M. Palencia / Xiaojing Lin
- Marceau Limousin / Rachel Gledhill / Anna Niemiec /
Wenlei Chen
- Rogier A. Windhorst / Mitchell F. Struble / Tom Broadhurst
Summary
We present a new lens model for the  galaxy cluster
Abell 370 based on previously spectroscopically confirmed lensed
galaxies and new lensed systems identified in JWST data, including
recent data from the MAGNIF program. Based on the best models able to
reproduce two radial arcs near the BCGs, we compare the stellar mass to
the total mass from the lens model and find that the fraction of dark
matter in the south BCG is consistent with
galaxy cluster
Abell 370 based on previously spectroscopically confirmed lensed
galaxies and new lensed systems identified in JWST data, including
recent data from the MAGNIF program. Based on the best models able to
reproduce two radial arcs near the BCGs, we compare the stellar mass to
the total mass from the lens model and find that the fraction of dark
matter in the south BCG is consistent with  CDM while in the north BCG we find a
very small amount of dark matter, more consistent with alternative
models to
CDM while in the north BCG we find a
very small amount of dark matter, more consistent with alternative
models to  CDM. We discuss possible causes for this
and conclude that additional data is needed to clarify the situation. We
study the lensing properties, magnification, time delay and strength of
the critical curve, along the Dragon arc, where previous studies have
reported tens of alleged microlensing events from supergiant stars at
CDM. We discuss possible causes for this
and conclude that additional data is needed to clarify the situation. We
study the lensing properties, magnification, time delay and strength of
the critical curve, along the Dragon arc, where previous studies have
reported tens of alleged microlensing events from supergiant stars at
 . The new lens
model is able to reproduce the distribution of microlensing events with
great accuracy. Some of the microlensing events may be reinterpreted as
long-period Cepheid in future observations. We consider this possibility
and study in more detail the challenges for such detection from
intervening microlenses.
. The new lens
model is able to reproduce the distribution of microlensing events with
great accuracy. Some of the microlensing events may be reinterpreted as
long-period Cepheid in future observations. We consider this possibility
and study in more detail the challenges for such detection from
intervening microlenses.
The
Cosmic Owl: Twin Active Collisional Ring Galaxies with Starburst Merging
Front at 
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Mingyu Li / Bjorn H. C. Emonts / Zheng Cai / Takumi S. Tanaka
- Wilfried Mercier / Yunjing Wu / Fujiang Yu / Fengwu
Sun
- Fuyan Bian / Emanuele Daddi / Xiaohui Fan / Xiaojing Lin
- Jianwei Lyu / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Francesco Valentino
Summary
Galaxy mergers play a critical role in driving galaxy evolution,
especially by transforming galaxy morphology, redistributing the gas
around galaxies, triggering AGN activity and star formation. We present
the Cosmic Owl, a galaxy merger at  , identified in the
COSMOS field. Deep imaging and spectroscopy from JWST, ALMA, and VLA
reveal a complex system of twin collisional ring galaxies, exhibiting a
nearly identical morphology. The grism spectra from the JWST COSMOS-3D
program confirm that both galaxies host an AGN. A bipolar radio jet from
one AGN extends to strike the merging front. In addition, we detect a
starburst at the merging front, characterized by luminous extended
nebular line emission and a massive cold gas reservoir. This starburst
is likely triggered by interstellar shocks induced by galaxy collision
and the AGN jet. The twin ring structure of the Cosmic Owl requires
further numerical simulations to clarify the precise conditions that
lead to the formation of this rare morphology. This system exemplifies
how shock-induced star formation, driven by galaxy collision or AGN jet,
can act as a previously underappreciated yet crucial mechanism for
efficient gas-to-star conversion and rapid stellar mass assembly in the
early Universe.
, identified in the
COSMOS field. Deep imaging and spectroscopy from JWST, ALMA, and VLA
reveal a complex system of twin collisional ring galaxies, exhibiting a
nearly identical morphology. The grism spectra from the JWST COSMOS-3D
program confirm that both galaxies host an AGN. A bipolar radio jet from
one AGN extends to strike the merging front. In addition, we detect a
starburst at the merging front, characterized by luminous extended
nebular line emission and a massive cold gas reservoir. This starburst
is likely triggered by interstellar shocks induced by galaxy collision
and the AGN jet. The twin ring structure of the Cosmic Owl requires
further numerical simulations to clarify the precise conditions that
lead to the formation of this rare morphology. This system exemplifies
how shock-induced star formation, driven by galaxy collision or AGN jet,
can act as a previously underappreciated yet crucial mechanism for
efficient gas-to-star conversion and rapid stellar mass assembly in the
early Universe.
A
circularly polarized low-frequency radio burst from the exoplanetary
system HD 189733
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- X. Zhang / P. Zarka / J. N. Girard / C. Tasse
- A. Loh / E. Mauduit / F. G. Mertens / E. Bonnassieux
- C. K. Louis / J-M. Grießmeier / J. D. Turner / L.
Lamy
- A. Strugarek / S. Corbel / B. Cecconi / O. Konovalenko
- V. Zakharenko / O. Ulyanov / P. Tokarsky / M. Tagger
Summary
We aim to detect low-frequency radio emission from exoplanetary
systems, which can provide insights into planetary magnetic fields,
star-planet interactions, stellar activity, and exo-space weather. The
HD 189733 system, hosting a well-studied hot Jupiter, is a prime target
for such searches. We conducted NenuFAR imaging observations in the
15-62 MHz range, in order to cover the entire orbital phase of HD 189733
b. Dynamic spectra were generated for the target and other sources in
the field, followed by a transient search in the time-frequency plane.
The data processing pipeline incorporated direction-dependent
calibration and noise characterization to improve sensitivity. We also
searched for periodic signals using Lomb-Scargle analysis. A highly
circularly polarized radio burst was detected at 50 MHz with a flux
density of 1.5 Jy and a significance of 6 sigma at the position of HD
189733. No counterpart was found in Stokes I, likely because the
emission is embedded in confusion noise and remains below the detection
threshold. The estimated minimum fractional circular polarization of 38%
suggests a coherent emission process. A periodicity search revealed no
weaker signals linked to the planet’s orbital period, the star’s
rotational period, or the synodic period and harmonic period between
them. The burst’s properties are consistent with cyclotron maser
instability (CMI) emission, but the origin is still ambiguous. The
comparison with theoretical models suggests star-planet interaction or
stellar activity as potential origins. However, alternative explanations
such as contamination from other sources along the line of sight
(e.g. the companion M dwarf) or noise fluctuation cannot be ruled
out.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alice P. Curtin / Shion Andrew / Sunil Simha / Alice Cai
- Kenzie Nimmo / Shami Chatterjee / Amanda M. Cook / Fengqiu Adam
Dong
- Yuxin Dong / Tarraneh Eftekhari / Wen-fai Fong / Emmanuel
Fonseca
- Jason W. T. Hessels / Ronniy C. Joseph / Victoria Kaspi / Calvin
Leung
- Robert Main / Kiyoshi W. Masui / Ryan Mckinven / Daniele
Michilli
- Mason Ng / Ayush Pandhi / Aaron B. Pearlman / Ziggy Pleunis
- Mawson W. Sammons / Ketan R. Sand / Paul Scholz / Vishwangi
Shah
- Kaitlyn Shin / Aaron Tohuvavohu
Summary
On 2024 December 28, CHIME/FRB detected the thus-far non-repeating
FRB 20241228A with a real-time signal-to-noise ratio of  . Approximately 112~s
later, the X-ray Telescope onboard the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory
was on source, the fastest follow-up to-date of a non-repeating FRB
(Tohuvavohu et al. in prep.). Using CHIME/FRB and two of the three
CHIME/FRB Outriggers, we obtained a Very Long Baseline Interferometry
localization for FRB 20241228A with a 1
. Approximately 112~s
later, the X-ray Telescope onboard the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory
was on source, the fastest follow-up to-date of a non-repeating FRB
(Tohuvavohu et al. in prep.). Using CHIME/FRB and two of the three
CHIME/FRB Outriggers, we obtained a Very Long Baseline Interferometry
localization for FRB 20241228A with a 1 confidence ellipse of 11
confidence ellipse of 11 by
0.2
by
0.2 .
This represents the first published localization using both the
CHIME-KKO and CHIME-GBO Outriggers. We associate FRB 20241228A with a
star-forming galaxy at a redshift of
.
This represents the first published localization using both the
CHIME-KKO and CHIME-GBO Outriggers. We associate FRB 20241228A with a
star-forming galaxy at a redshift of  . The persistent X-ray luminosity limit at this
source’s location and distance is
. The persistent X-ray luminosity limit at this
source’s location and distance is  erg s
erg s in the
in the  keV band, the most
stringent limit of any non-repeating FRB to-date (Tohuvavohu et al. in
prep.). The stellar mass (
keV band, the most
stringent limit of any non-repeating FRB to-date (Tohuvavohu et al. in
prep.). The stellar mass ( ) and
star formation rate (
) and
star formation rate ( ~yr
~yr ) of the host galaxy of
FRB 20241228A are consistent with the broader FRB host galaxy
population. We measure significant scattering ($
) of the host galaxy of
FRB 20241228A are consistent with the broader FRB host galaxy
population. We measure significant scattering ($ $20 kHz at 600 MHz) along the line of sight to
this source, and suggest the scintillation screen is Galactic while the
scattering screen is extragalactic. FRB 20241228A represents an exciting
example of a new era in which we can harness VLBI-localizations and
rapid high-energy follow-up to probe FRB progenitors.
$20 kHz at 600 MHz) along the line of sight to
this source, and suggest the scintillation screen is Galactic while the
scattering screen is extragalactic. FRB 20241228A represents an exciting
example of a new era in which we can harness VLBI-localizations and
rapid high-energy follow-up to probe FRB progenitors.
Euclid
preparation. Accurate and precise data-driven angular power spectrum
covariances
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / K. Naidoo / J. Ruiz-Zapatero / N.
Tessore
- B. Joachimi / A. Loureiro / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / L. Amendola / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / D. Bagot / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / L. Moscardini
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / C. Rosset
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- A. Balaguera-Antolinez / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A.
Blanchard
- L. Blot / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Conseil / A. R.
Cooray
- S. Davini / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- S. Joudaki / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- M. Lattanzi / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi
- T. I. Liaudat / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante
- S. Nadathur / A. Navarro-Alsina / L. Pagano / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
We develop techniques for generating accurate and precise internal
covariances for measurements of clustering and weak lensing angular
power spectra. These methods are designed to produce non-singular and
unbiased covariances for Euclid’s large anticipated data vector and will
be critical for validation against observational systematic effects. We
construct jackknife segments that are equal in area to high precision by
adapting the binary space partition algorithm to work on arbitrarily
shaped regions on the unit sphere. Jackknife estimates of the
covariances are internally derived and require no assumptions about
cosmology or galaxy population and bias. Our covariance estimation,
called DICES (Debiased Internal Covariance Estimation with Shrinkage),
first estimates a noisy covariance through conventional delete-1
jackknife resampling. This is followed by linear shrinkage of the
empirical correlation matrix towards the Gaussian prediction, rather
than linear shrinkage of the covariance matrix. Shrinkage ensures the
covariance is non-singular and therefore invertible, critical for the
estimation of likelihoods and validation. We then apply a delete-2
jackknife bias correction to the diagonal components of the jackknife
covariance that removes the general tendency for jackknife error
estimates to be biased high. We validate internally derived covariances,
which use the jackknife resampling technique, on synthetic Euclid-like
lognormal catalogues. We demonstrate that DICES produces accurate,
non-singular covariance estimates, with the relative error improving by
 for the covariance and
for the covariance and
 for the correlation
structure in comparison to jackknife estimates. These estimates can be
used for highly accurate regression and inference.
for the correlation
structure in comparison to jackknife estimates. These estimates can be
used for highly accurate regression and inference.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Harrison J. Souchereau / Jeffrey D. P. Kenney / Pavel Jachym / Ming
Sun
- William J. Cramer / Masafumi Yagi / Alessandro
Boselli / Elias Brinks
- Francoise Combes / Luca Cortese / Boris Deshev / Matteo Fossati
- Romana Grossova / Rongxin Luo / Jan Palous / Tom C. Scott
Summary
We present new CO(2-1) observations (resolution  pc) of the Coma cluster jellyfish galaxy NGC 4858
obtained from the ALMA-JELLY large program. Analyzing this data
alongside complimentary Subaru H
pc) of the Coma cluster jellyfish galaxy NGC 4858
obtained from the ALMA-JELLY large program. Analyzing this data
alongside complimentary Subaru H and HST (F600LP / F350LP) observations,
we find numerous structural and kinematic features indicative of the
effects from strong, inclined ram pressure, including an asymmetric
inner gas tail. We estimate a highly-inclined disk-wind angle of
and HST (F600LP / F350LP) observations,
we find numerous structural and kinematic features indicative of the
effects from strong, inclined ram pressure, including an asymmetric
inner gas tail. We estimate a highly-inclined disk-wind angle of  . By subtracting a simple circular velocity model,
we find (1): gas clumps that are being accelerated by ram pressure, and
(2): signatures of gas clumps that had been previously pushed out of the
disk but are now falling inwards. We also discuss head-tail morphologies
in star complexes within the stellar disk that appear to be
RPS-influenced. Lastly, we compare this galaxy to state-of-the-art
galaxy ``wind tunnel’’ simulations. We find that this galaxy is one of
the best nearby examples of strong and inclined ram pressure gas
stripping, and of gas that is perturbed by ram pressure but not fully
stripped and falls back. We emphasize the importance of torques due to
ram pressure in highly-inclined interactions, which help drive gas
inwards on the side rotating against the wind, contributing to the
formation of asymmetric inner RPS tails.
. By subtracting a simple circular velocity model,
we find (1): gas clumps that are being accelerated by ram pressure, and
(2): signatures of gas clumps that had been previously pushed out of the
disk but are now falling inwards. We also discuss head-tail morphologies
in star complexes within the stellar disk that appear to be
RPS-influenced. Lastly, we compare this galaxy to state-of-the-art
galaxy ``wind tunnel’’ simulations. We find that this galaxy is one of
the best nearby examples of strong and inclined ram pressure gas
stripping, and of gas that is perturbed by ram pressure but not fully
stripped and falls back. We emphasize the importance of torques due to
ram pressure in highly-inclined interactions, which help drive gas
inwards on the side rotating against the wind, contributing to the
formation of asymmetric inner RPS tails.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / W. Gillard / T. Maciaszek / E.
Prieto
- F. Grupp / A. Costille / K. Jahnke / J.
Clemens
- S. Dusini / M. Carle / C. Sirignano / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Ligori / E. Franceschi / M. Trifoglio / W.
Bon
- R. Barbier / S. Ferriol / A. Secroun / N. Auricchio
- P. Battaglia / C. Bonoli / L. Corcione / F. Hormuth
- D. Le Mignant / G. Morgante / C. Padilla / R.
Toledo-Moreo
- L. Valenziano / R. Bender / F. J. Castander / P. B. Lilje
- A. Balestra / J.-J. C. Barriere / M. Berthe / C. Boderndorf
- A. Bonnefoi / V. Capobianco / R. Casas / H.
Cho
- F. Ducret / J.-L. Gimenez / W.
Holmes / A. Hornstrup
- M. Jhabvala / E. Jullo / R. Kohley / B. Kubik
- R. Laureijs / I. Lloro / C. Macabiau / Y. Mellier
- G. Polenta / G. D. Racca / A. Renzi / M. Schirmer
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / G. Sirri / G. Smadja
- L. Stanco / S. Wachter / H. Aussel / T. Auphan
- B. R. Granett / R. Chary / Y. Copin / P. Hudelot
- V. Le Brun / F. Torradeflot / P. N. Appleton / P.
Casenove
- P.-Y. Chabaud / M. Frailis / M. Fumana / L.
Guzzo
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / M. Moresco / W. J. Percival
- R. Scaramella / M. Scodeggio / N. R. Stickley / D.
Vibert
- Y. Wang / J. Zoubian / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / J.-G. Cuby / A. Da
Silva
- R. da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit / P. Franzetti
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / S. V. H.
Haugan
- J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / I. M. Hook / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / P. Liebing
- V. Lindholm / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / E.
Sefusatti
- P. Simon / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D.
Tavagnacco
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- I. Tutusaus / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo
- L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- Y. Charles / F. Cogato / S.
Conseil / A. R. Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P. Dimauro / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. M. N. Ferguson / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J.
Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / C. J. R. McPartland / M.
Miluzio
- P. Monaco / A. Montoro / C. Moretti / S. Nadathur
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / N. A. Walton / L. Zalesky
Summary
ESA’s Euclid cosmology mission relies on the very sensitive and
accurately calibrated spectroscopy channel of the Near-Infrared
Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP). With three operational grisms in two
wavelength intervals, NISP provides diffraction-limited slitless
spectroscopy over a field of  deg
deg . A blue grism
. A blue grism  covers the wavelength range
covers the wavelength range  –
– ,nm at a spectral
resolution
,nm at a spectral
resolution  –
– for a
for a  diameter source with a dispersion of
diameter source with a dispersion of  nm px
nm px . Two red grisms
. Two red grisms  span
span  to
to  ,nm at
,nm at  –
– and a dispersion of
and a dispersion of  nm px
nm px . We describe the
construction of the grisms as well as the ground testing of the flight
model of the NISP instrument where these properties were
established.
. We describe the
construction of the grisms as well as the ground testing of the flight
model of the NISP instrument where these properties were
established.
Characterizing
the outer disk of eXtended-UV galaxies in the optical domain with deep
surveys
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- E. Bernaud / S. Boissier / Junais
/ K. Malek
- E. Hugot / G. Galaz
Summary
Aims : Extended-UV (XUV) galaxies are galaxies presenting an extended
outer ultraviolet disks. Although some Giant Low Surface Brightness
(GLSB) galaxies are also XUV, their relation has been seldom studied.
This work aims to determine whether a sample of nine XUV galaxies can be
classified as GLSBs, by analyzing their photometric properties in deep
optical images. Method : The method presented here uses optical data
from the Dark Energy Survey (DES) to construct surface brightness (SB)
profiles for each galaxy. A characteristic UV radius is defined to
examine the XUV disks. The surface brightness profiles are fitted using
simple exponential functions, and the extracted parameters are compared
with the literature to identify possible GLSB galaxies. We examined also
other diagnostics, including color profiles. Results : The analysis of
the optical surface brightness profiles of XUV galaxies reveal that they
can be classified into three different families. One third meet the GLSB
criteria in terms of diffuseness, another third are regular, and the
remaining have a stronger decline in the outer disk than in the inner
disk, opposite to GLSBs. The color profiles allowed us, in addition to
distinguish one of the galaxy, NGC1140, likely resulting from a rare
dwarf-dwarf merger.
ALMA
millimetre-wavelength imaging of HD 138965: New constraints on the
debris dust composition and presence of planetary companions
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. P. Marshall / S. Hengst / A. Trejo-Cruz / C. del Burgo
- J. Milli / M. Booth / J. C. Augereau / E.
Choquet
- F. Y. Morales / P. Thébault / F. Kemper / V. Faramaz-Gorka
- G. Bryden
Summary
HD 138965 is a young A type star and member of the nearby young Argus
association. This star is surrounded by a broad, bright debris disc with
two temperature components that was spatially resolved at far-infrared
wavelengths by Herschel. Here we present ALMA millimetre-wavelength
imaging of the cool outer belt. These reveal its radial extent to be
 au
with a width (
au
with a width ( ) of 49
) of 49 au (
au ( = 0.77), at a moderate
inclination of 49$
= 0.77), at a moderate
inclination of 49$ .
Due to the limited angular resolution, signal-to-noise, and inclination
we have no constraint on the disc’s vertical scale height. We modelled
the disc emission with both gravitational and radiation forces acting on
the dust grains. As the inner belt has not been spatially resolved, we
fixed its radius and width prior to modelling the outer belt. We find
astronomical silicate is the best fit for the dust composition. However,
we could not reject possible scenarios where there are at least 10 %
water-ice inclusions. Combining the spatially resolved imaging by ALMA
with non-detection at optical wavelengths by HST, we obtain a limit on
the scattering albedo
.
Due to the limited angular resolution, signal-to-noise, and inclination
we have no constraint on the disc’s vertical scale height. We modelled
the disc emission with both gravitational and radiation forces acting on
the dust grains. As the inner belt has not been spatially resolved, we
fixed its radius and width prior to modelling the outer belt. We find
astronomical silicate is the best fit for the dust composition. However,
we could not reject possible scenarios where there are at least 10 %
water-ice inclusions. Combining the spatially resolved imaging by ALMA
with non-detection at optical wavelengths by HST, we obtain a limit on
the scattering albedo  for the
debris dust in the outer belt. Analysis of the outer belt’s architecture
in conjunction with simple stirring models places a mass limit of
for the
debris dust in the outer belt. Analysis of the outer belt’s architecture
in conjunction with simple stirring models places a mass limit of  on a companion interior to the belt (
on a companion interior to the belt ( au), a factor
of two improvement over constraints from high contrast imaging.
au), a factor
of two improvement over constraints from high contrast imaging.
Articles for week 23 2025
A
large, chemically enriched, neutral gas reservoir in a galaxy at z =
6.782
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Saccardi / S. D. Vergani / L. Izzo / V. D’Elia
- K. E. Heintz / A. De Cia / D. B. Malesani / J. T. Palmerio
- P. Petitjean / S. Savaglio / N. R. Tanvir / R. Salvaterra
- R. Brivio / S. Campana / L. Christensen / S. Covino
- J. P. U. Fynbo / D. H. Hartmann / C. Konstantopoulou / A. J.
Levan
- A. Martin-Carrillo / A. Melandri / L. Piro / G. Pugliese
- P. Schady / B. Schneider
Summary
The chemical characterization of galaxies in the first billion years
after the Big Bang is one of the central goals of current astrophysics.
Optical/near-infrared spectroscopy of long gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) have
been heralded as an effective diagnostic to probe the interstellar
medium of their host galaxies and their metal and dust content, up to
the highest redshift. An opportunity to fulfill this expectation was
provided by the recent blast triggered by the Neil Gehrels Swift
Observatory of GRB 240218A at redshift z=6.782. We study a high-redshift
galaxy selected in a complementary way with respect to flux-limited
surveys, not depending on galaxy luminosity and stellar mass. We present
the VLT/X-shooter spectrum of its afterglow enabling the detection of
neutral-hydrogen, low-ionization, high-ionization and fine-structure
absorption lines. We determine the metallicity, kinematics and chemical
abundance pattern, providing the first detailed characterization of the
neutral gas of a galaxy at z>6.5. From the analysis of fine-structure
lines we estimate the distance of the closest gas clouds as  pc. We determine a high neutral hydrogen column
density,
pc. We determine a high neutral hydrogen column
density,  , which is
the highest one at z>6 determined so far for a GRB host galaxy, as
well as a surprisingly high metal column density,
, which is
the highest one at z>6 determined so far for a GRB host galaxy, as
well as a surprisingly high metal column density,  . The
observed metallicity of the host galaxy system is [Zn/H]>-0.8. We
find evidence of a high amount of dust depletion and of aluminum
overabundance, although a number of transitions are saturated. The high
hydrogen column density, metal abundances and dust depletion in the
neutral gas align with those of the ionized gas of very high-redshift
galaxies unveiled by ALMA and JWST, testifying that a rapid build up of
metals and dust, and massive neutral hydrogen reservoirs seem to be
common features of galaxies in the early Universe.
. The
observed metallicity of the host galaxy system is [Zn/H]>-0.8. We
find evidence of a high amount of dust depletion and of aluminum
overabundance, although a number of transitions are saturated. The high
hydrogen column density, metal abundances and dust depletion in the
neutral gas align with those of the ionized gas of very high-redshift
galaxies unveiled by ALMA and JWST, testifying that a rapid build up of
metals and dust, and massive neutral hydrogen reservoirs seem to be
common features of galaxies in the early Universe.
COSMOS-Web:
Comprehensive Data Reduction for Wide-Area JWST NIRCam Imaging
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Maximilien Franco / Caitlin M. Casey / Anton M. Koekemoer / Daizhong
Liu
- Micaela B. Bagley / Henry Joy McCracken / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe /
Hollis B. Akins
- Olivier Ilbert / Marko Shuntov / Santosh Harish /
Brant E. Robertson
- Rafael C. Arango-Toro / Andrew J. Battisti / Nima Chartab / Nicole
E. Drakos
- Andreas L. Faisst / Carter Flayhart / Ghassem Gozaliasl / Michaela
Hirschmann
- Richard Massey / Jason Rhodes / Zahra Sattari / Diana
Scognamiglio
- John R. Weaver / Lilan Yang / Jorge A. Zavala / Edward M.
Berman
- Fabrizio Gentile / Steven Gillman / Arianna S. Long / Georgios
Magdis
- Jacqueline E. McCleary / Jed McKinney / Bahram Mobasher / Louise
Paquereau
- Armin Rest / David B. Sanders / Sune Toft / Si-Yue Yu
Summary
We present the data reduction methodology used for the COSMOS-Web
survey JWST NIRCam data. Covering 0.54 deg^2 with four broadband filters
(F115W, F150W, F277W, F444W) and a total exposure time of approximately
270 hours, COSMOS-Web represents the largest contiguous field surveyed
during JWST Cycle 1, posing unique data reduction challenges due to its
extensive scale. By combining the official JWST Calibration Pipeline
with custom improvements for noise removal, background subtraction, and
astrometric alignment, we achieve high fidelity science-ready mosaics.
We detail the systematic approach employed in the three stages of the
JWST Calibration Pipeline. The data, collected in three epochs from
January 2023 to January 2024, encompass 152 visits and have been
processed into 20 mosaic tiles to optimize computational efficiency and
data processing. The final data products achieve 5 sigma depths of
26.7-28.3 AB mag in 0.15” apertures. The processed and calibrated
datasets are made available to the public.
Investigating
the HI distribution and kinematics of ESO444-G084 and [KKS2000]23: New
insights from the MHONGOOSE survey
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Brenda Namumba / Roger Ianjamasimanana / Bärbel Koribalski /
Albert Bosma
- Evangelia Athanassoula / Claude Carignan / Gyula I. G. Józsa / Peter
Kamphuis
- Roger P. Deane / Sinenhlanhla P. Sikhosana / Lourdes
Verdes-Montenegro / Amidou Sorgho
- Xola Ndaliso / Philippe Amram / Elias Brinks /
Laurent Chemin
- Francoise Combes / Erwin de Blok / Nathan Deg / Jayanne English
- Julia Healy / Sushma Kurapati / Antonino Marasco / Stacy
McGaugh
- Kyle Oman / Kristine Spekkens / Simone Veronese / O. Ivy Wong
Summary
We present the HI distribution, kinematics, mass modeling, and disk
stability of the dwarf irregular galaxies ESO444-G084 and [KKS2000]23
using high-resolution, high-sensitivity MHONGOOSE survey data from
MeerKAT. ESO444-G084 shows centrally concentrated HI emission, while
[KKS2000]23 exhibits irregular high-density clumps. Total HI fluxes
measured down to 10^19 and 10^18 cm^-2 are nearly identical, indicating
that the increased HI diameter at lower column densities results mainly
from the larger beam, with no significant extra emission detected. We
derive total HI masses of (1.1 +/- 0.1) x 10^8 and (6.1 +/- 0.3) x 10^8
solar masses for ESO444-G084 and [KKS2000]23, respectively. Using PyFAT
and TiRiFiC, we extract 3D rotation curves that reveal disk-like
kinematics in both galaxies. ESO444-G084 shows a warp beyond ~1.8 kpc
and a fast-rising curve consistent with a centrally concentrated dark
matter distribution, while [KKS2000]23’s more gradual rise suggests a
more extended halo. Mass modeling with an isothermal halo and stellar
mass-to-light ratios of 0.20 for ESO444-G084 and 0.18 for [KKS2000]23
yields consistent results. We analyze disk stability using spatially
resolved Toomre Q and gas-to-critical surface density ratios, linking
these with H-alpha and FUV-based star formation. ESO444-G084 supports
localized star formation despite global stability, while [KKS2000]23
appears gravitationally unstable yet lacks H-alpha, suggesting that
turbulence, gas depletion, or past feedback suppresses star formation.
No inflows or outflows are detected, indicating internal processes
regulate star formation. This study highlights the interplay between HI
morphology, kinematics, dark matter distribution, and disk stability,
showing how internal processes shape dwarf galaxy evolution.
COSMOS-Web:
Estimating Physical Parameters of Galaxies Using Self-Organizing
Maps
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Fatemeh Abedini / Ghassem Gozaliasl / Akram Hasani Zonoozi / Atousa
Kalantari
- Maarit Korpi-Lagg / Olivier Ilbert / Hollis Akins /
Natalie Allen
- Rafael Arango-Toro / Caitlin Casey / Nicole Drakos
/ Andreas Faisst
- Carter Flayhart / Maximilien Franco / Hosein Haghi / Santosh
Harish
- Hossein Hatamnia / Jeyhan Kartaltepe / Ali Khostovan / Anton
Koekemoer
- Vasily Kokorev / Rebecca Larson / Gavin Leroy / Daizhong Liu
- Henry McCracken / Jed McKinney / Nicolas McMahon / Wilfried
Mercier
- Bahram Mobasher / Sophie Newman / Louise Paquereau / Jason
Rhodes
- Brant Robertson / Marko Shuntov / Sina Taamoli / Sune Toft
- Francesco Valentino / Eleni Vardoulaki / John Weaver
Summary
The COSMOS-Web survey, with its unparalleled combination of multiband
data, notably, near-infrared imaging from JWST’s NIRCam (F115W, F150W,
F277W, and F444W), provides a transformative dataset down to  mag (F444W) for
studying galaxy evolution. In this work, we employ Self-Organizing Maps
(SOMs), an unsupervised machine learning method, to estimate key
physical parameters of galaxies – redshift, stellar mass, star formation
rate (SFR), specific SFR (sSFR), and age – directly from photometric
data out to
mag (F444W) for
studying galaxy evolution. In this work, we employ Self-Organizing Maps
(SOMs), an unsupervised machine learning method, to estimate key
physical parameters of galaxies – redshift, stellar mass, star formation
rate (SFR), specific SFR (sSFR), and age – directly from photometric
data out to  . SOMs efficiently
project high-dimensional galaxy color information onto 2D maps, showing
how physical properties vary among galaxies with similar spectral energy
distributions. We first validate our approach using mock galaxy catalogs
from the HORIZON-AGN simulation, where the SOM accurately recovers the
true parameters, demonstrating its robustness. Applying the method to
COSMOS-Web observations, we find that the SOM delivers robust estimates
despite the increased complexity of real galaxy populations. Performance
metrics (
. SOMs efficiently
project high-dimensional galaxy color information onto 2D maps, showing
how physical properties vary among galaxies with similar spectral energy
distributions. We first validate our approach using mock galaxy catalogs
from the HORIZON-AGN simulation, where the SOM accurately recovers the
true parameters, demonstrating its robustness. Applying the method to
COSMOS-Web observations, we find that the SOM delivers robust estimates
despite the increased complexity of real galaxy populations. Performance
metrics ( typically between
typically between  –
– , and Pearson correlation between
, and Pearson correlation between  and
and  ) confirm the precision of the method,
with
) confirm the precision of the method,
with 
 of predictions within
1
of predictions within
1 dex of reference values. Although
redshift estimation in COSMOS-Web remains challenging (median
dex of reference values. Although
redshift estimation in COSMOS-Web remains challenging (median  ), the overall success of the highlights its
potential as a powerful and interpretable tool for galaxy parameter
estimation.
), the overall success of the highlights its
potential as a powerful and interpretable tool for galaxy parameter
estimation.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- B. Kubik / R. Barbier / G. Smadja / S. Ferriol
- Y. Conseil / Y. Copin / W. Gillard / S. Dusini
- K. Jahnke / E. Prieto / N. Auricchio / E.
Balbi
- A. Balestra / P. Battaglia / V. Capobianco / R. Chary
- L. Corcione / F. Cogato / G. Delucchi / E. Franceschi
- L. Gabarra / F. Gianotti / F. Grupp / E. Lentini
- S. Ligori / E. Medinaceli / G. Morgante / K. Paterson
- E. Romelli / L. Sauniere / M. Schirmer / C. Sirignano G.
Testera
- M. Trifoglio / A. Troja / L. Valenziano / M. Frailis
- M. Scodeggio / J.-C. Barriere / M. Berthe / C. Bodendorf
- A. Caillat / M. Carle / R. Casas / H. Cho
- A. Costille / F. Ducret / B.
Garilli / W. Holmes
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / M. Jhabvala / R. Kohley
- D. Le Mignant / P. B. Lilje / I. Lloro / C.
Padilla
- G. Polenta / J.-C. Salvignol / G. Seidel / B. Serra
- A. Secroun / L. Stanco / R. Toledo-Moreo / S. Anselmi
- E. Borsato / L. Caillat / C. Colodro-Conde / V. Conforti
- J. E. Davies / A. Renzi / F. Dal Corso / S. Davini
- A. Derosa / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / D. Di Ferdinando
- R. Farinelli / A. G. Ferrari / F. Fornari / F. Giacomini
- O. Krause / F. Laudisio / J. Macias-Perez / J. Marpaud
- N. Mauri / R. da Silva / M. Niclas / F. Passalacqua
- I. Risso / P. Lagier / A. N. Sorensen / P. Stassi
- J. Steinwagner / M. Tenti / C. Thizy / S. Tosi
- R. Travaglini / O. Tubio / C. Valieri / S. Ventura
- C. Vescovi / J. Zoubian
Summary
Large-format infrared detectors are at the heart of major ground and
space-based astronomical instruments, and the HgCdTe HxRG is the most
widely used. The Near Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) of the
ESA’s Euclid mission launched in July 2023 hosts 16 H2RG detectors in
the focal plane. Their performance relies heavily on the effect of image
persistence, which results in residual images that can remain in the
detector for a long time contaminating any subsequent observations.
Deriving a precise model of image persistence is challenging due to the
sensitivity of this effect to observation history going back hours or
even days. Nevertheless, persistence removal is a critical part of image
processing because it limits the accuracy of the derived cosmological
parameters. We will present the empirical model of image persistence
derived from ground characterization data, adapted to the Euclid
observation sequence and compared with the data obtained during the
in-orbit calibrations of the satellite.
Low
noise flux estimate and data quality control monitoring in EUCLID-NISP
cosmological survey
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- B. Kubik / R. Barbier / P. Calabria / A. Castera
- E. Chabanat / F. Charlieu / J-C. Clemens / A. Ealet
- S. Ferriol / W. Gillard / T. Maciaszek / E.
Prieto
- F. Schirra / A. Secroun / B. Serra / G. Smadja
- A. Tilquin / J. Zoubianb
Summary
Euclid mission is designed to understand the dark sector of the
universe. Precise redshift measurements are provided by H2RG detectors.
We propose an unbiased method of fitting the flux with Poisson
distributed and correlated data, which has an analytic solution and
provides a reliable quality factor - fundamental features to ensure the
goals of the mission. We compare our method to other techniques of
signal estimation and illustrate the anomaly detection on the flight
like detectors. Although our discussion is focused on Euclid NISP
instrument, much of what is discussed will be of interest to any mission
using similar near-infrared sensors
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Y. Dong / C. D. Kilpatrick / W. Fong / A. P. Curtin
- S. Opoku / B. C. Andersen / A. M. Cook / T. Eftekhari
- E. Fonseca / B. M. Gaensler / R. C. Joseph / J. F. Kaczmarek
- L. A. Kahinga / V. Kaspi / A. E. Lanman / M. Lazda
- C. Leung / K. W. Masui / D. Michilli / K.
Nimmo
- A. Pandhi / A. B. Pearlman / M. Sammons / P. Scholz
- V. Shah / K. Shin / K. Smith
Summary
We present a systematic search for past supernovae (SNe) and other
historical optical transients at the positions of fast radio burst (FRB)
sources to test FRB progenitor systems. Our sample comprises 83 FRBs
detected by the Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME)
and its KKO Outrigger, along with 93 literature FRBs representing all
known well-localized FRBs. We search for optical transients coincident
in position and redshift with FRBs and find no significant associations
within the 5-sigma FRB localization uncertainties except for a
previously identified potential optical counterpart to FRB 20180916B. By
constraining the timescale for SN ejecta to become transparent to FRB
emission, we predict that it takes at least 6-10 years before the FRB
emission can escape. From this, we infer that approximately 7% of
matched optical transients, up to 30% of currently known SNe, and up to
40% of core-collapse SNe could have an observable FRB based on
timescales alone. We derive the number of new, well-localized FRBs
required to produce one FRB-SN match by chance, and find it will take ~
22,700 FRBs to yield one chance association at the projected CHIME/FRB
Outrigger detection rate. Looking forward, we demonstrate redshift
overlap between SNe detected by the upcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory
and CHIME/FRB Outrigger FRBs, indicating the prospect of an increase in
potential associations at redshift z < 1. Our framework is publicly
available, flexible to a wide range of transient timescales and FRB
localization sizes, and can be applied to any optical transient
populations in future searches.
The
Online Data Filter for the KM3NeT Neutrino Telescopes
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- O. Adriani / S. Aiello / A. Albert / A. R. Alhebsi
- M. Alshamsi / S. Alves Garre / A. Ambrosone / F. Ameli
- M. Andre / L. Aphecetche / M. Ardid / S. Ardid
- J. Aublin / F. Badaracco / L. Bailly-Salins / Z. Bardacova
- B. Baret / A. Bariego-Quintana / Y. Becherini / M. Bendahman
- F. Benfenati Gualandi / M. Benhassi / M. Bennani / D. M. Benoit
- E. Berbee / E. Berti / V. Bertin / P. Betti
- S. Biagi / M. Boettcher / D. Bonanno / S. Bottai
- A. B. Bouasla / J. Boumaaza / M. Bouta / M. Bouwhuis
- C. Bozza / R. M. Bozza / H. Branzas / F. Bretaudeau
- M. Breuhaus / R. Bruijn / J. Brunner / R. Bruno
- E. Buis / R. Buompane / J. Busto / B. Caiffi
- D. Calvo / A. Capone / F. Carenini / V. Carretero
- T. Cartraud / P. Castaldi / V. Cecchini / S. Celli
- L. Cerisy / M. Chabab / A. Chen / S. Cherubini
- T. Chiarusi / M. Circella / R. Clark / R. Cocimano
- J. A. B. Coelho / A. Coleiro / A. Condorelli / R. Coniglione
- P. Coyle / A. Creusot / G. Cuttone / R. Dallier
- A. De Benedittis / G. De Wasseige / V. Decoene / P. Deguire
- I. Del Rosso / L. S. Di Mauro / I. Di Palma / A. F. Diaz
- D. Diego-Tortosa / C. Distefano / A. Domi / C. Donzaud
- D. Dornic / E. Drakopoulou / D. Drouhin / J.-G. Ducoin
- P. Duverne / R. Dvornicky / T. Eberl / E. Eckerova
- A. Eddymaoui / T. van Eeden / M. Eff / D. van Eijk
- I. El Bojaddaini / S. El Hedri / S. El Mentawi / A. Enzenhofer
- G. Ferrara / M. D. Filipovic / F. Filippini / D. Franciotti
- L. A. Fusco / T. Gal / J. Garcia Mendez / A. Garcia Soto
- C. Gatius Oliver / N. Geiselbrecht / E. Genton / H. Ghaddari
- L. Gialanella / B. K. Gibson / E. Giorgio / I. Goos
- P. Goswami / S. R. Gozzini / R. Gracia / B. Guillon
- C. Haack / H. van Haren / A. Heijboer / L. Hennig
- J. J. Hernandez-Rey / A. Idrissi / W. Idrissi Ibnsalih / G.
Illuminati
- R. Jaimes / O. Janik / D. Joly / M. de Jong
- P. de Jong / B. J. Jung / P. Kalaczynski / J. Keegans
- V. Kikvadze / G. Kistauri / C. Kopper / A. Kouchner
- Y. Y. Kovalev / L. Krupa / V. Kueviakoe / V. Kulikovskiy
- R. Kvatadze / M. Labalme / R. Lahmann / M. Lamoureux
- G. Larosa / C. Lastoria / J. Lazar / A. Lazo
- S. Le Stum / G. Lehaut / V. Lemaitre / E. Leonora
- N. Lessing / G. Levi / M. Lindsey Clark / F. Longhitano
- F. Magnani / J. Majumdar / L. Malerba / F. Mamedov
- A. Manfreda / A. Manousakis / M. Marconi / A. Margiotta
- A. Marinelli / C. Markou / L. Martin / M.
Mastrodicasa
- S. Mastroianni / J. Mauro / K. C. K. Mehta / G. Miele
- P. Migliozzi / E. Migneco / M. L. Mitsou / C. M. Mollo
- L. Morales-Gallegos / N. Mori / A. Moussa / I. Mozun Mateo
- R. Muller / M. R. Musone / M. Musumeci / S. Navas
- A. Nayerhoda / C. A. Nicolau / B. Nkosi / B. O Fearraigh
- V. Oliviero / A. Orlando / E. Oukacha / L. Pacini
- D. Paesani / J. Palacios Gonzalez / G. Papalashvili / P. Papini
- V. Parisi / A. Parmar / E. J. Pastor Gomez / C. Pastore
- A. M. Paun / G. E. Pavalas / S. Pena Martinez / M.
Perrin-Terrin
- V. Pestel / M. Petropavlova / P. Piattelli / A. Plavin
- C. Poire / T. Pradier / J. Prado / S. Pulvirenti
- C. A. Quiroz-Rangel / N. Randazzo / A. Ratnani / S. Razzaque
- I. C. Rea / D. Real / G. Riccobene / J. Robinson
- A. Romanov / E. Ros / A. Saina / F. Salesa Greus
- D. F. E. Samtleben / A. Sanchez Losa / S. Sanfilippo / M.
Sanguineti
- D. Santonocito / P. Sapienza / M. Scaringella / M. Scarnera
- J. Schnabel / J. Schumann / J. Seneca / N. Sennan
- P. A. Sevle Myhr / I. Sgura / R. Shanidze / Chengyu Shao
- A. Sharma / Y. Shitov / F. Simkovic / A. Simonelli
- A. Sinopoulou / B. Spisso / M. Spurio / O. Starodubtsev
- D. Stavropoulos / I. Stekl / D. Stocco / M. Taiuti
- G. Takadze / Y. Tayalati / H. Thiersen / S. Thoudam
- I. Tosta e Melo / B. Trocme / V. Tsourapis / E. Tzamariudaki
- A. Ukleja / A. Vacheret / V. Valsecchi / V. Van Elewyck
- G. Vannoye / E. Vannuccini / G. Vasileiadis / F. Vazquez de
Sola
- A. Veutro / S. Viola / D. Vivolo / A. van Vliet
- E. de Wolf / I. Lhenry-Yvon / S. Zavatarelli / D. Zito
- J. D. Zornoza / J. Zuniga
Summary
The KM3NeT research infrastructure comprises two neutrino telescopes
located in the deep waters of the Mediterranean Sea, namely ORCA and
ARCA. KM3NeT/ORCA is designed for the measurement of neutrino properties
and KM3NeT/ARCA for the detection of high-energy neutrinos from the
cosmos. Neutrinos are indirectly detected using three-dimensional arrays
of photo-sensors which detect the Cherenkov light that is produced when
relativistic charged particles emerge from a neutrino interaction. The
analogue pulses from the photo-sensors are digitised offshore and all
digital data are sent to a station on shore where they are processed in
real time using a farm of commodity servers and custom software. In this
paper, the design and performance of the software that is used to filter
the data are presented. The performance of the data filter is evaluated
in terms of its efficiency, purity and capacity. The efficiency is
measured by the effective volumes of the sensor arrays as a function of
the energy of the neutrino. The purity is measured by a comparison of
the event rate caused by muons produced by cosmic ray interactions in
the Earth’s atmosphere with the event rate caused by the background from
decays of radioactive elements in the sea water and bioluminescence. The
capacity is measured by the minimal number of servers that is needed to
sustain the rate of incoming data. The results of these evaluations
comply with all specifications. The count rates of all photo-sensors are
measured with a sampling frequency of 10 Hz. These data are input to the
simulations of the detector response and will also be made available for
interdisciplinary research.
COSMOS2025:
The COSMOS-Web galaxy catalog of photometry, morphology, redshifts, and
physical parameters from JWST, HST, and ground-based imaging
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Marko Shuntov / Hollis B. Akins / Louise Paquereau / Caitlin M.
Casey
- Olivier Ilbert / Rafael C. Arango-Toro / Henry Joy
McCracken / Maximilien Franco
- Santosh Harish / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Anton M. Koekemoer / Lilan
Yang
- Marc Huertas-Company / Edward M. Berman / Jacqueline E. McCleary /
Sune Toft
- Raphaël Gavazzi / Mark J. Achenbach / Emmanuel Bertin / Malte
Brinch
- Jackie Champagne / Nima Chartab / Nicole E. Drakos / Eiichi
Egami
- Ryan Endsley / Andreas L. Faisst / Xiaohui Fan / Carter
Flayhart
- William G. Hartley / Hossein Hatamnia / Ghassem Gozaliasl / Fabrizio
Gentile
- Iris Jermann / Shuowen Jin / Koki Kakiichi / Ali Ahmad
Khostovan
- Martin Kümmel / Clotilde Laigle / Ronaldo Laishram / Erini
Lambrides
- Daizhong Liu / Jianwei Lyu / Georgios Magdis / Bahram Mobasher
- Thibaud Moutard / Alvio Renzini / Brant E. Robertson / Marc
Schefer
- Diana Scognamiglio / Nick Scoville / Zahra Sattari / David B.
Sanders
- Sina Taamoli / Benny Trakhtenbrot / Francesco Valentino / Feige
Wang
- John R. Weaver / Jinyl Yang
Summary
We present COSMOS2025, the COSMOS-Web catalog of photometry,
morphology, photometric redshifts and physical parameters for more than
700,000 galaxies in the Cosmic Evolution Survey (COSMOS) field. This
catalog is based on our 255,h COSMOS-Web program, which provides deep
near-infrared imaging in four NIRCam (F115W, F150W, F277W, F444W) and
one MIRI (F770W) filter over the central  (
( for MIRI) in COSMOS. These data are combined with
ground- and space-based data to derive photometric measurements of
NIRCam-detected sources using both fixed-aperture photometry (on the
space-based bands) and a profile-fitting technique on all 37 bands
spanning 0.3-8 micron. We provide morphology for all sources from
complementary techniques including profile fitting and machine-learning
classification. We derive photometric redshifts, physical parameters and
non-parametric star formation histories from spectral energy
distribution (SED) fitting. The catalog has been extensively validated
against previous COSMOS catalogs and other surveys. Photometric redshift
accuracy measured using spectroscopically confirmed galaxies out to
for MIRI) in COSMOS. These data are combined with
ground- and space-based data to derive photometric measurements of
NIRCam-detected sources using both fixed-aperture photometry (on the
space-based bands) and a profile-fitting technique on all 37 bands
spanning 0.3-8 micron. We provide morphology for all sources from
complementary techniques including profile fitting and machine-learning
classification. We derive photometric redshifts, physical parameters and
non-parametric star formation histories from spectral energy
distribution (SED) fitting. The catalog has been extensively validated
against previous COSMOS catalogs and other surveys. Photometric redshift
accuracy measured using spectroscopically confirmed galaxies out to  reaches
reaches  at
at  and remains at
and remains at  as a function of magnitude, color, and galaxy
type. This represents a factor of
as a function of magnitude, color, and galaxy
type. This represents a factor of  improvement at 26 AB
mag compared to COSMOS2020. The catalog is approximately 80% complete at
improvement at 26 AB
mag compared to COSMOS2020. The catalog is approximately 80% complete at
 at
at
 and at
and at  at
at
 , representing
a gain of 1,dex compared to COSMOS2020. COSMOS2025 represents the
definitive COSMOS-Web catalog. It is provided with complete
documentation, together with redshift probability distributions, and it
is ready for scientific exploitation today.
, representing
a gain of 1,dex compared to COSMOS2020. COSMOS2025 represents the
definitive COSMOS-Web catalog. It is provided with complete
documentation, together with redshift probability distributions, and it
is ready for scientific exploitation today.
Euclid
preparation. Constraining parameterised models of modifications of
gravity with the spectroscopic and photometric primary probes
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / I. S. Albuquerque / N. Frusciante / Z.
Sakr
- S. Srinivasan / L. Atayde / B. Bose / V. F. Cardone
- S. Casas / M. Martinelli / J. Noller / E. M. Teixeira
- D. B. Thomas / I. Tutusaus / M. Cataneo / K. Koyama
- L. Lombriser / F. Pace / A. Silvestri / N. Aghanim
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / D. Bonino
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / L. Corcione / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / S. Farrens / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / S. Ilić
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / E. A. Valentijn / L.
Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / S. Matthew / N. Mauri / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / V. Scottez / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / V. Allevato
- S. Alvi / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela
- A. Balaguera-Antolinez / M. Ballardini / D. Bertacca / A.
Blanchard
- L. Blot / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- R. Cabanac / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / A. Cappi
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- A. R. Cooray / S. Davini / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- S. Di Domizio / A. G. Ferrari / I. Ferrero / A. Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / F. Fornari / L. Gabarra / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / A. Jimenez Muñoz / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- M. Lattanzi / S. Lee / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- J. Martín-Fleitas / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / R. B.
Metcalf
- M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / C. Murray / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- Nicholas A. Walton / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- V. Popa / D. Potter / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci
- M. Sahlén / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / M. Sereno / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
Summary
The Euclid mission has the potential to understand the fundamental
physical nature of late-time cosmic acceleration and, as such, of
deviations from the standard cosmological model, LCDM. In this paper, we
focus on model-independent methods to modify the evolution of scalar
perturbations at linear scales. We consider two approaches: the first is
based on the two phenomenological modified gravity (PMG) parameters,
 and
and  , which are
phenomenologically connected to the clustering of matter and weak
lensing, respectively; and the second is the effective field theory
(EFT) of dark energy and modified gravity, which we use to parameterise
the braiding function,
, which are
phenomenologically connected to the clustering of matter and weak
lensing, respectively; and the second is the effective field theory
(EFT) of dark energy and modified gravity, which we use to parameterise
the braiding function,  , which defines
the mixing between the metric and the dark energy field. We discuss the
predictions from spectroscopic and photometric primary probes by Euclid
on the cosmological parameters and a given set of additional parameters
featuring the PMG and EFT models. We use the Fisher matrix method
applied to spectroscopic galaxy clustering (GCsp), weak lensing (WL),
photometric galaxy clustering (GCph), and cross-correlation (XC) between
GCph and WL. For the modelling of photometric predictions on nonlinear
scales, we use the halo model to cover two limits for the screening
mechanism: the unscreened (US) case, for which the screening mechanism
is not present; and the super-screened (SS) case, which assumes strong
screening. We also assume scale cuts to account for our uncertainties in
the modelling of nonlinear perturbation evolution. We choose a
time-dependent form for
, which defines
the mixing between the metric and the dark energy field. We discuss the
predictions from spectroscopic and photometric primary probes by Euclid
on the cosmological parameters and a given set of additional parameters
featuring the PMG and EFT models. We use the Fisher matrix method
applied to spectroscopic galaxy clustering (GCsp), weak lensing (WL),
photometric galaxy clustering (GCph), and cross-correlation (XC) between
GCph and WL. For the modelling of photometric predictions on nonlinear
scales, we use the halo model to cover two limits for the screening
mechanism: the unscreened (US) case, for which the screening mechanism
is not present; and the super-screened (SS) case, which assumes strong
screening. We also assume scale cuts to account for our uncertainties in
the modelling of nonlinear perturbation evolution. We choose a
time-dependent form for  , with two fiducial sets of values for the
corresponding model parameters at the present time,
, with two fiducial sets of values for the
corresponding model parameters at the present time,  , and two forms for
, and two forms for  , with one
fiducial set of values for each of the model parameters,
, with one
fiducial set of values for each of the model parameters,  and
and  . (Abridged)
. (Abridged)
COSMOS
Web: Morphological quenching and size-mass evolution of brightest group
galaxies from z = 3.7
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Ghassem Gozaliasl / Lilan Yang / Jeyhan Kartaltepe / Greta Toni
- Fatemeh Abedini / Hollis Akins / Natalie Allen / Rafael
Arango-Toro
- Arif Babul / Caitlin Casey / Nima Chartab / Nicole Drakos
- Andreas Faisst / Alexis Finoguenov / Carter Flayhart / Maximilien
Franco
- Gavin Leroy / Santosh Harish / Günther Hasinger / Hossein
Hatamnia
- Olivier Ilbert / Shuowen Jin / Darshan Kakkad /
Atousa Kalantari
- Ali Ahmad Khostovan / Anton Koekemoer / Maarit Korpi-Lagg / Clotilde
Laigle
- Daizhong Liu / Georgios Magdis / Matteo Maturi / Henry Joy
McCracken
- Jed McKinney / Nicolas McMahon / Bahram Mobasher / Lauro
Moscardini
- Jason Rhodes / Brant Robertson / Louise Paquereau / Annagrazia
Puglisi
- Rasha Samir / Mark Sargent / Zahra Sattari / Diana Scognamiglio
- Nick Scoville / Marko Shuntov / David Sanders / Sina Taamoli
- Sune Toft / Eleni Vardoulaki
Summary
We present a comprehensive study of the structural evolution of
Brightest Group Galaxies (BGGs) from redshift  to
to  using the ’s 255h
COSMOS-Web program. This survey provides deep NIRCam imaging in four
filters (F115W, F150W, F277W, F444W) across
using the ’s 255h
COSMOS-Web program. This survey provides deep NIRCam imaging in four
filters (F115W, F150W, F277W, F444W) across  and MIRI coverage in
and MIRI coverage in  of the COSMOS field. High-resolution NIRCam
imaging enables robust size and morphological measurements, while
multiwavelength photometry yields stellar masses, SFRs, and Sérsic
parameters. We classify BGGs as star-forming and quiescent using both
rest-frame NUV–
of the COSMOS field. High-resolution NIRCam
imaging enables robust size and morphological measurements, while
multiwavelength photometry yields stellar masses, SFRs, and Sérsic
parameters. We classify BGGs as star-forming and quiescent using both
rest-frame NUV– –
– colors and a redshift-dependent
specific star formation rate (sSFR) threshold. Our analysis reveals: (1)
quiescent BGGs are systematically more compact than their star-forming
counterparts and exhibit steeper size–mass slopes; (2) effective radii
evolve as
colors and a redshift-dependent
specific star formation rate (sSFR) threshold. Our analysis reveals: (1)
quiescent BGGs are systematically more compact than their star-forming
counterparts and exhibit steeper size–mass slopes; (2) effective radii
evolve as  , with
, with  (star-forming) and
(star-forming) and  (quiescent); (3) star formation surface density (
(quiescent); (3) star formation surface density ( )
increases with redshift and shows stronger evolution for massive BGGs
(
)
increases with redshift and shows stronger evolution for massive BGGs
( );
(4) in the
);
(4) in the  –sSFR plane, a structural
transition marks the quenching process, with bulge-dominated systems
comprising over 80% of the quiescent population. These results highlight
the co-evolution of structure and star formation in BGGs, shaped by both
internal and environmental processes, and establish BGGs as critical
laboratories for studying the baryonic assembly and morphological
transformation of central galaxies in group-scale halos.
–sSFR plane, a structural
transition marks the quenching process, with bulge-dominated systems
comprising over 80% of the quiescent population. These results highlight
the co-evolution of structure and star formation in BGGs, shaped by both
internal and environmental processes, and establish BGGs as critical
laboratories for studying the baryonic assembly and morphological
transformation of central galaxies in group-scale halos.
COSMOS-Web:
MIRI Data Reduction and Number Counts at 7.7 m using JWST
m using JWST
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Santosh Harish / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Daizhong Liu / Anton M.
Koekemoer
- Caitlin M. Casey / Maximilien Franco / Hollis B. Akins /
Olivier Ilbert
- Marko Shuntov / Nicole E. Drakos / Mike Engesser / Andreas L.
Faisst
- Ghassem Gozaliasl / Crystal L. Martin / Michaela Hirschmann / Vasily
Kokorev
- Erini Lambrides / Henry Joy McCracken / Jed McKinney / Louise
Paquereau
- Jason Rhodes / Brant E. Robertson
Summary
The COSMOS-Web survey is the largest JWST Cycle 1 General Observer
program covering a contiguous ~0.54 deg area with NIRCam imaging in four
broad-band filters and a non-contiguous ~0.2 deg
area with NIRCam imaging in four
broad-band filters and a non-contiguous ~0.2 deg with parallel MIRI imaging in a single
broad-band filter, F770W. Here we present a comprehensive overview of
the MIRI imaging observations, the data reduction procedure, the
COSMOS-Web MIRI photometric catalog, and the first data release
including the entire COSMOS-Web MIRI coverage. Data reduction is
predominantly based on the JWST Science Calibration Pipeline with an
additional step involving custom background subtraction to mitigate the
presence of strong instrumental features and sky background in the MIRI
images. We reach 5
with parallel MIRI imaging in a single
broad-band filter, F770W. Here we present a comprehensive overview of
the MIRI imaging observations, the data reduction procedure, the
COSMOS-Web MIRI photometric catalog, and the first data release
including the entire COSMOS-Web MIRI coverage. Data reduction is
predominantly based on the JWST Science Calibration Pipeline with an
additional step involving custom background subtraction to mitigate the
presence of strong instrumental features and sky background in the MIRI
images. We reach 5 (point source) limiting depths (
(point source) limiting depths ( ~25.51 based on
~25.51 based on
 ~0.3’’ circular apertures) that are
significantly better than initial expectations. We create a COSMOS-Web
MIRI catalog based on the images presented in this release and compare
the F770W flux densities with the Spitzer/IRAC CH4 measurements from the
COSMOS2020 catalog for CH4 detections with S/N
~0.3’’ circular apertures) that are
significantly better than initial expectations. We create a COSMOS-Web
MIRI catalog based on the images presented in this release and compare
the F770W flux densities with the Spitzer/IRAC CH4 measurements from the
COSMOS2020 catalog for CH4 detections with S/N  . We find that these are
in reasonable agreement with a small median offset of
. We find that these are
in reasonable agreement with a small median offset of  mag. We also
derive robust 7.7
mag. We also
derive robust 7.7 m number counts spanning five orders of
magnitude in flux ($$0.2-2300
m number counts spanning five orders of
magnitude in flux ($$0.2-2300  Jy)
Jy)  making COSMOS-Web the only JWST survey to date to efficiently sample
such a large flux range
making COSMOS-Web the only JWST survey to date to efficiently sample
such a large flux range  which is in good agreement with estimates from other JWST and IRAC
surveys.
which is in good agreement with estimates from other JWST and IRAC
surveys.
Articles for week 22 2025
EBLM
XV – Revised dynamical masses for the circumbinary planet host Kepler-16
AB, using the SOPHIE spectrograph
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- D. Sebastian / I. Boisse / A.
Santerne / A. H. M. J. Triaud
- T. A. Baycroft / Y. T. Davis / M. Deleuil /
S. Grouffal
- G. Hébrard / N. Heidari / D. V. Martin / P. F. L. Maxted
- R. P. Nelson / Lalitha S. / M. G. Scott / O. J. Scutt
- M. Standing
Summary
Eclipsing binaries are perfect laboratories to measure precise,
accurate and model-independent stellar radii and stellar masses, so long
as both components are spectroscopically resolved. Resolving both
components is difficult in high-contrast binaries, for instance, those
composed of an FGK main-sequence star with an M-type companion. In those
cases, the secondary can contribute <1% of the total flux in optical
wavelengths. This makes measuring dynamical masses challenging and has
typically only been attempted with large-aperture telescopes (8-10-m).
The High-Resolution Cross-Correlation Spectroscopy (HRCCS) method was
developed to extract weak emission and transmission spectra for
exoplanet atmospheres. This method was recently adapted and applied to
measure dynamical masses in high-contrast binaries. In this work, we
apply the HRCCS method to optical spectra of the high-contrast binary
and circumbinary planet host Kepler-16AB, obtained with the SOPHIE
spectrograph at the 1.93-m telescope at the Observatoire de
Haute-Provence. The secondary, which has a contrast ratio of ~ 6 x 10-3,
is resolved with a detection significance of 9.5-sigma. We derive
dynamical masses with a precision of 1.5% and 0.9% for the primary and
secondary respectively. These are comparable, but slightly higher
(within 2-7%) to previous mass-measurements, which has – within the
uncertainties – no implication for the mass of the known circumbinary
planet. This work demonstrates that dynamical mass measurements of
high-contrast binaries can be done with 2-m class telescopes. We also
investigate different analysis protocols to ensure we derive robust
uncertainties for dynamical masses.
A
black hole in a near-pristine galaxy 700 million years after the Big
Bang
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Roberto Maiolino / Hannah Uebler / Francesco D’Eugenio / Jan
Scholtz
- Ignas Juodzbalis / Xihan Ji / Michele Perna / Volker Bromm
- Pratika Dayal / Sophie Koudmani / Boyuan Liu / Raffaella
Schneider
- Debora Sijacki / Rosa Valiante / Alessandro Trinca / Saiyang
Zhang
- Marta Volonteri / Kohei Inayoshi / Stefano Carniani / Kimihiko
Nakajima
- Yuki Isobe / Joris Witstok / Gareth C. Jones / Sandro Tacchella
- Santiago Arribas / Andrew Bunker / Elisa Cataldi / Stephane
Charlot
- Giovanni Cresci / Mirko Curti / Andrew C. Fabian / Harley Katz
- Nimisha Kumari / Nicolas Laporte / Giovanni
Mazzolari / Brant Robertson
- Fengwu Sun / Bruno Rodriguez Del Pino / Giacomo Venturi
Summary
The recent discovery of a large number of massive black holes within
the first two billion years after the Big Bang, as well as their
peculiar properties, have been largely unexpected based on the
extrapolation of the properties of luminous quasars. These findings have
prompted the development of several theoretical models for the early
formation and growth of black holes, which are, however, difficult to
differentiate. We report the metallicity measurement around a
gravitationally lensed massive black hole at redshift 7.04 (classified
as a Little Red Dot), hosted in a galaxy with very low dynamical mass.
The weakness of the [OIII]5007 emission line relative to the narrow
H emission indicates extremely low
metallicity, less than
emission indicates extremely low
metallicity, less than  solar. We argue
that such properties cannot be uncommon among accreting black holes
around this early cosmic epoch. Explaining such a low chemical
enrichment in a system that has developed a massive black hole is
challenging for most theories. Models assuming heavy black hole seeds
(such as Direct Collapse Black Holes) or super-Eddington accretion
scenarios struggle to explain the observations, although they can
potentially reproduce the observed properties in some cases. Models
invoking “primordial black holes” (i.e. putative black holes formed
shortly after the Big Bang) may potentially explain the low chemical
enrichment associated with this black hole, although this class of
models also requires further developments for proper testing.
solar. We argue
that such properties cannot be uncommon among accreting black holes
around this early cosmic epoch. Explaining such a low chemical
enrichment in a system that has developed a massive black hole is
challenging for most theories. Models assuming heavy black hole seeds
(such as Direct Collapse Black Holes) or super-Eddington accretion
scenarios struggle to explain the observations, although they can
potentially reproduce the observed properties in some cases. Models
invoking “primordial black holes” (i.e. putative black holes formed
shortly after the Big Bang) may potentially explain the low chemical
enrichment associated with this black hole, although this class of
models also requires further developments for proper testing.
Jupiter’s
UV auroral response to a magnetospheric compression event
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- R. S. Giles / T. K. Greathouse / R. W. Ebert / W. S. Kurth
- C. K. Louis / M. F. Vogt / B. Bonfond / D. Grodent
- J.-C. Gérard / G. R. Gladstone / J. A. Kammer / V.
Hue
- R. J. Wilson / S. J. Bolton / J. E. P. Connerney
Summary
The highly elliptical polar orbit of the Juno mission provides a
unique opportunity to simultaneously measure the compression state of
Jupiter’s magnetosphere and the total power emitted by the planet’s
ultraviolet aurora, using a single spacecraft. This allows us to study
how Jupiter’s aurora respond to a compression event. In this paper, we
present a case study of an extreme compression event that occurred on
December 6-7 2022 when Juno was a distance of 70 R from Jupiter. This
extreme compression was accompanied by a very large increase in the
ultraviolet auroral emissions to 12 TW, a factor of six higher than the
baseline level. This event coincided with the predicted arrival of a
powerful interplanetary shock, which was expected to cause the largest
increase in the solar wind dynamic pressure seen thus far during the
Juno mission. The simultaneous occurrence of the interplanetary shock,
the extreme compression and the bright ultraviolet aurora suggests that
in this case, the auroral brightening was caused by the solar wind shock
compressing the magnetosphere.
from Jupiter. This
extreme compression was accompanied by a very large increase in the
ultraviolet auroral emissions to 12 TW, a factor of six higher than the
baseline level. This event coincided with the predicted arrival of a
powerful interplanetary shock, which was expected to cause the largest
increase in the solar wind dynamic pressure seen thus far during the
Juno mission. The simultaneous occurrence of the interplanetary shock,
the extreme compression and the bright ultraviolet aurora suggests that
in this case, the auroral brightening was caused by the solar wind shock
compressing the magnetosphere.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Koshy George / A. Boselli / J.-C. Cuillandre / M.
Kümmel
- A. Lançon / C. Bellhouse / T. Saifollahi / M. Mondelin
- M. Bolzonella / P. Joseph / I. D. Roberts / R. J. van Weeren
- Q. Liu / E. Sola / M. Urbano / M. Baes
- R. F. Peletier / M. Klein / C. T. Davies / I. A. Zinchenko
- J. G. Sorce / M. Poulain / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- A. Biviano / D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / J. J. Mohr
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca
- C. Burigana / L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / V. Scottez
Summary
Euclid is delivering optical and near-infrared imaging data over
14,000 deg on the sky at spatial resolution and
surface brightness levels that can be used to understand the
morphological transformation of galaxies within groups and clusters.
Using the Early Release Observations (ERO) of the Perseus cluster, we
demonstrate the capability offered by Euclid in studying the nature of
perturbations for galaxies in clusters. Filamentary structures are
observed along the discs of two spiral galaxies with no extended diffuse
emission expected from tidal interactions at surface brightness levels
of
on the sky at spatial resolution and
surface brightness levels that can be used to understand the
morphological transformation of galaxies within groups and clusters.
Using the Early Release Observations (ERO) of the Perseus cluster, we
demonstrate the capability offered by Euclid in studying the nature of
perturbations for galaxies in clusters. Filamentary structures are
observed along the discs of two spiral galaxies with no extended diffuse
emission expected from tidal interactions at surface brightness levels
of 
 . The
detected features exhibit a good correspondence in morphology between
optical and near-infrared wavelengths, with a surface brightness of
. The
detected features exhibit a good correspondence in morphology between
optical and near-infrared wavelengths, with a surface brightness of 
 , and the
knots within the features have sizes of
, and the
knots within the features have sizes of  100 pc, as observed
through
100 pc, as observed
through  imaging. Using the Euclid, CFHT,
UVIT, and LOFAR
imaging. Using the Euclid, CFHT,
UVIT, and LOFAR  radio
continuum observations, we conduct a detailed analysis to understand the
origin of the detected features. We constructed the
radio
continuum observations, we conduct a detailed analysis to understand the
origin of the detected features. We constructed the  ,
,  , and CFHT
, and CFHT  ,
,  colour-colour plane and
showed that these features contain recent star formation events, which
are also indicated by their H
colour-colour plane and
showed that these features contain recent star formation events, which
are also indicated by their H and NUV emissions. Euclid colours alone
are insufficient for studying stellar population ages in unresolved
star-forming regions, which require multi-wavelength optical imaging
data. The morphological shape, orientation, and mean age of the stellar
population, combined with the presence of extended radio continuum
cometary tails can be consistently explained if these features have been
formed during a recent ram-pressure stripping event. This result further
confirms the exceptional qualities of Euclid in the study of galaxy
evolution in dense environments.
and NUV emissions. Euclid colours alone
are insufficient for studying stellar population ages in unresolved
star-forming regions, which require multi-wavelength optical imaging
data. The morphological shape, orientation, and mean age of the stellar
population, combined with the presence of extended radio continuum
cometary tails can be consistently explained if these features have been
formed during a recent ram-pressure stripping event. This result further
confirms the exceptional qualities of Euclid in the study of galaxy
evolution in dense environments.
Articles for week 21 2025
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Cameron R. Morgan / Elizaveta Sazonova / Ian D. Roberts / Michael L.
Balogh
- Joel Roediger / Laura Ferrarese / Patrick Côté / Alessandro
Boselli
- Matteo Fossati / Jean-Charles Cuillandre / Stephen Gwyn
Summary
We analyze deep ( ) galaxy stellar mass functions (SMFs) of the
Virgo cluster using stellar masses derived as part of the Next
Generation Virgo Survey (NGVS). The total SMF has a slope of
) galaxy stellar mass functions (SMFs) of the
Virgo cluster using stellar masses derived as part of the Next
Generation Virgo Survey (NGVS). The total SMF has a slope of  which is similar to or steeper than typical field
values. Using deep data from the Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing
Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE) we separate out star-forming galaxies,
quiescent galaxies with no ongoing star formation, and low-SFR galaxies
that are intermediate between these two populations. For each of these
populations, the shape of the SMF is found to be universal throughout
the cluster, from the core to the outskirts. The star-forming and
quiescent SMFs show stark differences with values seen in field
galaxies. The relative fraction of quiescent galaxies is highest in the
core of the cluster, with low-SFR and star-forming galaxies more
significant in the outer regions of the cluster. At low stellar masses
(
which is similar to or steeper than typical field
values. Using deep data from the Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing
Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE) we separate out star-forming galaxies,
quiescent galaxies with no ongoing star formation, and low-SFR galaxies
that are intermediate between these two populations. For each of these
populations, the shape of the SMF is found to be universal throughout
the cluster, from the core to the outskirts. The star-forming and
quiescent SMFs show stark differences with values seen in field
galaxies. The relative fraction of quiescent galaxies is highest in the
core of the cluster, with low-SFR and star-forming galaxies more
significant in the outer regions of the cluster. At low stellar masses
( ), the quiescent fraction in the main cluster is
significantly higher than that of the field and even satellites of
massive groups. At high stellar masses, the quiescent fraction is
similar to other studies of cluster galaxies. We model the quiescent
population in the infall region of the cluster as a combination of
backsplash and field quiescent galaxies, and find that the backsplash
fractions needed to explain the observed population are unrealistically
high. This suggests the existence of a third population of low-mass
galaxies that are pre-processed outside the virial radius of the
cluster, possibly in groups prior to infall.
), the quiescent fraction in the main cluster is
significantly higher than that of the field and even satellites of
massive groups. At high stellar masses, the quiescent fraction is
similar to other studies of cluster galaxies. We model the quiescent
population in the infall region of the cluster as a combination of
backsplash and field quiescent galaxies, and find that the backsplash
fractions needed to explain the observed population are unrealistically
high. This suggests the existence of a third population of low-mass
galaxies that are pre-processed outside the virial radius of the
cluster, possibly in groups prior to infall.
The
CHIME/FRB Discovery of the Extremely Active Fast Radio Burst Source FRB
20240114A
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Kaitlyn Shin / Alice Curtin / Maxwell Fine / Ayush Pandhi
- Shion Andrew / Mohit Bhardwaj / Shami Chatterjee / Amanda M.
Cook
- Emmanuel Fonseca / B. M. Gaensler / Jason Hessels / Naman Jain
- Victoria M. Kaspi / Bikash Kharel / Adam E. Lanman / Mattias
Lazda
- Calvin Leung / Robert Main / Kiyoshi W. Masui / Daniele
Michilli
- Mason Ng / Kenzie Nimmo / Aaron B. Pearlman / Ue-Li Pen
- Ziggy Pleunis / Masoud Rafiei-Ravandi / Mawson Sammons / Ketan R.
Sand
- Paul Scholz / Kendrick Smith / Ingrid Stairs
Summary
Among the thousands of observed fast radio bursts (FRBs), a few
sources exhibit exceptionally high burst activity observable by many
telescopes across a broad range of radio frequencies. Almost all of
these highly active repeaters have been discovered by CHIME/FRB, due to
its daily observations of the entire Northern sky as a transit radio
telescope. FRB 20240114A is a source discovered and reported by
CHIME/FRB to the community in January 2024; given its low declination,
even the detection of a few bursts hints at a high burst rate. Following
the community announcement of this source as a potentially active
repeater, it was extensively followed up by other observatories and has
emerged as one of the most prolific FRB repeaters ever observed. This
paper presents the five bursts CHIME/FRB observed from FRB 20240114A,
with channelized raw voltage data saved for two bursts. We do not
observe changes in the DM of the source greater than ~1.3 pc cm in our observations
over nearly a year baseline. We find an RM of ~ +320 rad m
in our observations
over nearly a year baseline. We find an RM of ~ +320 rad m . We do not find
evidence for scattering at the level of < 0.3 ms in the bursts, and
we find no evidence for astrophysical scintillation. In our observations
of FRB 20240114A, we see a burst rate ~49x higher than the median burst
rate of apparent non-repeaters also discovered by CHIME/FRB. Each
discovery of highly active FRBs provides a valuable opportunity to
investigate whether there is a fundamental difference between repeating
and apparently non-repeating sources.
. We do not find
evidence for scattering at the level of < 0.3 ms in the bursts, and
we find no evidence for astrophysical scintillation. In our observations
of FRB 20240114A, we see a burst rate ~49x higher than the median burst
rate of apparent non-repeaters also discovered by CHIME/FRB. Each
discovery of highly active FRBs provides a valuable opportunity to
investigate whether there is a fundamental difference between repeating
and apparently non-repeating sources.
Articles for week 20 2025
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- V. Rawat / M. R. Samal / A. Zavagno / Sami Dib
- Davide Elia / J. Jose / D. K. Ojha / K. Srivastav1
Summary
Numerical simulations predict that clumps ($$1 pc) should form stars
at high efficiency to produce bound star clusters. We conducted a
statistical study of 17 nearby cluster-forming clumps to examine the
star formation rate and gas mass surface density relations (i.e.  vs.
vs.  ) at the
clump scale. Using near-infrared point sources and Herschel dust
continuum analysis, we obtained the radius, age, and stellar mass for
most clusters in the ranges 0.5$-
) at the
clump scale. Using near-infrared point sources and Herschel dust
continuum analysis, we obtained the radius, age, and stellar mass for
most clusters in the ranges 0.5$- -
- -
- $, respectively, and
also found that they are associated with
$, respectively, and
also found that they are associated with  values
ranging from 80$-
values
ranging from 80$- $ pc
$ pc . We obtained the
best-fit scaling relations as
. We obtained the
best-fit scaling relations as 

 and
and 

 for the
studied sample of clumps. Comparing our results with existing scaling
relations at cloud and extragalactic scales, we found that while the
power-law exponent obtained in this work is similar to those found at
these scales, the star formation rate surface densities are relatively
higher for similar gas mass surface densities. From this work, we
obtained instantaneous median star formation efficiency (SFE) and
efficiency per free-fall time (
for the
studied sample of clumps. Comparing our results with existing scaling
relations at cloud and extragalactic scales, we found that while the
power-law exponent obtained in this work is similar to those found at
these scales, the star formation rate surface densities are relatively
higher for similar gas mass surface densities. From this work, we
obtained instantaneous median star formation efficiency (SFE) and
efficiency per free-fall time ( ) of $$20%
and $$13%, respectively, for the studied clumps. We discuss the cause of
the obtained high SFE and
) of $$20%
and $$13%, respectively, for the studied clumps. We discuss the cause of
the obtained high SFE and  in the
studied clumps and also discuss the results in the context of bound
cluster formation within molecular clouds. We conclude that our results
do not favour a universal scaling law with a constant value of
in the
studied clumps and also discuss the results in the context of bound
cluster formation within molecular clouds. We conclude that our results
do not favour a universal scaling law with a constant value of  in
star-forming systems across different scales.
in
star-forming systems across different scales.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Yuichi Harikane / Ryan L. Sanders / Richard Ellis / Tucker
Jones
- Masami Ouchi / Nicolas Laporte / Guido
Roberts-Borsani / Harley Katz
- Kimihiko Nakajima / Yoshiaki Ono / Mansi Gupta
Summary
We present a JWST and ALMA detailed study of the ISM properties of
high-redshift galaxies. Our JWST/NIRSpec IFU spectroscopy targeting
three galaxies at  detects key rest-frame
optical emission lines, allowing us to derive [OII]$λλ$3726,3729-based
electron densities of
detects key rest-frame
optical emission lines, allowing us to derive [OII]$λλ$3726,3729-based
electron densities of  cm
cm on average and
[OIII]$λ$4363-based metallicities of
on average and
[OIII]$λ$4363-based metallicities of  in two galaxies. New ALMA Band 9/10 observations
detect the [OIII]52
in two galaxies. New ALMA Band 9/10 observations
detect the [OIII]52 m line in one galaxy but do not in the
others, resulting in FIR-based densities of
m line in one galaxy but do not in the
others, resulting in FIR-based densities of  cm
cm from the [OIII]52
from the [OIII]52 m/[OIII]88
m/[OIII]88 m ratios, systematically lower than the
optical [OII]-based measurements. These low FIR-based densities are
comparable to those at both
m ratios, systematically lower than the
optical [OII]-based measurements. These low FIR-based densities are
comparable to those at both  and
and  in the literature,
including JADES-GS-z14-0 at
in the literature,
including JADES-GS-z14-0 at  , suggesting little
evolution up to
, suggesting little
evolution up to  , in contrast to the
increasing trend of optical-based densities with redshift. By conducting
a JWST and ALMA joint analysis using emission lines detected with both
telescopes, we find that the observed FIR [OIII]52,88
, in contrast to the
increasing trend of optical-based densities with redshift. By conducting
a JWST and ALMA joint analysis using emission lines detected with both
telescopes, we find that the observed FIR [OIII]52,88 m luminosities are too high to be
explained by the optical-based densities at which they would be
significantly collisionally de-excited. Instead, a 2-zone model with
distinct high- and low-density regions is required to reproduce all
observed lines, indicating that FIR [OIII] emission arises predominantly
from low-density gas, while optical [OIII] and [OII] lines trace both
regions. We further demonstrate that the direct-
m luminosities are too high to be
explained by the optical-based densities at which they would be
significantly collisionally de-excited. Instead, a 2-zone model with
distinct high- and low-density regions is required to reproduce all
observed lines, indicating that FIR [OIII] emission arises predominantly
from low-density gas, while optical [OIII] and [OII] lines trace both
regions. We further demonstrate that the direct- method
can sometimes significantly underestimate metallicities up to 0.8 dex
due to the presence of the low-density gas not fully traced by optical
lines alone, highlighting the importance of combining optical and FIR
lines to accurately determine gas-phase metallicities in the early
universe.
method
can sometimes significantly underestimate metallicities up to 0.8 dex
due to the presence of the low-density gas not fully traced by optical
lines alone, highlighting the importance of combining optical and FIR
lines to accurately determine gas-phase metallicities in the early
universe.
Conditions
for accretion favoring an unmelted Callisto and a differentiated
Ganymede
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Yannis Bennacer / Olivier Mousis /
Marc Monnereau / Vincent Hue
- Antoine Schneeberger
Summary
Analysis of Callisto’s moments of inertia, derived from Galileo’s
gravity data, suggests that its structure is not fully differentiated.
This possibly undifferentiated state contrasts sharply with the globally
molten state inferred in its counterpart, Ganymede, and poses unique
challenges to theories of the formation and evolution of the Galilean
moons. During their formation, both moons experienced multiple heating
mechanisms, including tidal heating, radiogenic heating from short-lived
radionuclides, accretional heating from impacts, and heat from the
surrounding circumplanetary disk. Our study investigates the optimal
conditions required to account for Callisto’s partially differentiated
state in contrast to Ganymede’s complete differentiation. We investigate
crucial accretion parameters, such as the timing of accretion onset, the
duration of accretion, and the impactor size distribution. We find that
the observed dichotomy between Ganymede and Callisto can be attributed
to similar formation conditions, assuming an identical impactor size
distribution and composition in the Jovian circumplanetary disk. The key
differences in the formation of Ganymede and Callisto are the disk
temperature at their respective formation locations and their final
radii. Our results indicate that both moons accreted gradually over more
than 2 Myr, concluding at least 5.5 Myr after the formation of
calcium-aluminum-rich inclusions in the protosolar nebula. Our model
demonstrates that Callisto can remain undifferentiated despite accreting
a substantial influx of kilometer-sized impactors, potentially
contributing up to 30% of the total mass inflow, while still allowing
for the complete differentiation of Ganymede.
Euclid:
Photometric redshift calibration with the clustering redshifts
technique
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- W. d’Assignies / M. Manera / C. Padilla / O.
Ilbert
- H. Hildebrandt / L. Reynolds / J. Chaves-Montero / A. H. Wright
- P. Tallada-Crespí / M. Eriksen / J. Carretero / W. Roster
- Y. Kang / K. Naidoo / R. Miquel / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- D. Bagot / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone
- S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Crocce / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / M. Douspis
- X. Dupac / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / D. C. Masters / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor
- H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca
- M. Bolzonella / C. Burigana / L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Viel
Summary
Aims: The precision of cosmological constraints from imaging surveys
hinges on accurately estimating the redshift distribution $ n(z) $ of
tomographic bins, especially their mean redshifts. We assess the
effectiveness of the clustering redshifts technique in constraining
Euclid tomographic redshift bins to meet the target uncertainty of $ σ(
z ) < 0.002 (1 + z) $. In this work, these mean redshifts are
inferred from the small-scale angular clustering of Euclid galaxies,
which are distributed into bins with spectroscopic samples localised in
narrow redshift slices. Methods: We generate spectroscopic mocks from
the Flagship2 simulation for the Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey
(BOSS), the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), and Euclid’s
Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) spectroscopic survey.
We evaluate and optimise the clustering redshifts pipeline, introducing
a new method for measuring photometric galaxy bias (clustering), which
is the primary limitation of this technique. Results: We have
successfully constrained the means and standard deviations of the
redshift distributions for all of the tomographic bins (with a maximum
photometric redshift of 1.6), achieving precision beyond the required
thresholds. We have identified the main sources of bias, particularly
the impact of the 1-halo galaxy distribution, which imposed a minimal
separation scale of 1.5 Mpc for evaluating cross-correlations. These
results demonstrate the potential of clustering redshifts to meet the
precision requirements for Euclid, and we highlight several avenues for
future improvements.
Articles for week 19 2025
CHEX-MATE:
exploring the kinematical properties of Planck galaxy clusters
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Lorenzo Pizzuti / Rafael Barrena / Mauro Sereno / Alina
Streblyanska
- Antonio Ferragamo / Sophie Maurogordato / Alberto Cappi / Stefano
Ettori
- Gabriel W. Pratt / Gianluca Castignani / Megan Donahue / Dominique
Eckert
- Fabio Gastaldello / Raphael Gavazzi / Christopher
P. Haines / Scott T. Kay
- Lorenzo Lovisari / Ben J. Maughan / Etienne Pointecouteau / Elena
Rasia
- Mario Radovich / Jack Sayers
Summary
We analyse the kinematical properties of the CHEX-MATE (Cluster
HEritage project with XMM-Newton - Mass Assembly and Thermodynamics at
the Endpoint of structure formation) galaxy cluster sample. […] We
derive cluster mass profiles for 75 clusters using the procedure, which
recovers the gravitational potential and the anisotropy profiles from
line-of-sight velocities and projected positions of galaxy members. The
standard NFW and the Burkert models with flatter cores than NFW both
adequately fit the kinematic data, with only marginal statistical
preference for one model over the other. An estimation of the mass bias
$(1-B_1) = M^{SZ}{500}/M^{M}{500} $ is performed from the
comparison with SZ-X-ray-calibrated mass estimates, resulting in a value
of $ 0.54 $ when four evidently disturbed clusters are removed from the
sample. We assess the dynamical state of the clusters by inferring the
Anderson-Darling coefficient  and the fraction of
galaxies in substructures (
and the fraction of
galaxies in substructures ( ). Except
for a few cases, we found relatively low values for
). Except
for a few cases, we found relatively low values for  , suggesting that CHEX-MATE
clusters are not too far from relaxation. Moreover, no significant
trends emerge among
, suggesting that CHEX-MATE
clusters are not too far from relaxation. Moreover, no significant
trends emerge among  and the difference between the log-masses
estimated by and by SZ-X-ray. We study the concentration-mass relation
for the sample; despite the large scatter, we observe signs of an
increasing trend for large-mass clusters, in agreement with recent
theoretical expectations. Finally, the analysis of radial anisotropy
profiles of member galaxies - stacked in five bins of mass and redshift
- reveals that orbits tend to be isotropic at the center and more radial
towards the edge, as already found in previous studies. A slight trend
of increasing radial orbits at
and the difference between the log-masses
estimated by and by SZ-X-ray. We study the concentration-mass relation
for the sample; despite the large scatter, we observe signs of an
increasing trend for large-mass clusters, in agreement with recent
theoretical expectations. Finally, the analysis of radial anisotropy
profiles of member galaxies - stacked in five bins of mass and redshift
- reveals that orbits tend to be isotropic at the center and more radial
towards the edge, as already found in previous studies. A slight trend
of increasing radial orbits at  is observed in
clusters with larger velocity dispersion
is observed in
clusters with larger velocity dispersion
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Paolo Suin / Doris Arzoumanian / Annie
Zavagno / Patrick Hennebelle
Summary
Context: Filaments are common features in molecular clouds and they
play a key role in star formation (SF). Studying their life cycle is
essential to fully understand the SF process. Aims: We aim to
characterise the impact of magnetic field ( ) and stellar feedback on the evolution
of filamentary structures in star-forming clouds. Methods: We performed
two numerical simulations of a collapsing
) and stellar feedback on the evolution
of filamentary structures in star-forming clouds. Methods: We performed
two numerical simulations of a collapsing  M
M cloud with different
mass-to-flux ratios (
cloud with different
mass-to-flux ratios ( and
and  ), including early stellar
feedback (jets and HII regions). Using DisPerSE, we extracted the
three-dimensional filamentary network and analysed its properties as it
evolves throughout the SF event. Results: We observed that the
filamentary network in the simulations follow two distinct evolutionary
pathways. In the strongly magnetised case, the cloud maintains a sparser
filamentary network, and the arising filaments are predominantly
perpendicular to
), including early stellar
feedback (jets and HII regions). Using DisPerSE, we extracted the
three-dimensional filamentary network and analysed its properties as it
evolves throughout the SF event. Results: We observed that the
filamentary network in the simulations follow two distinct evolutionary
pathways. In the strongly magnetised case, the cloud maintains a sparser
filamentary network, and the arising filaments are predominantly
perpendicular to  lines. With a weak field, the cloud
develops a single central hub, with converging filaments favouring a
parallel alignment relative to
lines. With a weak field, the cloud
develops a single central hub, with converging filaments favouring a
parallel alignment relative to  . Furthermore, while always accreting,
filaments exhibit faster flows towards the hub relative to the
surrounding gas. In the weakly magnetised run, the central hub dominates
the dynamics, and filaments exhibit faster flows as they approach the
central hub. Finally, once the expanding HII region impacts the
filaments, they align to
. Furthermore, while always accreting,
filaments exhibit faster flows towards the hub relative to the
surrounding gas. In the weakly magnetised run, the central hub dominates
the dynamics, and filaments exhibit faster flows as they approach the
central hub. Finally, once the expanding HII region impacts the
filaments, they align to  independently of the initial
configuration. Conclusions: Magnetic fields play a critical role in
shaping the structure and dynamics of molecular clouds. Stronger
magnetic fields slow the cloud’s evolution and inhibit the formation of
central hubs, promoting a broader filamentary network instead. However,
ionising feedback dominates the late-stage evolution, overriding the
initial differences and dictating the final filament configuration.
independently of the initial
configuration. Conclusions: Magnetic fields play a critical role in
shaping the structure and dynamics of molecular clouds. Stronger
magnetic fields slow the cloud’s evolution and inhibit the formation of
central hubs, promoting a broader filamentary network instead. However,
ionising feedback dominates the late-stage evolution, overriding the
initial differences and dictating the final filament configuration.
CAPERS-LRD-z9:
A Gas Enshrouded Little Red Dot Hosting a Broad-line AGN at z=9.288
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Anthony J. Taylor / Vasily Kokorev / Dale D. Kocevski / Hollis B.
Akins
- Fergus Cullen / Mark Dickinson / Steven L. Finkelstein / Pablo
Arrabal Haro
- Volker Bromm / Mauro Giavalisco / Kohei Inayoshi / Stephanie
Juneau
- Gene C. K. Leung / Pablo G. Perez-Gonzalez / Rachel S. Somerville /
Jonathan R. Trump
- Ricardo O. Amorin / Guillermo Barro / Denis
Burgarella / Madisyn Brooks
- Adam Carnall / Caitlin M. Casey / Yingjie Cheng / John Chisholm
- Katherine Chworowsky / Kelcey Davis / Callum T. Donnan / James S.
Dunlop
- Richard S. Ellis / Vital Fernandez / Seiji Fujimoto / Norman A.
Grogin
- Ansh R. Gupta / Nimish P. Hathi / Intae Jung / Michaela
Hirschmann
- Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Anton M. Koekemoer / Rebecca L. Larson /
Ho-Hin Leung
- Mario Llerena / Ray A. Lucas / Derek J. McLeod / Ross McLure
- Lorenzo Napolitano / Casey Papovich / Thomas M. Stanton / Roberta
Tripodi
- Xin Wang / Stephen M. Wilkins / L. Y. Aaron Yung / Jorge A.
Zavala
Summary
We present CAPERS-LRD-z9, a little red dot (LRD) which we confirm to
be a  broad-line AGN
(BLAGN). First identified as a high-redshift LRD candidate from PRIMER
NIRCam photometry, follow-up NIRSpec/PRISM spectroscopy of CAPERS-LRD-z9
from the CANDELS-Area Prism Epoch of Reionization Survey (CAPERS) has
revealed a broad
broad-line AGN
(BLAGN). First identified as a high-redshift LRD candidate from PRIMER
NIRCam photometry, follow-up NIRSpec/PRISM spectroscopy of CAPERS-LRD-z9
from the CANDELS-Area Prism Epoch of Reionization Survey (CAPERS) has
revealed a broad  km s
km s H
H emission line and narrow [O III]
emission line and narrow [O III] lines, indicative of a BLAGN. Based on the broad H
lines, indicative of a BLAGN. Based on the broad H line, we compute a canonical black-hole
mass of
line, we compute a canonical black-hole
mass of  , although full consideration of systematic
uncertainties yields a conservative range of
, although full consideration of systematic
uncertainties yields a conservative range of  . These observations suggest that either a massive
black hole seed, or a lighter stellar remnant seed undergoing periods of
super-Eddington accretion, is necessary to grow such a massive black
hole in
. These observations suggest that either a massive
black hole seed, or a lighter stellar remnant seed undergoing periods of
super-Eddington accretion, is necessary to grow such a massive black
hole in  Myr of
cosmic time. CAPERS-LRD-z9 exhibits a strong Balmer break, consistent
with a central AGN surrounded by dense (
Myr of
cosmic time. CAPERS-LRD-z9 exhibits a strong Balmer break, consistent
with a central AGN surrounded by dense ( ) neutral
gas. We model CAPERS-LRD-z9 using CLOUDY to fit the emission red-ward of
the Balmer break with a dense gas-enshrouded AGN, and bagpipes to fit
the rest-ultraviolet emission as a host-galaxy stellar population. This
upper limit on the stellar mass of the host galaxy (
) neutral
gas. We model CAPERS-LRD-z9 using CLOUDY to fit the emission red-ward of
the Balmer break with a dense gas-enshrouded AGN, and bagpipes to fit
the rest-ultraviolet emission as a host-galaxy stellar population. This
upper limit on the stellar mass of the host galaxy ( ) implies that the black-hole to stellar mass
ratio may be extremely large, possibly
) implies that the black-hole to stellar mass
ratio may be extremely large, possibly  (although
systematic uncertainties on the black-hole mass prevent strong
conclusions). However, the shape of the UV continuum differs from
typical high-redshift star-forming galaxies, indicating that this UV
emission may also be of AGN origin, and hence the true stellar mass of
the host may be still lower.
(although
systematic uncertainties on the black-hole mass prevent strong
conclusions). However, the shape of the UV continuum differs from
typical high-redshift star-forming galaxies, indicating that this UV
emission may also be of AGN origin, and hence the true stellar mass of
the host may be still lower.
A
catalogue of candidate milli-parsec separation massive black hole
binaries from long term optical photometric monitoring
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Vincent Foustoul / Natalie A. Webb / Raphaël
Mignon-Risse / Elias Kammoun
- Marta Volonteri / Chi An Dong-Páez
Summary
The role of mergers in the evolution of massive black holes is still
unclear, and their dynamical evolution, from the formation of pairs to
binaries and the final coalescence, carries large physical
uncertainties. The identification of the elusive population of close
massive binary black holes (MBBHs) is crucial to understand the
importance of mergers in the formation and evolution of supermassive
black holes. It has been proposed that MBBHs may display periodic
optical/ultra-violet variability. Optical surveys provide photometric
measurements of a large variety of objects, over decades and searching
for periodicities coming from galaxies in their long-term optical/UV
lightcurves may help identify new MBBH candidates. Using the Catalina
Real-Time Transient Survey (CRTS) and Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF)
data, we studied the long-term periodicity of variable sources in the
centre of galaxies identified using the galaxy catalogue Glade+. We
report 36 MBBHs candidates, with sinusoidal variability with amplitudes
between 0.1 and 0.8 magnitudes over 3-5 cycles, through fitting 15 years
of data. The periodicities are also detected when adding a red noise
contribution to the sine model. Moreover, the periodicities are
corroborated through Generalized Lomb Scargle (GLS) periodograms
analysis, providing supplementary evidence for the observed modulation.
We also indicate 58 objects, that were previously proposed to be MBBH
candidates from analysis of CRTS data only. Adding ZTF data clearly
shows that the previously claimed modulation is due to red noise. We
also created a catalogue of 221 weaker candidates which require further
observations over the coming years to help validate their nature. Based
on our 36 MBBHs candidates, we expect ~20 MBBHs at z<1, which is
commensurate with simulations. Further observations will help confirm
these results.
Gravitational
Lenses in UNIONS and Euclid (GLUE) I: A Search for Strong Gravitational
Lenses in UNIONS with Subaru, CFHT, and Pan-STARRS Data
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Christopher J. Storfer / Eugene A. Magnier / Xiaosheng Huang / David
Rubin
- David J. Schlegel / Saurav Banka / Kenneth C. Chambers /
Jean-Charles Cuillandre
- Thomas de Boer / Raphael Gavazzi / Stephen Gwyn /
Michael J. Hudson
- Gregory S. H. Paek / Douglas Scott
Summary
We present the results of our pipeline for discovering strong
gravitational lenses in the ongoing Ultraviolet Near-Infrared Optical
Northern Survey (UNIONS). We successfully train the deep residual neural
network (ResNet) based on CMU-Deeplens architecture, which is designed
to detect strong lenses in ground-based imaging surveys. We train on
images of real strong lenses and deploy on a sample of 8 million
galaxies in areas with full coverage in the g, r, and i filters, the
first multi-band search for strong gravitational lenses in UNIONS.
Following human inspection and grading, we report the discovery of a
total of 1346 new strong lens candidates of which 146 are grade A, 199
grade B, and 1001 grade C. Of these candidates, 283 have lens-galaxy
spectroscopic redshifts from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) and an
additional 297 from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Data
Release 1 (DR1). We find 15 of these systems display evidence of both
lens and source galaxy redshifts in spectral superposition. We
additionally report the spectroscopic confirmation of seven lensed
sources in highquality systems, all with z > 2.1, using the Keck
Near-Infrared Echelle Spectrograph (NIRES) and Gemini Near-Infrared
Spectrograph (GNIRS).
Variability of
X-ray polarization of Cyg X-1
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Vadim Kravtsov / Anastasiia Bocharova / Alexandra Veledina / Juri
Poutanen
- Andrew K. Hughes / Michal Dovčiak / Elise Egron / Fabio Muleri
- Jakub Podgorny / Jiři Svoboda / Sofia V. Forsblom / Andrei V.
Berdyugin
- Dmitry Blinov / Joe S. Bright / Francesco Carotenuto / David A.
Green
- Adam Ingram / Ioannis Liodakis / Nikos Mandarakas /
Anagha P. Nitindala
- Lauren Rhodes / Sergei A. Trushkin / Sergey S. Tsygankov / Maimouna
Brigitte
- Alessandro Di Marco / Noemi Iacolina / Henric Krawczynski / Fabio La
Monaca
- Vladislav Loktev / Guglielmo Mastroserio / Pierre-Olivier Petrucci /
Maura Pilia
- Francesco Tombesi / Andrzej A. Zdziarski
Summary
We present the results of a three-year X-ray, optical, and radio
polarimetric monitoring campaign of the prototypical black hole X-ray
binary Cyg X-1, conducted from 2022 to 2024. The X-ray polarization of
Cyg X-1 was measured 13 times with the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry
Explorer (IXPE), covering both hard and soft spectral states. The X-ray
polarization degree (PD) in the hard state was found to be  , roughly
twice as high as in the soft state, where it was around
, roughly
twice as high as in the soft state, where it was around  . In both states, a
statistically significant increase of PD with the energy was found.
Moreover, a linear relation between PD and spectral hardness suggests a
gradual and continuous evolution of the polarization properties, rather
than an abrupt change of polarization production mechanism between
states. The polarization angle (PA) was independent of the spectral
state and showed no trend with the photon energy. The X-ray PA is well
aligned with the orientation of the radio jet, as well as the optical
and radio PAs. We find significant orbital changes of PA in the hard
state, which we attribute to scattering of X-ray emission at intrabinary
structure. No significant superorbital variability in PD or PA was found
at the period
. In both states, a
statistically significant increase of PD with the energy was found.
Moreover, a linear relation between PD and spectral hardness suggests a
gradual and continuous evolution of the polarization properties, rather
than an abrupt change of polarization production mechanism between
states. The polarization angle (PA) was independent of the spectral
state and showed no trend with the photon energy. The X-ray PA is well
aligned with the orientation of the radio jet, as well as the optical
and radio PAs. We find significant orbital changes of PA in the hard
state, which we attribute to scattering of X-ray emission at intrabinary
structure. No significant superorbital variability in PD or PA was found
at the period  = 294 d. We
also find no correlation between the X-ray and optical polarization; if
any, there is a long-term anti-correlation between the X-ray PD and the
radio PD.
= 294 d. We
also find no correlation between the X-ray and optical polarization; if
any, there is a long-term anti-correlation between the X-ray PD and the
radio PD.
Euclid
preparation. The impact of redshift interlopers on the two-point
correlation function analysis
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / I. Risso / A. Veropalumbo / E. Branchini
- E. Maragliano / S. de la Torre / E. Sarpa / P. Monaco
- B. R. Granett / S. Lee / G. E. Addison / S. Bruton
- C. Carbone / G. Lavaux / K. Markovic / K. McCarthy
- G. Parimbelli / F. Passalacqua / W. J. Percival / C. Scarlata
- E. Sefusatti / Y. Wang / M. Bonici / F. Oppizzi
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- D. Bonino / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Crocce / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole / M. Douspis
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- A. M. C. Le Brun / P. Liebing / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / C. Surace / P.
Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- D. Vibert / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M.
Zerbi
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G.
Hartley
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / S. Avila / A. Balaguera-Antolinez / C.
Benoist
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / S. Hemmati
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / S.
Joudaki
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / V. Le
Brun
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / J. G. Sorce
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / N. A. Walton
Summary
The Euclid survey aims to measure the spectroscopic redshift of
emission-line galaxies by identifying the H line in their slitless
spectra. This method is sensitive to the signal-to-noise ratio of the
line, as noise fluctuations or other strong emission lines can be
misidentified as H
line in their slitless
spectra. This method is sensitive to the signal-to-noise ratio of the
line, as noise fluctuations or other strong emission lines can be
misidentified as H , depending on redshift.
These effects lead to catastrophic redshift errors and the inclusion of
interlopers in the sample. We forecast the impact of such redshift
errors on galaxy clustering measurements. In particular, we study the
effect of interloper contamination on the two-point correlation function
(2PCF), the growth rate of structures, and the Alcock-Paczynski (AP)
parameters. We analyze 1000 synthetic spectroscopic catalogues, the
EuclidLargeMocks, designed to match the area and selection function of
the Data Release 1 (DR1) sample. We estimate the 2PCF of the
contaminated catalogues, isolating contributions from correctly
identified galaxies and from interlopers. We explore different models
with increasing complexity to describe the measured 2PCF at fixed
cosmology. Finally, we perform a cosmological inference and evaluate the
systematic error on the inferred
, depending on redshift.
These effects lead to catastrophic redshift errors and the inclusion of
interlopers in the sample. We forecast the impact of such redshift
errors on galaxy clustering measurements. In particular, we study the
effect of interloper contamination on the two-point correlation function
(2PCF), the growth rate of structures, and the Alcock-Paczynski (AP)
parameters. We analyze 1000 synthetic spectroscopic catalogues, the
EuclidLargeMocks, designed to match the area and selection function of
the Data Release 1 (DR1) sample. We estimate the 2PCF of the
contaminated catalogues, isolating contributions from correctly
identified galaxies and from interlopers. We explore different models
with increasing complexity to describe the measured 2PCF at fixed
cosmology. Finally, we perform a cosmological inference and evaluate the
systematic error on the inferred  ,
,  and
and
 values
associated with different models. Our results demonstrate that a minimal
modelling approach, which only accounts for an attenuation of the
clustering signal regardless of the type of contaminants, is sufficient
to recover the correct values of
values
associated with different models. Our results demonstrate that a minimal
modelling approach, which only accounts for an attenuation of the
clustering signal regardless of the type of contaminants, is sufficient
to recover the correct values of  ,
,  , and
, and
 at DR1. The
accuracy and precision of the estimated AP parameters are largely
insensitive to the presence of interlopers. The adoption of a minimal
model induces a 1%-3% systematic error on the growth rate of structure
estimation, depending on the redshift. However, this error remains
smaller than the statistical error expected for the Euclid DR1
analysis.
at DR1. The
accuracy and precision of the estimated AP parameters are largely
insensitive to the presence of interlopers. The adoption of a minimal
model induces a 1%-3% systematic error on the growth rate of structure
estimation, depending on the redshift. However, this error remains
smaller than the statistical error expected for the Euclid DR1
analysis.
Noble
gas depletion on Titan: Clathrate sequestration during the open ocean
phase
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alizée Amsler Moulanier / Olivier Mousis / Alexis
Bouquet / Ngan H. D. Trinh
Summary
A plausible explanation for the absence of primordial argon, krypton,
and xenon in Titan’s current atmosphere is that these gases were
sequestered in clathrate hydrates during Titan’s “open-ocean” phase. We
examine how clathrate hydrate formation at Titan’s ocean surface in its
early history may have contributed to noble gas depletion in the
primordial atmosphere. Starting with vapor-liquid equilibrium modeling
between water and volatiles, we used a statistical thermodynamic model
to determine the clathrate hydrate crust thickness needed to deplete the
primordial atmosphere of noble gases. Our computations suggest that if
Titan’s volatile budget was delivered by icy planetesimals with a
comet-like composition, its primordial atmosphere should be rich in
CO and CH
and CH , with NH
, with NH largely retained in water as ions. We
show that at 273.15 K, a clathrate crust tens of kilometers thick would
deplete the primordial atmosphere of xenon and krypton. The lack of
primordial argon in Titan’s atmosphere may result from the partial
de-volatilization of its accreted materials.
largely retained in water as ions. We
show that at 273.15 K, a clathrate crust tens of kilometers thick would
deplete the primordial atmosphere of xenon and krypton. The lack of
primordial argon in Titan’s atmosphere may result from the partial
de-volatilization of its accreted materials.
Articles for week 18 2025
Continuum,
CO and Water vapour maps of the Orion Nebula. First millimetre spectral
imaging with Concerto
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- F.-X. Désert / J. F. Macías-Pérez / A. Beelen / A.
Benoît
- M. Béthermin / J. Bounmy / O. Bourrion / M. Calvo
- A. Catalano / C. De Breuck / C. Dubois / C. A Durán
- A. Fasano / J. Goupy / W. Hu / E. Ibar
- G. Lagache / A. Lundgren / A. Monfardini / N.
Ponthieu
- D. Quinatoa / M. Van Cuyck / R. Adam / P. Ade
- H. Ajeddig / S. Amarantidis / P. André / H. Aussel
- S. Berta / A. Bongiovanni / D. Chérouvrier / M. De Petris
- S. Doyle / E. F. C. Driessen / G. Ejlali / A. Ferragamo
- A. Gomez / C. Hanser / S. Katsioli / F. Kéruzoré
- C. Kramer / B. Ladjelate / S. Leclercq / J.-F. Lestrade
- S. C. Madden / A. Maury / F. Mayet / A. Moyer-Anin
- M. Muñoz-Echeverría / I. Myserlis / A. Paliwal / L. Perotto
- G. Pisano / V. Revéret / A. J. Rigby / A. Ritacco
- H. Roussel / F. Ruppin / M. Sánchez-Portal / S. Savorgnano
- A. Sievers / C. Tucker / R. Zylka
Summary
The millimetre spectrum of Galactic regions and galaxies is rich in
continuum and molecular lines. This diversity is mostly explored using
either broad-band photometry or high-resolution heterodyne spectroscopy.
We aim to map the millimetre continuum emission of Galactic regions with
an intermediate spectral resolution between broad-band photometry and
heterodyne spectroscopy, enabling us to rapidly cover large sky areas
with spectroscopy. We report observations of the Orion Nebula with the
CONCERTO instrument, which was installed at the APEX telescope focal
plane from 2021 to 2023. We find that the spectrum of Orion is dominated
by dust emission with an emissivity index ranging between 1.3 and 2.0,
along with strong CO(2-1) and H O lines, which are naturally separated
from the continuum due to the CONCERTO spectral capabilities. Many
regions also show strong free-free emission at lower frequencies. We
demonstrate the spectral capabilities of CONCERTO at intermediate
spectral resolution, with a frequency coverage from 130 to 310 GHz. A
sensitivity of 200 mK is achieved in one second, for one beam and a 6
GHz frequency width, over an 18 arcmin diameter field of view, which is
within a factor of three of the expectations. We show that we can
spectrally disentangle the continuum from the CO line emission, but the
line is not resolved at a resolution of
O lines, which are naturally separated
from the continuum due to the CONCERTO spectral capabilities. Many
regions also show strong free-free emission at lower frequencies. We
demonstrate the spectral capabilities of CONCERTO at intermediate
spectral resolution, with a frequency coverage from 130 to 310 GHz. A
sensitivity of 200 mK is achieved in one second, for one beam and a 6
GHz frequency width, over an 18 arcmin diameter field of view, which is
within a factor of three of the expectations. We show that we can
spectrally disentangle the continuum from the CO line emission, but the
line is not resolved at a resolution of  . The slope
of the millimetre continuum is line-free mapped for the first time in
Orion.
. The slope
of the millimetre continuum is line-free mapped for the first time in
Orion.
Dark
skies of the slightly eccentric WASP-18 b from its optical-to-infrared
dayside emission
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Deline / P. E. Cubillos / L. Carone / B.-O. Demory
- M. Lendl / W. Benz / A. Brandeker / M. N. Günther
- A. Heitzmann / S. C. C. Barros / L. Kreidberg / G. Bruno
- D. Kitzmann / A. Bonfanti / M. Farnir / C. M. Persson
- S. G. Sousa / T. G. Wilson / D. Ehrenreich / V. Singh
- N. Iro / Y. Alibert / R. Alonso / T. Bárczy
- D. Barrado Navascues / W. Baumjohann / M. Bergomi / N. Billot
- L. Borsato / C. Broeg / M.-D. Busch / A. Collier Cameron
- A. C. M. Correia / Sz. Csizmadia / M. B. Davies / M.
Deleuil
- L. Delrez / O. D. S. Demangeon / A. Derekas / B. Edwards
- A. Erikson / A. Fortier / L. Fossati / M. Fridlund
- D. Gandolfi / K. Gazeas / M. Gillon / M. Güdel
- J. Hasiba / Ch. Helling / K. G. Isaak / L. L. Kiss
- J. Korth / K. W. F. Lam / J. Laskar / A. Lecavelier des Étangs
- D. Magrin / P. F. L. Maxted / B. Merín / C. Mordasini
- V. Nascimbeni / G. Olofsson / R. Ottensamer / I. Pagano
- E. Pallé / G. Peter / D. Piazza / G. Piotto
- D. Pollacco / D. Queloz / R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando
- F. Ratti / H. Rauer / I. Ribas / N. C. Santos
- G. Scandariato / D. Ségransan / A. E. Simon / A. M. S. Smith
- M. Stalport / S. Sulis / Gy. M. Szabó / S.
Udry
- V. Van Grootel / J. Venturini / E. Villaver / N. A. Walton
- K. Westerdorff
Summary
We performed a joint analysis of phase-curve observations of the
ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-18 b from the visible to the mid-infrared, using
data from CHEOPS, TESS and Spitzer. We aim to characterise the planetary
atmosphere with a consistent view over the large wavelength range
covered using GCMs and retrieval analyses, and including JWST data. We
obtained new ephemerides with unprecedented precisions of 1 second and
1.4 millisecond on the time of inferior conjunction and orbital period,
respectively. We computed a planetary radius of  with a precision of 0.65% (or 550 km). Based on a
timing inconsistency with JWST, we discuss and confirm orbital
eccentricity (
with a precision of 0.65% (or 550 km). Based on a
timing inconsistency with JWST, we discuss and confirm orbital
eccentricity ( ). We also constrain the argument of periastron to
). We also constrain the argument of periastron to
 deg. We show that the large dayside emission
implies the presence of magnetic drag and super-solar metallicity. We
find a steep thermally inverted gradient in the planetary atmosphere,
which is common for UHJs. We detected the presence of strong CO emission
lines at 4.5
deg. We show that the large dayside emission
implies the presence of magnetic drag and super-solar metallicity. We
find a steep thermally inverted gradient in the planetary atmosphere,
which is common for UHJs. We detected the presence of strong CO emission
lines at 4.5  m from an excess of dayside brightness
in the Spitzer/IRAC/Ch2 passband. Using these models to constrain the
reflected contribution in the CHEOPS passband, we derived an extremely
low geometric albedo of
m from an excess of dayside brightness
in the Spitzer/IRAC/Ch2 passband. Using these models to constrain the
reflected contribution in the CHEOPS passband, we derived an extremely
low geometric albedo of  .
.
Articles for week 17 2025
Euclid
preparation: TBD. Cosmic Dawn Survey: evolution of the galaxy stellar
mass function across 0.2<z<6.5 measured over 10 square
degrees
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / L. Zalesky / J. R. Weaver / C. J. R.
McPartland
- G. Murphree / I. Valdes / C. K. Jespersen / S. Taamoli
- N. Chartab / N. Allen / S. W. J. Barrow / D. B. Sanders
- S. Toft / B. Mobasher / I. Szapudi / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- A. Caillat / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant
/ S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- V. Pettorino / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D.
Tavagnacco
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L.
Gabarra
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / V. Scottez / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / V. Allevato / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / M.
Ballardini
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / R. Cabanac
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / A. Cappi / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / R. Chary / F. Cogato
- T. Contini / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / M. Huertas-Company / O.
Ilbert
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / G. Leroy / J. Lesgourgues
- T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- J. Martín-Fleitas / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / R. B.
Metcalf
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante
- C. Murray / K. Naidoo / P. Natoli / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci / M. Sahlén
- E. Sarpa / J. Schaye / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / M. Sereno / F. Shankar
- L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
The Cosmic Dawn Survey Pre-launch (PL) catalogues cover an effective
10.13 deg area with uniform deep
Spitzer/IRAC data (
area with uniform deep
Spitzer/IRAC data ( mag, 5
mag, 5 ), the largest area covered to these
depths in the infrared. These data are used to gain new insight into the
growth of stellar mass across cosmic history by characterising the
evolution of the galaxy stellar mass function (GSMF) through
), the largest area covered to these
depths in the infrared. These data are used to gain new insight into the
growth of stellar mass across cosmic history by characterising the
evolution of the galaxy stellar mass function (GSMF) through  . The total volume (0.62 Gpc
. The total volume (0.62 Gpc ) represents a tenfold
increase compared to previous works that have explored
) represents a tenfold
increase compared to previous works that have explored  and significantly
reduces cosmic variance, yielding strong constraints on the abundance of
massive galaxies. Results are generally consistent with the literature
but now provide firm estimates of number density where only upper limits
were previously available. Contrasting the GSMF with the dark matter
halo mass function suggests that massive galaxies (
and significantly
reduces cosmic variance, yielding strong constraints on the abundance of
massive galaxies. Results are generally consistent with the literature
but now provide firm estimates of number density where only upper limits
were previously available. Contrasting the GSMF with the dark matter
halo mass function suggests that massive galaxies ( M
M ) at
) at  required
integrated star-formation efficiencies of
required
integrated star-formation efficiencies of  0.25–0.5,
in excess of the commonly-held view of ``universal peak efficiency” from
studies on the stellar-to-halo mass relation (SHMR). Such increased
efficiencies imply an evolving peak in the SHMR at
0.25–0.5,
in excess of the commonly-held view of ``universal peak efficiency” from
studies on the stellar-to-halo mass relation (SHMR). Such increased
efficiencies imply an evolving peak in the SHMR at  which can be
maintained if feedback mechanisms from active galactic nuclei and
stellar processes are ineffective at early times. In addition, a
significant fraction of the most massive quiescent galaxies are observed
to be in place already by
which can be
maintained if feedback mechanisms from active galactic nuclei and
stellar processes are ineffective at early times. In addition, a
significant fraction of the most massive quiescent galaxies are observed
to be in place already by  –3. The apparent
lack in change of their number density by
–3. The apparent
lack in change of their number density by  is consistent
with relatively little mass growth from mergers. Utilising the unique
volume, evidence for an environmental dependence of the galaxy stellar
mass function is found all the way through
is consistent
with relatively little mass growth from mergers. Utilising the unique
volume, evidence for an environmental dependence of the galaxy stellar
mass function is found all the way through  for the first
time, though a more careful characterisation of the density field is
ultimately required for confirmation.
for the first
time, though a more careful characterisation of the density field is
ultimately required for confirmation.
Unraveling
the Lyman Continuum Emission of Ion3: Insights from HST multi-band
imaging and X-Shooter spectroscopy
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- U. Meštrić / E. Vanzella / A. Beckett / M.
Rafelski
- C. Grillo / M. Giavalisco / M. Messa / M. Castellano
- F. Calura / G. Cupani / A. Zanella / P. Bergamini
- M. Meneghetti / A. Mercurio / P. Rosati / M. Nonino
- K. Caputi / A. Comastri
Summary
We provide a comprehensive analysis of Ion3, the most distant LyC
leaker at  , using multi-band
HST photometry and X-Shooter spectroscopy. Deep HST F390W imaging probe
uncontaminated LyC flux blueward $
, using multi-band
HST photometry and X-Shooter spectroscopy. Deep HST F390W imaging probe
uncontaminated LyC flux blueward $ z$ interlopers and prevent contamination of
measured LyC radiation. We confirm the detection of LyC flux at SNR
$$3.5 and estimate the escape fraction of ionizing photons to be in the
range
z$ interlopers and prevent contamination of
measured LyC radiation. We confirm the detection of LyC flux at SNR
$$3.5 and estimate the escape fraction of ionizing photons to be in the
range  =
0.06 – 1, depending on the adopted IGM attenuation. Morphological
analysis reveals a clumpy structure made of two main components, with
effective radii of R
=
0.06 – 1, depending on the adopted IGM attenuation. Morphological
analysis reveals a clumpy structure made of two main components, with
effective radii of R $
$ _{}$ <
100 pc, and a total estimated de-lensed area in the rest-frame 1600Å~of
4.2~kpc
_{}$ <
100 pc, and a total estimated de-lensed area in the rest-frame 1600Å~of
4.2~kpc . We confirm the presence
of faint ultraviolet spectral features HeII$λ
. We confirm the presence
of faint ultraviolet spectral features HeII$λ![1640, CIII] 1640, CIII]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%201640%2C%20CIII%5D) λ
λ![1907,1909 and [NeIII] 1907,1909 and [NeIII]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%201907%2C1909%20and%20%5BNeIII%5D) λ
λ
![0.7)Å and EW(CIII]) = (6.5 0.7)Å and EW(CIII]) = (6.5](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%200.7%29%C3%85%20and%20EW%28CIII%5D%29%20%3D%20%286.5)
![3)Å. From [OII] 3)Å. From [OII]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%203%29%C3%85.%20From%20%5BOII%5D) λ
λ![λ$3726,3729 and [CIII]$λ$1909/CIII]$λ$1906 we derive electron densities $n_{\rm e}^{\rm [OII]}$ = 2300$\pm$1900 cm$^{-3}$ and $n_{\rm e}^{\rm CIII]}$ > 10$^{4}$ cm$^{-3}$, corresponding to an ISM pressure log(P/k) > 7.90. Furthermore, we derive an intrinsic SFR(H$α$) $\approx$ 77 M$_{\odot}$ yr$^{-1}$ (corresponding to $Σ_{\rm SFR} = 20$~M$_{\odot}$~yr$^{-1}$~kpc$^{-2}$ for the entire galaxy) and sub-solar metallicity $12+\rm log(O/H)$ = 8.02$\pm$0.20 using the EW(CIII]) as a diagnostic. The detection of [NeIII]$λ$3968 line and [OII]$λ λ$3726,3729 and [CIII]$λ$1909/CIII]$λ$1906 we derive electron densities $n_{\rm e}^{\rm [OII]}$ = 2300$\pm$1900 cm$^{-3}$ and $n_{\rm e}^{\rm CIII]}$ > 10$^{4}$ cm$^{-3}$, corresponding to an ISM pressure log(P/k) > 7.90. Furthermore, we derive an intrinsic SFR(H$α$) $\approx$ 77 M$_{\odot}$ yr$^{-1}$ (corresponding to $Σ_{\rm SFR} = 20$~M$_{\odot}$~yr$^{-1}$~kpc$^{-2}$ for the entire galaxy) and sub-solar metallicity $12+\rm log(O/H)$ = 8.02$\pm$0.20 using the EW(CIII]) as a diagnostic. The detection of [NeIII]$λ$3968 line and [OII]$λ](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Cdisplaystyle%20%CE%BB%243726%2C3729%20and%20%5BCIII%5D%24%CE%BB%241909%2FCIII%5D%24%CE%BB%241906%20we%20derive%20electron%20densities%20%24n_%7B%5Crm%20e%7D%5E%7B%5Crm%20%5BOII%5D%7D%24%20%3D%202300%24%5Cpm%241900%20cm%24%5E%7B-3%7D%24%20and%20%24n_%7B%5Crm%20e%7D%5E%7B%5Crm%20CIII%5D%7D%24%20%3E%2010%24%5E%7B4%7D%24%20cm%24%5E%7B-3%7D%24%2C%20corresponding%20to%20an%20ISM%20pressure%20log%28P%2Fk%29%20%3E%207.90.%20Furthermore%2C%20we%20derive%20an%20intrinsic%20SFR%28H%24%CE%B1%24%29%20%24%5Capprox%24%2077%20M%24_%7B%5Codot%7D%24%20yr%24%5E%7B-1%7D%24%20%28corresponding%20to%20%24%CE%A3_%7B%5Crm%20SFR%7D%20%3D%2020%24~M%24_%7B%5Codot%7D%24~yr%24%5E%7B-1%7D%24~kpc%24%5E%7B-2%7D%24%20for%20the%20entire%20galaxy%29%20and%20sub-solar%20metallicity%20%2412%2B%5Crm%20log%28O%2FH%29%24%20%3D%208.02%24%5Cpm%240.20%20using%20the%20EW%28CIII%5D%29%20as%20a%20diagnostic.%20The%20detection%20of%20%5BNeIII%5D%24%CE%BB%243968%20line%20and%20%5BOII%5D%24%CE%BB) λ
λ![3726,3729, provide an estimate of the ratio [OIII] 3726,3729, provide an estimate of the ratio [OIII]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%203726%2C3729%2C%20provide%20an%20estimate%20of%20the%20ratio%20%5BOIII%5D) λ
λ![5007/[OII] 5007/[OII]](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%205007%2F%5BOII%5D) λ$$λ
λ$$λ U$ > $-$1.5 using empirical and theoretical
correlations.
U$ > $-$1.5 using empirical and theoretical
correlations.
Exploring
the Neptunian Desert: Insights from a Homogeneous Planetary Sample
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Lauren Doyle / David J. Armstrong / Lorena Acuña / Ares Osborn
- Sérgio A. G. Sousa / Amadeo Castro-González / Vincent Bourrier /
Douglas Alves
- David Barrado / Susana C. C. Barros / Daniel Bayliss / Kaiming
Cui
- Olivier Demangeon / Rodrigo F. Díaz / Xavier Dumusque / Fintan
Eeles-Nolle
- Samuel Gill / Alejandro Hacker / James S. Jenkins / Marcelo Aron
Fetzner Keniger
- Marina Lafarga / Jorge Lillo-Box / Isobel Lockley / Louise D.
Nielsen
- Léna Parc / José Rodrigues / Alexandre Santerne /
Nuno C. Santos
- Peter J. Wheatley
Summary
In this paper, we present a homogeneous analysis of close-in Neptune
planets. To do this, we compile a sample of TESS-observed planets using
a ranking criterion which takes into account the planet’s period,
radius, and the visual magnitude of its host star. We use archival and
new HARPS data to ensure every target in this sample has precise radial
velocities. This yields a total of 64 targets, 46 of which are confirmed
planets and 18 of which show no significant radial velocity signal. We
explore the mass-radius distribution, planetary density, stellar host
metallicity, and stellar and planetary companions of our targets. We
find 26 of our sample are in
multi-planet systems, which are typically seen for planets located near
the lower edge of the Neptunian desert. We define a ‘gold’ subset of our
sample consisting of 33 confirmed planets with planetary radii between
2
of our sample are in
multi-planet systems, which are typically seen for planets located near
the lower edge of the Neptunian desert. We define a ‘gold’ subset of our
sample consisting of 33 confirmed planets with planetary radii between
2 and 10
and 10 . With these
targets, we calculate envelope mass fractions (EMF) using the GAS gianT
modeL for Interiors (GASTLI). We find a clear split in EMF between
planets with equilibrium temperatures below and above 1300~K, equivalent
to an orbital period of $
. With these
targets, we calculate envelope mass fractions (EMF) using the GAS gianT
modeL for Interiors (GASTLI). We find a clear split in EMF between
planets with equilibrium temperatures below and above 1300~K, equivalent
to an orbital period of $ %$ to 40
%$ to 40 , scaling linearly with the
planetary mass. The orbital period separating these two populations
coincides with the transition between the Neptunian desert and the
recently identified Neptunian ridge, further suggesting that different
formation and/or evolution mechanisms are at play for Neptune planets
across different close-in orbital regions.
, scaling linearly with the
planetary mass. The orbital period separating these two populations
coincides with the transition between the Neptunian desert and the
recently identified Neptunian ridge, further suggesting that different
formation and/or evolution mechanisms are at play for Neptune planets
across different close-in orbital regions.
Articles for week 16 2025
Euclid
preparation. Estimating galaxy physical properties using CatBoost
chained regressors with attention
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / A. Humphrey / P. A. C. Cunha / L.
Bisigello
- C. Tortora / M. Bolzonella / L. Pozzetti / M. Baes
- B. R. Granett / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / A. Biviano
- C. Bodendorf / D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / J. Dinis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / S. Farrens / S. Ferriol / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / E. Munari
- R. Nakajima / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- R. Scaramella / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / A. Spurio Mancini / L.
Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / J. Zoubian
- E. Zucca / A. Boucaud / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- M. Calabrese / N. Mauri / V. Scottez / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / V. Allevato
- S. Anselmi / M. Ballardini / A. Blanchard / S. Borgani
- S. Bruton / R. Cabanac / A. Calabro / A. Cappi
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / S. Contarini / A. R. Cooray
- J. Coupon / O. Cucciati / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- S. Di Domizio / J. A. Escartin Vigo / A. G. Ferrari / P. G.
Ferreira
- I. Ferrero / F. Fornari / L. Gabarra / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / G. Gozaliasl
- A. Gregorio / A. Hall / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / C. C.
Kirkpatrick
- L. Legrand / G. Libet / A. Loureiro / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- S. Matthew / L. Maurin / R. B. Metcalf / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / Nicholas A. Walton / J. Odier
- L. Patrizii / M. Pöntinen / V. Popa / C. Porciani
- D. Potter / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci / M. Sahlén
- A. Schneider / M. Sereno / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / D. Vergani / G. Verza
Summary
Euclid will image ~14000 deg^2 of the extragalactic sky at visible
and NIR wavelengths, providing a dataset of unprecedented size and
richness that will facilitate a multitude of studies into the evolution
of galaxies. In the vast majority of cases the main source of
information will come from broad-band images and data products thereof.
Therefore, there is a pressing need to identify or develop scalable yet
reliable methodologies to estimate the redshift and physical properties
of galaxies using broad-band photometry from Euclid, optionally
including ground-based optical photometry also. To address this need, we
present a novel method to estimate the redshift, stellar mass,
star-formation rate, specific star-formation rate, E(B-V), and age of
galaxies, using mock Euclid and ground-based photometry. The main
novelty of our property-estimation pipeline is its use of the CatBoost
implementation of gradient-boosted regression-trees, together with
chained regression and an intelligent, automatic optimization of the
training data. The pipeline also includes a computationally-efficient
method to estimate prediction uncertainties, and, in the absence of
ground-truth labels, provides accurate predictions for metrics of model
performance up to z~2. We apply our pipeline to several datasets
consisting of mock Euclid broad-band photometry and mock ground-based
ugriz photometry, to evaluate the performance of our methodology for
estimating the redshift and physical properties of galaxies detected in
the Euclid Wide Survey. The quality of our photometric redshift and
physical property estimates are highly competitive overall, validating
our modeling approach. We find that the inclusion of ground-based
optical photometry significantly improves the quality of the property
estimation, highlighting the importance of combining Euclid data with
ancillary ground-based optical data. (Abridged)
JWST
Discovery of a High-Redshift Tidal Disruption Event Candidate in
COSMOS-Web
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Mitchell Karmen / Suvi Gezari / Erini Lambrides / Hollis B.
Akins
- Colin Norman / Caitlin M. Casey / Justin Pierel / David Coulter
- Armin Rest / Ori Fox / Yukta Ajay / Natalie Allen
- Nicole E. Drakos / Seiji Fujimoto / Sebastian Gomez / Ghassem
Gozaliasl
- Olivier Ilbert / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Anton M.
Koekemoer / Zachary G. Lane
- Henry Joy McCracken / Louise Paquereau / Jason Rhodes / Brant E.
Robertson
- Marko Shuntov / Matthew R. Siebert / Sune Toft / Thomas Wevers
- Yossef Zenati
Summary
The rates and properties of tidal disruption events (TDEs) provide
valuable insights into their host galaxy central stellar densities and
the demographics of their central supermassive black holes (SMBHs). TDEs
have been observed only at low redshifts ( ), due to
the difficulty in conducting deep time-domain surveys. In this work, we
present the discovery of a high-redshift TDE candidate, HZTDE-1, in the
COSMOS-Web survey with JWST’s NIRCam, using a novel selection technique
based on color and morphology. We first outline a methodology for
identifying high-z TDEs in deep infrared imaging surveys, leveraging
their unique spectral energy distributions (SEDs) and morphologies of
these transients. We apply this technique to COSMOS-Web in filters
F115W, F150W, F277W, and F444W, and identify HZTDE-1, a transient point
source relative to archival UltraVISTA infrared observations. If we
assume it is a TDE, we estimate its photometric redshift to be
), due to
the difficulty in conducting deep time-domain surveys. In this work, we
present the discovery of a high-redshift TDE candidate, HZTDE-1, in the
COSMOS-Web survey with JWST’s NIRCam, using a novel selection technique
based on color and morphology. We first outline a methodology for
identifying high-z TDEs in deep infrared imaging surveys, leveraging
their unique spectral energy distributions (SEDs) and morphologies of
these transients. We apply this technique to COSMOS-Web in filters
F115W, F150W, F277W, and F444W, and identify HZTDE-1, a transient point
source relative to archival UltraVISTA infrared observations. If we
assume it is a TDE, we estimate its photometric redshift to be  . HZTDE-1 cannot be explained by reasonable
supernova or AGN models. However, we cannot rule out a superluminous
supernova at
. HZTDE-1 cannot be explained by reasonable
supernova or AGN models. However, we cannot rule out a superluminous
supernova at  . If confirmed
with follow-up observations, HZTDE-1 would represent the
highest-redshift TDE discovery to date, and would suggest an enhancement
of the TDE rate in the high-redshift universe. Our method, which can be
applied to future deep surveys with JWST and Roman, offers a pathway to
identify TDEs at
. If confirmed
with follow-up observations, HZTDE-1 would represent the
highest-redshift TDE discovery to date, and would suggest an enhancement
of the TDE rate in the high-redshift universe. Our method, which can be
applied to future deep surveys with JWST and Roman, offers a pathway to
identify TDEs at  and probe black hole
demographics at early cosmic times.
and probe black hole
demographics at early cosmic times.
Perihelion
history and atmospheric survival as primary drivers of the Earth`s
meteorite record
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Patrick M. Shober / Hadrien A. R. Devillepoix / Jeremie Vaubaillon /
Simon Anghel
- Sophie E. Deam / Eleanor K. Sansom / Francois Colas / Brigitte
Zanda
- Pierre Vernazza / Phil Bland
Summary
Models predict that more than half of all impacting meteoroids should
be carbonaceous, reflecting the abundance of carbon-rich asteroids in
the main belt and near-Earth space. Yet carbonaceous chondrites
represent only about 4% of meteorites recovered worldwide. Here we
analyse 7,982 meteoroid impacts and 540 potential meteorite falls from
19 global observation networks and demonstrate that intense thermal
stress at low perihelion distances coupled with the filtering effect of
Earths atmosphere explains this mismatch. Meteoroids repeatedly subjected to intense thermal cycling near the Sun fracture and weaken, removing the most friable objects even before atmospheric entry. Our data also show that tidally disrupted meteoroid streams produce especially fragile fragments that rarely survive to the ground. Consequently, compact, higher-strength, thermally cycled bodies dominate the meteorite record. These findings reconcile the predicted carbonaceous flux with its scarcity in collections, underscoring how orbital evolution and atmospheric filtering shape the materials that reach Earths
surface.
MIRI-JWST
mid-infrared direct imaging of the debris disk of HD106906
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Daniel Rouan / Anthony Boccaletti / Clément Perrot / Pierre
Baudoz
- Mathilde Mâlin / Pierre-Olivier Lagage / Rens Waters / Manuel
Güdel
- Thomas Henning / Bart Vandenbussche / Olivier Absil / David
Barrado
- Christophe Cossou / Leen Decin / Adrian M. Glauser / John Pye
- Polychronis Patapis / Niall Whiteford / Eugene Serabyn /
Elodie Choquet
- Göran Ostlin / Tom P. Ray / Gillian Wright
Summary
We report MIRI-JWST coronagraphic observations at 11.3 and 15.5 mic
of the debris disk around the young star HD 106906. The observations
were made to characterize the structure, temperature and mass of the
disk through the thermal emission of the dust heated by the central
star. Another goal was also to constrain the size distribution of the
grains. The data were reduced and calibrated using the JWST pipeline.
The analysis was based on a forward-modeling of the images using a
multiparameter radiative transfer model coupled to an optical code for
coronagraphy processing. The disk is clearly detected at both
wavelengths. The slight asymmetry is geometrically consistent with the
asymmetry observed in the near-IR, but it is inconsistent the brightness
distribution. The observed structure is well reproduced with a model of
a disk (or belt) with a critical radius 70 au, a mildly
inward-increasing density (index 2) and a steeper decrease outward
(index -6). This indication of a filled disk inside the critical radius
is inconsistent with sculpting from an inner massive planet. The size
distribution of the grains that cause the mid-IR emission is well
constrained by the flux ratio at the two wavelengths : 0.45 10 mic and
0.65 10 mic for silicate and graphite grains, respectively. The minimum
size is consistent with predictions of blowout through radiative
pressure. We derive a mass of the dust that causes the mid-IR emission
of 3.3 5.0 E3 Mearth. When the larger grains (up to 1 cm) that cause the
millimeter emission are included, we extrapolate this mass to 0.10 0.16
Mearth. We point out to that this is fully consistent with ALMA
observations of the disk in terms of dust mass and of its millimeter
flux. We estimate the average dust temperature in the planetesimal belt
to be 74 K, and a temperature range within the whole disk from 40 to 130
K.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- David Trevascus / Sarah Blunt / Valentin Christiaens / Elisabeth
Matthews
- Iain Hammond / Wolfgang Brandner / Jason Wang / Sylvestre
Lacour
- Arthur Vigan / William O. Balmer / Mickael Bonnefoy
/ Remo Burn
- Gaël Chauvin / Raffaele Gratton / Mathis Houllé / Sasha Hinkley
- Jens Kammerer / Laura Kreidberg / Gabriel-Dominique Marleau / Dino
Mesa
- Gilles Otten / Mathias Nowak / Emily Rickman / Joel
Sanchez-Bermudez
- Jonas Sauter
Summary
Hot- and cold-start planet formation models predict differing
luminosities for the young, bright planets that direct imaging surveys
are most sensitive to. However, precise mass estimates are required to
distinguish between these models observationally. The presence of two
directly imaged planets, PDS 70 b and c, in the PDS 70 protoplanetary
disk provides us a unique opportunity for dynamical mass measurements,
since the masses for these planets are currently poorly constrained.
Fitting orbital parameters to new astrometry of these planets, taken
with VLTI/GRAVITY in the  ~band, we find
~band, we find  dynamical upper mass limits
of 4.9
dynamical upper mass limits
of 4.9  for b and
13.6
for b and
13.6  for
c. Adding astrometry from the newly proposed planet candidate PDS 70 d
into our model, we determine
for
c. Adding astrometry from the newly proposed planet candidate PDS 70 d
into our model, we determine  dynamical upper mass limits
of 5.3
dynamical upper mass limits
of 5.3  , 7.5
, 7.5  and 2.2
and 2.2
 for b, c,
and the candidate d respectively. However,
for b, c,
and the candidate d respectively. However, 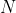 -body analysis of the orbits fit in this
case suggest that the inclusion of
-body analysis of the orbits fit in this
case suggest that the inclusion of  makes the system unstable. Using the
upper mass limits for b and c we rule out the coldest-start formation
models for both planets, calculating minimum post-formation entropies
(
makes the system unstable. Using the
upper mass limits for b and c we rule out the coldest-start formation
models for both planets, calculating minimum post-formation entropies
( ) of 9.5
) of 9.5  and 8.4
and 8.4  respectively. This places PDS 70 b and c on the
growing list of directly-imaged planets inconsistent with cold-start
formation.
respectively. This places PDS 70 b and c on the
growing list of directly-imaged planets inconsistent with cold-start
formation.
CEERS:
Forging the First Dust Grains in the Universe? A Population of Galaxies
with spectroscopically-derived Extremely Low Dust Attenuation (GELDA) at
4.0<z<11.4
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Denis Burgarella / Véronique Buat / Patrice Theulé
/ Jorge Zavala
- Mark Dickinson / Pablo Arrabal Haro / Micaela B. Bagley / Médéric
Boquien
- Nikko Cleri / Tim Dewachter / Henry C. Ferguson /
Vital Fernàndez
- Steven L. Finkelstein / Eric Gawiser / Andrea Grazian / Norman
Grogin
- Benne W. Holwerda / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Lisa Kewley / Allison
Kirkpatrick
- Dale Kocevski / Anton M. Koekemoer / Arianna Long / Jennifer
Lotz
- Ray A. Lucas / Bahram Mobasher / Casey Papovich / Pablo G.
Pérez-Gonzàlez
- Nor Pirzkal / Swara Ravindranath / Giulia Rodighiero /
Yannick Roehlly
- Caitlin Rose / Lise-Marie Seillé / Rachel Somerville / Steve
Wilkins
- Guang Yang / L. Y. Aaron Yung
Summary
We investigate the coevolution of metals and dust in 173 galaxies at
 using NIRSpec spectroscopy. Focusing on galaxies with extremely low dust
attenuation, we explore their physical processes using a new CIGALE
version that incorporates spectroscopic and photometric data. Comparing
observations with models, we derive key physical parameters. We identify
49 galaxies with extremely low dust attenuation (GELDAs), characterized
by
using NIRSpec spectroscopy. Focusing on galaxies with extremely low dust
attenuation, we explore their physical processes using a new CIGALE
version that incorporates spectroscopic and photometric data. Comparing
observations with models, we derive key physical parameters. We identify
49 galaxies with extremely low dust attenuation (GELDAs), characterized
by  within
within  and
and  . The stacked spectra reveal a very blue UV slope
(
. The stacked spectra reveal a very blue UV slope
( ) and Balmer decrement H
) and Balmer decrement H /H
/H , consistent with no dust attenuation. GELDAs are
more common at
, consistent with no dust attenuation. GELDAs are
more common at  (83.3%) than at
(83.3%) than at
 (26.3%)
suggesting they dominate the early Universe. Assuming a prior FIR dust
spectrum (from ALPINE), we examine dust-stellar mass trends. The
(26.3%)
suggesting they dominate the early Universe. Assuming a prior FIR dust
spectrum (from ALPINE), we examine dust-stellar mass trends. The  vs.
vs.  diagram shows
upper and lower sequences linked by possible transitional galaxies. A
transition at
diagram shows
upper and lower sequences linked by possible transitional galaxies. A
transition at  (
( or
or  ) may
mark the shift from stellar dust production to ISM grain growth, in
agreement with theoretical predictions. Our full sample has a high mean
gas fraction (
) may
mark the shift from stellar dust production to ISM grain growth, in
agreement with theoretical predictions. Our full sample has a high mean
gas fraction ( ),
indicating retained gas across all galaxies. Their small sizes and large
gas masses imply high gas surface densities but relatively low star
formation efficiency. High-redshift GELDAs may naturally explain the
observed excess of bright galaxies at
),
indicating retained gas across all galaxies. Their small sizes and large
gas masses imply high gas surface densities but relatively low star
formation efficiency. High-redshift GELDAs may naturally explain the
observed excess of bright galaxies at  compared to
theoretical expectations.
compared to
theoretical expectations.
Articles for week 15 2025
[C
II]-deficit caused by self-absorption in an ionized carbon-filled bubble
in RCW79
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Eduard Keilmann / Simon Dannhauer / Slawa Kabanovic / Nicola
Schneider
- Volker Ossenkopf-Okada / Robert Simon / Lars Bonne / Paul F.
Goldsmith
- Rolf Güsten / Annie Zavagno / Jürgen Stutzki /
Dominik Riechers
- Markus Röllig / Juan L. Verbena / Alexander G. G. M. Tielens
Summary
Recent spectroscopic observations of the [C II] 158 fine-structure line of ionized carbon (C
fine-structure line of ionized carbon (C ), using the Stratospheric
Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), have revealed expanding [C
II] shells in Galactic H II regions. We report the discovery of a
bubble-shaped source (S144 in RCW79), associated with a compact H II
region, excited by a single O7.5–9.5V/III star, which is consistent with
a scenario that the bubble is still mostly ``filled’’ with C
), using the Stratospheric
Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), have revealed expanding [C
II] shells in Galactic H II regions. We report the discovery of a
bubble-shaped source (S144 in RCW79), associated with a compact H II
region, excited by a single O7.5–9.5V/III star, which is consistent with
a scenario that the bubble is still mostly ``filled’’ with C . This indicates most likely a
very early evolutionary state, in which the stellar wind has not yet
blown material away, as it is the case for more evolved H II regions.
Using the SimLine non-LTE radiative transfer code, the [C II] emission
can be modeled to originate from three regions. First, a central H II
region with little C
. This indicates most likely a
very early evolutionary state, in which the stellar wind has not yet
blown material away, as it is the case for more evolved H II regions.
Using the SimLine non-LTE radiative transfer code, the [C II] emission
can be modeled to originate from three regions. First, a central H II
region with little C in the fully ionized phase,
followed by two layers with gas density around
in the fully ionized phase,
followed by two layers with gas density around  of partially photo-dissociated gas. The second
layer is a slowly expanding [C II] shell with an expansion velocity of
of partially photo-dissociated gas. The second
layer is a slowly expanding [C II] shell with an expansion velocity of

 . The outermost layer exhibits a temperature and
velocity gradient that produces the observed self-absorption features in
the optically thick [C II] line (
. The outermost layer exhibits a temperature and
velocity gradient that produces the observed self-absorption features in
the optically thick [C II] line ( ) leading to an
apparent deficit in [C II] emission and a low ratio of [C II] to total
far-infrared (FIR) emission. We developed a procedure to approximate the
missing [C II] flux and find a linear correlation between [C II] and FIR
without a [C II]-deficit. This demonstrates that at least some of the [C
II]-deficit found in Galactic H II bubbles can be attributed to
self-absorption.
) leading to an
apparent deficit in [C II] emission and a low ratio of [C II] to total
far-infrared (FIR) emission. We developed a procedure to approximate the
missing [C II] flux and find a linear correlation between [C II] and FIR
without a [C II]-deficit. This demonstrates that at least some of the [C
II]-deficit found in Galactic H II bubbles can be attributed to
self-absorption.
CHIME/FRB Outriggers:
Design Overview
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The CHIME/FRB Collaboration / Mandana Amiri / Bridget C. Andersen /
Shion Andrew
- Kevin Bandura / Mohit Bhardwaj / Kalyani Bhopi / Vadym Bidula
- P. J. Boyle / Charanjot Brar / Mark Carlson / Tomas Cassanelli
- Alyssa Cassity / Shami Chatterjee / Jean-François Cliche / Alice P.
Curtin
- Rachel Darlinger / David R. DeBoer / Matt Dobbs / Fengqiu Adam
Dong
- Gwendolyn Eadie / Emmanuel Fonseca / B. M. Gaensler / Nina
Gusinskaia
- Mark Halpern / Ian Hendricksen / Jason Hessels / Ronniy C.
Joseph
- Jane Kaczmarek / Victoria M. Kaspi / Kholoud Khairy / T. L.
Landecker
- Adam E. Lanman / Albert Wai Kit Lau / Mattias Lazda / Calvin
Leung
- Robert A. Main / Kiyoshi W. Masui / Ryan Mckinven / Juan
Mena-Parra
- Bradley W. Meyers / Daniele Michilli / Nikola
Milutinovic / Kenzie Nimmo
- Gavin Noble / Ayush Pandhi / Aaron B. Pearlman / Jeffrey B.
Peterson
- Emily Petroff / Ziggy Pleunis / Alexander W. Pollak / Masoud
Rafiei-Ravandi
- Andre Renard / Mawson W. Sammons / Ketan R. Sand / Pranav
Sanghavi
- Paul Scholz / Vishwangi Shah / Kaitlyn Shin / Seth R. Siegel
- Andrew Siemion / Jonathan L. Sievers / Kendrick Smith / David
Spear
- Ingrid Stairs / Keith Vanderlinde / Haochen Wang / Jacob P.
Willis
- Tarik J. Zegmott
Summary
The Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment (CHIME) has
emerged as the world’s premier facility for studying fast radio bursts
(FRBs) through its fast transient search backend CHIME/FRB@. The
CHIME/FRB Outriggers project will augment this high detection rate of
2–3 FRBs per day with the ability to precisely localize them using very
long baseline interferometry (VLBI). Using three strategically located
stations in North America and deploying recently developed synoptic VLBI
observing techniques, the Outriggers will provide  ~milliarcsecond
localization precision for the majority of detected FRBs. This paper
presents an overview of the design and implementation of the Outriggers,
covering their geographic distribution, structural design, and
observational capabilities. We detail the scientific objectives driving
the project, including the characterization of FRB populations, host
galaxy demographics, and the use of FRBs as cosmological probes. We also
discuss the calibration strategies available to mitigate ionospheric and
instrumental effects, ensuring high-precision localization. With two
stations currently in science operations, and the third in
commissioning, the CHIME/FRB Outriggers project is poised to become a
cornerstone of the FRB field, offering unprecedented insights into this
enigmatic cosmic phenomenon.
~milliarcsecond
localization precision for the majority of detected FRBs. This paper
presents an overview of the design and implementation of the Outriggers,
covering their geographic distribution, structural design, and
observational capabilities. We detail the scientific objectives driving
the project, including the characterization of FRB populations, host
galaxy demographics, and the use of FRBs as cosmological probes. We also
discuss the calibration strategies available to mitigate ionospheric and
instrumental effects, ensuring high-precision localization. With two
stations currently in science operations, and the third in
commissioning, the CHIME/FRB Outriggers project is poised to become a
cornerstone of the FRB field, offering unprecedented insights into this
enigmatic cosmic phenomenon.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Lilan Yang / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Maximilien Franco / Xuheng
Ding
- Mark J. Achenbach / Rafael C. Arango-Toro / Caitlin M. Casey /
Nicole E. Drakos
- Andreas L. Faisst / Steven Gillman / Ghassem Gozaliasl / Marc
Huertas-Company
- Shuowen Jin / Daizhong Liu / Georgios Magdis / Richard Massey
- John D. Silverman / Takumi S. Tanaka / Si-Yue Yu / Hollis B.
Akins
- Natalie Allen / Olivier Ilbert / Anton M. Koekemoer
/ Henry Joy McCracken
- Louise Paquereau / Jason Rhodes / Brant E. Robertson / Marko
Shuntov
- Sune Toft
Summary
We measure galaxy sizes from  using COSMOS-Web, the largest-area JWST imaging survey to date, covering
$
using COSMOS-Web, the largest-area JWST imaging survey to date, covering
$ ^2
^2 R_eM_*^α$) for star-forming and quiescent
galaxies. For star-forming galaxies, the slope
R_eM_*^α$) for star-forming and quiescent
galaxies. For star-forming galaxies, the slope  remains approximately 0.20 at
remains approximately 0.20 at  ,
showing no significant evolution over this redshift range. At higher
redshifts, the slopes are
,
showing no significant evolution over this redshift range. At higher
redshifts, the slopes are  and
and
 for
for
 and
and
 ,
respectively. At fixed galaxy mass, the size evolution for star-forming
galaxies follows
,
respectively. At fixed galaxy mass, the size evolution for star-forming
galaxies follows  , with
, with  .
For quiescent galaxies, the slope is steeper
.
For quiescent galaxies, the slope is steeper  -
- at
at  ,
and
,
and  . We
find that the size-mass relation is consistent between UV and optical at
. We
find that the size-mass relation is consistent between UV and optical at
 for star-forming
galaxies. However, we observe a decrease in the slope from UV to optical
at
for star-forming
galaxies. However, we observe a decrease in the slope from UV to optical
at  , with a tentative
negative slope in the optical at
, with a tentative
negative slope in the optical at  ,
suggesting a complex interplay between intrinsic galaxy properties and
observational effects such as dust attenuation. We discuss the ratio
between galaxies’ half-light radius, and underlying halos’ virial
radius,
,
suggesting a complex interplay between intrinsic galaxy properties and
observational effects such as dust attenuation. We discuss the ratio
between galaxies’ half-light radius, and underlying halos’ virial
radius,  , and find the
median value of
, and find the
median value of  . The star formation rate surface density evolves
as
. The star formation rate surface density evolves
as  , and the
, and the  -
- relation remains flat at
relation remains flat at
 . Lastly,
we identify a threshold in stellar mass surface density
. Lastly,
we identify a threshold in stellar mass surface density  -
- marking the transition to compact, quenched
galaxies from extended, star-forming progenitors. In summary, our
findings show that the extensive COSMOS-Web dataset at
marking the transition to compact, quenched
galaxies from extended, star-forming progenitors. In summary, our
findings show that the extensive COSMOS-Web dataset at  provides new
insights into galaxy size and related properties in the rest-frame
optical.
provides new
insights into galaxy size and related properties in the rest-frame
optical.
EP
250108a/SN 2025kg: Observations of the most nearby Broad-Line Type Ic
Supernova following an Einstein Probe Fast X-ray Transient
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. C. Rastinejad / A. J. Levan / P. G. Jonker / C. D.
Kilpatrick
- C. L. Fryer / N. Sarin / B. P. Gompertz / C. Liu
- R. A. J. Eyles-Ferris / W. Fong / E. Burns / J. H. Gillanders
- I. Mandel / D. B. Malesani / P. T. O’Brien / N. R. Tanvir
- K. Ackley / A. Aryan / F. E. Bauer / S. Bloemen
- T. de Boer / C. R. Bom / J. A. Chacon / K. Chambers
- T.-W. Chen / A. A. Chrimes / J. N. D. van Dalen / V. D’Elia
- M. De Pasquale / M. D. Fulton / P. J. Groot / R. Gupta
- D. H. Hartmann / A. P. C. van Hoof / M. E. Huber / L. Izzo
- W. Jacobson-Galan / P. Jakobsson / A. Kong / T. Laskar
- T. B. Lowe / E. A. Magnier / E. Maiorano / A. Martin-Carrillo
- L. Mas-Ribas / D. Mata Sanchez / M. Nicholl / C. J. Nixon
- S. R. Oates / G. Paek / J. Palmerio / D. Paris
- D. L. A. Pieterse / G. Pugliese / J. A. Quirola Vasquez / J. van
Roestel
- A. Rossi / A. Rouco Escorial. R. Salvaterra / B.
Schneider / S. J. Smartt
- K. Smith / I. A. Smith / S. Srivastav / M. A. P. Torres
- C. Ventura / P. Vreeswijk / R. Wainscoat / Y.-J. Yang
- S. Yang
Summary
With a small sample of fast X-ray transients (FXTs) with
multi-wavelength counterparts discovered to date, the progenitors of
FXTs and their connections to gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) and supernovae
(SNe) remain ambiguous. Here, we present photometric and spectroscopic
observations of SN 2025kg, the supernova counterpart to the FXT EP
250108a. At  , this is the
closest known SN discovered following an Einstein Probe (EP) FXT. We
show that SN 2025kg’s optical spectra reveal the hallmark features of a
broad-lined Type Ic SN. Its light curve evolution and expansion
velocities are also comparable to those of GRB-SNe, including SN 1998bw,
and several past FXT SNe. We present JWST/NIRSpec spectroscopy taken
around SN 2025kg’s maximum light, and find weak absorption due to He I
, this is the
closest known SN discovered following an Einstein Probe (EP) FXT. We
show that SN 2025kg’s optical spectra reveal the hallmark features of a
broad-lined Type Ic SN. Its light curve evolution and expansion
velocities are also comparable to those of GRB-SNe, including SN 1998bw,
and several past FXT SNe. We present JWST/NIRSpec spectroscopy taken
around SN 2025kg’s maximum light, and find weak absorption due to He I

 m and a broad, unidentified feature at
m and a broad, unidentified feature at
 4-4.5
4-4.5  m. Further, we observe clear evidence
for broadened H
m. Further, we observe clear evidence
for broadened H in optical data at 42.5 days that is
not detected at other epochs, indicating interaction with hydrogen-rich
material. From its light curve, we derive a
in optical data at 42.5 days that is
not detected at other epochs, indicating interaction with hydrogen-rich
material. From its light curve, we derive a  Ni mass of 0.2 - 0.6
Ni mass of 0.2 - 0.6
 . Together with
our companion paper (Eyles-Ferris et al. 2025), our broadband data of EP
250108a/SN 2025kg are consistent with a trapped or low energy (
. Together with
our companion paper (Eyles-Ferris et al. 2025), our broadband data of EP
250108a/SN 2025kg are consistent with a trapped or low energy ( ergs) jet-driven explosion from a collapsar with a zero-age main
sequence mass of 15-30
ergs) jet-driven explosion from a collapsar with a zero-age main
sequence mass of 15-30  . Finally, we
show that the sample of EP FXT SNe support past rate estimates that
low-luminosity jets seen through FXTs are more common than successful
(GRB) jets, and that similar FXT-like signatures are likely present in
at least a few percent of the brightest Ic-BL SNe.
. Finally, we
show that the sample of EP FXT SNe support past rate estimates that
low-luminosity jets seen through FXTs are more common than successful
(GRB) jets, and that similar FXT-like signatures are likely present in
at least a few percent of the brightest Ic-BL SNe.
ALMACAL
XIV: X-Shooter Spectroscopy, Infrared Properties and Radio SEDs of
Calibrators
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Simon Weng / Elaine M. Sadler / Emily Kerrison /
Victoria Bollo
- Céline Péroux / Martin Zwaan / Elizabeth K. Mahony / James R.
Allison
- Jianhang Chen / Roland Szakacs / Hyein Yoon
Summary
The ALMACAL-22 survey includes over 2700 hours of observations of
ALMA phase and amplitude calibrators, spanning frequencies from 84 to
950 GHz across bands 3 to 10. In total, 687 out of the 1,047 calibrators
have redshifts confirmed with spectroscopy and we find an additional 50
featureless blazars. The redshift distribution of the ALMACAL-22 sample
peaks at  and spans a
wide range, from the nuclei of nearby galaxies at
and spans a
wide range, from the nuclei of nearby galaxies at  to quasars at
to quasars at
 . 70 new
VLT/X-Shooter spectra of these sources covering UV to NIR wavelengths
are also presented, which will be used in future stacking experiments to
search for cold gas in the circumgalactic medium. Infrared magnitudes
from WISE indicate that the majority of the sources are consistent with
being quasars or blazars. After fitting the radio spectral energy
distributions of the calibrators, we find that most ALMA calibrators
exhibit peaked spectra or are re-triggered which is surprising given the
large number of blazars in the sample. The peak frequencies span three
orders of magnitude from 100 MHz to 170 GHz, corresponding to linear
sizes ranging from sub-pc to
. 70 new
VLT/X-Shooter spectra of these sources covering UV to NIR wavelengths
are also presented, which will be used in future stacking experiments to
search for cold gas in the circumgalactic medium. Infrared magnitudes
from WISE indicate that the majority of the sources are consistent with
being quasars or blazars. After fitting the radio spectral energy
distributions of the calibrators, we find that most ALMA calibrators
exhibit peaked spectra or are re-triggered which is surprising given the
large number of blazars in the sample. The peak frequencies span three
orders of magnitude from 100 MHz to 170 GHz, corresponding to linear
sizes ranging from sub-pc to  10 kpc. In the future, when combined
with high-resolution radio imaging, these results will offer valuable
constraints on the molecular gas content of the CGM, as well as the ages
and duty cycles of AGN jets. The ever-growing ALMACAL data set will
remain an indispensable resource for studying the various aspects of
galaxy formation and evolution.
10 kpc. In the future, when combined
with high-resolution radio imaging, these results will offer valuable
constraints on the molecular gas content of the CGM, as well as the ages
and duty cycles of AGN jets. The ever-growing ALMACAL data set will
remain an indispensable resource for studying the various aspects of
galaxy formation and evolution.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Silvia Leanza / Emanuele Dalessandro / Mario Cadelano / Cristiano
Fanelli
- Greta Ettorre / Sebastian Kamann / Nate Bastian / Silvia
Martocchia
- Maurizio Salaris / Carmela Lardo / Alessio Mucciarelli / Sara
Saracino
Summary
Over the past decade, stellar rotation has emerged as a key factor in
shaping the morphology of color-magnitude diagrams of young and
intermediate-age star clusters. In this study, we use MUSE
integral-field spectroscopy to investigate the stellar rotation of ~2300
stars in the 1.5 Gyr old cluster NGC 1783 in the Large Magellanic Cloud.
The effective temperature, surface gravity, radial velocity, and
projected rotational velocity ( ) of
the entire sample were obtained within a Bayesian framework to derive
robust estimates of these parameters along with their associated errors.
The analysis shows that stars along the extended main sequence turn-off
(eMSTO) cover a wide range of rotational velocities, from values
consistent with no/slow rotation up to
) of
the entire sample were obtained within a Bayesian framework to derive
robust estimates of these parameters along with their associated errors.
The analysis shows that stars along the extended main sequence turn-off
(eMSTO) cover a wide range of rotational velocities, from values
consistent with no/slow rotation up to  ~ 250
km/s. The distribution of stellar rotation velocities appears to play a
crucial role in explaining the broadening of the eMSTO in this cluster,
and a correlation is observed between
~ 250
km/s. The distribution of stellar rotation velocities appears to play a
crucial role in explaining the broadening of the eMSTO in this cluster,
and a correlation is observed between  and
the color of the eMSTO stars, with
and
the color of the eMSTO stars, with  increasing as the color becomes redder. Among the eMSTO stars, we
investigate the peculiar population of stars strongly dimmed in the UV
(so-called UV-dim stars), recently discovered in NGC 1783. UV-dim stars
show clear photometric evidence of self-extinction and mild
spectroscopic signatures typically observed in shell stars, thus
suggesting that they have likely a decretion disc observed nearly
equator-on. Interestingly, the study also shows that a significant
fraction of UV-dim stars are slow rotators. We discuss potential
implications these results may have on our understanding of the
formation and evolution of UV-dim stars and we propose that the
rotational properties of the UV-dim stars should vary with cluster
age.
increasing as the color becomes redder. Among the eMSTO stars, we
investigate the peculiar population of stars strongly dimmed in the UV
(so-called UV-dim stars), recently discovered in NGC 1783. UV-dim stars
show clear photometric evidence of self-extinction and mild
spectroscopic signatures typically observed in shell stars, thus
suggesting that they have likely a decretion disc observed nearly
equator-on. Interestingly, the study also shows that a significant
fraction of UV-dim stars are slow rotators. We discuss potential
implications these results may have on our understanding of the
formation and evolution of UV-dim stars and we propose that the
rotational properties of the UV-dim stars should vary with cluster
age.
Gas
properties as a function of environment in the proto-supercluster
Hyperion at z ~ 2.45
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- G. Gururajan / O. Cucciati / B. C. Lemaux / M. Talia
- G. Zamorani / F. Pozzi / R. Decarli / B. Forrest
- L. Shen / G. De Lucia / F. Fontanot / S. Bardelli
- D. C. Baxter / L. P. Cassarà / E. Golden-Marx / D. Sikorski
- E. A. Shah / R. R. Gal / M. Giavalisco / F. Giddings
- N. P. Hathi / D. Hung / A. M. Koekemoer / V. Le
Brun
- L. M. Lubin / L. A. M. Tasca / L. Tresse / D.
Vergani
- E. Zucca
Summary
The cosmic star-formation rate density, molecular gas density and the
AGN activity of the Universe peak at z~ 2-3, showing the Universe is
most active at this epoch. The nature of the galaxies at these redshifts
and their properties as a function of their environment are particularly
interesting to understand the mechanisms driving their star-formation
and quenching. At z~ 2.5, a massive (~ 4.8 X 10^15 Msun)
proto-supercluster, Hyperion, was identified Cucciati et al. 2018,
consisting of 7 groups/peaks and extending over a comoving volume of 60
X 60 X 150 Mpc^3, providing an excellent laboratory to probe the
properties and evolution of galaxies as a function of their
environments. We use a large compilation of photometric (optical to
radio wavelengths, COSMOS2020, COSMOS-Super-deblended, and, A3COSMOS)
and spectroscopic (C3VO, HST-Hyperion, VUDS, zCOSMOS, DEIMOS10K,
MAGAZ3NE) data to assign membership and study the relation between the
local environment and the molecular gas mass, the star-formation rate
(SFR), gas depletion timescales, and quenching mechanisms. We find that
the depletion timescales and the molecular gas fractions decrease and
SFR increases in denser environments at the ~ 2 sigma level, suggesting
accelerated evolution in the densest regions of this proto-supercluster
resulting from gas stripping, over-consumption, and/or cessation of cold
flows. Dedicated observations at sub-millimeter wavelengths enabling
further spectroscopic confirmation and better coverage in the
sub-millimetric (sub-mm) wavelengths can provide more conclusive results
on the environmental implications on gas reservoirs of galaxies in
Hyperion.
On Soft
Clustering For Correlation Estimators
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Edward Berman / Sneh Pandya / Jacqueline McCleary / Marko
Shuntov
- Caitlin Casey / Nicole Drakos / Andreas Faisst / Steven Gillman
- Ghassem Gozaliasl / Natalie Hogg / Jeyhan Kartaltepe / Anton
Koekemoer
- Wilfried Mercier / Diana Scognamiglio / COSMOS-Web
/ :
- The JWST Cosmic Origins Survey
Summary
Properly estimating correlations between objects at different spatial
scales necessitates  distance calculations. For this reason, most widely adopted packages for
estimating correlations use clustering algorithms to approximate local
trends. However, methods for quantifying the error introduced by this
clustering have been understudied. In response, we present an algorithm
for estimating correlations that is probabilistic in the way that it
clusters objects, enabling us to quantify the uncertainty caused by
clustering simply through model inference. These soft clustering
assignments enable correlation estimators that are theoretically
differentiable with respect to their input catalogs. Thus, we also build
a theoretical framework for differentiable correlation functions and
describe their utility in comparison to existing surrogate models.
Notably, we find that repeated normalization and distance function calls
slow gradient calculations and that sparse Jacobians destabilize
precision, pointing towards either approximate or surrogate methods as a
necessary solution to exact gradients from correlation functions. To
that end, we close with a discussion of surrogate models as proxies for
correlation functions. We provide an example that demonstrates the
efficacy of surrogate models to enable gradient-based optimization of
astrophysical model parameters, successfully minimizing a correlation
function output. Our numerical experiments cover science cases across
cosmology, from point spread function (PSF) modeling efforts to
gravitational simulations to galaxy intrinsic alignment (IA).
distance calculations. For this reason, most widely adopted packages for
estimating correlations use clustering algorithms to approximate local
trends. However, methods for quantifying the error introduced by this
clustering have been understudied. In response, we present an algorithm
for estimating correlations that is probabilistic in the way that it
clusters objects, enabling us to quantify the uncertainty caused by
clustering simply through model inference. These soft clustering
assignments enable correlation estimators that are theoretically
differentiable with respect to their input catalogs. Thus, we also build
a theoretical framework for differentiable correlation functions and
describe their utility in comparison to existing surrogate models.
Notably, we find that repeated normalization and distance function calls
slow gradient calculations and that sparse Jacobians destabilize
precision, pointing towards either approximate or surrogate methods as a
necessary solution to exact gradients from correlation functions. To
that end, we close with a discussion of surrogate models as proxies for
correlation functions. We provide an example that demonstrates the
efficacy of surrogate models to enable gradient-based optimization of
astrophysical model parameters, successfully minimizing a correlation
function output. Our numerical experiments cover science cases across
cosmology, from point spread function (PSF) modeling efforts to
gravitational simulations to galaxy intrinsic alignment (IA).
Bridging
Quasars and Little Red Dots: Insights into Broad-Line AGNs at  from the First JWST
COSMOS-3D Dataset
from the First JWST
COSMOS-3D Dataset
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Xiaojing Lin / Xiaohui Fan / Feige Wang / Fengwu Sun
- Jaclyn B. Champagne / Eiichi Egami / Koki Kakiichi / Jianwei
Lyu
- Wei Leong Tee / Jinyi Yang / Fuyan Bian / Sarah E. I. Bosman
- Zheng Cai / Caitlin M. Casey / Roberto Decarli / Andreas L.
Faisst
- Seiji Fujimoto / Santosh Harish / Olivier Ilbert /
Akio K. Inoue
- Xiangyu Jin / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Dale D. Kocevski / Mingyu
Li
- Weizhe Liu / Yichen Liu / Jan-Torge Schindler / Marko Shuntov
- Takumi S. Tanaka / Marianne Vestergaard / Yunjing Wu / Haowen
Zhang
- Zijian Zhang
Summary
We report the discovery of 13 broad-line AGNs at  from the first
10% data of the JWST Cycle 3 Treasury Program COSMOS-3D. These AGNs are
identified by their broad H
from the first
10% data of the JWST Cycle 3 Treasury Program COSMOS-3D. These AGNs are
identified by their broad H or H
or H emission lines through the NIRCam grism
wide-field slitless spectroscopy. One object at
emission lines through the NIRCam grism
wide-field slitless spectroscopy. One object at  with broad
H
with broad
H emission has an F444W magnitude of 23.6
mag, making it one of the brightest
emission has an F444W magnitude of 23.6
mag, making it one of the brightest  broad-line
AGNs yet known. Among the 13 AGNs, 10 objects have reddened optical
continua with slopes
broad-line
AGNs yet known. Among the 13 AGNs, 10 objects have reddened optical
continua with slopes  .
The remaining three objects have their overall SEDs that resemble those
of UV-luminous quasars at similar redshifts, but their
.
The remaining three objects have their overall SEDs that resemble those
of UV-luminous quasars at similar redshifts, but their  , though
negative, are not as blue as those of unobscured quasars. We also obtain
MIRI photometry at 7.7-18
, though
negative, are not as blue as those of unobscured quasars. We also obtain
MIRI photometry at 7.7-18  m for two AGNs and place strong
constraints on their rest-frame near-IR SED. We find no significant
variability in the rest-frame UV by comparing the COSMOS-3D and
COSMOS-Web F115W images taken apart by 60 days in the rest-frame. We
compute the H
m for two AGNs and place strong
constraints on their rest-frame near-IR SED. We find no significant
variability in the rest-frame UV by comparing the COSMOS-3D and
COSMOS-Web F115W images taken apart by 60 days in the rest-frame. We
compute the H luminosity functions (LFs) for the
broad H
luminosity functions (LFs) for the
broad H emitters at
emitters at  and
find a potential redshift evolution when compared with that of the
and
find a potential redshift evolution when compared with that of the  sample.
We also derive the H
sample.
We also derive the H LF at
LF at  for AGNs and galaxies
by combining our sample with those from the literature. The broad H
for AGNs and galaxies
by combining our sample with those from the literature. The broad H emitters in this work suggest a number
density two orders of magnitude higher than that predicted by the quasar
LF based on rest-frame UV-selected samples. As a preview, our work
showcases the ability of the COSMOS-3D grism survey to provide a
complete view of the properties, growth, and evolution of bright
broad-line AGNs at
emitters in this work suggest a number
density two orders of magnitude higher than that predicted by the quasar
LF based on rest-frame UV-selected samples. As a preview, our work
showcases the ability of the COSMOS-3D grism survey to provide a
complete view of the properties, growth, and evolution of bright
broad-line AGNs at  .
.
Articles for week 14 2025
Characterizing
planetary systems with SPIRou: Detection of a sub-Neptune in a 6-day
period orbit around the M dwarf Gl 410
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Carmona / X. Delfosse / M. Ould-Elhkim / P.
Cortés-Zuleta
- N. C. Hara / E. Artigau / C. Moutou / A. C. Petit
- L. Mignon / J. F. Donati / N. J. Cook / J. Gagné
- T. Forveille / R. F. Diaz / E. Martioli / L. Arnold
- C. Cadieux / I. Boisse / J. Morin / P. Petit
- P. Fouqué / X. Bonfils / G. Hébrard / L. Acuña
- J.-D. do Nascimento / R. Cloutier / N. Astudillo-Defru / F.
Bouchy
- V. Bourrier / S. Dalal / M. Deleuil / R. Doyon
- X. Dumusque / S. Grouffal / N. Heidari / S.
Hoyer
- P. Larue / F. Kiefer / A. Santerne / D.
Ségransan
- J. Serrano Bell / M. Stalport / S. Sulis / S.
Udry
- H. Vivien
Summary
The search for exoplanets around nearby M dwarfs represents a crucial
milestone in the census of planetary systems in the vicinity of our
Solar System. Since 2018 our team is carrying a radial-velocity blind
search program for planets around nearby M dwarfs with the near-IR
spectro-polarimeter and velocimeter SPIRou at the CFHT and the optical
velocimeter SOPHIE at the OHP in France. Here we present our results on
Gl 410, a 0.55 Msun 480+-150 Myr old active M dwarf distant 12 pc. We
used the line-by-line (LBL) technique to measure the RVs with SPIRou and
the template matching method with SOPHIE. Three different methods were
employed, two based on principal component analysis (PCA), to clean the
SPIRou RVs for systematics. We applied Gaussian processes (GP) modeling
to correct the SOPHIE RVs for stellar activity. The l1 and apodize sine
periodogram analysis was used to search for planetary signals in the
SPIRou data taking into account activity indicators. We analyzed TESS
data and searched for planetary transits. We report the detection of a M
sin(i)=8.4+-1.3 Mearth sub-Neptune planet at a period of 6.020+-0.004
days in circular orbit with SPIRou. The same signal, although with lower
significance, was also retrieved in the SOPHIE RV data after correction
for activity using a GP trained on SPIRou’s longitudinal magnetic field
(Bl) measurements. The TESS data indicate that the planet is not
transiting. Within the SPIRou wPCA RVs, we find tentative evidence for
two additional planetary signals at 2.99 and 18.7 days. In conclusion,
infrared RVs are a powerful method to detect extrasolar planets around
active M dwarfs. Care should be taken however to correct/filter
systematics generated by residuals of the telluric correction or small
structures in the detector plane. The LBL technique combined with PCA
offers a promising way to reach this objective. Further monitoring of Gl
410 is necessary.
ATOMIUM:
Continuum emission and evidence of dust enhancement from binary
motion
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- T. Danilovich / N. Samaratunge / Y. Mori / A. M. S. Richards
- A. Baudry / S. Etoka / M. Montargès / P. Kervella
- I. McDonald / C. A. Gottlieb / A. Wallace / D. J. Price
- L. Decin / J. Bolte / T. Ceulemans / F. De Ceuster
- A. de Koter / D. Dionese / I. El Mellah / M. Esseldeurs
- M. Gray / F. Herpin / T. Khouri / E. Lagadec
- C. Landri / L. Marinho / K. M. Menten / T. J. Millar
- H. S. P. Müller / B. Pimpanuwat / J. M. C. Plane / R. Sahai
- L. Siess / M. Van de Sande / O. Vermeulen / K. T. Wong
- J. Yates / A. Zijlstra
Summary
Low- and intermediate-mass stars on the asymptotic giant branch (AGB)
account for a significant portion of the dust and chemical enrichment in
their host galaxy. Here we present ALMA observations of the continuum
emission at 1.24 mm around a sample of 17 stars from the ATOMIUM survey.
From our analysis of the stellar contributions to the continuum flux, we
find that the semi-regular variables all have smaller physical radii and
fainter monochromatic luminosities than the Mira variables. Comparing
these properties with pulsation periods, we find a positive trend
between stellar radius and period only for the Mira variables with
periods above 300 days and a positive trend between the period and the
monochromatic luminosity only for the red supergiants and the most
extreme AGB stars with periods above 500 days. We find that the
continuum emission at 1.2 mm can be classified into four groups.
“Featureless” continuum emission is confined to the (unresolved) regions
close to the star for five stars in our sample, relatively uniform
extended flux is seen for four stars, tentative elongated features are
seen for three stars, and the remaining five stars have unique or
unusual morphological features in their continuum maps. These features
can be explained by binary companions to 10 out of the 14 AGB stars in
our sample. Based on our results we conclude that there are two modes of
dust formation: well established pulsation-enhanced dust formation and
our newly proposed companion-enhanced dust formation. If the companion
is located close to the AGB star, in the wind acceleration region, then
additional dust formed in the wake of the companion can increase the
mass lost through the dust driven wind. This explains the different dust
morphologies seen around our stars and partly accounts for a large
scatter in literature mass-loss rates, especially among semiregular
stars with small pulsation periods.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Philippe André / Michael Mattern / Doris Arzoumanian / Yoshito
Shimajiri
- Annie Zavagno / Daisei Abe / Delphine
Russeil
Summary
Dense filaments are believed to be representative of the initial
conditions of star formation in molecular clouds. We have used the MIRI
instrument on JWST to image the massive filament NGC6334M at d~1.3 kpc
with unprecedented resolution and dynamic range at 7.7 and 25.5 microns.
Our observations reveal the fine structure of the filament in absorption
against mid-infrared background emission. From the absorption data, we
derive high-resolution column density maps and perform a detailed
analysis of the filament structure. We find a median filament width of
0.12+/-0.02 pc at both wavelengths, resolved by almost two orders of
magnitude by MIRI, and consistent with the typical half-power width of
Herschel filaments in nearby (d<0.5 kpc) clouds. The JWST data also
reveal the presence of a quasi-periodic series of side filaments with a
similar projected spacing of 0.125+/-0.015 pc. Combining our JWST
results with Spitzer and APEX/Herschel data, we perform a study of cloud
structure over four orders of magnitude in linear scale. A convergence
test shows that our width estimates for NGC6334M are robust and reflect
the presence of a true characteristic scale. While there is evidence of
a Kolmogorov-like spectrum of small-scale fluctuations down the
1.6x10^-3 pc resolution of the JWST observations, we identify a break in
the power spectrum of column density fluctuations at a scale ~0.1-0.4 pc
comparable to the width of NGC6334M and its side filaments. This
characteristic scale ~0.1pc has important implications for the origin of
the star formation efficiency in dense gas and the IMF.
Articles for week 13 2025
The
planetary nebula NGC 3132 revisited: high definition 3D photoionization
model
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- H. Monteiro / C. Mendes de Oliveira / P. Amram / L.
Stanghellini
- R. Wesson / K. Bouvis / S. Akras / M. Matsuura
- B. C. Quint
Summary
We present a detailed 3D photoionization model of the planetary
nebula NGC 3132, constrained by the latest observations. Using the
MOCASSIN code, the model incorporates integrated and spatially resolved
spectroscopy, velocity-resolved line profiles, emission line maps, and
photometry, including recent high-quality data from MUSE (VLT) and JWST
among others. Based on new data from the SAMFP instrument at SOAR, the
three-dimensional density structure of the nebula was obtained by
assuming homologous expansion of the surrounding nebular gas. The final
fitted model successfully reproduces all key observational constraints
available, particularly in terms of the detailed emission line
integrated fluxes and ionization structures across different ionic
stages. The results of the model show that the progenitor star had a
mass of  and is surrounded by a He poor shell of dust and
gas. The abundances of He, C, N, O, and S determined by the model show
that the nebula has C/O=
and is surrounded by a He poor shell of dust and
gas. The abundances of He, C, N, O, and S determined by the model show
that the nebula has C/O= and
N/O=
and
N/O= consistent with the progenitor mass found.
consistent with the progenitor mass found.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): A photometric search for ultracool dwarfs in
the Euclid Deep Fields
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Žerjal / C. Dominguez-Tagle / N. Sedighi / E. L. Martín
- N. Lodieu / B. Goldman / C. Reylé / R. L. Smart
- A. Mohandasan / M. R. Zapatero Osorio / D. Barrado / P. Mas
Buitrago
- N. Vitas / P. Cruz / V. J. S. Béjar / H. Bouy
- A. Burgasser / S. Muñoz Torres / N. Phan-Bao / E. Solano
- R. Tata / S. Tsilia / J.-Y. Zhang / N. Aghanim
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / J.-G. Cuby / A. Da Silva / H.
Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / C. Dolding / H. Dole / M. Douspis
- F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan
- J. Hoar / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / J. Martín-Fleitas / V. Scottez
Summary
We present a catalogue of more than 5000 new ultracool dwarf (UCD)
candidates in the three Euclid Deep Fields in the Q1 data release. They
range from late M to late T dwarfs, and include 1200 L and T dwarfs.
More than 100 of them have been spectroscopically confirmed, with seven
of them being T dwarfs. Our UCD selection criteria are based only on
colour ( ). The
combined requirement for optical detection and stringent signal-to-noise
ratio threshold ensure a high purity of the sample, but at the expense
of completeness, especially for T dwarfs. The detections range from
magnitudes 19 and 24 in the near-infrared bands, and extend down to 26
in the optical band. The average surface density of detected UCDs on the
sky is approximately 100 objects per
). The
combined requirement for optical detection and stringent signal-to-noise
ratio threshold ensure a high purity of the sample, but at the expense
of completeness, especially for T dwarfs. The detections range from
magnitudes 19 and 24 in the near-infrared bands, and extend down to 26
in the optical band. The average surface density of detected UCDs on the
sky is approximately 100 objects per  ,
including 20 L and T dwarfs per
,
including 20 L and T dwarfs per  . This
leads to an expectation of at least 1.4 million ultracool dwarfs in the
final data release of the Euclid Wide Survey, including at least 300,000
L dwarfs, and more than 2,600 T dwarfs, using the strict selection
criteria from this work. We provide empirical Euclid colours as a
function of spectral type, and a probability that an object with a given
colour has a certain spectral type.
. This
leads to an expectation of at least 1.4 million ultracool dwarfs in the
final data release of the Euclid Wide Survey, including at least 300,000
L dwarfs, and more than 2,600 T dwarfs, using the strict selection
criteria from this work. We provide empirical Euclid colours as a
function of spectral type, and a probability that an object with a given
colour has a certain spectral type.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1) Ultracool dwarfs in the Euclid Deep Field
North
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Mohandasan / R. L. Smart / C. Reylé / V. Le
Brun
- A. Pérez-Garrido / E. Bañados / B. Goldman / S. L. Casewell
- M. R. Zapatero Osorio / T. Dupuy / M. Rejkuba / E. L. Martín
- C. Dominguez-Tagle / M. {Ž}erjal / N. Huélamo / N. Lodieu
- P. Cruz / R. Rebolo / M. W. Phillips / J.-Y. Zhang
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / A.
Costille
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / H. Dole / M. Douspis
- F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George
- W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan
- J. Hoar / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / C. Surace / P. Tallada-Crespí / A.
N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / D. Vibert / Y.
Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- E. Zucca / J. Martín-Fleitas / V. Scottez
Summary
Ultracool dwarfs (UCDs) encompass the lowest mass stars and brown
dwarfs, defining the stellar substellar boundary. They have significant
potential for advancing the understanding of substellar physics;
however, these objects are challenging to detect due to their low
luminosity. The wide coverage and deep sensitivity of the Euclid survey
will increase the number of confirmed and well characterised UCDs by
several orders of magnitude. In this study, we take advantage of the
Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1) and in particular we look in detail at
the known and new UCDs in the Euclid Deep Field North (22.9 deg2 down to
JE = 24.5 mag), to understand the advantages of using the slitless
Euclid spectroscopy. We compile a comparison sample of known UCDs and
use their spectra to demonstrate the capability of Euclid to derive
spectral types using a template matching method. This method is then
applied to the spectra of the newly identified candidates. We confirm
that 33 of these candidates are new UCDs, with spectral types ranging
from M7 to T1 and JE = 17 to 21 mag. We look at their locus in colour
colour diagrams and compare them with the expected colours of QSOs. A
machine readable catalogue is provided for further study, containing
both the comparison sample and the newly identified UCDs, along with
their spectral classifications where the Q1 spectra quality allows for
confident determination
How
to detect periodic radio emissions from an exoplanet, star, or their
interaction?
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. K. Louis / A. Loh / P. Zarka / L. Lamy
- E. Mauduit / J. N. Girard / J.-M. Griessmeier / B. Cecconi
- Q. Nénon / S. Corbel
Summary
The search for radio signals from exoplanets or star-planet
interactions is a major challenge, as it is likely the best way to
detect and measure a planetary magnetic field and thus prob exoplanets’
interior structure. The aim of this article is to demonstrate the
relevance of using statistical tools to detect periodic radio signals in
unevenly spaced observations, and identify the implications of eas
measured period. Identification of periodic radio signal is achieved
here by a Lomb-Scargle (LS) analysis. We first apply the technique on
simulated astrophysical observations with controlled simulated noise.
This allows to characterize the origin of spurious detection peaks in
the resulting periodograms, as well as identifying peaks due to real
periods in the studied system, as well as resonance or beat periods. We
then validate this method on a real signal, using ~1400 hours of data
from observations of Jupiter’s radio emissions by the NenuFAR radio
telescope over more than six years to detect jovian radio emissions
periodicities (auroral and induced by the Galilean moons). We
demonstrate with the simulation that the LS periodogram allows to
correctly identify periodic radio signal, even in a diluted signal. On
real measurements, it correctly detects the rotation period of the
strong signal produced by Jupiter and the synodic period of the emission
triggered by the interaction between Jupiter and its Galilean moon Io,
but also possibly weaker signal such as the one produced by the
interaction between Jupiter and Europa or between Jupiter and Ganymede.
It is important to note that secondary peaks in the LS periodogram will
be observed at the synodic and resonance periods between all the
detected signal periodicities (i.e. real signals, but also periodicities
in the observation). These secondary peaks can then be used to
strengthen the detections of weak signals.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / T. Dusserre / H. Dole / F. Sarron
- G. Castignani / N. Ramos-Chernenko / N. Aghanim / A. Garic
- I.-E. Mellouki / N. Dagoneau / O. Chapuis / B. L. Frye
- M. Polletta / H. Dannerbauer / M. Langer / L. Maurin
- E. Soubrie / A. Biviano / S. Mei / N. Mai
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M.
Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / W. Holmes
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / S.
Maurogordato
- E. Medinaceli / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / G. Fabbian / L.
Gabarra
- M. Huertas-Company / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / M. Maturi
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / K. Benson / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- F. Cogato / T. Contini / A. R. Cooray / M. Costanzi
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P. Dimauro / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / A. H. Gonzalez
- G. Gozaliasl / A. Gruppuso / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / M. Migliaccio
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Philippon
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- F. Shankar / L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / J. R. Weaver
- J. G. Sorce / D. Scott
Summary
We search for galaxy protoclusters at redshifts  in the first
data release (Q1) of the
in the first
data release (Q1) of the  survey. We make use of the catalogues delivered by the
survey. We make use of the catalogues delivered by the  Science Ground Segment (SGS). After a galaxy selection on the
Science Ground Segment (SGS). After a galaxy selection on the  magnitude
and on the photometric redshift quality, we undertake the search using
the
magnitude
and on the photometric redshift quality, we undertake the search using
the  algorithm, an overdensity finder based on
Delaunay tessellation that uses photometric redshift probability
distributions through Monte Carlo simulations. In this pilot study, we
conduct a search in the 11
algorithm, an overdensity finder based on
Delaunay tessellation that uses photometric redshift probability
distributions through Monte Carlo simulations. In this pilot study, we
conduct a search in the 11  tiles that contain previously known
tiles that contain previously known  high star-forming galaxy protocluster candidates and focus on the two
detections that coincide with these regions. These counterparts lie at
photometric redshifts
high star-forming galaxy protocluster candidates and focus on the two
detections that coincide with these regions. These counterparts lie at
photometric redshifts  and
and
 and
have both been confirmed by two other independent protocluster detection
algorithms. We study their colours, their derived stellar masses and
star-formation rates, and we estimate their halo mass lower limits. We
investigate whether we are intercepting these galaxy overdensities in
their `dying’ phase, such that the high star-formation rates would be
due to their last unsustainable starburst before transitioning to groups
or clusters of galaxies. Indeed, some galaxy members are found to lie
above the main sequence of galaxies (star-formation rate versus stellar
mass). These overdense regions occupy a specific position in the dark
matter halo mass / redshift plane where forming galaxy clusters are
expected to have experienced a transition between cold flows to shock
heating in the halo. Finally, we empirically update the potential for
galaxy protocluster discoveries at redshift up to
and
have both been confirmed by two other independent protocluster detection
algorithms. We study their colours, their derived stellar masses and
star-formation rates, and we estimate their halo mass lower limits. We
investigate whether we are intercepting these galaxy overdensities in
their `dying’ phase, such that the high star-formation rates would be
due to their last unsustainable starburst before transitioning to groups
or clusters of galaxies. Indeed, some galaxy members are found to lie
above the main sequence of galaxies (star-formation rate versus stellar
mass). These overdense regions occupy a specific position in the dark
matter halo mass / redshift plane where forming galaxy clusters are
expected to have experienced a transition between cold flows to shock
heating in the halo. Finally, we empirically update the potential for
galaxy protocluster discoveries at redshift up to  (wide survey)
and
(wide survey)
and  (deep
survey) with
(deep
survey) with  for
the next data release (DR1).
for
the next data release (DR1).
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). First detections from the galaxy cluster
workflow
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / S. Bhargava / C. Benoist / A. H.
Gonzalez
- M. Maturi / J.-B. Melin / S. A. Stanford / E. Munari
- M. Vannier / C. Murray / S. Maurogordato / A. Biviano
- J. Macias-Perez / J. G. Bartlett / F. Pacaud / A. Widmer
- M. Meneghetti / B. Sartoris / M. Aguena / G. Alguero
- S. Andreon / S. Bardelli / L. Baumont / M. Bolzonella
- R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / G. Castignani / C. Combet
- J. Comparat / S. Farrens / Z. Ghaffari / P. A. Giles
- C. Giocoli / M. Girardi / N. A. Hatch / L. Ingoglia
- A. Iovino / G. A. Mamon / S. Mei / L. Moscardini
- S. Mourre / J. Odier / G. W. Pratt / P. Tarrío
- G. Toni / J. Weller / E. Zucca / N. Aghanim
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / P. Battaglia / F. Bellagamba
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- S. Ilić / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- P. Liebing / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback
- A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / J.
Skottfelt
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / P. Casenove / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / G. Fabbian / L. Gabarra / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / K. Benson / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- Y. Charles / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / M.
Costanzi
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P. Dimauro / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E.
Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu
- A. Loureiro / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / A. Montoro
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P.-F. Rocci / P. Rosati / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / J. Schaye / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
- E. Soubrie / D. Scott
Summary
The first survey data release by the Euclid mission covers
approximately  in the Euclid Deep Fields to the same depth as
the Euclid Wide Survey. This paper showcases, for the first time, the
performance of cluster finders on Euclid data and presents examples of
validated clusters in the Quick Release 1 (Q1) imaging data. We identify
clusters using two algorithms (AMICO and PZWav) implemented in the
Euclid cluster-detection pipeline. We explore the internal consistency
of detections from the two codes, and cross-match detections with known
clusters from other surveys using external multi-wavelength and
spectroscopic data sets. This enables assessment of the Euclid
photometric redshift accuracy and also of systematics such as
mis-centring between the optical cluster centre and centres based on
X-ray and/or Sunyaev–Zeldovich observations. We report 426 joint PZWav
and AMICO-detected clusters with high signal-to-noise ratios over the
full Q1 area in the redshift range
in the Euclid Deep Fields to the same depth as
the Euclid Wide Survey. This paper showcases, for the first time, the
performance of cluster finders on Euclid data and presents examples of
validated clusters in the Quick Release 1 (Q1) imaging data. We identify
clusters using two algorithms (AMICO and PZWav) implemented in the
Euclid cluster-detection pipeline. We explore the internal consistency
of detections from the two codes, and cross-match detections with known
clusters from other surveys using external multi-wavelength and
spectroscopic data sets. This enables assessment of the Euclid
photometric redshift accuracy and also of systematics such as
mis-centring between the optical cluster centre and centres based on
X-ray and/or Sunyaev–Zeldovich observations. We report 426 joint PZWav
and AMICO-detected clusters with high signal-to-noise ratios over the
full Q1 area in the redshift range  . The chosen redshift and signal-to-noise
thresholds are motivated by the photometric quality of the early Euclid
data. We provide richness estimates for each of the Euclid-detected
clusters and show its correlation with various external cluster mass
proxies. Out of the full sample, 77 systems are potentially new to the
literature. Overall, the Q1 cluster catalogue demonstrates a successful
validation of the workflow ahead of the Euclid Data Release 1, based on
the consistency of internal and external properties of Euclid-detected
clusters.
. The chosen redshift and signal-to-noise
thresholds are motivated by the photometric quality of the early Euclid
data. We provide richness estimates for each of the Euclid-detected
clusters and show its correlation with various external cluster mass
proxies. Out of the full sample, 77 systems are potentially new to the
literature. Overall, the Q1 cluster catalogue demonstrates a successful
validation of the workflow ahead of the Euclid Data Release 1, based on
the consistency of internal and external properties of Euclid-detected
clusters.
CHEX-MATE:
Multi-probe analysis of Abell 1689
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- L. Chappuis / D. Eckert / M. Sereno / A. Gavidia
- J. Sayers / J. Kim / M. Rossetti / K. Umetsu
- H. Saxena / I. Bartalucci / R. Gavazzi / A.
Rowlands Doblas
- E. Pointecouteau / S. Ettori / G. W. Pratt / H. Bourdin
- R. Cassano / F. De Luca / M. Donahue / M. Gaspari
- F. Gastaldello / V. Ghirardini / M. Gitti / B. Maughan
- P. Mazzotta / F. Oppizzi / E. Rasia / M. Radovich
Summary
The nature of the elusive dark matter can be probed by comparing the
predictions of the cold dark matter framework with the gravitational
field of massive galaxy clusters. However, a robust test of dark matter
can only be achieved if the systematic uncertainties in the
reconstruction of the gravitational potential are minimized. Techniques
based on the properties of intracluster gas rely on the assumption that
the gas is in hydrostatic equilibrium within the potential well, whereas
gravitational lensing is sensitive to projection effects. Here we
attempt to minimize systematics in galaxy cluster mass reconstructions
by jointly exploiting the weak gravitational lensing signal and the
properties of the hot intracluster gas determined from X-ray and
millimeter (Sunyaev-Zel’dovich) observations. We construct a model to
fit the multi-probe information within a common framework, accounting
for non-thermal pressure support and elongation of the dark matter halo
along the line of sight. We then apply our framework to the massive
cluster Abell 1689, which features unparalleled multi-wavelength data.
In accordance with previous works, we find that the cluster is
significantly elongated along the line of sight. Accounting for
line-of-sight projections, we require a non-thermal pressure support of
 at
at
 to match the gas
and weak lensing observables. The joint model retrieves a concentration
to match the gas
and weak lensing observables. The joint model retrieves a concentration
 , which is
lower and more realistic than the high concentration retrieved from weak
lensing data alone under the assumption of spherical symmetry (
, which is
lower and more realistic than the high concentration retrieved from weak
lensing data alone under the assumption of spherical symmetry ( ).
Application of our method to a larger sample will allow us to study at
the same time the shape of dark matter mass profiles and the level of
non-thermal pressure support in galaxy clusters.
).
Application of our method to a larger sample will allow us to study at
the same time the shape of dark matter mass profiles and the level of
non-thermal pressure support in galaxy clusters.
The
COSMOS Wall at z ~ 0.73: Quiescent galaxies and their evolution in
different environments
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- F. R. Ditrani / M. Longhetti / A. Iovino / M. Fossati
- S. Zhou / S. Bardelli / M. Bolzonella / O. Cucciati
- A. Finoguenov / L. Pozzetti / M. Salvato / M. Scodeggio
- L. Tasca / D. Vergani / E. Zucca
Summary
The evolution of quiescent galaxies is driven by numerous physical
processes, often considered to be related to their stellar mass and
environment over cosmic time. Tracing their stellar populations can
provide insight into the processes that transformed these galaxies into
their observed quiescent state. In particular, higher-redshift galaxies
exhibit more pronounced relative age differences. At early stages, even
small differences in age remain significant, whereas as galaxies evolve,
these differences become harder to detect in the local Universe. The
COSMOS Wall is a structure at z ~ 0.73 that contains a large variety of
environments, from rich clusters down to field-like regions. This sample
offers a great opportunity to study the effect of the environment on the
quiescent galaxy population. Leveraging high-quality spectroscopic data
from the LEGA-C survey, and photometric data from the COSMOS2020
catalogue, we performed a full-index and photometry fitting of 74
massive quiescent galaxies, deriving their mass-weighted ages,
metallicities, and star formation timescales. We characterised the
environment in three subsamples: X-ray and non-X-ray groups and a field
subsample. We find a decreasing trend in mass-weighted age with
increasing environmental density, with galaxies groups > 1 Gyr older
than those in the field. Conversely, we do not find any significant
difference in stellar metallicity between galaxies in X-ray and
non-X-ray groups, while we find galaxies with 0.15 dex higher
metallicities in the field. Our results indicate that, at z ~ 0.7, the
environment plays a crucial role in shaping the evolution of massive
quiescent galaxies, noticeably affecting both their mass-weighted age
and star formation timescale. These results support faster quenching
mechanisms, at fixed stellar mass, in the dense X-ray-detected groups
compared to the field.
The
Parallel Ionizing Emissivity Survey (PIE). I. Survey design and
selection of candidate Lyman Continuum leakers at 3.1<z<3.5
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alexander Beckett / Marc Rafelski / Claudia
Scarlata / Wanjia Hu
- Keunho Kim / Ilias Goovaerts / Matthew A. Malkan /
Wayne Webb
- Harry Teplitz / Matthew Hayes / Vihang Mehta / Anahita Alavi
- Andrew J. Bunker / Annalisa Citro / Nimish Hathi / Alaina Henry
- Alexandra Le Reste / Alessia Moretti / Michael J. Rutkowski / Maxime
Trebitsch
- Anita Zanella
Summary
We present the survey design and initial results from the Parallel
Ionizing Emissivity (PIE) survey. PIE is a large HST survey designed to
detect Lyman continuum (LyC) emitting galaxies at 3.1 z $<
z $< <$ z $<$3.5, which can be followed up using
ground-based spectrographs to confirm their redshifts. Unlike previous
surveys, we use many independent fields to remove biases caused by
correlated absorption in the IGM. In this paper, we describe the survey
design, photometric measurements, and the use of mock galaxy samples to
optimize our color selection. With 3 filters, we can select a galaxy
sample of which $
<$ z $<$3.5, which can be followed up using
ground-based spectrographs to confirm their redshifts. Unlike previous
surveys, we use many independent fields to remove biases caused by
correlated absorption in the IGM. In this paper, we describe the survey
design, photometric measurements, and the use of mock galaxy samples to
optimize our color selection. With 3 filters, we can select a galaxy
sample of which $ <$ z $<$3.5 range for which we can detect
uncontaminated LyC emission in F336W. We also use mock IGM sightlines to
measure the expected transmission of the IGM, which will allow us to
determine escape fractions from our stacked galaxies. We color-select
$$1400 galaxies, and predict that this includes $$80 LyC-emitting
galaxies and $$500 that we can use in stacking. Finally, we present the
Keck/LRIS spectrum of a galaxy at z
<$ z $<$3.5 range for which we can detect
uncontaminated LyC emission in F336W. We also use mock IGM sightlines to
measure the expected transmission of the IGM, which will allow us to
determine escape fractions from our stacked galaxies. We color-select
$$1400 galaxies, and predict that this includes $$80 LyC-emitting
galaxies and $$500 that we can use in stacking. Finally, we present the
Keck/LRIS spectrum of a galaxy at z  2.99, demonstrating
that we can confirm the redshifts of z
2.99, demonstrating
that we can confirm the redshifts of z  3 galaxies from the
ground.
3 galaxies from the
ground.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- S. Zhou / A. Iovino / M. Longhetti / M. Scodeggio
- S. Bardelli / M. Bolzonella / O. Cucciati / F. R. Ditrani
- A. Finoguenov / L. Pozzetti / M. Salvato / L.
Tasca
- D. Vergani / E. Zucca
Summary
We present a study of the evolution of star-forming galaxies within
the so-called Wall structure at z$$0.73 in the field of the COSMOS
survey. We use a sample of star-forming galaxies from a comprehensive
range of environments and across a wide stellar mass range and discuss
the correlation between the environment and the galaxy’s internal
properties, including its metallicity from the present-day gas-phase
value measured from emission-lines and its past evolution as imprinted
in its stellar populations. We build a simple yet comprehensive galaxy
chemical evolution model, which is constrained by the gas-phase
metallicities, stacked spectra and photometry of galaxies to reach a
full description of the galaxies’ past star formation and chemical
evolution histories in different environments. We reproduce the
`downsizing’ formation of galaxies in both their star formation
histories and chemical evolution histories at  so that more
massive galaxies tend to grow their stellar mass and become enriched in
metals earlier than less massive ones. In addition, the current
gas-phase metallicity of a galaxy and its past evolution correlate with
the environment it inhabits. Galaxies in groups, especially massive
groups that have X-ray counterparts, tend to have higher gas-phase
metallicities and are enriched in metals earlier than field galaxies of
similar stellar mass. Galaxies in the highest stellar mass bin and
located in X-ray groups exhibit a more complex and varied chemical
composition. Strangulation due to interactions with the group
environment, leading to an early cessation of gas supply, may have
driven the faster mass growth and chemical enrichment observed in group
galaxies. Additionally, the removal of metal-enriched gas could play a
key role in the evolution of the most massive galaxies. Alternative
mechanisms other than environmental processes are also discussed.
so that more
massive galaxies tend to grow their stellar mass and become enriched in
metals earlier than less massive ones. In addition, the current
gas-phase metallicity of a galaxy and its past evolution correlate with
the environment it inhabits. Galaxies in groups, especially massive
groups that have X-ray counterparts, tend to have higher gas-phase
metallicities and are enriched in metals earlier than field galaxies of
similar stellar mass. Galaxies in the highest stellar mass bin and
located in X-ray groups exhibit a more complex and varied chemical
composition. Strangulation due to interactions with the group
environment, leading to an early cessation of gas supply, may have
driven the faster mass growth and chemical enrichment observed in group
galaxies. Additionally, the removal of metal-enriched gas could play a
key role in the evolution of the most massive galaxies. Alternative
mechanisms other than environmental processes are also discussed.
Low
Surface Brightness structures from annotated deep CFHT images: effects
of the host galaxy’s properties and environment
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Elisabeth Sola / Pierre-Alain Duc / Mathias Urbano / Felix
Richards
- Adeline Paiement / Michal Bílek / Mustafa K. Yıldız /
Alessandro Boselli
- Patrick Côté / Jean-Charles Cuillandre / Laura Ferrarese / Stephen
Gwyn
- Olivier Marchal / Alan W. McConnachie / Matthieu Baumann / Thomas
Boch
- Florence Durret / Matteo Fossati / Rebecca Habas / Francine
Marleau
- Oliver Müller / Mélina Poulain / Vasily Belokurov
Summary
Hierarchical galactic evolution models predict that mergers drive
galaxy growth, producing low surface brightness (LSB) tidal features
that trace galaxies’ late assembly. These faint structures encode
information about past mergers and are sensitive to the properties and
environment of the host galaxy. We investigated the relationships
between LSB features and their hosts in a sample of 475 nearby massive
galaxies spanning diverse environments (field, groups, Virgo cluster)
using deep optical imaging from the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope
(MATLAS, UNIONS/CFIS, VESTIGE, NGVS). Using Jafar, an online annotation
tool, we manually annotated tidal features and extended stellar haloes,
including 199 tidal tails and 100 streams. Geometric and photometric
measurements were extracted to analyse their dependence on galaxy mass,
environment, and internal kinematics. At our surface brightness limit of
29 mag arcsec
arcsec , tidal features and
stellar haloes contribute 2% and 10% of total galaxy luminosity,
respectively. Tidal features are detected in 36% of galaxies, with none
fainter than 27.8 mag
, tidal features and
stellar haloes contribute 2% and 10% of total galaxy luminosity,
respectively. Tidal features are detected in 36% of galaxies, with none
fainter than 27.8 mag arcsec
arcsec . The most massive
galaxies are twice as likely to host tidal debris, and for early-type
galaxies their halos are twice as luminous as those in lower-mass
systems, a trend not observed in late-type galaxies. Although
small-scale interactions increase the frequency of tidal features, the
large-scale environment does not influence it. An anticorrelation
between this frequency and rotational support is found, but may reflect
the mass-driven effect. We release our database of annotated features
for deep learning applications. Our findings confirm that galaxy mass is
the dominant factor influencing tidal feature prevalence, consistent
with hierarchical formation models.
. The most massive
galaxies are twice as likely to host tidal debris, and for early-type
galaxies their halos are twice as luminous as those in lower-mass
systems, a trend not observed in late-type galaxies. Although
small-scale interactions increase the frequency of tidal features, the
large-scale environment does not influence it. An anticorrelation
between this frequency and rotational support is found, but may reflect
the mass-driven effect. We release our database of annotated features
for deep learning applications. Our findings confirm that galaxy mass is
the dominant factor influencing tidal feature prevalence, consistent
with hierarchical formation models.
Articles for week 12 2025
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). NIR processing and data products
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / G. Polenta / M. Frailis / A. Alavi
- P. N. Appleton / P. Awad / A. Bonchi / R. Bouwens
- L. Bramante / D. Busonero / G. Calderone / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / M. Correnti / R. da Silva / I.
Das
- F. Faustini / Y. Fu / T. Gasparetto / W. Gillard
- A. Grazian / S. Hemmati / J. Jacobson / K. Jahnke
- B. Kubik / X. Liu / C. Macabiau / E. Medinaceli
- P. W. Morris / K. Paterson / M. Radovich / M. Schirmer
- A. Shulevski / H. I. Teplitz / B. Venemans / N. Aghanim
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia / A. N. Belikov
- R. Bender / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / L. Corcione
- A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da
Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou
- N. Fourmanoit / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan
- J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / P. Liebing / S.
Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / G. D. Racca
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- B. Rusholme / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno
- N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / P. Casenove / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / G. Fabbian / L. Gabarra / M.
Huertas-Company
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri / A. A. Nucita
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / P.
Bergamini
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / S. Borgani / A. S. Borlaff / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / Y. Charles / R.
Chary
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. M. N. Ferguson / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A.
Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- A. H. Gonzalez / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / A. Gruppuso
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E.
Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / V. Le Brun / J. Le
Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / C. J. R. McPartland / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- A. Montoro / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur
- K. Naidoo / P. Natoli / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- L. Nicastro / F. Passalacqua / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- C. Scarlata / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- F. Shankar / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / J. R. Weaver
- M. Bella / D. Scott
Summary
This paper describes the near-infrared processing function (NIR PF)
that processes near-infrared images from the Near-Infrared Spectrometer
and Photometer (NISP) instrument onboard the Euclid satellite. NIR PF
consists of three main components: (i) a common pre-processing stage for
both photometric (NIR) and spectroscopic (SIR) data to remove
instrumental effects; (ii) astrometric and photometric calibration of
NIR data, along with catalogue extraction; and (iii) resampling and
stacking. The necessary calibration products are generated using
dedicated pipelines that process observations from both the early
performance verification (PV) phase in 2023 and the nominal survey
operations. After outlining the pipeline’s structure and algorithms, we
demonstrate its application to Euclid Q1 images. For Q1, we achieve an
astrometric accuracy of 9-15 mas, a relative photometric accuracy of 5
mmag, and an absolute flux calibration limited by the 1% uncertainty of
the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) CALSPEC database. We characterise the
point-spread function (PSF) that we find very stable across the focal
plane, and we discuss current limitations of NIR PF that will be
improved upon for future data releases.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1) The Strong Lensing Discovery Engine B – Early
strong lens candidates from visual inspection of high velocity
dispersion galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / K. Rojas / T. E. Collett / J. A. Acevedo
Barroso
- J. W. Nightingale / D. Stern / L. A. Moustakas / S. Schuldt
- G. Despali / A. Melo / M. Walmsley / D. J. Ballard
- W. J. R. Enzi / T. Li / A. Sainz de Murieta / I. T. Andika
- B. Clément / F. Courbin / L. R. Ecker / R.
Gavazzi
- N. Jackson / A. Kovács / P. Matavulj / M. Meneghetti
- S. Serjeant / D. Sluse / C. Tortora / A. Verma
- L. Marchetti / C. M. O’Riordan / K. McCarthy / S. H. Suyu
- R. B. Metcalf / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- R. Bender / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / P. Liebing / S.
Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- S. Alvi / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela
- C. Benoist / K. Benson / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E.
Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- C. Scarlata / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Vernardos / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / J. Wilde / D. Scott
Summary
We present a search for strong gravitational lenses in Euclid imaging
with high stellar velocity dispersion ( km/s)
reported by SDSS and DESI. We performed expert visual inspection and
classification of
km/s)
reported by SDSS and DESI. We performed expert visual inspection and
classification of  images. We
discovered 38 grade A and 40 grade B candidate lenses, consistent with
an expected sample of $$32. Palomar spectroscopy confirmed 5 lens
systems, while DESI spectra confirmed one, provided ambiguous results
for another, and help to discard one. The automated lens modeler
modelled 53 candidates, confirming 38 as lenses, failing to model 9, and
ruling out 6 grade B candidates. For the remaining 25 candidates we
could not gather additional information. More importantly, our
expert-classified non-lenses provide an excellent training set for
machine learning lens classifiers. We create high-fidelity simulations
of lenses by painting realistic lensed sources behind the expert tagged
(non-lens) luminous red galaxies. This training set is the foundation
stone for the galaxy-galaxy strong lensing discovery engine.
images. We
discovered 38 grade A and 40 grade B candidate lenses, consistent with
an expected sample of $$32. Palomar spectroscopy confirmed 5 lens
systems, while DESI spectra confirmed one, provided ambiguous results
for another, and help to discard one. The automated lens modeler
modelled 53 candidates, confirming 38 as lenses, failing to model 9, and
ruling out 6 grade B candidates. For the remaining 25 candidates we
could not gather additional information. More importantly, our
expert-classified non-lenses provide an excellent training set for
machine learning lens classifiers. We create high-fidelity simulations
of lenses by painting realistic lensed sources behind the expert tagged
(non-lens) luminous red galaxies. This training set is the foundation
stone for the galaxy-galaxy strong lensing discovery engine.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). The first catalogue of strong-lensing galaxy
clusters
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / P. Bergamini / M. Meneghetti / A.
Acebron
- B. Clément / M. Bolzonella / C. Grillo / P. Rosati
- D. Abriola / J. A. Acevedo Barroso / G. Angora / L. Bazzanini
- R. Cabanac / B. C. Nagam / A. R. Cooray / G. Despali
- G. Di Rosa / J. M. Diego / M. Fogliardi / A. Galan
- R. Gavazzi / G. Granata / N. B. Hogg / K.
Jahnke
- L. Leuzzi / T. Li / M. Lombardi / G. Mahler
- A. Manjón-García / R. B. Metcalf / M. Oguri / C. Olave
- J. M. Palencia / J. Richard / K. Rojas / L. R. Ecker
- C. Scarlata / M. Schirmer / S. Schuldt / D. Sluse
- G. P. Smith / C. Tortora / G. Vernardos / G. L. Walth
- J. Wilde / Y. Xie / M. Zumalacarregui / N. Aghanim
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / L. Amendola / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia
- R. Bender / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- R. Kohley / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / R. Laureijs
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
P. Liebing
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- S. Mourre / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- B. Rusholme / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / A. Cappi
- P. Casenove / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L.
Gabarra
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / M. Maturi / N. Mauri
- A. A. Nucita / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist
- K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / O. Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / A. H. Gonzalez / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / C.
Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / O. Ilbert / M.
Jauzac
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / C. Murray / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P. Reimberg / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- A. Schneider / M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- F. Shankar / L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
- E. Soubrie / D. Scott
Summary
We present the first catalogue of strong lensing galaxy clusters
identified in the Euclid Quick Release 1 observations (covering  ). This catalogue is the result of the visual
inspection of 1260 cluster fields. Each galaxy cluster was ranked with a
probability,
). This catalogue is the result of the visual
inspection of 1260 cluster fields. Each galaxy cluster was ranked with a
probability,  , based on the number and plausibility of the
identified strong lensing features. Specifically, we identified 83
gravitational lenses with
, based on the number and plausibility of the
identified strong lensing features. Specifically, we identified 83
gravitational lenses with  , of
which 14 have
, of
which 14 have  , and
clearly exhibiting secure strong lensing features, such as giant
tangential and radial arcs, and multiple images. Considering the
measured number density of lensing galaxy clusters, approximately
, and
clearly exhibiting secure strong lensing features, such as giant
tangential and radial arcs, and multiple images. Considering the
measured number density of lensing galaxy clusters, approximately  for
for  , we
predict that will likely see more than 4500 strong lensing clusters
over the course of the mission. Notably, only three of the identified
cluster-scale lenses had been previously observed from space. Thus, has
provided the first high-resolution imaging for the remaining
, we
predict that will likely see more than 4500 strong lensing clusters
over the course of the mission. Notably, only three of the identified
cluster-scale lenses had been previously observed from space. Thus, has
provided the first high-resolution imaging for the remaining 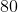 galaxy cluster lenses, including those
with the highest probability. The identified strong lensing features
will be used for training deep-learning models for identifying
gravitational arcs and multiple images automatically in observations.
This study confirms the huge potential of for finding new strong lensing
clusters, enabling exciting new discoveries on the nature of dark matter
and dark energy and the study of the high-redshift Universe.
galaxy cluster lenses, including those
with the highest probability. The identified strong lensing features
will be used for training deep-learning models for identifying
gravitational arcs and multiple images automatically in observations.
This study confirms the huge potential of for finding new strong lensing
clusters, enabling exciting new discoveries on the nature of dark matter
and dark energy and the study of the high-redshift Universe.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Galaxy shapes and alignments in the cosmic
web
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / C. Laigle / C. Gouin / F. Sarron
- L. Quilley / C. Pichon / K. Kraljic / F. Durret
- N. E. Chisari / U. Kuchner / N. Malavasi / M. Magliocchetti
- H. J. McCracken / J. G. Sorce / Y. Kang / C. J. R. McPartland
- S. Toft / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Basset
- P. Battaglia / F. Bernardeau / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George
- W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik
- K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
P. Liebing
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / B. Rusholme
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- N. Tessore / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / A. Balaguera-Antolinez / C.
Benoist
- K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / T. Contini
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- A. H. Gonzalez / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / S. Joudaki / J. J. E. Kajava / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi
- T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / A. Montoro
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar
- L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / J. R. Weaver / D. Scott
Summary
Galaxy morphologies and shape orientations are expected to correlate
with their large-scale environment, since they grow by accreting matter
from the cosmic web and are subject to interactions with other galaxies.
Cosmic filaments are extracted in projection from the Euclid Quick Data
Release 1 (covering 63.1  ) at
) at
 in
tomographic slices of 170 comoving
in
tomographic slices of 170 comoving  using photometric redshifts. Galaxy morphologies
are accurately retrieved thanks to the excellent resolution of VIS data.
The distribution of massive galaxies (
using photometric redshifts. Galaxy morphologies
are accurately retrieved thanks to the excellent resolution of VIS data.
The distribution of massive galaxies ( ) in the projected cosmic web is analysed as a
function of morphology measured from VIS data. Specifically, the 2D
alignment of galaxy shapes with large-scale filaments is quantified as a
function of Sérsic indices and masses. We find the known trend that more
massive galaxies are closer to filament spines. At fixed stellar masses,
morphologies correlate both with densities and distances to large-scale
filaments. In addition, the large volume of this data set allows us to
detect a signal indicating that there is a preferential alignment of the
major axis of massive early-type galaxies along projected cosmic
filaments. Overall, these results demonstrate our capabilities to carry
out detailed studies of galaxy environments with Euclid, which will be
extended to higher redshift and lower stellar masses with the future
Euclid Deep Survey.
) in the projected cosmic web is analysed as a
function of morphology measured from VIS data. Specifically, the 2D
alignment of galaxy shapes with large-scale filaments is quantified as a
function of Sérsic indices and masses. We find the known trend that more
massive galaxies are closer to filament spines. At fixed stellar masses,
morphologies correlate both with densities and distances to large-scale
filaments. In addition, the large volume of this data set allows us to
detect a signal indicating that there is a preferential alignment of the
major axis of massive early-type galaxies along projected cosmic
filaments. Overall, these results demonstrate our capabilities to carry
out detailed studies of galaxy environments with Euclid, which will be
extended to higher redshift and lower stellar masses with the future
Euclid Deep Survey.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). The Strong Lensing Discovery Engine E –
Ensemble classification of strong gravitational lenses: lessons for Data
Release 1
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / P. Holloway / A. Verma / M. Walmsley
- P. J. Marshall / A. More / T. E. Collett / N. E. P. Lines
- L. Leuzzi / A. Manjón-García / S. H. Vincken / J. Wilde
- R. Pearce-Casey / I. T. Andika / J. A. Acevedo Barroso / T. Li
- A. Melo / R. B. Metcalf / K. Rojas / B. Clément
- H. Degaudenzi / F. Courbin / G. Despali / R.
Gavazzi
- S. Schuldt / B. C. Nagam / D. Sluse / C. Tortora
- H. Domínguez Sánchez / K. Finner / A. Galan / C. Giocoli
- L. Guzzo / N. B. Hogg / K. Jahnke / S. Kruk
- G. Mahler / M. Millon / P. Nugent / J. Pearson
- L. R. Ecker / A. Sainz de Murieta / C. Scarlata / S. Serjeant
- A. Sonnenfeld / C. Spiniello / T. T. Thai / L. Ulivi
- L. Weisenbach / M. Zumalacarregui / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / W. Holmes
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- P. Schneider / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / A. A. Nucita / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela
- C. Benoist / K. Benson / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / C.
Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / A. Montoro
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Vernardos / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / D. Scott
Summary
The Euclid Wide Survey (EWS) is expected to identify of order  galaxy-galaxy
strong lenses across
galaxy-galaxy
strong lenses across  deg
deg . The Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1) of
. The Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1) of
 deg
deg Euclid images provides an excellent
opportunity to test our lens-finding ability, and to verify the
anticipated lens frequency in the EWS. Following the Q1 data release,
eight machine learning networks from five teams were applied to
approximately one million images. This was followed by a citizen science
inspection of a subset of around
Euclid images provides an excellent
opportunity to test our lens-finding ability, and to verify the
anticipated lens frequency in the EWS. Following the Q1 data release,
eight machine learning networks from five teams were applied to
approximately one million images. This was followed by a citizen science
inspection of a subset of around  images, of which
images, of which
 received high network
scores, with the remainder randomly selected. The top scoring outputs
were inspected by experts to establish confident (grade A), likely
(grade B), possible (grade C), and unlikely lenses. In this paper we
combine the citizen science and machine learning classifiers into an
ensemble, demonstrating that a combined approach can produce a purer and
more complete sample than the original individual classifiers. Using the
expert-graded subset as ground truth, we find that this ensemble can
provide a purity of
received high network
scores, with the remainder randomly selected. The top scoring outputs
were inspected by experts to establish confident (grade A), likely
(grade B), possible (grade C), and unlikely lenses. In this paper we
combine the citizen science and machine learning classifiers into an
ensemble, demonstrating that a combined approach can produce a purer and
more complete sample than the original individual classifiers. Using the
expert-graded subset as ground truth, we find that this ensemble can
provide a purity of  (grade A/B
lenses) with
(grade A/B
lenses) with  completeness (for
context, due to the rarity of lenses a random classifier would have a
purity of
completeness (for
context, due to the rarity of lenses a random classifier would have a
purity of  ). We discuss future
lessons for the first major Euclid data release (DR1), where the
big-data challenges will become more significant and will require
analysing more than
). We discuss future
lessons for the first major Euclid data release (DR1), where the
big-data challenges will become more significant and will require
analysing more than  million galaxies,
and thus time investment of both experts and citizens must be carefully
managed.
million galaxies,
and thus time investment of both experts and citizens must be carefully
managed.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). The active galaxies of Euclid
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / T. Matamoro Zatarain / S. Fotopoulou / F.
Ricci
- M. Bolzonella / F. La Franca / A. Viitanen / G. Zamorani
- M. B. Taylor / M. Mezcua / B. Laloux / A. Bongiorno
- K. Jahnke / G. Stevens / R. A. Shaw / L. Bisigello
- W. Roster / Y. Fu / B. Margalef-Bentabol / A. La Marca
- F. Tarsitano / A. Feltre / J. Calhau / X. Lopez Lopez
- M. Scialpi / M. Salvato / V. Allevato / M. Siudek
- C. Saulder / D. Vergani / M. N. Bremer / L. Wang
- M. Giulietti / D. M. Alexander / D. Sluse / F. Shankar
- L. Spinoglio / D. Scott / R. Shirley / H. Landt
- M. Selwood / Y. Toba / P. Dayal / N. Aghanim
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- A. Basset / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- P. Liebing / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / D. C.
Masters
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / H. J. A. Rottgering / B. Rusholme
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko
- E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo
- G. Fabbian / L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- C. Benoist / K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / T. Contini
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / F. Fontanot
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi
- T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / A. Shulevski
- L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / E. Soubrie
Summary
We present a catalogue of candidate active galactic nuclei (AGN) in
the  Quick Release (Q1)
fields. For each
Quick Release (Q1)
fields. For each  source we collect
multi-wavelength photometry and spectroscopy information from Galaxy
Evolution Explorer (GALEX),
source we collect
multi-wavelength photometry and spectroscopy information from Galaxy
Evolution Explorer (GALEX),  , Dark Energy Survey
(DES), Wise-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE),
, Dark Energy Survey
(DES), Wise-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE),  , Dark Energy Survey
(DESI), and Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), including spectroscopic
redshift from public compilations. We investigate the AGN contents of
the Q1 fields by applying selection criteria using
, Dark Energy Survey
(DESI), and Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), including spectroscopic
redshift from public compilations. We investigate the AGN contents of
the Q1 fields by applying selection criteria using  colours and
WISE-AllWISE cuts finding respectively 292,222 and 65,131 candidates. We
also create a high-purity QSO catalogue based on
colours and
WISE-AllWISE cuts finding respectively 292,222 and 65,131 candidates. We
also create a high-purity QSO catalogue based on  DR3 information
containing 1971 candidates. Furthermore, we utilise the collected
spectroscopic information from DESI to perform broad-line and
narrow-line AGN selections, leading to a total of 4392 AGN candidates in
the Q1 field. We investigate and refine the Q1 probabilistic random
forest QSO population, selecting a total of 180,666 candidates.
Additionally, we perform SED fitting on a subset of sources with
available
DR3 information
containing 1971 candidates. Furthermore, we utilise the collected
spectroscopic information from DESI to perform broad-line and
narrow-line AGN selections, leading to a total of 4392 AGN candidates in
the Q1 field. We investigate and refine the Q1 probabilistic random
forest QSO population, selecting a total of 180,666 candidates.
Additionally, we perform SED fitting on a subset of sources with
available  ,
and by utilizing the derived AGN fraction, we identify a total of 7766
AGN candidates. We discuss purity and completeness of the selections and
define two new colour selection criteria (
,
and by utilizing the derived AGN fraction, we identify a total of 7766
AGN candidates. We discuss purity and completeness of the selections and
define two new colour selection criteria (
 and
and

 ) to improve on purity, finding 313,714
and 267,513 candidates respectively in the Q1 data. We find a total of
229,779 AGN candidates equivalent to an AGN surface density of 3641
deg
) to improve on purity, finding 313,714
and 267,513 candidates respectively in the Q1 data. We find a total of
229,779 AGN candidates equivalent to an AGN surface density of 3641
deg for
for  , and a subsample of 30,422 candidates
corresponding to an AGN surface density of 482 deg
, and a subsample of 30,422 candidates
corresponding to an AGN surface density of 482 deg when limiting the depth
to
when limiting the depth
to  . The surface density of AGN recovered from this
work is in line with predictions based on the AGN X-ray luminosity
functions.
. The surface density of AGN recovered from this
work is in line with predictions based on the AGN X-ray luminosity
functions.
Euclid:
Quick Data Release (Q1) – Photometric studies of known transients
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. Duffy / E. Cappellaro / M. T. Botticella / I. M. Hook
- F. Poidevin / T. J. Moriya / A. A. Chrimes / V. Petrecca
- K. Paterson / A. Goobar / L. Galbany / R. Kotak
- C. Gall / C. M. Gutierrez / C. Tao / L. Izzo
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- R. Casas / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / P. Franzetti
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / B. Kubik
- K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
P. Liebing
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / E. Medinaceli / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / M. Moresco
- P. W. Morris / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / L. Gabarra / V. Scottez / D. Scott
- M. Sullivan
Summary
We report on serendipitous Euclid observations of previously known
transients, using the Euclid Q1 data release. By cross-matching with the
Transient Name Server (TNS) we identify 164 transients that coincide
with the data release. Although the Euclid Q1 release only includes
single-epoch data, we are able to make Euclid photometric measurements
at the location of 161 of these transients. Euclid obtained deep
photometric measurements or upper limits of these transients in the  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  bands at various phases of the
transient light-curves, including before, during, and after the
observations of ground-based transient surveys. Approximately 70% of
known transients reported in the six months before the Euclid
observation date and with discovery magnitude brighter than 24 were
detected in Euclid
bands at various phases of the
transient light-curves, including before, during, and after the
observations of ground-based transient surveys. Approximately 70% of
known transients reported in the six months before the Euclid
observation date and with discovery magnitude brighter than 24 were
detected in Euclid  images. Our observations
include one of the earliest near-infrared detections of a Type~Ia
supernova (SN 2024pvw) 15 days prior to its peak brightness, and the
late-phase (435.9 days post peak) observations of the enigmatic
core-collapse SN 2023aew. Euclid deep photometry provides valuable
information on the nature of these transients such as their progenitor
systems and power sources, with late time observations being a uniquely
powerful contribution. In addition, Euclid is able to detect the host
galaxies of some transients that were previously classed as hostless.
The Q1 data demonstrate the power of the Euclid data even with only
single-epoch observations available, as will be the case for much larger
areas of sky in the Euclid Wide Survey.
images. Our observations
include one of the earliest near-infrared detections of a Type~Ia
supernova (SN 2024pvw) 15 days prior to its peak brightness, and the
late-phase (435.9 days post peak) observations of the enigmatic
core-collapse SN 2023aew. Euclid deep photometry provides valuable
information on the nature of these transients such as their progenitor
systems and power sources, with late time observations being a uniquely
powerful contribution. In addition, Euclid is able to detect the host
galaxies of some transients that were previously classed as hostless.
The Q1 data demonstrate the power of the Euclid data even with only
single-epoch observations available, as will be the case for much larger
areas of sky in the Euclid Wide Survey.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1), A first look at the fraction of bars in massive
galaxies at 
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / M. Huertas-Company / M. Walmsley / M.
Siudek
- P. Iglesias-Navarro / J. H. Knapen / S. Serjeant / H. J.
Dickinson
- L. Fortson / I. Garland / T. Géron / W. Keel
- S. Kruk / C. J. Lintott / K. Mantha / K. Masters
- D. O’Ryan / J. J. Popp / H. Roberts / C. Scarlata
- J. S. Makechemu / B. Simmons / R. J. Smethurst / A. Spindler
- M. Baes / E. M. Corsini / H. Domínguez Sánchez / E.
Duran-Camacho
- H. Fu / J. Junais / J. Mendez-Abreu / A. Nersesian
- F. Shankar / M. N. Le / J. Vega-Ferrero / L. Wang
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia / F. Bernardeau
- A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / B. Kubik
- K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / S.
Matthew
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- C. Benoist / K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- Y. Charles / F. Cogato / T. Contini / A. R.
Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / F. Fontanot / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E.
Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / J. Schaye
- A. Schneider / M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / E. Soubrie / D. Scott
Summary
Stellar bars are key structures in disc galaxies, driving angular
momentum redistribution and influencing processes such as bulge growth
and star formation. Quantifying the bar fraction as a function of
redshift and stellar mass is therefore important for constraining the
physical processes that drive disc formation and evolution across the
history of the Universe. Leveraging the unprecedented resolution and
survey area of the Euclid Q1 data release combined with the Zoobot
deep-learning model trained on citizen-science labels, we identify 7711
barred galaxies with  in a magnitude-selected sample
in a magnitude-selected sample  spanning
spanning  . We measure a
mean bar fraction of
. We measure a
mean bar fraction of  , consistent with
prior studies. At fixed redshift, massive galaxies exhibit higher bar
fractions, while lower-mass systems show a steeper decline with
redshift, suggesting earlier disc assembly in massive galaxies.
Comparisons with cosmological simulations (e.g., TNG50, Auriga) reveal a
broadly consistent bar fraction, but highlight overpredictions for
high-mass systems, pointing to potential over-efficiency in central
stellar mass build-up in simulations. These findings demonstrate
Euclid’s transformative potential for galaxy morphology studies and
underscore the importance of refining theoretical models to better
reproduce observed trends. Future work will explore finer mass bins,
environmental correlations, and additional morphological indicators.
, consistent with
prior studies. At fixed redshift, massive galaxies exhibit higher bar
fractions, while lower-mass systems show a steeper decline with
redshift, suggesting earlier disc assembly in massive galaxies.
Comparisons with cosmological simulations (e.g., TNG50, Auriga) reveal a
broadly consistent bar fraction, but highlight overpredictions for
high-mass systems, pointing to potential over-efficiency in central
stellar mass build-up in simulations. These findings demonstrate
Euclid’s transformative potential for galaxy morphology studies and
underscore the importance of refining theoretical models to better
reproduce observed trends. Future work will explore finer mass bins,
environmental correlations, and additional morphological indicators.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): VIS processing and data products
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / H. J. McCracken / K. Benson / C. Dolding
- T. Flanet / C. Grenet / O. Herent / P. Hudelot
- C. Laigle / G. Leroy / P. Liebing / R. Massey
- S. Mottet / R. Nakajima / H. N. Nguyen-Kim / J. W. Nightingale
- J. Skottfelt / L. C. Smith / F. Soldano / E. Vilenius
- M. Wander / M. von Wietersheim-Kramsta / M. Akhlaghi / H.
Aussel
- S. Awan / R. Azzollini / A. Basset / G. P. Candini
- P. Casenove / M. Cropper / H. Hoekstra / H. Israel
- A. Khalil / K. Kuijken / Y. Mellier / L. Miller
- S.-M. Niemi / M. J. Page / K. Paterson / M. Schirmer
- N. A. Walton / A. Zacchei / J. P. L. G. Barrios / T. Erben
- R. Hayes / J. A. Kegerreis / D. J. Lagattuta / A. Lançon
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- P. N. Appleton / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. N. Belikov
- R. Bender / F. Bernardeau / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / R. da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R.
Granett
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / M. Hailey
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- D. C. Masters / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner
- R. C. Nichol / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- G. D. Racca / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / B. Rusholme / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin
Vigo
- G. Fabbian / L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- S. Borgani / A. S. Borlaff / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Conseil / A. R.
Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. M. N. Ferguson
- A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / A. H. Gonzalez
- G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / C. J. R. McPartland / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- A. Montoro / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- F. Passalacqua / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P. Reimberg / P.-F. Rocci
- G. Rodighiero / R. P. Rollins / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar
- A. Silvestri / K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera
- M. Tewes / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / J. R. Weaver / D. Scott
Summary
This paper describes the VIS Processing Function (VIS PF) of the
Euclid ground segment pipeline, which processes and calibrates raw data
from the VIS camera. We present the algorithms used in each processing
element, along with a description of the on-orbit performance of VIS PF,
based on Performance Verification (PV) and Q1 data. We demonstrate that
the principal performance metrics (image quality, astrometric accuracy,
photometric calibration) are within pre-launch specifications. The
image-to-image photometric scatter is less than  , and absolute
astrometric accuracy compared to Gaia is
, and absolute
astrometric accuracy compared to Gaia is  mas Image quality is stable over all Q1
images with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) of
mas Image quality is stable over all Q1
images with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) of  . The stacked images (combining four nominal and
two short exposures) reach
. The stacked images (combining four nominal and
two short exposures) reach  (
( , measured as the variance
of
, measured as the variance
of  diameter apertures). We also describe quality
control metrics provided with each image, and an appendix provides a
detailed description of the provided data products. The excellent
quality of these images demonstrates the immense potential of Euclid VIS
data for weak lensing. VIS data, covering most of the extragalactic sky,
will provide a lasting high-resolution atlas of the Universe.
diameter apertures). We also describe quality
control metrics provided with each image, and an appendix provides a
detailed description of the provided data products. The excellent
quality of these images demonstrates the immense potential of Euclid VIS
data for weak lensing. VIS data, covering most of the extragalactic sky,
will provide a lasting high-resolution atlas of the Universe.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): From images to multiwavelength catalogues: the
Euclid MERge Processing Function
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / E. Romelli / M. Kümmel / H. Dole
- J. Gracia-Carpio / E. Merlin / S. Galeotta / Y. Fang
- M. Castellano / F. Caro / E. Soubrie / L. Maurin
- R. Cabanac / P. Dimauro / M. Huertas-Company / M. D. Lepinzan
- T. Vassallo / M. Walmsley / I. A. Zinchenko / A. Boucaud
- A. Calabro / V. Roscani / A. Tramacere / M. Douspis
- A. Fontana / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Basset
- P. Battaglia / A. N. Belikov / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / J.-G.
Cuby
- A. Da Silva / R. da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik
- K. Kuijken / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / R. Laureijs
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
P. Liebing
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / G. D. Racca / F. Raison / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A.
Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / A. Cappi / P. Casenove
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G.
Hartley
- H. Israel / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / B. Camacho Quevedo / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- R. Chary / F. Cogato / S. Conseil / A. R.
Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / A. M. N. Ferguson / A. Finoguenov
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- R. Gavazzi / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F.
Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / V. Le
Brun
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- E. A. Magnier / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P. Reimberg / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata
- A. Schneider / M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / J. R. Weaver / J. G. Sorce / D. Scott
Summary
The Euclid satellite is an ESA mission that was launched in July
2023. is working in its regular observing mode with the target of
observing an area of  with two instruments, the Visible Camera (VIS)
and the Near IR Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) down to
with two instruments, the Visible Camera (VIS)
and the Near IR Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) down to  (
( ) in the Euclid Wide
Survey. Ground-based imaging data in the bands complement the data to
enable photo-
) in the Euclid Wide
Survey. Ground-based imaging data in the bands complement the data to
enable photo- determination and VIS PSF modeling for
week lensing analysis. Euclid investigates the distance-redshift
relation and the evolution of cosmic structures by measuring shapes and
redshifts of galaxies and clusters of galaxies out to
determination and VIS PSF modeling for
week lensing analysis. Euclid investigates the distance-redshift
relation and the evolution of cosmic structures by measuring shapes and
redshifts of galaxies and clusters of galaxies out to  . Generating the
multi-wavelength catalogues from and ground-based data is an essential
part of the data processing system. In the framework of the Science
Ground Segment (SGS), the aim of the MER Processing Function (PF)
pipeline is to detect objects in the imaging data, measure their
properties, and MERge them into a single multi-wavelength catalogue. The
MER PF pipeline performs source detection on both visible (VIS) and
near-infrared (NIR) images and offers four different photometric
measurements: Kron total flux, aperture photometry on PSF-matched
images, template fitting photometry, and Sérsic fitting photometry.
Furthermore, the MER PF pipeline measures a set of ancillary quantities,
spanning from morphology to quality flags, to better characterise all
detected sources. In this paper, we show how the MER PF pipeline is
designed, detailing its main steps, and we show that the pipeline
products meet the tight requirements that Euclid aims to achieve on
photometric accuracy. We also present the other measurements
(e.g. morphology) that are included in the OU-MER output catalogues and
we list all output products coming out of the MER PF pipeline.
. Generating the
multi-wavelength catalogues from and ground-based data is an essential
part of the data processing system. In the framework of the Science
Ground Segment (SGS), the aim of the MER Processing Function (PF)
pipeline is to detect objects in the imaging data, measure their
properties, and MERge them into a single multi-wavelength catalogue. The
MER PF pipeline performs source detection on both visible (VIS) and
near-infrared (NIR) images and offers four different photometric
measurements: Kron total flux, aperture photometry on PSF-matched
images, template fitting photometry, and Sérsic fitting photometry.
Furthermore, the MER PF pipeline measures a set of ancillary quantities,
spanning from morphology to quality flags, to better characterise all
detected sources. In this paper, we show how the MER PF pipeline is
designed, detailing its main steps, and we show that the pipeline
products meet the tight requirements that Euclid aims to achieve on
photometric accuracy. We also present the other measurements
(e.g. morphology) that are included in the OU-MER output catalogues and
we list all output products coming out of the MER PF pipeline.
The
rise of the galactic empire: luminosity functions at  and
and  estimated with the
MIDIS
estimated with the
MIDIS NGDEEP ultra-deep JWST/NIRCam
dataset
NGDEEP ultra-deep JWST/NIRCam
dataset
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Pablo G. Pérez-González / Göran Östlin / Luca Costantin / Jens
Melinder
- Steven L. Finkelstein / Rachel S. Somerville / Marianna
Annunziatella / Javier Álvarez-Márquez
- Luis Colina / Avishai Dekel / Mark Dickinson / Henry C.
Ferguson
- Zhaozhou Li / L. Y. Aaron Yung / Mic B. Bagley / Leindert A.
Boogaard
- Denis Burgarella / Antonello Calabrò / Karina I.
Caputi / Yingjie Cheng
- Andreas Eckart / Mauro Giavalisco / Steven Gillman / Thomas R.
Greve
- Mahmoud Hamed / Nimish P. Hathi / Jens Hjorth / Marc
Huertas-Company
- Jeyhan Kartaltepe / Anton M. Koekemoer / Vasily Kokorev / Álvaro
Labiano
- Danial Langeroodi / Gene C. K. Leung / Priyamvada Natarajan / Casey
Papovich
- Florian Peissker / Laura Pentericci / Nor Pirzkal / Pierluigi
Rinaldi
- Paul van der Werf / Fabian Walter
Summary
We present a sample of six F200W and three F277W dropout sources
identified as  galaxy
candidates using the deepest JWST/NIRCam data to date (5
galaxy
candidates using the deepest JWST/NIRCam data to date (5 depths
depths  mag at
mag at 
 m), provided by the MIRI Deep Imaging
Survey (MIDIS) and the Next Generation Deep Extragalactic Exploratory
Public survey (NGDEEP). We estimate ultraviolet (UV) luminosity
functions and densities at
m), provided by the MIRI Deep Imaging
Survey (MIDIS) and the Next Generation Deep Extragalactic Exploratory
Public survey (NGDEEP). We estimate ultraviolet (UV) luminosity
functions and densities at  and
and  . The number density
of galaxies with absolute magnitudes
. The number density
of galaxies with absolute magnitudes  at
at  (
( ) is a factor of 4
(25) smaller than at
) is a factor of 4
(25) smaller than at  ; the luminosity
density presents a similar evolution. Compared to state-of-the-art
galaxy simulations, we find the need for an enhanced UV-photon
production at
; the luminosity
density presents a similar evolution. Compared to state-of-the-art
galaxy simulations, we find the need for an enhanced UV-photon
production at  in
in  M
M dark matter halos,
provided by an increase in the star formation efficiency at early times
and/or by intense compact starbursts with enhanced emissivity linked to
strong burstiness, low or primordial gas metallicities, and/or a
top-heavy initial mass function. There are few robust theoretical
predictions for the evolution of galaxies above
dark matter halos,
provided by an increase in the star formation efficiency at early times
and/or by intense compact starbursts with enhanced emissivity linked to
strong burstiness, low or primordial gas metallicities, and/or a
top-heavy initial mass function. There are few robust theoretical
predictions for the evolution of galaxies above  in the literature,
however, the continuing rapid drop in the halo mass function would
predict a more rapid evolution than we observe if photon production
efficiencies remained constant. Our
in the literature,
however, the continuing rapid drop in the halo mass function would
predict a more rapid evolution than we observe if photon production
efficiencies remained constant. Our  candidates present
mass-weighted ages around 30 Myr, and attenuations
candidates present
mass-weighted ages around 30 Myr, and attenuations  mag. Their average stellar mass is
mag. Their average stellar mass is  , implying a stellar-to-baryon mass fraction
around 10% if the emissivity increases with redshift, or significantly
higher otherwise. Three candidates present very blue UV spectral slopes
(
, implying a stellar-to-baryon mass fraction
around 10% if the emissivity increases with redshift, or significantly
higher otherwise. Three candidates present very blue UV spectral slopes
( ) compatible with
Pop III young (
) compatible with
Pop III young ( Myr) stars
and/or high escape fractions of ionizing photons; the rest have
Myr) stars
and/or high escape fractions of ionizing photons; the rest have  similar to
similar to  samples.
samples.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). A probabilistic classification of quenched
galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / P. Corcho-Caballero / Y. Ascasibar / G.
Verdoes Kleijn
- C. C. Lovell / G. De Lucia / C. Cleland / F. Fontanot
- C. Tortora / L. V. E. Koopmans / S. Eales / T. Moutard
- C. Laigle / A. Nersesian / F. Shankar / M. Dunn
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M.
Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik
- K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno
- N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / K. Benson / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier
- C. Mancini / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- C. Scarlata / J. Schaye / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / J. R. Weaver
- J. G. Sorce
Summary
Investigating what drives the quenching of star formation in galaxies
is key to understanding their evolution. The Euclid mission will provide
rich data from optical to infrared wavelengths for millions of galaxies,
and enable precise measurements of their star formation histories. Using
the first Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1), we developed a probabilistic
classification framework that combines the average specific
star-formation rate inferred over two timescales ( yr) to
categorise galaxies as
yr) to
categorise galaxies as
ageing' (secularly evolving),quenched’ (recently halted
star formation), or `retired’ (dominated by old stars). Two
classification methods were employed: a probabilistic approach, which
integrates posterior distributions, and a model-driven method, which
optimises sample purity and completeness using IllustrisTNG. At  and
and  , we
obtain Euclid class fractions of 68-72%, 8-17%, and 14-19% for ageing,
quenched, and retired populations, respectively. Ageing and retired
galaxies dominate at the low- and high-mass end, respectively, while
quenched galaxies surpass the retired fraction for
, we
obtain Euclid class fractions of 68-72%, 8-17%, and 14-19% for ageing,
quenched, and retired populations, respectively. Ageing and retired
galaxies dominate at the low- and high-mass end, respectively, while
quenched galaxies surpass the retired fraction for  . The
evolution with redshift shows increasing and decreasing fractions of
ageing and retired galaxies, respectively. More massive galaxies usually
undergo quenching episodes at earlier times than to their low-mass
counterparts. In terms of the mass-size-metallicity relation, ageing
galaxies generally exhibit disc morphologies and low metallicities.
Retired galaxies show compact structures and enhanced chemical
enrichment, while quenched galaxies form an intermediate population that
is more compact and chemically evolved than ageing systems. This work
demonstrates Euclid’s great potential for elucidating the physical
nature of the quenching mechanisms that govern galaxy evolution.
. The
evolution with redshift shows increasing and decreasing fractions of
ageing and retired galaxies, respectively. More massive galaxies usually
undergo quenching episodes at earlier times than to their low-mass
counterparts. In terms of the mass-size-metallicity relation, ageing
galaxies generally exhibit disc morphologies and low metallicities.
Retired galaxies show compact structures and enhanced chemical
enrichment, while quenched galaxies form an intermediate population that
is more compact and chemically evolved than ageing systems. This work
demonstrates Euclid’s great potential for elucidating the physical
nature of the quenching mechanisms that govern galaxy evolution.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Photometric redshifts and physical properties
of galaxies through the PHZ processing function
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / M. Tucci / S. Paltani / W. G. Hartley
- F. Dubath / N. Morisset / M. Bolzonella / S. Fotopoulou
- F. Tarsitano / C. Saulder / L. Pozzetti / A. Enia
- Y. Kang / H. Degaudenzi / R. Saglia / M. Salvato
- O. Ilbert / S. A. Stanford / W. Roster / F. J.
Castander
- A. Humphrey / H. Landt / M. Selwood / G. Stevens
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. N. Belikov
- F. Bernardeau / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- H. Dole / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / P. Liebing / S.
Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / D. C. Masters / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / G. D. Racca
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / B. Rusholme
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / A. Secroun
- E. Sefusatti / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P.
Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- P. Casenove / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / G.
Fabbian
- L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J. Martín-Fleitas / S.
Matthew
- M. Maturi / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. A. Nucita
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / K. Benson
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / R. Chary / F. Cogato
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / Y. Fang / A. M. N. Ferguson
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / A. H. Gonzalez
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J.
Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- M. Oguri / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / J. Schaye
- A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / J. R. Weaver
- J. G. Sorce / E. Soubrie / D. Scott
Summary
The ESA Euclid mission will measure the photometric redshifts of
billions of galaxies in order to provide an accurate 3D view of the
Universe at optical and near-infrared wavelengths. Photometric redshifts
are determined by the PHZ processing function on the basis of the
multi-wavelength photometry of Euclid and ground-based observations. In
this paper, we describe the PHZ processing used for the Euclid Quick
Data Release, the output products, and their validation. The PHZ
pipeline is responsible for the following main tasks: source
classification into star, galaxy, and QSO classes based on photometric
colours; determination of photometric redshifts and of physical
properties of galaxies. The classification is able to provide a star
sample with a high level of purity, a highly complete galaxy sample, and
reliable probabilities of belonging to those classes. The identification
of QSOs is more problematic: photometric information seems to be
insufficient to accurately separate QSOs from galaxies. The performance
of the pipeline in the determination of photometric redshifts has been
tested using the COSMOS2020 catalogue and a large sample of
spectroscopic redshifts. The results are in line with expectations: the
precision of the estimates are compatible with Euclid requirements,
while, as expected, a bias correction is needed to achieve the accuracy
level required for the cosmological probes. Finally, the pipeline
provides reliable estimates of the physical properties of galaxies, in
good agreement with findings from the COSMOS2020 catalogue, except for
an unrealistically large fraction of very young galaxies with very high
specific star-formation rates. The application of appropriate priors is,
however, sufficient to obtain reliable physical properties for those
problematic objects. We present several areas for improvement for future
Euclid data releases.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1) Exploring galaxy properties with a multi-modal
foundation model
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / M. Siudek / M. Huertas-Company / M.
Smith
- G. Martinez-Solaeche / F. Lanusse / S. Ho / E. Angeloudi
- P. A. C. Cunha / H. Domínguez Sánchez / M. Dunn / Y. Fu
- P. Iglesias-Navarro / J. Junais / J. H. Knapen / B. Laloux
- M. Mezcua / W. Roster / G. Stevens / J. Vega-Ferrero
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis
- C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / S.
Maurogordato
- H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / K. Benson / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / Y.
Charles
- F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- D. Scognamiglio / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / J. G. Sorce
Summary
Modern astronomical surveys, such as the Euclid mission, produce
high-dimensional, multi-modal data sets that include imaging and
spectroscopic information for millions of galaxies. These data serve as
an ideal benchmark for large, pre-trained multi-modal models, which can
leverage vast amounts of unlabelled data. In this work, we present the
first exploration of Euclid data with AstroPT, an autoregressive
multi-modal foundation model trained on approximately 300 000 optical
and infrared Euclid images and spectral energy distributions (SEDs) from
the first Euclid Quick Data Release. We compare self-supervised
pre-training with baseline fully supervised training across several
tasks: galaxy morphology classification; redshift estimation; similarity
searches; and outlier detection. Our results show that: (a) AstroPT
embeddings are highly informative, correlating with morphology and
effectively isolating outliers; (b) including infrared data helps to
isolate stars, but degrades the identification of edge-on galaxies,
which are better captured by optical images; (c) simple fine-tuning of
these embeddings for photometric redshift and stellar mass estimation
outperforms a fully supervised approach, even when using only 1% of the
training labels; and (d) incorporating SED data into AstroPT via a
straightforward multi-modal token-chaining method improves photo-z
predictions, and allow us to identify potentially more interesting
anomalies (such as ringed or interacting galaxies) compared to a model
pre-trained solely on imaging data.
Strong
LensIng and Cluster Evolution (SLICE) with JWST: Early Results, Lens
Models, and High-Redshift Detections
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Catherine Cerny / Guillaume Mahler / Keren Sharon / Mathilde
Jauzac
- Gourav Khullar / Benjamin Beauchesne / Jose M. Diego / David J.
Lagattuta
- Marceau Limousin / Nency R. Patel / Johan Richard /
Carla Cornil-Baiotto
- Michael D. Gladders / Stephane Werner / Jessica E. Doppel / Benjamin
Floyd
- Anthony H. Gonzalez / Richard J. Massey / Mireia Montes / Matthew B.
Bayliss
- Lindsey E. Bleem / Rebecca E. A. Canning / Alastair C. Edge /
Michael McDonald
- Priyamvada Natarjan / Anthony A. Stark / Raven Gassis
Summary
We leverage JWST’s superb resolution to derive strong lensing mass
maps of 14 clusters, spanning a redshift range of  and a mass range of
and a mass range of  ,
from the Strong LensIng and Cluster Evolution (SLICE) JWST program.
These clusters represent a small subsample of the first clusters
observed in the SLICE program that are chosen based on the detection of
new multiple image constraints in the SLICE-JWST NIRCam/F150W2 and
F322W2 imaging. These constraints include new lensed dusty galaxies and
new substructures in previously identified lensed background galaxies.
Four clusters have never been modeled before. For the remaining 10
clusters, we present updated models based on JWST and HST imaging and,
where available, ground-based spectroscopy. We model the global mass
profile for each cluster and report the mass enclosed within 200 and 500
kpc. We report the number of new systems identified in the JWST imaging,
which in one cluster is as high as 19 new systems. The addition of new
lensing systems and constraints from substructure clumps in lensed
galaxies improves the ability of strong lensing models to accurately
reproduce the interior mass distribution of each cluster. We also report
the discovery of a candidate transient in a lensed image of the galaxy
cluster SPT-CL J0516-5755. All lens models and their associated products
are available for download at the Strong Lensing Cluster Atlas Data
Base, which is hosted at Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille.
,
from the Strong LensIng and Cluster Evolution (SLICE) JWST program.
These clusters represent a small subsample of the first clusters
observed in the SLICE program that are chosen based on the detection of
new multiple image constraints in the SLICE-JWST NIRCam/F150W2 and
F322W2 imaging. These constraints include new lensed dusty galaxies and
new substructures in previously identified lensed background galaxies.
Four clusters have never been modeled before. For the remaining 10
clusters, we present updated models based on JWST and HST imaging and,
where available, ground-based spectroscopy. We model the global mass
profile for each cluster and report the mass enclosed within 200 and 500
kpc. We report the number of new systems identified in the JWST imaging,
which in one cluster is as high as 19 new systems. The addition of new
lensing systems and constraints from substructure clumps in lensed
galaxies improves the ability of strong lensing models to accurately
reproduce the interior mass distribution of each cluster. We also report
the discovery of a candidate transient in a lensed image of the galaxy
cluster SPT-CL J0516-5755. All lens models and their associated products
are available for download at the Strong Lensing Cluster Atlas Data
Base, which is hosted at Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): The Strong Lensing Discovery Engine A – System
overview and lens catalogue
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / M. Walmsley / P. Holloway / N. E. P.
Lines
- K. Rojas / T. E. Collett / A. Verma / T. Li
- J. W. Nightingale / G. Despali / S. Schuldt / R.
Gavazzi
- A. Melo / R. B. Metcalf / I. T. Andika / L. Leuzzi
- A. Manjón-García / R. Pearce-Casey / S. H. Vincken / J. Wilde
- V. Busillo / C. Tortora / J. A. Acevedo Barroso / H. Dole
- L. R. Ecker / J. Pearson / P. J. Marshall / A. More
- T. Saifollahi / J. Gracia-Carpio / E. Baeten / C. Cornen
- L. C. Johnson / C. Macmillan / S. Kruk / K. A. Remmelgas
- B. Clément / H. Degaudenzi / F. Courbin / J. Bovy
- S. Casas / H. Dannerbauer / J. M. Diego / K. Finner
- A. Galan / C. Giocoli / N. B. Hogg / K. Jahnke
- J. Katona / A. Kovács / C. De Leo / G. Mahler
- M. Millon / B. C. Nagam / P. Nugent / A. Sainz de Murieta
- C. M. O’Riordan / D. Sluse / A. Sonnenfeld / C. Spiniello
- S. Serjeant / T. T. Thai / L. Ulivi / G. L. Walth
- L. Weisenbach / M. Zumalacarregui / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / F. Bernardeau / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / L. Corcione / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- W. Gillard / B. Gillis / P. Gómez-Alvarez / B. R. Granett
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- O. Lahav / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra
- M. Huertas-Company / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / K. Benson / P. Bergamini
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Blot / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / Y.
Charles
- F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / C. Murray / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / J. Schaye
- A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Vernardos / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / D. Scott
Summary
We present a catalogue of 497 galaxy-galaxy strong lenses in the
Euclid Quick Release 1 data (63 deg ). In the initial 0.45% of Euclid’s
surveys, we double the total number of known lens candidates with
space-based imaging. Our catalogue includes 250 grade A candidates, the
vast majority of which (243) were previously unpublished. Euclid’s
resolution reveals rare lens configurations of scientific value
including double-source-plane lenses, edge-on lenses, complete Einstein
rings, and quadruply-imaged lenses. We resolve lenses with small
Einstein radii (
). In the initial 0.45% of Euclid’s
surveys, we double the total number of known lens candidates with
space-based imaging. Our catalogue includes 250 grade A candidates, the
vast majority of which (243) were previously unpublished. Euclid’s
resolution reveals rare lens configurations of scientific value
including double-source-plane lenses, edge-on lenses, complete Einstein
rings, and quadruply-imaged lenses. We resolve lenses with small
Einstein radii ( ) in large numbers for the first time. These
lenses are found through an initial sweep by deep learning models,
followed by Space Warps citizen scientist inspection, expert vetting,
and system-by-system modelling. Our search approach scales
straightforwardly to Euclid Data Release 1 and, without changes, would
yield approximately 7000 high-confidence (grade A or B) lens candidates
by late 2026. Further extrapolating to the complete Euclid Wide Survey
implies a likely yield of over 100000 high-confidence candidates,
transforming strong lensing science.
) in large numbers for the first time. These
lenses are found through an initial sweep by deep learning models,
followed by Space Warps citizen scientist inspection, expert vetting,
and system-by-system modelling. Our search approach scales
straightforwardly to Euclid Data Release 1 and, without changes, would
yield approximately 7000 high-confidence (grade A or B) lens candidates
by late 2026. Further extrapolating to the complete Euclid Wide Survey
implies a likely yield of over 100000 high-confidence candidates,
transforming strong lensing science.
Euclid:
Star clusters in IC 342, NGC 2403, and Holmberg II
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- S. S. Larsen / A. M. N. Ferguson / J. M. Howell / F. Annibali
- J.-C. Cuillandre / L. K. Hunt / A. Lançon / T. Saifollahi
- D. Massari / M. N. Le / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- R. Kohley / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- E. Zucca / J. Martín-Fleitas / V. Scottez
Summary
We examine the star cluster populations in the three nearby galaxies
IC 342, NGC 2403, and Holmberg II, observed as part of the Euclid Early
Release Observations programme. Our main focus is on old globular
clusters (GCs), for which the wide field-of-view and excellent image
quality of Euclid offer substantial advantages over previous work. For
IC 342 this is the first study of stellar clusters other than its
nuclear cluster. After selection based on size and magnitude criteria,
followed by visual inspection, we identify 111 old (> 1 Gyr) GC
candidates in IC 342, 50 in NGC 2403 (of which 15 were previously
known), and 7 in Holmberg II. In addition, a number of younger and/or
intermediate-age candidates are identified. The colour distributions of
GC candidates in the two larger galaxies show hints of bimodality with
peaks at IE-HE = 0.36 and 0.79 (IC 342) and IE-HE = 0.36 and 0.80 (NGC
2403), corresponding to metallicities of [Fe/H]=-1.5 and [Fe/H]=-0.5,
similar to those of the metal-poor and metal-rich GC subpopulations in
the Milky Way. The luminosity functions of our GC candidates exhibit an
excess of relatively faint objects, relative to a canonical,
approximately Gaussian GC luminosity function (GCLF). The excess objects
may be similar to those previously identified in other galaxies. The
specific frequency of classical old GCs in IC 342, as determined based
on the brighter half of the GCLF, appears to be unusually low with
SN=0.2-0.3. The combined luminosity function of young and
intermediate-age clusters in all three galaxies is consistent with a
power-law distribution, dN/dL ~ L^(-2.3+/-0.1) and the total numbers of
young clusters brighter than M(IE)=-8 in NGC 2403 and Holmberg II are
comparable with those found in their Local Group counterparts, that is,
M33 and the Small Magellanic Cloud, respectively.
Euclid
preparation. Spatially resolved stellar populations of local galaxies
with Euclid: a proof of concept using synthetic images with the TNG50
simulation
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / Abdurro’uf / C. Tortora / M. Baes
- A. Nersesian / I. Kovačić / M. Bolzonella / A. Lançon
- L. Bisigello / F. Annibali / M. N. Bremer / D. Carollo
- C. J. Conselice / A. Enia / A. M. N. Ferguson / A. Ferré-Mateu
- L. K. Hunt / E. Iodice / J. H. Knapen / A. Iovino
- F. R. Marleau / R. F. Peletier / R. Ragusa / M. Rejkuba
- A. S. G. Robotham / J. Román / T. Saifollahi / P. Salucci
- M. Scodeggio / M. Siudek / A. van der Wel / K. Voggel
- B. Altieri / S. Andreon / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- S. Bardelli / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Farrens / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / S.
Matthew
- N. Mauri / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / V. Scottez
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- V. Allevato / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela
- M. Ballardini / D. Bertacca / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / R. Cabanac
- A. Calabro / A. Cappi / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / T. Contini / A. R. Cooray
- O. Cucciati / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio
- A. G. Ferrari / I. Ferrero / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- F. Fornari / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / M. Huertas-Company
- A. Jimenez Muñoz / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi
- S. Lee / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / R. B. Metcalf / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo
- Nicholas A. Walton / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- V. Popa / D. Potter / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci
- M. Sahlén / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / M. Sereno / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / D. Vergani / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf
Summary
The European Space Agency’s Euclid mission will observe approximately
14,000  of the
extragalactic sky and deliver high-quality imaging for many galaxies.
The depth and high spatial resolution of the data will enable a detailed
analysis of stellar population properties of local galaxies. In this
study, we test our pipeline for spatially resolved SED fitting using
synthetic images of Euclid, LSST, and GALEX generated from the TNG50
simulation. We apply our pipeline to 25 local simulated galaxies to
recover their resolved stellar population properties. We produce 3 types
of data cubes: GALEX + LSST + Euclid, LSST + Euclid, and Euclid-only. We
perform the SED fitting tests with two SPS models in a Bayesian
framework. Because the age, metallicity, and dust attenuation estimates
are biased when applying only classical formulations of flat priors, we
examine the effects of additional priors in the forms of mass-age-
of the
extragalactic sky and deliver high-quality imaging for many galaxies.
The depth and high spatial resolution of the data will enable a detailed
analysis of stellar population properties of local galaxies. In this
study, we test our pipeline for spatially resolved SED fitting using
synthetic images of Euclid, LSST, and GALEX generated from the TNG50
simulation. We apply our pipeline to 25 local simulated galaxies to
recover their resolved stellar population properties. We produce 3 types
of data cubes: GALEX + LSST + Euclid, LSST + Euclid, and Euclid-only. We
perform the SED fitting tests with two SPS models in a Bayesian
framework. Because the age, metallicity, and dust attenuation estimates
are biased when applying only classical formulations of flat priors, we
examine the effects of additional priors in the forms of mass-age- relations, constructed using a
combination of empirical and simulated data. Stellar-mass surface
densities can be recovered well using any of the 3 data cubes,
regardless of the SPS model and prior variations. The new priors then
significantly improve the measurements of mass-weighted age and
relations, constructed using a
combination of empirical and simulated data. Stellar-mass surface
densities can be recovered well using any of the 3 data cubes,
regardless of the SPS model and prior variations. The new priors then
significantly improve the measurements of mass-weighted age and  compared to results obtained without
priors, but they may play an excessive role compared to the data in
determining the outcome when no UV data is available. The spatially
resolved SED fitting method is powerful for mapping the stellar
populations of galaxies with the current abundance of high-quality
imaging data. Our study re-emphasizes the gain added by including
multiwavelength data from ancillary surveys and the roles of priors in
Bayesian SED fitting. With the Euclid data alone, we will be able to
generate complete and deep stellar mass maps of galaxies in the local
Universe, thus exploiting the telescope’s wide field, NIR sensitivity,
and high spatial resolution.
compared to results obtained without
priors, but they may play an excessive role compared to the data in
determining the outcome when no UV data is available. The spatially
resolved SED fitting method is powerful for mapping the stellar
populations of galaxies with the current abundance of high-quality
imaging data. Our study re-emphasizes the gain added by including
multiwavelength data from ancillary surveys and the roles of priors in
Bayesian SED fitting. With the Euclid data alone, we will be able to
generate complete and deep stellar mass maps of galaxies in the local
Universe, thus exploiting the telescope’s wide field, NIR sensitivity,
and high spatial resolution.
Advancing
European High-Contrast Imaging R&D Towards the Habitable Worlds
Observatory
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Iva Laginja / Óscar Carrión-González / Romain Laugier / Elisabeth
Matthews
- Lucie Leboulleux / Axel Potier / Alexis Lau / Olivier Absil
- Pierre Baudoz / Beth Biller / Anthony Boccaletti / Wolfgang
Brandner
- Alexis Carlotti / Gaël Chauvin / Élodie Choquet / David Doelman
- Kjetil Dohlen / Marc Ferrari /
Sasha Hinkley / Elsa Huby
- Mikael Karlsson / Oliver Krause / Jonas Kühn / Jean-Michel Le
Duigou
- Johan Mazoyer / Dino Mesa / Michiel Min / David Mouillet
- Laurent M. Mugnier / Gilles Orban de Xivry / Frans Snik / Daniele
Vassallo
- Arthur Vigan / Pieter de Visser
Summary
The Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO) will enable a transformative
leap in the direct imaging and characterization of Earth-like
exoplanets. For this, NASA is focusing on early investment in technology
development prior to mission definition and actively seeking
international partnerships earlier than for previous missions. The
“R&D for Space-Based HCI in Europe” workshop, held in March 2024 at
Paris Observatory, convened leading experts in high-contrast imaging
(HCI) to discuss European expertise and explore potential strategies for
European contributions to HWO. This paper synthesizes the discussions
and outcomes of the workshop, highlighting Europe’s critical
contributions to past and current HCI efforts, the synergies between
ground- and space-based technologies, and the importance of laboratory
testbeds and collaborative funding mechanisms. Key conclusions include
the need for Europe to invest in technology development for areas such
as deformable mirrors and advanced detectors, and establish or enhance
laboratory facilities for system-level testing. Putting emphasis on the
urgency of aligning with the timeline of the HWO, the participants
called on an open affirmation by the European Space Agency (ESA) that a
European contribution to HWO is clearly anticipated, to signal national
agencies and unlock funding opportunities at the national level. Based
on the expertise demonstrated through R&D, Europe is poised to play
a pivotal role in advancing global HCI capabilities, contributing to the
characterization of temperate exoplanets and fostering innovation across
domains.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). The Strong Lensing Discovery Engine D –
Double-source-plane lens candidates
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / T. Li / T. E. Collett / M. Walmsley
- N. E. P. Lines / K. Rojas / J. W. Nightingale / W. J. R. Enzi
- L. A. Moustakas / C. Krawczyk / R. Gavazzi / G.
Despali
- P. Holloway / S. Schuldt / F. Courbin / R. B. Metcalf
- D. J. Ballard / A. Verma / B. Clément / H. Degaudenzi
- A. Melo / J. A. Acevedo Barroso / L. Leuzzi / A. Manjón-García
- R. Pearce-Casey / D. Sluse / C. Tortora / R. Massey
- G. Mahler / A. More / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / R. Bender / F. Bernardeau / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Escoffier
- M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan
- H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra
- M. Huertas-Company / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / K. Benson
- P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- W. G. Hartley / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J.
Hjorth
- M. Jauzac / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / J. Schaye / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Vernardos / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
- J. Wilde / D. Scott
Summary
Strong gravitational lensing systems with multiple source planes are
powerful tools for probing the density profiles and dark matter
substructure of the galaxies. The ratio of Einstein radii is related to
the dark energy equation of state through the cosmological scaling
factor  . However, galaxy-scale
double-source-plane lenses (DSPLs) are extremely rare. In this paper, we
report the discovery of four new galaxy-scale double-source-plane lens
candidates in the Euclid Quick Release 1 (Q1) data. These systems were
initially identified through a combination of machine learning
lens-finding models and subsequent visual inspection from citizens and
experts. We apply the widely-used {} lens forecasting model to predict
that the full survey will discover 1700 DSPLs, which scales to
. However, galaxy-scale
double-source-plane lenses (DSPLs) are extremely rare. In this paper, we
report the discovery of four new galaxy-scale double-source-plane lens
candidates in the Euclid Quick Release 1 (Q1) data. These systems were
initially identified through a combination of machine learning
lens-finding models and subsequent visual inspection from citizens and
experts. We apply the widely-used {} lens forecasting model to predict
that the full survey will discover 1700 DSPLs, which scales to  DSPLs in 63 deg
DSPLs in 63 deg , the area of Q1. The number of
discoveries in this work is broadly consistent with this forecast. We
present lens models for each DSPL and infer their
, the area of Q1. The number of
discoveries in this work is broadly consistent with this forecast. We
present lens models for each DSPL and infer their  values. Our initial Q1 sample
demonstrates the promise of to discover such rare objects.
values. Our initial Q1 sample
demonstrates the promise of to discover such rare objects.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1) First study of red quasars selection
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / F. Tarsitano / S. Fotopoulou / M.
Banerji
- J. Petley / A. L. Faisst / M. Tucci / S. Tacchella
- Y. Toba / H. Landt / Y. Fu / P. A. C. Cunha
- K. Duncan / W. Roster / M. Salvato / B. Laloux
- P. Dayal / F. Ricci / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / A. Costille / F.
Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Escoffier
- M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R.
Granett
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / B. Rusholme / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo
- L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist
- K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- Y. Charles / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / O.
Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc
- A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / A. Viitanen / N. A. Walton
- J. G. Sorce
Summary
Red quasars constitute an important but elusive phase in the
evolution of supermassive black holes, where dust obscuration can
significantly alter their observed properties. They have broad emission
lines, like other quasars, but their optical continuum emission is
significantly reddened, which is why they were traditionally identified
based on near- and mid-infrared selection criteria. This work showcases
the capability of the space telescope to find a large sample of red
quasars, using near infrared (NIR) photometry. We first conduct a
forecast analysis, comparing a synthetic catalogue of red QSOs with
COSMOS2020. Using template fitting, we reconstruct -like photometry for
the COSMOS sources and identify a sample of candidates in a
multidimensional colour-colour space achieving  completeness for mock red
QSOs with
completeness for mock red
QSOs with  contaminants. To refine
our selection function, we implement a probabilistic Random Forest
classifier, and use UMAP visualisation to disentangle non-linear
features in colour-space, reaching
contaminants. To refine
our selection function, we implement a probabilistic Random Forest
classifier, and use UMAP visualisation to disentangle non-linear
features in colour-space, reaching  completeness and
completeness and  purity. A preliminary
analysis of the candidates in the Deep Field Fornax (EDF-F) shows that,
compared to VISTA+DECAm-based colour selection criteria, ’s superior
depth, resolution and optical-to-NIR coverage improves the
identification of the reddest, most obscured sources. Notably, the
exquisite resolution in the
purity. A preliminary
analysis of the candidates in the Deep Field Fornax (EDF-F) shows that,
compared to VISTA+DECAm-based colour selection criteria, ’s superior
depth, resolution and optical-to-NIR coverage improves the
identification of the reddest, most obscured sources. Notably, the
exquisite resolution in the  filter unveils the presence of a
candidate dual quasar system, highlighting the potential for this
mission to contribute to future studies on the population of dual AGN.
The resulting catalogue of candidates, including more the 150 000
sources, provides a first census of red quasars in Q1 and sets the
groundwork for future studies in the Euclid Wide Survey (EWS), including
spectral follow-up analyses and host morphology characterisation.
filter unveils the presence of a
candidate dual quasar system, highlighting the potential for this
mission to contribute to future studies on the population of dual AGN.
The resulting catalogue of candidates, including more the 150 000
sources, provides a first census of red quasars in Q1 and sets the
groundwork for future studies in the Euclid Wide Survey (EWS), including
spectral follow-up analyses and host morphology characterisation.
Data
Release 1 of the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- DESI Collaboration / M. Abdul-Karim / A. G. Adame / D. Aguado
- J. Aguilar / S. Ahlen / S. Alam / G. Aldering
- D. M. Alexander / R. Alfarsy / L. Allen / C. Allende Prieto
- O. Alves / A. Anand / U. Andrade / E. Armengaud
- S. Avila / A. Aviles / H. Awan / S. Bailey
- A. Baleato Lizancos / O. Ballester / A. Bault / J. Bautista
- S. BenZvi / L. Beraldo e Silva / J. R. Bermejo-Climent / F.
Beutler
- D. Bianchi / C. Blake / R. Blum / A. S. Bolton
- M. Bonici / S. Brieden / A. Brodzeller / D. Brooks
- E. Buckley-Geer / E. Burtin / R. Canning / A. Carnero Rosell
- A. Carr / P. Carrilho / L. Casas / F. J. Castander
- R. Cereskaite / J. L. Cervantes-Cota / E. Chaussidon / J.
Chaves-Montero
- S. Chen / X. Chen / T. Claybaugh / S. Cole
- A. P. Cooper / M.-C. Cousinou / A. Cuceu / T. M. Davis
- K. S. Dawson / R. de Belsunce / R. de la Cruz / A. de la
Macorra
- A. de Mattia / N. Deiosso / J. Della Costa / R. Demina
- U. Demirbozan / J. DeRose / A. Dey / B. Dey
- J. Ding / Z. Ding / P. Doel / K. Douglass
- M. Dowicz / H. Ebina / J. Edelstein / D. J. Eisenstein
- W. Elbers / N. Emas / S. Escoffier / P. Fagrelius
- X. Fan / K. Fanning / V. A. Fawcett / E. Fernández-García
- S. Ferraro / N. Findlay / A. Font-Ribera / J. E. Forero-Romero
- D. Forero-Sánchez / C. S. Frenk / B. T. Gänsicke / L. Galbany
- J. García-Bellido / C. Garcia-Quintero / L. H. Garrison / E.
Gaztañaga
- H. Gil-Marín / O. Y. Gnedin / S. Gontcho A Gontcho / A. X.
Gonzalez-Morales
- V. Gonzalez-Perez / C. Gordon / O. Graur / D. Green
- D. Gruen / R. Gsponer / C. Guandalin / G. Gutierrez
- J. Guy / C. Hahn / J. J. Han / J. Han
- S. He / H. K. Herrera-Alcantar / K. Honscheid / J. Hou
- C. Howlett / D. Huterer / V. Iršič / M. Ishak
- A. Jacques / J. Jimenez / Y. P. Jing / B. Joachimi
- S. Joudaki / R. Joyce / E. Jullo / S. Juneau
- N. G. Karaçaylı / T. Karim / R. Kehoe / S. Kent
- A. Khederlarian / D. Kirkby / T. Kisner / F.-S. Kitaura
- N. Kizhuprakkat / H. Kong / S. E. Koposov / A. Kremin
- A. Krolewski / O. Lahav / Y. Lai / C. Lamman
- T.-W. Lan / M. Landriau / D. Lang / J. U. Lange
- J. Lasker / J. M. Le Goff / L. Le Guillou / A. Leauthaud
- M. E. Levi / S. Li / T. S. Li / K. Lodha
- M. Lokken / Y. Luo / C. Magneville / M. Manera
- C. J. Manser / D. Margala / P. Martini / M. Maus
- J. McCullough / P. McDonald / G. E. Medina / L. Medina-Varela
- A. Meisner / J. Mena-Fernández / A. Menegas / M. Mezcua
- R. Miquel / P. Montero-Camacho / J. Moon / J. Moustakas
- A. Muñoz-Gutiérrez / D. Muñoz-Santos / A. D. Myers / J. Myles
- S. Nadathur / J. Najita / L. Napolitano / J. A. Newman
- F. Nikakhtar / R. Nikutta / G. Niz / H. E. Noriega
- N. Padmanabhan / E. Paillas / N. Palanque-Delabrouille / A.
Palmese
- J. Pan / Z. Pan / D. Parkinson / J. Peacock
- W. J. Percival / A. Pérez-Fernández / I. Pérez-Ràfols / P.
Peterson
- J. Piat / M. M. Pieri / M. Pinon / C. Poppett
- A. Porredon / F. Prada / R. Pucha / F. Qin
- D. Rabinowitz / A. Raichoor / C. Ramírez-Pérez / S.
Ramirez-Solano
- M. Rashkovetskyi / C. Ravoux / A. H. Riley / A. Rocher
- C. Rockosi / J. Rohlf / A. J. Ross / G. Rossi
- R. Ruggeri / V. Ruhlmann-Kleider / C. G. Sabiu / K. Said
- A. Saintonge / L. Samushia / E. Sanchez / N. Sanders
- C. Saulder / E. F. Schlafly / D. Schlegel / D. Scholte
- M. Schubnell / H. Seo / A. Shafieloo / R. Sharples
- J. Silber / M. Siudek / A. Smith / D. Sprayberry
- J. Suárez-Pérez / J. Swanson / T. Tan / G. Tarlé
- P. Taylor / G. Thomas / R. Tojeiro / R. J. Turner
- W. Turner / L. A. Ureña-López / R. Vaisakh / M. Valluri
- M. Vargas-Magaña / L. Verde / M. Walther / B. Wang
- M. S. Wang / W. Wang / B. A. Weaver / N. Weaverdyck
- R. H. Wechsler / M. White / M. Wolfson / J. Yang
- C. Yèche / S. Youles / J. Yu / S. Yuan
- E. A. Zaborowski / P. Zarrouk / H. Zhang / C. Zhao
- R. Zhao / Z. Zheng / R. Zhou / H. Zou
- S. Zou / Y. Zu
Summary
In 2021 May the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI)
collaboration began a 5-year spectroscopic redshift survey to produce a
detailed map of the evolving three-dimensional structure of the universe
between  and
and  . DESI’s
principle scientific objectives are to place precise constraints on the
equation of state of dark energy, the gravitationally driven growth of
large-scale structure, and the sum of the neutrino masses, and to
explore the observational signatures of primordial inflation. We present
DESI Data Release 1 (DR1), which consists of all data acquired during
the first 13 months of the DESI main survey, as well as a uniform
reprocessing of the DESI Survey Validation data which was previously
made public in the DESI Early Data Release. The DR1 main survey includes
high-confidence redshifts for 18.7M objects, of which 13.1M are
spectroscopically classified as galaxies, 1.6M as quasars, and 4M as
stars, making DR1 the largest sample of extragalactic redshifts ever
assembled. We summarize the DR1 observations, the spectroscopic
data-reduction pipeline and data products, large-scale structure
catalogs, value-added catalogs, and describe how to access and interact
with the data. In addition to fulfilling its core cosmological
objectives with unprecedented precision, we expect DR1 to enable a wide
range of transformational astrophysical studies and discoveries.
. DESI’s
principle scientific objectives are to place precise constraints on the
equation of state of dark energy, the gravitationally driven growth of
large-scale structure, and the sum of the neutrino masses, and to
explore the observational signatures of primordial inflation. We present
DESI Data Release 1 (DR1), which consists of all data acquired during
the first 13 months of the DESI main survey, as well as a uniform
reprocessing of the DESI Survey Validation data which was previously
made public in the DESI Early Data Release. The DR1 main survey includes
high-confidence redshifts for 18.7M objects, of which 13.1M are
spectroscopically classified as galaxies, 1.6M as quasars, and 4M as
stars, making DR1 the largest sample of extragalactic redshifts ever
assembled. We summarize the DR1 observations, the spectroscopic
data-reduction pipeline and data products, large-scale structure
catalogs, value-added catalogs, and describe how to access and interact
with the data. In addition to fulfilling its core cosmological
objectives with unprecedented precision, we expect DR1 to enable a wide
range of transformational astrophysical studies and discoveries.
Euclid:
Early Release Observations – Interplay between dwarf galaxies and their
globular clusters in the Perseus galaxy cluster
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- T. Saifollahi / A. Lançon / Michele Cantiello / J.-C.
Cuillandre
- M. Bethermin / D. Carollo / P.-A. Duc / A. Ferré-Mateu
- N. A. Hatch / M. Hilker / L. K. Hunt / F. R. Marleau
- J. Román / R. Sánchez-Janssen / C. Tortora / M. Urbano
- K. Voggel / M. Bolzonella / H. Bouy / M. Kluge
- M. Schirmer / C. Stone / C. Giocoli / J. H. Knapen
- M. N. Le / M. Mondelin / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / D. Bagot
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Basset
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino
- W. Bon / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J.
Brinchmann
- S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / J. Gracia-Carpio
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar
- H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / R. Laureijs
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus
- E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / C. Burigana
- J. Martín-Fleitas / V. Scottez
Summary
We present an analysis of globular clusters (GCs) of dwarf galaxies
in the Perseus galaxy cluster to explore the relationship between dwarf
galaxy properties and their GCs. Our focus is on GC numbers ( ) and GC
half-number radii (
) and GC
half-number radii ( ) around dwarf
galaxies, and their relations with host galaxy stellar masses (
) around dwarf
galaxies, and their relations with host galaxy stellar masses ( ), central surface
brightnesses (
), central surface
brightnesses ( ), and effective radii (
), and effective radii ( ).
Interestingly, we find that at a given stellar mass,
).
Interestingly, we find that at a given stellar mass,  is almost
independent of the host galaxy
is almost
independent of the host galaxy  and
and  , while
, while  depends on
depends on  and
and  ; lower surface
brightness and diffuse dwarf galaxies show
; lower surface
brightness and diffuse dwarf galaxies show  while
higher surface brightness and compact dwarf galaxies show
while
higher surface brightness and compact dwarf galaxies show  -
-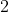 . This means that for dwarf galaxies of
similar stellar mass, the GCs have a similar median extent; however,
their distribution is different from the field stars of their host.
Additionally, low surface brightness and diffuse dwarf galaxies on
average have a higher
. This means that for dwarf galaxies of
similar stellar mass, the GCs have a similar median extent; however,
their distribution is different from the field stars of their host.
Additionally, low surface brightness and diffuse dwarf galaxies on
average have a higher  than high
surface brightness and compact dwarf galaxies at any given stellar mass.
We also find that UDGs (ultra-diffuse galaxies) and non-UDGs have
similar
than high
surface brightness and compact dwarf galaxies at any given stellar mass.
We also find that UDGs (ultra-diffuse galaxies) and non-UDGs have
similar  , while UDGs
have smaller
, while UDGs
have smaller  (typically less than 1) and 3-4 times higher
(typically less than 1) and 3-4 times higher  than
non-UDGs. Examining nucleated and not-nucleated dwarf galaxies, we find
that for
than
non-UDGs. Examining nucleated and not-nucleated dwarf galaxies, we find
that for  , nucleated dwarf galaxies seem to have smaller
, nucleated dwarf galaxies seem to have smaller
 and
and  , with no significant differences between their
, with no significant differences between their
 , except at
, except at
 where the nucleated dwarf galaxies tend to have a
higher
where the nucleated dwarf galaxies tend to have a
higher  . Lastly, we
explore the stellar-to-halo mass ratio (SHMR) of dwarf galaxies and
conclude that the Perseus cluster dwarf galaxies follow the expected
SHMR at
. Lastly, we
explore the stellar-to-halo mass ratio (SHMR) of dwarf galaxies and
conclude that the Perseus cluster dwarf galaxies follow the expected
SHMR at  extrapolated down to
extrapolated down to  .
.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Exploring galaxy morphology across cosmic time
through Sersic fits
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / L. Quilley / I. Damjanov / V. de
Lapparent
- A. Paulino-Afonso / H. Domínguez Sánchez / A. Ferré-Mateu / M.
Huertas-Company
- M. Kümmel / D. Delley / C. Spiniello / M. Baes
- L. Wang / U. Kuchner / F. Tarsitano / R. Ragusa
- M. Siudek / C. Tortora / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M.
Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
P. Liebing
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / M. Scodeggio
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra
- W. G. Hartley / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist
- K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / F. Buitrago / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / Y.
Charles
- F. Cogato / T. Contini / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc
- A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira
- A. Finoguenov / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / R. Gavazzi / E.
Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- O. Ilbert / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V.
Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- E. A. Magnier / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / J. Schaye / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar / L. C. Smith
- S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / J. G. Sorce / E. Soubrie / D. Scott
Summary
We present the results of the single-component Sérsic profile fitting
for the magnitude-limited sample of  galaxies within the
63.1 deg
galaxies within the
63.1 deg area of the Euclid Quick Data Release
(Q1). The associated morphological catalogue includes two sets of
structural parameters fitted using : one for VIS images and one for a
combination of three NISP images in , and bands. We compare the
resulting Sérsic parameters to other morphological measurements provided
in the Q1 data release, and to the equivalent parameters based on
higher-resolution imaging. These comparisons confirm the consistency and
the reliability of the fits to Q1 data. Our analysis of colour gradients
shows that NISP profiles have systematically smaller effective radii
(
area of the Euclid Quick Data Release
(Q1). The associated morphological catalogue includes two sets of
structural parameters fitted using : one for VIS images and one for a
combination of three NISP images in , and bands. We compare the
resulting Sérsic parameters to other morphological measurements provided
in the Q1 data release, and to the equivalent parameters based on
higher-resolution imaging. These comparisons confirm the consistency and
the reliability of the fits to Q1 data. Our analysis of colour gradients
shows that NISP profiles have systematically smaller effective radii
( ) and larger
Sérsic indices (
) and larger
Sérsic indices ( ) than in VIS. In addition, we highlight
trends in NISP-to-VIS parameter ratios with both magnitude and
) than in VIS. In addition, we highlight
trends in NISP-to-VIS parameter ratios with both magnitude and  . From the
2D bimodality of the
. From the
2D bimodality of the  colour-
colour- plane, we define a
plane, we define a
 that separates early- and late-type galaxies
(ETGs and LTGs). We use the two subpopulations to examine the variations
of
that separates early- and late-type galaxies
(ETGs and LTGs). We use the two subpopulations to examine the variations
of  across well-known scaling relations at
across well-known scaling relations at
 . ETGs display a
steeper size–stellar mass relation than LTGs, indicating a difference in
the main drivers of their mass assembly. Similarly, LTGs and ETGs occupy
different parts of the stellar mass–star-formation rate plane, with ETGs
at higher masses than LTGs, and further down below the Main Sequence of
star-forming galaxies. This clear separation highlights the link known
between the shutdown of star formation and morphological transformations
in the Euclid imaging data set. In conclusion, our analysis demonstrates
both the robustness of the Sérsic fits available in the Q1 morphological
catalogue and the wealth of information they provide for studies of
galaxy evolution with Euclid.
. ETGs display a
steeper size–stellar mass relation than LTGs, indicating a difference in
the main drivers of their mass assembly. Similarly, LTGs and ETGs occupy
different parts of the stellar mass–star-formation rate plane, with ETGs
at higher masses than LTGs, and further down below the Main Sequence of
star-forming galaxies. This clear separation highlights the link known
between the shutdown of star formation and morphological transformations
in the Euclid imaging data set. In conclusion, our analysis demonstrates
both the robustness of the Sérsic fits available in the Q1 morphological
catalogue and the wealth of information they provide for studies of
galaxy evolution with Euclid.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Optical and near-infrared identification and
classification of point-like X-ray selected sources
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / W. Roster / M. Salvato / J. Buchner
- R. Shirley / E. Lusso / H. Landt / G. Zamorani
- M. Siudek / B. Laloux / T. Matamoro Zatarain / F. Ricci
- S. Fotopoulou / A. Ferré-Mateu / X. Lopez Lopez / N. Aghanim
- B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / P. Fosalba
- N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- D. C. Masters / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei / F. M. Zerbi
- I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra
- M. Huertas-Company / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist
- K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi
- T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / A. Viitanen
- N. A. Walton / E. Soubrie / D. Scott
Summary
To better understand the role of active galactic nuclei (AGN) in
galaxy evolution, it is crucial to achieve a complete and pure AGN
census. X-ray surveys are key to this, but identifying their
counterparts (CTPs) at other wavelengths remains challenging due to
their larger positional uncertainties and limited availability of
deeper, uniform ancillary data. Euclid is revolutionising this effort,
offering extensive coverage of nearly the entire extragalactic sky,
particularly in the near-infrared bands, where AGN are more easily
detected. With the first Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1), we identifyed,
classifyed, and determined the redshifts of Euclid CTPs to known
point-like sources from major X-ray surveys, including XMM-Newton,
Chandra, and eROSITA. Using Bayesian statistics, combined with machine
learning (ML), we identify the CTPs to 11 286 X-ray sources from the
three X-ray telescopes. For the large majority of 10 194 sources, the
associations are unique, with the remaining  10% of multi-CTP cases
equally split between XMM-Newton and eROSITA. ML is then used to
distinguish between Galactic (8%) and extragalactic (92%) sources. We
computed photo-zs using deep learning for the 8617 sources detected in
the 10th data release of the DESI Legacy Survey, reaching an accuracy
and a fraction of outliers of about 5%. Based on their X-ray
luminosities, over 99% of CTPs identified as extragalactic are
classified as AGN, most of which appear unobscured given their hardness
ratios. With this paper, we release our catalogue, which includes
identifiers, basic X-ray properties, the details of the associations,
and additional features such as Galactic/extragalactic classifications
and photometric/spectroscopic redshifts. We also provide probabilities
for sub-selecting the sample based on purity and completeness, allowing
users to tailor the sample according to their specific needs.
10% of multi-CTP cases
equally split between XMM-Newton and eROSITA. ML is then used to
distinguish between Galactic (8%) and extragalactic (92%) sources. We
computed photo-zs using deep learning for the 8617 sources detected in
the 10th data release of the DESI Legacy Survey, reaching an accuracy
and a fraction of outliers of about 5%. Based on their X-ray
luminosities, over 99% of CTPs identified as extragalactic are
classified as AGN, most of which appear unobscured given their hardness
ratios. With this paper, we release our catalogue, which includes
identifiers, basic X-ray properties, the details of the associations,
and additional features such as Galactic/extragalactic classifications
and photometric/spectroscopic redshifts. We also provide probabilities
for sub-selecting the sample based on purity and completeness, allowing
users to tailor the sample according to their specific needs.
Euclid
preparation LXX. Forecasting detection limits for intracluster light in
the Euclid Wide Survey
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / C. Bellhouse / J. B. Golden-Marx / S. P.
Bamford
- N. A. Hatch / M. Kluge / A. Ellien / S. L. Ahad
- P. Dimauro / F. Durret / A. H. Gonzalez / Y. Jimenez-Teja
- M. Montes / M. Sereno / E. Slezak / M. Bolzonella
- G. Castignani / O. Cucciati / G. De Lucia / Z. Ghaffari
- L. Moscardini / R. Pello / L. Pozzetti / T.
Saifollahi
- A. S. Borlaff / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- A. Basset / P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / A. Caillat
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / J.-C. Cuillandre / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Farrens
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan
- H. Hoekstra / M. S. Holliman / W. Holmes / I. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / A. M. C. Le Brun / P. Liebing / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / I. Tereno
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L.
Gabarra
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / M. Pöntinen / V. Scottez
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- M. Ballardini / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- R. Cabanac / A. Calabro / A. Cappi / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / T. Contini
- A. R. Cooray / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / A. G. Ferrari
- P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / A. Jimenez Muñoz / J. J. E. Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu
- A. Loureiro / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- J. Martín-Fleitas / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / R. B.
Metcalf
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante
- C. Murray / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / V. Popa
- D. Potter / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci / M. Sahlén
- E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
The intracluster light (ICL) permeating galaxy clusters is a tracer
of the cluster’s assembly history, and potentially a tracer of their
dark matter structure. In this work we explore the capability of the
Euclid Wide Survey to detect ICL using H-band mock images. We simulate
clusters across a range of redshifts (0.3-1.8) and halo masses ( -
- M
M ), using an
observationally motivated model of the ICL. We identify a 50-200 kpc
circular annulus around the brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) in which the
signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of the ICL is maximised and use the S/N
within this aperture as our figure of merit for ICL detection. We
compare three state-of-the-art methods for ICL detection, and find that
a method that performs simple aperture photometry after high-surface
brightness source masking is able to detect ICL with minimal bias for
clusters more massive than
), using an
observationally motivated model of the ICL. We identify a 50-200 kpc
circular annulus around the brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) in which the
signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of the ICL is maximised and use the S/N
within this aperture as our figure of merit for ICL detection. We
compare three state-of-the-art methods for ICL detection, and find that
a method that performs simple aperture photometry after high-surface
brightness source masking is able to detect ICL with minimal bias for
clusters more massive than  M
M . The S/N of the ICL
detection is primarily limited by the redshift of the cluster, driven by
cosmological dimming, rather than the mass of the cluster. Assuming the
ICL in each cluster contains 15% of the stellar light, we forecast that
Euclid will be able to measure the presence of ICL in up to
. The S/N of the ICL
detection is primarily limited by the redshift of the cluster, driven by
cosmological dimming, rather than the mass of the cluster. Assuming the
ICL in each cluster contains 15% of the stellar light, we forecast that
Euclid will be able to measure the presence of ICL in up to  clusters of
clusters of
 M
M between
between  and 1.5 with a S/N
and 1.5 with a S/N . Half of these clusters
will reside below
. Half of these clusters
will reside below  and the majority of
those below
and the majority of
those below  will be detected with a
S/N
will be detected with a
S/N  . A few thousand
clusters at
. A few thousand
clusters at  will have ICL detectable with a S/N greater than 3. The surface
brightness profile of the ICL model is strongly dependent on both the
mass of the cluster and the redshift at which it is observed so the
outer ICL is best observed in the most massive clusters of
will have ICL detectable with a S/N greater than 3. The surface
brightness profile of the ICL model is strongly dependent on both the
mass of the cluster and the redshift at which it is observed so the
outer ICL is best observed in the most massive clusters of  M
M . Euclid will detect
the ICL at more than 500 kpc distance from the BCG, up to
. Euclid will detect
the ICL at more than 500 kpc distance from the BCG, up to  , in several hundred of
these massive clusters over its large survey volume.
, in several hundred of
these massive clusters over its large survey volume.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). The role of cosmic connectivity in shaping
galaxy clusters
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / C. Gouin / C. Laigle / F. Sarron
- T. Bonnaire / J. G. Sorce / N. Aghanim / M. Magliocchetti
- L. Quilley / P. Boldrini / F. Durret / C. Pichon
- U. Kuchner / N. Malavasi / K. Kraljic / R.
Gavazzi
- Y. Kang / S. A. Stanford / P. Awad / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- A. Basset / P. Battaglia / F. Bernardeau / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun
- D. Le Mignant / P. Liebing / S. Ligori / P. B.
Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / J. A. Peacock / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / B. Rusholme / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / J.
Skottfelt
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / M. Maturi / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / A.
Balaguera-Antolinez
- C. Benoist / K. Benson / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / E. A. Magnier
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / A. Montoro
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / D. Scognamiglio
- E. Sellentin / F. Shankar / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / D. Scott
Summary
The matter distribution around galaxy clusters is distributed over
several filaments, reflecting their positions as nodes in the
large-scale cosmic web. The number of filaments connected to a cluster,
namely its connectivity, is expected to affect the physical properties
of clusters. Using the first Euclid galaxy catalogue from the Euclid
Quick Release 1 (Q1), we investigate the connectivity of galaxy clusters
and how it correlates with their physical and galaxy member properties.
Around 220 clusters located within the three fields of Q1 (covering  ), are analysed in the redshift range
), are analysed in the redshift range  . Due to the photometric redshift uncertainty, we
reconstruct the cosmic web skeleton, and measure cluster connectivity,
in 2-D projected slices with a thickness of 170 comoving
. Due to the photometric redshift uncertainty, we
reconstruct the cosmic web skeleton, and measure cluster connectivity,
in 2-D projected slices with a thickness of 170 comoving  and centred on each cluster redshift, by using two different filament
finder algorithms on the most massive galaxies (
and centred on each cluster redshift, by using two different filament
finder algorithms on the most massive galaxies ( ). In
agreement with previous measurements, we recover the mass-connectivity
relation independently of the filament detection algorithm, showing that
the most massive clusters are, on average, connected to a larger number
of cosmic filaments, consistent with hierarchical structure formation
models. Furthermore, we explore possible correlations between
connectivities and two cluster properties: the fraction of early-type
galaxies and the Sérsic index of galaxy members. Our result suggests
that the clusters populated by early-type galaxies exhibit higher
connectivity compared to clusters dominated by late-type galaxies. These
preliminary investigations highlight our ability to quantify the impact
of the cosmic web connectivity on cluster properties with Euclid.
). In
agreement with previous measurements, we recover the mass-connectivity
relation independently of the filament detection algorithm, showing that
the most massive clusters are, on average, connected to a larger number
of cosmic filaments, consistent with hierarchical structure formation
models. Furthermore, we explore possible correlations between
connectivities and two cluster properties: the fraction of early-type
galaxies and the Sérsic index of galaxy members. Our result suggests
that the clusters populated by early-type galaxies exhibit higher
connectivity compared to clusters dominated by late-type galaxies. These
preliminary investigations highlight our ability to quantify the impact
of the cosmic web connectivity on cluster properties with Euclid.
Euclid:
Quick Data Release (Q1) – A census of dwarf galaxies across a range of
distances and environments
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- F. R. Marleau / R. Habas / D. Carollo / C. Tortora
- P.-A. Duc / E. Sola / T. Saifollahi / M. Fügenschuh
- M. Walmsley / R. Zöller / A. Ferré-Mateu / M. Cantiello
- M. Urbano / E. Saremi / R. Ragusa / R. Laureijs
- M. Hilker / O. Müller / M. Poulain / R. F. Peletier
- S. J. Sprenger / O. Marchal / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- A. Basset / P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice L. Conversi / Y.
Copin
- L. Corcione / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- J.-C. Cuillandre / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / P. Fosalba
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / P. Franzetti
- M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / B. Rusholme
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / M. Sauvage / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca
- M. Bolzonella / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / L. Gabarra
- M. Huertas-Company / V. Scottez / D. Scott
Summary
The Euclid Q1 fields were selected for calibration purposes in
cosmology and are therefore relatively devoid of nearby galaxies.
However, this is precisely what makes them interesting fields in which
to search for dwarf galaxies in local density environments. We take
advantage of the unprecedented depth, spatial resolution, and field of
view of the Euclid Quick Release (Q1) to build a census of dwarf
galaxies in these regions. We have identified dwarfs in a representative
sample of 25 contiguous tiles in the Euclid Deep Field North (EDF-N),
covering an area of 14.25 sq. deg. The dwarf candidates were identified
using a semi-automatic detection method, based on properties measured by
the Euclid pipeline and listed in the MER catalogue. A selection cut in
surface brightness and magnitude was used to produce an initial dwarf
candidate catalogue, followed by a cut in morphology and colour. This
catalogue was visually classified to produce a final sample of dwarf
candidates, including their morphology, number of nuclei, globular
cluster (GC) richness, and presence of a blue compact centre. We
identified 2674 dwarf candidates, corresponding to 188 dwarfs per sq.
deg. The visual classification of the dwarfs reveals a slightly uneven
morphological mix of 58% ellipticals and 42% irregulars, with very few
potentially GC-rich (1.0%) and nucleated (4.0%) candidates but a
noticeable fraction (6.9%) of dwarfs with blue compact centres. The
distance distribution of 388 (15%) of the dwarfs with spectroscopic
redshifts peaks at about 400 Mpc. Their stellar mass distribution
confirms that our selection effectively identifies dwarfs while
minimising contamination. The most prominent dwarf overdensities are
dominated by dEs, while dIs are more evenly distributed. This work
highlights Euclid’s remarkable ability to detect and characterise dwarf
galaxies across diverse masses, distances, and environments.
Primordial
Origin of Methane on Eris and Makemake Supported by D/H Ratios
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Olivier Mousis / Aaron Werlen / Tom Benest Couzinou
/ Antoine Schneeberger
Summary
Deuterium, a heavy isotope of hydrogen, is a key tracer of the
formation of the Solar System. Recent JWST observations have expanded
the dataset of D/H ratios in methane on the KBOs Eris and Makemake,
providing new insights into their origins. This study examines the
elevated D/H ratios in methane on these KBOs in the context of
protosolar nebula dynamics and chemistry, and proposes a primordial
origin for the methane, in contrast to previous hypotheses suggesting
abiotic production by internal heating. A time-dependent disk model
coupled with a deuterium chemistry module was used to simulate the
isotopic exchange between methane and hydrogen. Observational
constraints, including the D/H ratio measured in methane in comet
67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, were used to refine the primordial D/H
abundance. The simulations show that the observed D/H ratios in methane
on Eris and Makemake are consistent with a primordial origin. The
results suggest that methane on these KBOs likely originates from the
protosolar nebula, similar to cometary methane, and was sequestered in
solid form – either as pure condensates or clathrates – within their
building blocks prior to accretion. These results provide a { simple}
explanation for the high D/H ratios in methane on Eris and Makemake,
without the need to invoke internal production mechanisms.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). LEMON – Lens Modelling with Neural networks.
Automated and fast modelling of Euclid gravitational lenses with a
singular isothermal ellipsoid mass profile
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / V. Busillo / C. Tortora / R. B. Metcalf
- J. W. Nightingale / M. Meneghetti / F. Gentile / R.
Gavazzi
- F. Zhong / R. Li / B. Clément / G. Covone
- N. R. Napolitano / F. Courbin / M. Walmsley / E.
Jullo
- J. Pearson / D. Scott / A. M. C. Le Brun / L. Leuzzi
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / H. Dole / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / S.
Maurogordato
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / G. Smadja / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin
Vigo
- L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- A. A. Nucita / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- V. Scottez / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca / M.
Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / A. Cappi
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- S. Conseil / S. Contarini / A. R. Cooray / O.
Cucciati
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P. Dimauro / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley
- S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J.
Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas / C. J. A. P.
Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / P. Natoli
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / M. Sereno / L. C. Smith
- J. Stadel / K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Vernardos
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
The Euclid mission aims to survey around 14000 deg^{2} of
extragalactic sky, providing around 10^{5} gravitational lens images.
Modelling of gravitational lenses is fundamental to estimate the total
mass of the lens galaxy, along with its dark matter content. Traditional
modelling of gravitational lenses is computationally intensive and
requires manual input. In this paper, we use a Bayesian neural network,
LEns MOdelling with Neural networks (LEMON), for modelling Euclid
gravitational lenses with a singular isothermal ellipsoid mass profile.
Our method estimates key lens mass profile parameters, such as the
Einstein radius, while also predicting the light parameters of
foreground galaxies and their uncertainties. We validate LEMON’s
performance on both mock Euclid data sets, real Euclidised lenses
observed with Hubble Space Telescope (hereafter HST), and real Euclid
lenses found in the Perseus ERO field, demonstrating the ability of
LEMON to predict parameters of both simulated and real lenses. Results
show promising accuracy and reliability in predicting the Einstein
radius, axis ratio, position angle, effective radius, Sérsic index, and
lens magnitude for simulated lens galaxies. The application to real
data, including the latest Quick Release 1 strong lens candidates,
provides encouraging results, particularly for the Einstein radius. We
also verified that LEMON has the potential to accelerate traditional
modelling methods, by giving to the classical optimiser the LEMON
predictions as starting points, resulting in a speed-up of up to 26
times the original time needed to model a sample of gravitational
lenses, a result that would be impossible with randomly initialised
guesses. This work represents a significant step towards efficient,
automated gravitational lens modelling, which is crucial for handling
the large data volumes expected from Euclid.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). A first view of the star-forming main sequence
in the Euclid Deep Fields
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / A. Enia / L. Pozzetti / M. Bolzonella
- L. Bisigello / W. G. Hartley / C. Saulder / E. Daddi
- M. Siudek / G. Zamorani / P. Cassata / F. Gentile
- L. Wang / G. Rodighiero / V. Allevato / P. Corcho-Caballero
- H. Domínguez Sánchez / C. Tortora / M. Baes / Abdurro’uf
- A. Nersesian / L. Spinoglio / J. Schaye / Y. Ascasibar
- D. Scott / E. Duran-Camacho / S. Quai / M. Talia
- Z. Mao / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Basset
- P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- P. Franzetti / S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R.
Granett
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / D. C. Masters / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / B. Rusholme
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / C.
Surace
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M.
Huertas-Company
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / K. Benson
- P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / A. S. Borlaff
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- T. Contini / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- F. Fontanot / A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido
- T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi
- T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar
- L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / E. Soubrie
Summary
The star-forming main sequence (SFMS) is a tight relation observed
between stellar masses and star formation rates (SFR) in a population of
galaxies. This relation is observed at different redshifts, in various
morphological, and environmental domains, and is key to understanding
the underlying relations between a galaxy budget of cold gas and its
stellar content. Euclid Quick Data Release 1 (Q1) gives us the
opportunity to investigate this fundamental relation in galaxy formation
and evolution. We complement the Euclid release with public IRAC
observations of the Euclid Deep Fields, improving the quality of
recovered photometric redshifts, stellar masses, and SFRs, as is shown
both with simulations and a comparison with available spectroscopic
redshifts. From Q1 data alone, we recover more than  galaxies with
galaxies with  ,
giving a precise constraint of the SFMS at the high-mass end. We
investigated the SFMS, in a redshift interval between
,
giving a precise constraint of the SFMS at the high-mass end. We
investigated the SFMS, in a redshift interval between  and
and  , comparing our results with the
existing literature and fitting them with a parameterisation taking into
account the presence of a bending of the relation at the high-mass end,
depending on the bending mass,
, comparing our results with the
existing literature and fitting them with a parameterisation taking into
account the presence of a bending of the relation at the high-mass end,
depending on the bending mass,  . We find good agreement with previous
results in terms of
. We find good agreement with previous
results in terms of  values, and an increasing trend for
the relation scatter at higher stellar masses. We also investigate the
distribution of physical (e.g. dust absorption,
values, and an increasing trend for
the relation scatter at higher stellar masses. We also investigate the
distribution of physical (e.g. dust absorption,  , and formation age) and morphological
properties (e.g., Sérsic index and radius) in the SFR–stellar mass
plane, and their relation with the SFMS. These results highlight the
potential of Euclid in studying the fundamental scaling relations that
regulate galaxy formation and evolution in anticipation of the
forthcoming Data Release 1.
, and formation age) and morphological
properties (e.g., Sérsic index and radius) in the SFR–stellar mass
plane, and their relation with the SFMS. These results highlight the
potential of Euclid in studying the fundamental scaling relations that
regulate galaxy formation and evolution in anticipation of the
forthcoming Data Release 1.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1) – Characteristics and limitations of the
spectroscopic measurements
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / V. Le Brun / M. Bethermin /
M. Moresco
- D. Vibert / D. Vergani / C. Surace
/ G. Zamorani
- A. Allaoui / T. Bedrine / P.-Y.
Chabaud / G. Daste
- F. Dufresne / M. Gray / E.
Rossetti / Y. Copin
- S. Conseil / E. Maiorano / Z. Mao / E. Palazzi
- L. Pozzetti / S. Quai / C. Scarlata / M. Talia
- H. M. Courtois / L. Guzzo / B. Kubik / A. M. C. Le Brun
- J. A. Peacock / D. Scott / D. Bagot / A. Basset
- P. Casenove / R. Gimenez / G. Libet / M. Ruffenach
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- F. J. Castander / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / A. Costille / F. Courbin /
J.-G. Cuby
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier
- M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan
- J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Sauvage / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato
- M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo
- G. Fabbian / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / J. Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / M. Maturi / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / S. Avila
- M. Bella / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / L. Blot
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- Y. Charles / R. Chary / F. Cogato / A. R.
Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P. Dimauro / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. M. N. Ferguson / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / C. Mancini
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / A. Montoro / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
- J. R. Weaver / L. Zalesky / J. G. Sorce
Summary
The SPE processing function (PF) of the pipeline is dedicated to the
automatic analysis of one-dimensional spectra to determine redshifts,
line fluxes, and spectral classifications. The first Quick Data Release
(Q1) delivers these measurements for all  objects identified in the photometric survey. In
this paper, we present an overview of the SPE PF algorithm and assess
its performance by comparing its results with high-quality spectroscopic
redshifts from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) survey in
the Euclid Deep Field North. Our findings highlight remarkable accuracy
in successful redshift measurements, with a bias of less than
objects identified in the photometric survey. In
this paper, we present an overview of the SPE PF algorithm and assess
its performance by comparing its results with high-quality spectroscopic
redshifts from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) survey in
the Euclid Deep Field North. Our findings highlight remarkable accuracy
in successful redshift measurements, with a bias of less than  in
in  and a high precision of approximately
and a high precision of approximately  . The majority of
spectra have only a single spectral feature or none at all. To avoid
spurious detections, where noise features are misinterpreted as lines or
lines are misidentified, it is therefore essential to apply well-defined
criteria on quantities such as the redshift probability or the flux and
signal-to-noise ratio. Using a well-tuned quality selection, we achieve
an 89% redshift success rate in the target redshift range for cosmology
(
. The majority of
spectra have only a single spectral feature or none at all. To avoid
spurious detections, where noise features are misinterpreted as lines or
lines are misidentified, it is therefore essential to apply well-defined
criteria on quantities such as the redshift probability or the flux and
signal-to-noise ratio. Using a well-tuned quality selection, we achieve
an 89% redshift success rate in the target redshift range for cosmology
( ),
which is well covered by DESI for
),
which is well covered by DESI for  . Outside this
range where the line is observable, redshift measurements are less
reliable, except for sources showing specific spectral features (e.g.,
two bright lines or strong continuum). Ongoing refinements along the
entire chain of PFs are expected to enhance both the redshift
measurements and the spectral classification, allowing us to define the
large and reliable sample required for cosmological analyses. Overall,
the Q1 SPE results are promising, demonstrating encouraging potential
for cosmology.
. Outside this
range where the line is observable, redshift measurements are less
reliable, except for sources showing specific spectral features (e.g.,
two bright lines or strong continuum). Ongoing refinements along the
entire chain of PFs are expected to enhance both the redshift
measurements and the spectral classification, allowing us to define the
large and reliable sample required for cosmological analyses. Overall,
the Q1 SPE results are promising, demonstrating encouraging potential
for cosmology.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Combined Euclid and Spitzer galaxy density
catalogues at  1.3 and detection of
significant Euclid passive galaxy overdensities in Spitzer overdense
regions
1.3 and detection of
significant Euclid passive galaxy overdensities in Spitzer overdense
regions
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / N. Mai / S. Mei / C. Cleland
- R. Chary / J. G. Bartlett / G. Castignani / H. Dannerbauer
- G. De Lucia / F. Fontanot / D. Scott / S. Andreon
- S. Bhargava / H. Dole / T. DUSSERRE / S. A. Stanford
- V. P. Tran / J. R. Weaver / P.-A. Duc / I. Risso
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / N. Auricchio
- H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- A. Caillat / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- A. M. Di Giorgio / M. Douspis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- F. Finelli / P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant /
S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / Y. Charles / F. Cogato / A. R.
Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P. Dimauro / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / A. H. Gonzalez / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / E. A. Magnier / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / F. Shankar / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
Euclid will detect tens of thousands of clusters and protoclusters at
 >1.3. With a total coverage of
63.1deg
>1.3. With a total coverage of
63.1deg , the Euclid Quick Data Release 1 (Q1)
is large enough to detect tens of clusters and hundreds of protoclusters
at these early epochs. The Q1 photometric redshift catalogue enables us
to detect clusters out to
, the Euclid Quick Data Release 1 (Q1)
is large enough to detect tens of clusters and hundreds of protoclusters
at these early epochs. The Q1 photometric redshift catalogue enables us
to detect clusters out to  < 1.5; however, infrared imaging
from Spitzer extends this limit to higher redshifts by using high local
projected densities of Spitzer-selected galaxies as signposts for
cluster and protocluster candidates. We use Spitzer imaging of the
Euclid Deep Fields (EDFs) to derive densities for a sample of
Spitzer-selected galaxies at redshifts
< 1.5; however, infrared imaging
from Spitzer extends this limit to higher redshifts by using high local
projected densities of Spitzer-selected galaxies as signposts for
cluster and protocluster candidates. We use Spitzer imaging of the
Euclid Deep Fields (EDFs) to derive densities for a sample of
Spitzer-selected galaxies at redshifts  > 1.3, building Spitzer IRAC1 and
IRAC2 photometric catalogues that are 95% complete at a magnitude limit
of IRAC2=22.2, 22.6, and 22.8 for the EDF-S, EDF-F, and EDF-N,
respectively. We apply two complementary methods to calculate galaxy
densities: (1) aperture and surface density; and (2) the
Nth-nearest-neighbour method. When considering a sample selected at a
magnitude limit of IRAC2 < 22.2, at which all three EDFs are 95%
complete, our surface density distributions are consistent among the
three EDFs and with the SpUDS blank field survey. We also considered a
deeper sample (IRAC2 < 22.8), finding that 2% and 3% of the surface
densities in the North and Fornax fields are 3
> 1.3, building Spitzer IRAC1 and
IRAC2 photometric catalogues that are 95% complete at a magnitude limit
of IRAC2=22.2, 22.6, and 22.8 for the EDF-S, EDF-F, and EDF-N,
respectively. We apply two complementary methods to calculate galaxy
densities: (1) aperture and surface density; and (2) the
Nth-nearest-neighbour method. When considering a sample selected at a
magnitude limit of IRAC2 < 22.2, at which all three EDFs are 95%
complete, our surface density distributions are consistent among the
three EDFs and with the SpUDS blank field survey. We also considered a
deeper sample (IRAC2 < 22.8), finding that 2% and 3% of the surface
densities in the North and Fornax fields are 3 higher than the average field
distribution and similar to densities found in the CARLA cluster survey.
Our surface densities are also consistent with predictions from the GAEA
semi-analytical model. Using combined Euclid and ground-based i-band
photometry we show that our highest Spitzer-selected galaxy overdense
regions, found at
higher than the average field
distribution and similar to densities found in the CARLA cluster survey.
Our surface densities are also consistent with predictions from the GAEA
semi-analytical model. Using combined Euclid and ground-based i-band
photometry we show that our highest Spitzer-selected galaxy overdense
regions, found at  ~1.5, also host high densities of
passive galaxies. This means that we measure densities consistent with
those found in clusters and protoclusters at
~1.5, also host high densities of
passive galaxies. This means that we measure densities consistent with
those found in clusters and protoclusters at  >1.3.
>1.3.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). An investigation of optically faint, red
objects in the Euclid Deep Fields
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / G. Girardi / G. Rodighiero / L.
Bisigello
- A. Enia / A. Grazian / E. Dalla Bontà / E. Daddi
- S. Serjeant / G. Gandolfi / C. C. Lovell / K. I. Caputi
- A. Bianchetti / A. Vietri / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / F. Grupp / S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / B. Rusholme / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / K. Benson / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P.-A. Duc / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / F. Fontanot / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi
- T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / J. Schaye
- A. Schneider / M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- F. Shankar / L. C. Smith / J. Stadel / K. Tanidis
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
- D. Scott
Summary
Our understanding of cosmic star-formation at  used to largely rely
on rest-frame UV observations. However, these observations overlook
dusty and massive sources, resulting in an incomplete census of early
star-forming galaxies. Recently, infrared data from Spitzer and the
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a hidden population at
$z$3-6 with extreme red colours. Taking advantage of the overlap between
imaging in the Euclid Deep Fields (EDFs), covering
used to largely rely
on rest-frame UV observations. However, these observations overlook
dusty and massive sources, resulting in an incomplete census of early
star-forming galaxies. Recently, infrared data from Spitzer and the
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a hidden population at
$z$3-6 with extreme red colours. Taking advantage of the overlap between
imaging in the Euclid Deep Fields (EDFs), covering  60 deg
60 deg , and ancillary Spitzer observations,
we identified 27000 extremely red objects with
, and ancillary Spitzer observations,
we identified 27000 extremely red objects with  (dubbed HIEROs) down to a
(dubbed HIEROs) down to a  completeness magnitude
limit of IRAC2
completeness magnitude
limit of IRAC2  22.5 AB. After a visual inspection to
discard artefacts and objects with troubling photometry, we ended up
with a final sample of 3900 candidates. We retrieved the physical
parameter estimates for these objects from the SED-fitting tool CIGALE.
Our results confirm that HIERO galaxies may populate the high-mass end
of the stellar mass function at
22.5 AB. After a visual inspection to
discard artefacts and objects with troubling photometry, we ended up
with a final sample of 3900 candidates. We retrieved the physical
parameter estimates for these objects from the SED-fitting tool CIGALE.
Our results confirm that HIERO galaxies may populate the high-mass end
of the stellar mass function at  , with some reaching
extreme stellar masses (
, with some reaching
extreme stellar masses ( ) and exhibiting high dust attenuation (
) and exhibiting high dust attenuation ( ). However, we
consider stellar mass estimates unreliable for
). However, we
consider stellar mass estimates unreliable for  , favouring a
lower-z solution. The challenges faced by SED-fitting tools in
characterising these objects highlight the need for further studies,
incorporating shorter-wavelength and spectroscopic data. Euclid spectra
will help resolve degeneracies and better constrain the physical
properties of the brightest galaxies. Given the extreme nature of this
population, characterising these sources is crucial for understanding
galaxy evolution. This work demonstrates Euclid’s potential to provide
statistical samples of rare, massive, dust-obscured galaxies at
, favouring a
lower-z solution. The challenges faced by SED-fitting tools in
characterising these objects highlight the need for further studies,
incorporating shorter-wavelength and spectroscopic data. Euclid spectra
will help resolve degeneracies and better constrain the physical
properties of the brightest galaxies. Given the extreme nature of this
population, characterising these sources is crucial for understanding
galaxy evolution. This work demonstrates Euclid’s potential to provide
statistical samples of rare, massive, dust-obscured galaxies at  , which will be prime
targets for JWST, ALMA, and ELT.
, which will be prime
targets for JWST, ALMA, and ELT.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). First Euclid statistical study of the active
galactic nuclei contribution fraction
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / B. Margalef-Bentabol / L. Wang / A. La
Marca
- V. Rodriguez-Gomez / A. Humphrey / S. Fotopoulou / F. Ricci
- Y. Toba / G. Stevens / M. Mezcua / W. Roster
- J. H. Knapen / M. Salvato / M. Siudek / F. Shankar
- T. Matamoro Zatarain / L. Spinoglio / P. Dayal / J. Petley
- R. Kondapally / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / A. Costille / F.
Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun
- D. Le Mignant / P. Liebing / S. Ligori / P. B.
Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / H. J. A. Rottgering / B. Rusholme / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra
- M. Huertas-Company / J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist
- K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / R. Gavazzi / E. Gaztanaga / F.
Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo
- H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick
- S. Kruk / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- C. Scarlata / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / D. Scott
Summary
Active galactic nuclei (AGN) play a key role in galaxy evolution but
are challenging to identify due to their varied observational
signatures. Furthermore, understanding their impact requires quantifying
their strength relative to their host galaxies. We developed a deep
learning (DL) model for identifying AGN in imaging data by deriving the
contribution of the central point source. Trained on Euclidised mock
galaxy images with injected AGN levels, in the form of varying
contributions of the point-spread function (PSF), our model can
precisely and accurately recover the injected AGN contribution fraction
 , with a
mean difference between the predicted and true
, with a
mean difference between the predicted and true  of
of  and an overall root
mean square error (RMSE) of 0.051. This method moves beyond binary AGN
classification, enabling precise AGN contribution measurements. Applying
our model to a stellar-mass-limited sample (
and an overall root
mean square error (RMSE) of 0.051. This method moves beyond binary AGN
classification, enabling precise AGN contribution measurements. Applying
our model to a stellar-mass-limited sample ( ,
,  ) from the first quick data release (Q1), we
identify
) from the first quick data release (Q1), we
identify  AGN
over 63.1 deg
AGN
over 63.1 deg (
( %) using a
threshold of
%) using a
threshold of  . We compare our DL-selected AGN with those
identified in X-ray, mid-infrared (MIR), and optical spectroscopy and
investigate their overlapping fractions depending on different
thresholds on the PSF contribution. We find that the overlap increases
with increasing X-ray or bolometric AGN luminosity. The AGN luminosity
in the
. We compare our DL-selected AGN with those
identified in X-ray, mid-infrared (MIR), and optical spectroscopy and
investigate their overlapping fractions depending on different
thresholds on the PSF contribution. We find that the overlap increases
with increasing X-ray or bolometric AGN luminosity. The AGN luminosity
in the  filter
correlates with host galaxy stellar mass, suggesting faster supermassive
black hole (SMBH) growth in more massive galaxies. Moreover, the mean
relative contribution of the AGN is higher in quiescent galaxies than in
star-forming ones. Starburst galaxies and the most massive galaxies
(across the star-formation main sequence) tend to host the most luminous
AGN, indicating concomitant assembly of the SMBH and the host
galaxy.
filter
correlates with host galaxy stellar mass, suggesting faster supermassive
black hole (SMBH) growth in more massive galaxies. Moreover, the mean
relative contribution of the AGN is higher in quiescent galaxies than in
star-forming ones. Starburst galaxies and the most massive galaxies
(across the star-formation main sequence) tend to host the most luminous
AGN, indicating concomitant assembly of the SMBH and the host
galaxy.
Euclid Quick
Data Release (Q1) – Data release overview
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / H. Aussel / I. Tereno / M. Schirmer
- G. Alguero / B. Altieri / E. Balbinot / T. de Boer
- P. Casenove / P. Corcho-Caballero / H. Furusawa / J. Furusawa
- M. J. Hudson / K. Jahnke / G. Libet / J. Macias-Perez
- N. Masoumzadeh / J. J. Mohr / J. Odier / D. Scott
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Zacchei / N. Aghanim
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / S. Awan
- R. Azzollini / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra
- S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia / A. N. Belikov
- R. Bender / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino
- E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera
- G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- J.-G. Cuby / A. Da Silva / R. da Silva / H.
Degaudenzi
- J. T. A. de Jong / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis
- C. Dolding / H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet
- S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / P. Franzetti / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan
- O. Herent / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / M. S. Holliman
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / S. Ilić / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik
- K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- O. Lahav / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- P. Liebing / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / P. W. Morris
- L. Moscardini / S. Mourre / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / T. Nutma
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / J. A. Peacock
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / J. E. Pollack / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / G. D. Racca / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / H.-W. Rix
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / B. Rusholme
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / M. Sauvage / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider
- M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / J. Skottfelt / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / C. Surace / P. Tallada-Crespí / D.
Tavagnacco
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus
- E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / O. R. Williams / G. Zamorani
- F. M. Zerbi / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- R. P. Blake / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana
- R. Cabanac / M. Calabrese / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley / M.
Huertas-Company
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / M. Maturi / N. Mauri
- R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti
- M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- S. Avila / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- S. Borgani / A. S. Borlaff / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- F. Buitrago / A. Calabro / G. Calderone / B. Camacho Quevedo
- F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / Y.
Charles
- F. Cogato / S. Conseil / A. R. Cooray / M.
Costanzi
- O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez
- A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- P. Dimauro / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. M. N. Ferguson / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- F. Fontanot / A. Franco / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- R. Gavazzi / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F.
Gianotti
- A. H. Gonzalez / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gruppuso / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. Jacobson / S. Joudaki / J. J. E. Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / F. Lacasa / C. Laigle
- M. Lattanzi / V. Le Brun / J. Le Graet / L.
Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro
- M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / C. J. R.
McPartland
- J.-B. Melin / M. Migliaccio / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- A. Montoro / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- L. Nicastro / M. Oguri / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson
- L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai
- M. Radovich / P. Reimberg / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero
- R. P. Rollins / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / J. Schaye / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / D. Scognamiglio / E. Sellentin
- F. Shankar / L. C. Smith / E. Soubrie / S. A. Stanford
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / M. Tewes
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / J. R. Weaver
- J. Wilde / L. Zalesky
Summary
The first Euclid Quick Data Release, Q1, comprises 63.1 sq deg of the
Euclid Deep Fields (EDFs) to nominal wide-survey depth. It encompasses
visible and near-infrared space-based imaging and spectroscopic data,
ground-based photometry in the u, g, r, i and z bands, as well as
corresponding masks. Overall, Q1 contains about 30 million objects in
three areas near the ecliptic poles around the EDF-North and EDF-South,
as well as the EDF-Fornax field in the constellation of the same name.
The purpose of this data release – and its associated technical papers –
is twofold. First, it is meant to inform the community of the enormous
potential of the Euclid survey data, to describe what is contained in
these data, and to help prepare expectations for the forthcoming first
major data release DR1. Second, it enables a wide range of initial
scientific projects with wide-survey Euclid data, ranging from the early
Universe to the Solar System. The Q1 data were processed with early
versions of the processing pipelines, which already demonstrate good
performance, with numerous improvements in implementation compared to
pre-launch development. In this paper, we describe the sky areas
released in Q1, the observations, a top-level view of the data
processing of Euclid and associated external data, the Q1 photometric
masks, and how to access the data. We also give an overview of initial
scientific results obtained using the Q1 data set by Euclid Consortium
scientists, and conclude with important caveats when using the data. As
a complementary product, Q1 also contains observations of a star-forming
area in Lynd’s Dark Nebula 1641 in the Orion~A Cloud, observed for
technical purposes during Euclid’s performance-verification phase. This
is a unique target, of a type not commonly found in Euclid’s nominal sky
survey.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): The evolution of the passive-density and
morphology-density relations between  and
and 
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / C. Cleland / S. Mei / G. De Lucia
- F. Fontanot / H. Fu / C. C. Lovell / M. Magliocchetti
- N. Mai / D. Roberts / F. Shankar / J. G. Sorce
- M. Baes / P. Corcho-Caballero / S. Eales / C. Tortora
- N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / A. M. Di Giorgio
- C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- O. Lahav / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / M. Scodeggio
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon
- C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / M. Maturi / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist
- K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc
- A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / A. H. Gonzalez / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E.
Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina
- S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / J. Schaye
- A. Schneider / M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza
- P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / D. Scott
Summary
The extent to which the environment affects galaxy evolution has been
under scrutiny by researchers for decades. With the first data from
Euclid, we can begin to study a wide range of environments and their
effects as a function of redshift, using 63 sq deg of space-based data.
In this paper, we present results from the Euclid Q1 Release, where we
measure the passive-density and morphology-density relations at  -1. We determine if a
galaxy is passive using the specific star-formation rate, and we
classify the morphologies of galaxies using the Sérsic index n and the
u-r colours. We measure the local environmental density of each galaxy
using the Nth-nearest neighbour method. We find that at fixed stellar
mass, the quenched fraction increases with increasing density up to
-1. We determine if a
galaxy is passive using the specific star-formation rate, and we
classify the morphologies of galaxies using the Sérsic index n and the
u-r colours. We measure the local environmental density of each galaxy
using the Nth-nearest neighbour method. We find that at fixed stellar
mass, the quenched fraction increases with increasing density up to  . This result shows
the separability of the effects from the stellar mass and the
environment, at least at
. This result shows
the separability of the effects from the stellar mass and the
environment, at least at  . At
. At  , we observe
weak environmental effects, with most high mass galaxies being quenched
independently of environment. Up to
, we observe
weak environmental effects, with most high mass galaxies being quenched
independently of environment. Up to  , the ETG fraction
increases with density at fixed stellar mass, meaning the environment
also transforms the morphology of the galaxy independently of stellar
mass, at low mass. For high mass galaxies, almost all galaxies are
early-types, with low impact from the environment. At
, the ETG fraction
increases with density at fixed stellar mass, meaning the environment
also transforms the morphology of the galaxy independently of stellar
mass, at low mass. For high mass galaxies, almost all galaxies are
early-types, with low impact from the environment. At  , the morphology
depends mostly on stellar mass, with only low-mass galaxies being
affected by the environment. Given that the morphology classifications
use u-r colours, these are correlated to the star-formation rate, and as
such our morphology results should be taken with caution; future
morphology classifications should verify these results. To summarise, we
identify the passive-density and morphology-density relations at
, the morphology
depends mostly on stellar mass, with only low-mass galaxies being
affected by the environment. Given that the morphology classifications
use u-r colours, these are correlated to the star-formation rate, and as
such our morphology results should be taken with caution; future
morphology classifications should verify these results. To summarise, we
identify the passive-density and morphology-density relations at  , but at
, but at  the relations
are less strong. At
the relations
are less strong. At  , the
uncertainties are large, and future Euclid data releases are key to
confirm these trends.
, the
uncertainties are large, and future Euclid data releases are key to
confirm these trends.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Extending the quest for little red dots to
z<4
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / L. Bisigello / G. Rodighiero / S.
Fotopoulou
- F. Ricci / K. Jahnke / A. Feltre / V. Allevato
- F. Shankar / P. Cassata / E. Dalla Bontà / G. Gandolfi
- G. Girardi / M. Giulietti / A. Grazian / C. C. Lovell
- R. Maiolino / T. Matamoro Zatarain / M. Mezcua / I. Prandoni
- D. Roberts / W. Roster / M. Salvato / M. Siudek
- F. Tarsitano / Y. Toba / A. Vietri / L. Wang
- G. Zamorani / M. Baes / S. Belladitta / A. Nersesian
- L. Spinoglio / X. Lopez Lopez / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- A. Basset / P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George
- W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / F. Grupp / S. Gwyn
- S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / P. Liebing / S.
Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio
- E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / H. J. A. Rottgering
- B. Rusholme / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko
- E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / M. Maturi / N. Mauri / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / K. Benson / D. Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / Y. Charles / F. Cogato / T.
Contini
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari
- P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / F. Fontanot
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- W. G. Hartley / S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H.
Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori
- G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi
- T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / C. Mancini / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata
- J. Schaye / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- A. Shulevski / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / A. Viitanen / N. A. Walton
- J. R. Weaver / E. Soubrie / D. Scott
Summary
Recent James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observations have revealed a
population of sources with a compact morphology and a characteristic
v-shaped' continuum, namely blue at rest-frame $λ<4000$A and red at longer wavelengths. The nature of these sources, calledlittle
red dots’ (LRDs), is still debated, as it is unclear if they host active
galactic nuclei (AGN) and their number seems to drastically drop at
z<4. We take advantage of the  covered by the quick
Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1) to extend the search for LRDs to brighter
magnitudes and to lower redshifts than what has been possible with JWST.
The selection is performed by fitting the available photometric data
(Euclid, the Spitzer Infrared Array Camera (IRAC), and ground-based
covered by the quick
Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1) to extend the search for LRDs to brighter
magnitudes and to lower redshifts than what has been possible with JWST.
The selection is performed by fitting the available photometric data
(Euclid, the Spitzer Infrared Array Camera (IRAC), and ground-based  data) with two power
laws, to retrieve both the rest-frame optical and UV slopes consistently
over a large redshift range (i.e, z<7.6). We exclude extended objects
and possible line emitters, and perform a careful visual inspection to
remove any imaging artefacts. The final selection includes 3341 LRD
candidates at z=0.33-3.6, with 29 detected also in IRAC. The resulting
rest-frame UV luminosity function, in contrast with previous JWST
studies, shows that the number density of LRD candidates increases from
high-z down to z=1.5-2.5 and decreases at lower z. However, less
evolution is apparent focusing on the subsample of more robust LRD
candidates having IRAC detections, which however has low statistics and
limited by the IRAC resolution. The comparison with previous quasar
(QSO) UV luminosity functions shows that LRDs are not the dominant AGN
population at z<4 and
data) with two power
laws, to retrieve both the rest-frame optical and UV slopes consistently
over a large redshift range (i.e, z<7.6). We exclude extended objects
and possible line emitters, and perform a careful visual inspection to
remove any imaging artefacts. The final selection includes 3341 LRD
candidates at z=0.33-3.6, with 29 detected also in IRAC. The resulting
rest-frame UV luminosity function, in contrast with previous JWST
studies, shows that the number density of LRD candidates increases from
high-z down to z=1.5-2.5 and decreases at lower z. However, less
evolution is apparent focusing on the subsample of more robust LRD
candidates having IRAC detections, which however has low statistics and
limited by the IRAC resolution. The comparison with previous quasar
(QSO) UV luminosity functions shows that LRDs are not the dominant AGN
population at z<4 and  . Follow-up studies of these LRD candidates are
pivotal to confirm their nature, probe their physical properties and
check for their compatibility with JWST sources, given the different
spatial resolution and wavelength coverage of Euclid and JWST.
. Follow-up studies of these LRD candidates are
pivotal to confirm their nature, probe their physical properties and
check for their compatibility with JWST sources, given the different
spatial resolution and wavelength coverage of Euclid and JWST.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): From spectrograms to spectra: the SIR
spectroscopic Processing Function
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / Y. Copin / M. Fumana / C. Mancini
- P. N. Appleton / R. Chary / S. Conseil / A. L.
Faisst
- S. Hemmati / D. C. Masters / C. Scarlata / M. Scodeggio
- A. Alavi / A. Carle / P. Casenove / T. Contini
- I. Das / W. Gillard / G. Herzog / J. Jacobson
- V. Le Brun / D. Maino / G. Setnikar / N. R.
Stickley
- D. Tavagnacco / Q. Xie / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- A. Basset / P. Battaglia / A. N. Belikov / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / R. da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Farina / R. Farinelli
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / P. Franzetti / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes
- I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P.
B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior
- Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- A. Mora / M. Moresco / P. W. Morris / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- G. D. Racca / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / M.
Huertas-Company
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso
- V. Scottez / M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel
- M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist
- K. Benson / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc
- A. Enia / Y. Fang / A. M. N. Ferguson / A. G. Ferrari
- A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / S.
Hosseini
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- C. J. R. McPartland / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / A. Montoro
- C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray / S. Nadathur
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / M. Bella / D. Scott
Summary
The Euclid space mission aims to investigate the nature of dark
energy and dark matter by mapping the large-scale structure of the
Universe. A key component of Euclid’s observational strategy is slitless
spectroscopy, conducted using the Near Infrared Spectrometer and
Photometer (NISP). This technique enables the acquisition of large-scale
spectroscopic data without the need for targeted apertures, allowing
precise redshift measurements for millions of galaxies. These data are
essential for Euclid’s core science objectives, including the study of
cosmic acceleration and the evolution of galaxy clustering, as well as
enabling many non-cosmological investigations. This study presents the
SIR processing function (PF), which is responsible for processing
slitless spectroscopic data. The objective is to generate science-grade
fully-calibrated one-dimensional spectra, ensuring high-quality
spectroscopic data. The processing function relies on a source catalogue
generated from photometric data, effectively corrects detector effects,
subtracts cross-contaminations, minimizes self-contamination, calibrates
wavelength and flux, and produces reliable spectra for later scientific
use. The first Quick Data Release (Q1) of Euclid’s spectroscopic data
provides approximately three million validated spectra for sources
observed in the red-grism mode from a selected portion of the Euclid
Wide Survey. We find that wavelength accuracy and measured resolving
power are within requirements, thanks to the excellent optical quality
of the instrument. The SIR PF represents a significant step in
processing slitless spectroscopic data for the Euclid mission. As the
survey progresses, continued refinements and additional features will
enhance its capabilities, supporting high-precision cosmological and
astrophysical measurements.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1): First visual morphology catalogue
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / M. Walmsley / M. Huertas-Company / L.
Quilley
- K. L. Masters / S. Kruk / K. A. Remmelgas / J. J. Popp
- E. Romelli / D. O’Ryan / H. J. Dickinson / C. J. Lintott
- S. Serjeant / R. J. Smethurst / B. Simmons / J. Shingirai
Makechemu
- I. L. Garland / H. Roberts / K. Mantha / L. F. Fortson
- T. Géron / W. Keel / E. M. Baeten / C. Macmillan
- J. Bovy / S. Casas / C. De Leo / H. Domínguez Sánchez
- J. Katona / A. Kovács / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- A. Basset / P. Battaglia / R. Bender / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / F. Finelli
- P. Fosalba / S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi
- S. Galeotta / K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / H. Hoekstra
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / R. Kohley
- B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun
- D. Le Mignant / P. Liebing / S. Ligori / P. B.
Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / M. Roncarelli / B. Rusholme / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / M.
Scodeggio
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N.
Taylor
- H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / E. A.
Valentijn
- L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi / I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca
- V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J. Martín-Fleitas / S.
Matthew
- N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- C. Benoist / K. Benson / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / F. Buitrago / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini
- F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley
- S. Hemmati / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J.
Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci
- J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro
- J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / C. Murray
- S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci
- G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders
- E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / J. Schaye / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar
- L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- A. Venhola / D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton / E. Soubrie / D. Scott
Summary
We present a detailed visual morphology catalogue for Euclid’s Quick
Release 1 (Q1). Our catalogue includes galaxy features such as bars,
spiral arms, and ongoing mergers, for the 378000 bright ( ) or
extended (area
) or
extended (area  pixels)
galaxies in Q1. The catalogue was created by finetuning the Zoobot
galaxy foundation models on annotations from an intensive one month
campaign by Galaxy Zoo volunteers. Our measurements are fully automated
and hence fully scaleable. This catalogue is the first 0.4% of the
approximately 100 million galaxies where Euclid will ultimately resolve
detailed morphology.
pixels)
galaxies in Q1. The catalogue was created by finetuning the Zoobot
galaxy foundation models on annotations from an intensive one month
campaign by Galaxy Zoo volunteers. Our measurements are fully automated
and hence fully scaleable. This catalogue is the first 0.4% of the
approximately 100 million galaxies where Euclid will ultimately resolve
detailed morphology.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). The Strong Lensing Discovery Engine C: Finding
lenses with machine learning
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / N. E. P. Lines / T. E. Collett / M.
Walmsley
- K. Rojas / T. Li / L. Leuzzi / A. Manjón-García
- S. H. Vincken / J. Wilde / P. Holloway / A. Verma
- R. B. Metcalf / I. T. Andika / A. Melo / M. Melchior
- H. Domínguez Sánchez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. A. Acevedo Barroso / B.
Clément
- C. Krawczyk / R. Pearce-Casey / S. Serjeant / F. Courbin
- G. Despali / R. Gavazzi / S. Schuldt / H.
Degaudenzi
- L. R. Ecker / W. J. R. Enzi / K. Finner / A. Galan
- C. Giocoli / N. B. Hogg / K. Jahnke / S. Kruk
- G. Mahler / A. More / B. C. Nagam / J. Pearson
- A. Sainz de Murieta / C. Scarlata / D. Sluse / A. Sonnenfeld
- C. Spiniello / T. T. Thai / C. Tortora / L. Ulivi
- L. Weisenbach / M. Zumalacarregui / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel
- C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / R. Bender / F. Bernardeau / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / A. Costille / H. M.
Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- C. Dolding / H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio / B. R. Granett / A.
Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan
- W. Holmes / I. M. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T.
Schrabback
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / A. Spurio
Mancini
- L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / E. A. Valentijn / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen
- C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist
- K. Benson / P. Bergamini / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin
- A. Blanchard / L. Blot / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro
- Y. Charles / F. Cogato / A. R. Cooray / O.
Cucciati
- S. Davini / F. De Paolis / G. Desprez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / A. Franco
- K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / W. G. Hartley
- C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / J. J. E.
Kajava
- Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / K. Kiiveri
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / M. Lembo
- F. Lepori / G. Leroy / G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues
- T. I. Liaudat / S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / S. Nadathur
- K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / F. Passalacqua
- K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani / D. Potter
- S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci / S. Sacquegna
- M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Vernardos / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
- D. Scott
Summary
Strong gravitational lensing has the potential to provide a powerful
probe of astrophysics and cosmology, but fewer than 1000 strong lenses
have been confirmed so far. With a 0.16’’ resolution covering a third of
the sky, the Euclid telescope will revolutionise the identification of
strong lenses, with 170 000 lenses forecasted to be discovered amongst
the 1.5 billion galaxies it will observe. We present an analysis of the
performance of five machine-learning models at finding strong
gravitational lenses in the quick release of Euclid data (Q1) covering
63 deg2. The models have been validated by citizen scientists and expert
visual inspection. We focus on the best-performing network: a fine-tuned
version of the Zoobot pretrained model originally trained to classify
galaxy morphologies in heterogeneous astronomical imaging surveys. Of
the one million Q1 objects that Zoobot was tasked to find strong lenses
within, the top 1000 ranked objects contain 122 grade A lenses
(almost-certain lenses) and 41 grade B lenses (probable lenses). A
deeper search with the five networks combined with visual inspection
yielded 250 (247) grade A (B) lenses, of which 224 (182) are ranked in
the top 20 000 by Zoobot. When extrapolated to the full Euclid survey,
the highest ranked one million images will contain 75 000 grade A or B
strong gravitational lenses.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). First Euclid statistical study of galaxy
mergers and their connection to active galactic nuclei
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / A. La Marca / L. Wang / B.
Margalef-Bentabol
- L. Gabarra / Y. Toba / M. Mezcua / V. Rodriguez-Gomez
- F. Ricci / S. Fotopoulou / T. Matamoro Zatarain / V. Allevato
- F. La Franca / F. Shankar / L. Bisigello / G. Stevens
- M. Siudek / W. Roster / M. Salvato / C. Tortora
- L. Spinoglio / A. W. S. Man / J. H. Knapen / M. Baes
- D. O’Ryan / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / A. Biviano
- A. Bonchi / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / A.
Costille
- F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / C. Dolding
- H. Dole / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- A. Ealet / S. Escoffier / M. Fabricius / M. Farina
- R. Farinelli / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / F. Finelli
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / K. George
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez / J. Gracia-Carpio
- B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. Gwyn / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h / A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le
Mignant
- S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro
- G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi
- J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / B. Rusholme
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- J. A. Schewtschenko / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / M.
Scodeggio
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano
- P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- I. Tereno / N. Tessore / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / M. Ballardini / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac / A. Cappi
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / M. Huertas-Company / J.
Martín-Fleitas
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani / I. Risso / V. Scottez
- M. Sereno / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / S. Alvi / I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi
- M. Archidiacono / F. Atrio-Barandela / C. Benoist / K. Benson
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot
- H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Conseil / T.
Contini
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio
- J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia / Y. Fang
- A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana / F. Fontanot
- A. Franco / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall
- W. G. Hartley / C. Hernández-Monteagudo / H. Hildebrandt / J.
Hjorth
- J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- K. Kiiveri / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy
- G. F. Lesci / J. Lesgourgues / L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- E. A. Magnier / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins
- L. Maurin / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / K. Naidoo / A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris
- F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich / P.-F. Rocci
- S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén / D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa
- C. Scarlata / J. Schaye / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti
- E. Sellentin / L. C. Smith / S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis
- G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton / E. Soubrie
- D. Scott
Summary
Galaxy major mergers are a key pathway to trigger AGN. We present the
first detection of major mergers in the Euclid Deep Fields and analyse
their connection with AGN. We constructed a stellar-mass-complete ( ) sample of galaxies from the first quick data
release (Q1), in the redshift range z=0.5-2. We selected AGN using X-ray
data, optical spectroscopy, mid-infrared colours, and processing
observations with an image decomposition algorithm. We used CNNs trained
on cosmological simulations to classify galaxies as mergers and
non-mergers. We found a larger fraction of AGN in mergers compared to
the non-merger controls for all AGN selections, with AGN excess factors
ranging from 2 to 6. Likewise, a generally larger merger fraction (
) sample of galaxies from the first quick data
release (Q1), in the redshift range z=0.5-2. We selected AGN using X-ray
data, optical spectroscopy, mid-infrared colours, and processing
observations with an image decomposition algorithm. We used CNNs trained
on cosmological simulations to classify galaxies as mergers and
non-mergers. We found a larger fraction of AGN in mergers compared to
the non-merger controls for all AGN selections, with AGN excess factors
ranging from 2 to 6. Likewise, a generally larger merger fraction ( ) is seen in
active galaxies than in the non-active controls. We analysed
) is seen in
active galaxies than in the non-active controls. We analysed  as a function of
the AGN bolometric luminosity (
as a function of
the AGN bolometric luminosity ( ) and the
contribution of the point-source to the total galaxy light in the -band
(
) and the
contribution of the point-source to the total galaxy light in the -band
( ) as a proxy for the
relative AGN contribution fraction. We uncovered a rising
) as a proxy for the
relative AGN contribution fraction. We uncovered a rising  , with increasing
, with increasing
 up to
up to  , after
which we observed a decreasing trend. We then derived the point-source
luminosity (
, after
which we observed a decreasing trend. We then derived the point-source
luminosity ( ) and showed that
) and showed that
 monotonically
increases as a function of
monotonically
increases as a function of  at z<0.9, with
$f_{merg}>$50% for
at z<0.9, with
$f_{merg}>$50% for  erg/s. At z>0.9,
erg/s. At z>0.9,  rises as a
function of
rises as a
function of  , though mergers do
not dominate until
, though mergers do
not dominate until  erg/s. For X-ray and spectroscopic AGN, we computed
erg/s. For X-ray and spectroscopic AGN, we computed  , which has a
positive correlation with
, which has a
positive correlation with  for X-ray AGN,
while shows a less pronounced trend for spectroscopic AGN due to the
smaller sample size. At
for X-ray AGN,
while shows a less pronounced trend for spectroscopic AGN due to the
smaller sample size. At  erg/s, AGN mostly reside in mergers. We concluded
that mergers are strongly linked to the most powerful, dust-obscured
AGN, associated with rapid supermassive black hole growth.
erg/s, AGN mostly reside in mergers. We concluded
that mergers are strongly linked to the most powerful, dust-obscured
AGN, associated with rapid supermassive black hole growth.
Euclid
Quick Data Release (Q1). Active galactic nuclei identification using
diffusion-based inpainting of Euclid VIS images
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / G. Stevens / S. Fotopoulou / M. N.
Bremer
- T. Matamoro Zatarain / K. Jahnke / B. Margalef-Bentabol / M.
Huertas-Company
- M. J. Smith / M. Walmsley / M. Salvato / M. Mezcua
- A. Paulino-Afonso / M. Siudek / M. Talia / F. Ricci
- W. Roster / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / S. Andreon
- H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / A. Costille / F. Courbin / H. M.
Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- C. Dolding / H. Dole / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / S. Escoffier / M. Farina
- S. Ferriol / K. George / C. Giocoli / B. R. Granett
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / I. M. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / M. Jhabvala
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kümmel / H. Kurki-Suonio / Q. Le Boulc’h
- A. M. C. Le Brun / D. Le Mignant / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Marggraf / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / H. J. McCracken / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- R. Saglia / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / J. A. Schewtschenko
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- S. Serrano / P. Simon / C. Sirignano / G.
Sirri
- J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / J. Valiviita
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- I. A. Zinchenko / E. Zucca / V. Allevato / M. Ballardini
- M. Bolzonella / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / R. Cabanac
- A. Cappi / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / W. G. Hartley
- J. Martín-Fleitas / S. Matthew / R. B. Metcalf / A. Pezzotta
- M. Pöntinen / I. Risso / V. Scottez / M. Sereno
- M. Tenti / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami / S. Alvi
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / L. Bisigello / A. Blanchard
- L. Blot / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton
- A. Calabro / F. Caro / T. Castro / F. Cogato
- S. Davini / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. J. Diaz
- S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego / P.-A. Duc / A. Enia
- Y. Fang / A. G. Ferrari / A. Finoguenov / A. Fontana
- A. Franco / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard
- E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / L. Legrand
- M. Lembo / F. Lepori / G. Leroy / J. Lesgourgues
- L. Leuzzi / T. I. Liaudat / J. Macias-Perez / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / G. Morgante / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / F. Passalacqua / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / D. Potter / S. Quai / M. Radovich
- P.-F. Rocci / G. Rodighiero / S. Sacquegna / M. Sahlén
- D. B. Sanders / E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / M. Schultheis
- D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / F. Shankar / L. C. Smith
- K. Tanidis / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / N. A. Walton
Summary
Light emission from galaxies exhibit diverse brightness profiles,
influenced by factors such as galaxy type, structural features and
interactions with other galaxies. Elliptical galaxies feature more
uniform light distributions, while spiral and irregular galaxies have
complex, varied light profiles due to their structural heterogeneity and
star-forming activity. In addition, galaxies with an active galactic
nucleus (AGN) feature intense, concentrated emission from gas accretion
around supermassive black holes, superimposed on regular galactic light,
while quasi-stellar objects (QSO) are the extreme case of the AGN
emission dominating the galaxy. The challenge of identifying AGN and QSO
has been discussed many times in the literature, often requiring
multi-wavelength observations. This paper introduces a novel approach to
identify AGN and QSO from a single image. Diffusion models have been
recently developed in the machine-learning literature to generate
realistic-looking images of everyday objects. Utilising the spatial
resolving power of the Euclid VIS images, we created a diffusion model
trained on one million sources, without using any source pre-selection
or labels. The model learns to reconstruct light distributions of normal
galaxies, since the population is dominated by them. We condition the
prediction of the central light distribution by masking the central few
pixels of each source and reconstruct the light according to the
diffusion model. We further use this prediction to identify sources that
deviate from this profile by examining the reconstruction error of the
few central pixels regenerated in each source’s core. Our approach,
solely using VIS imaging, features high completeness compared to
traditional methods of AGN and QSO selection, including optical,
near-infrared, mid-infrared, and X-rays.
Articles for week 11 2025
The
COSMOS-Web Lens Survey (COWLS) II: depth, resolution, and NIR coverage
from JWST reveal 17 spectacular lenses
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Guillaume Mahler / James W. Nightingale / Natalie B. Hogg / Ghassem
Gozaliasl
- Jacqueline McCleary / Qiuhan He / Edward Berman / Maximilien
Franco
- Daizhong Liu / Richard J. Massey / Wilfried Mercier
/ Diana Scognamiglio
- Marko Shuntov / Maximilian von Wietersheim-Kramsta / Louise
Paquereau / Olivier Ilbert
- Natalie Allen / Sune Toft / Hollis B. Akins / Caitlin M. Casey
- Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Anton M. Koekemoer / Henry Joy McCracken /
Jason D. Rhodes
- Brant E. Robertson / Jorge A. Zavala / Nicole E. Drakos / Andreas L.
Faisst
- Georgios E. Magdis / Shuowen Jin
Summary
The COSMOS-Web Lens Survey (COWLS) presents the first systematic
search for strong gravitational lenses in the COSMOS-Web field using
data from the Space Telescope (). Using high-resolution NIRCam imaging,
we visually inspected over 42,660 galaxies and identified over 400
lensing candidates. From this sample and based on /NIRCam imaging only,
we report here the 17 most obvious and spectacular strong lensing
systems. These lenses, characterised by large Einstein rings and arcs
and their distinct lens and source colours, were found through only the
visual inspection of the lens-light-subtracted image data and were
immediately visible due to their spectacular appearance. We showcase how
spectacular strong lenses are at the extremes of lens parameter space.
Their exceptionally high signal-to-noise, multi-wavelength imaging
enables unprecedented lensing analysis, including `-dark’ source
galaxies that are also invisible in the deeper bluer wavebands, enabling
clean deblending between the lens and the source. Sources may exhibit
dramatic morphological changes across wavelengths, and dust absorption
within lenses may be detectable by eye. No other instrument, including
the Space Telescope, can discover or image such lenses with comparable
detail. We estimate that uncovers a new spectacular lens approximately
every 10 to 12 NIRCam pointings, suggesting that over 40 such lenses
remain undetected within its first three years of observations. All
COWLS data is publicly available on GitHub.
The
COSMOS-Web Lens Survey (COWLS) I: Discovery of >100 high redshift
strong lenses in contiguous JWST imaging
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- James Nightingale / Guillaume Mahler / Jacqueline McCleary / Qiuhan
He
- Natalie B. Hogg / Aristeidis Amvrosiadis / Ghassem Gozaliasl /
Wilfried Mercier
- Diana Scognamiglio / Edward Berman / Gavin Leroy / Daizhong Liu
- Richard J. Massey / Marko Shuntov / Maximilian von
Wietersheim-Kramsta / Maximilien Franco
- Louise Paquereau / Olivier Ilbert / Natalie Allen /
Sune Toft
- Hollis B. Akins / Caitlin M. Casey / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Anton M.
Koekemoer
- Henry Joy McCracken / Jason D. Rhodes / Brant E. Robertson / Nicole
E. Drakos
- Andreas L. Faisst / Shuowen Jin
Summary
We present the COSMOS-Web Lens Survey (COWLS), a sample of over 100
strong lens candidates from the  ,deg
,deg COSMOS-Web survey, discovered using
exquisite James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) imaging across four
wavebands. Following two rounds of visual inspection, over 100
candidates were ranked as
COSMOS-Web survey, discovered using
exquisite James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) imaging across four
wavebands. Following two rounds of visual inspection, over 100
candidates were ranked as high confidence' orlikely’ by at
least  of inspectors. The COWLS
sample has several notable properties: (i) magnified source galaxies
spanning redshifts
of inspectors. The COWLS
sample has several notable properties: (i) magnified source galaxies
spanning redshifts  to
to  , which therefore
extend into the epoch of reionisation; (ii) the highest-redshift lens
galaxies known, pushing galaxy density profile evolution studies beyond
, which therefore
extend into the epoch of reionisation; (ii) the highest-redshift lens
galaxies known, pushing galaxy density profile evolution studies beyond
 ; (iii) all lenses
are distributed within a contiguous
; (iii) all lenses
are distributed within a contiguous  ,deg
,deg region, allowing for joint strong and
weak lensing analyses; and (iv) a subset exhibits lensed source emission
ray-traced near the lens galaxy centers, enabling studies of
supermassive black holes and dust absorption. A key innovation of our
approach is the use of lens modelling to aid in identifying lenses that
may otherwise be missed. This paper is accompanied by the first COWLS
public release, providing JWST NIRCam imaging in four bands, lens
models, pixelized source reconstructions and lens redshift estimates :
https://github.com/Jammy2211/COWLS_COSMOS_Web_Lens_Survey
region, allowing for joint strong and
weak lensing analyses; and (iv) a subset exhibits lensed source emission
ray-traced near the lens galaxy centers, enabling studies of
supermassive black holes and dust absorption. A key innovation of our
approach is the use of lens modelling to aid in identifying lenses that
may otherwise be missed. This paper is accompanied by the first COWLS
public release, providing JWST NIRCam imaging in four bands, lens
models, pixelized source reconstructions and lens redshift estimates :
https://github.com/Jammy2211/COWLS_COSMOS_Web_Lens_Survey
The
COSMOS-Web Lens Survey (COWLS) III: forecasts versus data
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Natalie B. Hogg / James W. Nightingale / Quihan He / Jacqueline
McCleary
- Guillaume Mahler / Aristeidis Amvrosiadis / Ghassem Gozaliasl /
Edward Berman
- Richard J. Massey / Diana Scognamiglio / Maximilien Franco /
Daizhong Liu
- Marko Shuntov / Louise Paquereau / Olivier Ilbert /
Natalie Allen
- Sune Toft / Hollis B. Akins / Caitlin M. Casey / Jeyhan S.
Kartaltepe
- Anton M. Koekemoer / Henry Joy McCracken / Jason D. Rhodes / Brant
E. Robertson
- Nicole E. Drakos / Andreas L. Faisst / Hossein Hatamnia / Sophie L.
Newman
Summary
We compare forecasts for the abundance and properties of strong
gravitational lenses in the COSMOS-Web survey, a  deg
deg survey of the COSMOS field using the
NIRCam and MIRI instruments aboard JWST, with the first catalogue of
strong lens candidates identified in the observed NIRCam data, COWLS. We
modify the lenspop package to produce a forecast for strong lensing in
COSMOS-Web. We add a new mock galaxy catalogue to use as the source
population, as well as the COSMOS-Web survey specifications, including
the transmission data for the four NIRCam filters used. We forecast 107
strong lenses can be detected in COSMOS-Web across all bands, assuming
complete subtraction of the lens galaxy light. The majority of the
lenses are forecast to have small Einstein radii (
survey of the COSMOS field using the
NIRCam and MIRI instruments aboard JWST, with the first catalogue of
strong lens candidates identified in the observed NIRCam data, COWLS. We
modify the lenspop package to produce a forecast for strong lensing in
COSMOS-Web. We add a new mock galaxy catalogue to use as the source
population, as well as the COSMOS-Web survey specifications, including
the transmission data for the four NIRCam filters used. We forecast 107
strong lenses can be detected in COSMOS-Web across all bands, assuming
complete subtraction of the lens galaxy light. The majority of the
lenses are forecast to have small Einstein radii ( arcsecond) and lie at redshifts between
arcsecond) and lie at redshifts between  ,
whilst the source redshift distribution peaks at
,
whilst the source redshift distribution peaks at  and has a long tail
extending up to
and has a long tail
extending up to  , unambiguously
showing that strong lensing in JWST can probe the entirety of the epoch
of reionisation. We compare our forecast with the distributions of
Einstein radii, lens photometric redshifts, and lens and source
magnitudes in the observed lenses, finding that whilst the forecast and
observed Einstein radii distributions match, the redshifts and
magnitudes do not. The observed lens redshift distribution peaks at a
slightly lower redshift than the forecast one, whilst the lens
magnitudes are systematically brighter in the observed data than in the
forecast.
, unambiguously
showing that strong lensing in JWST can probe the entirety of the epoch
of reionisation. We compare our forecast with the distributions of
Einstein radii, lens photometric redshifts, and lens and source
magnitudes in the observed lenses, finding that whilst the forecast and
observed Einstein radii distributions match, the redshifts and
magnitudes do not. The observed lens redshift distribution peaks at a
slightly lower redshift than the forecast one, whilst the lens
magnitudes are systematically brighter in the observed data than in the
forecast.
The Spectroscopic Stage-5
Experiment
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Robert Besuner / Arjun Dey / Alex Drlica-Wagner / Haruki Ebina
- Guillermo Fernandez Moroni / Simone Ferraro / Jaime Forero-Romero /
Klaus Honscheid
- Pat Jelinsky / Dustin Lang / Michael Levi / Paul Martini
- Adam Myers / Nathalie Palanque-Delabrouille / Swayamtrupta Panda /
Claire Poppett
- Noah Sailer / David Schlegel / Arman Shafieloo / Joseph Silber
- Martin White / Timothy Abbott / Lori Allen / Santiago Avila
- Roberto Avilés / Stephen Bailey / Abby Bault / Mohamed Bouri
- Konstantina Boutsia / Eienne Burtin / Fernando Chierchie / William
Coulton
- Kyle Dawson / Biprateep Dey / Olivier Doré / Patrick Dunlop
- Daniel Eisenstein / Castorina Emanuele / Stephanie Escoffier / Juan
Estrada
- Parker Fagrelius / Kevin Fanning / Timothy Fanning / Andreu
Font-Ribera
- Joshua Frieman / Malak Galal / Vera Gluscevic / Satya Gontcho A
Gontcho
- Daniel Green / Gaston Gutierrez / Julien Guy / Kevan Hashemi
- Steve Heathcote / Steve Holland / Jiamin Hou / Dragan Huterer
- Blas Irigoyen Gimenez / Mikhail Ivanov / Richard Joyce /
Eric Jullo
- Stephanie Juneau / Claire Juramy / Armin Karcher / Stephen Kent
- David Kirkby / Jean-Paul Kneib / Elisabeth Krause / Alex
Krolewski
- Ofer Lahav / Agustin Lapi / Alexie Leauthaud / Matthew
Lewandowski
- Ting Li / Kenneth Lin / Marilena Loverde / Sean MacBride
- Christophe Magneville / Jennifer Marshall / Patrick McDonald /
Timothy Miller
- John Moustakas / Moritz Münchmeyer / Joan Najita / Jeff Newman
- Will Percival / Oliver Philcox / Priscila Pires / Anand
Raichoor
- Brandon Roach / Constance Rockosi / Maxime Rombach / Ashley
Ross
- Eusebio Sanchez / Luke Schmidt / Michael Schubnell / Rebekah
Sebok
- Uros Seljak / Eva Silverstein / Zachay Slepian / Chris Stone
- Robert Stupak / Gregory Tarlé / Ting Li / Luke Tyas
- Mariana Vargas-Magaña / Alistair Walker / Nicholas Wenner /
Christophe Yèche
- Yuanyuan Zhang / Rongpu Zhou
Summary
The existence, properties, and dynamics of the dark sectors of our
universe pose fundamental challenges to our current model of physics,
and large-scale astronomical surveys may be our only hope to unravel
these long-standing mysteries. In this white paper, we describe the
science motivation, instrumentation, and survey plan for the
next-generation spectroscopic observatory, the Stage-5 Spectroscopic
Experiment (Spec-S5). Spec-S5 is a new all-sky spectroscopic instrument
optimized to efficiently carry out cosmological surveys of unprecedented
scale and precision. The baseline plan for Spec-S5 involves upgrading
two existing 4-m telescopes to new 6-m wide-field facilities, each with
a highly multiplexed spectroscopic instrument capable of simultaneously
measuring the spectra of 13,000 astronomical targets. Spec-S5, which
builds and improves on the hardware used for previous cosmology
experiments, represents a cost-effective and rapid approach to realizing
a more than 10 gain in spectroscopic
capability compared to the current state-of-the-art represented by the
Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument project (DESI). Spec-S5 will
provide a critical scientific capability in the post-Rubin and post-DESI
era for advancing cosmology, fundamental physics, and astrophysics in
the 2030s.
gain in spectroscopic
capability compared to the current state-of-the-art represented by the
Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument project (DESI). Spec-S5 will
provide a critical scientific capability in the post-Rubin and post-DESI
era for advancing cosmology, fundamental physics, and astrophysics in
the 2030s.
A
panchromatic view of N2CLS GOODS-N: the evolution of the dust cosmic
density since z~7
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- S. Berta / G. Lagache / A. Beelen
/ R. Adam
- P. Ade / H. Ajeddig / S. Amarantidis / P. André
- H. Aussel / A. Benoît / M. Bethermin / L.-J. Bing
- A. Bongiovanni / J. Bounmy / O. Bourrion / M. Calvo
- A. Catalano / D. Chérouvrier / L. Ciesla / M. De
Petris
- F.-X. Désert / S. Doyle / E. F. C. Driessen / G. Ejlali
- D. Elbaz / A. Ferragamo / A. Gomez / J. Goupy
- C. Hanser / S. Katsioli / F. Kéruzoré / C. Kramer
- B. Ladjelate / S. Leclercq / J.-F. Lestrade / J. F.
Macías-Pérez
- S. C. Madden / A. Maury / F. Mayet / H. Messias
- A. Monfardini / A. Moyer-Anin / M. Muñoz-Echeverría / I.
Myserlis
- R. Neri / A. Paliwal / L. Perotto / G. Pisano
- N. Ponthieu / V. Revéret / A. J. Rigby / A. Ritacco
- H. Roussel / F. Ruppin / M. Sánchez-Portal / S. Savorgnano
- K. Schuster / A. Sievers / C. Tucker / M.-Y. Xiao
- R. Zylka
Summary
(abridged) To understand early star formation, it is essential to
determine the dust mass budget of high-redshift galaxies. Sub-millimeter
rest-frame emission, dominated by cold dust, is an unbiased tracer of
dust mass. The NIKA2 camera conducted a deep blank field survey at 1.2
and 2.0 mm in the GOODS-N field as part of the NIKA2 Cosmological Legacy
Survey (N2CLS), detecting 65 sources with SNR>=4.2. Thanks to a
dedicated interferometric program with NOEMA and other high-angular
resolution data, we identify the multi-wavelength counterparts of these
sources and resolve them into 71 individual galaxies. We build detailed
SEDs and assign a redshift to 68 of them, over the range
0.6<z<7.2. We fit these SEDs using MBB and Draine & Li (2007)
models, and the panchromatic approaches MAGPHYS, CIGALE, and SED3FIT,
thus deriving their dust mass, M(dust), infrared luminosity (LIR), and
stellar mass, M(star). Eight galaxies require an AGN-torus component and
other six require an unextinguished young stellar population. A
significant fraction of our galaxies are classified as starbursts based
on their position on the M(star) versus SFR plane or their depletion
timescales. We compute the dust mass function in three redshift bins
(1.6<z<=2.4, 2.4<z<=4.2 and 4.2<z<=7.2) and determine
the Schechter function that best describes it. We observe an increase of
the dust cosmic density, rho(dust), by at least an order of magnitude
from z~7 to z~1.5, consistent with theoretical predictions. At lower
redshift the evolution flattens; significant differences exist between
results obtained with different selections and methods. The superb
GOODS-N dataset enabled a systematic investigation into the dust
properties of distant galaxies. N2CLS holds promise for combining these
deep field findings with the wide COSMOS field into a self-consistent
analysis of dust in galaxies both near and far.
Euclid:
Early Release Observations – The Intracluster Light of Abell 2390
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Ellien / M. Montes / S. L. Ahad / P. Dimauro
- J. B. Golden-Marx / Y. Jimenez-Teja / F. Durret / C. Bellhouse
- J. M. Diego / S. P. Bamford / A. H. Gonzalez / N. A. Hatch
- M. Kluge / R. Ragusa / E. Slezak / J.-C. Cuillandre
- R. Gavazzi / H. Dole / G. Mahler / G. Congedo
- T. Saifollahi / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia
- A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat / S. Camera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- J. Dinis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / M. Farina / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol
- S. Fotopoulou / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan
- J. Hoar / H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / R. Laureijs / D. Le Mignant / S.
Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin
- O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / R. Scaramella / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel
- M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri
- L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / O. R. Williams / E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella
- C. Burigana / V. Scottez
Summary
Intracluster light (ICL) provides a record of the dynamical
interactions undergone by clusters, giving clues on cluster formation
and evolution. Here, we analyse the properties of ICL in the massive
cluster Abell 2390 at redshift z=0.228. Our analysis is based on the
deep images obtained by the Euclid mission as part of the Early Release
Observations in the near-infrared (Y, J, H bands), using the NISP
instrument in a 0.75 deg field. We subtracted a point–spread
function (PSF) model and removed the Galactic cirrus contribution in
each band after modelling it with the DAWIS software. We then applied
three methods to detect, characterise, and model the ICL and the
brightest cluster galaxy (BCG): the CICLE 2D multi-galaxy fitting; the
DAWIS wavelet-based multiscale software; and a mask-based 1D profile
fitting. We detect ICL out to 600 kpc. The ICL fractions derived by our
three methods range between 18% and 36% (average of 24%), while the
BCG+ICL fractions are between 21% and 41% (average of 29%), depending on
the band and method. A galaxy density map based on 219 selected cluster
members shows a strong cluster substructure to the south-east and a
smaller feature to the north-west. Based on colours, the ICL (out to
about 400 kpc) seems to be built by the accretion of small systems (M ~
field. We subtracted a point–spread
function (PSF) model and removed the Galactic cirrus contribution in
each band after modelling it with the DAWIS software. We then applied
three methods to detect, characterise, and model the ICL and the
brightest cluster galaxy (BCG): the CICLE 2D multi-galaxy fitting; the
DAWIS wavelet-based multiscale software; and a mask-based 1D profile
fitting. We detect ICL out to 600 kpc. The ICL fractions derived by our
three methods range between 18% and 36% (average of 24%), while the
BCG+ICL fractions are between 21% and 41% (average of 29%), depending on
the band and method. A galaxy density map based on 219 selected cluster
members shows a strong cluster substructure to the south-east and a
smaller feature to the north-west. Based on colours, the ICL (out to
about 400 kpc) seems to be built by the accretion of small systems (M ~
 solar mass), or
from stars coming from the outskirts of Milky Way-type galaxies (M ~
solar mass), or
from stars coming from the outskirts of Milky Way-type galaxies (M ~
 solar mass). Though
Abell 2390 does not seem to be undergoing a merger, it is not yet fully
relaxed, since it has accreted two groups that have not fully merged
with the cluster core. We estimate that the contributions to the inner
300 kpc of the ICL of the north-west and south-east subgroups are 21%
and 9% respectively.
solar mass). Though
Abell 2390 does not seem to be undergoing a merger, it is not yet fully
relaxed, since it has accreted two groups that have not fully merged
with the cluster core. We estimate that the contributions to the inner
300 kpc of the ICL of the north-west and south-east subgroups are 21%
and 9% respectively.
Towards
sustainable space research in France
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alexandre Santerne / Héloïse Meheut / Didier Barret
/ Olivier Berné
- Etienne Berthier / Agnès Ducharne / Jürgen Knödlseder / Aurélie
Marchaudon
- Thierry Pellarin / Aymeric Spiga / Peter Wolf
Summary
During the 2024’s quinquennial scientific roadmap of CNES, a specific
group worked on setting recommendations to decrease the environmental
footprint of space science activities. This correspondence to Nature
Astronomy highlights the efforts of the french space research to move
towards sustainability. It relies on two complementary methods:
decarbonisation and frugality.
The
Complete Spitzer Survey of Stellar Structure in Galaxies (CS G)
G)
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- P. M. Sánchez-Alarcón / H. Salo / J. H. Knapen / S. Comerón
- J. Román / A. E. Watkins / R. J. Buta / S. Laine
- J. M. Falcón-Ramírez / M. Anetjärvi / E.
Athanassoula / A. Bosma
- D. A. Gadotti / J. L. Hinz / L. C. Ho / B. W. Holwerda
- J. Janz / T. Kim / J. Koda / J. Laine
- E. Laurikainen / B. F. Madore / K. Menéndez-Delmestre / R. F.
Peletier
- M. Querejeta / A. Ruokanen / K. Sheth / D. Zaritsky
Summary
The Spitzer Survey of Stellar Structure in Galaxies (S G), together with its Early Type Galaxy
(ETG) extension, stand as the most extensive dataset of deep, uniform
mid-infrared (mid-IR; 3.6 and 4.5
G), together with its Early Type Galaxy
(ETG) extension, stand as the most extensive dataset of deep, uniform
mid-infrared (mid-IR; 3.6 and 4.5 m) imaging for a sample of
m) imaging for a sample of
 nearby (
nearby ( Mpc) galaxies.
However, the velocity criterion used to select the original sample
results in an additional 422 galaxies without HI detection that ought to
have been included in the S
Mpc) galaxies.
However, the velocity criterion used to select the original sample
results in an additional 422 galaxies without HI detection that ought to
have been included in the S G on the basis of their optical
recession velocities. In order to create a complete magnitude-, size-
and volume-limited sample of nearby galaxies, we collect
G on the basis of their optical
recession velocities. In order to create a complete magnitude-, size-
and volume-limited sample of nearby galaxies, we collect  m and
m and  -band images using archival data from
different surveys and complement it with new observations for the
missing galaxies. We denote the sample of these additional galaxies as
Disc Galaxy (DG) extension. We present the Complete Spitzer Survey of
Stellar Structure in Galaxies (CS
-band images using archival data from
different surveys and complement it with new observations for the
missing galaxies. We denote the sample of these additional galaxies as
Disc Galaxy (DG) extension. We present the Complete Spitzer Survey of
Stellar Structure in Galaxies (CS G), encompassing a sample of
G), encompassing a sample of  galaxies with consistent
imaging, surface brightness profiles, photometric parameters, and
revised morphological classification. Following the original strategy of
the S
galaxies with consistent
imaging, surface brightness profiles, photometric parameters, and
revised morphological classification. Following the original strategy of
the S G survey, we produce masks, surface
brightness profiles, and curves of growth using masked
G survey, we produce masks, surface
brightness profiles, and curves of growth using masked  m and
m and  -band images. From these profiles, we
derive the integrated quantities: total magnitude, stellar mass,
concentration parameter, and galaxy size, converting to
-band images. From these profiles, we
derive the integrated quantities: total magnitude, stellar mass,
concentration parameter, and galaxy size, converting to  m. We re-measure these
parameters also for the S
m. We re-measure these
parameters also for the S G and ETG to create a homogenous
sample. We present new morphological revised
G and ETG to create a homogenous
sample. We present new morphological revised  -types, and we showcase mid-IR scaling
relations for the photometric parameters. We complete the S
-types, and we showcase mid-IR scaling
relations for the photometric parameters. We complete the S G sample by incorporating 422 galaxies.
The CS
G sample by incorporating 422 galaxies.
The CS G includes at least 99.94% of the
complete sample of nearby galaxies, meeting the original selection
criteria, and it will enable a wide set of investigations into galaxy
structure and evolution.
G includes at least 99.94% of the
complete sample of nearby galaxies, meeting the original selection
criteria, and it will enable a wide set of investigations into galaxy
structure and evolution.
Experimental
study of the first telescope with a toroidal curved detector
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Eduard Muslimov / Simona Lombardo / Thibault Behaghel / Jiawei
Liu
- Emmanuel Hugot
Summary
We describe a practical implementation of the anamorphically curved
detector concept. In order to demonstrate its advantages, a telescope
lab prototype was developed, built, and tested. It is based on a
4-mirror all-spherical unobscured design, similar to that proposed by D.
Shafer. The telescope is open at F/#=5.5 and its extended field of view
is 10.6x8 degrees. We explore the design parameter space to demonstrate
the change in gain introduced by the curved detector and to substantiate
the chosen parameters. If the image surface is curved to the shape of a
toroid, the image quality reaches the diffraction limit over the entire
field by design. The design was optimized to use standard concave
spherical mirrors. The detector was curved down toroidally with an
exquisite surface precision of approximately 11 micrometers
Peak-to-Valley. The experimental tests of the prototype have shown that
use of the toroidally curved detector allows to increase the contrast in
the field corner by up to 0.3 units, which is in good agreement with the
modeling results. We also propose a few prospective applications of the
demonstrated concept.
Searching
for strong lensing by late-type galaxies in UNIONS
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. A. Acevedo Barroso / B. Clément / F. Courbin / R.
Gavazzi
- C. Lemon / K. Rojas / D. Scott / S. Gwyn
- F. Hammer / M. J. Hudson / E. A. Magnier
Summary
Recent wide-field galaxy surveys have led to an explosion in numbers
of galaxy-scale strong gravitational lens candidates. However, the vast
majority feature massive luminous red galaxies as the main deflectors,
with late-type galaxies being vastly under-represented. This work
presents a dedicated search for lensing by edge-on late-type galaxies in
the Ultraviolet Near Infrared Optical Northern Survey (UNIONS). The
search covers  deg
deg of
of  -band observations taken from the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope. We consider all sources with magnitudes
in the range
-band observations taken from the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope. We consider all sources with magnitudes
in the range  , without any colour preselection, yielding a
parent sample of seven million sources. We characterise our parent
sample via the visual inspection of
, without any colour preselection, yielding a
parent sample of seven million sources. We characterise our parent
sample via the visual inspection of  sources selected
at random. From it, we estimate, with a 68% confidence interval, that 1
in every
sources selected
at random. From it, we estimate, with a 68% confidence interval, that 1
in every  sources is an
edge-on lens candidate, with at least eight high-quality candidates in
the parent sample. This corresponds to 1 candidate per
sources is an
edge-on lens candidate, with at least eight high-quality candidates in
the parent sample. This corresponds to 1 candidate per  edge-on late-type
galaxies. Our search relies on a convolutional neural network (CNN) to
select a reduced sample of candidates, followed by a visual inspection
to curate the final sample. The CNN is trained from scratch using
simulated
edge-on late-type
galaxies. Our search relies on a convolutional neural network (CNN) to
select a reduced sample of candidates, followed by a visual inspection
to curate the final sample. The CNN is trained from scratch using
simulated  -band observations of edge-on lenses,
and real observations of non-lenses. We find 61 good edge-on lens
candidates using the CNN. Moreover, combining the CNN candidates with
those found serendipitously, and those identified while characterising
the parent sample, we discovered 4 grade A, 20 grade B, and 58 grade C
edge-on lens candidates; effectively doubling the known sample of these
systems. We also discovered 16 grade A, 16 grade B, and 18 grade C lens
candidates of other types. Finally, based on the characterisation of the
parent sample, we estimate that our search found around 60% of the
bright grade A and B edge-on lens candidates within the parent
sample.
-band observations of edge-on lenses,
and real observations of non-lenses. We find 61 good edge-on lens
candidates using the CNN. Moreover, combining the CNN candidates with
those found serendipitously, and those identified while characterising
the parent sample, we discovered 4 grade A, 20 grade B, and 58 grade C
edge-on lens candidates; effectively doubling the known sample of these
systems. We also discovered 16 grade A, 16 grade B, and 18 grade C lens
candidates of other types. Finally, based on the characterisation of the
parent sample, we estimate that our search found around 60% of the
bright grade A and B edge-on lens candidates within the parent
sample.
Euclid
preparation. BAO analysis of photometric galaxy clustering in
configuration space
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / V. Duret / S. Escoffier / W. Gillard
- I. Tutusaus / S. Camera / N. Tessore / F. J. Castander
- N. Aghanim / A. Amara / L. Amendola / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- P. Battaglia / A. Biviano / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat / G. Cañas-Herrera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone / J. Carretero
- S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- K. C. Chambers / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- S. de la Torre / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / H. Dole
- F. Dubath / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet
- M. Farina / R. Farinelli / S. Farrens / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / F. Finelli / S. Fotopoulou / N. Fourmanoit
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / J. Gracia-Carpio / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio
- O. Lahav / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / S. Marcin / O. Marggraf
- K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F.
Marulli
- R. Massey / S. Maurogordato / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco / B. Morin
- L. Moscardini / E. Munari / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner
- R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / J. A. Schewtschenko
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / P. Simon / C.
Sirignano
- G. Sirri / A. Spurio Mancini / L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / D. Tavagnacco / A. N.
Taylor
- I. Tereno / S. Toft / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- J. Valiviita / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo
- Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani / F. M. Zerbi
- E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella / C. Burigana / M. Calabrese
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / L. Gabarra / S.
Matthew
- N. Mauri / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- V. Scottez / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / V. Allevato / I. T. Andika / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / A. Balaguera-Antolinez / M. Ballardini / D.
Bertacca
- M. Bethermin / A. Blanchard / L. Blot / H. Böhringer
- S. Borgani / M. L. Brown / S. Bruton / R. Cabanac
- A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo / A. Cappi / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / F. Cogato / S. Contarini
- T. Contini / A. R. Cooray / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio / J. M. Diego
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini
- F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / M. Guidi
- C. M. Gutierrez / A. Hall / S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt
- J. Hjorth / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang / V. Kansal
- D. Karagiannis / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk / M. Lattanzi
- M. Lembo / G. Leroy / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat
- S. J. Liu / A. Loureiro / G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti
- F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas / C. J. A. P.
Martins
- L. Maurin / R. B. Metcalf / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco
- C. Moretti / C. Murray / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / K. Paterson / A. Pisani
- D. Potter / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci / M. Sahlén
- E. Sarpa / A. Schneider / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin
- M. Sereno / A. Silvestri / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis
- C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Tosi
- A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri / A. Venhola
- D. Vergani / F. Vernizzi / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
- N. A. Walton
Summary
With about 1.5 billion galaxies expected to be observed, the very
large number of objects in the Euclid photometric survey will allow for
precise studies of galaxy clustering from a single survey, over a large
range of redshifts  . In this work, we use photometric redshifts to
extract the baryon acoustic oscillation signal (BAO) from the Flagship
galaxy mock catalogue with a tomographic approach to constrain the
evolution of the Universe and infer its cosmological parameters. We
measure the two-point angular correlation function in 13 redshift bins.
A template-fitting approach is applied to the measurement to extract the
shift of the BAO peak through the transverse Alcock–Paczynski parameter
. In this work, we use photometric redshifts to
extract the baryon acoustic oscillation signal (BAO) from the Flagship
galaxy mock catalogue with a tomographic approach to constrain the
evolution of the Universe and infer its cosmological parameters. We
measure the two-point angular correlation function in 13 redshift bins.
A template-fitting approach is applied to the measurement to extract the
shift of the BAO peak through the transverse Alcock–Paczynski parameter
 . A joint analysis of all redshift bins
is performed to constrain
. A joint analysis of all redshift bins
is performed to constrain  at the effective redshift
at the effective redshift  with MCMC and profile likelihood techniques. We
also extract one
with MCMC and profile likelihood techniques. We
also extract one  parameter per redshift bin
to quantify its evolution as a function of time. From these 13
parameter per redshift bin
to quantify its evolution as a function of time. From these 13  , which are directly
proportional to the ratio
, which are directly
proportional to the ratio  , we
constrain
, we
constrain  ,
,  , and
, and  . From
the joint analysis, we constrain
. From
the joint analysis, we constrain  , which represents a three-fold improvement over
current constraints from the Dark Energy Survey. As expected, the
constraining power in the analysis of each redshift bin is lower, with
an uncertainty ranging from
, which represents a three-fold improvement over
current constraints from the Dark Energy Survey. As expected, the
constraining power in the analysis of each redshift bin is lower, with
an uncertainty ranging from  to
to  . From these
results, we constrain
. From these
results, we constrain 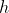 at 0.45 %,
at 0.45 %,  at 0.91
%, and
at 0.91
%, and  at
7.7 %. We quantify the influence of analysis choices like the template,
scale cuts, redshift bins, and systematic effects like redshift-space
distortions over our constraints both at the level of the extracted
at
7.7 %. We quantify the influence of analysis choices like the template,
scale cuts, redshift bins, and systematic effects like redshift-space
distortions over our constraints both at the level of the extracted  parameters and at the level
of cosmological inference.
parameters and at the level
of cosmological inference.
Articles for week 10 2025
EP240801a/XRF
240801B: An X-ray Flash Detected by the Einstein Probe and Implications
of its Multiband Afterglow
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Shuai-Qing Jiang / Dong Xu / Agnes P. C. van Hoof / Wei-Hua Lei
- Yuan Liu / Hao Zhou / Yong Chen / Shao-Yu Fu
- Jun Yang / Xing Liu / Zi-Pei Zhu / Alexei V. Filippenko
- Peter G. Jonker / A. S. Pozanenko / He Gao / Xue-Feng Wu
- Bing Zhang / Gavin P Lamb / Massimiliano De Pasquale / Shiho
Kobayashi
- Franz Erik Bauer / Hui Sun / Giovanna Pugliese / Jie An
- Valerio D’Elia / Johan P. U. Fynbo / WeiKang Zheng / Alberto J. C.
Tirado
- Yi-Han Iris Yin / Yuan-Chuan Zou / Adam T. Deller / N. S.
Pankov
- A. A. Volnova / A. S. Moskvitin / O. I. Spiridonova / D. V.
Oparin
- V. Rumyantsev / O. A. Burkhonov / Sh. A. Egamberdiyev / V. Kim
- M. Krugov / A. M. Tatarnikov / R. Inasaridze / Andrew J. Levan
- Daniele Bjørn Malesani / Maria E. Ravasio / Jonathan Quirola-Vásquez
/ Joyce N. D. van Dalen
- Javi Sánchez-Sierras / Daniel Mata Sánchez / Stuart P. Littlefair /
Jennifer A. Chacón
- Manuel A. P. Torres / Ashley A. Chrimes / Nikhil Sarin / Antonio
Martin-Carrillo
- Vik Dhillon / Yi Yang / Thomas G. Brink / Rebecca L. Davies
- Sheng Yang / Amar Aryan / Ting-Wan Chen / Albert K. H. Kong
- Wen-Xiong Li / Rui-Zhi Li / Jirong Mao / Ignacio Pérez-García
- Emilio J. Fernández-García / Moira Andrews / Joseph Farah / Zhou
Fan
- Estefania Padilla Gonzalez / D. Andrew Howell / Dieter Hartmann /
Jing-Wei Hu
- Páll Jakobsson / Cheng-Kui Li / Zhi-Xing Ling / Curtis McCully
- Megan Newsome / Benjamin Schneider / Kaew Samaporn
Tinyanont / Ning-Chen Sun
- Giacomo Terreran / Qing-Wen Tang / Wen-Xin Wang / Jing-Jing Xu
- Wei-Min Yuan / Bin-Bin Zhang / Hai-Sheng Zhao / Juan Zhang
Summary
We present multiband observations and analysis of EP240801a, a
low-energy, extremely soft gamma-ray burst (GRB) discovered on August 1,
2024 by the Einstein Probe (EP) satellite, with a weak contemporaneous
signal also detected by Fermi/GBM. Optical spectroscopy of the
afterglow, obtained by GTC and Keck, identified the redshift of  . EP240801a
exhibits a burst duration of 148 s in X-rays and 22.3 s in gamma-rays,
with X-rays leading by 80.61 s. Spectral lag analysis indicates the
gamma-ray signal arrived 8.3 s earlier than the X-rays. Joint spectral
fitting of EP/WXT and Fermi/GBM data yields an isotropic energy
. EP240801a
exhibits a burst duration of 148 s in X-rays and 22.3 s in gamma-rays,
with X-rays leading by 80.61 s. Spectral lag analysis indicates the
gamma-ray signal arrived 8.3 s earlier than the X-rays. Joint spectral
fitting of EP/WXT and Fermi/GBM data yields an isotropic energy  , a peak energy
, a peak energy  , a fluence ratio
, a fluence ratio  , classifying EP240801a as an X-ray flash (XRF).
The host-galaxy continuum spectrum, inferred using Prospector, was used
to correct its contribution for the observed outburst optical data.
Unusual early
, classifying EP240801a as an X-ray flash (XRF).
The host-galaxy continuum spectrum, inferred using Prospector, was used
to correct its contribution for the observed outburst optical data.
Unusual early 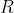 -band behavior and EP/FXT observations
suggest multiple components in the afterglow. Three models are
considered: two-component jet model, forward-reverse shock model and
forward-shock model with energy injection. Both three provide reasonable
explanations. The two-component jet model and the energy injection model
imply a relatively small initial energy and velocity of the jet in the
line of sight, while the forward-reverse shock model remains typical.
Under the two-component jet model, EP240801a may resemble GRB 221009A
(BOAT) if the bright narrow beam is viewed on-axis. Therefore, EP240801a
can be interpreted as an off-beam (narrow) jet or an intrinsically weak
GRB jet. Our findings provide crucial clues for uncovering the origin of
XRFs.
-band behavior and EP/FXT observations
suggest multiple components in the afterglow. Three models are
considered: two-component jet model, forward-reverse shock model and
forward-shock model with energy injection. Both three provide reasonable
explanations. The two-component jet model and the energy injection model
imply a relatively small initial energy and velocity of the jet in the
line of sight, while the forward-reverse shock model remains typical.
Under the two-component jet model, EP240801a may resemble GRB 221009A
(BOAT) if the bright narrow beam is viewed on-axis. Therefore, EP240801a
can be interpreted as an off-beam (narrow) jet or an intrinsically weak
GRB jet. Our findings provide crucial clues for uncovering the origin of
XRFs.
Can
we disentangle between the emission of an accretion disc around a single
black hole and a circumbinary disc ?
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Peggy Varniere / Raphaël Mignon-Risse / Fabien
Casse
Summary
The detection of gravitational waves from binary black holes (BBHs)
started the hunt for their pre-merger electromagnetic emission. In that
respect, numerical simulations have been looking for the “smoking gun”
signal that could help identify pre-merger systems. Here we study if any
of the expected features of circumbinary discs, such as the periodic
modulation from the orbiting “lump”, could be used to identify
pre-merger BBHs or if they could be easily confused with other systems.
Indeed, while the timing feature associated with the “lump” seems to be
present for a large part of the parameter space defined by the binary
separation and mass ratio in circular binaries, it was recently proposed
to form thanks to an instability occurring naturally at the edge of
accretion discs around single black holes (SBH). In order to check if
features of a circumbinary disc could be reproduced by a SBH system, we
search for at least one SBH fit able to replicate the given synthetic
observations of a circumbinary disc. We found that many of the features
from a circumbinary disc can be reproduced by a SBH system with
different masses, distances or inner disc positions. Interestingly,
while we can always find a SBH model providing a good enough fit to the
data, the presence of two variabilities, associated with the lump and
the binary, or binary-lump beat, period, is a necessary condition for a
wide range of BBH system parameters and should be used as a test to
disqualify some BBH candidates.
Understanding
the formation of Saturn’s regular moons in the context of giant planet
moons formation scenarios
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Michel Blanc / Aurélien Crida / Yuhito Shibaike / Sebastien
Charnoz
- Maryame El Moutamid / Paul Estrada / Olivier Mousis
/ Julien Salmon
- Antoine Schneeberger / Pierre
Vernazza
Summary
This article explores the different formation scenarios of the
Kronian moons system in the context of a highly dissipative Saturn, with
the objective of identifying the most likely of these scenarios. First,
we review the diversity of objects - moons and rings - orbiting solar
system giant planets, and the diversity of their architectures, which
formation scenarios must reproduce. We then identify in this broader
context the specific features of the Saturn system, such as the
particularly large spectrum of its moon masses, the uniqueness of Titan
and the presence of both dense and tenuous rings, before discussing the
applicability of the different giant planet moon formation scenarios to
the Saturn case. We discuss each of the most relevant scenarios and
their respective merits. Finally, we tentatively propose a “favorite”
scenario and we identify the key observations to be made by future space
missions and/or Earth-based telescopic observations to validate this
scenario or possibly alternative ones.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Sushma Kurapati / D. J. Pisano / W. J. G. de Blok / Peter
Kamphuis
- Nikki Zabel / Mikhail de Villiers / Julia Healy / Filippo M.
Maccagni
- Dane Kleiner / Elizabeth A. K. Adams / Philippe
Amram / E. Athanassoula
- Frank Bigiel / Albert Bosma / Elias Brinks /
Laurent Chemin
- Francoise Combes / Ralf-Jürgen Dettmar / Gyula Józsa / Baerbel
Koribalski
- Antonino Marasco / Gerhardt Meurer / Moses Mogotsi / Abhisek
Mohapatra
- Sambatriniaina H. A. Rajohnson / Eva Schinnerer / Amidou Sorgho /
Kristine Spekkens
- Lourdes Verdes-Montenegro / Simone Veronese / Fabian Walter
Summary
We use the neutral atomic hydrogen (HI) observations of the edge-on
galaxy UGCA 250, taken as part of the MeerKAT HI Observations of Nearby
Galactic Objects - Observing Southern Emitters (MHONGOOSE) survey to
investigate the amount, morphology, and kinematics of extraplanar gas.
The combination of high column density sensitivity and high spatial
resolution of the survey over a large field of view is ideal for
studying the underlying physics governing the extraplanar gas. These
data reveal 9 additional detections within the field of view along with
UGCA 250, with 8 of them being within  200 km s
200 km s of the galaxy’s
systemic velocity. The galaxy seems to have a tail-like feature
extending away from it in the southern direction up to
of the galaxy’s
systemic velocity. The galaxy seems to have a tail-like feature
extending away from it in the southern direction up to  41 kpc (in projection).
We also detect a cloud at anomalous velocities, but we did not find any
optical counterpart. We construct a detailed tilted ring model for this
edge-on galaxy to gain a deeper understanding of the vertical structure
of its neutral hydrogen. The model that best matches the data features a
thick disc with a scale height of
41 kpc (in projection).
We also detect a cloud at anomalous velocities, but we did not find any
optical counterpart. We construct a detailed tilted ring model for this
edge-on galaxy to gain a deeper understanding of the vertical structure
of its neutral hydrogen. The model that best matches the data features a
thick disc with a scale height of  3$
3$ %$ of the
total HI mass. This extraplanar gas is detected for the first time in
UGCA 250. Our analysis favours a mixed origin for the extraplanar gas in
UGCA 250, likely arising from a combination of internal stellar feedback
and external tidal interactions.
%$ of the
total HI mass. This extraplanar gas is detected for the first time in
UGCA 250. Our analysis favours a mixed origin for the extraplanar gas in
UGCA 250, likely arising from a combination of internal stellar feedback
and external tidal interactions.
MeerKAT
view of Hickson Compact Groups: II. HI deficiency in the core and
surrounding regions
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Sorgho / L. Verdes-Montenegro / R. Ianjamasimanana / K. M.
Hess
- M. G. Jones / M. Korsaga / Jing Wang / Xuchen Lin
- J. M. Solanes / M. E. Cluver / J. M. Cannon / A.
Bosma
- E. Athanassoula / A. del Olmo / J. Perea / J.
Moldón
- T. Wiegert / S. Sanchez-Expósito / J. Garrido / R.
García-Benito
- G. I. G. Józsa / S. Borthakur / T. Jarrett / B. Namumba
- E. Pérez / Javier Román / O. M. Smirnov / M. Yun
Summary
Hickson compact groups (HCGs) offer an ideal environment for
investigating galaxy transformation as a result of interactions. It has
been established that the evolutionary sequence of HCGs is marked by an
intermediate stage characterised by a substantial amount of HI in their
intragroup medium (IGrM) in the form of tidal tails and bridges (Phase
2), rapidly followed by a final stage where no IGrM gas is found and
where their member galaxies are highly HI-deficient (Phase 3). Despite
numerous single-dish and interferometric HI studies on the HCGs, a clear
HI picture of the groups within their large-scale environment still
remains to be uncovered. Taking advantage of the MeerKAT’s high column
density sensitivity and large field-of-view, we aim to investigate the
rapid transformation of HCGs from the intermediate to late phases, and
establish a picture of their gas content variations in the context of
their large-scale environments. We performed MeerKAT observations of six
HCGs selected to represent the intermediate and late phases of the
proposed evolutionary sequence. Combining the HI observations with data
from recent wide-field optical surveys, we evaluated the HI deficiencies
of galaxies in a ~30’ radius of the HCGs. We find that galaxies
surrounding both phases exhibit similar distributions in their gas
content. Similarly, galaxies making up the cores of Phase 2 HCGs are
comparable to their neighbours in terms of HI deficiencies. However,
Phase 3 groups are over an order of magnitude more deficient than their
surroundings, supporting previous findings that late-phase HCG galaxies
are more evolved than their large-scale environments.
Constraining
self-interacting scalar field dark matter with strong gravitational
lensing in cluster scale?
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Raquel Galazo García / Eric Jullo /
Emmanuel Nezri / Marceau Limousin
Summary
We present a method to investigate the properties of solitonic cores
in the Thomas-Fermi regime under the self-interacting scalar field dark
matter framework. Using semi-analytical techniques, we characterize
soliton signatures through their density profiles, gravitational lensing
deflection angles, and surface mass density excess in the context of
strong lensing by galaxy clusters. Focusing on halos spanning two mass
scales –  and
and
 – we compute lensing observables to assess the
viability of the SFDM model. Our analysis establishes constraints on the
soliton core mass, directly probing the self-interaction parameter space
of scalar field dark matter. This work bridges semi-analytical
predictions with astrophysical observations, offering a lensing-based
framework to test ultralight dark matter scenarios in galaxy cluster
environments.
– we compute lensing observables to assess the
viability of the SFDM model. Our analysis establishes constraints on the
soliton core mass, directly probing the self-interaction parameter space
of scalar field dark matter. This work bridges semi-analytical
predictions with astrophysical observations, offering a lensing-based
framework to test ultralight dark matter scenarios in galaxy cluster
environments.
HI
within and around observed and simulated galaxy discs – Comparing
MeerKAT observations with mock data from TNG50 and FIRE-2
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Marasco / W. J. G. de Blok / F. M. Maccagni / F. Fraternali
- K. A. Oman / T. Oosterloo / F. Combes / S. S. McGaugh
- P. Kamphuis / K. Spekkens / D. Kleiner / S. Veronese
- P. Amram / L. Chemin / E. Brinks
Summary
Atomic hydrogen (HI) is an ideal tracer of gas flows in and around
galaxies, and it is uniquely observable in the nearby Universe. Here we
make use of wide-field (~1 square degree), spatially resolved (down to
22”), high-sensitivity (~ cm
cm ) HI observations of 5
nearby galaxies with stellar mass of
) HI observations of 5
nearby galaxies with stellar mass of  M
M , taken with the
MeerKAT radio telescope. Four of these were observed as part of the
MHONGOOSE survey. We characterise their main HI properties and compare
these with synthetic HI data from a sample of 25 similarly massive
star-forming galaxies from the TNG50 (20) and FIRE-2 (5) suites of
cosmological hydrodynamical simulations. Globally, the simulated systems
have HI and molecular hydrogen (H
, taken with the
MeerKAT radio telescope. Four of these were observed as part of the
MHONGOOSE survey. We characterise their main HI properties and compare
these with synthetic HI data from a sample of 25 similarly massive
star-forming galaxies from the TNG50 (20) and FIRE-2 (5) suites of
cosmological hydrodynamical simulations. Globally, the simulated systems
have HI and molecular hydrogen (H ) masses in good agreement with the
observations, but only when the H
) masses in good agreement with the
observations, but only when the H recipe of Blitz & Rosolowsky
(2006) is employed. The other recipes that we tested overestimate the
H
recipe of Blitz & Rosolowsky
(2006) is employed. The other recipes that we tested overestimate the
H -to-HI mass fraction by up to an order
of magnitude. On a local scale, we find two main discrepancies between
observed and simulated data. First, the simulated galaxies show a more
irregular HI morphology than the observed ones due to the presence of HI
with column density
-to-HI mass fraction by up to an order
of magnitude. On a local scale, we find two main discrepancies between
observed and simulated data. First, the simulated galaxies show a more
irregular HI morphology than the observed ones due to the presence of HI
with column density  cm
cm up to ~100 kpc from the
galaxy centre, in spite of the fact that they inhabit more isolated
environments than the observed targets. Second, the simulated galaxies
and in particular those from the FIRE-2 suite, feature more complex and
overall broader HI line profiles than the observed ones. We interpret
this as being due to the combined effect of stellar feedback and gas
accretion, which lead to a large-scale gas circulation that is more
vigorous than in the observed galaxies. Our results indicate that, with
respect to the simulations, gentler processes of gas inflows and
outflows are at work in the nearby Universe, leading to more regular and
less turbulent HI discs.
up to ~100 kpc from the
galaxy centre, in spite of the fact that they inhabit more isolated
environments than the observed targets. Second, the simulated galaxies
and in particular those from the FIRE-2 suite, feature more complex and
overall broader HI line profiles than the observed ones. We interpret
this as being due to the combined effect of stellar feedback and gas
accretion, which lead to a large-scale gas circulation that is more
vigorous than in the observed galaxies. Our results indicate that, with
respect to the simulations, gentler processes of gas inflows and
outflows are at work in the nearby Universe, leading to more regular and
less turbulent HI discs.
Using
the XMM-Newton small window mode to investigate systematic uncertainties
in the particle background of X-ray charge-coupled device detectors
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Gerrit Schellenberger / Ralph Kraft / Paul Nulsen / Eric D.
Miller
- Marshall W. Bautz / Catherine E. Grant / Dan Wilkins / Steven
Allen
- Silvano Molendi / David N. Burrows / Abraham D. Falcone / Valentina
Fioretti
- Richard F. Foster / David Hall / Michael W. J. Hubbard / Emanuele
Perinati
- Artem Poliszczuk / Arne Rau / Arnab Sarkar / Benjamin
Schneider
Summary
The level and uncertainty of the particle induced background in CCD
detectors plays a crucial role for future X-ray instruments, such as the
Wide Field Imager (WFI) onboard Athena. To mitigate the background
systematic uncertainties, which will limit the Athena science goals, we
aim to understand the relationship between the energetic charged
particles interacting in the detector and satellite, and the
instrumental science background to an unprecedented level. These
particles produce easily identified “cosmic-ray tracks” along with less
easily identified signals produced by secondary particles, e.g., X-rays
generated by particle interactions with the instrument and
indistinguishable from genuine sky X-rays. We utilize the Small Window
Mode of the PN camera onboard XMM-Newton to understand the time, spatial
and energy dependence of the various background components, particularly
the particle induced background. While the distribution of particle
events follows expected detector readout patterns, we find a particle
track length distribution inconsistent with the simple, isotropic model.
We also find that the detector mode-specific readout results in a
shifted Cu fluorescent line. We illustrate that on long timescales the
variability of the particle background correlates well with the solar
cycle. This 20-year lightcurve, can be reproduced by a particle detector
onboard Chandra, the HRC anti-coincidence shield. We conclude that the
self-anti-coincidence method of removing X-ray-like events near detected
particle tracks in the same frame can be optimized with the inclusion of
additional information, such as the energy of the X-ray. The results
presented here are relevant for any future pixelated X-ray imaging
detector, and could allow the WFI to probe to truly faint X-ray surface
brightness.
Articles for week 9 2025
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Fabrizio Gentile / Margherita Talia / Andrea Enia / Francesca
Pozzi
- Alberto Traina / Giovanni Zamorani / Irham T. Andika / Meriem
Behiri
- Laia Barrufet / Caitlin M. Casey / Andrea Cimatti / Nicole E.
Drakos
- Andreas L. Faisst / Maximilien Franco / Steven Gillman / Marika
Giulietti
- Rashmi Gottumukkala / Christopher C. Hayward / Olivier
Ilbert / Shuowen Jin
- Andrea Lapi / Jed McKinney / Marko Shuntov / Mattia Vaccari
- Cristian Vignali / Hollis B. Akins / Natalie Allen / Santosh
Harish
- Henry Joy McCracken / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Anton M. Koekemoer /
Daizhong Liu
- Louise Paquereau / Jason Rhodes / Micheal R. Rich / Brant E.
Robertson
- Sune Toft
Summary
We present the first follow-up with JWST of radio-selected NIRfaint
galaxies as part of the COSMOS-Web survey. By selecting galaxies
detected at radio frequencies (
 Jy; i.e. S/N
Jy; i.e. S/N ) and with faint
counterparts at NIR wavelengths (F150W
) and with faint
counterparts at NIR wavelengths (F150W mag), we collect
a sample of 127 likely dusty star-forming galaxies (DSFGs). We estimate
their physical properties through SED fitting, compute the first radio
luminosity function for these types of sources, and their contribution
to the total cosmic star formation rate density. Our analysis confirms
that these sources represent a population of highly dust-obscured (
mag), we collect
a sample of 127 likely dusty star-forming galaxies (DSFGs). We estimate
their physical properties through SED fitting, compute the first radio
luminosity function for these types of sources, and their contribution
to the total cosmic star formation rate density. Our analysis confirms
that these sources represent a population of highly dust-obscured ( mag),
massive (
mag),
massive ( M
M ) and star-forming
galaxies (
) and star-forming
galaxies ( M
M yr
yr ) located at
) located at  , representing the high-redshift tail of the full
distribution of radio sources. Our results also indicate that these
galaxies could dominate the bright end of the radio luminosity function
and reach a total contribution to the cosmic star formation rate density
equal to that estimated only considering NIR-bright sources at
, representing the high-redshift tail of the full
distribution of radio sources. Our results also indicate that these
galaxies could dominate the bright end of the radio luminosity function
and reach a total contribution to the cosmic star formation rate density
equal to that estimated only considering NIR-bright sources at  . Finally, our
analysis further confirms that the radio selection can be employed to
collect statistically significant samples of DSFGs, representing a
complementary alternative to the other selections based on JWST colors
or detection at FIR/(sub)mm wavelengths.
. Finally, our
analysis further confirms that the radio selection can be employed to
collect statistically significant samples of DSFGs, representing a
complementary alternative to the other selections based on JWST colors
or detection at FIR/(sub)mm wavelengths.
A
Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE) XVII.
Statistical properties of individual HII regions in unperturbed
systems
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Boselli / M. Fossati / Y.
Roehlly / P. Amram
- S. Boissier / M. Boquien / J. Braine / P. Cote
- J. C. Cuillandre / L. Ferrarese / G. Gavazzi / S. Gwyn
- G. Hensler / G. Trinchieri / A. Zavagno
Summary
The Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE)
is a blind narrow-band Halpha+[NII] imaging survey of the Virgo cluster
carried out with MegaCam at the CFHT telescope. The survey provides deep
narrow-band images for 385 galaxies hosting star forming HII regions. We
identify individual HII regions and measure their main physical
properties such as Halpha luminosity, equivalent diameter, and electron
density with the purpose of deriving standard relations as reference for
future local and high-z studies of HII regions in star forming systems
in different environments. For this purpose we use a complete sample of
~ 13.000 HII regions of luminosity L(Halpha)>= 10^37 erg s^-1 to
derive the main statistical properties of HII regions in unperturbed
systems, identified as those galaxies with a normal HI gas content (64
objects). These are the composite Halpha luminosity function, equivalent
diameter and electron density distribution, and luminosity-size
relation. We also derive the main scaling relations between several
parameters representative of the HII regions properties (total number,
luminosity of the first ranked regions, fraction of the diffuse
component, best fit parameters of the Schechter luminosity function
measured for individual galaxies) and those characterising the
properties of the host galaxies (stellar mass, star formation rate and
specific star formation rate, stellar mass and star formation rate
surface density, metallicity, molecular-to-atomic gas ratio, total
gas-to-dust mass ratio). We briefly discuss the results of this analysis
and their implications in the study of the star formation process in
galaxy discs.
FEASTS
Combined with Interferometry (IV): Mapping HI Emission to a limit of
 in
Seven Edge-on Galaxies
in
Seven Edge-on Galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Dong Yang / Jing Wang / Zhijie Qu / Zezhong Liang
- Xuchen Lin / Simon Weng / Xinkai Chen / Barbara
Catinella
- Luca Cortese / D. B. Fisher / Luis C. Ho / Yingjie Jing
- Fangzhou Jiang / Peng Jiang / Ziming Liu / Céline Péroux
- Li Shao / Lister Staveley-Smith / Q. Daniel Wang / Jie Wang
Summary
We present a statistical study of the neutral atomic hydrogen (HI)
gas extending into the circumgalactic medium perpendicular to the disk
for 7 edge-on galaxies with inclinations above  from the
FEASTS program with a
from the
FEASTS program with a  (
( ) column density (
) column density ( ) depth
of
) depth
of  . We develop
two photometric methods to separate the extraplanar HI from the disk
component, based on existing interferometric data and parametric
modeling of the disk flux distribution respectively. With both methods,
the FEASTS data exhibit clear extended wings beyond the disk along the
minor axis. The extraplanar HI accounts for 5% to 20% of the total HI
mass and extends to
. We develop
two photometric methods to separate the extraplanar HI from the disk
component, based on existing interferometric data and parametric
modeling of the disk flux distribution respectively. With both methods,
the FEASTS data exhibit clear extended wings beyond the disk along the
minor axis. The extraplanar HI accounts for 5% to 20% of the total HI
mass and extends to  kpc at
kpc at
 . We
find a tight positive correlation between vertical extensions of the
extraplanar HI and total HI mass
. We
find a tight positive correlation between vertical extensions of the
extraplanar HI and total HI mass  . The
iso-density shape of HI at
. The
iso-density shape of HI at  has
an average axis ratio of
has
an average axis ratio of  . The
off-disk
. The
off-disk  profiles of these edge-on galaxies well represent the lower envelop of
previous Lyman-
profiles of these edge-on galaxies well represent the lower envelop of
previous Lyman- absorption measurements at
low-redshift. Our results suggest that at
absorption measurements at
low-redshift. Our results suggest that at  , the HI extends considerably further than the
known thin and thick disks in the vertical direction, but still remains
much flattener than a spherical distribution, consistent with
theoretical expectations that outflow, circulation, and accretion should
have different impacts in these two directions. We show the tension of
our results with Illustris and TNG predictions, highlighting the
constraining power of our results for future simulations.
, the HI extends considerably further than the
known thin and thick disks in the vertical direction, but still remains
much flattener than a spherical distribution, consistent with
theoretical expectations that outflow, circulation, and accretion should
have different impacts in these two directions. We show the tension of
our results with Illustris and TNG predictions, highlighting the
constraining power of our results for future simulations.
CHEX-MATE:
Scaling relations of radio halo profiles for clusters in the LoTSS DR2
area
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Balboni / S. Ettori / F. Gastaldello / R. Cassano
- A. Bonafede / V. Cuciti / A. Botteon / G. Brunetti
- I. Bartalucci / M. Gaspari / R. Gavazzi / S.
Ghizzardi
- M. Gitti / L. Lovisari / B. J. Maughan / S. Molendi
- E. Pointecouteau / G. W. Pratt / E. Rasia / G. Riva
- M. Rossetti / H. Rottgering / J. Sayers / R. J. van Weeren
Summary
The thermal and non-thermal components in galaxy clusters have
properties that, although shaped from different physical phenomena, can
share some similarities, mainly driven by their halo mass and the
accretion processes. Scaling relations have been proven to exist for
both components and studied in X-ray (thermal) and radio (non-thermal)
bands. At the radio wavelength, such investigations are so far limited
to the integrated quantities (e.g. total power and mass). We aimed to
investigate the scaling relations between the mass of a galaxy cluster
and its radio emission at low frequencies, treating both the integrated
and the spatially resolved quantities for a sample of well-selected
targets. We crossmatched LoTSS DR2 and CHEX-MATE datasets in order to
get the deepest and most homogeneous radio data of a representative
sample of objects. We analytically derived the expected relation between
the radio power ( ) and radio surface
brightness profile, and performed a comparison with observational
results. We obtained that properly accounting for the mass and redshift
dependence in the radio profile can reduce the overall scatter by a
factor of
) and radio surface
brightness profile, and performed a comparison with observational
results. We obtained that properly accounting for the mass and redshift
dependence in the radio profile can reduce the overall scatter by a
factor of  , with an evident
residual dependence on the cluster dynamical status. We showed that
assuming no relation between the halo size (
, with an evident
residual dependence on the cluster dynamical status. We showed that
assuming no relation between the halo size ( ) and the cluster mass
(
) and the cluster mass
( ) allowed us to reconcile the observed
radio profile mass scaling and the one predicted starting from the
) allowed us to reconcile the observed
radio profile mass scaling and the one predicted starting from the  relation. We discuss
the implications of a lack of
relation. We discuss
the implications of a lack of  relation, assessing
possible systematics and biases in the analyses, and interpreting it as
a natural consequence of the structure formation process. Finally, we
also considered the role of the magnetic field in the
relation, assessing
possible systematics and biases in the analyses, and interpreting it as
a natural consequence of the structure formation process. Finally, we
also considered the role of the magnetic field in the  relation, putting
constraints on its dependence upon the cluster mass and finding
consistent results with expectations from our radio power mass
scaling.
relation, putting
constraints on its dependence upon the cluster mass and finding
consistent results with expectations from our radio power mass
scaling.
Characterization
of AF Lep b at high spectral resolution with VLT/HiRISE
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Denis / A. Vigan / J. Costes /
G. Chauvin
- A. Radcliffe / M. Ravet / W. Balmer / P. Palma-Bifani
- S. Petrus / V. Parmentier / S. Martos / A. Simonnin
- M. Bonnefoy / R. Cadet / T. Forveille / B. Charnay
- F. Kiefer / A.-M. Lagrange / A. Chiavassa / T. Stolker
- A. Lavail / N. Godoy / M. Janson / R.
Pourcelot
- P. Delorme / E. Rickman / D. Cont / A. Reiners
- R. De Rosa / H. Anwand-Heerwart / Y. Charles /
A. Costille
- M. El Morsy / J. Garcia / M. Houllé / M. Lopez
- G. Murray / E. Muslimov / G. P. P. L. Otten / J. Paufique
- M. Phillips / U. Seemann / A. Viret / G. Zins
Summary
Since the recent discovery of the directly imaged super-Jovian planet
AF Lep b, several studies have been conducted to characterize its
atmosphere and constrain its orbital parameters. AF Lep b has a measured
dynamical mass of  MJup, a
radius of
MJup, a
radius of  RJup, a
nearly circular orbit in spin-orbit alignment with the host star, a
relatively high metallicity, and a near-solar to super-solar C/O ratio.
However, key parameters such as the rotational velocity and radial
velocity could not be estimated as they require high-resolution
spectroscopic data that is impossible to obtain with classical
spectrographs. AF Lep b was recently observed with the new HiRISE
visitor instrument at the VLT, with the goal of obtaining
high-resolution (R~140,000) spectroscopic observations to better
constrain the orbital and atmospheric parameters of the young giant
exoplanet. We compare the extracted spectrum of AF Lep b to
self-consistent atmospheric models using ForMoSA. We then use our
measurements of the radial velocity of the planet to provide new
constraints on the orbit of the planet. From the forward modeling, we
find a C/O ratio that aligns with previous low-resolution analyses, and
we confirm the super-solar metallicity. We also confirm unambiguously
the presence of methane in the atmosphere of the companion. Based on all
available relative astrometry and radial velocity measurements of the
host star, we show that two distinct orbital populations are possible
for the companion. We derive the radial velocity of AF Lep b to be
RJup, a
nearly circular orbit in spin-orbit alignment with the host star, a
relatively high metallicity, and a near-solar to super-solar C/O ratio.
However, key parameters such as the rotational velocity and radial
velocity could not be estimated as they require high-resolution
spectroscopic data that is impossible to obtain with classical
spectrographs. AF Lep b was recently observed with the new HiRISE
visitor instrument at the VLT, with the goal of obtaining
high-resolution (R~140,000) spectroscopic observations to better
constrain the orbital and atmospheric parameters of the young giant
exoplanet. We compare the extracted spectrum of AF Lep b to
self-consistent atmospheric models using ForMoSA. We then use our
measurements of the radial velocity of the planet to provide new
constraints on the orbit of the planet. From the forward modeling, we
find a C/O ratio that aligns with previous low-resolution analyses, and
we confirm the super-solar metallicity. We also confirm unambiguously
the presence of methane in the atmosphere of the companion. Based on all
available relative astrometry and radial velocity measurements of the
host star, we show that two distinct orbital populations are possible
for the companion. We derive the radial velocity of AF Lep b to be  km/s,
and show that this value agrees well with one of the two orbital
solutions, allowing us to rule out an entire family of orbits.
Additionally, assuming that the rotation and orbit are coplanar, the
derived planet’s rotation rate is consistent with the observed trend of
increasing spin velocity with higher planet mass.
km/s,
and show that this value agrees well with one of the two orbital
solutions, allowing us to rule out an entire family of orbits.
Additionally, assuming that the rotation and orbit are coplanar, the
derived planet’s rotation rate is consistent with the observed trend of
increasing spin velocity with higher planet mass.
The
COSMOS-Web ring: Spectroscopic confirmation of the background source at
z = 5.1
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Marko Shuntov / Shuowen Jin / Wilfried Mercier / S.
Jeyhan Kartaltepe
- Rebecca Larson / Ali Ahmad Khostovan / Raphaël Gavazzi / W. James
Nightingale
- Olivier Ilbert / Rafael
Arango-Toro / Maximilien Franco / B. Hollis Akins
- M. Caitlin Casey / Henry Joy McCracken / Laure
Ciesla / E. Georgios Magdis
- Aristeidis Amvrosiadis / Andrea Enia / L. Andreas Faisst / M. Anton
Koekemoer
- Clotilde Laigle / Damien Le Borgne / Richard Massey / Thibaud
Moutard
- Mattia Vaccari
Summary
We report the spectroscopic confirmation of the background source of
the most distant Einstein ring known to date, the COSMOS-Web ring. This
system consists of a complete Einstein ring at  , lensed by a massive
early-type galaxy at
, lensed by a massive
early-type galaxy at  . The redshift
. The redshift  is unambiguously identified with our NOEMA and Keck/MOSFIRE
spectroscopy, where the NOEMA observations reveal the CO(4-3) and
CO(5-4) lines at
is unambiguously identified with our NOEMA and Keck/MOSFIRE
spectroscopy, where the NOEMA observations reveal the CO(4-3) and
CO(5-4) lines at  , and the MOSFIRE
data detect [O] at
, and the MOSFIRE
data detect [O] at  . Using
multi-wavelength photometry spanning near-infrared to radio bands, we
find that the lensed galaxy is a dust-obscured starburst (
. Using
multi-wavelength photometry spanning near-infrared to radio bands, we
find that the lensed galaxy is a dust-obscured starburst ( ,
,  ) with high star-formation efficiency (gas
depletion time
) with high star-formation efficiency (gas
depletion time  Myr) as indicated by the C
non-detection. The redshift confirmation revalidates that the total lens
mass budget within the Einstein radius is fully accounted for by the
stellar and dark matter components, without the need of modifying the
initial mass function or dark matter distribution profile. This work
paves the way for detailed studies and future follow-ups of this unique
lensing system, providing an ideal laboratory for studying mass
distribution at
Myr) as indicated by the C
non-detection. The redshift confirmation revalidates that the total lens
mass budget within the Einstein radius is fully accounted for by the
stellar and dark matter components, without the need of modifying the
initial mass function or dark matter distribution profile. This work
paves the way for detailed studies and future follow-ups of this unique
lensing system, providing an ideal laboratory for studying mass
distribution at  and physical
conditions of star formation at
and physical
conditions of star formation at  .
.
COSMOS
Spectroscopic Redshift Compilation (First Data Release): 488k Redshifts
Encompassing Two Decades of Spectroscopy
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Ali Ahmad Khostovan / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Mara Salvato /
Olivier Ilbert
- Caitlin M. Casey / Hiddo Algera / Jacqueline Antwi-Danso / Andrew
Battisti
- Malte Brinch / Marcella Brusa / Antonello Calabro / Peter L.
Capak
- Nima Chartab / Olivia R. Cooper / Isa G. Cox / Behnam Darvish
- Nicole E. Drakos / Andreas L. Faisst / Matthew R. George / Ghassem
Gozaliasl
- Santosh Harish / Gunther Hasinger / Hossein Hatamnia / Angela
Iovino
- Shuowen Jin / Daichi Kashino / Anton M. Koekemoer / Ronaldo
Laishram
- Khee-Gan Lee / Jitrapon Lertprasertpong / Simon J. Lilly / Daizhong
Liu
- Daniel C. Masters / Bahram Mobasher / Tohru Nagao / Masato
Onodera
- Yingjie Peng / David B. Sanders / Ryan L. Sanders / Zahra
Sattari
- Nick Scoville / Ekta A. Shah / John D. Silverman / Nao Suzuki
- Sina Taamoli / Masayuki Tanaka / Lidia A. M. Tasca / Sune Toft
- Greta Toni / Benny Trakhtenbrot / Jonathan R. Trump / Mattia
Vaccari
- Francesco Valentino / Brittany N. Vanderhoof / John R. Weaver / Min
S. Yun
- Jorge A. Zavala
Summary
We present the COSMOS Spectroscopic Redshift Compilation encompassing
~ 20 years of spectroscopic redshifts within a 10 deg area centered on the 2 deg
area centered on the 2 deg COSMOS legacy field. This compilation
contains 487,666 redshifts of 266,284 unique objects from 138 individual
observing programs up to
COSMOS legacy field. This compilation
contains 487,666 redshifts of 266,284 unique objects from 138 individual
observing programs up to  with median
stellar mass
with median
stellar mass  to
to  M
M (redshift dependent).
Rest-frame
(redshift dependent).
Rest-frame  colors and SFR –
stellar mass correlations show the compilation primarily contains low-
to intermediate-mass star-forming and massive, quiescent galaxies at
colors and SFR –
stellar mass correlations show the compilation primarily contains low-
to intermediate-mass star-forming and massive, quiescent galaxies at
 and mostly
low-mass bursty star-forming galaxies at
and mostly
low-mass bursty star-forming galaxies at  . Sources in the
compilation cover a diverse range of environments, including
protoclusters such as ``Hyperion’’. The full compilation is 50%
spectroscopically complete by
. Sources in the
compilation cover a diverse range of environments, including
protoclusters such as ``Hyperion’’. The full compilation is 50%
spectroscopically complete by  and
and  mag;
however, this is redshift dependent. Spatially, the compilation is
mag;
however, this is redshift dependent. Spatially, the compilation is  % (
% ( %) complete within the
central (outer) region limited to
%) complete within the
central (outer) region limited to  mag and
mag and  mag,
separately. We demonstrate how the compilation can be used to validate
photometric redshifts and investigate calibration metrics. By training
self-organizing maps on COSMOS2020/Classic and projecting the
compilation onto it, we find key galaxy subpopulations that currently
lack spectroscopic coverage including
mag,
separately. We demonstrate how the compilation can be used to validate
photometric redshifts and investigate calibration metrics. By training
self-organizing maps on COSMOS2020/Classic and projecting the
compilation onto it, we find key galaxy subpopulations that currently
lack spectroscopic coverage including  intermediate-mass
quiescent galaxies and low-/intermediate-mass bursty star-forming
galaxies,
intermediate-mass
quiescent galaxies and low-/intermediate-mass bursty star-forming
galaxies,  massive quiescent
galaxies, and
massive quiescent
galaxies, and  massive
star-forming galaxies. This highlights how combining self-organizing
maps with our compilation can provide guidance for future spectroscopic
observations to get a complete spectroscopic view of galaxy populations.
Lastly, the compilation will undergo periodic data releases that
incorporate new spectroscopic redshift measurements, providing a lasting
legacy resource for the community.
massive
star-forming galaxies. This highlights how combining self-organizing
maps with our compilation can provide guidance for future spectroscopic
observations to get a complete spectroscopic view of galaxy populations.
Lastly, the compilation will undergo periodic data releases that
incorporate new spectroscopic redshift measurements, providing a lasting
legacy resource for the community.
Articles for week 8 2025
Calibration
of MAJIS (Moons And Jupiter Imaging Spectrometer): I. On-ground setup
description and characterisation
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Mathieu Vincendon / Pierre Guiot / Benoît Lecomte / Mathieu
Condamin
- François Poulet / Antoine Arondel / Julien Barbay / John
Carter
- Simone De Angelis / Cydalise Dumesnil / Gianrico Filacchione / Paolo
Haffoud
- Jérémie Hansotte / Yves Langevin / Pierre-Louis Mayeur / Giuseppe
Piccioni
- Cédric Pilorget / Eric Quirico / Sébastien Rodriguez
Summary
The visible and infrared Moon And Jupiter Imaging Spectrometer
(MAJIS), aboard the JUpiter ICy Moons Explorer (JUICE) spacecraft, will
characterize the composition of the surfaces and atmospheres of the
Jupiter system. Prior to the launch, a campaign was carried out to
obtain the measurements needed to calibrate the instrument. The aim was
not only to produce data for the calculation of the radiometric,
spectral, and spatial transfer functions, but also to evaluate MAJIS
performance, such as signal-to-noise ratio and amount of straylight,
under near-flight conditions. Here, we first describe the setup
implemented to obtain these measurements, based on five optical
channels. We notably emphasize the concepts used to mitigate thermal
infrared emissions generated at ambient temperatures, since the MAJIS
spectral range extends up to 5.6  m. Then, we characterize the performance
of the setup by detailing the validation measurements obtained before
the campaign. In particular, the radiometric, geometric, and spectral
properties of the setup needed for the inversion of collected data and
the calculation of the instrument’s calibration functions are presented
and discussed. Finally, we provide an overview of conducted measurements
with MAJIS, and we discuss unforeseen events encountered during the
on-ground calibration campaign.
m. Then, we characterize the performance
of the setup by detailing the validation measurements obtained before
the campaign. In particular, the radiometric, geometric, and spectral
properties of the setup needed for the inversion of collected data and
the calculation of the instrument’s calibration functions are presented
and discussed. Finally, we provide an overview of conducted measurements
with MAJIS, and we discuss unforeseen events encountered during the
on-ground calibration campaign.
A
Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE) XVIII.
Reconstructing the star formation history of early-type galaxies through
the combination of their UV and H emission
emission
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- S. Martocchia / A. Boselli / C.
Maraston / D. Thomas
- M. Boquien / Y. Roehlly / M. Fossati / L.-M.
Seillé
- P. Amram / S. Boissier /
V. Buat / P. Côté
- J-C. Cuillandre / L. Ferrarese / S. Gwyn / J. Hutchings
- Junais / C. R. Morgan / J. Postma / T. E. Woods
- J. Roediger / A. Subramaniam / M. Sun / H.-X. Zhang
Summary
We reconstruct the SFHs of 7 massive ( )
early-type galaxies (ETGs) in the Virgo cluster by analysing their
spatially resolved stellar population (SP), including their UV and H
)
early-type galaxies (ETGs) in the Virgo cluster by analysing their
spatially resolved stellar population (SP), including their UV and H emission. As part of the VESTIGE
survey, we used H
emission. As part of the VESTIGE
survey, we used H images to select ETGs that show no
signs of ongoing star formation. We combined VESTIGE with images from
Astrosat/UVIT, GALEX and CFHT from the NGVS to analyse radial spectral
energy distributions (SEDs) from the FUV to the NIR. The UV emission in
these galaxies is likely due to old, low mass stars in post main
sequence (PMS) phases, the UV upturn. We fit the radial SEDs with novel
SP models that include an old, hot stellar component of PMS stars with
various temperatures and energetics. This way, we explore the main
stellar parameters responsible for UV upturn stars irregardless of their
evolutionary path. Standard models are not able to reproduce the
galaxies’ central FUV emission (SMA/
images to select ETGs that show no
signs of ongoing star formation. We combined VESTIGE with images from
Astrosat/UVIT, GALEX and CFHT from the NGVS to analyse radial spectral
energy distributions (SEDs) from the FUV to the NIR. The UV emission in
these galaxies is likely due to old, low mass stars in post main
sequence (PMS) phases, the UV upturn. We fit the radial SEDs with novel
SP models that include an old, hot stellar component of PMS stars with
various temperatures and energetics. This way, we explore the main
stellar parameters responsible for UV upturn stars irregardless of their
evolutionary path. Standard models are not able to reproduce the
galaxies’ central FUV emission (SMA/ ),
while the new models well characterise it through PMS stars with
temperatures T$$25000 K. All galaxies are old (mass-weighted ages
),
while the new models well characterise it through PMS stars with
temperatures T$$25000 K. All galaxies are old (mass-weighted ages  Gyr) and the
most massive M49 and M87 are supersolar within SMA/
Gyr) and the
most massive M49 and M87 are supersolar within SMA/ . Overall, we found flat age gradients (
. Overall, we found flat age gradients ( Log(Age)
Log(Age) dex)
and shallow metallicity gradients (
dex)
and shallow metallicity gradients ( Log(Z)
Log(Z) dex), except for
M87 (
dex), except for
M87 ( Log(
Log( )
) dex). Our
results show that these ETGs formed with timescales
dex). Our
results show that these ETGs formed with timescales  Myr,
having assembled between
Myr,
having assembled between  of their
stellar mass at
of their
stellar mass at  . This is consistent
with recent JWST observations of quiescent massive galaxies at high
. This is consistent
with recent JWST observations of quiescent massive galaxies at high , which are likely the ancestors of the
largest ETGs in the nearby Universe. The derived flat/shallow gradients
indicate that major mergers might have contributed to the formation and
evolution of these galaxies.
, which are likely the ancestors of the
largest ETGs in the nearby Universe. The derived flat/shallow gradients
indicate that major mergers might have contributed to the formation and
evolution of these galaxies.
Euclid:
Galaxy morphology and photometry from bulge-disc decomposition of Early
Release Observations
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- L. Quilley / V. de Lapparent / M. Baes / M. Bolzonella
- I. Damjanov / B. Häußler / F. R. Marleau / A. Nersesian
- T. Saifollahi / D. Scott / J. G. Sorce / C. Tortora
- M. Urbano / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia
- A. Biviano / A. Bonchi / D. Bonino / E. Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat / S. Camera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper
- J.-C. Cuillandre / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / M. Farina
- S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / S. Fotopoulou
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / K. Kuijken
- M. Kümmel / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / R. Laureijs
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / A. Mora / M. Moresco
- L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun
- E. Sefusatti / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani
- E. Zucca / C. Burigana / V. Scottez
Summary
The background galaxies in Euclid Early Release Observations images
of the Perseus cluster make up a remarkable sample in its combination of
0.57 deg area, 25.3 and 23.2 AB mag depth, as
well as 0.1” and 0.3” angular resolutions, in optical and near-IR bands,
respectively. Towards characterising the history of the Hubble sequence,
we perform a morphological analysis of 2445 and 12,786 galaxies with
area, 25.3 and 23.2 AB mag depth, as
well as 0.1” and 0.3” angular resolutions, in optical and near-IR bands,
respectively. Towards characterising the history of the Hubble sequence,
we perform a morphological analysis of 2445 and 12,786 galaxies with
 and
and  ,
respectively. We use single-Sérsic profiles and the sums of a Sérsic
bulge and an exponential disc to model these galaxies with
SourceXtractor++ and analyse their parameters in order to assess their
consistencies and discrepancies. The fitted galaxies to
,
respectively. We use single-Sérsic profiles and the sums of a Sérsic
bulge and an exponential disc to model these galaxies with
SourceXtractor++ and analyse their parameters in order to assess their
consistencies and discrepancies. The fitted galaxies to  span the
various Hubble types with ubiquitous bulge and disc components, and a
bulge-to-total light ratio B/T taking all values from 0 to 1. The
effective radius of the single-Sérsic profile is an intermediate
estimate of galaxy size, between the bulge and disc effective radii,
depending on B/T. The axis ratio of the single-Sérsic profile is higher
than the disc axis ratio, increasingly so with B/T. The model impacts
the photometry with -0.08 to 0.01 mag median systematic
span the
various Hubble types with ubiquitous bulge and disc components, and a
bulge-to-total light ratio B/T taking all values from 0 to 1. The
effective radius of the single-Sérsic profile is an intermediate
estimate of galaxy size, between the bulge and disc effective radii,
depending on B/T. The axis ratio of the single-Sérsic profile is higher
than the disc axis ratio, increasingly so with B/T. The model impacts
the photometry with -0.08 to 0.01 mag median systematic  offsets between single-Sérsic and
bulge+disc total magnitudes, and a 0.05 to 0.15 mag dispersion, from low
to high B/T. We measure a median 0.3 mag bulge-disk colour difference in
rest-frame
offsets between single-Sérsic and
bulge+disc total magnitudes, and a 0.05 to 0.15 mag dispersion, from low
to high B/T. We measure a median 0.3 mag bulge-disk colour difference in
rest-frame  that originates
from the disc-dominated galaxies, whereas bulge-dominated galaxies have
similar median colours of their components. Remarkably, we also measure
redder-inside disc colour gradients, based on 5 to 10% systematic
variations of disc effective radii between the optical and near-IR
bands. This analysis demonstrates the usefulness and limitations of
single-Sérsic profile modelling, and the power of bulge-disc
decomposition for reliably characterising the morphology of lenticulars
and spirals in Euclid images.
that originates
from the disc-dominated galaxies, whereas bulge-dominated galaxies have
similar median colours of their components. Remarkably, we also measure
redder-inside disc colour gradients, based on 5 to 10% systematic
variations of disc effective radii between the optical and near-IR
bands. This analysis demonstrates the usefulness and limitations of
single-Sérsic profile modelling, and the power of bulge-disc
decomposition for reliably characterising the morphology of lenticulars
and spirals in Euclid images.
KM3NeT
Constraint on Lorentz-Violating Superluminal Neutrino Velocity
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- KM3NeT Collaboration / O. Adriani / S. Aiello / A. Albert
- A. R. Alhebsi / M. Alshamsi / S. Alves Garre / A. Ambrosone
- F. Ameli / M. Andre / L. Aphecetche / M. Ardid
- S. Ardid / C. Argüelles / J. Aublin / F. Badaracco
- L. Bailly-Salins / Z. Bardačová / A. Bariego-Quintana / Y.
Becherini
- M. Bendahman / F. Benfenati Gualandi / M. Benhassi / M. Bennani
- D. M. Benoit / E. Berbee / E. Berti / V. Bertin
- P. Betti / S. Biagi / M. Boettcher / D. Bonanno
- S. Bottai / A. B. Bouasla / J. Boumaaza / M. Bouta
- M. Bouwhuis / C. Bozza / R. M. Bozza / H. Brânzaş
- F. Bretaudeau / M. Breuhaus / R. Bruijn / J. Brunner
- R. Bruno / E. Buis / R. Buompane / J. Busto
- B. Caiffi / D. Calvo / A. Capone / F. Carenini
- V. Carretero / T. Cartraud / P. Castaldi / V. Cecchini
- S. Celli / L. Cerisy / M. Chabab / A. Chen
- S. Cherubini / T. Chiarusi / M. Circella / R. Clark
- R. Cocimano / J. A. B. Coelho / A. Coleiro / A. Condorelli
- R. Coniglione / P. Coyle / A. Creusot / G. Cuttone
- R. Dallier / A. De Benedittis / G. De Wasseige / V. Decoene
- P. Deguire / I. Del Rosso / L. S. Di Mauro / I. Di Palma
- A. F. Díaz / D. Diego-Tortosa / C. Distefano / A. Domi
- C. Donzaud / D. Dornic / E. Drakopoulou / D. Drouhin
- J.-G. Ducoin / P. Duverne / R. Dvornický / T. Eberl
- E. Eckerová / A. Eddymaoui / T. van Eeden / M. Eff
- D. van Eijk / I. El Bojaddaini / S. El Hedri / S. El Mentawi
- V. Ellajosyula / A. Enzenhöfer / G. Ferrara / M. D. Filipović
- F. Filippini / D. Franciotti / L. A. Fusco / S. Gagliardini
- T. Gal / J. García Méndez / A. Garcia Soto / C. Gatius Oliver
- N. Geißelbrecht / E. Genton / H. Ghaddari / L. Gialanella
- B. K. Gibson / E. Giorgio / I. Goos / P. Goswami
- S. R. Gozzini / R. Gracia / C. Guidi / B. Guillon
- M. Gutiérrez / C. Haack / H. van Haren / A. Heijboer
- L. Hennig / J. J. Hernández-Rey / A. Idrissi / W. Idrissi
Ibnsalih
- G. Illuminati / O. Janik / D. Joly / M. de Jong
- P. de Jong / B. J. Jung / P. Kalaczyński / N. Kamp
- J. Keegans / V. Kikvadze / G. Kistauri / C. Kopper
- A. Kouchner / Y. Y. Kovalev / L. Krupa / V. Kueviakoe
- V. Kulikovskiy / R. Kvatadze / M. Labalme / R. Lahmann
- M. Lamoureux / G. Larosa / C. Lastoria / J. Lazar
- A. Lazo / S. Le Stum / G. Lehaut / V. Lemaître
- E. Leonora / N. Lessing / G. Levi / M. Lindsey Clark
- F. Longhitano / F. Magnani / J. Majumdar / L. Malerba
- F. Mamedov / A. Manfreda / A. Manousakis / M. Marconi
- A. Margiotta / A. Marinelli / C. Markou / L.
Martin
- M. Mastrodicasa / S. Mastroianni / J. Mauro / K. C. K. Mehta
- A. Meskar / G. Miele / P. Migliozzi / E. Migneco
- M. L. Mitsou / C. M. Mollo / L. Morales-Gallegos / N. Mori
- A. Moussa / I. Mozun Mateo / R. Muller / M. R. Musone
- M. Musumeci / S. Navas / A. Nayerhoda / C. A. Nicolau
- B. Nkosi / B. Ó Fearraigh / V. Oliviero / A. Orlando
- E. Oukacha / L. Pacini / D. Paesani / J. Palacios González
- G. Papalashvili / P. Papini / V. Parisi / A. Parmar
- E. J. Pastor Gomez / C. Pastore / A. M. Păun / G. E. Păvălaş
- S. Peña Martínez / M. Perrin-Terrin / V. Pestel / R. Pestes
- M. Petropavlova / P. Piattelli / A. Plavin / C. Poirè
- V. Popa / T. Pradier / J. Prado / S. Pulvirenti
- C. A. Quiroz-Rangel / N. Randazzo / A. Ratnani / S. Razzaque
- I. C. Rea / D. Real / G. Riccobene / J. Robinson
- A. Romanov / E. Ros / A. Šaina / F. Salesa Greus
- D. F. E. Samtleben / A. Sánchez Losa / S. Sanfilippo / M.
Sanguineti
- D. Santonocito / P. Sapienza / M. Scaringella / M. Scarnera
- J. Schnabel / J. Schumann / H. M. Schutte / J. Seneca
- N. Sennan / P. A. Sevle Myhr / I. Sgura / R. Shanidze
- A. Sharma / Y. Shitov / F. Šimkovic / A. Simonelli
- A. Sinopoulou / B. Spisso / M. Spurio / O. Starodubtsev
- D. Stavropoulos / I. Štekl / D. Stocco / M. Taiuti
- G. Takadze / Y. Tayalati / H. Thiersen / S. Thoudam
- I. Tosta e Melo / B. Trocmé / V. Tsourapis / E. Tzamariudaki
- A. Ukleja / A. Vacheret / V. Valsecchi / V. Van Elewyck
- G. Vannoye / E. Vannuccini / G. Vasileiadis / F. Vazquez de
Sola
- A. Veutro / S. Viola / D. Vivolo / A. van Vliet
- A. Y. Wen / E. de Wolf / I. Lhenry-Yvon / S. Zavatarelli
- A. Zegarelli / D. Zito / J. D. Zornoza / J. Zúñiga
- N. Zywucka
Summary
Lorentz invariance is a fundamental symmetry of spacetime and
foundational to modern physics. One of its most important consequences
is the constancy of the speed of light. This invariance, together with
the geometry of spacetime, implies that no particle can move faster than
the speed of light. In this article, we present the most stringent
neutrino-based test of this prediction, using the highest energy
neutrino ever detected to date, KM3-230213A. The arrival of this event,
with an energy of  , sets a
constraint on
, sets a
constraint on  .
.
A
Catalog of Local Universe Fast Radio Bursts from CHIME/FRB and the KKO
Outrigger
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The CHIME/FRB Collaboration / : / Mandana Amiri / Daniel
Amouyal
- Bridget C. Andersen / Shion Andrew / Kevin Bandura / Mohit
Bhardwaj
- P. J. Boyle / Charanjot Brar / Alyssa Cassity / Shami
Chatterjee
- Alice P. Curtin / Matt Dobbs / Fengqiu Adam Dong / Yuxin Dong
- Gwendolyn M. Eadie / Tarraneh Eftekhari / Wen-fai Fong / Emmanuel
Fonseca
- B. M. Gaensler / Mark Halpern / Jason W. T. Hessels / Hans
Hopkins
- Adaeze L. Ibik / Ronniy C. Joseph / Jane Kaczmarek / Lordrick
Kahinga
- Victoria Kaspi / Kholoud Khairy / Charles D. Kilpatrick / Adam E.
Lanman
- Mattias Lazda / Calvin Leung / Robert Main / Lluis Mas-Ribas
- Kiyoshi W. Masui / Ryan Mckinven / Juan Mena-Parra / Bradley W.
Meyers
- Daniele Michilli / Nikola Milutinovic / Kenzie
Nimmo / Gavin Noble
- Ayush Pandhi / Swarali Shivraj Patil / Aaron B. Pearlman / Emily
Petroff
- Ziggy Pleunis / J. Xavier Prochaska / Masoud Rafiei-Ravandi / Mubdi
Rahman
- Andre Renard / Mawson W. Sammons / Ketan R. Sand / Paul Scholz
- Vishwangi Shah / Kaitlyn Shin / Seth R. Siegel / Sunil Simha
- Kendrick Smith / Ingrid Stairs / Keith Vanderlinde / Haochen
Wang
- Dallas Wulf / Tarik J. Zegmott
Summary
We present the first catalog of fast radio burst (FRB) host galaxies
from CHIME/FRB Outriggers, selected uniformly in the radio and the
optical by localizing 81 new bursts to 2’’ x ~60’’ accuracy using CHIME
and the KKO Outrigger, located 66 km from CHIME. Of the 81 localized
bursts, we use the Probabilistic Association of Transients to their
Hosts (PATH) algorithm to securely identify 21 new FRB host galaxies,
and compile spectroscopic redshifts for 19 systems, 15 of which are
newly obtained via spectroscopic observations. The most nearby source is
FRB 20231229A, at a distance of 90 Mpc. One burst in our sample is from
a previously reported repeating source in a galaxy merger (FRB
20190303A). Three new FRB host galaxies (FRBs 20230203A, 20230703A, and
20231206A) are found towards X-ray and optically selected galaxy
clusters, potentially doubling the sample of known galaxy cluster FRBs.
A search for radio counterparts reveals that FRB 20231128A is associated
with a luminous persistent radio source (PRS) candidate with high
significance ( ). If its compactness is confirmed, it would be
the nearest known compact PRS at
). If its compactness is confirmed, it would be
the nearest known compact PRS at  . Our catalog
significantly increases the statistics of the Macquart relation at low
redshifts (
. Our catalog
significantly increases the statistics of the Macquart relation at low
redshifts ( ). In the near
future, the completed CHIME/FRB Outriggers array will produce hundreds
of FRBs localized with very long baseline interferometry (VLBI). This
will significantly expand the known sample and pave the way for future
telescopes relying on VLBI for FRB localization.
). In the near
future, the completed CHIME/FRB Outriggers array will produce hundreds
of FRBs localized with very long baseline interferometry (VLBI). This
will significantly expand the known sample and pave the way for future
telescopes relying on VLBI for FRB localization.
Articles for week 7 2025
The
SPIRou Legacy Survey: near-infrared and optical radial velocity analysis
of Gl 480 and Gl 382 using SPIRou, HARPS and CARMENES spectrographs
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Ould-Elhkim / C. Moutou / J-F. Donati / É.
Artigau
- C. Cadieux / E. Martioli / T. Forveille / J. Gomes da Silva
- R. Cloutier / A. Carmona / P. Fouqué / P. Charpentier
- P. Larue / N. J. Cook / X. Delfosse / R. Doyon
Summary
Context: Advancements in the field of exoplanetary research have
extended radial velocity (RV) observations from the optical to the
near-infrared (nIR) domain. M dwarf stars, characterized by their lower
masses and higher prevalence of rocky planets, have become a focal point
of investigation. This study uses data from the near-infrared
spectropolarimeter SPIRou and data available in the literature from the
HARPS and CARMENES spectrographs operating in the optical to analyze RVs
of two nearby M dwarfs, Gl 480 and Gl 382. Aims: This work aims to
detect and characterize exoplanetary companions around Gl 480 and Gl 382
by mitigating stellar activity effects through advanced data analysis
techniques. The study seeks to improve the reliability of RV signals by
integrating multi-wavelength observations and stellar activity
diagnostics. Methods: The study employs a comprehensive approach that
combines the line-by-line (LBL) framework with the Wapiti (Weighted
principAl comPonent analysIs reconsTructIon) method to correct for
systematics in SPIRou data. Through an extensive analysis of available
stellar activity indicators and by combining optical data from the HARPS
and CARMENES instruments, we perform a joint analysis of RV measurements
in both the nIR and optical domains. Results: Our analysis confirms the
detection of a planet orbiting Gl 480 with a period of  d and a minimum mass of
d and a minimum mass of  M
M . Additionally, we
detect a tentative signal at 6.4 d, whose significance depends strongly
on the choice of Gaussian Process priors constrained by stellar activity
indicators and would require further observations for confirmation. In
contrast, no planetary signals are detected for Gl 382, where RV
variations are dominated by stellar activity.
. Additionally, we
detect a tentative signal at 6.4 d, whose significance depends strongly
on the choice of Gaussian Process priors constrained by stellar activity
indicators and would require further observations for confirmation. In
contrast, no planetary signals are detected for Gl 382, where RV
variations are dominated by stellar activity.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Philippe Peille / Didier Barret / Edoardo Cucchetti / Vincent
Albouys
- Luigi Piro / Aurora Simionescu / Massimo Cappi / Elise
Bellouard
- Céline Cénac-Morthé / Christophe Daniel / Alice Pradines / Alexis
Finoguenov
- Richard Kelley / J. Miguel Mas-Hesse / Stéphane Paltani / Gregor
Rauw
- Agata Rozanska / Jiri Svoboda / Joern Wilms / Marc Audard
- Enrico Bozzo / Elisa Costantini / Mauro Dadina / Thomas Dauser
- Anne Decourchelle / Jan-Willem den Herder / Andrea Goldwurm / Peter
Jonker
- Alex Markowitz / Mariano Mendez / Giovanni Miniutti / Silvano
Molendi
- Fabrizio Nicastro / François Pajot / Etienne Pointecouteau / Gabriel
W. Pratt
- Joop Schaye / Jacco Vink / Natalie Webb / Simon Bandler
- Marco Barbera / Maria Teresa Ceballos / Ivan Charles / Roland den
Hartog
- W. Bertrand Doriese / Jean-Marc Duval / Flavio Gatti / Brian
Jackson
- Caroline Kilbourne / Claudio Macculi / Sylvain Martin / Yann
Parot
- Frederick Porter / Damien Prêle / Laurent Ravera / Stephen
Smith
- Jan Soucek / Tanguy Thibert / Eija Tuominen / Fabio Acero
- Stefano Ettori / Nicolas Grosso / Jelle Kaastra /
Pasquale Mazzotta
- Jon Miller / Salvatore Sciortino / Sophie Beaumont / Matteo
D’Andrea
- Jelle de Plaa / Megan Eckart / Luciano Gottardi / Maurice
Leutenegger
- Simone Lotti / Alexei Molin / Lorenzo Natalucci / Muhammad Qazi
Adil
- Andrea Argan / Elisabetta Cavazzuti / Mauro Fiorini / Pourya
Khosropanah
- Eduardo Medinaceli Villegas / Gabriele Minervini / James Perry /
Frederic Pinsard
- Desi Raulin / Manuela Rigano / Peter Roelfsema / Denis
Schwander
- Santiago Terron / Guido Torrioli / Joel Ullom / Monika Zuchniak
- Laurence Chaoul / Jose Miguel Torrejon / Frank Brachet / Beatriz
Cobo
- Malcolm Durkin / Valentina Fioretti / Hervé Geoffray / Lionel
Jacques
- Christian Kirsch / Ugo Lo Cicero / Joseph Adams / Emilie
Gloaguen
- Manuel Gonzalez / Samuel Hull / Erik Jellyman / Mikko Kiviranta
- Kazuhiro Sakai / Emanuele Taralli / Davide Vaccaro / Paul van der
Hulst
- Jan van der Kuur / Bert-Joost van Leeuwen / Dennis van Loon /
Nicholas Wakeham
- Natalia Auricchio / Daniele Brienza / Oscar Cheatom / Philippe
Franssen
- Sabine Julien / Isabelle Le Mer / David Moirin / Vitor Silva
- Michela Todaro / Nicolas Clerc / Alexis Coleiro / Andy Ptak
- Simonetta Puccetti / Christian Surace / Shariefa
Abdoelkariem / Christophe Adami
- Corinne Aicardi / Jérôme André / Matteo Angelinelli / Shebli
Anvar
- Luis Horacio Arnaldi / Anthony Attard / Damian Audley / Florian
Bancel
- Kimberly Banks / Vivian Bernard / Jan Geralt Bij de Vaate / Donata
Bonino
- Anthony Bonnamy / Patrick Bonny / Charles Boreux / Ayoub Bounab
- Maïmouna Brigitte / Marcel Bruijn / Clément Brysbaert / Andrea
Bulgarelli
- Simona Calarco / Thierry Camus / Florent Canourgues / Vito
Capobianco
- Nicolas Cardiel / Edvige Celasco / Si Chen / James Chervenak
- Fabio Chiarello / Sébastien Clamagirand / Odile Coeur-Joly /
Leonardo Corcione
- Mickael Coriat / Anais Coulet / Bernard Courty / Alexandre
Coynel
- Antonino D’Ai / Eugenio Dambrauskas / Fabio D’anca / Lea Dauner
- Matteo De Gerone / Natalie DeNigris / Johannes Dercksen / Martin de
Wit
- Pieter Dieleman / Michael DiPirro / Eric Doumayrou / Lionel
Duband
- Luc Dubbeldam / Michel Dupieux / Simon Dupourqué / Jean Louis
Durand
- Dominique Eckert / Philippe Ferrando / Lorenzo Ferrari Barusso /
Fred Finkbeiner
- Mariateresa Fiocchi / Hervé Fossecave / Stefano Gabici / Giovanni
Gallucci
- Florent Gant / Jian-Rong Gao / Fabio Gastaldello / Ludovic
Genolet
- Simona Ghizzardi / Elisa Giovannini / Margherita Giustini / Alain
Givaudan
- Olivier Godet / Alicia Gomez / Raoul Gonzalez / Ghassem
Gozaliasl
- Laurent Grandsire / David Granena / Michel Gros / Corentin
Guerin
- Emmanuel Guilhem / Gian Paolo Guizzo / Liyi Gu / Kent Irwin
- Christian Jacquey / Agnieszka Janiuk / Jean Jaubert / Antoine
Jolly
- Thierry Jourdan / Jürgen Knödlseder / Ole König / Andrew Korb
- Ingo Kreykenbohm / David Lafforgue / Radek Lan / Maélyss
Larrieu
- Philippe Laudet / Philippe Laurent / Sylvain
Laurent / Monica Laurenza
- Maël Le Cam / Jean Lesrel / Sebastiano Ligori / Maximilian
Lorenz
- Alfredo Luminari / Kristin Madsen / Océane Maisonnave / Lorenzo
Marelli
- Wilfried Marty / Zoé Massida / Didier Massonet / Irwin Maussang
- Pablo Eleazar Merino Alonso / Jean Mesquida / Teresa Mineo / Nicola
Montinaro
- David Murat / Kenichiro Nagayoshi / Yaël Nazé / Loïc Noguès
- François Nouals / Cristina Ortega / Francesca Panessa / Luigi
Parodi
- Enrico Piconcelli / Ciro Pinto / Delphine Porquet /
Thomas Prouvé
- Michael Punch / Guillaume Rioland / Marc-Olivier Riollet / Louis
Rodriguez
- Anton Roig / Mauro Roncarelli / Lionel Roucayrol / Gilles
Roudil
- Lander Ruiz de Ocenda / Luisa Sciortino / Olivier Simonella /
Michael Sordet
- Ulrich Taubenschuss / Guilhem Terrasa / Régis Terrier / Pietro
Ubertini
- Ludek Uhlir / Michela Uslenghi / Henk van Weers / Salvatore
Varisco
- Peggy Varniere / Angela Volpe / Gavin Walmsley / Michael Wise
- Andreas Wolnievik / Grzegorz Woźniak
Summary
The Athena mission entered a redefinition phase in July 2022, driven
by the imperative to reduce the mission cost at completion for the
European Space Agency below an acceptable target, while maintaining the
flagship nature of its science return. This notably called for a
complete redesign of the X-ray Integral Field Unit (X-IFU) cryogenic
architecture towards a simpler active cooling chain. Passive cooling via
successive radiative panels at spacecraft level is now used to provide a
50 K thermal environment to an X-IFU owned cryostat. 4.5 K cooling is
achieved via a single remote active cryocooler unit, while a multi-stage
Adiabatic Demagnetization Refrigerator ensures heat lift down to the 50
mK required by the detectors. Amidst these changes, the core concept of
the readout chain remains robust, employing Transition Edge Sensor
microcalorimeters and a SQUID-based Time-Division Multiplexing scheme.
Noteworthy is the introduction of a slower pixel. This enables an
increase in the multiplexing factor (from 34 to 48) without compromising
the instrument energy resolution, hence keeping significant system
margins to the new 4 eV resolution requirement. This allows reducing the
number of channels by more than a factor two, and thus the resource
demands on the system, while keeping a 4’ field of view (compared to 5’
before). In this article, we will give an overview of this new
architecture, before detailing its anticipated performances. Finally, we
will present the new X-IFU schedule, with its short term focus on
demonstration activities towards a mission adoption in early 2027.
Characterizing
Candidate Blazar Counterparts of the Ultra-High-Energy Event
KM3-230213A
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- KM3NeT Collaboration / MessMapp Group / Fermi-LAT Collaboration /
Owens Valley Radio Observatory 40-m Telescope Group
- SVOM Collaboration / P. Baldini / J. Buchner / A. K. Erkenov
- N. Globus / A. Merloni / A. Paggi / A. V. Popkov
- D. Porquet / M. Salvato / Y. V. Sotnikova / P. A.
Voitsik
Summary
High-energy astrophysical neutrinos serve as crucial messengers for
understanding hadronic acceleration processes and identifying the
origins of cosmic rays, with blazars among the most promising neutrino
sources. The KM3NeT experiment reported the detection of an
ultra-high-energy neutrino with an energy estimate of ~ 220 PeV, the
most energetic yet observed. The neutrino arrival direction has a 99%
confidence region of 3° radius centered at RA 94.3°, Dec -7.8° (J2000).
In this work, seventeen candidate blazars located within this region are
identified. Comprehensive new observations and archival data analysis
for these sources are presented. The study provides a complete
multiwavelength coverage across radio, optical, X-ray, and gamma-ray
bands, including proprietary data and dedicated follow-up observations.
This study highlights flaring behavior in several candidate
counterparts. One object exhibits a radio flare coinciding with the
neutrino arrival time, with a pre-trial chance probability of 0.26%.
Another candidate displays a rising trend in X-ray flux in a one-year
window around the neutrino arrival time, while a third undergoes a
gamma-ray flare during the same period. Based on the observational
findings here presented, while none of these candidates can conclusively
be linked to the neutrino, the implications of a possible blazar origin
for the KM3NeT event are discussed.
On
the Potential Galactic Origin of the Ultra-High-Energy Event
KM3-230213A
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- O. Adriani / S. Aiello / A. Albert / A. R. Alhebsi
- M. Alshamsi / S. Alves Garre / A. Ambrosone / F. Ameli
- M. Andre / L. Aphecetche / M. Ardid / S. Ardid
- J. Aublin / F. Badaracco / L. Bailly-Salins / Z. Bardačová
- B. Baret / A. Bariego-Quintana / Y. Becherini / M. Bendahman
- F. Benfenati Gualandi / M. Benhassi / M. Bennani / D. M. Benoit
- E. Berbee / E. Berti / V. Bertin / P. Betti
- S. Biagi / M. Boettcher / D. Bonanno / S. Bottai
- A. B. Bouasla / J. Boumaaza / M. Bouta / M. Bouwhuis
- C. Bozza / R. M. Bozza / H. Brânzaş / F. Bretaudeau
- M. Breuhaus / R. Bruijn / J. Brunner / R. Bruno
- E. Buis / R. Buompane / J. Busto / B. Caiffi
- D. Calvo / A. Capone / F. Carenini / V. Carretero
- T. Cartraud / P. Castaldi / V. Cecchini / S. Celli
- L. Cerisy / M. Chabab / A. Chen / S. Cherubini
- T. Chiarusi / M. Circella / R. Clark / R. Cocimano
- J. A. B. Coelho / A. Coleiro / A. Condorelli / R. Coniglione
- P. Coyle / A. Creusot / G. Cuttone / R. Dallier
- A. De Benedittis / G. De Wasseige / V. Decoene / P. Deguire
- I. Del Rosso / L. S. Di Mauro / I. Di Palma / A. F. Díaz
- D. Diego-Tortosa / C. Distefano / A. Domi / C. Donzaud
- D. Dornic / E. Drakopoulou / D. Drouhin / J.-G. Ducoin
- P. Duverne / R. Dvornický / T. Eberl / E. Eckerová
- A. Eddymaoui / T. van Eeden / M. Eff / D. van Eijk
- I. El Bojaddaini / S. El Hedri / S. El Mentawi / V. Ellajosyula
- A. Enzenhöfer / G. Ferrara / M. D. Filipović / F. Filippini
- D. Franciotti / L. A. Fusco / T. Gal / J. García Méndez
- A. Garcia Soto / C. Gatius Oliver / N. Geißelbrecht / E. Genton
- H. Ghaddari / L. Gialanella / B. K. Gibson / E. Giorgio
- I. Goos / P. Goswami / S. R. Gozzini / R. Gracia
- C. Guidi / B. Guillon / M. Gutiérrez / C. Haack
- H. van Haren / A. Heijboer / L. Hennig / J. J. Hernández-Rey
- A. Idrissi / W. Idrissi Ibnsalih / G. Illuminati / O. Janik
- D. Joly / M. de Jong / P. de Jong / B. J. Jung
- P. Kalaczyński / J. Keegans / V. Kikvadze / G. Kistauri
- C. Kopper / A. Kouchner / Y. Y. Kovalev / L. Krupa
- V. Kueviakoe / V. Kulikovskiy / R. Kvatadze / M. Labalme
- R. Lahmann / M. Lamoureux / G. Larosa / C. Lastoria
- J. Lazar / A. Lazo / S. Le Stum / G. Lehaut
- V. Lemaître / E. Leonora / N. Lessing / G. Levi
- M. Lindsey Clark / F. Longhitano / F. Magnani / J. Majumdar
- L. Malerba / F. Mamedov / A. Manfreda / A. Manousakis
- M. Marconi / A. Margiotta / A. Marinelli / C. Markou
- L. Martin / M. Mastrodicasa / S. Mastroianni / J.
Mauro
- K. C. K. Mehta / A. Meskar / G. Miele / P. Migliozzi
- E. Migneco / M. L. Mitsou / C. M. Mollo / L. Morales-Gallegos
- N. Mori / A. Moussa / I. Mozun Mateo / R. Muller
- M. R. Musone / M. Musumeci / S. Navas / A. Nayerhoda
- C. A. Nicolau / B. Nkosi / B. Ó Fearraigh / V. Oliviero
- A. Orlando / E. Oukacha / L. Pacini / D. Paesani
- J. Palacios González / G. Papalashvili / P. Papini / V. Parisi
- A. Parmar / E. J. Pastor Gomez / C. Pastore / A. M. Păun
- G. E. Păvălaş / S. Peña Martínez / M. Perrin-Terrin / V. Pestel
- R. Pestes / M. Petropavlova / P. Piattelli / A. Plavin
- C. Poirè / V. Popa / T. Pradier / J. Prado
- S. Pulvirenti / C. A. Quiroz-Rangel / N. Randazzo / A. Ratnani
- S. Razzaque / I. C. Rea / D. Real / G. Riccobene
- J. Robinson / A. Romanov / E. Ros / A. Šaina
- F. Salesa Greus / D. F. E. Samtleben / A. Sánchez Losa / S.
Sanfilippo
- M. Sanguineti / D. Santonocito / P. Sapienza / M. Scaringella
- M. Scarnera / J. Schnabel / J. Schumann / H. M. Schutte
- J. Seneca / N. Sennan / P. A. Sevle Myhr / I. Sgura
- R. Shanidze / A. Sharma / Y. Shitov / F. Šimkovic
- A. Simonelli / A. Sinopoulou / B. Spisso / M. Spurio
- O. Starodubtsev / D. Stavropoulos / I. Štekl / D. Stocco
- M. Taiuti / G. Takadze / Y. Tayalati / H. Thiersen
- S. Thoudam / I. Tosta e Melo / B. Trocmé / V. Tsourapis
- E. Tzamariudaki / A. Ukleja / A. Vacheret / V. Valsecchi
- V. Van Elewyck / G. Vannoye / E. Vannuccini / G. Vasileiadis
- F. Vazquez de Sola / A. Veutro / S. Viola / D. Vivolo
- A. van Vliet / E. de Wolf / I. Lhenry-Yvon / S. Zavatarelli
- A. Zegarelli / D. Zito / J. D. Zornoza / J. Zúñiga
- N. Zywucka
Summary
The KM3NeT observatory detected the most energetic neutrino candidate
ever observed, with an energy between 72 PeV and 2.6 EeV at the 90%
confidence level. The observed neutrino is likely of cosmic origin. In
this article, it is investigated if the neutrino could have been
produced within the Milky Way. Considering the low fluxes of the
Galactic diffuse emission at these energies, the lack of a nearby
potential Galactic particle accelerator in the direction of the event
and the difficulty to accelerate particles to such high energies in
Galactic systems, we conclude that if the event is indeed cosmic, it is
most likely of extragalactic origin.
Tracing
High-z Galaxies in X-rays with JWST and Chandra
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Kaminsky / N. Cappelluti / G. Hasinger / A. Peca
- C. M. Casey / N. E. Drakos / A. Faisst / G. Gozaliasl
- O. Ilbert / J. S. Kartaltepe / A. Kashlinsky / A.
M. Koekemoer
- H. J. McCracken / J. Rhodes / B. E. Robertson / M. Shuntov
- J. Sterling
Summary
We leverage JWST data from the COSMOS-Web Survey in order to provide
updated measurements on the auto-power spectrum of the now resolved
Cosmic Infrared Background (CIB) and its coherence with the unresolved
soft Cosmic X-ray Background (CXB) observed by Chandra at z > 6. Maps
of the CIB in the F277W and F444W NIRCam filters are constructed with
sources fainter than AB mag = 25 and cross-correlated with the CXB in
the [0.5-2] keV band. We find that on scales between 1 and 1000’’ the
CIB-CXB cross-power in both NIRCam filters is statistically significant
with signal-to-noise ratios (S/N) of 4.80 and 6.20 respectively from
redshifts 0 < z < 13. In our high-z (6 < z < 13) interval we
find coherence in both filters with a S/N of 7.32 and 5.39 respectively.
These results suggest that there are X-ray emitting galaxies resolved by
JWST, including star-forming galaxies (SFGs) and active galactic nuclei
(AGNs). We fit the large-scale biasing of the IR sources producing the
CIB as a function of z with results consistent with prior measurements
and place constraints on the CXB flux and biasing at low- and high-z.
The CXB flux measurements presented in this study suggest that
approximately 94% of the [0.5-2] keV CXB is resolved, and this value is
consistent within 2 with the complete resolution of the
[0.5-2] keV CXB.
with the complete resolution of the
[0.5-2] keV CXB.
Euclid: A complete
Einstein ring in NGC 6505
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. M. O’Riordan / L. J. Oldham / A. Nersesian / T. Li
- T. E. Collett / D. Sluse / B. Altieri / B. Clément
- K. Vasan G. C. / S. Rhoades / Y. Chen / T. Jones
- C. Adami / R. Gavazzi / S. Vegetti
/ D. M. Powell
- J. A. Acevedo Barroso / I. T. Andika / R. Bhatawdekar / A. R.
Cooray
- G. Despali / J. M. Diego / L. R. Ecker / A. Galan
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / L. Leuzzi / M. Meneghetti / R. B. Metcalf
- M. Schirmer / S. Serjeant / C. Tortora / M. Vaccari
- G. Vernardos / M. Walmsley / A. Amara / S. Andreon
- N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi
- A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / A. Basset / P. Battaglia
- R. Bender / D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat / S. Camera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti
- C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi
- Y. Copin / L. Corcione / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / M. Farina / S. Farrens
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta / W. Gillard
- B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian
- F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar
- H. Hoekstra / W. Holmes / I. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling
- M. Kilbinger / R. Kohley / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / O. Lahav / R. Laureijs
- D. Le Mignant / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V.
Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / E. Merlin / G. Meylan
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / R. C. Nichol
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino
- S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa
- L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / H.-W. Rix / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / B. Rusholme / R. Saglia
- Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / L. Stanco
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / I. Tereno / R.
Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / T. Vassallo
- G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller
- A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / C. Burigana
- P. Casenove / A. Mora / V. Scottez / M. Viel
- M. Jauzac / H. Dannerbauer
Summary
We report the discovery of a complete Einstein ring around the
elliptical galaxy NGC 6505, at  . This is the first
strong gravitational lens discovered in Euclid and the first in an NGC
object from any survey. The combination of the low redshift of the lens
galaxy, the brightness of the source galaxy (
. This is the first
strong gravitational lens discovered in Euclid and the first in an NGC
object from any survey. The combination of the low redshift of the lens
galaxy, the brightness of the source galaxy ( lensed,
lensed,  unlensed), and the completeness of the ring make this an exceptionally
rare strong lens, unidentified until its observation by Euclid. We
present deep imaging data of the lens from the Euclid Visible Camera
(VIS) and Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) instruments,
as well as resolved spectroscopy from the Keck Cosmic Web Imager (KCWI).
The Euclid imaging in particular presents one of the highest
signal-to-noise ratio optical/near-infrared observations of a strong
gravitational lens to date. From the KCWI data we measure a source
redshift of
unlensed), and the completeness of the ring make this an exceptionally
rare strong lens, unidentified until its observation by Euclid. We
present deep imaging data of the lens from the Euclid Visible Camera
(VIS) and Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) instruments,
as well as resolved spectroscopy from the Keck Cosmic Web Imager (KCWI).
The Euclid imaging in particular presents one of the highest
signal-to-noise ratio optical/near-infrared observations of a strong
gravitational lens to date. From the KCWI data we measure a source
redshift of  . Using data from
the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) we measure a velocity
dispersion for the lens galaxy of
. Using data from
the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) we measure a velocity
dispersion for the lens galaxy of  . We
model the lens galaxy light in detail, revealing angular structure that
varies inside the Einstein ring. After subtracting this light model from
the VIS observation, we model the strongly lensed images, finding an
Einstein radius of 2.5 arcsec, corresponding to
. We
model the lens galaxy light in detail, revealing angular structure that
varies inside the Einstein ring. After subtracting this light model from
the VIS observation, we model the strongly lensed images, finding an
Einstein radius of 2.5 arcsec, corresponding to  at the redshift of the lens. This is small compared to the effective
radius of the galaxy,
at the redshift of the lens. This is small compared to the effective
radius of the galaxy,  .
Combining the strong lensing measurements with analysis of the
spectroscopic data we estimate a dark matter fraction inside the
Einstein radius of
.
Combining the strong lensing measurements with analysis of the
spectroscopic data we estimate a dark matter fraction inside the
Einstein radius of  and a stellar initial mass-function (IMF) mismatch parameter of
and a stellar initial mass-function (IMF) mismatch parameter of  ,
indicating a heavier-than-Chabrier IMF in the centre of the galaxy.
,
indicating a heavier-than-Chabrier IMF in the centre of the galaxy.
Euclid:
Finding strong gravitational lenses in the Early Release Observations
using convolutional neural networks
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- B. C. Nagam / J. A. Acevedo Barroso / J. Wilde / I. T. Andika
- A. Manjón-García / R. Pearce-Casey / D. Stern / J. W.
Nightingale
- L. A. Moustakas / K. McCarthy / E. Moravec / L. Leuzzi
- K. Rojas / S. Serjeant / T. E. Collett / P. Matavulj
- M. Walmsley / B. Clément / C. Tortora / R.
Gavazzi
- R. B. Metcalf / C. M. O’Riordan / G. Verdoes Kleijn / L. V. E.
Koopmans
- E. A. Valentijn / V. Busillo / S. Schuldt / F. Courbin
- G. Vernardos / M. Meneghetti / A. Díaz-Sánchez / J. M. Diego
- L. R. Ecker / T. T. Thai / A. R. Cooray / H. M. Courtois
- L. Delchambre / G. Despali / D. Sluse / L. Ulivi
- A. Melo / P. Corcho-Caballero / B. Altieri / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / H. Aussel / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / A. Balestra / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- A. Caillat / S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / M. Cropper
- A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio
- J. Dinis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / M. Fabricius / M. Farina / S. Farrens
- S. Ferriol / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar / W. Holmes / I. Hook
- F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot / K. Jahnke
- M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / R. Laureijs / D. Le Mignant / S.
Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R.
Massey
- E. Medinaceli / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima
- C. Neissner / R. C. Nichol / S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer
- P. Schneider / T. Schrabback / A. Secroun / G. Seidel
- S. Serrano / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri / J. Skottfelt
- L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus
- L. Valenziano / T. Vassallo / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / E. Zucca / C. Burigana
- A. Mora / M. Pöntinen / V. Scottez
Summary
The Early Release Observations (ERO) from Euclid have detected
several new galaxy-galaxy strong gravitational lenses, with the all-sky
survey expected to find 170,000 new systems, greatly enhancing studies
of dark matter, dark energy, and constraints on the cosmological
parameters. As a first step, visual inspection of all galaxies in one of
the ERO fields (Perseus) was carried out to identify candidate strong
lensing systems and compared to the predictions from Convolutional
Neural Networks (CNNs). However, the entire ERO data set is too large
for expert visual inspection. In this paper, we therefore extend the CNN
analysis to the whole ERO data set, using different CNN architectures
and methodologies. Using five CNN architectures, we identified 8,469
strong gravitational lens candidates from IE-band cutouts of 13 Euclid
ERO fields, narrowing them to 97 through visual inspection, including 14
grade A and 31 grade B candidates. We present the spectroscopic
confirmation of a strong gravitational lensing candidate,
EUCLJ081705.61+702348.8. The foreground lensing galaxy, an early-type
system at redshift z = 0.335, and the background source, a star-forming
galaxy at redshift z = 1.475 with [O II] emission, are both identified.
Lens modeling using the Euclid strong lens modeling pipeline reveals two
distinct arcs in a lensing configuration, with an Einstein radius of
1.18 arcseconds, confirming the lensing nature of the system. These
findings highlight the importance of a broad CNN search to efficiently
reduce candidates, followed by visual inspection to eliminate false
positives and achieve a high-purity sample of strong lenses in
Euclid.
The
ultra-high-energy event KM3-230213A within the global neutrino
landscape
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- KM3NeT Collaboration / O. Adriani / S. Aiello / A. Albert
- A. R. Alhebsi / M. Alshamsi / S. Alves Garre / A. Ambrosone
- F. Ameli / M. Andre / L. Aphecetche / M. Ardid
- S. Ardid / C. Argüelles / J. Aublin / F. Badaracco
- L. Bailly-Salins / Z. Bardačová / B. Baret / A.
Bariego-Quintana
- Y. Becherini / M. Bendahman / F. Benfenati Gualandi / M.
Benhassi
- M. Bennani / D. M. Benoit / E. Berbee / E. Berti
- V. Bertin / P. Betti / S. Biagi / M. Boettcher
- D. Bonanno / S. Bottai / A. B. Bouasla / J. Boumaaza
- M. Bouta / M. Bouwhuis / C. Bozza / R. M. Bozza
- H. Brânzaš / F. Bretaudeau / M. Breuhaus / R. Bruijn
- J. Brunner / R. Bruno / E. Buis / R. Buompane
- J. Busto / B. Caiffi / D. Calvo / A. Capone
- F. Carenini / V. Carretero / T. Cartraud / P. Castaldi
- V. Cecchini / S. Celli / L. Cerisy / M. Chabab
- A. Chen / S. Cherubini / T. Chiarusi / M. Circella
- R. Clark / R. Cocimano / J. A. B. Coelho / A. Coleiro
- A. Condorelli / R. Coniglione / P. Coyle / A. Creusot
- G. Cuttone / R. Dallier / A. De Benedittis / G. De Wasseige
- V. Decoene / P. Deguire / I. Del Rosso / L. S. Di Mauro
- I. Di Palma / A. F. Díaz / D. Diego-Tortosa / C. Distefano
- A. Domi / C. Donzaud / D. Dornic / E. Drakopoulou
- D. Drouhin / J.-G. Ducoin / P. Duverne / R. Dvornický
- T. Eberl / E. Eckerová / A. Eddymaoui / T. van Eeden
- M. Eff / D. van Eijk / I. El Bojaddaini / S. El Hedri
- S. El Mentawi / V. Ellajosyula / A. Enzenhöfer / G. Ferrara
- M. D. Filipović / F. Filippini / D. Franciotti / L. A. Fusco
- T. Gal / J. García Méndez / A. Garcia Soto / C. Gatius Oliver
- N. Geißelbrecht / E. Genton / H. Ghaddari / L. Gialanella
- B. K. Gibson / E. Giorgio / I. Goos / P. Goswami
- S. R. Gozzini / R. Gracia / C. Guidi / B. Guillon
- M. Gutiérrez / C. Haack / H. van Haren / A. Heijboer
- L. Hennig / J. J. Hernández-Rey / A. Idrissi / W. Idrissi
Ibnsalih
- G. Illuminati / O. Janik / D. Joly / M. de Jong
- P. de Jong / B. J. Jung / P. Kalaczyński / N. Kamp
- J. Keegans / V. Kikvadze / G. Kistauri / C. Kopper
- A. Kouchner / Y. Y. Kovalev / L. Krupa / V. Kueviakoe
- V. Kulikovskiy / R. Kvatadze / M. Labalme / R. Lahmann
- M. Lamoureux / G. Larosa / C. Lastoria / J. Lazar
- A. Lazo / S. Le Stum / G. Lehaut / V. Lemaître
- E. Leonora / N. Lessing / G. Levi / M. Lindsey Clark
- F. Longhitano / F. Magnani / J. Majumdar / L. Malerba
- F. Mamedov / A. Manfreda / A. Manousakis / M. Marconi
- A. Margiotta / A. Marinelli / C. Markou / L.
Martin
- M. Mastrodicasa / S. Mastroianni / J. Mauro / K. C. K. Mehta
- A. Meskar / G. Miele / P. Migliozzi / E. Migneco
- M. L. Mitsou / C. M. Mollo / L. Morales-Gallegos / N. Mori
- A. Moussa / I. Mozun Mateo / R. Muller / M. R. Musone
- M. Musumeci / S. Navas / A. Nayerhoda / C. A. Nicolau
- B. Nkosi / B. Ó Fearraigh / V. Oliviero / A. Orlando
- E. Oukacha / L. Pacini / D. Paesani / J. Palacios González
- G. Papalashvili / P. Papini / V. Parisi / A. Parmar
- E. J. Pastor Gomez / C. Pastore / A. M. Păun / G. E. Păvălaš
- S. Peña Martínez / M. Perrin-Terrin / V. Pestel / R. Pestes
- M. Petropavlova / P. Piattelli / A. Plavin / C. Poirè
- V. Popa / T. Pradier / J. Prado / S. Pulvirenti
- C. A. Quiroz-Rangel / N. Randazzo / A. Ratnani / S. Razzaque
- I. C. Rea / D. Real / G. Riccobene / J. Robinson
- A. Romanov / E. Ros / A. Šaina / F. Salesa Greus
- D. F. E. Samtleben / A. Sánchez Losa / S. Sanfilippo / M.
Sanguineti
- D. Santonocito / P. Sapienza / M. Scaringella / M. Scarnera
- J. Schnabel / J. Schumann / H. M. Schutte / J. Seneca
- N. Sennan / P. A. Sevle Myhr / I. Sgura / R. Shanidze
- A. Sharma / Y. Shitov / F. Šimkovic / A. Simonelli
- A. Sinopoulou / B. Spisso / M. Spurio / O. Starodubtsev
- D. Stavropoulos / I. Štekl / D. Stocco / M. Taiuti
- G. Takadze / Y. Tayalati / H. Thiersen / S. Thoudam
- I. Tosta e Melo / B. Trocmé / V. Tsourapis / E. Tzamariudaki
- A. Ukleja / A. Vacheret / V. Valsecchi / V. Van Elewyck
- G. Vannoye / E. Vannuccini / G. Vasileiadis / F. Vazquez de
Sola
- A. Veutro / S. Viola / D. Vivolo / A. van Vliet
- A. Y. Wen / E. de Wolf / I. Lhenry-Yvon / S. Zavatarelli
- A. Zegarelli / D. Zito / J. D. Zornoza / J. Zúñiga
- N. Zywucka
Summary
On February 13th, 2023, the KM3NeT/ARCA telescope detected a neutrino
candidate with an estimated energy in the hundreds of PeVs. In this
article, the observation of this ultra-high-energy neutrino is discussed
in light of null observations above tens of PeV from the IceCube and
Pierre Auger observatories. Performing a joint fit of all experiments
under the assumption of an isotropic  flux, the best-fit
single-flavour flux normalisation is
flux, the best-fit
single-flavour flux normalisation is  in the 90% energy range of the KM3NeT event.
Furthermore, the ultra-high-energy data are then fit together with the
IceCube measurements at lower energies, either with a single power law
or with a broken power law, allowing for the presence of a new component
in the spectrum. The joint fit including non-observations by other
experiments in the ultra-high-energy region shows a slight preference
for a break in the PeV regime if the ``High-Energy Starting Events’’
sample is included, and no such preference for the other two IceCube
samples investigated. A stronger preference for a break appears if only
the KM3NeT data is considered in the ultra-high-energy region, though
the flux resulting from such a fit would be inconsistent with null
observations from IceCube and Pierre Auger. In all cases, the observed
tension between KM3NeT and other datasets is of the order of
in the 90% energy range of the KM3NeT event.
Furthermore, the ultra-high-energy data are then fit together with the
IceCube measurements at lower energies, either with a single power law
or with a broken power law, allowing for the presence of a new component
in the spectrum. The joint fit including non-observations by other
experiments in the ultra-high-energy region shows a slight preference
for a break in the PeV regime if the ``High-Energy Starting Events’’
sample is included, and no such preference for the other two IceCube
samples investigated. A stronger preference for a break appears if only
the KM3NeT data is considered in the ultra-high-energy region, though
the flux resulting from such a fit would be inconsistent with null
observations from IceCube and Pierre Auger. In all cases, the observed
tension between KM3NeT and other datasets is of the order of  , and increased
statistics are required to resolve this apparent tension and better
characterise the neutrino landscape at ultra-high energies.
, and increased
statistics are required to resolve this apparent tension and better
characterise the neutrino landscape at ultra-high energies.
Searching
for Hot Water World Candidates with CHEOPS: Refining the radii and
analysing the internal structures and atmospheric lifetimes of TOI-238 b
and TOI-1685 b
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. A. Egger / D. Kubyshkina / Y. Alibert / H. P. Osborn
- A. Bonfanti / T. G. Wilson / A. Brandeker / M. N. Günther
- M. Lendl / D. Kitzmann / L. Fossati / C. Mordasini
- S. G. Sousa / V. Adibekyan / M. Fridlund / C. Pezzotti
- D. Gandolfi / S. Ulmer-Moll / R. Alonso / T. Bárczy
- D. Barrado Navascues / S. C. Barros / W. Baumjohann / W. Benz
- N. Billot / L. Borsato / C. Broeg / A. Collier Cameron
- A. C. M. Correia / Sz. Csizmadia / P. E. Cubillos / M. B.
Davies
- M. Deleuil / A. Deline / O. D. S. Demangeon / B.-O.
Demory
- A. Derekas / B. Edwards / D. Ehrenreich / A. Erikson
- A. Fortier / K. Gazeas / M. Gillon / M. Güdel
- A. Heitzmann / Ch. Helling / K. G. Isaak / L. Kiss
- J. Korth / K. W. F. Lam / J. Laskar / A. Lecavelier des Etangs
- A. Luntzer / R. Luque / D. Magrin / P. F. L. Maxted
- B. Merín / M. Munari / V. Nascimbeni / G. Olofsson
- R. Ottensamer / I. Pagano / E. Pallé / G. Peter
- D. Piazza / G. Piotto / D. Pollacco / D. Queloz
- R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando / H. Rauer / I. Ribas
- N. C. Santos / G. Scandariato / D. Ségransan / A. E. Simon
- A. M. S. Smith / R. Southworth / M. Stalport / S.
Sulis
- M. Gy. Szabó / S. Udry / V. Van Grootel / J. Venturini
- E. Villaver / N. A. Walton / S. Wolf / D. Wolter
Summary
Studying the composition of exoplanets is one of the most promising
approaches to observationally constrain planet formation and evolution
processes. However, this endeavour is complicated for small exoplanets
by the fact that a wide range of compositions is compatible with their
bulk properties. To overcome this issue, we identify triangular regions
in the mass-radius space where part of this degeneracy is lifted for
close-in planets, since low-mass H/He envelopes would not be stable due
to high-energy stellar irradiation. Planets in these Hot Water World
triangles need to contain at least some heavier volatiles and are
therefore interesting targets for atmospheric follow-up observations. We
perform a demographic study to show that only few well-characterised
planets in these regions are currently known and introduce our CHEOPS
GTO programme aimed at identifying more of these potential hot water
worlds. Here, we present CHEOPS observations for the first two targets
of our programme, TOI-238 b and TOI-1685 b. Combined with TESS
photometry and published RVs, we use the precise radii and masses of
both planets to study their location relative to the corresponding Hot
Water World triangles, perform an interior structure analysis and study
the lifetimes of H/He and water-dominated atmospheres under these
conditions. We find that TOI-238 b lies, at the 1-sigma level, inside
the corresponding triangle. While a pure H/He atmosphere would have
evaporated after 0.4-1.3 Myr, it is likely that a water-dominated
atmosphere would have survived until the current age of the system,
which makes TOI-238 b a promising hot water world candidate. Conversely,
TOI-1685 b lies below the mass-radius model for a pure silicate planet,
meaning that even though a water-dominated atmosphere would be
compatible both with our internal structure and evaporation analysis, we
cannot rule out the planet to be a bare core.
MeerKAT
view of Hickson Compact Groups:I. Data description and release
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- R. Ianjamasimanana / L. Verdes-Montenegro / A. Sorgho / K. M.
Hess
- M. G. Jones / J. M. Cannon / J. M. Solanes / M. E. Cluver
- J. Moldón / B. Namumba / J. Román / I. Labadie-García
- C. C. de la Casa / S. Borthakur / J. Wang / R. García-Benito
- A. del Olmo / J. Perea / T. Wiegert / M. Yun
- J. Garrido / S. Sanchez-Expósito / A. Bosma /
E. Athanassoula
- G. I. G. Józsa / T. H. Jarrett / C. K. Xu / O. M. Smirnov
Summary
Context: Hickson Compact Groups (HCGs) are dense
gravitationally-bound collections of 4-10 galaxies ideal for studying
gas and star formation quenching processes. Aims: We aim to understand
the transition of HCGs from possessing complex HI tidal structures
(so-called phase 2 groups) to a phase where galaxies have lost most or
all their HI (phase 3). We also seek to detect diffuse H i gas that was
previously missed by the Very Large Array (VLA). Methods: We observed
three phase 2 and three phase 3 HCGs with MeerKAT and reduced the data
using the Containerized Automated Radio Astronomy Calibration (CARACal)
pipeline. We produced data cubes, moment maps, integrated spectra, and
compared our findings with previous VLA and Green Bank Telescope (GBT)
observations. Results: Compared with previous VLA observations, MeerKAT
reveals much more extended tidal features in phase 2 and some new high
surface brightness features in phase 3 groups. However, no diffuse HI
component was found in phase 3 groups. We also detected many surrounding
galaxies for both phase 2 and phase 3 groups, most of which are normal
disk galaxies. Conclusions: The difference between phase 2 and phase 3
groups is still substantial, supporting previous findings that the
transition between the two phases must be abrupt.
ALMACAL
XIII. Evolution of the CO luminosity function and the molecular gas mass
density out to  ~ 6
~ 6
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Victoria Bollo / Céline Péroux / Martin Zwaan / Aleksandra
Hamanowicz
- Jianhang Chen / Simon Weng / Claudia del P. Lagos /
Matías Bravo
- R. J. Ivison / Andrew Biggs
Summary
Cold molecular gas, largely traced by CO emission, is the primary
fuel for star formation, making it essential for understanding galaxy
evolution. ALMA has made significant progress in the study of the cosmic
evolution of cold molecular gas. Here, we exploit the ALMACAL survey to
address issues relating to small sample sizes and cosmic variance,
utilising calibration data from ALMA to compile a statistically
significant and essentially unbiased sample of CO-selected galaxies. By
employing a novel statistical approach to emission-line classification
using semi-analytical models, we place strong constraints on the CO
luminosity function and the cosmic evolution of molecular gas mass
density ( ) back to
) back to  . The cosmic
molecular gas mass density increases with redshift, peaking around
. The cosmic
molecular gas mass density increases with redshift, peaking around  , then slowly
declines towards higher redshifts by
, then slowly
declines towards higher redshifts by  dex. Our findings
confirm the key role of molecular gas in fuelling star formation. The
new
dex. Our findings
confirm the key role of molecular gas in fuelling star formation. The
new  estimates allow us
to revisit the cosmic baryon cycle, showing that the ratio of molecular
gas-to-stellar mass density is consistent with the so-called ‘bathtub
model’ of baryons, which implies a continuous replenishment of gas. The
cosmic gas depletion timescale, estimated on a global scale, is shown to
be fairly constant at all redshifts. We emphasise the importance of
surveys using multiple small fields rather than a single contiguous area
to mitigate the effects of cosmic variance.
estimates allow us
to revisit the cosmic baryon cycle, showing that the ratio of molecular
gas-to-stellar mass density is consistent with the so-called ‘bathtub
model’ of baryons, which implies a continuous replenishment of gas. The
cosmic gas depletion timescale, estimated on a global scale, is shown to
be fairly constant at all redshifts. We emphasise the importance of
surveys using multiple small fields rather than a single contiguous area
to mitigate the effects of cosmic variance.
Articles for week 6 2025
Machine
learning based Photometric Redshifts for Galaxies in the North Ecliptic
Pole Wide field: catalogs of spectroscopic and photometric
redshifts
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Taewan Kim / Jubee Sohn / Ho Seong Hwang / Simon C.-C. Ho
- Denis Burgarella / Tomotsugu Goto / Tetsuya
Hashimoto / Woong-Seob Jeong
- Seong Jin Kim / Matthew A. Malkan / Takamitsu Miyaji / Nagisa
Oi
- Hyunjin Shim / Hyunmi Song / Narae Hwang / Byeong-Gon Park
Summary
We perform an MMT/Hectospec redshift survey of the North Ecliptic
Pole Wide (NEPW) field covering 5.4 square degrees, and use it to
estimate the photometric redshifts for the sources without spectroscopic
redshifts. By combining 2572 newly measured redshifts from our survey
with existing data from the literature, we create a large sample of 4421
galaxies with spectroscopic redshifts in the NEPW field. Using this
sample, we estimate photometric redshifts of 77755 sources in the
band-merged catalog of the NEPW field with a random forest model. The
estimated photometric redshifts are generally consistent with the
spectroscopic redshifts, with a dispersion of 0.028, an outlier fraction
of 7.3%, and a bias of -0.01. We find that the standard deviation of the
prediction from each decision tree in the random forest model can be
used to infer the fraction of catastrophic outliers and the measurement
uncertainties. We test various combinations of input observables,
including colors and magnitude uncertainties, and find that the details
of these various combinations do not change the prediction accuracy
much. As a result, we provide a catalog of 77755 sources in the NEPW
field, which includes both spectroscopic and photometric redshifts up to
z~2. This dataset has significant legacy value for studies in the NEPW
region, especially with upcoming space missions such as JWST, Euclid,
and SPHEREx.
Pearls
on a string: Dark and bright galaxies on a strikingly straight and
narrow filament
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Maryam Arabsalmani / Sambit Roychowdhury / Benjamin
Schneider / Volker Springel
- Emeric Le Floc’h / Frederic Bournaud / Andreas Burkert /
Jean-Charles Cuillandre
- Pierre-Alain Duc / Eric Emsellem / Daniela Galárraga-Espinosa /
Elena Pian
- Florent Renaud / Martin A. Zwaan
Summary
We identify a chain of galaxies along an almost straight line in the
nearby Universe with a projected length of ~5 Mpc. The galaxies are
distributed within projected distances of only 7-105 kpc from the axis
of the identified filament. They have redshifts in a very small range of
z=0.0361-0.0370 so that their radial velocities are consistent with
galaxy proper motions. The filament galaxies are mainly star-forming and
have stellar masses in a range of  . We
search for systems with similar geometrical properties in the full-sky
mock galaxy catalogue of the MillenniumTNG simulations and find that
although such straight filaments are unusual and rare, they are
predicted by
. We
search for systems with similar geometrical properties in the full-sky
mock galaxy catalogue of the MillenniumTNG simulations and find that
although such straight filaments are unusual and rare, they are
predicted by  CDM simulations (4% incidence). We study
the cold HI gas in a 1.3 Mpc section of the filament through HI-21cm
emission line observations and detect eleven HI sources, many more than
expected from the HI mass function in a similar volume. They have HI
masses
CDM simulations (4% incidence). We study
the cold HI gas in a 1.3 Mpc section of the filament through HI-21cm
emission line observations and detect eleven HI sources, many more than
expected from the HI mass function in a similar volume. They have HI
masses  and are
mostly within ~120 kpc projected distance from the filament axis. None
of these HI sources has a confirmed optical counterpart. Their darkness
together with their large HI-21cm line-widths indicate that they contain
gas that might not yet be virialized. These clouds must be marking the
peaks of the dark matter and HI distributions over large scales within
the filament. The presence of such gas clouds around the filament spines
is predicted by simulations, but this is the first time that the
existence of such clouds in a filament is observationally confirmed.
and are
mostly within ~120 kpc projected distance from the filament axis. None
of these HI sources has a confirmed optical counterpart. Their darkness
together with their large HI-21cm line-widths indicate that they contain
gas that might not yet be virialized. These clouds must be marking the
peaks of the dark matter and HI distributions over large scales within
the filament. The presence of such gas clouds around the filament spines
is predicted by simulations, but this is the first time that the
existence of such clouds in a filament is observationally confirmed.
DESI
Strong Lens Foundry I: HST Observations and Modeling with GIGA-Lens
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- X. Huang / S. Baltasar / N. Ratier-Werbin / C. Storfer
- W. Sheu / S. Agarwal / M. Tamargo-Arizmendi / D. J. Schlegel
- J. Aguilar / S. Ahlen / G. Aldering / S. Banka
- S. BenZvi / D. Bianchi / A. Bolton / D. Brooks
- A. Cikota / T. Claybaugh / A. de la Macorra / A. Dey
- P. Doel / J. Edelstein / A. Filipp / J. E. Forero-Romero
- E. Gaztanaga / S. Gontcho A Gontcho / A. Gu / G. Gutierrez
- K. Honscheid / E. Jullo / S. Juneau / R. Kehoe
- D. Kirkby / T. Kisner / A. Kremin / K. J. Kwon
- A. Lambert / M. Landriau / D. Lang / L. Le Guillou
- J. Liu / A. Meisner / R. Miquel / J. Moustakas
- A. D. Myers / S. Perlmutter / I. Perez-Rafols / F. Prada
- G. Rossi / D. Rubin / E. Sanchez / M. Schubnell
- Y. Shu / E. Silver / D. Sprayberry / N. Suzuki
- G. Tarle / B. A. Weaver / H. Zou
Summary
We present the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Strong
Lens Foundry. We discovered  new strong
gravitational lens candidates in the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys using
residual neural networks (ResNet). We observed a subset (51) of our
candidates using the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). All of them were
confirmed to be strong lenses. We also briefly describe spectroscopic
follow-up observations by DESI and Keck NIRES programs. From this very
rich dataset, a number of studies will be carried out, including
evaluating the quality of the ResNet search candidates and lens
modeling. In this paper, we present our initial effort in these
directions. In particular, as a demonstration, we present the lens model
for DESI-165.4754-06.0423, with imaging data from HST, and lens and
source redshifts from DESI and Keck NIRES, respectively. In this effort,
we have applied a forward-modeling Bayesian approach (GIGA-Lens), using
GPUs, for the first time in both regards, to a strong lens with HST
data, or any high resolution imaging.
new strong
gravitational lens candidates in the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys using
residual neural networks (ResNet). We observed a subset (51) of our
candidates using the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). All of them were
confirmed to be strong lenses. We also briefly describe spectroscopic
follow-up observations by DESI and Keck NIRES programs. From this very
rich dataset, a number of studies will be carried out, including
evaluating the quality of the ResNet search candidates and lens
modeling. In this paper, we present our initial effort in these
directions. In particular, as a demonstration, we present the lens model
for DESI-165.4754-06.0423, with imaging data from HST, and lens and
source redshifts from DESI and Keck NIRES, respectively. In this effort,
we have applied a forward-modeling Bayesian approach (GIGA-Lens), using
GPUs, for the first time in both regards, to a strong lens with HST
data, or any high resolution imaging.
COSMOS-Web: The
emergence of the Hubble Sequence
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Huertas-Company / M. Shuntov / Y. Dong / M. Walmsley
- O. Ilbert / H. J. McCracken / H. B. Akins / N.
Allen
- C. M. Casey / L. Costantin / E. Daddi / A. Dekel
- M. Franco / I. L. Garland / T. Géron / G. Gozaliasl
- M. Hirschmann / J. S. Kartaltepe / A. M. Koekemoer / C. Lintott
- D. Liu / R. Lucas / K. Masters / F. Pacucci
- L. Paquereau / P. G. P’erez-Gonz’alez / J. D. Rhodes / B. E.
Robertson
- B. Simmons / R. Smethurst / S. Toft / L. Yang
Summary
Leveraging the wide area coverage of the COSMOS-Web survey, we
quantify the abundance of different morphological types from  with unprecedented
statistics and establish robust constraints on the epoch of emergence of
the Hubble sequence. We measure the global (spheroids, disk-dominated,
bulge-dominated, peculiar) and resolved (stellar bars) morphologies for
about 400,000 galaxies down to F150W=27 using deep learning,
representing a two-orders-of-magnitude increase over previous studies.
We then provide reference Stellar Mass Functions (SMFs) of different
morphologies between
with unprecedented
statistics and establish robust constraints on the epoch of emergence of
the Hubble sequence. We measure the global (spheroids, disk-dominated,
bulge-dominated, peculiar) and resolved (stellar bars) morphologies for
about 400,000 galaxies down to F150W=27 using deep learning,
representing a two-orders-of-magnitude increase over previous studies.
We then provide reference Stellar Mass Functions (SMFs) of different
morphologies between  and
and  and best-fit
parameters to inform models of galaxy formation. All catalogs and data
are made publicly available. (a)At redshift z > 4.5, the massive
galaxy population (
and best-fit
parameters to inform models of galaxy formation. All catalogs and data
are made publicly available. (a)At redshift z > 4.5, the massive
galaxy population ( ) is dominated by disturbed morphologies (~70%) –
even in the optical rest frame – and very compact objects (~30%) with
effective radii smaller than ~500pc. This confirms that a significant
fraction of the star formation at cosmic dawn occurs in very dense
regions, although the stellar mass for these systems could be
overestimated.(b)Galaxies with Hubble-type morphologies – including
bulge and disk-dominated galaxies – arose rapidly around
) is dominated by disturbed morphologies (~70%) –
even in the optical rest frame – and very compact objects (~30%) with
effective radii smaller than ~500pc. This confirms that a significant
fraction of the star formation at cosmic dawn occurs in very dense
regions, although the stellar mass for these systems could be
overestimated.(b)Galaxies with Hubble-type morphologies – including
bulge and disk-dominated galaxies – arose rapidly around  and dominate the
morphological diversity of massive galaxies as early as
and dominate the
morphological diversity of massive galaxies as early as  . (c)Using stellar
bars as a proxy, we speculate that stellar disks in massive galaxies
might have been common (>50%) among the star-forming population since
cosmic noon (
. (c)Using stellar
bars as a proxy, we speculate that stellar disks in massive galaxies
might have been common (>50%) among the star-forming population since
cosmic noon ( -2.5) and formed as
early as
-2.5) and formed as
early as  (d)Massive quenched
galaxies are predominantly bulge-dominated from z~4 onward, suggesting
that morphological transformations briefly precede or are simultaneous
to quenching mechanisms at the high-mass end. (e) Low-mass (
(d)Massive quenched
galaxies are predominantly bulge-dominated from z~4 onward, suggesting
that morphological transformations briefly precede or are simultaneous
to quenching mechanisms at the high-mass end. (e) Low-mass ( ) quenched galaxies are typically disk-dominated,
pointing to different quenching routes in the two ends of the stellar
mass spectrum from cosmic dawn.
) quenched galaxies are typically disk-dominated,
pointing to different quenching routes in the two ends of the stellar
mass spectrum from cosmic dawn.
The
XXL Survey LIV. X-ray Luminosity Function and Luminosity-Mass Relation
of Optically Selected Galaxy Groups
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. Wood / B. J. Maughan / J. P. Crossett / D. Eckert
- M. Pierre / M. E. Ramos-Ceja / A. S. G. Robotham / C.
Adami
- L. Faccioli / E. Koulouridis / S. L. McGee / F. Pacaud
- S. Phillipps
Summary
The overlap between the GAMA spectroscopic survey and the XXL X-ray
survey was used to study the X-ray properties of optically-selected
groups of galaxies. Forced X-ray aperture photometry was applied to an
optically-selected sample of 235 groups (containing at least five member
galaxies) to measure their X-ray luminosities in the regime of low
signal to noise X-ray data. The sample encompasses X-ray luminosities
over an order of magnitude fainter than typical X-ray selected samples,
and avoids X-ray selection biases. This gives access to low mass groups
where the effects of non-gravitational processes, such as AGN-feedback,
should be most apparent and could inhibit their detection in an X-ray
survey. We measured the X-ray luminosity function (XLF) of the sample,
and found it to be consistent with the extrapolation of the XLF from
X-ray selected samples at higher luminosities. The XLF was combined with
a theoretical halo mass function to infer the form of the scaling
relation between X-ray luminosity and mass (LM relation) for the GAMA
groups. We found a slope of  , which
is steeper than self similarity in this mass regime. When comparing with
other measurements of the LM relation, we find evidence for a steepening
of the slope in the low mass regime, likely due to the impact of
non-gravitational processes. Our approach can be translated to eROSITA
data using multi-wavelength surveys to constrain the X-ray properties of
galaxy groups in the limits of high redshift and low mass.
, which
is steeper than self similarity in this mass regime. When comparing with
other measurements of the LM relation, we find evidence for a steepening
of the slope in the low mass regime, likely due to the impact of
non-gravitational processes. Our approach can be translated to eROSITA
data using multi-wavelength surveys to constrain the X-ray properties of
galaxy groups in the limits of high redshift and low mass.
Radio
emission from a massive node of the cosmic web. A discovery powered by
machine learning
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- C. Stuardi / A. Botteon / M. Sereno / K. Umetsu
- R. Gavazzi / A. Bonafede / C. Gheller
Summary
Aims. We aim to understand the nature of the diffuse radio emission
surrounding the massive galaxy cluster PSZ2 G083.29-31.03, at z=0.412,
already known to host a radio halo. Our investigation was triggered by
Radio U-Net, a novel machine learning algorithm for detecting diffuse
radio emission, which was previously applied to the LOFAR Two Meter Sky
Survey (LoTSS). Methods. We re-processed LoTSS (120-168 MHz) data and
analyzed archival XMM-Newton (0.7-1.2 keV) observations. We also
analyzed optical and near-infrared data from the DESI Legacy Imaging
Surveys and asses the mass distribution with weak-lensing analysis based
on archival Subaru Suprime-Cam and CFHT MegaPrime/MegaCam observations.
Results. We report the discovery of large-scale diffuse radio emission
around PSZ2 G083.29-31.03, with a projected largest linear size of 5 Mpc
at 144 MHz. The radio emission is aligned with the thermal X-ray
emission and the distribution of galaxies, unveiling the presence of two
low-mass systems, at similar redshifts on either side of the central
cluster. The weak lensing analysis supports this scenario, demonstrating
the presence of an extended and complex mass distribution. Conclusions.
We propose to interpret the two faint radio sources as connected to the
central cluster, thus illuminating the presence of two substructures
merging into a massive node of the cosmic web. However, because of
uncertainties in redshift and mass estimates, combined with the low
resolution required to detect these sources, the classification of the
two sources as independent radio halos associated with nearby low-mass
clusters or even as a mixture of different types of diffuse radio
emission cannot be definitively ruled out.
KOBE-1:
The first planetary system from the KOBE survey. Two planets likely
residing in the sub-Neptune mass regime around a late K-dwarf
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- O. Balsalobre-Ruza / J. Lillo-Box / A. M. Silva / S.
Grouffal
- J. Aceituno / A. Castro-González / C. Cifuentes / M. R.
Standing
- J. P. Faria / P. Figueira / A. Santerne / E.
Marfil
- A. Abreu / A. Aguichine / L. González-Ramírez / J. C. Morales
- N. Santos / N. Huélamo / E. Delgado Mena / D. Barrado
- V. Adibekyan / S. C. C. Barros / Á. Berihuete / M.
Morales-Calderón
- E. Nagel / E. Solano / S. G. Sousa / J. F. Agüí Fernández
- M. Azzaro / G. Bergond / S. Cikota / A. Fernández-Martín
- J. Flores / S. Góngora / A. Guijarro / I. Hermelo
- V. Pinter / J. I. Vico-Linares
Summary
K-dwarf stars are promising targets in the exploration of potentially
habitable planets. Their properties, falling between G and M dwarfs,
provide an optimal trade-off between the prospect of habitability and
ease of detection. The KOBE experiment is a blind-search survey
exploiting this niche, monitoring the radial velocity of 50 late-type
K-dwarf stars. It employs the CARMENES spectrograph, with an
observational strategy designed to detect planets in the habitable zone
of their system. In this work, we exploit the KOBE data set to
characterize planetary signals in the K7V star HIP 5957 (KOBE-1) and to
constrain the planetary population within its habitable zone. We used 82
CARMENES spectra over a time span of three years. We employed a GLS
periodogram to search for significant periodic signals that would be
compatible with Keplerian motion on KOBE-1. We carried out a model
comparison within a Bayesian framework to ensure the significance of the
planetary model over alternative configurations of lower complexity. We
also inspected two available TESS sectors in search of planetary
signals. We identified two signals: at 8.5d and 29.7d. We confirmed
their planetary nature through ruling out other non-planetary
configurations. Their minimum masses are 8.80+/-0.76ME and 12.4+/-1.1ME,
corresponding to absolute masses within the planetary regime at a high
certainty (>99.7%). By analyzing the sensitivity of the CARMENES time
series to additional signals, we discarded planets above 8.5ME within
the habitable zone. We identified a single transit-like feature in TESS,
whose origin is still uncertain, but still compatible within 1sigma with
a transit from planet c. We have explored future prospects for
characterizing this system, concluding that nulling interferometry with
the LIFE mission could be capable of directly imaging both planets and
characterizing their atmospheres in future studies.
Ultra
High-Redshift or Closer-by, Dust-Obscured Galaxies? Deciphering the
Nature of Faint, Previously Missed F200W-Dropouts in CEERS
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- G. Gandolfi / G. Rodighiero / L. Bisigello / A. Grazian
- S. L. Finkelstein / M. Dickinson / M. Castellano / E. Merlin
- A. Calabrò / C. Papovich / A. Bianchetti / E. Bañados
- P. Benotto / F. Buitrago / E. Daddi / G. Girardi
- M. Giulietti / M. Hirschmann / B. W. Holwerda / P. Arrabal Haro
- A. Lapi / R. A. Lucas / Y. Lyu / M. Massardi
- F. Pacucci / P. G. Pérez-González / T. Ronconi / M. Tarrasse
- S. Wilkins / B. Vulcani / L. Y. A. Yung / J. A. Zavala
- B. Backhaus / M. Bagley / V. Buat / D.
Burgarella
- J. Kartaltepe / Y. Khusanova / A. Kirkpatrick / D. Kocevski
- A. M. Koekemoer / E. Lambrides / N. Pirzkal / G. Yang
Summary
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is revolutionizing our
understanding of the Universe by unveiling faint, near-infrared dropouts
previously beyond our reach, ranging from exceptionally dusty sources to
galaxies up to redshift  . In this paper,
we identify F200W-dropout objects in the Cosmic Evolution Early Release
Science (CEERS) survey which are absent from existing catalogs. Our
selection method can effectively identify obscured low-mass (
. In this paper,
we identify F200W-dropout objects in the Cosmic Evolution Early Release
Science (CEERS) survey which are absent from existing catalogs. Our
selection method can effectively identify obscured low-mass ( ) objects at
) objects at  , massive
dust-rich sources up to
, massive
dust-rich sources up to  , and
ultra-high-redshift (
, and
ultra-high-redshift ( ) candidates.
Primarily relying on NIRCam photometry from the latest CEERS data
release and supplementing with Mid-Infrared/(sub-)mm data when
available, our analysis pipeline combines multiple SED-fitting codes,
star formation histories, and CosMix - a novel tool for astronomical
stacking. Our work highlights three
) candidates.
Primarily relying on NIRCam photometry from the latest CEERS data
release and supplementing with Mid-Infrared/(sub-)mm data when
available, our analysis pipeline combines multiple SED-fitting codes,
star formation histories, and CosMix - a novel tool for astronomical
stacking. Our work highlights three  dusty dwarf
galaxies which have larger masses compared to the typical dusty dwarfs
previously identified in CEERS. Additionally, we reveal five faint
sources with significant probability of lying above
dusty dwarf
galaxies which have larger masses compared to the typical dusty dwarfs
previously identified in CEERS. Additionally, we reveal five faint
sources with significant probability of lying above  , with best-fit
masses compatible with
, with best-fit
masses compatible with  CDM and a standard baryons-to-star
conversion efficiency. Their bi-modal redshift probability distributions
suggest they could also be
CDM and a standard baryons-to-star
conversion efficiency. Their bi-modal redshift probability distributions
suggest they could also be  dwarf galaxies
with extreme dust extinction. We also identify a strong line emitter
galaxy at
dwarf galaxies
with extreme dust extinction. We also identify a strong line emitter
galaxy at  mimicking the
near-infrared emission of a
mimicking the
near-infrared emission of a  galaxy. Our
sample holds promising candidates for future follow-ups. Confirming
ultra high-redshift galaxies or lower-z dusty dwarfs will offer valuable
insights into early galaxy formation, evolution with their central black
holes and the nature of dark matter, and/or cosmic dust production
mechanisms in low-mass galaxies, and will help us to understand
degeneracies and contamination in high-z object searches.
galaxy. Our
sample holds promising candidates for future follow-ups. Confirming
ultra high-redshift galaxies or lower-z dusty dwarfs will offer valuable
insights into early galaxy formation, evolution with their central black
holes and the nature of dark matter, and/or cosmic dust production
mechanisms in low-mass galaxies, and will help us to understand
degeneracies and contamination in high-z object searches.
SIGNALS
on the mixing of oxygen and nitrogen in the spiral galaxy NGC 6946
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Fabio Bresolin / David Fernández-Arenas / Laurie Rousseau-Nepton /
Ray Garner
- Almudena Zurita / Carmelle Robert / Laurent Drissen / René Pierre
Martin
- Philippe Amram / Salvador Duarte Puertas / Gabriel
Savard / Sébastien Vicens
- Mykola Posternak
Summary
As part of the SIGNALS survey, which comprises a sample of
approximately 40 nearby galaxies observed with the Fourier transform
spectrometer SITELLE, we present a study of metal mixing in the spiral
galaxy NGC 6946. Taking advantage of the blue sensitivity of our setup,
we measure the oxygen and nitrogen abundances of 638 H II regions, and
focus our analysis on the abundance fluctuations about the radial
gradients. We detect an azimuthal variation of about 0.1 dex in these
abundances across the NE spiral arm, with the leading edge being more
metal-poor than the trailing edge. This result aligns with galaxy
simulations, where radial gas flows along the spiral arms lead to
dilution on the leading edge and enrichment on the trailing edge, due to
the presence of radial metallicity gradients. Our 2D analysis reveals
that oxygen and nitrogen exhibit comparable spatial correlation scales,
despite the different injection energies and distinct nucleosynthetic
origins – core-collapse supernovae in the case of oxygen and primarily
AGB stars for nitrogen. The observed similarity suggests that stellar
processes drive these two elements into the ISM over equivalent spatial
scales.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Nemanja Jovanovic / Daniel Echeverri / Jacques-Robert Delorme / Luke
Finnerty
- Tobias Schofield / Jason J. Wang / Yinzi Xin / Jerry Xuan
- J. Kent Wallacee / Dimitri Mawet / Aniket Sanghi / Ashley Baker
- Randall Bartos / Charlotte Z. Bond / Benjamin Calvin / Sylvain
Cetre
- Greg Doppmann / Michael P. Fitzgerald / Jason Fucik / Maodong
Gao
- Jinhao Ge / Charlotte Guthery / Katelyn Horstman / Chih-Chun
Hsud
- Joshua Liberman / Stephanie Leifer / Scott Lilley / Ronald
Lopez
- Eduardo Marin / Emily C. Martin / Bertrand Mennesson / Evan
Morris
- Reston Nash / Jacklyn Pezzato / Michael Porter / Mitsuko
Roberts
- Garreth Ruane / Jean-Baptiste Ruffio / Ben Sappey / Eugene
Serabyn
- Boqiang Shen / Andrew Skemer / Ji Wang / Edward Wetherell
- Peter Wizinowich / Maissa Salama / Vincent
Chambouleyron / Rebecca Jensen-Clem
- Chas Beichman
Summary
The Keck Planet Imager and Characterizer (KPIC) is a series of
upgrades for the Keck II Adaptive Optics (AO) system and the NIRSPEC
spectrograph to enable diffraction limited, high resolution (R>30000)
spectroscopy of exoplanets and low mass companions in the K and L bands.
Phase I consisted of single mode fiber injection/extraction units
(FIU/FEU) used in conjunction with a H band pyramid wavefront sensor.
The use of single mode fibers provides a gain in stellar rejection, a
substantial reduction in sky background, and an extremely stable line
spread function in the spectrograph. Phase II, deployed and commissioned
in 2022, brought a 1000 actuator deformable mirror, beam shaping optics,
a vortex mask, and other upgrades to the FIU/FEU. An additional service
mission in 2024 extended operations down to y band, delivered an
atmospheric dispersion corrector, and provided access to two laser
frequency combs. KPIC phase II brings higher planet throughput, lower
stellar leakage and many new observing modes which extend its ability to
characterize exoplanets at high spectral resolution, building on the
success of phase I. In this paper we present a description of the final
phase II version of KPIC, along with results of system level laboratory
testing and characterization showing the instrument’s phase II
throughput, stability, repeatability, and other key performance metrics
prior to delivery and during installation at Keck. We outlined the
capabilities of the various observing modes enabled by the new modules
as well as efforts to compensate for static aberrations and non common
path errors at Keck, which were issues that plagued phase I. Finally, we
show results from commissioning.
Articles for week 5 2025
Euclid
preparation. 3-dimensional galaxy clustering in configuration space.
Part I. 2-point correlation function estimation
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / S. de la Torre / F. Marulli / E.
Keihänen
- A. Viitanen / M. Viel / A. Veropalumbo / E. Branchini
- D. Tavagnacco / F. Rizzo / J. Valiviita / V. Lindholm
- V. Allevato / G. Parimbelli / E. Sarpa / Z. Ghaffari
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / A. Basset / D. Bonino
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / A. Caillat / S. Camera
- V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas
- F. J. Castander / M. Castellano / G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti
- A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois
- M. Crocce / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / F. Dubath / C. A. J. Duncan
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / M. Farina / S. Farrens
- F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / N. Fourmanoit / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / P. Franzetti / M. Fumana / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- P. Gómez-Alvarez / B. R. Granett / A. Grazian / F. Grupp
- L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / S. Ilić / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala
- B. Joachimi / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / D. Maino
- E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic
- M. Martinelli / N. Martinet / R. Massey / S.
Maurogordato
- E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin / G. Meylan / M. Moresco
- B. Morin / L. Moscardini / E. Munari / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / W. J. Percival / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr
- A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider
- T. Schrabback / M. Scodeggio / A. Secroun / E. Sefusatti
- G. Seidel / M. Seiffert / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / C.
Surace
- P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo
- F. Torradeflot / A. Tsyganov / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- T. Vassallo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- G. Zamorani / E. Zucca / A. Biviano / M. Bolzonella
- E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / M. Calabrese / D. Di Ferdinando
- J. A. Escartin Vigo / R. Farinelli / F. Finelli / L. Gabarra
- J. Gracia-Carpio / S. Matthew / N. Mauri / A. Mora
- A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / V. Scottez / P.
Simon
- A. Spurio Mancini / M. Tenti / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- I. T. Andika / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono / F.
Atrio-Barandela
- A. Balaguera-Antolinez / D. Bertacca / M. Bethermin / A.
Blanchard
- L. Blot / H. Böhringer / S. Borgani / M. L. Brown
- S. Bruton / R. Cabanac / A. Calabro / B. Camacho Quevedo
- G. Cañas-Herrera / A. Cappi / F. Caro / C. S. Carvalho
- T. Castro / K. C. Chambers / F. Cogato / S. Contarini
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / S. Davini / F. De Paolis
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio / H. Dole
- S. Escoffier / A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / A. Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto
- V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga / F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti
- G. Gozaliasl / A. Gregorio / M. Guidi / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- A. Jimenez Muñoz / S. Joudaki / J. J. E. Kajava / Y. Kang
- V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / C. C. Kirkpatrick / S. Kruk
- M. Lattanzi / A. M. C. Le Brun / S. Lee / J. Le Graet
- L. Legrand / M. Lembo / J. Lesgourgues / T. I. Liaudat
- A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci
- R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas / C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin
- R. B. Metcalf / M. Miluzio / P. Monaco / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / C. Murray / S. Nadathur / K. Naidoo
- A. Navarro-Alsina / S. Nesseris / K. Paterson / L. Patrizii
- A. Pisani / V. Popa / D. Potter / P. Reimberg
- I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci / M. Sahlén / A. Schneider
- M. Schultheis / D. Sciotti / E. Sellentin / M. Sereno
- A. Silvestri / L. C. Smith / K. Tanidis / C. Tao
- N. Tessore / G. Testera / R. Teyssier / S. Toft
- S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci / C. Valieri
- D. Vergani / G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf / N. A. Walton
Summary
The 2-point correlation function of the galaxy spatial distribution
is a major cosmological observable that enables constraints on the
dynamics and geometry of the Universe. The Euclid mission aims at
performing an extensive spectroscopic survey of approximately 20–30
million H -emitting galaxies up to about redshift
two. This ambitious project seeks to elucidate the nature of dark energy
by mapping the 3-dimensional clustering of galaxies over a significant
portion of the sky. This paper presents the methodology and software
developed for estimating the 3-dimensional 2-point correlation function
within the Euclid Science Ground Segment. The software is designed to
overcome the significant challenges posed by the large and complex
Euclid data set, which involves millions of galaxies. Key challenges
include efficient pair counting, managing computational resources, and
ensuring the accuracy of the correlation function estimation. The
software leverages advanced algorithms, including kd-tree, octree, and
linked-list data partitioning strategies, to optimise the pair-counting
process. The implementation also includes parallel processing
capabilities using shared-memory open multi-processing to further
enhance performance and reduce computation times. Extensive validation
and performance testing of the software are presented. The results
indicate that the software is robust and can reliably estimate the
2-point correlation function, which is essential for deriving
cosmological parameters with high precision. Furthermore, the paper
discusses the expected performance of the software during different
stages of the Euclid Wide Survey observations and forecasts how the
precision of the correlation function measurements will improve over the
mission’s timeline, highlighting the software’s capability to handle
large data sets efficiently.
-emitting galaxies up to about redshift
two. This ambitious project seeks to elucidate the nature of dark energy
by mapping the 3-dimensional clustering of galaxies over a significant
portion of the sky. This paper presents the methodology and software
developed for estimating the 3-dimensional 2-point correlation function
within the Euclid Science Ground Segment. The software is designed to
overcome the significant challenges posed by the large and complex
Euclid data set, which involves millions of galaxies. Key challenges
include efficient pair counting, managing computational resources, and
ensuring the accuracy of the correlation function estimation. The
software leverages advanced algorithms, including kd-tree, octree, and
linked-list data partitioning strategies, to optimise the pair-counting
process. The implementation also includes parallel processing
capabilities using shared-memory open multi-processing to further
enhance performance and reduce computation times. Extensive validation
and performance testing of the software are presented. The results
indicate that the software is robust and can reliably estimate the
2-point correlation function, which is essential for deriving
cosmological parameters with high precision. Furthermore, the paper
discusses the expected performance of the software during different
stages of the Euclid Wide Survey observations and forecasts how the
precision of the correlation function measurements will improve over the
mission’s timeline, highlighting the software’s capability to handle
large data sets efficiently.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Christopher Layden / Jill Juneau / Gustav Pettersson / Nathan
Lourie
- Benjamin Schneider / Beverly LaMarr / F. Elio
Angile / Fadi Farag
- Michelle Luo / Zhi Zheng Ong / Gabor Furesz
Summary
The Teledyne COSMOS-66 is a next-generation CMOS camera designed for
astronomical imaging, featuring a large-format sensor ( pixels, each
pixels, each  ), high quantum
efficiency, high frame rates, and a correlated multi-sampling mode that
achieves low read noise. We performed a suite of bench-top and on-sky
tests to characterize this sensor and analyze its suitability for use in
astronomical instruments. This paper presents measurements of linearity,
conversion gain, read noise, dark current, quantum efficiency, image
lag, and crosstalk. We found that the sensor exhibits nonlinear response
below 5% of saturation. This nonlinearity is plausibly attributable to
the trapping of electrons in each pixel. We developed and implemented a
pixel-by-pixel nonlinearity correction, enabling accurate photometric
measurements across the dynamic range. After implementing this
correction, operating in the correlated multi-sampling mode, the sensor
achieved an effective read noise of
), high quantum
efficiency, high frame rates, and a correlated multi-sampling mode that
achieves low read noise. We performed a suite of bench-top and on-sky
tests to characterize this sensor and analyze its suitability for use in
astronomical instruments. This paper presents measurements of linearity,
conversion gain, read noise, dark current, quantum efficiency, image
lag, and crosstalk. We found that the sensor exhibits nonlinear response
below 5% of saturation. This nonlinearity is plausibly attributable to
the trapping of electrons in each pixel. We developed and implemented a
pixel-by-pixel nonlinearity correction, enabling accurate photometric
measurements across the dynamic range. After implementing this
correction, operating in the correlated multi-sampling mode, the sensor
achieved an effective read noise of  and dark current of
and dark current of
 at
at
 . The
quantum efficiency exceeded 50% from 250 nm to 800 nm, peaking at 89% at
600 nm. We observed significant optical crosstalk between the pixels,
likely caused by photoelectron diffusion. To demonstrate the sensor’s
astronomical performance, we mounted it on the WINTER 1m telescope at
Palomar Observatory. These tests confirmed that the linearity
calibration enables accurate stellar photometry and validated our
measured noise levels. Overall, the COSMOS-66 delivers similar noise
performance to large-format CCDs, with higher frame rates and relaxed
cooling requirements. If pixel design improvements are made to mitigate
the nonlinearity and crosstalk, then the camera may combine the
advantages of low-noise CMOS image sensors with the integration
simplicity of large-format CCDs, broadening its utility to a host of
astronomical science cases.
. The
quantum efficiency exceeded 50% from 250 nm to 800 nm, peaking at 89% at
600 nm. We observed significant optical crosstalk between the pixels,
likely caused by photoelectron diffusion. To demonstrate the sensor’s
astronomical performance, we mounted it on the WINTER 1m telescope at
Palomar Observatory. These tests confirmed that the linearity
calibration enables accurate stellar photometry and validated our
measured noise levels. Overall, the COSMOS-66 delivers similar noise
performance to large-format CCDs, with higher frame rates and relaxed
cooling requirements. If pixel design improvements are made to mitigate
the nonlinearity and crosstalk, then the camera may combine the
advantages of low-noise CMOS image sensors with the integration
simplicity of large-format CCDs, broadening its utility to a host of
astronomical science cases.
Glimmers
in the Cosmic Dawn. II. A variability census of supermassive black holes
across the Universe
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Vieri Cammelli / Jonathan C. Tan / Alice R. Young / Matthew J.
Hayes
- Jasbir Singh / Richard S. Ellis / Aayush Saxena / Nicolas
Laporte
- Pierluigi Monaco / Benjamin W. Keller
Summary
Understanding the origin and evolution of supermassive black holes
(SMBH) stands as one of the most important challenges in astrophysics
and cosmology, with little current theoretical consensus. Improved
observational constraints on the cosmological evolution of SMBH
demographics are needed. Here we report results of a search via
photometric variability for SMBHs appearing as active galactic nuclei
(AGN) in the cosmological volume defined by the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
(HUDF). This work includes particular focus on a new observation carried
out in 2023 with the using the WFC3/IR/F140W, which is compared directly
to equivalent data taken 11 years earlier in 2012. Two earlier pairs of
observations from 2009 to 2012 with WFC3/IR/F105W and WFC3/IR/F160W are
also analysed. We identify 521, 188, and 109 AGN candidates as nuclear
sources that exhibit photometric variability at a level of 2, 2.5 and
3~ in at least one filter. This sample
includes 13, 3, and 2 AGN candidates at redshifts
in at least one filter. This sample
includes 13, 3, and 2 AGN candidates at redshifts  , when the Universe
was
, when the Universe
was  ~Myr old.
After variability and luminosity function (down to
~Myr old.
After variability and luminosity function (down to  mag) completeness corrections, we estimate the
co-moving number density of SMBHs,
mag) completeness corrections, we estimate the
co-moving number density of SMBHs,  . At
. At
 ,
,  . At low-
. At low- our observations are sensitive to AGN
fainter than
our observations are sensitive to AGN
fainter than  mag, and we estimate
mag, and we estimate  . We discuss how these results place strong
constraints on a variety of SMBH seeding theories.
. We discuss how these results place strong
constraints on a variety of SMBH seeding theories.
New
constraints on the evolution of the MHI-M* scaling relation combining
CHILES and MIGHTEE-HI data
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Alessandro Bianchetti / Francesco Sinigaglia / Giulia Rodighiero /
Ed Elson
- Mattia Vaccari / D. J. Pisano / Nicholas Luber / Isabella
Prandoni
- Kelley Hess / Maarten Baes / Elizabeth A. K. Adams / Filippo M.
Maccagni
- Alvio Renzini / Laura Bisigello / Min Yun / Emmanuel Momjian
- Hansung B. Gim / Hengxing Pan / Thomas A. Oosterloo / Richard
Dodson
- Danielle Lucero / Bradley S. Frank / Olivier Ilbert
/ Luke J. M. Davies
- Ali A. Khostovan / Mara Salvato
Summary
The improved sensitivity of interferometric facilities to the 21-cm
line of atomic hydrogen (HI) enables studies of its properties in
galaxies beyond the local Universe. In this work, we perform a 21 cm
line spectral stacking analysis combining the MIGHTEE and CHILES surveys
in the COSMOS field to derive a robust HI-stellar mass relation at
z=0.36. In particular, by stacking thousands of star-forming galaxies
subdivided into stellar mass bins, we optimize the signal-to-noise ratio
of targets and derive mean HI masses in the different stellar mass
intervals for the investigated galaxy population. We combine spectra
from the two surveys, estimate HI masses, and derive the scaling
relation log10(MHI) = (0.32 +- 0.04)log10(M*) + (6.65 +- 0.36). Our
findings indicate that galaxies at z=0.36 are HI richer than those at
z=0, but HI poorer than those at z=1, with a slope consistent across
redshift, suggesting that stellar mass does not significantly affect HI
exchange mechanisms. We also observe a slower growth rate HI relative to
the molecular gas, supporting the idea that the accretion of cold gas is
slower than the rate of consumption of molecular gas to form stars. This
study contributes to understanding the role of atomic gas in galaxy
evolution and sets the stage for future development of the field in the
upcoming SKA era.
Articles for week 4 2025
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. Chomez / P. Delorme / A.-M. Lagrange / R. Gratton
- O. Flasseur / G. Chauvin / M. Langlois / J. Mazoyer
- A. Zurlo / S. Desidera / D. Mesa / M. Bonnefoy
- M. Feldt / J. Hagelberg / M. Meyer / A. Vigan
- C. Ginski / M. Kenworthy / D. Albert / S. Bergeon
- J.-L. Beuzit / B. Biller / T. Bhowmik / A.
Boccaletti
- M. Bonavita / W. Brandner / F. Cantalloube / A. Cheetham
- V. D’Orazi / C. Dominik / C. Fontanive / R. Galicher
- Th. Henning / M. Janson / Q. Kral / E. Lagadec
- C. Lazzoni / H. Le Coroller / R. Ligi / A.-L.
Maire
- G.-D. Marleau / F. Menard / S. Messina / N. Meunier
- C. Mordasini / C. Moutou / A. Müller / C. Perrot
- M. Samland / H. M. Schmid / T. Schmidt / V. Squicciarini
- E. Sissa / M. Turatto / S. Udry / L. Abe
- J. Antichi / R. Asensio-Torres / A. Baruffolo / P. Baudoz
- J. Baudrand / A. Bazzon / P. Blanchard / A. J.
Bohn
- S. Brown Sevilla / M. Carbillet / M. Carle / E.
Cascone
- J. Charton / R. Claudi / A. Costille / V. De
Caprio
- A. Delboulbe / K. Dohlen / N. Engler / D.
Fantinel
- P. Feautrier / T. Fusco / P. Gigan / J. H.
Girard
- E. Giro / D. Gisler / L. Gluck / C. Gry
- N. Hubin / E. Hugot / M. Jaquet /
M. Kasper
- D. Le Mignant / M. Llored / F.
Madec / Y. Magnard
- P. Martinez / D. Maurel / O. Möller-Nilsson / D. Mouillet
- T. Moulin / A. Origné / A. Pavlov / D. Perret
- C. Petit / J. Pragt / P. Puget / P. Rabou
- J. Ramos / E. L. Rickman / F. Rigal / S. Rochat
- R. Roelfsema / G. Rousset / A. Roux / B. Salasnich
- J.-F. Sauvage / A. Sevin / C. Soenke / E.
Stadler
- M. Suarez / Z. Wahhaj / L. Weber / F. Wildi
Summary
During the past decade, state-of-the-art planet-finder instruments
like SPHERE@VLT, coupling coronagraphic devices and extreme adaptive
optics systems, unveiled, thanks to large surveys, around 20 planetary
mass companions at semi-major axis greater than 10 astronomical units.
Direct imaging being the only detection technique to be able to probe
this outer region of planetary systems, the SPHERE infrared survey for
exoplanets (SHINE) was designed and conducted from 2015 to 2021 to study
the demographics of such young gas giant planets around 400 young nearby
solar-type stars. In this paper, we present the observing strategy, the
data quality, and the point sources analysis of the full SHINE
statistical sample as well as snapSHINE. Both surveys used the
SPHERE@VLT instrument with the IRDIS dual band imager in conjunction
with the integral field spectrograph IFS and the angular differential
imaging observing technique. All SHINE data (650 datasets),
corresponding to 400 stars, including the targets of the F150 survey,
are processed in a uniform manner with an advanced post-processing
algorithm called PACO ASDI. An emphasis is put on the classification and
identification of the most promising candidate companions. Compared to
the previous early analysis SHINE F150, the use of advanced
post-processing techniques significantly improved by one or 2 magnitudes
(x3-x6) the contrast detection limits, which will allow us to put even
tighter constraints on the radial distribution of young gas giants. This
increased sensitivity directly places SHINE as the largest and deepest
direct imaging survey ever conducted. We detected and classified more
than 3500 physical sources. One additional substellar companion has been
confirmed during the second phase of the survey (HIP 74865 B), and
several new promising candidate companions are awaiting second epoch
confirmations.
Transit-timing
variations in the AU Mic system observed with CHEOPS
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Á. Boldog / Gy. M. Szabó / L. Kriskovics / L. Borsato
- D. Gandolfi / M. Lendl / M. N. Günther / A. Heitzmann
- T. G. Wilson / A. Brandeker / Z. Garai / Y. Alibert
- R. Alonso / T. Bárczy / D. Barrado Navascues / S. C. C. Barros
- W. Baumjohann / W. Benz / N. Billot / C. Broeg
- A. Collier Cameron / A. C. M. Correia / Sz. Csizmadia / P. E.
Cubillos
- M. B. Davies / M. Deleuil / A. Deline / O. D. S.
Demangeon
- B.-O. Demory / A. Derekas / B. Edwards / J. A. Egger
- D. Ehrenreich / A. Erikson / A. Fortier / L. Fossati
- M. Fridlund / K. Gazeas / M. Gillon / M. Güdel
- P. Guterman / Ch. Helling / K. G. Isaak / L. L. Kiss
- E. Kopp / J. Korth / K. W. F. Lam / J. Laskar
- A. Lecavelier des Etangs / A. Luntzer / D. Magrin / G. Mantovan
- L. Marafatto / P. F. L. Maxted / B. Merín / C. Mordasini
- M. Munari / V. Nascimbeni / G. Olofsson / R. Ottensamer
- I. Pagano / E. Pallé / G. Peter / D. Piazza
- G. Piotto / D. Pollacco / K. Poppenhaeger / D. Queloz
- R. Ragazzoni / N. Rando / H. Rauer / I. Ribas
- M. Rieder / N. C. Santos / G. Scandariato / D. Ségransan
- A. E. Simon / A. M. S. Smith / S. G. Sousa / R. Southworth
- M. Stalport / S. Sulis / S. Udry / S.
Ulmer-Moll
- V. Van Grootel / J. Venturini / E. Villaver / N. A. Walton
- T. Zingales
Summary
AU Mic is a very active M dwarf with an edge-on debris disk and two
transiting sub-Neptunes with a possible third planetary companion. The
two transiting planets exhibit significant transit-timing variations
(TTVs) that are caused by the gravitational interaction between the
bodies in the system. Using photometrical observations taken with the
CHaracterizing ExOPlanet Satellite (CHEOPS), our goal is to constrain
the planetary radii, the orbital distances and periods of AU Mic b and
c. We aim to determine the superperiod of the TTVs for AU Mic b and to
update the transit ephemeris for both planets. Based on the observed
TTVs, we study the possible presence of a third planet in the system. We
conducted high precision photometric observations with CHEOPS in 2022
and 2023. We used Allesfitter to fit the planetary transits and to
constrain the planetary and orbital parameters. We combined our new
measurements with results from previous years to determine the periods
and amplitudes of the TTVs. We applied dynamical modelling based on TTV
measurements from the 2018-2023 period to reconstruct the perceived
variations. The orbital distances and periods for AU Mic b and c agree
with the results from previous works. However, the values for the
planetary radii deviate slightly from previous values, which we
attribute to the effect of stellar spots. AU Mic c showed very strong
TTVs, with transits that occurred ~80 minutes later in 2023 than in
2021. Through dynamical analysis of the system, we found that the
observed TTVs can be explained by a third planet with an orbital period
of ~12.6 days and a mass of 0.203+0.022-0.024 M_E. We explored the
orbital geometry of the system and found that AU Mic c has a misaligned
retrograde orbit. Due limited number of observations the exact
configuration and planetary parameters could not be determined. Further
monitoring with CHEOPS may improve these results.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / I. Kovačić / M. Baes / A. Nersesian
- N. Andreadis / L. Nemani / Abdurro’uf / L. Bisigello
- M. Bolzonella / C. Tortora / A. van der Wel / S. Cavuoti
- C. J. Conselice / A. Enia / L. K. Hunt / P. Iglesias-Navarro
- E. Iodice / J. H. Knapen / F. R. Marleau / O. Müller
- R. F. Peletier / J. Román / R. Ragusa / P. Salucci
- T. Saifollahi / M. Scodeggio / M. Siudek / T. De Waele
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / R. Bender
- C. Bodendorf / D. Bonino / W. Bon / E.
Branchini
- M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / V. Capobianco
- C. Carbone / J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander
- M. Castellano / G. Castignani / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- G. Congedo / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / M. Douspis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / A. Ealet / M. Farina
- S. Farrens / F. Faustini / S. Ferriol / P. Fosalba
- M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / B. Gillis
- C. Giocoli / A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo
- S. V. H. Haugan / W. Holmes / I. Hook / F. Hormuth
- A. Hornstrup / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / B. Joachimi
- E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger
- B. Kubik / K. Kuijken / M. Kümmel / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / D. Maino / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- S. Marcin / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli
- N. Martinet / F. Marulli / R. Massey / E.
Medinaceli
- S. Mei / M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti
- E. Merlin / G. Meylan / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla / S. Paltani
- F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- D. Tavagnacco / A. N. Taylor / H. I. Teplitz / I. Tereno
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / A. Zacchei / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca
- A. Biviano / E. Bozzo / C. Burigana / M. Calabrese
- D. Di Ferdinando / J. A. Escartin Vigo / F. Finelli / J.
Gracia-Carpio
- S. Matthew / N. Mauri / M. Pöntinen / V. Scottez
- M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann / Y. Akrami
- V. Allevato / S. Alvi / S. Anselmi / M. Archidiacono
- F. Atrio-Barandela / M. Ballardini / M. Bethermin / L. Blot
- S. Borgani / S. Bruton / R. Cabanac / A. Calabro
- B. Camacho Quevedo / G. Cañas-Herrera / A. Cappi / F. Caro
- C. S. Carvalho / T. Castro / K. C. Chambers / T. Contini
- A. R. Cooray / O. Cucciati / G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez
- J. J. Diaz / S. Di Domizio / H. Dole / S. Escoffier
- A. G. Ferrari / P. G. Ferreira / I. Ferrero / A. Finoguenov
- A. Fontana / F. Fornari / L. Gabarra / K. Ganga
- J. García-Bellido / T. Gasparetto / V. Gautard / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / C. M. Gutierrez
- A. Hall / S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth
- A. Jimenez Muñoz / J. J. E. Kajava / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis
- C. C. Kirkpatrick / A. M. C. Le Brun / J. Le Graet / J.
Lesgourgues
- T. I. Liaudat / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez / G. Maggio
- M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli / J. Martín-Fleitas
- C. J. A. P. Martins / L. Maurin / R. B. Metcalf / M. Miluzio
- P. Monaco / A. Montoro / A. Mora / C. Moretti
- G. Morgante / Nicholas A. Walton / L. Patrizii / V. Popa
- D. Potter / I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci / M. Sahlén
- E. Sarpa / C. Scarlata / A. Schneider / M. Sereno
- F. Shankar / P. Simon / A. Spurio Mancini / J.
Stadel
- S. A. Stanford / K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera
- R. Teyssier / S. Toft / S. Tosi / A. Troja
- M. Tucci / C. Valieri / J. Valiviita / D. Vergani
- G. Verza / P. Vielzeuf
Summary
The Euclid mission is generating a vast amount of imaging data in
four broadband filters at high angular resolution. This will allow the
detailed study of mass, metallicity, and stellar populations across
galaxies, which will constrain their formation and evolutionary
pathways. Transforming the Euclid imaging for large samples of galaxies
into maps of physical parameters in an efficient and reliable manner is
an outstanding challenge. We investigate the power and reliability of
machine learning techniques to extract the distribution of physical
parameters within well-resolved galaxies. We focus on estimating stellar
mass surface density, mass-averaged stellar metallicity and age. We
generate noise-free, synthetic high-resolution imaging data in the
Euclid photometric bands for a set of 1154 galaxies from the TNG50
cosmological simulation. The images are generated with the SKIRT
radiative transfer code, taking into account the complex 3D distribution
of stellar populations and interstellar dust attenuation. We use a
machine learning framework to map the idealised mock observational data
to the physical parameters on a pixel-by-pixel basis. We find that
stellar mass surface density can be accurately recovered with a  scatter. Conversely, stellar metallicity and age
estimates are, as expected, less robust, but still contain significant
information which originates from underlying correlations at a sub-kpc
scale between stellar mass surface density and stellar population
properties.
scatter. Conversely, stellar metallicity and age
estimates are, as expected, less robust, but still contain significant
information which originates from underlying correlations at a sub-kpc
scale between stellar mass surface density and stellar population
properties.
Tracing
the galaxy-halo connection with galaxy clustering in COSMOS-Web from z =
0.1 to z ~ 12
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Louise Paquereau / Clotilde Laigle / Henry Joy McCracken / Marko
Shuntov
- Olivier Ilbert / Hollis B. Akins / Natalie Allen /
Rafael Arango- Togo
- Eddie M. Berman / Matthieu Bethermin / Caitlin M. Casey / Jacqueline
McCleary
- Yohan Dubois / Nicole E. Drakos / Andreas L. Faisst / Maximilien
Franco
- Santosh Harish / Christian K. Jespersen / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe /
Anton M. Koekemoer
- Vasily Kokorev / Erini Lambrides / Rebecca Larson / Daizhong
Liu
- Damien Le Borgne / Joseph S. W. Lewis / Jed McKinney /
Wilfried Mercier
- Jason D. Rhodes / Brant E. Robertson / Sune Toft / Maxime
Trebitsch
- Laurence Tresse / John R. Weaver
Summary
We explore the evolving relationship between galaxies and their dark
matter halos from  to
to  using
mass-limited angular clustering measurements in the 0.54 deg
using
mass-limited angular clustering measurements in the 0.54 deg of the COSMOS-Web survey. This study
provides the first measurements of the mass-limited two-point
correlation function at
of the COSMOS-Web survey. This study
provides the first measurements of the mass-limited two-point
correlation function at  and a consistent
analysis spanning 13.4 Gyr of cosmic history, setting new benchmarks for
future simulations and models. Using a halo occupation distribution
(HOD) framework, we derive characteristic halo masses and the
stellar-to-halo mass relationship (SHMR) across redshifts and stellar
mass bins. Our results first indicate that HOD models fit data at
and a consistent
analysis spanning 13.4 Gyr of cosmic history, setting new benchmarks for
future simulations and models. Using a halo occupation distribution
(HOD) framework, we derive characteristic halo masses and the
stellar-to-halo mass relationship (SHMR) across redshifts and stellar
mass bins. Our results first indicate that HOD models fit data at  best when
incorporating a non-linear scale-dependent halo bias, boosting
clustering at non-linear scales (r = 10-100 kpc). We find that galaxies
at z > 10.5 with
best when
incorporating a non-linear scale-dependent halo bias, boosting
clustering at non-linear scales (r = 10-100 kpc). We find that galaxies
at z > 10.5 with  are
hosted by halos with
are
hosted by halos with  ,
achieving a star formation efficiency (SFE) $M_/ (f_b M_{}) $ up to 1
dex higher than at
,
achieving a star formation efficiency (SFE) $M_/ (f_b M_{}) $ up to 1
dex higher than at  . The high galaxy
bias at
. The high galaxy
bias at  suggests that these
galaxies reside in massive halos with intrinsic high SFE. Our SHMR
evolves significantly with redshift, starting high at
suggests that these
galaxies reside in massive halos with intrinsic high SFE. Our SHMR
evolves significantly with redshift, starting high at  , decreasing
until
, decreasing
until  , then
increasing again until the present. Current simulations fail to
reproduce both massive high-
, then
increasing again until the present. Current simulations fail to
reproduce both massive high- galaxies and this evolution, while
semi-empirical models linking SFE to halo mass, accretion rates, and
redshift align with our findings. We propose that
galaxies and this evolution, while
semi-empirical models linking SFE to halo mass, accretion rates, and
redshift align with our findings. We propose that  galaxies
experience bursty star formation without significant feedback altering
their growth, driving the rapid growth of massive galaxies observed by
JWST. Over time, increasing feedback efficiency and exponential halo
growth suppress star formation. At
galaxies
experience bursty star formation without significant feedback altering
their growth, driving the rapid growth of massive galaxies observed by
JWST. Over time, increasing feedback efficiency and exponential halo
growth suppress star formation. At  and
after, halo growth slows down while star formation continues, supported
by gas reservoirs in halos.
and
after, halo growth slows down while star formation continues, supported
by gas reservoirs in halos.
Articles for week 3 2025
The
COSMOS-Web deep galaxy group catalog up to 
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Greta Toni / Ghassem Gozaliasl / Matteo Maturi / Lauro
Moscardini
- Alexis Finoguenov / Gianluca Castignani / Fabrizio Gentile / Kaija
Virolainen
- Caitlin M. Casey / Jeyhan S. Kartaltepe / Hollis B. Akins / Natalie
Allen
- Rafael C. Arango-Toro / Arif Babul / Malte Brinch / Nicole E.
Drakos
- Andreas L. Faisst / Maximilien Franco / Richard E. Griffiths /
Santosh Harish
- Günther Hasinger / Olivier Ilbert / Shuowen Jin /
Ali Ahmad Khostovan
- Anton M. Koekemoer / Maarit Korpi-Lagg / Rebecca L. Larson /
Jitrapon Lertprasertpong
- Daizhong Liu / Georgios Magdis / Richard Massey / Henry J.
McCracken
- Jed McKinney / Louise Paquereau / Jason Rhodes / Brant E.
Robertson
- Mark Sargent / Marko Shuntov / Masayuki Tanaka / Sina Taamoli
- Elmo Tempel / Sune Toft / Eleni Vardoulaki / Lilan Yang
Summary
Galaxy groups with 
 and up to a few
tens of members are the most common galaxy environment, marking the
transition between field and massive clusters. Identifying groups plays
a crucial role in understanding structure formation and galaxy
evolution. Modern deep surveys allow us to build well-characterized
samples of groups up to the regime where structures were taking shape.
We aimed to build the largest deep catalog of galaxy groups to date over
the COSMOS-Web field effective area of 0.45 deg
and up to a few
tens of members are the most common galaxy environment, marking the
transition between field and massive clusters. Identifying groups plays
a crucial role in understanding structure formation and galaxy
evolution. Modern deep surveys allow us to build well-characterized
samples of groups up to the regime where structures were taking shape.
We aimed to build the largest deep catalog of galaxy groups to date over
the COSMOS-Web field effective area of 0.45 deg , leveraging the deep high quality data
of the new COSMOS-Web photometric catalog resulted from the James Webb
Space Telescope observations of the COSMOS-Web field. We performed the
group search with the AMICO algorithm, a linear matched filter based on
an analytical model for the group signal. AMICO has already been tested
in wide and deep field surveys, including COSMOS data up to
, leveraging the deep high quality data
of the new COSMOS-Web photometric catalog resulted from the James Webb
Space Telescope observations of the COSMOS-Web field. We performed the
group search with the AMICO algorithm, a linear matched filter based on
an analytical model for the group signal. AMICO has already been tested
in wide and deep field surveys, including COSMOS data up to  . In this work, we tested
the algorithm performances at even higher redshift and searched for
protocluster cores at
. In this work, we tested
the algorithm performances at even higher redshift and searched for
protocluster cores at  . We compiled a list
of known protoclusters in COSMOS at
. We compiled a list
of known protoclusters in COSMOS at  , matched them with our detections and studied the
clustering of the detected cores. We estimated purity and completeness
of our sample by creating data-driven mocks with the SinFoniA code and
linked signal-to-noise to purity. We detected 1678 groups in the
COSMOS-Web field up to
, matched them with our detections and studied the
clustering of the detected cores. We estimated purity and completeness
of our sample by creating data-driven mocks with the SinFoniA code and
linked signal-to-noise to purity. We detected 1678 groups in the
COSMOS-Web field up to  , including lists of
members extending nearly two magnitudes deeper than the previous
AMICO-COSMOS catalog. 756 groups were detected with purity of 80%. More
than 500 groups have their redshift confirmed by assigning spectroscopic
counterparts. This group catalog offers a unique opportunity to explore
galaxy evolution in different environments spanning $$12 Gyr and to
study groups, from the least rich population to the formation of the
most massive clusters.
, including lists of
members extending nearly two magnitudes deeper than the previous
AMICO-COSMOS catalog. 756 groups were detected with purity of 80%. More
than 500 groups have their redshift confirmed by assigning spectroscopic
counterparts. This group catalog offers a unique opportunity to explore
galaxy evolution in different environments spanning $$12 Gyr and to
study groups, from the least rich population to the formation of the
most massive clusters.
The
PLATO field selection process. II. Characterization of LOPS2, the first
long-pointing field
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- V. Nascimbeni / G. Piotto / J. Cabrera / M. Montalto
- S. Marinoni / P. M. Marrese / C. Aerts / G. Altavilla
- S. Benatti / A. Börner / M. Deleuil / S.
Desidera
- L. Gizon / M. J. Goupil / V. Granata / A. M. Heras
- D. Magrin / L. Malavolta / J. M. Mas-Hesse / H. P. Osborn
- I. Pagano / C. Paproth / D. Pollacco / L. Prisinzano
- R. Ragazzoni / G. Ramsay / H. Rauer / A. Tkachenko
- S. Udry
Summary
PLAnetary Transits and Oscillations of stars (PLATO) is an ESA
M-class mission to be launched by the end of 2026 to discover and
characterize transiting planets around bright and nearby stars, and in
particular habitable rocky planets hosted by solar-like stars. Over the
mission lifetime, an average of 8% of the science data rate will be
allocated to Guest Observer programs (GOs) selected by ESA through
public calls, hence it is essential for the community to know in advance
where the observing fields will be located. In a previous paper, we
identified two preliminary long-pointing fields (LOPN1 and LOPS1) for
PLATO, respectively in the northern and southern hemisphere. Here we
present LOPS2, a slightly adjusted version of the southern field that
has recently been selected by the PLATO Science Working Team as the
first field to be observed by PLATO for at least two continuous years,
following the scientific requirements. In this paper, we describe the
astrophysical content of LOPS2 in detail, including known planetary
systems, bright/variable/binary stars, clusters and synergies with other
current and future facilities.
Euclid:
Optimising tomographic redshift binning for 3$$2pt power spectrum
constraints on dark energy
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- J. H. W. Wong / M. L. Brown / C. A. J. Duncan / A. Amara
- S. Andreon / C. Baccigalupi / M. Baldi / S. Bardelli
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- A. Caillat / S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde / G. Congedo
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi / G. De Lucia
- A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / F. Dubath / X. Dupac
- S. Dusini / M. Farina / S. Farrens / F. Faustini
- S. Ferriol / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta
- K. George / W. Gillard / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan
- W. Holmes / I. Hook / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup
- S. Ilić / K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen
- S. Kermiche / A. Kiessling / B. Kubik / M. Kunz
- H. Kurki-Suonio / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm
- I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / E. Maiorano / O. Mansutti
- O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei
- M. Melchior / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / E. Merlin
- G. Meylan / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / C. Neissner
- S.-M. Niemi / C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian
- K. Pedersen / V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta
- M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / F. Raison / A. Renzi
- J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli
- E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez
- D. Sapone / B. Sartoris / P. Schneider / T. Schrabback
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / G. Zamorani
- E. Zucca / C. Burigana / M. Calabrese / A. Pezzotta
- V. Scottez / A. Spurio Mancini / M. Viel
Summary
We present a simulation-based method to explore the optimum
tomographic redshift binning strategy for 3x2pt analyses with Euclid,
focusing on the expected configuration of its first major data release
(DR1). To do this, we 1) simulate a Euclid-like observation and generate
mock shear catalogues from multiple realisations of the 3x2pt fields on
the sky, and 2) measure the 3x2pt Pseudo-Cl power spectra for a given
tomographic configuration and derive the constraints that they place on
the standard dark energy equation of state parameters (w0, wa). For a
simulation including Gaussian-distributed photometric redshift
uncertainty and shape noise under a LambdaCDM cosmology, we find that
bins equipopulated with galaxies yield the best constraints on (w0, wa)
for an analysis of the full 3x2pt signal, or the angular clustering
component only. For the cosmic shear component, the optimum (w0, wa)
constraints are achieved by bins equally spaced in fiducial comoving
distance. However, the advantage with respect to alternative binning
choices is only a few percent in the size of the  (w0, wa) contour, and
we conclude that the cosmic shear is relatively insensitive to the
binning methodology. We find that the information gain extracted on (w0,
wa) for any 3x2pt component starts to saturate at
(w0, wa) contour, and
we conclude that the cosmic shear is relatively insensitive to the
binning methodology. We find that the information gain extracted on (w0,
wa) for any 3x2pt component starts to saturate at  7-8 bins. Any
marginal gains resulting from a greater number of bins is likely to be
limited by additional uncertainties present in a real measurement, and
the increasing demand for accuracy of the covariance matrix. Finally, we
consider a 5% contamination from catastrophic photometric redshift
outliers and find that, if these errors are not mitigated in the
analysis, the bias induced in the 3x2pt signal for 10 equipopulated bins
results in dark energy constraints that are inconsistent with the
fiducial LambdaCDM cosmology at
7-8 bins. Any
marginal gains resulting from a greater number of bins is likely to be
limited by additional uncertainties present in a real measurement, and
the increasing demand for accuracy of the covariance matrix. Finally, we
consider a 5% contamination from catastrophic photometric redshift
outliers and find that, if these errors are not mitigated in the
analysis, the bias induced in the 3x2pt signal for 10 equipopulated bins
results in dark energy constraints that are inconsistent with the
fiducial LambdaCDM cosmology at  .
.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- M. Latour / S. Kamann / S. Martocchia / T.-O.
Husser
- S. Saracino / S. Dreizler
Summary
Multiple populations are ubiquitous in the old massive globular
clusters (GCs) of the Milky Way. It is still unclear how they arose
during the formation of a GC. The topic of iron and metallicity
variations has recently attracted attention with the measurement of iron
variations among the primordial population (P1) stars of Galactic GCs.
We use the spectra of more than 8000 RGB stars in 21 Galactic GCs
observed with MUSE to derive individual stellar metallicities [M/H]. For
each cluster, we use the HST photometric catalogs to separate the stars
into two main populations (P1 and P2). We measure the metallicity spread
within the primordial population of each cluster by combining our
metallicity measurements with the stars  pseudo-color. We also derive metallicity
dispersions (
pseudo-color. We also derive metallicity
dispersions (![σ_{\rm [M/H]} σ_{\rm [M/H]}](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%CF%83_%7B%5Crm%20%5BM%2FH%5D%7D) ) for
the P1 and P2 stars of each GC. In all but three GCs, we measure a
significant correlation between the metallicity and the
) for
the P1 and P2 stars of each GC. In all but three GCs, we measure a
significant correlation between the metallicity and the  pseudo-color of the P1 stars such that stars with
larger
pseudo-color of the P1 stars such that stars with
larger  have higher metallicities. We measure metallicity
spreads that range from 0.03 to 0.24 dex and correlate with the GC
masses. As for the intrinsic metallicity dispersions, when combining the
P1 and P2 stars, we measure values ranging from 0.02 dex to 0.08 dex
that correlate very well with the GC masses. We compared the metallicity
dispersion among the P1 and P2 stars and found that the P2 stars have
metallicity dispersions that are smaller or equal to that of the P1
stars. We find that both the metallicity spreads of the P1 stars (from
the
have higher metallicities. We measure metallicity
spreads that range from 0.03 to 0.24 dex and correlate with the GC
masses. As for the intrinsic metallicity dispersions, when combining the
P1 and P2 stars, we measure values ranging from 0.02 dex to 0.08 dex
that correlate very well with the GC masses. We compared the metallicity
dispersion among the P1 and P2 stars and found that the P2 stars have
metallicity dispersions that are smaller or equal to that of the P1
stars. We find that both the metallicity spreads of the P1 stars (from
the  spread in the chromosome maps) and the
metallicity dispersions (
spread in the chromosome maps) and the
metallicity dispersions (![σ_{\rm [M/H]} σ_{\rm [M/H]}](https://latex.codecogs.com/png.latex?%5Ctextstyle%20%CF%83_%7B%5Crm%20%5BM%2FH%5D%7D) )
correlate with the GC masses, as predicted by some theoretical
self-enrichment models presented in the literature.
)
correlate with the GC masses, as predicted by some theoretical
self-enrichment models presented in the literature.
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Euclid Collaboration / D. Scognamiglio / T. Schrabback / M.
Tewes
- B. Gillis / H. Hoekstra / E. M. Huff / O. Marggraf
- T. Kitching / R. Massey / I. Tereno / C. S. Carvalho
- A. Robertson / G. Congedo / N. Aghanim / B. Altieri
- A. Amara / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio / C. Baccigalupi
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / P. Battaglia / C. Bodendorf
- D. Bonino / E. Branchini / M. Brescia / J. Brinchmann
- S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone / V. F. Cardone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / F. J. Castander / M. Castellano
- G. Castignani / S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / C. Colodro-Conde
- C. J. Conselice / L. Conversi / Y. Copin / F. Courbin
- H. M. Courtois / M. Cropper / A. Da Silva / H. Degaudenzi
- G. De Lucia / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / F. Dubath
- C. A. J. Duncan / X. Dupac / S. Dusini / M. Farina
- S. Farrens / S. Ferriol / P. Fosalba / M. Frailis
- E. Franceschi / S. Galeotta / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / L. Guzzo / S. V. H. Haugan
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / B. Joachimi / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / B. Kubik / M. Kümmel
- M. Kunz / H. Kurki-Suonio / S. Ligori / P. B. Lilje
- V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / G. Mainetti / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / K. Markovic / M. Martinelli / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / E. Medinaceli / S. Mei / Y. Mellier
- M. Meneghetti / G. Meylan / M. Moresco / L. Moscardini
- R. Nakajima / S.-M. Niemi / J. W. Nightingale / C. Padilla
- S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen / S. Pires
- G. Polenta / M. Poncet / L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti
- F. Raison / R. Rebolo / A. Renzi / J. Rhodes
- G. Riccio / E. Romelli / M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti
- R. Saglia / Z. Sakr / A. G. Sánchez / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / R. Scaramella / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider
- A. Secroun / G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano
- G. Sirri / J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J.-L. Starck
- J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí / A. N. Taylor / H. I.
Teplitz
- R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot / I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano
- T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn / A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang
- J. Weller / M. Wetzstein / G. Zamorani / E. Zucca
- A. Biviano / M. Bolzonella / A. Boucaud / E. Bozzo
- C. Burigana / M. Calabrese / J. A. Escartin Vigo / J.
Gracia-Carpio
- N. Mauri / A. Pezzotta / M. Pöntinen / C. Porciani
- V. Scottez / M. Tenti / M. Viel / M. Wiesmann
- Y. Akrami / V. Allevato / S. Anselmi / M. Ballardini
- L. Blot / S. Borgani / S. Bruton / R. Cabanac
- A. Calabro / A. Cappi / T. Castro / K. C. Chambers
- S. Contarini / A. R. Cooray / S. Davini / B. De Caro
- G. Desprez / A. Díaz-Sánchez / S. Di Domizio / H. Dole
- S. Escoffier / A. G. Ferrari / I. Ferrero / F. Fornari
- L. Gabarra / K. Ganga / J. García-Bellido / E. Gaztanaga
- F. Giacomini / F. Gianotti / G. Gozaliasl / A. Hall
- S. Hemmati / H. Hildebrandt / J. Hjorth / A. Jimenez Muñoz
- J. J. E. Kajava / V. Kansal / D. Karagiannis / C. C.
Kirkpatrick
- J. Le Graet / L. Legrand / A. Loureiro / J. Macias-Perez
- G. Maggio / M. Magliocchetti / F. Mannucci / R. Maoli
- C. J. A. P. Martins / S. Matthew / L. Maurin / R. B. Metcalf
- P. Monaco / C. Moretti / G. Morgante / Nicholas A. Walton
- L. Patrizii / V. Popa / D. Potter / P. Reimberg
- I. Risso / P.-F. Rocci / R. P. Rollins / M. Sahlén
- A. Schneider / M. Sereno / P. Simon / A. Spurio
Mancini
- K. Tanidis / C. Tao / G. Testera / R. Teyssier
- S. Toft / S. Tosi / A. Troja / M. Tucci
- C. Valieri / J. Valiviita / D. Vergani / G. Verza
Summary
Data from the Euclid space telescope will enable cosmic shear
measurements with very small statistical errors, requiring corresponding
systematic error control level. A common approach to correct for shear
biases involves calibrating shape measurement methods using image
simulations with known input shear. Given their high resolution, Hubble
Space Telescope (HST) galaxies can, in principle, be utilised to emulate
Euclid observations. In this work, we employ a GalSim-based testing
environment to investigate whether uncertainties in the HST point spread
function (PSF) model or in data processing techniques introduce
significant biases in weak-lensing (WL) shear calibration. We used
single Sérsic galaxy models to simulate both HST and Euclid
observations. We then `Euclidised’ our HST simulations and compared the
results with the directly simulated Euclid-like images. For this
comparison, we utilised a moment-based shape measurement algorithm and
galaxy model fits. Through the Euclidisation procedure, we effectively
reduced the residual multiplicative biases in shear measurements to
sub-percent levels. This achievement was made possible by employing
either the native pixel scales of the instruments, utilising the
Lanczos15 interpolation kernel, correcting for noise correlations, and
ensuring consistent galaxy signal-to-noise ratios between simulation
branches. However, the Euclidisation procedure requires further analysis
on the impact of the correlated noise, to estimate calibration bias.
Additionally, we conducted an in-depth analysis of the accuracy of
TinyTim HST PSF models using star fields observed in the F606W and F814W
filters. We observe that F606W images exhibit a broader scatter in the
recovered best-fit focus, compared to those in the F814W filter.
Articles for week 2 2025
The
NewAthena mission concept in the context of the next decade of X-ray
astronomy
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Mike Cruise / Matteo Guainazzi / James Aird / Francisco J.
Carrera
- Elisa Costantini / Lia Corrales / Thomas Dauser / Dominique
Eckert
- Fabio Gastaldello / Hironori Matsumoto / Rachel Osten /
Pierre-Olivier Petrucci
- Delphine Porquet / Gabriel W. Pratt / Nanda Rea /
Thomas H. Reiprich
- Aurora Simionescu / Daniele Spiga / Eleonora Troja
Summary
Large X-ray observatories such as Chandra and XMM-Newton have been
delivering scientific breakthroughs in research fields as diverse as our
Solar System, the astrophysics of stars, stellar explosions and compact
objects, accreting super-massive black holes, and large-scale structures
traced by the hot plasma permeating and surrounding galaxy groups and
clusters. The recently launched observatory XRISM is opening in earnest
the new observational window of non-dispersive high-resolution
spectroscopy. However, several quests are left open, such as the effect
of the stellar radiation field on the habitability of nearby planets,
the Equation-of-State regulating matter in neutron stars, the origin and
distribution of metals in the Universe, the processes driving the
cosmological evolution of the baryons locked in the gravitational
potential of Dark Matter and the impact of supermassive black hole
growth on galaxy evolution, just to mention a few. Furthermore, X-ray
astronomy is a key player in multi-messenger astrophysics. Addressing
these quests experimentally requires an order-of-magnitude leap in
sensitivity, spectroscopy and survey capabilities with respect to
existing X-ray observatories. This paper succinctly summarizes the main
areas where high-energy astrophysics is expected to contribute to our
understanding of the Universe in the next decade and describes a new
mission concept under study by the European Space Agency, the scientific
community worldwide and two International Partners (JAXA and NASA),
designed to enable transformational discoveries: NewAthena. This concept
inherits its basic payload design from a previous study carried out
until 2022, Athena.
Clumps
as multiscale structures in cosmic noon galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Boris S Kalita / Tomoko L Suzuki / Daichi Kashino / John D
Silverman
- Emanuele Daddi / Luis C Ho / Xuheng Ding / Wilfried
Mercier
- Andreas L Faisst / Kartik Sheth / Francesco Valentino / Annagrazia
Puglisi
- Toshiki Saito / Darshan Kakkad / Olivier Ilbert /
Ali Ahmad Khostovan
- Zhaoxuan Liu / Takumi Tanaka / Georgios Magdis / Jorge A Zavala
- Qinghua Tan / Jeyhan S Kartaltepe / Lilan Yang / Anton M
Koekemoer
- Jed McKinney / Brant E Robertson / Shuowen Jin / Christopher C
Hayward
- Michaela Hirschmann / Maximilien Franco / Marko Shuntov / Ghassem
Gozaliasl
- Aidan Kaminsky / R Michael Rich
Summary
Star-forming clumps have been found to significantly influence the
star formation of gas-rich  galaxies. Using
public data from JWST/NIRCam (COSMOS-Web) and ALMA (FMOS-COSMOS), we
study a sample of 32 massive (
galaxies. Using
public data from JWST/NIRCam (COSMOS-Web) and ALMA (FMOS-COSMOS), we
study a sample of 32 massive ( ) main-sequence galaxies at
) main-sequence galaxies at  with
with  resolution. We create composite morphological models consisting of
bulge, disk, and clumps to fully ‘deconstruct’ the galaxy images. With
the resulting measurements of the flux and size of these components, we
find the following: (I)The combined contribution of clumps is
resolution. We create composite morphological models consisting of
bulge, disk, and clumps to fully ‘deconstruct’ the galaxy images. With
the resulting measurements of the flux and size of these components, we
find the following: (I)The combined contribution of clumps is  towards the net star
formation rate (SFR) of the host while contributing
towards the net star
formation rate (SFR) of the host while contributing  to its stellar mass.
The clumps show a correlation between their stellar mass and SFR, but
have an increased specific-SFR (sSFR) relative to the star-forming main
sequence, with offsets ranging from
to its stellar mass.
The clumps show a correlation between their stellar mass and SFR, but
have an increased specific-SFR (sSFR) relative to the star-forming main
sequence, with offsets ranging from  . They
feature star formation surface densities of
. They
feature star formation surface densities of  ,
consistent with values observed in local star-forming and starburst
galaxies. (II)The clumps span a large range of characteristic sizes
(
,
consistent with values observed in local star-forming and starburst
galaxies. (II)The clumps span a large range of characteristic sizes
( ) and stellar masses (
) and stellar masses ( ). We
estimate a mass-size relation (
). We
estimate a mass-size relation ( ) along with a stellar mass function (slope,
) along with a stellar mass function (slope,  ),
both suggesting a hierarchical nature similar to that expected in
star-forming regions in local galaxies. (III)Our measurements agree with
the properties of stellar clumps in
),
both suggesting a hierarchical nature similar to that expected in
star-forming regions in local galaxies. (III)Our measurements agree with
the properties of stellar clumps in  lensed systems,
bridging the gap between lensed and unlensed studies by detecting
structures at sub-kpc scales.(IV)Clumps are found to be preferentially
located along spiral features visible primarily in the residual
rest-frame near-IR images. In conclusion, we present an
observation-based, coherent picture of star-forming clumps at
lensed systems,
bridging the gap between lensed and unlensed studies by detecting
structures at sub-kpc scales.(IV)Clumps are found to be preferentially
located along spiral features visible primarily in the residual
rest-frame near-IR images. In conclusion, we present an
observation-based, coherent picture of star-forming clumps at  .
.
TOI-5108
b and TOI 5786 b: Two transiting sub-Saturns detected and characterized
with TESS, MaHPS and SOPHIE
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Luis Thomas / Guillaume Hébrard / Hanna Kellermann / Judith
Korth
- Neda Heidari / Thierry Forveille / Sérgio G. Sousa / Laura
Schöller
- Arno Riffeser / Claus Gössl / Juan Serrano Bell / Flavien
Kiefer
- Nathan Hara / Frank Grupp / Juliana Ehrhardt /
Felipe Murgas
- Karen A. Collins / Allyson Bieryla / Hannu Parviainen / Alexandr A.
Belinski
- Emma Esparza-Borges / David R. Ciardi / Catherine A. Clark / Akihiko
Fukui
- Emily A. Gilbert / Ulrich Hopp / Kai Ikuta / Jon M. Jenkins
- David W. Latham / Norio Narita / Louise D. Nielsen / Samuel N.
Quinn
- Enric Palle / Jan-Niklas Pippert / Alex S. Polanski / Christoph
Ries
- Michael Schmidt / Richard P. Schwarz / Sara Seager / Ivan A.
Strakhov
- Stephanie Striegel / Julian C. van Eyken / Noriharu Watanabe /
Cristilyn N. Watkins
- Joshua N. Winn / Carl Ziegler / Raphael Zöller
Summary
We report the discovery and characterization of two sub-Saturns from
the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite () using high-resolution
spectroscopic observations from the MaHPS spectrograph at the
Wendelstein Observatory and the SOPHIE spectrograph at the
Haute-Provence Observatory. Combining photometry from TESS, KeplerCam,
LCOGT, and MuSCAT2 with the radial velocity measurements from MaHPS and
SOPHIE we measure precise radii and masses for both planets. TOI-5108 b
is a sub-Saturn with a radius of 
 and a mass of
and a mass of

 . TOI-5786 b is
similar to Saturn with a radius of
. TOI-5786 b is
similar to Saturn with a radius of 
 and a mass of
and a mass of

 . The host star
for TOI-5108 b is a moderately bright (Vmag 9.75) G-type star. TOI-5786
is a slightly dimmer (Vmag 10.2) F-type star. Both planets are close to
their host stars with periods of 6.75 days and 12.78 days respectively.
This puts TOI-5108 b just inside the bounds of the Neptune desert while
TOI-5786 b is right above the upper edge. We estimate hydrogen-helium
envelope mass fractions of
. The host star
for TOI-5108 b is a moderately bright (Vmag 9.75) G-type star. TOI-5786
is a slightly dimmer (Vmag 10.2) F-type star. Both planets are close to
their host stars with periods of 6.75 days and 12.78 days respectively.
This puts TOI-5108 b just inside the bounds of the Neptune desert while
TOI-5786 b is right above the upper edge. We estimate hydrogen-helium
envelope mass fractions of  for TOI-5108 b and $74
% $ for TOI-5786 b. However, using a model for the interior structure
that includes tidal effects the envelope fraction of TOI-5108 b could be
much lower (
for TOI-5108 b and $74
% $ for TOI-5786 b. However, using a model for the interior structure
that includes tidal effects the envelope fraction of TOI-5108 b could be
much lower ( ) depending
on the obliquity. We estimate mass-loss rates between 1.0 *
) depending
on the obliquity. We estimate mass-loss rates between 1.0 *  g/s and 9.8 *
g/s and 9.8 *  g/s for TOI-5108 b and
between 3.6 *
g/s for TOI-5108 b and
between 3.6 *  g/s and 3.5 *
g/s and 3.5 *  g/s for TOI-5786 b. Given
their masses, this means that both planets are stable against
photoevaporation. We also detect a transit signal for a second planet
candidate in the TESS data of TOI-5786 with a period of 6.998 days and a
radius of
g/s for TOI-5786 b. Given
their masses, this means that both planets are stable against
photoevaporation. We also detect a transit signal for a second planet
candidate in the TESS data of TOI-5786 with a period of 6.998 days and a
radius of 
 . Using our RV
data and photodynamical modeling, we are able to provide a 3-
. Using our RV
data and photodynamical modeling, we are able to provide a 3- upper limit of 26.5
upper limit of 26.5  for the mass of
the potential inner companion to TOI-5786 b.
for the mass of
the potential inner companion to TOI-5786 b.
Euclid:
Detecting Solar System objects in Euclid images and classifying them
using Kohonen self-organising maps
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- A. A. Nucita / L. Conversi / A. Verdier / A. Franco
- S. Sacquegna / M. Pöntinen / B. Altieri / B. Carry
- F. De Paolis / F. Strafella / V. Orofino / M. Maiorano
- V. Kansal / R. D. Vavrek / M. Miluzio / M. Granvik
- V. Testa / N. Aghanim / S. Andreon / N. Auricchio
- M. Baldi / S. Bardelli / E. Branchini / M. Brescia
- J. Brinchmann / S. Camera / V. Capobianco / C. Carbone
- J. Carretero / S. Casas / M. Castellano / G. Castignani
- S. Cavuoti / A. Cimatti / G. Congedo / C. J. Conselice
- Y. Copin / F. Courbin / H. M. Courtois / A. Da Silva
- H. Degaudenzi / A. M. Di Giorgio / J. Dinis / F. Dubath
- X. Dupac / S. Dusini / M. Farina / S. Farrens
- S. Ferriol / M. Frailis / E. Franceschi / M. Fumana
- S. Galeotta / B. Gillis / C. Giocoli / P. Gómez-Alvarez
- A. Grazian / F. Grupp / S. V. H. Haugan / J. Hoar
- W. Holmes / F. Hormuth / A. Hornstrup / P. Hudelot
- K. Jahnke / M. Jhabvala / E. Keihänen / S. Kermiche
- A. Kiessling / M. Kilbinger / R. Kohley / B. Kubik
- M. Kümmel / H. Kurki-Suonio / R. Laureijs / S. Ligori
- P. B. Lilje / V. Lindholm / I. Lloro / E. Maiorano
- O. Mansutti / O. Marggraf / K. Markovic / N.
Martinet
- F. Marulli / R. Massey / D. C. Masters / E. Medinaceli
- S. Mei / Y. Mellier / M. Meneghetti / G. Meylan
- M. Moresco / L. Moscardini / R. Nakajima / S.-M. Niemi
- C. Padilla / S. Paltani / F. Pasian / K. Pedersen
- V. Pettorino / S. Pires / G. Polenta / M. Poncet
- L. A. Popa / L. Pozzetti / F. Raison / R. Rebolo
- A. Renzi / J. Rhodes / G. Riccio / E. Romelli
- M. Roncarelli / E. Rossetti / R. Saglia / D. Sapone
- B. Sartoris / M. Schirmer / P. Schneider / A. Secroun
- G. Seidel / S. Serrano / C. Sirignano / G. Sirri
- J. Skottfelt / L. Stanco / J. Steinwagner / P. Tallada-Crespí
- A. N. Taylor / I. Tereno / R. Toledo-Moreo / F. Torradeflot
- I. Tutusaus / L. Valenziano / T. Vassallo / G. Verdoes Kleijn
- A. Veropalumbo / Y. Wang / J. Weller / A. Zacchei
- E. Zucca / M. Bolzonella / C. Burigana / V. Scottez
Summary
The ESA Euclid mission will survey more than 14,000 deg of the sky in visible and
near-infrared wavelengths, mapping the extra-galactic sky to constrain
our cosmological model of the Universe. Although the survey focusses on
regions further than 15 deg from the ecliptic, it should allow for the
detection of more than about
of the sky in visible and
near-infrared wavelengths, mapping the extra-galactic sky to constrain
our cosmological model of the Universe. Although the survey focusses on
regions further than 15 deg from the ecliptic, it should allow for the
detection of more than about  Solar System objects
(SSOs). After simulating the expected signal from SSOs in Euclid images
acquired with the visible camera (VIS), we describe an automated
pipeline developed to detect moving objects with an apparent velocity in
the range of 0.1-10 arcsec/h, typically corresponding to sources in the
outer Solar System (from Centaurs to Kuiper-belt objects). In
particular, the proposed detection scheme is based on Sourcextractor
software and on applying a new algorithm capable of associating moving
objects amongst different catalogues. After applying a suite of filters
to improve the detection quality, we study the expected purity and
completeness of the SSO detections. We also show how a Kohonen
self-organising neural network can be successfully trained (in an
unsupervised fashion) to classify stars, galaxies, and SSOs. By
implementing an early-stopping method in the training scheme, we show
that the network can be used in a predictive way, allowing one to assign
the probability of each detected object being a member of each
considered class.
Solar System objects
(SSOs). After simulating the expected signal from SSOs in Euclid images
acquired with the visible camera (VIS), we describe an automated
pipeline developed to detect moving objects with an apparent velocity in
the range of 0.1-10 arcsec/h, typically corresponding to sources in the
outer Solar System (from Centaurs to Kuiper-belt objects). In
particular, the proposed detection scheme is based on Sourcextractor
software and on applying a new algorithm capable of associating moving
objects amongst different catalogues. After applying a suite of filters
to improve the detection quality, we study the expected purity and
completeness of the SSO detections. We also show how a Kohonen
self-organising neural network can be successfully trained (in an
unsupervised fashion) to classify stars, galaxies, and SSOs. By
implementing an early-stopping method in the training scheme, we show
that the network can be used in a predictive way, allowing one to assign
the probability of each detected object being a member of each
considered class.
A
multi-wavelength investigation of spiral structures in  galaxies with
JWST
galaxies with
JWST
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Boris S. Kalita / Si-Yue Yu / John D. Silverman / Emanuele
Daddi
- Luis C. Ho / Andreas L. Faisst / Miroslava Dessauges-Zavadsky /
Annagrazia Puglisi
- Simon Birrer / Daichi Kashino / Xuheng Ding / Jeyhan S.
Kartaltepe
- Zhaoxuan Liu / Darshan Kakkad / Francesco Valentino /
Olivier Ilbert
- Georgios Magdis / Arianna S. Long / Shuowen Jin / Anton M.
Koekemoer
- Richard Massey
Summary
Recent JWST observations have revealed the prevalence of spiral
structures at  . Unlike in the
local Universe, the origin and the consequence of spirals at this epoch
remain unexplored. We use public JWST/NIRCam data from the COSMOS-Web
survey to map spiral structures in eight massive (
. Unlike in the
local Universe, the origin and the consequence of spirals at this epoch
remain unexplored. We use public JWST/NIRCam data from the COSMOS-Web
survey to map spiral structures in eight massive ( )
star-forming galaxies at
)
star-forming galaxies at  . We present a method for systematically
quantifying spiral arms at
. We present a method for systematically
quantifying spiral arms at  , enabling direct
measurements of flux distributions. Using rest-frame near-IR images, we
construct morphological models accurately tracing spiral arms. We detect
offsets (
, enabling direct
measurements of flux distributions. Using rest-frame near-IR images, we
construct morphological models accurately tracing spiral arms. We detect
offsets ( ) between the rest-frame optical and near-IR flux
distributions across most arms. Drawing parallels to the local Universe,
we conclude that these offsets reflect the presence of density waves.
For nine out of eighteen arms, the offsets indicate spiral shocks
triggered by density waves. Five arms have offsets in the opposite
direction and are likely associated with tidal interactions. For the
remaining cases with no detected offsets, we suggest that stochastic
‘clumpy’ star formation is the primary driver of their formation. In
conclusion, we find a multi-faceted nature of spiral arms at
) between the rest-frame optical and near-IR flux
distributions across most arms. Drawing parallels to the local Universe,
we conclude that these offsets reflect the presence of density waves.
For nine out of eighteen arms, the offsets indicate spiral shocks
triggered by density waves. Five arms have offsets in the opposite
direction and are likely associated with tidal interactions. For the
remaining cases with no detected offsets, we suggest that stochastic
‘clumpy’ star formation is the primary driver of their formation. In
conclusion, we find a multi-faceted nature of spiral arms at  , similar to that
in the local Universe.
, similar to that
in the local Universe.
Articles for week 1 2025
First
unambiguous detection of ammonia in the atmosphere of a planetary mass
companion with JWST/MIRI coronagraphs
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Mathilde Mâlin / Anthony Boccaletti / Clément Perrot / Pierre
Baudoz
- Daniel Rouan / Pierre-Olivier Lagage / Rens Waters / Manuel
Güdel
- Thomas Henning / Bart Vandenbussche / Olivier Absil / David
Barrado
- Benjamin Charnay / Elodie Choquet / Christophe
Cossou / Camilla Danielski
- Leen Decin / Adrian M. Glauser / John Pye / Goran Olofsson
- Alistair Glasse / Polychronis Patapis / Pierre Royer / Silvia
Scheithauer
- Eugene Serabyn / Pascal Tremblin / Niall Whiteford / Ewine F. van
Dishoeck
- Göran Ostlin / Tom P. Ray / Gillian Wright
Summary
The newly accessible mid-infrared (MIR) window offered by the James
Webb Space Telescope (JWST) for exoplanet imaging is expected to provide
valuable information to characterize their atmospheres. In particular,
coronagraphs on board the JWST Mid-InfraRed instrument (MIRI) are
capable of imaging the coldest directly imaged giant planets at the
wavelengths where they emit most of their flux. The MIRI coronagraphs
have been specially designed to detect the NH3 absorption around 10.5
microns, which has been predicted by atmospheric models. We aim to
assess the presence of NH3 while refining the atmospheric parameters of
one of the coldest companions detected by directly imaging GJ 504 b. Its
mass is still a matter of debate and depending on the host star age
estimate, the companion could either be placed in the brown dwarf regime
or in the young Jovian planet regime. We present an analysis of MIRI
coronagraphic observations of the GJ 504 system. We took advantage of
previous observations of reference stars to build a library of images
and to perform a more efficient subtraction of the stellar diffraction
pattern. We detected the presence of NH3 at 12.5 sigma in the
atmosphere, in line with atmospheric model expectations for a
planetary-mass object and observed in brown dwarfs within a similar
temperature range. The best-fit model with Exo-REM provides updated
values of its atmospheric parameters, yielding a temperature of Teff =
512 K and radius of R = 1.08 RJup. These observations demonstrate the
capability of MIRI coronagraphs to detect NH3 and to provide the first
MIR observations of one of the coldest directly imaged companions.
Overall, NH3 is a key molecule for characterizing the atmospheres of
cold planets, offering valuable insights into their surface gravity.
These observations provide valuable information for spectroscopic
observations planned with JWST.
Search
for continuous gravitational waves from known pulsars in the first part
of the fourth LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA observing run
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration / the Virgo Collaboration / the
KAGRA Collaboration / A. G. Abac
- R. Abbott / I. Abouelfettouh / F. Acernese / K. Ackley
- S. Adhicary / N. Adhikari / R. X. Adhikari / V. K. Adkins
- D. Agarwal / M. Agathos / M. Aghaei Abchouyeh / O. D. Aguiar
- I. Aguilar / L. Aiello / A. Ain / P. Ajith
- T. Akutsu / S. Albanesi / R. A. Alfaidi / A. Al-Jodah
- C. Alléné / A. Allocca / S. Al-Shammari / P. A. Altin
- S. Alvarez-Lopez / A. Amato / L. Amez-Droz / A. Amorosi
- C. Amra / A. Ananyeva / S. B. Anderson / W. G. Anderson
- M. Andia / M. Ando / T. Andrade / N. Andres
- M. Andrés-Carcasona / T. Andrić / J. Anglin / S. Ansoldi
- J. M. Antelis / S. Antier / M. Aoumi / E. Z. Appavuravther
- S. Appert / S. K. Apple / K. Arai / A. Araya
- M. C. Araya / J. S. Areeda / L. Argianas / N. Aritomi
- F. Armato / N. Arnaud / M. Arogeti / S. M. Aronson
- G. Ashton / Y. Aso / M. Assiduo / S. Assis de Souza Melo
- S. M. Aston / P. Astone / F. Attadio / F. Aubin
- K. AultONeal / G. Avallone / S. Babak / F. Badaracco
- C. Badger / S. Bae / S. Bagnasco / E. Bagui
- J. G. Baier / L. Baiotti / R. Bajpai / T. Baka
- M. Ball / G. Ballardin / S. W. Ballmer / S. Banagiri
- B. Banerjee / D. Bankar / P. Baral / J. C. Barayoga
- B. C. Barish / D. Barker / P. Barneo / F. Barone
- B. Barr / L. Barsotti / M. Barsuglia / D. Barta
- A. M. Bartoletti / M. A. Barton / I. Bartos / S. Basak
- A. Basalaev / R. Bassiri / A. Basti / D. E. Bates
- M. Bawaj / P. Baxi / J. C. Bayley / A. C. Baylor
- P. A. Baynard / M. Bazzan / V. M. Bedakihale / F. Beirnaert
- M. Bejger / D. Belardinelli / A. S. Bell / V. Benedetto
- W. Benoit / J. D. Bentley / M. Ben Yaala / S. Bera
- M. Berbel / F. Bergamin / B. K. Berger / S. Bernuzzi
- M. Beroiz / D. Bersanetti / A. Bertolini / J. Betzwieser
- D. Beveridge / N. Bevins / R. Bhandare / U. Bhardwaj
- R. Bhatt / D. Bhattacharjee / S. Bhaumik / S. Bhowmick
- A. Bianchi / I. A. Bilenko / G. Billingsley / A. Binetti
- S. Bini / O. Birnholtz / S. Biscoveanu / A. Bisht
- M. Bitossi / M.-A. Bizouard / J. K. Blackburn / L. A. Blagg
- C. D. Blair / D. G. Blair / F. Bobba / N. Bode
- G. Boileau / M. Boldrini / G. N. Bolingbroke / A.
Bolliand
- L. D. Bonavena / R. Bondarescu / F. Bondu / E. Bonilla
- M. S. Bonilla / A. Bonino / R. Bonnand / P. Booker
- A. Borchers / V. Boschi / S. Bose / V. Bossilkov
- V. Boudart / A. Boudon / A. Bozzi / C. Bradaschia
- P. R. Brady / M. Braglia / A. Branch / M. Branchesi
- J. Brandt / I. Braun / M. Breschi / T. Briant
- A. Brillet / M. Brinkmann / P. Brockill / E. Brockmueller
- A. F. Brooks / B. C. Brown / D. D. Brown / M. L. Brozzetti
- S. Brunett / G. Bruno / R. Bruntz / J. Bryant
- F. Bucci / J. Buchanan / O. Bulashenko / T. Bulik
- H. J. Bulten / A. Buonanno / K. Burtnyk / R. Buscicchio
- D. Buskulic / C. Buy / R. L. Byer / G. S. Cabourn Davies
- G. Cabras / R. Cabrita / V. Cáceres-Barbosa / L. Cadonati
- G. Cagnoli / C. Cahillane / J. Calderón Bustillo / T. A.
Callister
- E. Calloni / J. B. Camp / M. Canepa / G. Caneva Santoro
- K. C. Cannon / H. Cao / L. A. Capistran / E. Capocasa
- E. Capote / G. Carapella / F. Carbognani / M. Carlassara
- J. B. Carlin / M. Carpinelli / G. Carrillo / J. J. Carter
- G. Carullo / J. Casanueva Diaz / C. Casentini / S. Y.
Castro-Lucas
- S. Caudill / M. Cavaglià / R. Cavalieri / G. Cella
- P. Cerdá-Durán / E. Cesarini / W. Chaibi / P. Chakraborty
- S. Chalathadka Subrahmanya / J. C. L. Chan / M. Chan / K.
Chandra
- R.-J. Chang / S. Chao / E. L. Charlton / P. Charlton
- E. Chassande-Mottin / C. Chatterjee / Debarati Chatterjee / Deep
Chatterjee
- M. Chaturvedi / S. Chaty / A. Chen / A. H.-Y. Chen
- D. Chen / H. Chen / H. Y. Chen / J. Chen
- K. H. Chen / Y. Chen / Yanbei Chen / Yitian Chen
- H. P. Cheng / P. Chessa / H. T. Cheung / S. Y. Cheung
- F. Chiadini / G. Chiarini / R. Chierici / A. Chincarini
- M. L. Chiofalo / A. Chiummo / C. Chou / S. Choudhary
- N. Christensen / S. S. Y. Chua / P. Chugh / G. Ciani
- P. Ciecielag / M. Cieślar / M. Cifaldi / R. Ciolfi
- F. Clara / J. A. Clark / J. Clarke / T. A. Clarke
- P. Clearwater / S. Clesse / E. Coccia / E. Codazzo
- P.-F. Cohadon / S. Colace / M. Colleoni / C. G. Collette
- J. Collins / S. Colloms / A. Colombo / M. Colpi
- C. M. Compton / G. Connolly / L. Conti / T. R. Corbitt
- I. Cordero-Carrión / S. Corezzi / N. J. Cornish / A. Corsi
- S. Cortese / C. A. Costa / R. Cottingham / M. W. Coughlin
- A. Couineaux / J.-P. Coulon / S. T. Countryman / J.-F.
Coupechoux
- P. Couvares / D. M. Coward / M. J. Cowart / R. Coyne
- K. Craig / R. Creed / J. D. E. Creighton / T. D. Creighton
- P. Cremonese / A. W. Criswell / J. C. G. Crockett-Gray / S.
Crook
- R. Crouch / J. Csizmazia / J. R. Cudell / T. J. Cullen
- A. Cumming / E. Cuoco / M. Cusinato / P. Dabadie
- T. Dal Canton / S. Dall’Osso / S. Dal Pra / G. Dálya
- B. D’Angelo / S. Danilishin / S. D’Antonio / K. Danzmann
- K. E. Darroch / L. P. Dartez / A. Dasgupta / S. Datta
- V. Dattilo / A. Daumas / N. Davari / I. Dave
- A. Davenport / M. Davier / T. F. Davies / D. Davis
- L. Davis / M. C. Davis / P. J. Davis / M. Dax
- J. De Bolle / M. Deenadayalan / J. Degallaix / M. De Laurentis
- S. Deléglise / F. De Lillo / D. Dell’Aquila / W. Del Pozzo
- F. De Marco / F. De Matteis / V. D’Emilio / N. Demos
- T. Dent / A. Depasse / N. DePergola / R. De Pietri
- R. De Rosa / C. De Rossi / R. DeSalvo / R. De Simone
- A. Dhani / R. Diab / M. C. Díaz / M. Di Cesare
- G. Dideron / N. A. Didio / T. Dietrich / L. Di Fiore
- C. Di Fronzo / M. Di Giovanni / T. Di Girolamo / D. Diksha
- A. Di Michele / J. Ding / S. Di Pace / I. Di Palma
- F. Di Renzo / Divyajyoti / A. Dmitriev / Z. Doctor
- E. Dohmen / P. P. Doleva / D. Dominguez / L. D’Onofrio
- F. Donovan / K. L. Dooley / T. Dooney / S. Doravari
- O. Dorosh / M. Drago / J. C. Driggers / J.-G. Ducoin
- L. Dunn / U. Dupletsa / D. D’Urso / H. Duval
- P.-A. Duverne / S. E. Dwyer / C. Eassa / M. Ebersold
- T. Eckhardt / G. Eddolls / B. Edelman / T. B. Edo
- O. Edy / A. Effler / J. Eichholz / H. Einsle
- M. Eisenmann / R. A. Eisenstein / A. Ejlli / R. M. Eleveld
- M. Emma / K. Endo / A. J. Engl / E. Enloe
- L. Errico / R. C. Essick / H. Estellés / D. Estevez
- T. Etzel / M. Evans / T. Evstafyeva / B. E. Ewing
- J. M. Ezquiaga / F. Fabrizi / F. Faedi / V. Fafone
- S. Fairhurst / A. M. Farah / B. Farr / W. M. Farr
- G. Favaro / M. Favata / M. Fays / M. Fazio
- J. Feicht / M. M. Fejer / R. Felicetti / E. Fenyvesi
- D. L. Ferguson / S. Ferraiuolo / I. Ferrante / T. A. Ferreira
- F. Fidecaro / P. Figura / A. Fiori / I. Fiori
- M. Fishbach / R. P. Fisher / R. Fittipaldi / V. Fiumara
- R. Flaminio / S. M. Fleischer / L. S. Fleming / E. Floden
- E. M. Foley / H. Fong / J. A. Font / B. Fornal
- P. W. F. Forsyth / K. Franceschetti / N. Franchini / S. Frasca
- F. Frasconi / A. Frattale Mascioli / Z. Frei / A. Freise
- O. Freitas / R. Frey / W. Frischhertz / P. Fritschel
- V. V. Frolov / G. G. Fronzé / M. Fuentes-Garcia / S. Fujii
- T. Fujimori / P. Fulda / M. Fyffe / B. Gadre
- J. R. Gair / S. Galaudage / V. Galdi / H. Gallagher
- S. Gallardo / B. Gallego / R. Gamba / A. Gamboa
- D. Ganapathy / A. Ganguly / B. Garaventa / J. García-Bellido
- C. García Núñez / C. García-Quirós / J. W. Gardner / K. A.
Gardner
- J. Gargiulo / A. Garron / F. Garufi / C. Gasbarra
- B. Gateley / V. Gayathri / G. Gemme / A. Gennai
- V. Gennari / J. George / R. George / O. Gerberding
- L. Gergely / Archisman Ghosh / Sayantan Ghosh / Shaon Ghosh
- Shrobana Ghosh / Suprovo Ghosh / Tathagata Ghosh / L. Giacoppo
- J. A. Giaime / K. D. Giardina / D. R. Gibson / D. T. Gibson
- C. Gier / P. Giri / F. Gissi / S. Gkaitatzis
- J. Glanzer / F. Glotin / J. Godfrey / P. Godwin
- N. L. Goebbels / E. Goetz / J. Golomb / S. Gomez Lopez
- B. Goncharov / Y. Gong / G. González / P. Goodarzi
- S. Goode / A. W. Goodwin-Jones / M. Gosselin / A. S. Göttel
- R. Gouaty / D. W. Gould / K. Govorkova / S. Goyal
- B. Grace / A. Grado / V. Graham / A. E. Granados
- M. Granata / V. Granata / S. Gras / P. Grassia
- A. Gray / C. Gray / R. Gray / G. Greco
- A. C. Green / S. M. Green / S. R. Green / A. M. Gretarsson
- E. M. Gretarsson / D. Griffith / W. L. Griffiths / H. L. Griggs
- G. Grignani / A. Grimaldi / C. Grimaud / H. Grote
- D. Guerra / D. Guetta / G. M. Guidi / A. R. Guimaraes
- H. K. Gulati / F. Gulminelli / A. M. Gunny / H. Guo
- W. Guo / Y. Guo / Anchal Gupta / Anuradha Gupta
- Ish Gupta / N. C. Gupta / P. Gupta / S. K. Gupta
- T. Gupta / N. Gupte / J. Gurs / N. Gutierrez
- F. Guzman / H.-Y. H / D. Haba / M. Haberland
- S. Haino / E. D. Hall / E. Z. Hamilton / G. Hammond
- W.-B. Han / M. Haney / J. Hanks / C. Hanna
- M. D. Hannam / O. A. Hannuksela / A. G. Hanselman / H. Hansen
- J. Hanson / R. Harada / A. R. Hardison / K. Haris
- T. Harmark / J. Harms / G. M. Harry / I. W. Harry
- J. Hart / B. Haskell / C.-J. Haster / J. S. Hathaway
- K. Haughian / H. Hayakawa / K. Hayama / R. Hayes
- A. Heffernan / A. Heidmann / M. C. Heintze / J. Heinze
- J. Heinzel / H. Heitmann / F. Hellman / P. Hello
- A. F. Helmling-Cornell / G. Hemming / O. Henderson-Sapir / M.
Hendry
- I. S. Heng / E. Hennes / C. Henshaw / T. Hertog
- M. Heurs / A. L. Hewitt / J. Heyns / S. Higginbotham
- S. Hild / S. Hill / Y. Himemoto / N. Hirata
- C. Hirose / W. C. G. Ho / S. Hoang / S. Hochheim
- D. Hofman / N. A. Holland / K. Holley-Bockelmann / Z. J. Holmes
- D. E. Holz / L. Honet / C. Hong / J. Hornung
- S. Hoshino / J. Hough / S. Hourihane / E. J. Howell
- C. G. Hoy / C. A. Hrishikesh / H.-F. Hsieh / C. Hsiung
- H. C. Hsu / W.-F. Hsu / P. Hu / Q. Hu
- H. Y. Huang / Y.-J. Huang / A. D. Huddart / B. Hughey
- D. C. Y. Hui / V. Hui / S. Husa / R. Huxford
- T. Huynh-Dinh / L. Iampieri / G. A. Iandolo / M. Ianni
- A. Iess / H. Imafuku / K. Inayoshi / Y. Inoue
- G. Iorio / M. H. Iqbal / J. Irwin / R. Ishikawa
- M. Isi / M. A. Ismail / Y. Itoh / H. Iwanaga
- M. Iwaya / B. R. Iyer / V. JaberianHamedan / C. Jacquet
- P.-E. Jacquet / S. J. Jadhav / S. P. Jadhav / T. Jain
- A. L. James / P. A. James / R. Jamshidi / J. Janquart
- K. Janssens / N. N. Janthalur / S. Jaraba / P. Jaranowski
- R. Jaume / W. Javed / A. Jennings / W. Jia
- J. Jiang / H. Jin / J. Kubisz / C. Johanson
- G. R. Johns / N. A. Johnson / M. C. Johnston / R. Johnston
- N. Johny / D. H. Jones / D. I. Jones / R. Jones
- S. Jose / P. Joshi / L. Ju / K. Jung
- J. Junker / V. Juste / T. Kajita / I. Kaku
- C. Kalaghatgi / V. Kalogera / M. Kamiizumi / N. Kanda
- S. Kandhasamy / G. Kang / J. B. Kanner / S. J. Kapadia
- D. P. Kapasi / S. Karat / C. Karathanasis / R. Kashyap
- M. Kasprzack / W. Kastaun / T. Kato / E. Katsavounidis
- W. Katzman / R. Kaushik / K. Kawabe / R. Kawamoto
- A. Kazemi / D. Keitel / J. Kelley-Derzon / J. Kennington
- R. Kesharwani / J. S. Key / R. Khadela / S. Khadka
- F. Y. Khalili / F. Khan / I. Khan / T. Khanam
- M. Khursheed / N. M. Khusid / W. Kiendrebeogo / N. Kijbunchoo
- C. Kim / J. C. Kim / K. Kim / M. H. Kim
- S. Kim / Y.-M. Kim / C. Kimball / M. Kinley-Hanlon
- M. Kinnear / J. S. Kissel / S. Klimenko / A. M. Knee
- N. Knust / K. Kobayashi / P. Koch / S. M. Koehlenbeck
- G. Koekoek / K. Kohri / K. Kokeyama / S. Koley
- P. Kolitsidou / M. Kolstein / K. Komori / A. K. H. Kong
- A. Kontos / M. Korobko / R. V. Kossak / X. Kou
- A. Koushik / N. Kouvatsos / M. Kovalam / D. B. Kozak
- S. L. Kranzhoff / V. Kringel / N. V. Krishnendu / A. Królak
- K. Kruska / G. Kuehn / P. Kuijer / S. Kulkarni
- A. Kulur Ramamohan / A. Kumar / Praveen Kumar / Prayush Kumar
- Rahul Kumar / Rakesh Kumar / J. Kume / K. Kuns
- N. Kuntimaddi / S. Kuroyanagi / N. J. Kurth / S. Kuwahara
- K. Kwak / K. Kwan / J. Kwok / G. Lacaille
- P. Lagabbe / D. Laghi / S. Lai / A. H. Laity
- M. H. Lakkis / E. Lalande / M. Lalleman / P. C. Lalremruati
- M. Landry / B. B. Lane / R. N. Lang / J. Lange
- B. Lantz / A. La Rana / I. La Rosa / A. Lartaux-Vollard
- P. D. Lasky / J. Lawrence / M. N. Lawrence / M. Laxen
- A. Lazzarini / C. Lazzaro / P. Leaci / Y. K. Lecoeuche
- H. M. Lee / H. W. Lee / K. Lee / R.-K. Lee
- R. Lee / S. Lee / Y. Lee / I. N. Legred
- J. Lehmann / L. Lehner / M. Le Jean / A. Lemaître
- M. Lenti / M. Leonardi / M. Lequime / N. Leroy
- M. Lesovsky / N. Letendre / M. Lethuillier / S. E. Levin
- Y. Levin / K. Leyde / A. K. Y. Li / K. L. Li
- T. G. F. Li / X. Li / Z. Li / A. Lihos
- C-Y. Lin / C.-Y. Lin / E. T. Lin / F. Lin
- H. Lin / L. C.-C. Lin / Y.-C. Lin / F. Linde
- S. D. Linker / T. B. Littenberg / A. Liu / G. C. Liu
- Jian Liu / F. Llamas Villarreal / J. Llobera-Querol / R. K. L.
Lo
- J.-P. Locquet / L. T. London / A. Longo / D. Lopez
- M. Lopez Portilla / M. Lorenzini / A. Lorenzo-Medina / V.
Loriette
- M. Lormand / G. Losurdo / T. P. Lott / J. D. Lough
- H. A. Loughlin / C. O. Lousto / M. J. Lowry / N. Lu
- H. Lück / D. Lumaca / A. P. Lundgren / A. W. Lussier
- L.-T. Ma / S. Ma / M. Ma’arif / R. Macas
- A. Macedo / M. MacInnis / R. R. Maciy / D. M. Macleod
- I. A. O. MacMillan / A. Macquet / D. Macri / K. Maeda
- S. Maenaut / I. Magaña Hernandez / S. S. Magare / C. Magazzù
- R. M. Magee / E. Maggio / R. Maggiore / M. Magnozzi
- M. Mahesh / S. Mahesh / M. Maini / S. Majhi
- E. Majorana / C. N. Makarem / E. Makelele / J. A.
Malaquias-Reis
- U. Mali / S. Maliakal / A. Malik / N. Man
- V. Mandic / V. Mangano / B. Mannix / G. L. Mansell
- G. Mansingh / M. Manske / M. Mantovani / M. Mapelli
- F. Marchesoni / D. Marín Pina / F. Marion / S. Márka
- Z. Márka / A. S. Markosyan / A. Markowitz / E. Maros
- S. Marsat / F. Martelli / I. W. Martin / R. M. Martin
- B. B. Martinez / M. Martinez / V. Martinez / A. Martini
- K. Martinovic / J. C. Martins / D. V. Martynov / E. J. Marx
- L. Massaro / A. Masserot / M. Masso-Reid / M. Mastrodicasa
- S. Mastrogiovanni / T. Matcovich / M. Matiushechkina / M.
Matsuyama
- N. Mavalvala / N. Maxwell / G. McCarrol / R. McCarthy
- D. E. McClelland / S. McCormick / L. McCuller / S. McEachin
- C. McElhenny / G. I. McGhee / J. McGinn / K. B. M. McGowan
- J. McIver / A. McLeod / T. McRae / D. Meacher
- Q. Meijer / A. Melatos / S. Mellaerts / A. Menendez-Vazquez
- C. S. Menoni / F. Mera / R. A. Mercer / L. Mereni
- K. Merfeld / E. L. Merilh / J. R. Mérou / J. D. Merritt
- M. Merzougui / C. Messenger / C. Messick / Z. Metzler
- M. Meyer-Conde / F. Meylahn / A. Mhaske / A. Miani
- H. Miao / I. Michaloliakos / C. Michel / Y. Michimura
- H. Middleton / A. L. Miller / S. Miller / M. Millhouse
- E. Milotti / V. Milotti / Y. Minenkov / N. Mio
- Ll. M. Mir / L. Mirasola / M. Miravet-Tenés / C.-A. Miritescu
- A. K. Mishra / A. Mishra / C. Mishra / T. Mishra
- A. L. Mitchell / J. G. Mitchell / S. Mitra / V. P. Mitrofanov
- R. Mittleman / O. Miyakawa / S. Miyamoto / S. Miyoki
- G. Mo / L. Mobilia / S. R. P. Mohapatra / S. R. Mohite
- M. Molina-Ruiz / C. Mondal / M. Mondin / M. Montani
- C. J. Moore / D. Moraru / A. More / S. More
- G. Moreno / C. Morgan / S. Morisaki / Y. Moriwaki
- G. Morras / A. Moscatello / P. Mourier / B. Mours
- C. M. Mow-Lowry / F. Muciaccia / Arunava Mukherjee / D.
Mukherjee
- Samanwaya Mukherjee / Soma Mukherjee / Subroto Mukherjee / Suvodip
Mukherjee
- N. Mukund / A. Mullavey / J. Munch / J. Mundi
- C. L. Mungioli / W. R. Munn Oberg / Y. Murakami / M. Murakoshi
- P. G. Murray / S. Muusse / D. Nabari / S. L. Nadji
- A. Nagar / N. Nagarajan / K. N. Nagler / K. Nakagaki
- K. Nakamura / H. Nakano / M. Nakano / D. Nandi
- V. Napolano / P. Narayan / I. Nardecchia / T. Narikawa
- H. Narola / L. Naticchioni / R. K. Nayak / J. Neilson
- A. Nelson / T. J. N. Nelson / M. Nery / A. Neunzert
- S. Ng / L. Nguyen Quynh / S. A. Nichols / A. B. Nielsen
- G. Nieradka / A. Niko / Y. Nishino / A. Nishizawa
- S. Nissanke / E. Nitoglia / W. Niu / F. Nocera
- M. Norman / C. North / J. Novak / J. F. Nuño Siles
- L. K. Nuttall / K. Obayashi / J. Oberling / J. O’Dell
- M. Oertel / A. Offermans / G. Oganesyan / J. J. Oh
- K. Oh / T. O’Hanlon / M. Ohashi / M. Ohkawa
- F. Ohme / A. S. Oliveira / R. Oliveri / B. O’Neal
- K. Oohara / B. O’Reilly / N. D. Ormsby / M. Orselli
- R. O’Shaughnessy / S. O’Shea / Y. Oshima / S. Oshino
- S. Ossokine / C. Osthelder / I. Ota / D. J. Ottaway
- A. Ouzriat / H. Overmier / B. J. Owen / A. E. Pace
- R. Pagano / M. A. Page / A. Pai / A. Pal
- S. Pal / M. A. Palaia / M. Pálfi / P. P. Palma
- C. Palomba / P. Palud / H. Pan / J. Pan
- K. C. Pan / R. Panai / P. K. Panda / S. Pandey
- L. Panebianco / P. T. H. Pang / F. Pannarale / K. A. Pannone
- B. C. Pant / F. H. Panther / F. Paoletti / A. Paolone
- E. E. Papalexakis / L. Papalini / G. Papigkiotis / A. Paquis
- A. Parisi / B.-J. Park / J. Park / W. Parker
- G. Pascale / D. Pascucci / A. Pasqualetti / R. Passaquieti
- L. Passenger / D. Passuello / O. Patane / D. Pathak
- M. Pathak / A. Patra / B. Patricelli / A. S. Patron
- K. Paul / S. Paul / E. Payne / T. Pearce
- M. Pedraza / R. Pegna / A. Pele / F. E. Peña Arellano
- S. Penn / M. D. Penuliar / A. Perego / Z. Pereira
- J. J. Perez / C. Périgois / G. Perna / A. Perreca
- J. Perret / S. Perriès / J. W. Perry / D. Pesios
- S. Petracca / C. Petrillo / H. P. Pfeiffer / H. Pham
- K. A. Pham / K. S. Phukon / H. Phurailatpam / M. Piarulli
- L. Piccari / O. J. Piccinni / M. Pichot / M. Piendibene
- F. Piergiovanni / L. Pierini / G. Pierra / V. Pierro
- M. Pietrzak / M. Pillas / F. Pilo / L. Pinard
- I. M. Pinto / M. Pinto / B. J. Piotrzkowski / M. Pirello
- M. D. Pitkin / A. Placidi / E. Placidi / M. L. Planas
- W. Plastino / R. Poggiani / E. Polini / L. Pompili
- J. Poon / E. Porcelli / E. K. Porter / C. Posnansky
- R. Poulton / J. Powell / M. Pracchia / B. K. Pradhan
- T. Pradier / A. K. Prajapati / K. Prasai / R. Prasanna
- P. Prasia / G. Pratten / G. Principe / M. Principe
- G. A. Prodi / L. Prokhorov / P. Prosposito / A. Puecher
- J. Pullin / M. Punturo / P. Puppo / M. Pürrer
- H. Qi / J. Qin / G. Quéméner / V. Quetschke
- C. Quigley / P. J. Quinonez / F. J. Raab / S. S. Raabith
- G. Raaijmakers / S. Raja / C. Rajan / B. Rajbhandari
- K. E. Ramirez / F. A. Ramis Vidal / A. Ramos-Buades / D. Rana
- S. Ranjan / K. Ransom / P. Rapagnani / B. Ratto
- S. Rawat / A. Ray / V. Raymond / M. Razzano
- J. Read / M. Recaman Payo / T. Regimbau / L. Rei
- S. Reid / D. H. Reitze / P. Relton / A. I. Renzini
- P. Rettegno / B. Revenu / R. Reyes / A. S. Rezaei
- F. Ricci / M. Ricci / A. Ricciardone / J. W. Richardson
- M. Richardson / A. Rijal / K. Riles / H. K. Riley
- S. Rinaldi / J. Rittmeyer / C. Robertson / F. Robinet
- M. Robinson / A. Rocchi / L. Rolland / J. G. Rollins
- A. E. Romano / R. Romano / A. Romero / I. M. Romero-Shaw
- J. H. Romie / S. Ronchini / T. J. Roocke / L. Rosa
- T. J. Rosauer / C. A. Rose / D. Rosińska / M. P. Ross
- M. Rossello / S. Rowan / S. K. Roy / S. Roy
- D. Rozza / P. Ruggi / N. Ruhama / E. Ruiz Morales
- K. Ruiz-Rocha / S. Sachdev / T. Sadecki / J. Sadiq
- P. Saffarieh / M. R. Sah / S. S. Saha / S. Saha
- T. Sainrat / S. Sajith Menon / K. Sakai / M. Sakellariadou
- S. Sakon / O. S. Salafia / F. Salces-Carcoba / L. Salconi
- M. Saleem / F. Salemi / M. Sallé / S. Salvador
- A. Sanchez / E. J. Sanchez / J. H. Sanchez / L. E. Sanchez
- N. Sanchis-Gual / J. R. Sanders / E. M. Sänger / F.
Santoliquido
- T. R. Saravanan / N. Sarin / S. Sasaoka / A. Sasli
- P. Sassi / B. Sassolas / H. Satari / R. Sato
- Y. Sato / O. Sauter / R. L. Savage / T. Sawada
- H. L. Sawant / S. Sayah / V. Scacco / D. Schaetzl
- M. Scheel / A. Schiebelbein / M. G. Schiworski / P. Schmidt
- S. Schmidt / R. Schnabel / M. Schneewind / R. M. S. Schofield
- K. Schouteden / B. W. Schulte / B. F. Schutz / E. Schwartz
- M. Scialpi / J. Scott / S. M. Scott / T. C. Seetharamu
- M. Seglar-Arroyo / Y. Sekiguchi / D. Sellers / A. S. Sengupta
- D. Sentenac / E. G. Seo / J. W. Seo / V. Sequino
- M. Serra / G. Servignat / A. Sevrin / T. Shaffer
- U. S. Shah / M. A. Shaikh / L. Shao / A. K. Sharma
- P. Sharma / S. Sharma-Chaudhary / M. R. Shaw / P. Shawhan
- N. S. Shcheblanov / E. Sheridan / Y. Shikano / M. Shikauchi
- K. Shimode / H. Shinkai / J. Shiota / D. H. Shoemaker
- D. M. Shoemaker / R. W. Short / S. ShyamSundar / A. Sider
- H. Siegel / M. Sieniawska / D. Sigg / L. Silenzi
- M. Simmonds / L. P. Singer / A. Singh / D. Singh
- M. K. Singh / S. Singh / A. Singha / A. M. Sintes
- V. Sipala / V. Skliris / B. J. J. Slagmolen / T. J.
Slaven-Blair
- J. Smetana / J. R. Smith / L. Smith / R. J. E. Smith
- W. J. Smith / J. Soldateschi / K. Somiya / I. Song
- K. Soni / S. Soni / V. Sordini / F. Sorrentino
- N. Sorrentino / H. Sotani / R. Soulard / A. Southgate
- V. Spagnuolo / A. P. Spencer / M. Spera / P. Spinicelli
- J. B. Spoon / C. A. Sprague / A. K. Srivastava / F. Stachurski
- D. A. Steer / J. Steinlechner / S. Steinlechner / N.
Stergioulas
- P. Stevens / M. StPierre / G. Stratta / M. D. Strong
- A. Strunk / R. Sturani / A. L. Stuver / M. Suchenek
- S. Sudhagar / N. Sueltmann / L. Suleiman / K. D. Sullivan
- L. Sun / S. Sunil / J. Suresh / P. J. Sutton
- T. Suzuki / Y. Suzuki / B. L. Swinkels / A. Syx
- M. J. Szczepańczyk / P. Szewczyk / M. Tacca / H. Tagoshi
- S. C. Tait / H. Takahashi / R. Takahashi / A. Takamori
- T. Takase / K. Takatani / H. Takeda / K. Takeshita
- C. Talbot / M. Tamaki / N. Tamanini / D. Tanabe
- K. Tanaka / S. J. Tanaka / T. Tanaka / D. Tang
- S. Tanioka / D. B. Tanner / L. Tao / R. D. Tapia
- E. N. Tapia San Martín / R. Tarafder / C. Taranto / A. Taruya
- J. D. Tasson / M. Teloi / R. Tenorio / H. Themann
- A. Theodoropoulos / M. P. Thirugnanasambandam / L. M. Thomas / M.
Thomas
- P. Thomas / J. E. Thompson / S. R. Thondapu / K. A. Thorne
- E. Thrane / J. Tissino / A. Tiwari / P. Tiwari
- S. Tiwari / V. Tiwari / M. R. Todd / A. M. Toivonen
- K. Toland / A. E. Tolley / T. Tomaru / K. Tomita
- T. Tomura / C. Tong-Yu / A. Toriyama / N. Toropov
- A. Torres-Forné / C. I. Torrie / M. Toscani / I. Tosta e Melo
- E. Tournefier / A. Trapananti / F. Travasso / G. Traylor
- M. Trevor / M. C. Tringali / A. Tripathee / G. Troian
- L. Troiano / A. Trovato / L. Trozzo / R. J. Trudeau
- T. T. L. Tsang / R. Tso / S. Tsuchida / L. Tsukada
- T. Tsutsui / K. Turbang / M. Turconi / C. Turski
- H. Ubach / T. Uchiyama / R. P. Udall / T. Uehara
- M. Uematsu / K. Ueno / S. Ueno / V. Undheim
- T. Ushiba / M. Vacatello / H. Vahlbruch / N. Vaidya
- G. Vajente / A. Vajpeyi / G. Valdes / J. Valencia
- M. Valentini / S. A. Vallejo-Peña / S. Vallero / V. Valsan
- N. van Bakel / M. van Beuzekom / M. van Dael / J. F. J. van den
Brand
- C. Van Den Broeck / D. C. Vander-Hyde / M. van der Sluys / A. Van de
Walle
- J. van Dongen / K. Vandra / H. van Haevermaet / J. V. van
Heijningen
- P. Van Hove / M. VanKeuren / J. Vanosky / M. H. P. M. van
Putten
- Z. van Ranst / N. van Remortel / M. Vardaro / A. F. Vargas
- J. J. Varghese / V. Varma / M. Vasúth / A. Vecchio
- G. Vedovato / J. Veitch / P. J. Veitch / S. Venikoudis
- J. Venneberg / P. Verdier / D. Verkindt / B. Verma
- P. Verma / Y. Verma / S. M. Vermeulen / F. Vetrano
- A. Veutro / A. M. Vibhute / A. Viceré / S. Vidyant
- A. D. Viets / A. Vijaykumar / A. Vilkha / V. Villa-Ortega
- E. T. Vincent / J.-Y. Vinet / S. Viret / A. Virtuoso
- S. Vitale / A. Vives / H. Vocca / D. Voigt
- E. R. G. von Reis / J. S. A. von Wrangel / S. P. Vyatchanin / L. E.
Wade
- M. Wade / K. J. Wagner / A. Wajid / M. Walker
- G. S. Wallace / L. Wallace / H. Wang / J. Z. Wang
- W. H. Wang / Z. Wang / G. Waratkar / J. Warner
- M. Was / T. Washimi / N. Y. Washington / D. Watarai
- K. E. Wayt / B. R. Weaver / B. Weaver / C. R. Weaving
- S. A. Webster / M. Weinert / A. J. Weinstein / R. Weiss
- F. Wellmann / L. Wen / P. Weßels / K. Wette
- J. T. Whelan / B. F. Whiting / C. Whittle / J. B. Wildberger
- O. S. Wilk / D. Wilken / A. T. Wilkin / D. J. Willadsen
- K. Willetts / D. Williams / M. J. Williams / N. S. Williams
- J. L. Willis / B. Willke / M. Wils / J. Winterflood
- C. C. Wipf / G. Woan / J. Woehler / J. K. Wofford
- N. E. Wolfe / H. T. Wong / H. W. Y. Wong / I. C. F. Wong
- J. L. Wright / M. Wright / C. Wu / D. S. Wu
- H. Wu / E. Wuchner / D. M. Wysocki / V. A. Xu
- Y. Xu / N. Yadav / H. Yamamoto / K. Yamamoto
- T. S. Yamamoto / T. Yamamoto / S. Yamamura / R. Yamazaki
- S. Yan / T. Yan / F. W. Yang / F. Yang
- K. Z. Yang / Y. Yang / Z. Yarbrough / H. Yasui
- S.-W. Yeh / A. B. Yelikar / X. Yin / J. Yokoyama
- T. Yokozawa / J. Yoo / H. Yu / S. Yuan
- H. Yuzurihara / A. Zadrożny / M. Zanolin / M. Zeeshan
- T. Zelenova / J.-P. Zendri / M. Zeoli / M. Zerrad
- M. Zevin / A. C. Zhang / L. Zhang / R. Zhang
- T. Zhang / Y. Zhang / C. Zhao / Yue Zhao
- Yuhang Zhao / Y. Zheng / H. Zhong / R. Zhou
- X.-J. Zhu / Z.-H. Zhu / A. B. Zimmerman / M. E. Zucker
- J. Zweizig / S. B. Araujo Furlan / Z. Arzoumanian / A. Basu
- A. Cassity / I. Cognard / K. Crowter / S. del Palacio
- C. M. Espinoza / E. Fonseca / C. M. L. Flynn / G. Gancio
- F. Garcia / K. C. Gendreau / D. C. Good / L. Guillemot
- S. Guillot / M. J. Keith / L. Kuiper / M. E. Lower
- A. G. Lyne / J. W. McKee / B. W. Meyers / J. L. Palfreyman
- A. B. Pearlman / G. E. Romero / R. M. Shannon / B. Shaw
- I. H. Stairs / B. W. Stappers / C. M. Tan / G. Theureau
- M. Thompson / P. Weltevrede / E. Zubieta
Summary
Continuous gravitational waves (CWs) emission from neutron stars
carries information about their internal structure and equation of
state, and it can provide tests of General Relativity. We present a
search for CWs from a set of 45 known pulsars in the first part of the
fourth LIGO–Virgo–KAGRA observing run, known as O4a. We conducted a
targeted search for each pulsar using three independent analysis methods
considering the single-harmonic and the dual-harmonic emission models.
We find no evidence of a CW signal in O4a data for both models and set
upper limits on the signal amplitude and on the ellipticity, which
quantifies the asymmetry in the neutron star mass distribution. For the
single-harmonic emission model, 29 targets have the upper limit on the
amplitude below the theoretical spin-down limit. The lowest upper limit
on the amplitude is  for the young energetic pulsar J0537-6910, while
the lowest constraint on the ellipticity is
for the young energetic pulsar J0537-6910, while
the lowest constraint on the ellipticity is  for the bright nearby millisecond pulsar
J0437-4715. Additionally, for a subset of 16 targets we performed a
narrowband search that is more robust regarding the emission model, with
no evidence of a signal. We also found no evidence of non-standard
polarizations as predicted by the Brans-Dicke theory.
for the bright nearby millisecond pulsar
J0437-4715. Additionally, for a subset of 16 targets we performed a
narrowband search that is more robust regarding the emission model, with
no evidence of a signal. We also found no evidence of non-standard
polarizations as predicted by the Brans-Dicke theory.
FEASTS:
Radial Distribution of HI surface densities down to 0.01 M pc
pc of 35 Nearby
Galaxies
of 35 Nearby
Galaxies
Link to the paper
Authors
Authors
- Jing Wang / Dong Yang / Xuchen Lin / Qifeng Huang
- Zhijie Qu / Hsiao-Wen Chen / Hong Guo / Luis C. Ho
- Peng Jiang / Zezhong Liang / Céline Péroux / Lister
Staveley-Smith
- Simon Weng
Summary
We present the HI surface density ( ) radial
distributions based on total-power HI images obtained by FAST in the
FEASTS program, for 35 galaxies with inclinations lower than 72 degree.
We derive the HI radius
) radial
distributions based on total-power HI images obtained by FAST in the
FEASTS program, for 35 galaxies with inclinations lower than 72 degree.
We derive the HI radius  , which is the
radius for the 0.01
, which is the
radius for the 0.01  (
( ) iso-density level, 100 times deeper than the 1
) iso-density level, 100 times deeper than the 1
 level previously commonly used to measure
level previously commonly used to measure  . The profile shapes show a large
diversity at a given radius in units of kpc, group virial radius, and
. The profile shapes show a large
diversity at a given radius in units of kpc, group virial radius, and
 , but align more tightly with radius
normalized by
, but align more tightly with radius
normalized by  . The universal HI
profile has a scatter of
. The universal HI
profile has a scatter of  dex, and a
scale-length of
dex, and a
scale-length of  in
the outer region. We derive a new
in
the outer region. We derive a new  -
- relation,
which has a scatter of 0.02 dex, and similar slope of $$0.5 as the
previously known
relation,
which has a scatter of 0.02 dex, and similar slope of $$0.5 as the
previously known  -
- relation.
Excluding strongly tidal-interacting galaxies, the ratio
relation.
Excluding strongly tidal-interacting galaxies, the ratio  (anti-)correlate strongly and significantly with the HI-to-stellar mass
ratio and sSFR, but not with the stellar mass,
(anti-)correlate strongly and significantly with the HI-to-stellar mass
ratio and sSFR, but not with the stellar mass,  , dark matter
mass, or SFR. The strongly tidal-interacting galaxies tend to show
deviations from these trends, and have the most flattened profiles.
These results imply that in absence of major tidal interactions,
physical processes must cooperate so that
, dark matter
mass, or SFR. The strongly tidal-interacting galaxies tend to show
deviations from these trends, and have the most flattened profiles.
These results imply that in absence of major tidal interactions,
physical processes must cooperate so that  distributes
in a self-similar way in the outer region down to the 0.01
distributes
in a self-similar way in the outer region down to the 0.01 level. Moreover, they may drive gas flows in such
a way, that HI-richer galaxies have HI disks not only extend further,
but also transport HI inward more efficiently from
level. Moreover, they may drive gas flows in such
a way, that HI-richer galaxies have HI disks not only extend further,
but also transport HI inward more efficiently from  to
to  .
.
specification across the 1 mHz to 1 Hz frequency band. We also identify
and characterize dominant noise sources from phasemeters and
correlations of beam tilt into the path length that were observed during
the test campaign.
-fit algorithm designed to improve the
reconstruction of neutrino events detected by a single line of the
ANTARES underwater telescope, usually associated with low energy
neutrino events (
100 GeV).
-Fit is a neural network model that
relies on deep learning and combines several advanced techniques in
machine learning –deep convolutional layers, mixture density output
layers, and transfer learning. This framework divides the reconstruction
process into two dedicated branches for each neutrino event topology
–tracks and showers– composed of sub-models for spatial estimation
–direction and position– and energy inference, which later on are
combined for event classification. Regarding the direction of
single-line events, the
-Fit algorithm significantly refines the
estimation of the zenithal angle, and delivers reliable azimuthal angle
predictions that were previously unattainable with traditional
-fit methods. Improving on
energy estimation of single-line events is a tall order;
-Fit benefits from transfer learning to
efficiently integrate key characteristics, such as the estimation of the
closest distance from the event to the detector.
-Fit also takes advantage from transfer
learning in event topology classification by freezing convolutional
layers of the pretrained branches. Tests on Monte Carlo simulations and
data demonstrate a significant reduction in mean and median absolute
errors across all reconstructed parameters. The improvements achieved by
-Fit highlight its potential for
advancing multimessenger astrophysics and enhancing our ability to probe
fundamental physics beyond the Standard Model using single-line events
from ANTARES data.
m wavelength range: an imaging
polarimeter (PRIMAger) and a spectrometer (FIRESS). The majority of
PRIMA’s time (75%) will be open to observations proposed by the
community (General Observer science / GO), and all of data will be
publicly available for archival research (Guest Investigator science /
GI). Following up on the successful community engagement created by the
first volume of the GO PRIMA Science Book (arXiv:2310.20572), Volume 2
gathers 120 new and updated contributed science cases which could be
performed within the context of the PRIMA GO/GI program. This volume
reflects the strong development of the community interest, awareness and
involvement in PRIMA, and further develops how PRIMA’s unprecedented
capabilities can be leveraged for an impactful and innovative GO/GI
program covering most areas of astrophysics and over 90% of the
scientific questions and discovery areas in the Astro2020 decadal
survey.
. We applied a
weighted kernel density estimation method to 160,000 galaxies with
robust photometric redshifts. We find that stellar mass has a positive
correlation with density at all redshifts, stronger for quiescent
galaxies (QGs) at
, while at
higher redshifts (
) this trend is confined to extreme overdense
environments, consistent with early mass assembly in proto-clusters. The
star-formation rate (SFR) shows a negative trend with density for QGs at
,
reversing at
, while
star-forming galaxies (SFGs) show a mild positive correlation up to
. The specific SFR
remains nearly flat for SFGs and declines with density for QGs at
.
Moreover, mass and environmental quenching efficiencies show that
mass-driven processes dominate at
, the two
processes act with comparable strength between
, and environmental quenching becomes stronger for
low-mass galaxies (
) at
. These
findings reveal that large-scale structure drives galaxy evolution by
enhancing early mass assembly in dense regions and increasingly
suppressing star formation in low-mass systems at later times,
establishing the environmental role of the cosmic web across cosmic
history. COSMOS-Web, the largest JWST survey, provides accurate and deep
photometric redshifts, reaching 80% mass completeness at
at
, enabling the first
view of how environments shaped galaxy evolution from the epoch of
reionization to the present day.
^{-3}$ per day per star. Our detection
implies that we are no longer restricted to extrapolating the solar CME
kinematics and rates to other stars, allowing us to establish the first
observational limits on the impact of CMEs on exoplanets.
bar
and the top of the eastern cloud deck
bar,
which is consistent with the predicted altitude of MgSiO
and Mg
SiO
clouds from JWST NIRISS/SOSS. While we
do not detect the reflected light spectrum of LTT-9779 b, we have
verified that this technique can be used in practice to characterise the
high spectral resolution reflected light of exoplanets so long as their
spectra contain a sufficient number of deep spectral lines. Therefore
this technique may become an important cornerstone of exoplanet
characterisation with the ELT and beyond.
from [CII] 158
m and four tentatively detected CO lines
in NOEMA and ALMA data. SED fitting to near-IR to millimetre photometry
yields
, an
SFR of
, heavy dust attenuation
mag, and a
stellar mass
.
From the millimetre continuum and [CII] emission, we infer a warm ISM
with
,
and
.
AC-2168 has a gas fraction (
) of
, a short
depletion time of
, a
compact (
)
dust-continuum size, and an SFR consistent with the star-forming main
sequence at its mass. These properties match expectations for
progenitors of massive quiescent galaxies at the peak of their assembly,
as implied by NIRSpec-based SFHs of
systems. Using
the blind detection, we estimate a space density of
for AC-2168-like NIRCam-dark galaxies at
,
of the abundance
of massive quiescent galaxies at
. No overdensity
of Ly
emitters or Lyman-break galaxies is
found nearby, suggesting AC-2168 does not lie in a prominent
protocluster and highlighting the importance of unbiased blind surveys
for this population.
: 0.99
;
: 1.13
;
age: 7.4 Gyr; V mag: 8.25) hosts a transiting sub-Neptune, HD 85426 b,
with an orbital period of 16.71 days and a blackbody equilibrium
temperature of
K.
By jointly analysing HARPS-N RVs, TESS, and CHEOPS photometric data and
using two different stellar activity mitigation techniques, we constrain
planet b’s mass to
and $8.5^{+1.3}_{-1.4} $
, depending on the mitigation technique. We
investigate the dependence of these results on the priors, data
selection, and inclusion of other Keplerians in the modelling. Using
this approach, we identify the presence of two non-transiting planetary
companions with minimum masses near 10
and orbital periods of 35.7 and 89 days. Additionally, we reject the
initial hypothesis that the 35.7-day periodic signal was due to stellar
activity. We also determine HD 85426 b’s radius to be
and compute a transmission spectroscopy metric in the range of 82 to
115, making this planet a highly valuable target for atmospheric
characterisation.
) of MACS0416_Y1 that
confirms the suspected warm dust (91
K) of
this Lyman-Break Galaxy (LBG) at
with
M
. A modified black-body fit to the ALMA Bands 3
through 9 data of MACS0416_Y1 finds an intrinsic infrared luminosity of
1.0
, placing this UV-selected LBG in the regime of
Ultra Luminous Infrared Galaxies (ULIRGs). Its luminous but modest dust
reservoir (1.4
) is co-spatial to regions with a UV-continuum
slope
as seen by James Webb Space Telescope (JWST)
imaging. Although this implies some dust obscuration, the JWST
photometry implies less obscured star formation than seen in the
complete characterization by ALMA, implying some spatial separation of
dust and stars on scales below 200 pc, i.e., smaller than those probed
by JWST and ALMA. This source is an extreme example of dust-obscured
star formation contributing strongly to the cosmic build-up of stellar
mass, which can only be revealed through direct and comprehensive
observations in the (sub)mm regime.
. We found its
early X-ray jet break at
days post-burst
to be at odds with the evolution of the multi-frequency radio light
curves that were traced over an unusually long duration of
days. The radio light curves
approximately evolved (with minor deviations) according to the standard
self-similar expansion for a relativistic blast wave in a homogeneous
environment prior to jet break, showing no evidence for evolution in the
microphysical parameters describing the electron acceleration processes.
We reconcile these features by proposing a two-component jet: the early
X-ray break originates from a narrow component with a half-opening angle
, while the evolution of the radio afterglow stems
from a wider component with a half-opening angle
. The PanRadio GRB program will establish a sample
of comprehensively followed GRBs, where a rigorous inspection of their
microphysical and dynamical parameters can be performed, thereby
revealing the diversity of features in their outflows and
environments.
limiting magnitude of 30.9 AB (measured
in a 0.2 arcsec diameter aperture). The field is supported by extensive
ancillary data, including deep HST imaging from the Hubble Frontier
Fields program, VLT/MUSE spectroscopy, and deep JWST/NIRSpec
medium-resolution multi-object spectroscopy. Exploiting the strong
gravitational lensing of the galaxy cluster Abell S1063, GLIMPSE probes
intrinsic depths beyond 33 AB magnitudes and covers an effective
source-plane area of approximately 4.4 arcmin
at
. The program’s
central aim is to constrain the abundance of the faintest galaxies from
up to the highest
redshifts, providing crucial benchmarks for galaxy formation models,
which have so far been tested primarily on relatively bright systems. We
present an initial sample of
galaxy candidates
identified at
,
with intrinsic UV magnitudes spanning
=
$-$20 to $-
z$ active galactic nuclei. This paper accompanies
the first public data release, which includes reduced JWST and HST
mosaics, photometric catalogs, and gravitational lensing models.
with a
post-trial p-value equal to 0.38. A dedicated search in the Galactic
Plane is also performed for extended sources, yielding no significant
excess. Additionally, a list of potential neutrino sources are
investigated. The blazar MG3 J225517+2409 is identified as the most
significant object, yet the excess remains compatible with background
fluctuations. A mild local excess of 2.4
is found for the blazar TXS 0506+056.
The full sky is also examined for the presence of flaring neutrino
emissions. The most significant excess in this case corresponds to a
$$4-day flare from the direction
, with
a post-trial p-value of 0.30. Finally, the directions of sources
highlighted in IceCube’s time-dependent searches are investigated.
Temporal overlaps between ANTARES and IceCube flares are identified for
PKS 1502+106 and TXS 0506+056, with an estimated chance probability of
about 0.02%, making this observation particularly noteworthy.
(2.4deg
) of overlapping Herschel (SCUBA-2)
data, containing 2.6 million (240000) MS galaxies. We bin the Euclid
catalogue by stellar mass and photometric redshift and perform a
stacking analysis following SimStack, which takes into account galaxy
clustering and bin-to-bin correlations. We detect stacked far-IR flux
densities across a significant fraction of the bins. We fit modified
blackbody spectral energy distributions in each bin and derive mean dust
temperatures, dust masses, and star-formation rates (SFRs). We find
similar mean SFRs compared to the Euclid catalogue, and we show that the
average dust-to-stellar mass ratios decreased from z$$1 to the present
day. Average dust temperatures are largely independent of stellar mass
and are well-described by the function
, where
is the age of the Universe,
K,
K, and
Gyr. We
argue that since the dust temperatures are converging to a non-zero
value below
, the dust is now primarily
heated by the existing cooler and older stellar population, as opposed
to hot young stars in star-forming regions at higher redshift. We show
that since the dust temperatures are independent of stellar mass, the
correlation between dust temperature and SFR depends on stellar mass.
Lastly, we estimate the contribution of the Euclid catalogue to the
cosmic IR background (CIB), finding that it accounts for >60% of the
CIB at 250, 350, and 500
m. Forthcoming Euclid data will extend
these results to higher redshifts, lower stellar masses, and recover
more of the CIB.
45 Angstrom). Here we aim to quantify
the AGN contribution within this system using the BEAGLE-AGN tool to
simultaneously fit the spectrum and photometry of GHZ2. We consider a
range of models with and without AGN components, allowing us to
disentangle the stellar and AGN contribution of GHZ2 for the first time.
We conclude that a partial contribution by an AGN is significantly
favored based on the Bayes factor comparison to models without an AGN
component, measuring an AGN contribution of 54
% and 26
% for the C
IV$λ
λ
L_{acc}
{10}
{BH}
{}
^{+0.04}{-0.04}$, for an Eddington ratio of
= 0.5 (with a systematic uncertainty of
$
^{+0.02}_{-0.02}$, consistent with other high
redshift AGN systems. If the black hole interpretation is confirmed,
GHZ2 would represent the most distant black hole identified to date,
making it an ideal laboratory to study AGN growth and their role in
shaping high-redshift galactic evolution.
, between the spectral measurements
calculated using both direct integration and Gaussian fitting
methodologies. The NeV candidates exhibit colours similar to bright
QSOs, with only a few in the tail of very red quasars. We observed a
higher stellar mass content, a lower continuum around the 4000A break,
and a similar Sérsic index distribution compared to the control sample.
This unique sample paves the way for a wide range of scientific
investigations, which will be pursued in the forthcoming data
releases.
contrast levels and
will be the goal of the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO). A key
technical barrier to reaching such deep contrasts is maintaining
wavefront stability on the order of tens of picometers, in particular in
the presence of a segmented primary mirror. Keck Observatory is the only
facility with all of the hardware components necessary for validating
HWO segment phasing strategies: a large segmented primary mirror,
capacitive edge sensors, deformable mirror, Zernike wavefront sensor
(ZWFS), and high contrast science instruments. Taking advantage of these
parallels, we are using Keck as a testbed for developing and validating
HWO wavefront sensing and control loop strategies, as well as
demonstrating the full system-level segment control architecture for
HWO, using existing infrastructure. Recently, we set the stage for this
work by using the ZWFS installed on the Keck II telescope to sense and
correct the primary mirror segment pistons in closed-loop in parallel
with science observations. This resulted in improved Strehl ratios on
the NIRC2 science camera (Salama et al. 2024a). We now aim to directly
address concerns related to control authority, actuator offload, and
loop stability - tasks which require Keck’s existing infrastructure, but
which do not require picometer wavefront stability. Moreover, successful
comparisons of observed and predicted performances will validate, on a
real operating observatory, the HWO error budget methodology and in
particular its approach to nested loops operating at multiple
timescales.
using the COSMOS2025 catalog built from
JWST imaging from COSMOS-Web. Galaxies are
selected by type using the
rest-frame color
diagram and classified morphologically by bulge-to-total light ratio
(
). The quiescent SMF shows
rapid early build-up, with the most massive systems (
) assembled by
and evolving little
since. The star-forming SMF evolves more slowly, following a
mass-evolution scenario where galaxies grow via star formation and
quench at the characteristic mass
.
Bulge systems (
) dominate the
quiescent SMF at
at all redshifts, while disks (
) dominate at
. However, most bulge-dominated galaxies are
star-forming, with their fraction increasing with redshift and
decreasing mass, consistent with being progenitors of quiescent bulges.
We find evidence for environmental quenching onset at
from the upturn in
the quiescent SMF at
, contributed by disk-dominated galaxies
consistent with satellite quenching that retains disk morphologies.
Number densities of
quiescent galaxies are lower than recent
literature by
dex, but agree well
with simulations at
. At
, simulations
increasingly underpredict observations. Finally, we build an empirical
model describing galaxy number density evolution by parametrizing
quenching rates, baryon conversion efficiency, and bulge formation. Our
model supports a scenario where star-forming galaxies grow central
bulges before quenching in massive halos.
. We divide the sample into four sub-populations
of galaxies, based on their star-formation activity and morphology. We
then analyse the physical properties of these populations and their
relative abundances in the stellar mass vs. local density plane.
Together with confirming the passivity-density relation and the
morphology-density relation, we find that quiescent discy galaxies are
more abundant in the low-mass regime of high-density environment. At the
same time, star-forming bulge-dominated galaxies are more common in
field regions, preferentially at high masses. Building on these results
and interpreting them through comparison with simulations, we propose a
scenario where the evolution of galaxies in the field significantly
differs from that in higher-density environments. The morphological
transformation in the majority of field galaxies takes place before the
onset of quenching and is mainly driven by secular processes taking
place within the main sequence, leading to the formation of star-forming
bulge-dominated galaxies as intermediate-stage galaxies. Conversely,
quenching of star formation precedes morphological transformation for
most galaxies in higher-density environments. This causes the formation
of quiescent disc-dominated galaxies before their transition into
bulge-dominated ones.
(separation of
gravitational
radii) to
before merger. Initial data for the inspiral runs
are produced from circular-orbits runs covering the formation timescale
of the overdense {}lump{}, orbiting the CBD inner edge. The CBD
non-axisymmetries (spiral waves and lump) lead to non-negligible angular
momentum transport with effective viscosity
. We post-process these simulations with a
general-relativistic ray-tracing code to obtain synthetic observations
in thermal emission. We find the lump and its associated electromagnetic
(EM) modulation, already reported in the pre-decoupling epoch, to
survive post-decoupling up until the end of the simulation. For LISA
sources, our findings point to an active EM signature in UV during
optimal gravitational wave source localization. For PTA sources and
current BBH candidates detected through their optical periodicity: the
lump{ in a low-viscosity CBD is a possible, though not unique, origin}
for the observed periodicity.
, its early-time
optical polarimetry observations, and the multi-wavelength monitoring of
its afterglow. We analysed three epochs of polarimetric data to derive
the early-time evolution of the polarisation. The multi-wavelength light
curve from the X-rays to the near-infrared band was also investigated to
give a broader perspective on the whole event. We find a high level of
polarisation,
,%, at 1740~s after the GRB trigger, followed by a
slight decrease up to
,% at 3059~s. On the same timescale, the
polarisation position angle is nearly constant. The multi-band afterglow
at the time of the polarisation measurements is consistent with a
forward shock (FS), while the earlier evolution at
s
can be associated with the interplay between the forward and the reverse
shocks or with energy injection. The detected polarised radiation when
the afterglow is FS-dominated and the stable position angle are
consistent with an ordered magnetic field plus a turbulent component
driven by large-scale magnetohydrodynamic instabilities. The lack of a
jet break in the light curve prevents a comparison of the polarisation
temporal evolution with theoretical expectations from magnetic fields
amplified by microscopic-scale turbulence, limiting …
raising the question of whether high-mass
circumbinary planets are possible, and also whether population features
such as the brown dwarf desert would appear in circumbinary
configurations like for single star systems. Here, we report
observations taken with the SOPHIE high-resolution spectrograph. These
observations reveal an
outer companion, on an eccentric (
),
orbit,
which we call BEBOP-4 (AB) b. Using dynamical arguments we constrain the
true mass
. The
inner binary’s two eclipsing stellar components have masses
, and
. Their
orbital period is
, and their
eccentricity is
. This system contains the
longest period binary surveyed by the BEBOP project. BEBOP-4b is
expected to be detectable using Gaia DR4 single epoch astrometric
measurements. Despite a large period ratio of
, the
substantial eccentricities of both orbits mean that the outer orbit is
on the edge of orbital stability, and located in between two
destabilising secular resonances. Should the outer companion survive,
the BEBOP-4 system appears like a precursor to several post-common
envelope binaries exhibiting eclipse timing variations where very
massive circumbinary companions have been proposed.
-body simulations, that capture the
cosmological parameter dependence of the halo mass function. Several
studies have shown that this can be obtained through a calibration
against haloes with spherical masses defined at the virial overdensity.
In contrast, if different mass definitions are used for the HMF and the
scaling relation, a mapping between them is required. Here, we
investigate the impact of such a mapping on the cosmological parameter
constraints inferred from galaxy cluster number counts. Using synthetic
data from
-body simulations, we show that the
standard approach, which relies on assuming a concentration-mass
relation, can introduce significant systematic bias. In particular,
depending on the mass definition and the relation assumed, this can lead
to biased constraints at more than 2
level. In contrast, we find that in all
the cases we have considered, the mass conversion based on the halo
sparsity statistics result in a systematic bias smaller than the
statistical error.
, GW241011 furthermore
yields stringent constraints on the Kerr nature of black holes, the
multipolar structure of gravitational-wave generation, and the existence
of ultralight bosons within the mass range
–
eV.
eV
that couple to photons or electrons, our constraints improve upon those
from the third observing run by one order of magnitude, with the
tightest limit of
at a mass
of
. For
vectors with masses between
eV
that couple to baryons, our constraints supersede those from MICROSCOPE
and Eöt-Wash by one to two orders of magnitude, reaching a minimum of
at a mass of
eV. For
tensors with masses of
eV
(the full mass range analyzed) that couple via a Yukawa interaction, our
constraints surpass those from fifth-force experiments by four to five
orders of magnitude, achieving a limit as low as
at
eV. Our results show that gravitational-wave
interferometers have become frontiers for new physics and laboratories
for direct multi-model dark-matter detection.
)
late-type galaxies selected from the Catalogue of Isolated Galaxies
(CIG). We analyse the H
kinematics derived from Fabry-Perot
data and integrate these findings with a comprehensive examination of
the UV, optical, and FIR properties of these galaxies to study their
dynamic evolutionary processes. We investigate the individual kinematics
by computing rotation curves and dynamical masses for each galaxy in the
sample. The accuracy of our kinematic results is confirmed through
comparisons with HI data and by applying the B- and K-band Tully-Fisher
relationships. Among the galaxies studied, we observed a rotational lag
along the
-axis in half of the total sample (7 out
of 14 cases), with an average lag (
) consistent with previous research findings.
Notably, not all galaxies exhibiting measurable lag display
morphological extraplanar components, leading us to conclude that this
cannot serve as a definitive marker for the extraplanar Diffuse Ionized
Gas (eDIG) component. While we found no significant correlations between
rotation lag and overall galaxy properties, there seems to be a
potential correlation with tidal strength. Based on the kinematic
characteristics observed in our sample, we suggest that that the
extended disc gas likely originates from interactions with the
Circumgalactic Medium (CGM) rather than arising internally within the
galaxies themselves.
,
where the disk energy spectrum peaks. For
, a
-amplitude lump modulation
is detectable with the Vera Rubin Observatory after six months of
observation, up to
. We
proposed a new, simple toy model that can be used, for instance, to test
the compatibility of the periodicity of BBH candidate sources with a
circumbinary disk origin.
in recovering the angular
power spectra of galaxy number counts in both cases and can be used to
simplify the computation of the full power spectrum in harmonic space
for the data analysis of DR3.
s), using a data set from the optical facilities
COLIBRÍ, the Harlingten 50 cm Telescope, and the Very Large Telescope.
We complement these observations with data from the and the , as well as
radio observations from the Very Large Array. GRB 250221A is among the
few short GRBs with direct afterglow spectroscopy, which gives a secure
redshift determination of
and allows the
unambiguous identification of the host as a galaxy with a star-formation
rate of
. The X-ray
and optical light curves up to
ks (where
refers to the GRB trigger time) are
well described by forward-shock synchrotron emission in the slow-cooling
regime within the standard fireball framework. However, at
days, both the
X-ray and optical bands exhibit an excess over the same interval, which
we interpret as evidence of energy injection into a jet with a
half-opening angle of
through a refreshed shock powered by late central engine activity or a
radially stratified ejecta. The burst properties (duration, spectral
hardness, peak energy, and location in the Amati plane) all favour a
compact binary merger origin. However, our modelling of the afterglow
suggests a dense circumburst medium (
cm
), which is more typical
of a Collapsar environment. This tension over the classification of this
burst (short-hard vs. long-soft) as inferred from the prompt and
afterglow emissions makes GRB~250221A an unusual event and underscores
the limitations of duration-based classifications and the importance of
multi-wavelength, time-resolved follow-up observations.
across all sky and frequency range
Hz. For
targeted sources – Scorpius X-1, SN 1987A, the Galactic Center, Terzan
5, and NGC 6397 – we constrain the strain amplitude with best limits
ranging from
to
. For persistent broadband sources, we constrain
the gravitational-wave flux
, depending on the sky direction
and spectral index
.
Finally, for extended sources, we place upper limits on the strain
angular power spectrum
.
are the most common planets around solar-type
stars in short-period (
d) orbits. It is
still unclear, however, what their most likely composition is, that is
whether they are predominantly gas dwarfs or water worlds. The
sub-Neptunes orbiting bright host stars are very valuable because they
are suitable for atmospheric characterization, which can break the
well-known degeneracy in planet composition from the planet bulk
density, when combined with a precise and accurate mass measurement.
Here we report on the characterization of the sub-Neptune TOI-5789 c,
which transits in front of the bright (
mag and
mag) and
magnetically inactive K1V dwarf HIP 99452 every 12.93 days, thanks to
TESS photometry and 141 high-precision radial velocities obtained with
the HARPS-N spectrograph. We find that its radius, mass, and bulk
density are
,
, and
g cm
, and we show that
TOI-5789 c is a promising target for atmospheric characterization with
both JWST and, in the future, Ariel. By analyzing the HARPS-N radial
velocities with different tools, we also detect three additional
non-transiting planets, namely TOI-5789 b, d, and e, with orbital
periods and minimum masses of
d,
,
d,
, and
d,
. The
mutual orbital inclination between planets b and c must be higher than
deg, which points to a
dynamically hot system. Nevertheless, from sensitivity studies based on
both the HARPS-N and archival HIRES radial-velocity measurements, we can
exclude that such high mutual inclinations are due to the perturbation
by an outer gaseous giant planet.
erg). In this precursor phase, we detected
persistent, localized heating (temperature increase of $
$10-20
km/s) deep in the atmosphere. This heating was co-spatial with a
bald-patch region, suggesting that low-altitude magnetic reconnection
could destabilize the filament of the region. The flare’s rise phase was
marked by the filament’s eruption, with a total speed larger than $$70
km/s, when combining inversions and plane-of-sky motions. Following the
eruption, the free energy decreased by $
%$ as post-flare loops formed,
connecting the flare ribbons and channeling the released energy into the
lower atmosphere. The flare ribbons exhibited significant heating to
$$8500 K and downflows up to $$10 km/s, consistent with energy
deposition along reconnected loops.
0.10
and a mass of
9.8
. TOI-756 c is a
cold eccentric (e
= 0.45
0.01) giant planet orbiting
with a period of 149.6 days around its star with a minimum mass of 4.05
0.11
.
Additionally, a linear trend of 146
is
visible in the radial velocities, hinting at a third component, possibly
in the planetary or brown dwarf regime. This system is unique in the
exoplanet landscape, standing as the first confirmed example of such a
planetary architecture around an M dwarf. With a density of 2.42
0.49 g cm
, the inner planet,
TOI-756 b, is a volatile-rich sub-Neptune. Assuming a pure H/He
envelope, we inferred an atmospheric mass fraction of 0.023 and a core
mass fraction of 0.27, which is well constrained by stellar refractory
abundances derived from NIRPS spectra. It falls within the still poorly
explored radius cliff and at the lower boundary of the Neptune desert,
making it a prime target for a future atmospheric characterization with
JWST to improve our understanding of this population.
, H
CO and c-C
H
in several transitions to derive the
physical parameters of the gas toward 31 protostellar systems in
Perseus. Gas kinetic temperature was obtained from DCO
, H
CO and c-C
H
line ratios. Column densities and gas
masses were then calculated for each species and transition. Gas kinetic
temperature and gas masses were compared with bolometric luminosity,
envelope dust mass, and multiplicity to search for statistically
significant correlations. Gas kinetic temperature derived from DCO
, H
CO and c-C
H
line ratios have average values of 14
K, 26 and 16 K, respectively, with a range of 10-26 K for DCO
and c-C
H
. The gas kinetic temperature obtained
from H
CO line ratios have a range of 13-82 K.
Column densities of all three molecular species are on the order of
10
to 10
cm
, resulting in gas
masses of 10
to 10
M
. Statistical
analysis of the physical parameters finds: i) similar envelope gas and
dust masses for single and binary protostellar systems; ii) multiple
(>2 components) protostellar systems tend to have slightly higher gas
and dust masses than binaries and single protostars; iii) a continuous
distribution of gas and dust masses is observed regardless of separation
between components in protostellar systems.
covered to date by
COSMOS-3D using NIRCam/WFSS F444W (90% of the survey) to perform the
largest spectroscopic search for [OIII] emitters at 6.75<z<9.05.
We present our catalogue of 237 [OIII] emitters and their associated
completeness function. The inferred constraints on the [OIII] LF enable
us to characterise the knee of the [OIII] LF, resulting in improved
[OIII] LF constraints at z~7,8. Notably, we find evidence for an
accelerated decline of the [OIII] luminosity density between z~7 and
z~8, which could be expected if the metallicity of [OIII] emitters, as
well as the cosmic star-formation rate density, is declining at these
redshifts. We find that theoretical models that reproduce the z~7,8
[OIII] LF do not reproduce well the [OIII] equivalent width
distribution, pointing to potential challenges in the modelling of[OIII]
and other nebular lines in the early Universe. Finally, we provide the
first constraints on the cosmic variance of [OIII] emitters, estimating
at 15% the relative uncertainty for the z~7,8 [OIII] LF in the 0.3
deg
field. This estimate is in good
agreement with that inferred from clustering, and shows that the [OIII]
LF derived from smaller extragalactic legacy fields is strongly affected
by cosmic variance. Our results highlight the fundamental role that
wide-area JWST slitless surveys play to map the galaxy large-scale
structure down into the reionisation era, serving as a springboard for a
variety of science cases.
and on the
power spectrum amplitude
. Combining cluster
clustering with number counts significantly improves cosmological
constraints, with the figure of merit increasing by over 300% compared
to number counts alone. We confirm that the two probes are uncorrelated,
and the cosmological constraints derived from their combination are
almost insensitive to the cosmology dependence of the covariance. We
find that photometric redshift uncertainties broaden cosmological
posteriors by 20–30%, while secondary effects like redshift-space
distortions (RSDs) have a smaller impact on the posteriors – 5% for
clustering alone, 10% when combining probes – but can significantly bias
the constraints if neglected. We show that clustering data below
Mpc
provides additional constraining power, while scales larger than
acoustic oscillation scale add almost no information on
and
parameters. RSDs and
photo-
uncertainties also influence the number
count covariance, with a significant impact, of about 15–20%, on the
parameter constraints.
R
and a mass of
M
; and TOI-2345 c to
have a radius of
R
and a mass of
M
. To explore
chemical links between these planets and their host star, we model their
interior structures newly accounting for devolatised stellar abundances.
TOI-2345 adds to the limited sample of well characterised planetary
systems around thick disk stars. This system challenges theories of
formation and populations of planets around thick disk stars with its
Ultra-Short Period super-Earth and the wide period distribution of these
two planets spanning the radius valley.
and outlier fractions around 10% in the 6-band
data, with performance degrading at faint magnitudes and z>1.2. The
overall bias and scatter of our machine-learning based photo-zs satisfy
the LSST Y1 requirement. We also use our photo-z to infer the ensemble
redshift distribution n(z). We study the photo-z improvement by
including near-infrared photometry from the Euclid mission, and find
that Euclid photometry improves photo-z at z>1.2. Our results
validate the RAIL pipeline for Rubin photo-z production and demonstrate
promising initial performance.
, up to
. Methods: We built 12
light cones of
from the Simulated Infrared Extragalactic Sky (SIDES) simulation. By
analyzing cross-power spectra between different CO transitions and the
galaxy density field, we recovered the CO background SLED. Combining it
with bias-weighted line intensities yielded
. We also assessed the detectability of the
CO(4–3) cross-power spectrum with a CONCERTO-like experiment. Results:
For a realistic spectroscopic depth, the CO background SLED is
accurately recovered up to
with
uncertainties.
Reconstructing
from millimeter LIM data requires an excitation correction relative to
CO(1–0). Interloper-induced variance does not prevent precise
estimation. In the two-star-formation-mode SIDES model, starbursts
dominate the SLED at
but do not bias
estimates from
. However,
CONCERTO lacks the sensitivity to detect the CO
galaxy cross-power on
relevant scales, even under ideal conditions.
redshift range. We assess the wavelength dependence of the bar fraction
in disc galaxies and bar length evolution by selecting a nearly
mass-complete CEERS disc sample and performing independent visual
classifications on the short (F200W) and long (F356W+F444W) wavelength
channels. A similar bar fraction is observed for both samples, and
combined we find a declining trend in the bar fraction:
at
;
at
;
at
.
This corroborates our previous work and other recent studies, suggesting
that dynamically cold and rotationally supported massive discs are
present at Cosmic Noon. No evolution in the F356W+F444W bar length is
measured from
to
, which has a mean of
3.6,kpc, but a slight increase of about 1,kpc towards
is measured in the
F200W sample, which has a mean of 2.9,kpc. The bar sample is shorter in
the short-wavelength channel due to the better physical spatial
resolution; however, we also suggest that dust obscuration plays a role.
We find that the correlation between bar length and galaxy mass for
massive galaxies observed at
is not seen at
. By adding
samples of barred galaxies at
, we show that there
is a modest increase in the bar length (
,kpc) towards
, but bars longer than
,kpc are only
found at
. We show that bars
and discs grow in tandem, for the bar length normalised by disc size
does not evolve from
to
. Not only is a
significant population of bars forming beyond
, but our results also
show that some of these bars are as long and strong as the average bar
at
.
, through time delays
between their multiple images. The accuracy of this measurement depends
critically on both the precision of time delay estimation and the
robustness of lens modeling. In many current cluster-scale modeling
algorithms, all multiple images used for modeling are simplified as
point sources to reduce computational costs. In the first paper of the
CURLING program, we demonstrated that such a point-like approximation
can introduce significant uncertainties and biases in both magnification
reconstruction and cosmological inference. In this study, we explore how
such simplifications affect
measurements from glSNe. We simulate
a lensed supernova at
, lensed by a galaxy
cluster at
, assuming time
delays are measured from LSST-like light curves. The lens model is
constructed using JWST-like imaging data, utilizing both Lenstool and a
pixelated method developed in CURLING. Under a fiducial cosmology with
, the
Lenstool model yields
, whereas the pixelated framework improves the
precision by over an order of magnitude,
. Our results indicate that in the next-generation
observations (e.g., JWST), uncertainties from lens modeling dominate the
error budget for
inference, emphasizing the importance
of incorporating the extended surface brightness of multiple images to
fully leverage the potential of glSNe for cosmology.
and
exceeding 400 when combining all
primary probes. Furthermore, we illustrate the behaviour of the
posterior probability distribution of the parameters of interest given
different priors and scale cuts. Finally, we emphasise the importance of
addressing computational challenges, proposing further exploration of
innovative data science techniques to efficiently navigate the Euclid
high-dimensional parameter space in upcoming cosmological data
releases.
m K-band contrast spectra. We then
derived stellar model atmospheres for all employed flux references,
which we used to convert the companion contrast into companion flux
spectra. Solely from the resulting GRAVITY spectra, we extracted
spectral types, spectral indices, and bulk physical properties for all
companions. Finally, and with the help of age constraints from the
literature, we also derived isochronal masses for most companions using
evolutionary models. The resulting library contains R ~ 500 GRAVITY
spectra of 39 substellar companions from late M to late T spectral
types, including the entire L-T transition. Throughout this transition,
a shift from CO-dominated late M- and L-type dwarfs to CH4-dominated
T-type dwarfs can be observed in the K-band. The GRAVITY spectra alone
constrain the objects’ bolometric luminosity to typically within $$0.15
dex. The derived isochronal masses agree with dynamical masses from the
literature where available, except for HD 4113 c for which we confirm
its previously reported potential underluminosity. Medium-resolution
spectroscopy of substellar companions with GRAVITY provides insight into
the carbon chemistry and the cloudiness of these objects’ atmospheres.
It also constrains these objects’ bolometric luminosities which can
yield measurements of their formation entropy if combined with dynamical
masses, for instance from Gaia and GRAVITY astrometry.
from the chosen
benchmark, and CLOE predictions are statistically compatible with
simulated data obtained from benchmark codes. The same holds for the
comparison of correlation function in configuration space for
spectroscopic and photometric observables.
m to 4.44
m. Alongside these data, we also include
ancillary HST imaging in seven filters from 0.435
m to 1.6
m. We used Source Extractor with hot and
cold detection settings to extract photometry. We derive photometric
redshifts using the spectral energy distribution (SED) modeling code,
LePHARE, and estimate their accuracy using spectroscopically confirmed
galaxies out to
, with
ranging from
0.035-0.073, depending strongly on galaxy magnitude and redshift. We
compute stellar masses, star formation rates, and E(B-V) using three
different SED fitting codes with different templates and assumptions
about the galaxy star formation histories. All of these measurements, as
well as the full mosaics in all filters, and redshift probability
distribution functions, are made available via the CEERS DR1.0 data
release.
,
) plane for a -like data release 1
(DR1) setup. We find that the 5 higher-order statistics (HOSs) that
satisfy the Gaussian likelihood assumption of the Fisher formalism
(1-point probability distribution function, $$1-norm, peak counts,
Minkowski functionals, and Betti numbers) each outperform the shear
2-point correlation functions by a factor
on the
forecasts, with only marginal
improvement when used in combination with 2-point estimators, suggesting
that every HOS is able to retrieve both the non-Gaussian and Gaussian
information of the matter density field. The similar performance of the
different estimators is explained by a homogeneous use of multi-scale
and tomographic information, optimized to lower computational costs.
These results hold for the
mass mapping techniques of the
pipeline: aperture mass, Kaiser–Squires, and Kaiser–Squires plus, and
are unaffected by the application of realistic star masks. Finally, we
explore the use of HOSs with the Bernardeau–Nishimichi–Taruya (BNT)
nulling scheme approach, finding promising results towards applying
physical scale cuts to HOSs.
on the Hubble constant
if neglected, followed by
mis-modelling of the redshift evolution of galaxy bias, yielding up to
on the parameter
.
Choosing a too optimistic prior for multiplicative bias can also result
in biases of the order of
on
. We also find that the precision on
the estimate of the purity of the spectroscopic sample will be an
important driver for the constraining power of the galaxy clustering
full-shape analysis. These results will help prioritise efforts to
improve the modelling and calibration of systematic effects in
Euclid.
CO,
CO, C
O, CN, HCN, CS, H
CO, c-C
H
, N
D
, DCN and
CS. We analyze molecular
tomographies and model data using the radiative transfer code DiskFit.
Results: We directly measure the altitude above the mid-plane for each
observed species. For the first time, we unambiguously demonstrate the
presence of a common molecular layer and measure its thickness: most
molecules are located at the same altitude versus radius. Beyond CO, as
predicted by chemical models, the CN emission traces the upper boundary
of the molecular layer, whereas the deuterated species (DCN and N2D+)
resides below one scale-height. Our best fits from DiskFit show that
most observed transitions in the molecular layer are thermalized because
their excitation temperature is the same, around 17-20 K. Conclusions:
These long-integration observations clearly reveal a molecular layer
predominantly located around 1-2 scale height, at a temperature above
the CO freeze-out temperature. The deuterated molecules are closer to
the mid-plane and N2D+ may be a good proxy for the CO snowline. Some
molecules, such as CN and H2CO, are likely influenced by the disk
environment, at least beyond the mm dust disk radius. The direct
observation of the molecular stratification opens the door to detailed
chemical modeling in this disk which appears representative of T Tauri
disks.
-body TNG50-Dark runs, we reconstruct
the cosmic web at redshifts
, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, and 4 with
the Monte Carlo Physarum Machine density estimator and the DisPerSE
structure identification framework. We confirm that dark matter halos
start out predominantly prolate (elongated) and their shapes are aligned
with their nearest filaments; prolate galaxies retain strong
shape-alignment with their outer halos to later times. The fraction of
prolate galaxies and halos increases toward lower stellar mass, higher
redshift, and lower-density filaments. Oblate and spheroidal galaxies
show weaker trends with filament density, but spheroidal halos
preferentially reside in higher-density filaments. We also find that
higher-density filaments favor extended rotationally-supported disks,
whereas lower-density filaments more often host smaller
dispersion-supported systems. Then, generating mock galaxy samples from
TNG100 and TNG50, we predict the early cosmic web accessible to Roman.
We find that the spectroscopic emission-line depth planned for the
High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey (HLWAS) yields a highly incomplete galaxy
sample that does not accurately trace the
cosmic web. A survey
deeper
over a few square degrees would enable a proper reconstruction and
reveal qualitatively correct filament-galaxy morphology relationships.
Nevertheless, the planned HLWAS Deep field should still identify most
galaxy overdensities; targeted deeper spectroscopy of these regions
would efficiently and adequately map the early filamentary
structure.
Lyman-break
galaxies using the
near-infrared UltraVISTA survey in the COSMOS
field, reaching
depths in
of 26.2. We incorporate deep optical
and Spitzer imaging for a full spectral energy distribution (SED)
fitting analysis. We find 289 candidate galaxies at
covering
, faint
enough to overlap with Hubble Space Telescope studies. We conduct a
separate selection by including complementary Euclid performance
verification imaging (reaching
depths of
), yielding 140 galaxies
in
, with 38 sources unique to this sample. We
compute the rest-frame UV luminosity function (UV LF) from our samples,
extending below the knee (
). We find that the shape of the UV LF is
consistent with both a Schechter function and double-power law (DPL) at
the magnitudes probed by this sample, with a DPL preferred at
when bright-end results are included. The
UltraVISTA+Euclid sample provides a clean measurement of the LF due to
the overlapping near-infrared filters identifying molecular absorption
features in the SEDs of ultra-cool dwarf interlopers, and additional
faint galaxies are recovered. A comparison with JWST LFs at
suggests a gentle
evolution in the bright-end slope, although this is limited by a lack of
robust bright-end measurements at
. We forecast that in
the Euclid Deep Fields, the removal of contaminant ultra-cool dwarfs as
point sources will be possible at
. Finally, we present a high-equivalent-width
Lyman-
emitter candidate identified by
combining HSC, VISTA, and Euclid broadband photometry, highlighting the
synergistic power these instruments will have in the Euclid Auxiliary
Fields for identifying extreme sources in the Epoch of Reionisation.
quasar, H1413+117,
offset to the north by 6. From
CO
–3,
–5, and part of the
–12 transitions, which all
spatially coincide with a compact submillimeter continuum emission, we
determine an unambiguous spectroscopic redshift,
.
This galaxy has a molecular mass
M
and a black hole mass
M
, estimated from
CO
–3 and archival {} X-ray
data (
,erg,s
), respectively. We also
estimate a total infrared luminosity of
L
and a stellar mass of
M
, from spectral
energy distribution fitting. According to these simple mass estimations,
this gas-rich and X-ray bright galaxy might be in a transition phase
from starburst to quasar offering a unique case for studying
galaxy-black hole co-evolution under extremely dusty conditions.
of
Pic b. These four high S/N ($$20)
K-band spectra conserve both the pseudo-continuum and molecular
absorption patterns. We analyze them with four self-consistent forward
model grids (Exo-REM, ATMO, BT-Settl, Sonora) exploring
,
log(g), metallicity, C/O, and
CO/
CO ratio. We also
upgrade our forward modeling code to account for the data multi-modality
and combine the GRAVITY epochs with published 1-5
m photometry, low- to medium-resolution
spectra (0.9-7
m), and high-resolution echelle spectra
(2.1-5.2
m). Sonora and Exo-REM are statistically
preferred. Exo-REM yields
K and log(g)
dex from GRAVITY alone, and
K and log(g)
dex when
including all datasets. Archival data significantly affect the retrieved
parameters. C/O remains solar (
) while [M/H] reaches super-solar values
(0.50$
{12}
{13}$CO) $
$)
, implying a heavy-element content of up to $
$)
given the system age and dynamical mass measurements. Access to both
continuum and molecular lines at K-band significantly impacts the
metallicity, possibly owing to collision-induced absorption shaping the
continuum. Echelle spectra do not dominate the final fit with respect to
lower resolution data. Future multi-modal frameworks should include
weighting schemes reflecting bandwidth and central wavelength
coverage.
morphology and are clearly related to
the location of the central stellar cluster and secondary stellar
groups. The maps of ionization-sensitive line ratios show substantial
variations across the face of NGC 604. We demonstrate that these
variations are unlikely to be due to chemical inhomogeneities but are
primarily caused by changes in ionization, which in turn affect the
observed line ratios. We present the H
kinematics of the region and connect it
to the excitation structure, showing how the dynamic motions influence
the spatial distribution of ionized gas. We note two distinct sources
identified in these excitation maps: a known supernova remnant and a
previously unknown planetary nebula. Such parsec-scale features
contribute only a small percentage to the overall light and would remain
undetected without the use of high-resolution spatial data. Throughout
the paper, we make comparisons to and raise concerns about
single-aperture and long-slit spectroscopic measurements of giant HII
regions, highlighting the limitations and potential inaccuracies of such
methods.
= 1.675 and 3.332. DESI observed one
of the remaining source redshifts, as well as an additional source
redshift within the six systems. The two systems with non-detections by
NIRES were observed for a considerably shorter 600s at high airmass.
Combining NIRES infrared spectroscopy with optical spectroscopy from our
DESI Strong Lensing Secondary Target Program, these results provide the
complete lens and source redshifts for six systems, a resource for
refining automated strong lens searches in future deep- and wide-field
imaging surveys and addressing a range of questions in astrophysics and
cosmology.
m. It will offer hyperspectral imaging
in medium resolution bands (R
8, using a linear
variable filter) from 25 to 80
m, and broad band (R
4) photometric and
polarimetric imaging in four bands spanning 80 to 260
m. The capabilities of PRIMAger will
enable a broad range of unique scientific programs, accessible through
General Observer (GO) projects. In this paper, we present and define a
PRIMAger survey over 25% of the sky, called
-IR survey. This survey would exploit
PRIMAger’s hyperspectral and polarimetric modes to collect data on about
8
10
galaxies to z
4. The R=8 spectral
resolution of the PRIMAger Hyperspectral Imaging (PHI) filters will
enable users to study the emission of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
(PAH). A large sample of galaxies will be observed with the polarimetric
bands of PRIMAger, allowing unique statistical information for galaxies
to be harvested for the first time.
, and the halo
mass where it peaks,
, when
fitted to mock data. We examine whether discrepancies arise from
emission assumptions (the HOD ingredients) or from more fundamental
components, such as bias and matter clustering. Using the M21 CIB HOD
model within the halo framework, we fit mock CIB power spectra and star
formation rate density (SFRD) data from the SIDES-Uchuu simulation, then
repeat the analysis with a simplified simulation (SSU) matched to the
HOD assumptions. Comparing best-fit parameters to known inputs, we find
that although the M21 model fits the mock data well, it fails to recover
intrinsic parameters, especially
, even when
applied to data generated with consistent assumptions. Emission-related
quantities (SFRD, emissivity) agree within 5%, but the two-halo term
shows a redshift- and scale-dependent offset exceeding 20%, likely due
to the linear treatment of halo bias and matter clustering. Scatter in
the SFR-halo mass relation and spectral energy distributions
significantly impacts shot noise (
) but only
modestly (
) the clustered
signal. We conclude that robust recovery of physical parameters from CIB
clustering requires improved cosmological ingredients in halo models,
including scale-dependent halo bias and nonlinear matter power spectra,
alongside refined emission modeling.
cm
) and infall velocity
(880 km s
) are probably
sufficient to explain the extensive stripping from the common gaseous
envelope of NGC 4532/DDO 137. The ongoing tidal interaction with the
Virgo cluster appears to have prevented a rapid merger of the binary
pair, with the mutual tidal interaction between the galaxy pair being
responsible for raising gas from the outer parts of the galaxy potential
wells into the HI bridge and common envelope. The NGC 4532/DDO 137
system mirrors many of the physical features of the Magellanic System,
and may lead to a better understanding of that system, as well as
casting more light on the relative importance of interaction mechanisms
in the outskirts of dynamically young galaxy clusters such as Virgo.
, we calibrate the distance scale, and therefore
the energetics, of this unique extragalactic transient. At this
distance, the resulting
-ray energy release is at least
,erg.
We find no evidence for ongoing transient emission at the GRB position,
and exclude any accompanying supernova with a luminosity comparable to
the Type Ic broad-line SN 2023lcr, though we are unable to constrain
fainter events. The inferred rate of such events, assuming at most one
in the lifetime of {}, suggests that such bursts are very rare, with
volumetric rates
times lower
than normal high luminosity long GRBs and
times lower
than core collapse supernovae when corrected for beaming. Furthermore,
we find that the host galaxy is unique amongst GRB host galaxies, and
extremely rare in the general galaxy population, being extremely large,
dusty and with high stellar mass. The identification of such an exotic
GRB in such an unusual galaxy raises the possibility that the
environment was important in the progenitor channel for this event.
-
+
observation of the
type 1 Seyfert PG 1426+015, a source of particular interest as the most
massive reverberation-mapped black hole to date (
=
). The high-resolution RGS data confirm the ‘bare’
nature of the source, showing no evidence for absorption beyond the
Galactic column, while the broadband spectrum unambiguously reveals the
presence of relativistic reflection from the innermost accretion disc
(in the form of a relativistically broadened iron emission and
associated Compton reflection hump) as well as confirming the presence
of the strong soft excess reported previously. We explore whether
relativistic reflection can successfully account for the soft excess
along with the higher-energy reflection features, utilizing the two
most-commonly used reflection codes (REFLIONX, XILLVER). Ultimately we
find that both models are able to successfully reproduce the soft
excess, though in the case of the XILLVER model this is contingent on
reducing the strength of the O VIII line included in the model, as
otherwise this feature prevents the model from reproducing the data. The
reflection models that successfully reproduce the broadband data imply a
relatively high density for the accretion disc of
,
consistent with the loose anti-correlation seen from other AGN in the
vs
plane, as well as a moderate-to-high black hole
spin of
.
This preliminary spin constraint is strongly dependent on the assumption
that the soft excess is dominated by relativistic reflection.
160 kg (72
6 cm diameter) asteroid
catastrophically fragmented around 28 km altitude, releasing 98% of its
total energy in a concentrated region of the atmosphere. The resulting
shockwave was spherical, not cylindrical, and released more energy
closer to the ground. This type of fragmentation increases the risk of
significant damage at ground level. These results warrant consideration
for a planetary defense strategy for cases where a >3-4 MPa dynamic
pressure is expected, including planning for evacuation of areas beneath
anticipated disruption locations.
and H
lines in the broad line region. We fit
the two lines simultaneously with an updated model that includes
distinct rotating and conical outflowing components. We find that more
than 80% of the HI line emission from the BLR originates in an outflow
with a velocity up to
km s
. This is oriented so
that our line of sight is along an edge of the conical structure, which
produces the prominent blue wing on the line profile. A combination of
anisotropic line emission and mid-plane opacity lead to the single-sided
phase signal. The model is able to qualitatively match both the
outflowing CIV line profile and the systemic OI fluorescent emission.
The derived black hole mass of
M
is the highest
redshift black hole mass measurement to date obtained directly from BLR
dynamics. It is an order of magnitude lower than that inferred from
various single epoch scaling relations, and implies that the accretion
is highly super-Eddington. With reference to recent simulations, the
data suggest that this QSO is emitting close to its radiative limit in a
regime where strong outflows are expected around a polar conical
region.
= 15.57 days) and HIP
41378 c (
= 31.71 days), are
close to (
%) a 2:1 period
commensurability. We report a clear detection of TTVs with amplitudes of
20 mins for planet b and greater than 3 hrs for planet c. We dynamically
confirm the planetary nature of HIP 41378 g, a non-transiting planet
with a period of about 64 days and a mass of about 7
, close to a
2:1 commensurability with planet c, suggesting a possible MMR chain in
the inner system. Our precise determination of the masses,
eccentricities, and radii of HIP 41378 b and c enabled us to investigate
their possible volatile-rich compositions. Finally, by leveraging on the
last TESS sectors we constrained the period of HIP 41378 d to three
possible aliases (
278, 371, and 1113
days) suggesting that the system could be placed in a double quasi
resonant chain, highlighting its complex dynamical architecture.
cluster with the
NOrthern Extended Millimeter Array (NOEMA). The high sensitivity of
these observations enabled the effective identification and removal of
the millimetre-wave sources contaminating the tSZ signal, thus isolating
the influence of the hot electron gas of the cluster on the cosmic
microwave background radiation from other emissions. The tSZ observed
with success by NOEMA was modelled together with previous single-dish
observations (IRAM 30-metre, Green Bank Telescope, and Caltech
Sub-millimeter Observatory) to obtain the first core-to-outskirts (from
15 to
1500 kpc) pressure
profile reconstruction on such a high-redshift galaxy cluster. NOEMA
observations with a high angular resolution have shown that the pressure
profile is flat in the core of the cluster. These observations confirm
the disturbed nature of CL J1226.9+3332 and map for the first time the
distribution of its thermal gas at arcsecond scales in the environments
of the central cluster galaxy. Our results showcase the excellent
capabilities of NOEMA to complement and enhance the data provided by
other millimetre-wave instruments in resolving the core of high-redshift
clusters via tSZ emission.
at 90% confidence level, which is inversely
proportional to a varying interstellar medium particle density of
cm
. In the wind-like
environment case, the baryon loading is
at 90% confidence level, which is proportional to
the sixth power of a varying density parameter of
.
elements relative to iron of [
/Fe]=
. With an
age of $$12.5 Gyr, TOI-1203 belongs to the old,
-element enhanced stellar population of
the galactic thick disk. We spectroscopically confirmed the planetary
nature of the 25.5 d sub-Neptune TOI-1203 d, measured its mass (
) and refined its radius (
). We discovered the presence of an additional
transiting super-Earth on a 4.2 d orbit (TOI-1203 b) with a mass of
and
a radius of
.
We also revealed the presence of two additional low-mass planets at 13.1
d and 204.6 d (TOI-1203 c and e), with minimum masses of
and
. We
found that the outer planet TOI-1203 e lies on an eccentric orbit with
. We performed a stability analysis of the system
confirming that there are configurations consistent with the observed
parameters that are dynamically stable over billion-year timescales.
While analyzing the HARPS time series, we discovered that the FWHM of
the HARPS cross-correlation function shows a significant long-period
signal ($$615 d) that has no counterpart in the radial velocity data or
in the remaining HARPS ancillary time series. We significantly detected
the same signal in the FWHM of the Th-Ar calibration lines used to
compute the nightly wavelength solution, and attributed this systematic
effect to a long-term variation of the HARPS instrumental profile.
cluster members using a dual
Pseudo-Isothermal Elliptical (dPIE) model based on the HST F160W filter,
while the BCG & ICL is modelled as a single component using a
multi-Gaussian expansion. To estimate stellar masses and velocity
dispersions, we rely on multi-band HST photometry and integral field
spectroscopy, respectively. Stellar masses are derived using three
different spectral energy distribution (SED) models. We measure the
line-of-sight velocity dispersions of the cluster members at their
half-light radii, as determined from their light profiles, while for the
BCG & ICL components, we use elliptical annular apertures. Thanks to
these measurements, we will be able to constrain the cluster stellar
mass content, which is detailed in the second paper of the series. We
publicly release these measurements with intermediary data products.
and richness dependence of the RS
parameters. We found that the quiescent galaxy population in groups
builds up steadily from z=1.5-2 across all richnesses, with faster and
earlier growth in the richest groups. The first galaxies settle onto the
RS ridgeline by
, consistent with
current evolutionary scenarios. Notably, we reported a rare overdensity
of quiescent galaxies at z=3.4, potentially one of the most distant
early RSs observed. Extending our study to X-rays, we found that X-ray
faint groups have, on average, lower quiescent fractions than X-ray
bright ones, likely reflecting their typical location in filaments.
Leveraging the broad wavelength coverage of COSMOS2025, we traced RS
evolution over
Gyr, finding no
significant trends in either slope or scatter of the ridgeline.
on the
multiple image positions. The kinematic profiles of the BCG & ICL,
as well as the X-ray surface brightness of the intra-cluster gas, are
accurately reproduced within observational uncertainties. However, a
scatter is required for the cluster member line-of-sight dispersions.
This method yields the most complex parametric mass model with
consistency among almost all available mass constraints. We find a
agreement between the
inferred stellar-to-subhalo mass relation and that predicted by
large-scale cosmological simulations. The ICL stellar mass derived from
our model is consistent with estimates from stellar population
modelling. We present the first multi-probe mass modelling method
capable of disentangling the dark matter from the baryonic mass
distributions in massive galaxy clusters. Its results, such as the
stellar-to-subhalo mass relation or the distribution of each mass
component, can be directly compared to hydrodynamical cosmological
simulations such as illustrisTNG.
and
, and
small spins
(90% credibility) and negligible eccentricity
.
Post-merger data excluding the peak region are consistent with the
dominant quadrupolar
mode of a Kerr black hole and its first overtone. We constrain the
modes’ frequencies to
of the Kerr
spectrum, providing a test of the remnant’s Kerr nature. We also examine
Hawking’s area law, also known as the second law of black hole
mechanics, which states that the total area of the black hole event
horizons cannot decrease with time. A range of analyses that exclude up
to 5 of the strongest merger cycles confirm that the remnant area is
larger than the sum of the initial areas to high credibility.
and
eV, respectively, at 30% confidence, assuming a
1% false alarm probability. Although these searches are only marginally
sensitive to signals from merger remnants at relatively large distances,
future observations are expected to yield more stringent constraints
with high confidence. For the BSD search targeting the BH in Cygnus X-1,
we exclude vector boson masses in the range
eV at 95% confidence, assuming an initial BH spin
larger than 0.5.
above the Amati
relation. Although their optical afterglows resemble those of typical
long GRBs, the prompt spectra are consistently harder than the long-GRB
average. Consistent modelling of six GOTO-discovered GRB afterglows
yields jet half-opening angles of a few degrees and beaming-corrected
kinetic energies (
) erg, consistent with the canonical long-GRB
population. These findings suggest that optical discovery of poorly
localised GRBs may be subject to observational biases favouring luminous
events with high spectral peak energy, while also providing insight into
jet microphysics and central engine diversity.
(1–4)
]. With Euclid, clusters are resolved into
individual stars across the main bodies and haloes of both galaxies.
Visual inspection of
images uncovers 30 new cluster
candidates in NGC 6822 and 16 in IC 10, from compact to extended
clusters. We re-evaluate literature candidates, producing combined
catalogues of 52 (NGC 6822) and 71 (IC 10) clusters with
confidence-based classifications. We present homogeneous photometry in
,
,
,
, and archival UBVRI data, alongside
size measurements and properties from BAGPIPES SED fitting. Synthetic
cluster injection shows our sample is
% complete to
for ages
Myr, and
to
for
Gyr. IC 10 has more
young clusters than NGC 6822, extending to higher masses, consistent
with its starburst nature. Both dwarfs host several old massive (
) clusters, including an exceptional
cluster in NGC 6822’s outskirts. In NGC 6822, we
identify a previously undetected, old, extended cluster (
pc). Using well-defined criteria, we identify 11
candidate GCs in NGC 6822 and eight in IC 10. Both galaxies have high
specific frequencies (
) but remain consistent with known GC
scaling relations at low luminosity [abridged].
0.04
and 20.1
1.6
, respectively,
five and two times more precise than the previously reported values. Our
radial velocity analysis reveals two additional non-transiting
companions with orbital periods of 5.46 and 60.45 days. Despite the
innermost planet’s high geometric transit probability, we find no
evidence for transits in the photometric data. The bulk properties of
TOI-2141 b suggest a significant volatile envelope atop an Earth-like
core, with modeling indicating a hydrogen-rich atmosphere that may have
experienced mild photoevaporation over the system’s history. Planets b
and c must exhibit a modest mutual inclination of at least 2.4
degrees.
z
0.9) galaxies with
stellar masses between $
^{8}$ - 10
M
. We probe a
cosmic time of approximately 6 Gyr and a range of environments, from
field (low-density systems) to rich groups (high-density systems). We
find that the galaxies’ stellar mean ages, metallicities, and star
formation rates (SFRs) follow similar trends to galaxies as those
characterising the nearby Universe. We modelled the derived SFRs,
quantifying and characterising the number of star-forming episodes
(SFEs). We found that more than 85
of the galaxies have more
than one event of star formation, typically described with an
exponentially decaying SFR and subsequent Gaussian-like episode(s) of
star formation. We also observe that massive galaxies have fewer SFEs
than low-mass systems and that they form their stellar mass and reach
quiescence faster than lower mass galaxies. Moreover, the history of
mass assembly for the most massive galaxies in the sample can be
described with only one episode of star formation in the early Universe,
which we detected as an exponential decrease that was longer in duration
than subsequent SF events. This early event has typically been completed
by z$$3 and it accounts for a high fraction of the total stellar mass,
from $
%$ for low-mass galaxies to more than
50
for higher-mass galaxies. We
also analysed the dependence of stellar population parameters with the
various environments probed by the sample, finding no significant
correlations between different group environments; however, our field
galaxies are generally distinct from group galaxies in terms of the
mass, metallicity, stellar ages, and formation timescales. We discuss
possible biases in the sample selection and examine how representative
our galaxies are of the overall galaxy population.
jointly with the population
properties of merging compact binaries. We measure the luminosity
distance and redshifted masses of GW sources directly; in contrast, we
infer GW source redshifts statistically through i) location of features
in the compact object mass spectrum and merger rate evolution, and ii)
identifying potential host galaxies in the GW localization volume.
Probing the relationship between source luminosity distances and
redshifts obtained in this way yields constraints on cosmological
parameters. We also constrain parameterized deviations from general
relativity which affect GW propagation, specifically those modifying the
dependence of a GW signal on the source luminosity distance. Assuming
our fiducial model for the source-frame mass distribution and using GW
candidates detected up to the end of the fourth observing run (O4a),
together with the GLADE+ all-sky galaxy catalog, we estimate
km s
Mpc
. This value is reported
as a median with 68.3% (90%) symmetric credible interval, and includes
combination with the
measurement from GW170817 and its
electromagnetic counterpart. Using a parametrization of modified GW
propagation in terms of the magnitude parameter
, we estimate
, where
recovers the
behavior of general relativity.
, indicating that FRB spectral indices are, on
average, flatter than known spectral indices from pulsars. From the
targeted campaign, we find that the prolific repeater FRB 20201124A
shows a positive
, implying
reduced low-frequency activity, unlike the typically negative
seen from FRBs at
higher frequency bands. We explore free-free absorption in the
circumburst environment as a cause of the non-detection at 150 MHz. The
non-detection of FRB 20201124A is consistent with either a very young
yr old supernova
remnant, or a typical HII region. Our simulations indicate that LOFAR2.0
can detect 0.3-9 FRBs per week, and up to 4 FRBs at redshifts in the
range
. Such
detections will provide robust constraints on cosmological parameters
due to their clean environments. Our results guide future low-frequency
FRB searches by showing how even non-detections can place meaningful
constraints on the repetition rates and circumburst environments of
FRBs.
, one of the
largest and most massive protostructures known. This dataset provides
the most statistically robust SMF of a single protostructure at
. By comparing the SMF
of overdense peaks within Hyperion to the coeval field, we ask: how
early, and how strongly, does a dense environment favor massive
galaxies? Using COSMOS2020 photometry with ground-based and new HST
grism spectroscopy, we construct a 3D overdensity map that assigns
galaxies to peaks, outskirts, or the field. We perform 100 Monte Carlo
realizations to propagate redshift and mass uncertainties, and derive
SMFs normalized to the field. The peaks show a clear excess of massive
galaxies: number densities at
are ~10x higher than the field, while those at
are enhanced by only ~3.5x. By contrast, the
outskirts and Hyperion as a whole mirror the field. Environmental
effects on stellar mass growth are thus evident by
. The densest
regions already host galaxies with accelerated growth, while the global
SMF masks this signal. Protostructures therefore begin shaping the
high-mass end of the SMF well before cluster quenching, and may drive
the elevated star formation at Cosmic Noon.
m and currently in Phase A study, will
achieve this and provide insights into early galaxy evolution, Black
Hole growth, and dust production mechanisms. Here we present PRIDES, a
possible deep and wide-area survey over 1.6 square-degrees of the COSMOS
field with PRIMA to study these science cases.
m). This region is particularly rich in
molecular spectral signatures, whose measurements can help recover
atmospheric parameters and provide a better understanding of giant
planet formation and atmospheric dynamics. In the past years, exoplanet
interferometry with the VLTI/GRAVITY instrument has provided
medium-resolution spectra of a dozen substellar companions in the near
infrared. The 100-meter interferometric baselines allow for the stellar
and planetary signals to be efficiently disentangled at close angular
separations (< 0.3’’). We aim to extend this technique to the
mid-infrared using MATISSE, the VLTI’s mid-infrared
spectro-interferometer. We take advantage of the fringe tracking and
off-axis pointing capabilities recently brought by the GRA4MAT upgrade.
Using this new mode, we observed the giant planet
Pictoris b in L and M bands (2.75-5
m) at a spectral resolution of 500. We
developed a method to correct chromatic dispersion and non-common paths
effects in the fringe phase and modelled the planet astrometry and
stellar contamination. We obtained a high-signal-to-noise spectrum of
Pictoris b, showing the planet
continuum in L (for the first time) and M bands, which contains broad
absorption features of H
O and CO. In conjunction with a new
GRAVITY spectrum, we modelled it with the ForMoSA nested sampling tool
and the Exo-REM grid of atmospheric models, and found a solar
carbon-to-oxygen ratio in the planet atmosphere. This study opens the
way to the characterization of fainter and closer-in planets with
MATISSE, which could complement the JWST at angular separations too
close for it to obtain exoplanet spectra. Starting in 2025, the new
adaptive optics system brought by the GRAVITY+ upgrade will further
extend the detection limits of MATISSE.
and that are not vetoed during event validation.
We also provide detailed source property measurements for 86 of these
that have a false alarm rate
. Based on the inferred component masses, these
new candidates are consistent with signals from binary black holes and
neutron star-black hole binaries (GW230518_125908 and GW230529_181500).
Median inferred component masses of binary black holes in the catalog
now range from
(GW230627_015337) to
(GW231123_135430), while GW231123_135430 was probably produced by the
most massive binary observed in the catalog. For the first time we have
discovered binary black hole signals with network signal-to-noise ratio
exceeding 30, GW230814_230901 and GW231226_01520, enabling high-fidelity
studies of the waveforms and astrophysical properties of these systems.
Combined with the 90 candidates included in GWTC-3.0, the catalog now
contains 218 candidates with
and not otherwise vetoed, doubling the size of
the catalog and further opening our view of the gravitational-wave
Universe.
erg/s. The associated INTEGRAL/IBIS count rate
was about ${}$10x higher than usual for the hard state. To our
knowledge, this is the first time that such strong flaring has been seen
in Cyg X-1, despite the more than 21 years of INTEGRAL monitoring, with
almost ${}$20 Ms of exposure, and the similarly deep monitoring with
RXTE/PCA that lasted from 1997 to 2012. The flares were seen in all
three X-ray and
-ray instruments of INTEGRAL. Radio
monitoring by the AMI Large Array with observations 6 h before and 40 h
after the X-ray flares did not detect a corresponding increase in radio
flux. The shape of the X-ray spectrum shows only marginal change during
the flares, i.e., photon index and cut-off energy are largely preserved.
The overall flaring behavior points toward a sudden and brief release of
energy, either due to the ejection of material in an unstable jet or due
to the interaction of the jet with the ambient clumpy stellar wind.
) quiescent galaxies (QGs) at redshifts
to place
constraints on the evolution of their cold interstellar medium (ISM) and
thereby obtain insights into the processes of galaxy quenching
throughout cosmic time. We used a robust sample of 458 colour-selected
QGs covered by the A
COSMOS+A
GOODSS database to perform a stacking
analysis in the
domain and measured their mean dust
masses from their stacked sub-millimetre luminosities. We used the
CIGALE spectral energy distribution fitting code to obtain star
formation histories and infer the time since quenching for all the QGs
in our sample. We used this information to gain insight into the time
evolution of the dust content after quenching. Most QGs in our sample
quenched around a redshift of
, following the
peak of cosmic star formation. The majority of QGs observed at
are recently quenched
(i.e. quenched for no longer than 500 Myr), whereas the majority of QGs
observed at
have already been
quenched for a significant amount of time (
Gyr). This
implies that high-redshift galaxies (
) are ideal for
studying the mechanisms of quenching and its effects on the ISM, while
lower-redshift galaxies are more suitable for studying the long-term
effects of the QG environment on their ISM. We obtain upper limits on
the dust mass fraction of the QG population that indicate a lower dust
content than what was found by earlier stacking studies, and
significantly lower (by a factor of
) than that of
normal star-forming galaxies. We also place constraints on the initial
gas fraction right after quenching. We find that within the first
Myr after
quenching, QGs already lose on average
of their
cold ISM. Our findings support a gas consumption or removal scenario
acting on short timescales.
and
with a
possible third feature at
.
These are departures from an otherwise power-law-like continuum that
steepens above
. Binary
black holes with primary masses near
are more
likely to have less massive secondaries, with a mass ratio distribution
peaking at
, potentially a signature of stable mass transfer
during binary evolution. Black hole spins are inferred to be
non-extremal, with 90% of black holes having
, and
preferentially aligned with binary orbits, implying many merging
binaries form in isolation. However, we find a significant fraction,
0.24-0.42, of binaries have negative effective inspiral spins,
suggesting many could be formed dynamically in gas-free environments. We
find evidence for correlation between effective inspiral spin and mass
ratio, though it is unclear if this is driven by variation in the mode
of the distribution or the width. (Abridged)
,
,
, and
photometric
bands based on panchromatic Hubble Space Telescope observations. The
software was used to create a simulated database of Euclid images for
the 27 galaxy clusters observed during the Cluster Lensing And Supernova
survey with Hubble (CLASH) and the Hubble Frontier Fields (HFF) program.
Since the mock images were generated from real observations, they
incorporate, by construction, all the complexity of the observed galaxy
clusters. The simulated Euclid data of the galaxy cluster MACS
J0416.1$-$2403 were then used to explore the possibility of developing
strong lensing models based on the Euclid data. In this context,
complementary photometric or spectroscopic follow-up campaigns are
required to measure the redshifts of multiple images and cluster member
galaxies. By Euclidising six parallel blank fields obtained during the
HFF program, we provide an estimate of the number of galaxies detectable
in Euclid images per
per
magnitude bin (number counts) and the distribution of the galaxy sizes.
Finally, we present a preview of the Chandra Deep Field South that will
be observed during the Euclid Deep Survey and two examples of
galaxy-scale strong lensing systems residing in regions of the sky
covered by the Euclid Wide Survey. The methodology developed in this
work lends itself to several additional applications, as simulated
Euclid fields based on HST (or JWST) imaging with extensive
spectroscopic information can be used to validate the feasibility of
legacy science cases or to train deep learning techniques in advance,
thus preparing for a timely exploitation of the Euclid Survey data.
(95% cred.), a factor of 1.7 improvement over
previous results. Scale-invariant backgrounds are constrained to
, representing a 2.1x sensitivity gain. We also
place new limits on gravity theories predicting non-standard
polarization modes and confirm that terrestrial magnetic noise sources
remain below detection threshold. Combining these spectral limits with
population models for GWTC-4, the latest gravitational-wave event
catalog, we find our constraints remain above predicted merger
backgrounds but are approaching detectability. The joint analysis
combining the background limits shown here with the GWTC-4 catalog
enables improved inference of the binary black hole merger rate
evolution across cosmic time. Employing GWTC-4 inference results and
standard modeling choices, we estimate that the total background arising
from compact binary coalescences is
at 90% confidence, where the largest contribution
is due to binary black holes only,
.
. The combination
of lensing with deep spectroscopic data reveals a rotation curve that is
inconsistent with a nuclear star cluster, yet can be well explained by
Keplerian rotation around a point mass of 50 million Solar masses,
consistent with virial BH mass estimates from the Balmer lines. The
Keplerian rotation leaves little room for any stellar component in a
host galaxy, as we conservatively infer
. Such a ‘’naked’’ black hole, together with its
near-pristine environment, indicates that this LRD is a massive black
hole seed caught in its earliest accretion phase.
, to the GAlaxy Evolution and Assembly (GAEA)
simulated galaxy sample which reproduces several characteristics of the
Euclid Wide Survey. We develop a method to compare skeletons derived
from photometric redshifts to those derived from true galaxy positions.
This method expands the commonly used measure of distance between
filaments to include geometrical (angles between filaments) and
astrophysical considerations (galaxy mass gradients and
connectivity-mass relations). We assess whether this approach
strengthens our ability to correctly identify filaments in very large
surveys such as the Euclid Wide Survey. [abridged]
due to
observational limitations and uncertainties in locally calibrated gas
tracers. The [CII]
line has
recently emerged as a key probe of the cold ISM and star formation in
the early Universe. We investigate whether the resolved [CII]-SFR and KS
relations established at low redshift remain valid at
by
analysing 13 main-sequence galaxies from the ALPINE and CRISTAL surveys,
using multi-wavelength data (HST, JWST, ALMA) at
kpc resolution. We
perform pixel-by-pixel spectral energy distribution (SED) modelling with
CIGALE on resolution-homogenised images. We develop a statistical
framework to fit the [CII]-SFR relation that accounts for pixel
covariance and compare our results to classical fitting methods. We test
two [CII]-to-gas conversion prescriptions to assess their impact on
inferred gas surface densities and depletion times. We find a resolved
[CII]-SFR relation with a slope of
and
intrinsic scatter of
dex,
which is shallower and tighter than previous studies at
. The resolved KS
relation is highly sensitive to the [CII]-to-gas conversion factor:
using a fixed global
yields
depletion times of
-
Gyr, while a surface
brightness-dependent
, places
some galaxies with high gas density in the starburst regime (
Gyr). Future inputs
from both simulations and observations are required to better understand
how the [CII]-to-gas conversion factor depends on local ISM properties.
We need to break this fundamental limit to properly study the KS
relation at
.
. The Australia
Telescope Compact Array automatically triggered a 9-hour observation of
GRB 231117A at 5.5 and 9 GHz following its detection by the Neil Gehrels
Swift Observatory just 1.3 hours post-burst. Splitting this observation
into 1-hour time bins, the early radio afterglow exhibited flaring,
scintillating and plateau phases. The scintillation allowed us to place
the earliest upper limit (
hours) on the size of
a GRB blast wave to date, constraining it to
cm. Multi-wavelength modeling of the full
afterglow required a period of significant energy injection between
and
day. The energy injection was modeled
as a violent collision of two shells: a reverse shock passing through
the injection shell explains the early radio plateau, while an X-ray
flare is consistent with a shock passing through the leading impulsive
shell. Beyond 1 day, the blast wave evolves as a classic decelerating
forward shock with an electron distribution index of
. Our
model also indicates a jet-break at
days, and a
half-opening angle of
.
Following the period of injection, the total energy is
times the initial
impulsive energy, with a final collimation-corrected energy of
erg.
The minimum Lorentz factors this model requires are consistent with
constraints from the early radio measurements of
to
between
and
day. These results demonstrate the
importance of rapid and sensitive radio follow-up of GRBs for exploring
their central engines and outflow behaviour.
and C
H
absorptions for perijoves (PJs) 6 and
10, two of Juno’s close approaches to Jupiter, by integrating auroral
H
emission over hydrocarbon-sensitive
spectral intervals. For CH
, we redefined the absorbed spectral
band, replacing the traditionally used 125-130 nm interval with 135-140
nm, in order to mitigate higher-order calibration issues. In regions of
intense auroral brightness, we developed a correction method to account
for spectral distortion due to detector non-linearities at high fluxes.
CH
and C
H
absorptions generally follow the
expected vertical distribution, with the CH
density extending to higher altitudes
than C
H
. However, several localized regions
show unexpected spatial distribution of the absorption. In PJ6, such
anomalies are attributed to instrumental non-linearities. After
correction, the CR distributions become consistent with standard
hydrocarbon vertical distributions. In PJ10, however, some anomalous
patterns persist despite correction. Spectral modeling indicates that
these can be explained by modifying the relative abundances of CH
and C
H
, suggesting horizontal compositional
variability and possible deviations in homopause altitude between
species. These findings underscore the importance of accounting for
local atmospheric composition when interpreting ultraviolet auroral
spectra and retrieving electron energy distributions.
Cen A, using the MIRI instrument on the
James Webb Space Telescope. With three epochs of observation (August
2024, February 2025, and April 2025), we achieve a sensitivity
sufficient to detect
225-250 K (1-1.2
) planets
between 1”-2” and exozodiacal dust emission at the level of $>
$ the brightness of our own zodiacal
cloud. The lack of exozodiacal dust emission sets an unprecedented limit
of a few times the brightness of our own zodiacal cloud
a factor of $
_ν$(15.5
m) = 3.5 mJy point source, called
, at a separation of 1.5” from
Cen A. Because the August 2024 epoch
had only one successful observation at a single roll angle, it is not
possible to unambiguously confirm
as a bona fide planet. Our analysis
confirms that
is neither a background nor a
foreground object.
is not recovered in the February and
April 2025 epochs. However, if
is the counterpart of the object,
, seen by the VLT/NEAR program in 2019,
we find that there is a 52% chance that the
candidate was missed in
both follow-up JWST/MIRI observations due to orbital motion.
Incorporating constraints from the non-detections, we obtain families of
dynamically stable orbits for
with periods between
2-3 years. These suggest that the planet candidate is on an eccentric
(
) orbit
significantly inclined with respect to
Cen AB orbital plane (
, or
). Based on the photometry and orbital properties,
the planet candidate could have a temperature of 225 K, a radius of
$$1-1.1
and a mass
between 90-150
,
consistent with RV limits.
3 and beyond. Its success
depends critically on obtaining highly accurate mean redshifts for
ensembles of galaxies
in all tomographic bins,
essential for deriving robust cosmological constraints. However,
photometric redshifts (photo-
s) suffer from systematic biases arising
from various sources of uncertainty. To address these challenges, we
utilised self-organising maps (SOMs) with mock samples resembling the
Euclid Wide Survey (EWS), to validate Euclid’s uncertainty requirement
of
per tomographic bin, assuming DR3-level data. We
observe that defining the redshift tomography using the mean
spectroscopic redshift (spec-
) per SOM cell, results in none of the
ten tomographic redshift bins satisfying the requirement. In contrast,
the redshift tomography on the photo-
s of the EWS-like sample yields superior
results, with eight out of ten bins [
]
meeting the Euclid requirement. To enhance the realism of our study, we
morph our calibration sample to mimic the C3R2 survey in incremental
steps. In this context, a maximum of six out of ten bins meet the
requirement, strongly advocating the adoption of a redshift tomography
defined by the photo-
s of individual galaxies rather than the
commonly used mean spec-
of SOM cells. To examine the impact on
the expected biases for
,
, and
measured by Euclid,
we perform a Fisher forecast for cosmic shear only, based on our
redshift uncertainties. Here, we find that even under an evaluation of
the uncertainty where the impact of the redshift bias is substantial,
most absolute biases remain below 0.1
in the idealised scenario and below
0.3
in the more realistic case.
Cen A, with the MIRI coronagraph in
F1550C (15.5
m) at three distinct epochs between
August 2024 and April 2025. For the first time with JWST, we demonstrate
the application of reference star differential imaging to simultaneously
subtract the coronagraphic image of a primary star and the point spread
function (PSF) of its binary companion to conduct a deep search for
exoplanets and dust emission. We achieve a typical 5
point source contrast sensitivity
between
-
at separations
1” and an
exozodiacal disk (coplanar with
Cen AB) sensitivity of $
$ the Solar System’s zodiacal cloud
around
Cen A. The latter is an extraordinary
limit, representing the deepest sensitivity to exozodiacal disks
achieved for any stellar system to date. Post-processing with the
PCA-KLIP algorithm reveals a point source, called
, in August 2024, detected at S/N
4-6 (3.3-4.3
), a separation of $$1.5” (2 au), and
with a F1550C flux (contrast) of $
^{-5}$).
Various tests conducted with the data show that
is unlikely to be a detector or PSF
subtraction artifact and confirm that it is neither a background nor a
foreground object.
is not re-detected in the two
follow-up observations (February and April 2025). If
is astrophysical in nature, the only
explanation is that it has moved to a region of poor sensitivity due to
orbital motion. We perform PSF injection-recovery tests and provide 2D
sensitivity maps for each epoch to enable orbital completeness
calculations. Additional observations are necessary to re-detect
candidate
and confirm its nature as a planet
orbiting our nearest solar-type neighbor.
O and its thermally dissociation
product OH on the dayside of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-121 b based on
high-resolution emission spectroscopy with the recently commissioned
Near InfraRed Planet Searcher (NIRPS). We retrieve a photospheric
abundance ratio of log
(OH/H
O)
indicating that there is about as much OH as H
O at photospheric pressures, which
confirms predictions from chemical equilibrium models. We compare the
dissociation on WASP-121 b with other ultra-hot Jupiters and show that a
trend in agreement with equilibrium models arises. We also discuss an
apparent velocity shift of $4.79^{+0.93}_{-0.97}
^{-1}$ in the H
O signal, which is not reproduced by
current global circulation models. Finally, in addition to H
O and OH, the NIRPS data reveal
evidence of Fe and Mg, from which we infer a Fe/Mg ratio consistent with
the solar and host star ratios. Our results demonstrate that NIRPS can
be an excellent instrument to obtain simultaneous measurements of
refractory and volatile molecular species, paving the way for many
future studies on the atmospheric composition, chemistry, and the
formation history of close-in exoplanets.
1 arcsec (
at
3.7 kpc) resolution and
continuum sensitivity (
at 30 K). We identified 1562 compact cores from
1.3 mm continuum emission using getsf. Observed linear core separations
(
) are
significantly less than the thermal Jeans length (
), with the
ratios peaking at
. This indicates
that thermal Jeans fragmentation has taken place within the IR-bright
protocluster clumps studied here. The observed low ratio of
could be the result of evolving core separation
or hierarchical fragmentation. Based on associated signatures of star
formation (e.g., outflows and ionized gas), we classified cores into
three categories: 127 starless, 971 warm, and 464 evolved cores. Two
starless cores have mass exceeding 16
, and
represent high-mass candidates. The scarcity of such candidates suggests
that competitive accretion-type models could be more applicable than
turbulent core accretion-type models in high-mass star formation within
these IR-bright protocluster clumps.
-14 from the JWST
COSMOS-Web survey. Our samples, selected using the dropout technique in
the HST/ACS F814W, JWST/NIRCam F115W, and F150W filters, contain a total
of 3099 galaxies spanning a wide luminosity range from faint (
mag) to bright (
mag). The galaxies are undergoing rapid star
formation, with blue stellar populations. Surprisingly, their median UV
spectral slope
does not evolve at
, suggesting minimal
dust, or physical separation of dust and star formation at early epochs.
The measured UVLF exhibits an excess at the bright-end (
mag) compared to pre-JWST empirical results and theoretical predictions
of an evolving Schechter function, with the excess beginning at
and becoming
increasingly prominent toward
. Our analysis
suggests that reproducing the observed abundance of UV-bright galaxies
at high redshift requires a combination of physical processes, including
elevated star formation efficiencies, moderate levels of stochasticity
in galaxy luminosities, and minimal dust attenuation.
0.055 Me, and 0.260
0.038 Me, respectively. Our
results show that, in the case of Proxima, NIRPS provides more precise
radial velocity data than HARPS, and a more significant detection of the
planetary signals. The standard deviation of the residuals of NIRPS
after the fit is 80 cm/s, showcasing the potential of NIRPS to measure
precise radial velocities in the near-infrared.
and cold dark matter (
CDM) model. A statistically significant
detection of any deviations would signify the presence of new physics or
the breakdown of any number of the underlying assumptions of the
standard cosmological model or possible systematic errors in the data.
In this paper, we quantify the ability of the LSS data products of the
spectroscopic survey of the Euclid mission, together with other
contemporary surveys, to improve the constraints on deviations from
CDM in the redshift range
. We
consider both currently available growth rate data and simulated data
with specifications from Euclid and external surveys, based on
CDM and a modified gravity (MoG) model
with an evolving Newton’s constant (denoted
CDM), and carry out a binning method and
a machine learning reconstruction, based on genetic algorithms (GAs), of
several LSS null tests. Using the forecast Euclid growth data from the
spectroscopic survey in the range
, we find that in combination with external data
products (covering the range
),
Euclid will be able to improve on current constraints of null tests of
the LSS on average by a factor of eight when using a binning method and
a factor of six when using the GAs. Our work highlights the need for
synergies between Euclid and other surveys, but also the usefulness of
statistical analyses, such as GAs, in order to disentangle any
degeneracies in the cosmological parameters. Both are necessary to
provide tight constraints over an extended redshift range and to probe
for deviations from the
CDM model.
, H
, and HeII nebulae around the two types
of AGN at
with ten massive
systems from the FIRE simulations based on the unified model to show
their differences and to test if they can be used to constrain the AGN
model. We post-process the data with the CLOUDY and the Ly
radiative transfer code, RASCAS.
Overall, we find that the Ly
nebulae around the unobscured AGN
(type-I nebulae) and obscured AGN (type-II nebulae) do not exhibit
significant differences in the luminosity, area, and HeII/Ly
when the simulated cutout is set to the
halo virial radius. Whereas, the type-II nebulae exhibit less symmetric
morphologies, flatter surface brightness profiles, and larger emission
line widths (at
kpc) than those
of the type-I nebulae. These nebulae properties exhibit complicated
correlations with the AGN, indicating that nebulae observations can be
applied to constrain the AGN engine. However, independent observations
on nebulae in the mentioned emissions are insufficient to test the
unified model as a priori in observations is not possible to know the
direction and opening angle of the ionization cone. We prompt that the
joint observations of Ly
nebulae and radio jets can help to
reveal the ionization cone to probe the unified model. Our calculations
suggest that this method requires
type-II Ly
nebulae with current instruments to
reach a confidence level of
.
7.3, deep in the era
of reionisation. The data are well described by a combination of faint
blue host, similar to many z
7 galaxies, with a
supernova of similar luminosity to the proto-type GRB supernova, SN
1998bw. Although larger galaxy contributions cannot be robustly
excluded, given the evidence from the blue afterglow colours of low dust
extinction, supernovae much brighter than SN 1998bw can be. These
observations suggest that, despite disparate physical conditions, the
star that created GRB 250314A was similar to GRB progenitors in the
local universe.
depth of 28.1 mag in F300M and covers
542 arcmin
, increasing the area of existing JWST
medium-band coverage in at least 8 bands by
7
. The MIRI imaging
reaches a 5
depth of 23.9 mag in F1280W and covers
275 arcmin
in at least 2 MIRI filters. When
combined with existing imaging, these data will provide a photometric
catalog with 20-26 JWST filters (depending on field) and 26-35 filters
total, including HST. This paper presents a detailed breakdown of the
filter coverage, exposure times, and field layout relative to previous
observations, as well as an overview of the primary science goals of the
project. These include uncovering the physics of enigmatic sources
hiding in current broadband catalogs, improving systematics on stellar
mass functions and number densities by factors of
3, and resolved
mapping of stellar mass and star formation at 1
6. When
complete, MINERVA will become an integral part of the treasury deep
field imaging datasets, significantly improving population studies with
well-understood completeness, robust photometric redshifts, stellar
masses, and sizes, and facilitating spectroscopic follow up for decades
to come.
. We also pin down the ephemeris of HD
95338b. Using injection/retrieval tests, we show that a
detection of an exomoon
would be possible at
~
with the
methodology presented here. We exclude the transit of an exomoon in the
system with
~
at the
level. The algorithm used for
finding the transit-like event can be used as a baseline for other
similar targets, observed by CHEOPS or other missions.
in
the pilot surveys of FLASH, an ongoing survey with the ASKAP radio
telescope. 11 of the 12 targets are resolved in the VLBA observations.
Using the parsec scale radio images, we have classified the source
morphology and identified the radio core. Six of the twelve targets have
core-jet morphology, four have two-sided jet morphology, one has a
complex morphology, and one is unresolved. We describe a methodology to
test whether the emission from the core or the total emission detected
in the VLBA image has sufficient flux density to cause the entire HI
21-cm absorption, and we estimate limits on the gas covering factor and
velocity-integrated optical depth (VOD). We find that for seven of the
twelve sources, the core has sufficient flux density to cause all the HI
21-cm absorption detected in the ASKAP spectrum. For three other
targets, with projected sizes in the range
,
a large fraction of the entire emission in the VLBA map could be
occulted by the gas. For 0903+010 (NVSS J090331+010846), we estimate
that at least
of the
peak absorption detected in the ASKAP spectrum could arise against the
emission detected in the VLBA image. For the target 0023+010 (NVSS
J002331+010114), we estimate an upper limit on the VOD of
, the highest in our sample. For 0903+010 (NVSS
J090331+010846) we estimate a lower limit of
on the VOD. We find that the distribution of HI
21-cm VODs at
could increase by up to a factor of three after correction for the
covering factors using our VLBA measurements.
decreasing to
within the
central
. SITELLE’s broad field coverage elucidates the
galaxy’s structural details, confirming that low-power jets
significantly influence the host galaxy across parsec and kpc scales.
The velocity dispersion map reveals asymmetric or double-peaked emission
lines, tracing jet-disk interactions likely responsible for the
formation of anomalous arm features. Small-scale ionizing clusters were
detected in regions with disrupted gas flows, possibly formed through
tidal interactions or shock compression. NGC~4258 thus presents a
compelling case for studying LLAGN-driven feedback, illustrating how
optical IFS combined with multi-wavelength data clarifies the impact of
outflows and shocks on nearby spiral galaxies, providing insights into
how these processes shape star formation and ISM conditions.
7.3 . This burst
happened when the Universe was only
5% of its current age. We
discuss the signature of these rare events within the context of the
SVOM operating model, and the ways to optimize their identification with
adapted ground follow-up observation strategies.
), low-metallicity (
) galaxies
at
, one of
which we identify as hosting a Type-II AGN. We measure flat strong-line
metallicity gradients, suggestive of ISM redistribution by outflows or
past merging, but also identify tension with the direct-
metallicity
gradient in one galaxy. We measure
in both galaxies, consistent with observations of
lower rotational support at early cosmic times. We identify broad
kinematical components decoupled from galactic rotation with velocities
of
and argue these components trace outflows, for
which we infer outflow rates of
with
. We
compare our findings to results from the new large-volume AESOPICA
simulations, which fully incorporate different models of black hole
growth and AGN feedback. We find that our observational results of
are consistent with the simulated dwarf AGN
population, hinting AGN-driven feedback may contribute to quenching both
in our systems and in a wider population of low-mass galaxies in the
early Universe. This novel study illustrates the necessity of deep IFU
observations to decompose the complex kinematics and morphology of
high-
galaxies, trace outflows, and constrain
the effect of feedback in the early Universe.
) galaxies at
observed with the
CAPERS Cycle 3 program. These galaxies exhibit extreme UV slopes
compared to typical galaxies at
. Of the three sources,
two of them are a close pair (0.22 - arcsec) of blue galaxies at
and
with UV slopes of
and
respectively, selected from PRIMER COSMOS NIRCam imaging. We perform
spectrophotometric modeling of the galaxies which suggests extremely
young stellar ages and a lack of dust attenuation. For the bluest
galaxy, its UV slope also suggests significant Lyman continuum escape.
In contrast, the third source (selected from CEERS NIRCam imaging) at
exhibits a red UV slope with
. We
rule out the possibility of a strong nebular continuum due to the lack
of a Balmer jump and find no evidence to support the presence of active
galactic nucleus continuum due to a lack of strong UV emission lines and
no broad component to H
or H
. Instead, it is most likely that the
red UV slope is due to dust-reddening (
) implying a significant level of dust-obscured
star-formation only
after the Big Bang. Under standard assumptions
for dust attenuation, EGS-25297 would be the most intrinsically
UV-luminous galaxy (
) yet spectroscopically confirmed at
. This work
highlights that luminous galaxies at
have a
diversity of dust properties and that spectroscopy of these galaxies is
essential to fully understand star-formation at
.
M
yr
in M87, with evidence
of a weak starburst $$125 Myr ago that formed
M
of stars. Unlike
other cool-core clusters where SF is stronger and directly linked to
cooling gas, we found no spatial correlation between YSS and H
filaments. Comparing SF activity with
M87’s AGN outburst history suggests that recent AGN feedback events
($
α$ filaments with similar lengths and widths,
though they are obscured by dust near the center. These filaments are
likely powered by metal-line emission from collisional ionization,
suggesting ongoing low-level precipitation of the intracluster medium.
Our results indicate that AGN feedback has quenched SF significantly in
M87 for at least 200 Myr, even though some precipitation persists.
Additionally, we identified a hotspot created by the counterjet, with
the spectral index also constrained.
. As a
result, the WL mass obtained from our triaxial fit,
, is significantly lower than the value of
obtained from a spherically-symmetric fit that
otherwise employs the same methodology. Our triaxial fit finds a
concentration of
, consistent
with the spherically-symmetric value of
, which suggests that the unexpectedly high
concentration in Abell 1689 is not due to triaxiality and orientation.
We also measure the non-thermal pressure fraction at radii between
0.18-1.37 Mpc, finding a minimum of approximately 20 per cent at
intermediate radii increasing to near 30 per cent at both the smallest
and largest radii, and with a typical measurement precision of $$5 per
cent.
-ray triggers (EP250702a). We present
the discovery of an extremely red infrared counterpart of the event with
the VLT, as well as radio observations from MeerKAT. Hubble Space
Telescope observations pinpoint the source to a non-nuclear location in
a host galaxy with complex morphology, implying GRB 250702BDE is an
extragalactic event. The multi-wavelength counterpart is well described
with standard afterglow models at a relatively low redshift
, but the
prompt emission does not readily fit within the expectations for either
collapsar or merger-driven GRBs. Indeed, a striking feature of the
multiple prompt outbursts is that the third occurs at an integer
multiple of the interval between the first two. Although not conclusive,
this could be indicative of periodicity in the progenitor system. We
discuss several possible scenarios to explain the exceptional properties
of the burst, which suggest that either a very unusual collapsar or the
tidal disruption of a white dwarf by an intermediate-mass black hole are
plausible explanations for this unprecedented GRB.
while the signal estimator
noise is measured at 7
in photometric mode and 9
in spectroscopic
acquisition mode. The deviation from linear response at signal levels up
to 80 k
is less than 5% for 95% of
the pixels. Median persistence amplitudes are less than 0.3% of the
signal, though persistence exhibits significant spatial variation and
differences between detectors.
and a minimum halo mass of
Msun/h. The relatively small box size makes this set unfit for measuring
very large scales. The EuclidLargeBox set consists of 1000 simulations
of 3.38 Gpc/h, with the same mass resolution and a footprint that covers
half of the sky, excluding the Milky Way zone of avoidance. From this we
produced a set of 1000 EuclidLargeMocks on the 30 deg radius footprint,
whose comoving volume is fully contained in the simulation box. We
validated the two sets of catalogues by analysing number densities,
power spectra, and 2-point correlation functions, showing that the
Flagship spectroscopic catalogue is consistent with being one of the
realisations of the simulated sets, although we noticed small deviations
limited to the quadrupole at k>0.2 h/Mpc. We show cosmological
parameter inference from these catalogues and demonstrate that using one
realisation of EuclidLargeMocks in place of the Flagship mock produces
the same posteriors, to within the expected shift given by sample
variance. These simulated skies will be used for the galaxy clustering
analysis of Euclid’s Data Release 1 (DR1).
per cent at a
polarization angle, measured east of north, of
within the 2-8 keV X-ray band. The X-ray
polarization angle and degree during this observation are consistent
with those obtained during the first two observations. The chromaticity
of the polarization across radio, optical, and X-ray bands is likewise
consistent with the result from the simultaneous campaigns during the
first two observations. Furthermore, we present two types of models to
explain the observed spectral energy distributions (SEDs) and
energy-resolved polarization: a synchrotron self-Compton model with an
anisotropic magnetic field probability distribution in the emitting
volume, as well as an energy-stratified shock model. Our results support
both the shock scenario as well as support that small levels of magnetic
field anisotropy can explain the observed polarization.
for periods of
up to 100 d, and a mass of 2-5M
for the star’s
HZ. (abridged)
,
with only a few prominent examples at higher redshifts. Here we report a
first strong-lensing analysis of the massive galaxy cluster SPT-CL
J0546-5345 at a redshift
. This cluster was
first detected through the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect, with a high
estimated mass for its redshift of
. Using recent JWST/NIRCam and archival HST
imaging, we identify at least 10 secure and 6 candidate sets of multiply
imaged background galaxies, which we use to constrain the mass
distribution in the cluster. We derive effective Einstein radii of
for a
source at
, and
for a
source at
. The total
projected mass within a
kpc radius around the strong-lensing
region is
. While our results rely on photometric redshifts
warranting spectroscopic follow-up, this central mass resembles that of
the Hubble Frontier Fields clusters - although SPT-CL J0546-5345 is
observed when the Universe was
Gyr younger.
Amongst the multiply-imaged sources, we identify a
hyperbolic-umbilic-like configuration, and, thanks to its point-like
morphology, a possible Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN). If confirmed
spectroscopically, it will add to just a handful of other quasars and
AGN known to be multiply lensed by galaxy clusters.
, NH
, and CN: symmetric around the
photocentre. The production rates of these species gently declined into
and beyond perihelion, until 2I’s outburst and splitting event in early
2020 March. C
, NH
, and CN production rates all
increased, with NH
being the most significant; the dust
emission also slightly reddened. 2I/Borisov is a carbon-depleted,
relatively NH
-rich comet when compared to those
comets yet measured in the Solar System.
and that HD
206505 B is spectral type
. Using the
BT-Settl atmospheric model grids, we find a bimodal solution for the
atmospheric model fit of HD 112863 B, such that
K or
K
and
or
, while for HD 206505 B,
K and
.
Comparing the bolometric luminosities of both companions with
evolutionary models imply that both companions are likely above the
hydrogen burning limit.
. We utilise
JWST NIRCam observations of the A2744-z7p9OD protocluster at
to constrain the
properties of resident galaxies. We identify seven new protocluster
members, bringing the total number to 23 and the total stellar mass of
the protocluster to in excess of
. These galaxies are remarkably evolved just 650
Myr after the Big Bang, preferentially showing redder UV-slopes and
stronger Balmer breaks than is typical of field galaxies. We use the
PROSPECTOR spectral energy distribution fitting code to derive key
galaxy properties, finding distinct populations in the core versus the
outskirts of the protocluster. The core is largely composed of dusty,
massive galaxies which can be characterised as undergoing a synchronised
(mini)-quenched phase, while galaxies in the protocluster outskirts are
undergoing recent bursts of star formation. Finally, a strong
suppression of the continuum around the Ly
-break evidences extreme neutral
hydrogen column densities in many resident galaxies (
).
The A2744-z7p9OD system is the most extreme, evolved overdensity yet
observed at
, with higher stellar
masses, gas densities, and dust attenuation, revealing the intersection
of local environment and high-redshift galaxy formation at their
extremes.
, and virial radius
), with
error bars representing one standard deviation. The profile is well
described by an NFW model with concentration c=6.5 and a small-scale
radius of 230 kpc in the 30,kpc
2000,kpc
range that is best constrained by SL and WL data. Abell 2390 is the
first of many examples where Euclid data will play a crucial role in
providing masses for clusters.
forest through the use of ‘strong,
blended Lyman-
’ (or SBLA) absorption. Specifically a
series of publications studied SBLA absorption systems with Lyman-
flux transmission,
on scales of 138 km s
in the Sloan Digital
Sky Survey (SDSS). In order to better understand the connection between
halos and these SBLAs, we make use of several million synthetic
absorption spectra from the TNG50 cosmological simulation, at z=2 and
z=3. We explore spectra with SDSS-like resolution in order to understand
the nature of SBLAs as defined thus far, as well as with high resolution
(or ‘resolved’) spectra to generalise and optimise SBLAs as halo
finders. For the SDSS SBLAs, we find that up to 78% of these absorption
systems reside in hlaos, where the stronger the absorption and the lower
the redshift, the higher the probability. We also manage to recover a
mean halo mass of
, in line with what is measured in observations.
For the resolved SBLAs, we expand on the previous definition and allow
the SBLA spectra size to vary between 54 km s
and 483 km s
. We find that the
largest absorbers have the highest probability of finding halos. When
applying a hierarchical framework, where we allow the largest SBLAs to
consume the smaller ones, we find that the halo mass distributions for
each SBLA spectral size becomes narrower with respect to the
non-hierarchical case. We are also able to probe halo masses from
(for 100
km s
SBLAs) to
(for 450
km s
SBLAs). With these
results, we show that we are able to transform the Lyman-
forest into a powerful halo finding
machine for not only identifying CGM regions, but also estimating their
host halo masses.
and
bands and obtained
and
spectroscopy. In addition, we carried
out VLTI/GRAVITY observations for the further astrometric and
spectroscopic confirmation of a detected companion. We discovered a
close-in young giant planet, HD 135344 Ab, with a mass of about 10
. The
multi-epoch astrometry confirms the bound nature based on common
parallax and common proper motion. This firmly rules out the scenario of
a non-stationary background star. The semi-major axis of the planetary
orbit is approximately 15-20 au, and the photometry is consistent with
that of a mid L-type object. The inferred atmospheric and bulk
parameters further confirm the young and planetary nature of the
companion. HD 135344 Ab is one of the youngest directly imaged planets
that has fully formed and orbits on Solar System scales. It is a
valuable target for studying the early evolution and atmosphere of a
giant planet that could have formed in the vicinity of the snowline.
and
(90% credible intervals), at luminosity distance
0.7-4.1 Gpc and redshift of
, and a network signal-to-noise ratio of $$20.7.
Both black holes exhibit high spins,
and
respectively. A massive black hole remnant is
supported by an independent ringdown analysis. Some properties of
GW231123 are subject to large systematic uncertainties, as indicated by
differences in inferred parameters between signal models. The primary
black hole lies within or above the theorized mass gap where black holes
between 60-130
should be rare due
to pair instability mechanisms, while the secondary spans the gap. The
observation of GW231123 therefore suggests the formation of black holes
from channels beyond standard stellar collapse, and that
intermediate-mass black holes of mass $$200
form through
gravitational-wave driven mergers.
-band for the bright galaxy sample
(BGS), based on the first three years of observations from the Dark
Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI). To achieve this, we applied the
subhalo abundance matching (SHAM) technique to the Uchuu
-body simulation, which follows the
evolution of 2.1 trillion particles within a volume of
, assuming a Planck base-
CDM cosmology. Using SHAM, we populated
Uchuu subhalos with LRGs and BGS-BRIGHT (
) galaxies up to
redshift
, assigning stellar
masses to LRGs and luminosities to BGS galaxies (up to
).
Furthermore, we analyzed the clustering dependence on stellar mass and
luminosity for each tracer. Our results show that the Uchuu BGS-BRIGHT
and LRG mocks accurately reproduce the observed redshift evolution of
clustering, with better than 5% agreement for separations of
and
below 10% for
. For
the Uchuu-LRG mock, we successfully captured the stellar mass dependence
of clustering, while for the Uchuu-BGS mock, we replicated the
clustering for various volume-limited subsamples. We also find good
agreement between the data and mocks in the dependence of large-scale
bias on luminosity for BGS-BRIGHT galaxies and on stellar mass for LRGs.
Altogether, these results equip DESI with robust tools for generating
high-fidelity lightcones for the remainder of the survey, thereby
enhancing our understanding of the galaxy–halo connection.
8 degrees and a significant
3D spin-orbit angle of 52
6 degrees, based on the
measurement of the stellar rotation period. HIP 41378 f is part of a
5-transiting planetary system with planets close to mean motion
resonances. The observed misalignment likely reflects a primordial tilt
of the stellar spin axis relative to the protoplanetary disk, rather
than dynamical interactions. HIP 41378 f is the first non-eccentric
long-period (P>100 days) planet observed with the RM effect, opening
new constraints on planetary formation theories. This observation should
motivate the exploration of planetary obliquities across a longer range
of orbital distances through international collaboration.
$50+ Mpc), providing access to the luminous
stellar populations in thousands of galaxies, enabling unprecedented
views of their morphology, stellar abundances, and dust content. The
principal technological requirement advanced by this science case is a
camera with a resolution of $$0.015’’ that is diffraction-limited, and
Nyquist-sampled (0.01’’ per pixel), to at least 550 nm
comparable to the High Definition
Imager from the LUVOIR concept.
from its host. The new orbit fit yields a dynamical mass of
and
an eccentricity of
. We also find that additional relative astrometry
epochs in the future will not enable further constraints on the
dynamical mass due to the dominating relative uncertainty on the
Hipparcos-Gaia proper motion anomaly. The publication of Gaia DR4 will
likely ease this predicament. We find that the companion is consistent
with spectral type L8 and exhibits a potential metal enrichment in its
atmosphere. Conclusions: These results do not yet allow for a definite
inference of the companion’s formation channel. Nevertheless, the new
constraints on its bulk properties and the additional GRAVITY spectrum
presented here will aid future efforts to determine the formation
history of HIP 99770 b.
) later.A
comprehensive analysis of the prompt emission spectrum observed by
Swift-BAT and Fermi-GBM/LAT reveals a rare and significant high-energy
cutoff at ~76 MeV. Assuming this cutoff is due to
absorption allows us to place
an upper limit on the initial Lorentz factor,
. The
optical/NIR and GeV afterglow light curves be described by the standard
external shock model, with early-time emission dominated by a reverse
shock (RS) and a subsequent transition to forward shock (FS) emission.
Our afterglow modelling yields a consistent estimate of the initial
Lorentz factor (
). Furthermore, the RS-to-FS magnetic field ratio
(
) indicates that the reverse shock region is
significantly more magnetized than the FS region. An
isotropic-equivalent kinetic energy of
erg is derived, and the corresponding
-ray radiation efficiency is estimated
to be
= 3.1%. On the other hand,
the standard afterglow model can not reproduce the X-ray light curve of
GRB 240825A, calling for improved models to characterize all
multiwavelength data.
galaxies by exploiting one of the richest JWST
NIRCam imaging data, taken in the CANUCS survey in Cycle 1 and the
Technicolor (TEC) survey in Cycle 2. The combination of the CANUCS+TEC
provides multi-epoch, deep NIRCam images in all medium bands (MBs) and
broad bands (BBs) onboard NIRCam (22 filters in total), over
in three independent lines of sight. We select
high-
galaxy candidates based on photometric
redshifts, and obtain eight candidates at
, including a
very robust candidate at
. The
ultraviolet (UV) luminosity function (LF) from our sample is consistent
with previous JWST studies showing a scatter of
dex across the
literature, marking the significance of the field-to-field variance in
interpreting galaxy abundance measurements at
. We find that the
UV LF moderately evolves at
, and the LF
normalization and the luminosity density decline by a factor of
from
to
, indicating less
steep evolution than
. We highlight the
importance of MB filters, not only to minimize the contamination by
low-
interlopers but also to maximize the
completeness. In particular, faint and less blue galaxies could be
missed when the sample is built solely on BB data. The contamination and
incompleteness of BB-only selected samples can bias our views of
earliest galaxy evolution at
, including the UV
LF by
dex, the
size-magnitude relation by
dex, and the UV
slope-magnitude relation by
.
) probed by upcoming
SZE-selected samples, current large surveys may be insufficient for
reliable confirmation. Deep, high-resolution infrared surveys like
Euclid will thus be essential for confirming most high-redshift
clusters. We present an analysis of the first sizeable Euclid dataset
(Q1), overlapping with several ICM-selected cluster samples. We apply an
adaptation of the MCMF cluster confirmation tool to estimate key
properties, including redshift and richness, and to predict Euclid’s
capabilities for high-redshift cluster confirmation. We find promising
performance, particularly at high redshifts, while richness estimates at
low redshifts (
) are currently
limited by Q1 data quality but should improve with future releases.
Using MCMF runs on random lines of sight, we predict that Euclid will
confirm clusters at
as
effectively as current optical surveys at
, significantly
enhancing high-redshift confirmation. SZE-selected samples will thus
greatly benefit from Euclid overlap. Among five known high-
SZE clusters in Q1, we identify the
highest-redshift jellyfish galaxy candidate to date,
EUCLJ035330.86$-
-
z=1.32
-
z=1.46
-
-$4845.
, the true-positive
rate (TPR) reaches
by the
7th observation and exceeds
by the
9th. Among the negative examples, SNe in LRGs remain the primary source
of FPR, as they can resemble their lensed counterparts under certain
conditions. The model detects quads more effectively than doubles and
performs better on systems with larger image separations. Although
trained and tested on HSC-like data, our approach applies to any
cadenced imaging survey, particularly LSST.
mag outburst that occurred in December
2018. Optical images and a 251-day lightcurve were examined to
characterize the outburst and the comet’s quiescent activity. Variations
in the quiescent lightcurve appear to be dominated by coma asymmetries,
rather than changing activity levels as the comet approached and receded
from the Sun. Furthermore, the lightcurve shows evidence for 1 to 2
additional small outbursts (
mag) occurring in
September 2018. The large December 2018 outburst likely ejected water
ice grains, yet no signatures of ice were found in color photometry, a
color map, nor a near-infrared spectrum. We discuss possible dynamical
and thermal reasons for this non-detection. In this context, we examined
the comae of comets 103P/Hartley 2 and C/2013 US
(Catalina), and show
that a one-to-one mapping between continuum color and the presence of
water ice cannot be supported. We also discuss possible causes for the
large outburst, and find that there is an apparent grouping in the
kinetic energy per mass estimates for the outbursts of 5 comets.
upper limit of
on spatially coincident radio emission, a factor
of 100 lower than any known compact persistent radio source associated
with an FRB. Our KCWI observations allow us to characterize the gas
density, metallicity, nature of gas ionization, dust extinction and
star-formation rate through emission line fluxes. We leverage the
exceptional brightness and proximity of this source to place deep
constraints on the repetition of FRB 20250316A, and find it is
inconsistent with all well-studied repeaters given the non-detection of
bursts at lower spectral energies. We explore the implications of a
measured offset of 190
pc from the center of
the nearest star-formation region, in the context of progenitor
channels. FRB 20250316A marks the beginning of an era of routine
localizations for one-off FRBs on tens of mas-scales, enabling
large-scale studies of their local environments.
, consistent with inefficient heat redistribution
and supported by a GCM with magnetic drag. CHEOPS data provide no
constraint on the sky-projected orbital obliquity. Retrieval results
strongly depend on the chemical framework. Free-chemistry fits are
better but risk unphysical solutions for ultrahot Jupiters. We applied a
coherent stellar variability correction to CHEOPS and TESS data; future
observations would benefit from similar treatment.
$0.004. We measure a mean redshift of
in GOODS-N,
which is marginally higher than expectations from SIDES (
) because of an
overdensity at
, and
in COSMOS,
which agrees with the
predicted by
SIDES. We also show that the observed S2/S1.2 colors exhibit a weak
dependence with redshift but a large dispersion, which limits its
efficiency to select high-z sources. Finally, we studied the nine 2mm
sources not detected at 1.2mm, and found that two of them are
radiogalaxies, one is a z~2 galaxy, and the remaining six are compatible
with the expected number of spurious detections. The N2CLS survey shows
no evidence for any exotic 2mm-only galaxy population. Using SIDES, we
show that 2mm samples have a higher mean redshift compared to 1.2mm
because they miss z~2 dusty galaxies. Finally, we compare the N2CLS with
the ex-MORA survey and show that N2CLS is more efficient than
interferometric observations to build samples of high-z dusty
galaxies.
(so-called mini-quenched galaxies), and one
massive quiescent galaxy at z>5 with
, without any such galaxy reported at intermediate
masses. Here, we present a systematic search for dormant galaxies at
5<z<7.4 which halted star formation at least 10 Myr before the
time of observation. To do this, we make use of all the publicly
available NIRSpec prism data in the DAWN JWST Archive and select
galaxies showing low Hα equivalent widths (
Å) and
strong Balmer breaks (
). We find 14 dormant galaxies with stellar masses
ranging from
, revealing an intermediate-mass population of
such galaxies. By construction, the 14 sources reported are located
about 1 dex below the star-forming main sequence. Their star formation
histories suggest that they halted star formation between 10 and 25 Myr
before the time of observation which, according to models, is comparable
with the timescales of internally regulated bursts driving a “breathing”
mode of star formation. Our results show that ~1% of the galaxies in the
DJA are in a dormant phase of their star formation histories and span a
wide stellar mass range. These galaxies can be empirically selected
using only their spectral features in NIRSpec prism data.
and tangential shear
for the
Bright Galaxy Sample and Luminous Red Galaxies measured within the first
year of observations with DESI. To ensure robustness, we test the
measurements for systematic biases, finding no significant trends
related to the properties of the lens galaxies. We identify a
significant trend with the average redshift of source galaxies, however,
this trend vanishes once we apply shifts to the Hyper Suprime-Cam Subaru
Strategic Survey redshift distributions that are also favored by their
fiducial cosmology analysis. Additionally, we compare the observed
scatter in the measurements with the theoretical covariance and find
excess scatter, driven primarily by small-scale measurements of
; measurements on larger scales are consistent at
the
level. We further present
the projected clustering measurements
of the galaxy samples in the the
first data release of DESI. These measurements, which will be made
publicly available, serve as a foundation for forthcoming cosmological
analyses.
region centered on (R.A., Dec.)
= (10h00m28.81s,
+02d17m30.44s). We first developed a dedicated data reduction pipeline
to construct NIKA2 maps at 2 mm. We then used a matched-filter algorithm
to extract cluster candidates assuming a universal pressure profile to
model the expected cluster tSZ signal. We computed the purity and
completeness of the sample by applying the previous algorithm to
simulated maps of the sky signal in the COSMOS field. We find a total of
16 cluster candidates at S/N > 4, from which eight have either an
optical or X-ray cluster (or group of galaxies) counterpart. This is the
first blind detection of clusters of galaxies at mm wavelengths at 18”
angular resolution. From this analysis, we confirm that NIKA2 and the
IRAM 30–m telescope should be sensitive to low-mass clusters at
intermediate and high redshift, complementing current and planned large
tSZ-based cluster surveys.
-body simulations from the BACCO suite
and apply a combination of cutting-edge techniques such as cosmology
scaling and baryonification to efficiently span a large cosmological and
astrophysical parameter space. A deep neural network is trained to
emulate baryonic effects on the matter bispectrum measured in
simulations, capturing modifications across various scales and redshifts
relevant to Euclid. We validate the emulator accuracy and robustness
using an analysis of mock data, employing predictions from the
state-of-the-art FLAMINGO hydrodynamical simulations. The emulator
reproduces baryonic suppression in the bispectrum to better than 2
for the
percentile across most
triangle configurations for
and
ensures consistency between cosmological posteriors inferred from
second- and third-order weak lensing statistics.
and orbits its host
binary in 550 days with an eccentricity of 0.25. Compared to most of the
previously known circumbinary planets, BEBOP-3b has a long period
(relative to the binary) and a high eccentricity. There also is a
candidate outer planet with a
day orbital
period. We test the stability of potential further candidate signals
inside the orbit of BEBOP-3b, and demonstrate that there are stable
orbital solutions for planets near the instability region which is where
the Kepler circumbinary planets are located. We also use our data to
obtain independent dynamical masses for the two stellar components of
the eclipsing binary using High Resolution Cross-Correlation
Spectroscopy (HRCCS), and compare those results to a more traditional
approach, finding them compatible with one another.
$0.11. No significant eclipse depth variability is
detected down to a level of $$37 ppm. Conclusions: Our results confirm
that LTT9779b exhibits a strikingly high optical albedo, which
substantially reduces the internal energy budget of the planet compared
to more opaque…
{}
{}
^{11}$ M
) and highly
obscured (with a median A
of 2.9), caught in a short-lived yet
extreme starburst phase at z$
{}$ yr
), efficient baryon to
stellar mass conversion ($ε{}>
_α$ emitters, and surpassing the cosmic average
star formation rate density for this epoch. Their properties suggest an
accelerated evolution that current models and simulations have
difficulty reproducing.
) that
has undergone significant environmental influence, with the aim of
exploring dwarf galaxy evolution under the combined effects of galaxy
interactions and environmental processes, and understanding its
relevance to the diversity of dwarf galaxies in cluster environments.
Our analysis is based on VLA and FAST HI emission line mapping from the
Atomic gas in Virgo Interacting Dwarf galaxies (AVID) survey. We also
perform idealized hydrodynamical simulations of dwarf-dwarf mergers to
help interpret the observations. We identify symmetric stellar shell
structures in VCC 479, indicative of a coalesced major merger of dwarf
galaxies. The galaxy features a central starburst, initiated $$600 Myr
ago, embedded within an exponential disk quenched $
$0.5% of the total stellar mass, and VCC 479’s
global star formation rate is 0.3 dex lower than typical dwarfs of
similar mass. The galaxy is highly HI deficient, with most HI gas
concentrated within the central 1 kpc and little extended HI envelope.
The misalignment of the HI velocity field with the stellar body is best
explained by merger-triggered gas inflow, as seen in our simulations.
Our analysis is consistent with a scenario that the majority of HI gas
of the progenitor galaxies was removed by the cluster environment prior
to the final coalescence. The merger concentrates the remaining gas
toward the galaxy center, triggering a central starburst. The combined
effect of environment stripping and galaxy merger has transformed VCC
479 into a blue-core dwarf undergoing morphological transition from a
late-type to an early-type galaxy.
galaxy cluster
Abell 370 based on previously spectroscopically confirmed lensed
galaxies and new lensed systems identified in JWST data, including
recent data from the MAGNIF program. Based on the best models able to
reproduce two radial arcs near the BCGs, we compare the stellar mass to
the total mass from the lens model and find that the fraction of dark
matter in the south BCG is consistent with
CDM while in the north BCG we find a
very small amount of dark matter, more consistent with alternative
models to
CDM. We discuss possible causes for this
and conclude that additional data is needed to clarify the situation. We
study the lensing properties, magnification, time delay and strength of
the critical curve, along the Dragon arc, where previous studies have
reported tens of alleged microlensing events from supergiant stars at
. The new lens
model is able to reproduce the distribution of microlensing events with
great accuracy. Some of the microlensing events may be reinterpreted as
long-period Cepheid in future observations. We consider this possibility
and study in more detail the challenges for such detection from
intervening microlenses.
, identified in the
COSMOS field. Deep imaging and spectroscopy from JWST, ALMA, and VLA
reveal a complex system of twin collisional ring galaxies, exhibiting a
nearly identical morphology. The grism spectra from the JWST COSMOS-3D
program confirm that both galaxies host an AGN. A bipolar radio jet from
one AGN extends to strike the merging front. In addition, we detect a
starburst at the merging front, characterized by luminous extended
nebular line emission and a massive cold gas reservoir. This starburst
is likely triggered by interstellar shocks induced by galaxy collision
and the AGN jet. The twin ring structure of the Cosmic Owl requires
further numerical simulations to clarify the precise conditions that
lead to the formation of this rare morphology. This system exemplifies
how shock-induced star formation, driven by galaxy collision or AGN jet,
can act as a previously underappreciated yet crucial mechanism for
efficient gas-to-star conversion and rapid stellar mass assembly in the
early Universe.
. Approximately 112~s
later, the X-ray Telescope onboard the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory
was on source, the fastest follow-up to-date of a non-repeating FRB
(Tohuvavohu et al. in prep.). Using CHIME/FRB and two of the three
CHIME/FRB Outriggers, we obtained a Very Long Baseline Interferometry
localization for FRB 20241228A with a 1
confidence ellipse of 11
by
0.2
.
This represents the first published localization using both the
CHIME-KKO and CHIME-GBO Outriggers. We associate FRB 20241228A with a
star-forming galaxy at a redshift of
. The persistent X-ray luminosity limit at this
source’s location and distance is
erg s
in the
keV band, the most
stringent limit of any non-repeating FRB to-date (Tohuvavohu et al. in
prep.). The stellar mass (
) and
star formation rate (
~yr
) of the host galaxy of
FRB 20241228A are consistent with the broader FRB host galaxy
population. We measure significant scattering ($
$20 kHz at 600 MHz) along the line of sight to
this source, and suggest the scintillation screen is Galactic while the
scattering screen is extragalactic. FRB 20241228A represents an exciting
example of a new era in which we can harness VLBI-localizations and
rapid high-energy follow-up to probe FRB progenitors.
for the covariance and
for the correlation
structure in comparison to jackknife estimates. These estimates can be
used for highly accurate regression and inference.
pc) of the Coma cluster jellyfish galaxy NGC 4858
obtained from the ALMA-JELLY large program. Analyzing this data
alongside complimentary Subaru H
and HST (F600LP / F350LP) observations,
we find numerous structural and kinematic features indicative of the
effects from strong, inclined ram pressure, including an asymmetric
inner gas tail. We estimate a highly-inclined disk-wind angle of
. By subtracting a simple circular velocity model,
we find (1): gas clumps that are being accelerated by ram pressure, and
(2): signatures of gas clumps that had been previously pushed out of the
disk but are now falling inwards. We also discuss head-tail morphologies
in star complexes within the stellar disk that appear to be
RPS-influenced. Lastly, we compare this galaxy to state-of-the-art
galaxy ``wind tunnel’’ simulations. We find that this galaxy is one of
the best nearby examples of strong and inclined ram pressure gas
stripping, and of gas that is perturbed by ram pressure but not fully
stripped and falls back. We emphasize the importance of torques due to
ram pressure in highly-inclined interactions, which help drive gas
inwards on the side rotating against the wind, contributing to the
formation of asymmetric inner RPS tails.
deg
. A blue grism
covers the wavelength range
–
,nm at a spectral
resolution
–
for a
diameter source with a dispersion of
nm px
. Two red grisms
span
to
,nm at
–
and a dispersion of
nm px
. We describe the
construction of the grisms as well as the ground testing of the flight
model of the NISP instrument where these properties were
established.
au
with a width (
) of 49
au (
= 0.77), at a moderate
inclination of 49$
.
Due to the limited angular resolution, signal-to-noise, and inclination
we have no constraint on the disc’s vertical scale height. We modelled
the disc emission with both gravitational and radiation forces acting on
the dust grains. As the inner belt has not been spatially resolved, we
fixed its radius and width prior to modelling the outer belt. We find
astronomical silicate is the best fit for the dust composition. However,
we could not reject possible scenarios where there are at least 10 %
water-ice inclusions. Combining the spatially resolved imaging by ALMA
with non-detection at optical wavelengths by HST, we obtain a limit on
the scattering albedo
for the
debris dust in the outer belt. Analysis of the outer belt’s architecture
in conjunction with simple stirring models places a mass limit of
on a companion interior to the belt (
au), a factor
of two improvement over constraints from high contrast imaging.
pc. We determine a high neutral hydrogen column
density,
, which is
the highest one at z>6 determined so far for a GRB host galaxy, as
well as a surprisingly high metal column density,
. The
observed metallicity of the host galaxy system is [Zn/H]>-0.8. We
find evidence of a high amount of dust depletion and of aluminum
overabundance, although a number of transitions are saturated. The high
hydrogen column density, metal abundances and dust depletion in the
neutral gas align with those of the ionized gas of very high-redshift
galaxies unveiled by ALMA and JWST, testifying that a rapid build up of
metals and dust, and massive neutral hydrogen reservoirs seem to be
common features of galaxies in the early Universe.
mag (F444W) for
studying galaxy evolution. In this work, we employ Self-Organizing Maps
(SOMs), an unsupervised machine learning method, to estimate key
physical parameters of galaxies – redshift, stellar mass, star formation
rate (SFR), specific SFR (sSFR), and age – directly from photometric
data out to
. SOMs efficiently
project high-dimensional galaxy color information onto 2D maps, showing
how physical properties vary among galaxies with similar spectral energy
distributions. We first validate our approach using mock galaxy catalogs
from the HORIZON-AGN simulation, where the SOM accurately recovers the
true parameters, demonstrating its robustness. Applying the method to
COSMOS-Web observations, we find that the SOM delivers robust estimates
despite the increased complexity of real galaxy populations. Performance
metrics (
typically between
–
, and Pearson correlation between
and
) confirm the precision of the method,
with
of predictions within
1
dex of reference values. Although
redshift estimation in COSMOS-Web remains challenging (median
), the overall success of the highlights its
potential as a powerful and interpretable tool for galaxy parameter
estimation.
(
for MIRI) in COSMOS. These data are combined with
ground- and space-based data to derive photometric measurements of
NIRCam-detected sources using both fixed-aperture photometry (on the
space-based bands) and a profile-fitting technique on all 37 bands
spanning 0.3-8 micron. We provide morphology for all sources from
complementary techniques including profile fitting and machine-learning
classification. We derive photometric redshifts, physical parameters and
non-parametric star formation histories from spectral energy
distribution (SED) fitting. The catalog has been extensively validated
against previous COSMOS catalogs and other surveys. Photometric redshift
accuracy measured using spectroscopically confirmed galaxies out to
reaches
at
and remains at
as a function of magnitude, color, and galaxy
type. This represents a factor of
improvement at 26 AB
mag compared to COSMOS2020. The catalog is approximately 80% complete at
at
and at
at
, representing
a gain of 1,dex compared to COSMOS2020. COSMOS2025 represents the
definitive COSMOS-Web catalog. It is provided with complete
documentation, together with redshift probability distributions, and it
is ready for scientific exploitation today.
and
, which are
phenomenologically connected to the clustering of matter and weak
lensing, respectively; and the second is the effective field theory
(EFT) of dark energy and modified gravity, which we use to parameterise
the braiding function,
, which defines
the mixing between the metric and the dark energy field. We discuss the
predictions from spectroscopic and photometric primary probes by Euclid
on the cosmological parameters and a given set of additional parameters
featuring the PMG and EFT models. We use the Fisher matrix method
applied to spectroscopic galaxy clustering (GCsp), weak lensing (WL),
photometric galaxy clustering (GCph), and cross-correlation (XC) between
GCph and WL. For the modelling of photometric predictions on nonlinear
scales, we use the halo model to cover two limits for the screening
mechanism: the unscreened (US) case, for which the screening mechanism
is not present; and the super-screened (SS) case, which assumes strong
screening. We also assume scale cuts to account for our uncertainties in
the modelling of nonlinear perturbation evolution. We choose a
time-dependent form for
, with two fiducial sets of values for the
corresponding model parameters at the present time,
, and two forms for
, with one
fiducial set of values for each of the model parameters,
and
. (Abridged)
to
using the ’s 255h
COSMOS-Web program. This survey provides deep NIRCam imaging in four
filters (F115W, F150W, F277W, F444W) across
and MIRI coverage in
of the COSMOS field. High-resolution NIRCam
imaging enables robust size and morphological measurements, while
multiwavelength photometry yields stellar masses, SFRs, and Sérsic
parameters. We classify BGGs as star-forming and quiescent using both
rest-frame NUV–
–
colors and a redshift-dependent
specific star formation rate (sSFR) threshold. Our analysis reveals: (1)
quiescent BGGs are systematically more compact than their star-forming
counterparts and exhibit steeper size–mass slopes; (2) effective radii
evolve as
, with
(star-forming) and
(quiescent); (3) star formation surface density (
)
increases with redshift and shows stronger evolution for massive BGGs
(
);
(4) in the
–sSFR plane, a structural
transition marks the quenching process, with bulge-dominated systems
comprising over 80% of the quiescent population. These results highlight
the co-evolution of structure and star formation in BGGs, shaped by both
internal and environmental processes, and establish BGGs as critical
laboratories for studying the baryonic assembly and morphological
transformation of central galaxies in group-scale halos.
area with NIRCam imaging in four
broad-band filters and a non-contiguous ~0.2 deg
with parallel MIRI imaging in a single
broad-band filter, F770W. Here we present a comprehensive overview of
the MIRI imaging observations, the data reduction procedure, the
COSMOS-Web MIRI photometric catalog, and the first data release
including the entire COSMOS-Web MIRI coverage. Data reduction is
predominantly based on the JWST Science Calibration Pipeline with an
additional step involving custom background subtraction to mitigate the
presence of strong instrumental features and sky background in the MIRI
images. We reach 5
(point source) limiting depths (
~25.51 based on
~0.3’’ circular apertures) that are
significantly better than initial expectations. We create a COSMOS-Web
MIRI catalog based on the images presented in this release and compare
the F770W flux densities with the Spitzer/IRAC CH4 measurements from the
COSMOS2020 catalog for CH4 detections with S/N
. We find that these are
in reasonable agreement with a small median offset of
mag. We also
derive robust 7.7
m number counts spanning five orders of
magnitude in flux ($$0.2-2300
Jy)
making COSMOS-Web the only JWST survey to date to efficiently sample
such a large flux range
which is in good agreement with estimates from other JWST and IRAC
surveys.
emission indicates extremely low
metallicity, less than
solar. We argue
that such properties cannot be uncommon among accreting black holes
around this early cosmic epoch. Explaining such a low chemical
enrichment in a system that has developed a massive black hole is
challenging for most theories. Models assuming heavy black hole seeds
(such as Direct Collapse Black Holes) or super-Eddington accretion
scenarios struggle to explain the observations, although they can
potentially reproduce the observed properties in some cases. Models
invoking “primordial black holes” (i.e. putative black holes formed
shortly after the Big Bang) may potentially explain the low chemical
enrichment associated with this black hole, although this class of
models also requires further developments for proper testing.
from Jupiter. This
extreme compression was accompanied by a very large increase in the
ultraviolet auroral emissions to 12 TW, a factor of six higher than the
baseline level. This event coincided with the predicted arrival of a
powerful interplanetary shock, which was expected to cause the largest
increase in the solar wind dynamic pressure seen thus far during the
Juno mission. The simultaneous occurrence of the interplanetary shock,
the extreme compression and the bright ultraviolet aurora suggests that
in this case, the auroral brightening was caused by the solar wind shock
compressing the magnetosphere.
on the sky at spatial resolution and
surface brightness levels that can be used to understand the
morphological transformation of galaxies within groups and clusters.
Using the Early Release Observations (ERO) of the Perseus cluster, we
demonstrate the capability offered by Euclid in studying the nature of
perturbations for galaxies in clusters. Filamentary structures are
observed along the discs of two spiral galaxies with no extended diffuse
emission expected from tidal interactions at surface brightness levels
of
. The
detected features exhibit a good correspondence in morphology between
optical and near-infrared wavelengths, with a surface brightness of
, and the
knots within the features have sizes of
100 pc, as observed
through
imaging. Using the Euclid, CFHT,
UVIT, and LOFAR
radio
continuum observations, we conduct a detailed analysis to understand the
origin of the detected features. We constructed the
,
, and CFHT
,
colour-colour plane and
showed that these features contain recent star formation events, which
are also indicated by their H
and NUV emissions. Euclid colours alone
are insufficient for studying stellar population ages in unresolved
star-forming regions, which require multi-wavelength optical imaging
data. The morphological shape, orientation, and mean age of the stellar
population, combined with the presence of extended radio continuum
cometary tails can be consistently explained if these features have been
formed during a recent ram-pressure stripping event. This result further
confirms the exceptional qualities of Euclid in the study of galaxy
evolution in dense environments.
) galaxy stellar mass functions (SMFs) of the
Virgo cluster using stellar masses derived as part of the Next
Generation Virgo Survey (NGVS). The total SMF has a slope of
which is similar to or steeper than typical field
values. Using deep data from the Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing
Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE) we separate out star-forming galaxies,
quiescent galaxies with no ongoing star formation, and low-SFR galaxies
that are intermediate between these two populations. For each of these
populations, the shape of the SMF is found to be universal throughout
the cluster, from the core to the outskirts. The star-forming and
quiescent SMFs show stark differences with values seen in field
galaxies. The relative fraction of quiescent galaxies is highest in the
core of the cluster, with low-SFR and star-forming galaxies more
significant in the outer regions of the cluster. At low stellar masses
(
), the quiescent fraction in the main cluster is
significantly higher than that of the field and even satellites of
massive groups. At high stellar masses, the quiescent fraction is
similar to other studies of cluster galaxies. We model the quiescent
population in the infall region of the cluster as a combination of
backsplash and field quiescent galaxies, and find that the backsplash
fractions needed to explain the observed population are unrealistically
high. This suggests the existence of a third population of low-mass
galaxies that are pre-processed outside the virial radius of the
cluster, possibly in groups prior to infall.
in our observations
over nearly a year baseline. We find an RM of ~ +320 rad m
. We do not find
evidence for scattering at the level of < 0.3 ms in the bursts, and
we find no evidence for astrophysical scintillation. In our observations
of FRB 20240114A, we see a burst rate ~49x higher than the median burst
rate of apparent non-repeaters also discovered by CHIME/FRB. Each
discovery of highly active FRBs provides a valuable opportunity to
investigate whether there is a fundamental difference between repeating
and apparently non-repeating sources.
vs.
) at the
clump scale. Using near-infrared point sources and Herschel dust
continuum analysis, we obtained the radius, age, and stellar mass for
most clusters in the ranges 0.5$-
-
-
$, respectively, and
also found that they are associated with
values
ranging from 80$-
$ pc
. We obtained the
best-fit scaling relations as
and
for the
studied sample of clumps. Comparing our results with existing scaling
relations at cloud and extragalactic scales, we found that while the
power-law exponent obtained in this work is similar to those found at
these scales, the star formation rate surface densities are relatively
higher for similar gas mass surface densities. From this work, we
obtained instantaneous median star formation efficiency (SFE) and
efficiency per free-fall time (
) of $$20%
and $$13%, respectively, for the studied clumps. We discuss the cause of
the obtained high SFE and
in the
studied clumps and also discuss the results in the context of bound
cluster formation within molecular clouds. We conclude that our results
do not favour a universal scaling law with a constant value of
in
star-forming systems across different scales.
detects key rest-frame
optical emission lines, allowing us to derive [OII]$λλ$3726,3729-based
electron densities of
cm
on average and
[OIII]$λ$4363-based metallicities of
in two galaxies. New ALMA Band 9/10 observations
detect the [OIII]52
m line in one galaxy but do not in the
others, resulting in FIR-based densities of
cm
from the [OIII]52
m/[OIII]88
m ratios, systematically lower than the
optical [OII]-based measurements. These low FIR-based densities are
comparable to those at both
and
in the literature,
including JADES-GS-z14-0 at
, suggesting little
evolution up to
, in contrast to the
increasing trend of optical-based densities with redshift. By conducting
a JWST and ALMA joint analysis using emission lines detected with both
telescopes, we find that the observed FIR [OIII]52,88
m luminosities are too high to be
explained by the optical-based densities at which they would be
significantly collisionally de-excited. Instead, a 2-zone model with
distinct high- and low-density regions is required to reproduce all
observed lines, indicating that FIR [OIII] emission arises predominantly
from low-density gas, while optical [OIII] and [OII] lines trace both
regions. We further demonstrate that the direct-
method
can sometimes significantly underestimate metallicities up to 0.8 dex
due to the presence of the low-density gas not fully traced by optical
lines alone, highlighting the importance of combining optical and FIR
lines to accurately determine gas-phase metallicities in the early
universe.
and the fraction of
galaxies in substructures (
). Except
for a few cases, we found relatively low values for
, suggesting that CHEX-MATE
clusters are not too far from relaxation. Moreover, no significant
trends emerge among
and the difference between the log-masses
estimated by and by SZ-X-ray. We study the concentration-mass relation
for the sample; despite the large scatter, we observe signs of an
increasing trend for large-mass clusters, in agreement with recent
theoretical expectations. Finally, the analysis of radial anisotropy
profiles of member galaxies - stacked in five bins of mass and redshift
- reveals that orbits tend to be isotropic at the center and more radial
towards the edge, as already found in previous studies. A slight trend
of increasing radial orbits at
is observed in
clusters with larger velocity dispersion
) and stellar feedback on the evolution
of filamentary structures in star-forming clouds. Methods: We performed
two numerical simulations of a collapsing
M
cloud with different
mass-to-flux ratios (
and
), including early stellar
feedback (jets and HII regions). Using DisPerSE, we extracted the
three-dimensional filamentary network and analysed its properties as it
evolves throughout the SF event. Results: We observed that the
filamentary network in the simulations follow two distinct evolutionary
pathways. In the strongly magnetised case, the cloud maintains a sparser
filamentary network, and the arising filaments are predominantly
perpendicular to
lines. With a weak field, the cloud
develops a single central hub, with converging filaments favouring a
parallel alignment relative to
. Furthermore, while always accreting,
filaments exhibit faster flows towards the hub relative to the
surrounding gas. In the weakly magnetised run, the central hub dominates
the dynamics, and filaments exhibit faster flows as they approach the
central hub. Finally, once the expanding HII region impacts the
filaments, they align to
independently of the initial
configuration. Conclusions: Magnetic fields play a critical role in
shaping the structure and dynamics of molecular clouds. Stronger
magnetic fields slow the cloud’s evolution and inhibit the formation of
central hubs, promoting a broader filamentary network instead. However,
ionising feedback dominates the late-stage evolution, overriding the
initial differences and dictating the final filament configuration.
broad-line AGN
(BLAGN). First identified as a high-redshift LRD candidate from PRIMER
NIRCam photometry, follow-up NIRSpec/PRISM spectroscopy of CAPERS-LRD-z9
from the CANDELS-Area Prism Epoch of Reionization Survey (CAPERS) has
revealed a broad
km s
H
emission line and narrow [O III]
lines, indicative of a BLAGN. Based on the broad H
line, we compute a canonical black-hole
mass of
, although full consideration of systematic
uncertainties yields a conservative range of
. These observations suggest that either a massive
black hole seed, or a lighter stellar remnant seed undergoing periods of
super-Eddington accretion, is necessary to grow such a massive black
hole in
Myr of
cosmic time. CAPERS-LRD-z9 exhibits a strong Balmer break, consistent
with a central AGN surrounded by dense (
) neutral
gas. We model CAPERS-LRD-z9 using CLOUDY to fit the emission red-ward of
the Balmer break with a dense gas-enshrouded AGN, and bagpipes to fit
the rest-ultraviolet emission as a host-galaxy stellar population. This
upper limit on the stellar mass of the host galaxy (
) implies that the black-hole to stellar mass
ratio may be extremely large, possibly
(although
systematic uncertainties on the black-hole mass prevent strong
conclusions). However, the shape of the UV continuum differs from
typical high-redshift star-forming galaxies, indicating that this UV
emission may also be of AGN origin, and hence the true stellar mass of
the host may be still lower.
, roughly
twice as high as in the soft state, where it was around
. In both states, a
statistically significant increase of PD with the energy was found.
Moreover, a linear relation between PD and spectral hardness suggests a
gradual and continuous evolution of the polarization properties, rather
than an abrupt change of polarization production mechanism between
states. The polarization angle (PA) was independent of the spectral
state and showed no trend with the photon energy. The X-ray PA is well
aligned with the orientation of the radio jet, as well as the optical
and radio PAs. We find significant orbital changes of PA in the hard
state, which we attribute to scattering of X-ray emission at intrabinary
structure. No significant superorbital variability in PD or PA was found
at the period
= 294 d. We
also find no correlation between the X-ray and optical polarization; if
any, there is a long-term anti-correlation between the X-ray PD and the
radio PD.
line in their slitless
spectra. This method is sensitive to the signal-to-noise ratio of the
line, as noise fluctuations or other strong emission lines can be
misidentified as H
, depending on redshift.
These effects lead to catastrophic redshift errors and the inclusion of
interlopers in the sample. We forecast the impact of such redshift
errors on galaxy clustering measurements. In particular, we study the
effect of interloper contamination on the two-point correlation function
(2PCF), the growth rate of structures, and the Alcock-Paczynski (AP)
parameters. We analyze 1000 synthetic spectroscopic catalogues, the
EuclidLargeMocks, designed to match the area and selection function of
the Data Release 1 (DR1) sample. We estimate the 2PCF of the
contaminated catalogues, isolating contributions from correctly
identified galaxies and from interlopers. We explore different models
with increasing complexity to describe the measured 2PCF at fixed
cosmology. Finally, we perform a cosmological inference and evaluate the
systematic error on the inferred
,
and
values
associated with different models. Our results demonstrate that a minimal
modelling approach, which only accounts for an attenuation of the
clustering signal regardless of the type of contaminants, is sufficient
to recover the correct values of
,
, and
at DR1. The
accuracy and precision of the estimated AP parameters are largely
insensitive to the presence of interlopers. The adoption of a minimal
model induces a 1%-3% systematic error on the growth rate of structure
estimation, depending on the redshift. However, this error remains
smaller than the statistical error expected for the Euclid DR1
analysis.
and CH
, with NH
largely retained in water as ions. We
show that at 273.15 K, a clathrate crust tens of kilometers thick would
deplete the primordial atmosphere of xenon and krypton. The lack of
primordial argon in Titan’s atmosphere may result from the partial
de-volatilization of its accreted materials.
O lines, which are naturally separated
from the continuum due to the CONCERTO spectral capabilities. Many
regions also show strong free-free emission at lower frequencies. We
demonstrate the spectral capabilities of CONCERTO at intermediate
spectral resolution, with a frequency coverage from 130 to 310 GHz. A
sensitivity of 200 mK is achieved in one second, for one beam and a 6
GHz frequency width, over an 18 arcmin diameter field of view, which is
within a factor of three of the expectations. We show that we can
spectrally disentangle the continuum from the CO line emission, but the
line is not resolved at a resolution of
. The slope
of the millimetre continuum is line-free mapped for the first time in
Orion.
with a precision of 0.65% (or 550 km). Based on a
timing inconsistency with JWST, we discuss and confirm orbital
eccentricity (
). We also constrain the argument of periastron to
deg. We show that the large dayside emission
implies the presence of magnetic drag and super-solar metallicity. We
find a steep thermally inverted gradient in the planetary atmosphere,
which is common for UHJs. We detected the presence of strong CO emission
lines at 4.5
m from an excess of dayside brightness
in the Spitzer/IRAC/Ch2 passband. Using these models to constrain the
reflected contribution in the CHEOPS passband, we derived an extremely
low geometric albedo of
.
area with uniform deep
Spitzer/IRAC data (
mag, 5
), the largest area covered to these
depths in the infrared. These data are used to gain new insight into the
growth of stellar mass across cosmic history by characterising the
evolution of the galaxy stellar mass function (GSMF) through
. The total volume (0.62 Gpc
) represents a tenfold
increase compared to previous works that have explored
and significantly
reduces cosmic variance, yielding strong constraints on the abundance of
massive galaxies. Results are generally consistent with the literature
but now provide firm estimates of number density where only upper limits
were previously available. Contrasting the GSMF with the dark matter
halo mass function suggests that massive galaxies (
M
) at
required
integrated star-formation efficiencies of
0.25–0.5,
in excess of the commonly-held view of ``universal peak efficiency” from
studies on the stellar-to-halo mass relation (SHMR). Such increased
efficiencies imply an evolving peak in the SHMR at
which can be
maintained if feedback mechanisms from active galactic nuclei and
stellar processes are ineffective at early times. In addition, a
significant fraction of the most massive quiescent galaxies are observed
to be in place already by
–3. The apparent
lack in change of their number density by
is consistent
with relatively little mass growth from mergers. Utilising the unique
volume, evidence for an environmental dependence of the galaxy stellar
mass function is found all the way through
for the first
time, though a more careful characterisation of the density field is
ultimately required for confirmation.
, using multi-band
HST photometry and X-Shooter spectroscopy. Deep HST F390W imaging probe
uncontaminated LyC flux blueward $
z$ interlopers and prevent contamination of
measured LyC radiation. We confirm the detection of LyC flux at SNR
$$3.5 and estimate the escape fraction of ionizing photons to be in the
range
=
0.06 – 1, depending on the adopted IGM attenuation. Morphological
analysis reveals a clumpy structure made of two main components, with
effective radii of R
$
_{}$ <
100 pc, and a total estimated de-lensed area in the rest-frame 1600Å~of
4.2~kpc
. We confirm the presence
of faint ultraviolet spectral features HeII$λ
λ
λ
λ
λ
λ
λ$$λ
U$ > $-$1.5 using empirical and theoretical
correlations.
of our sample are in
multi-planet systems, which are typically seen for planets located near
the lower edge of the Neptunian desert. We define a ‘gold’ subset of our
sample consisting of 33 confirmed planets with planetary radii between
2
and 10
. With these
targets, we calculate envelope mass fractions (EMF) using the GAS gianT
modeL for Interiors (GASTLI). We find a clear split in EMF between
planets with equilibrium temperatures below and above 1300~K, equivalent
to an orbital period of $
%$ to 40
, scaling linearly with the
planetary mass. The orbital period separating these two populations
coincides with the transition between the Neptunian desert and the
recently identified Neptunian ridge, further suggesting that different
formation and/or evolution mechanisms are at play for Neptune planets
across different close-in orbital regions.
), due to
the difficulty in conducting deep time-domain surveys. In this work, we
present the discovery of a high-redshift TDE candidate, HZTDE-1, in the
COSMOS-Web survey with JWST’s NIRCam, using a novel selection technique
based on color and morphology. We first outline a methodology for
identifying high-z TDEs in deep infrared imaging surveys, leveraging
their unique spectral energy distributions (SEDs) and morphologies of
these transients. We apply this technique to COSMOS-Web in filters
F115W, F150W, F277W, and F444W, and identify HZTDE-1, a transient point
source relative to archival UltraVISTA infrared observations. If we
assume it is a TDE, we estimate its photometric redshift to be
. HZTDE-1 cannot be explained by reasonable
supernova or AGN models. However, we cannot rule out a superluminous
supernova at
. If confirmed
with follow-up observations, HZTDE-1 would represent the
highest-redshift TDE discovery to date, and would suggest an enhancement
of the TDE rate in the high-redshift universe. Our method, which can be
applied to future deep surveys with JWST and Roman, offers a pathway to
identify TDEs at
and probe black hole
demographics at early cosmic times.
~band, we find
dynamical upper mass limits
of 4.9
for b and
13.6
for
c. Adding astrometry from the newly proposed planet candidate PDS 70 d
into our model, we determine
dynamical upper mass limits
of 5.3
, 7.5
and 2.2
for b, c,
and the candidate d respectively. However,
-body analysis of the orbits fit in this
case suggest that the inclusion of
makes the system unstable. Using the
upper mass limits for b and c we rule out the coldest-start formation
models for both planets, calculating minimum post-formation entropies
(
) of 9.5
and 8.4
respectively. This places PDS 70 b and c on the
growing list of directly-imaged planets inconsistent with cold-start
formation.
using NIRSpec spectroscopy. Focusing on galaxies with extremely low dust
attenuation, we explore their physical processes using a new CIGALE
version that incorporates spectroscopic and photometric data. Comparing
observations with models, we derive key physical parameters. We identify
49 galaxies with extremely low dust attenuation (GELDAs), characterized
by
within
and
. The stacked spectra reveal a very blue UV slope
(
) and Balmer decrement H
/H
, consistent with no dust attenuation. GELDAs are
more common at
(83.3%) than at
(26.3%)
suggesting they dominate the early Universe. Assuming a prior FIR dust
spectrum (from ALPINE), we examine dust-stellar mass trends. The
vs.
diagram shows
upper and lower sequences linked by possible transitional galaxies. A
transition at
(
or
) may
mark the shift from stellar dust production to ISM grain growth, in
agreement with theoretical predictions. Our full sample has a high mean
gas fraction (
),
indicating retained gas across all galaxies. Their small sizes and large
gas masses imply high gas surface densities but relatively low star
formation efficiency. High-redshift GELDAs may naturally explain the
observed excess of bright galaxies at
compared to
theoretical expectations.
fine-structure line of ionized carbon (C
), using the Stratospheric
Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA), have revealed expanding [C
II] shells in Galactic H II regions. We report the discovery of a
bubble-shaped source (S144 in RCW79), associated with a compact H II
region, excited by a single O7.5–9.5V/III star, which is consistent with
a scenario that the bubble is still mostly ``filled’’ with C
. This indicates most likely a
very early evolutionary state, in which the stellar wind has not yet
blown material away, as it is the case for more evolved H II regions.
Using the SimLine non-LTE radiative transfer code, the [C II] emission
can be modeled to originate from three regions. First, a central H II
region with little C
in the fully ionized phase,
followed by two layers with gas density around
of partially photo-dissociated gas. The second
layer is a slowly expanding [C II] shell with an expansion velocity of
. The outermost layer exhibits a temperature and
velocity gradient that produces the observed self-absorption features in
the optically thick [C II] line (
) leading to an
apparent deficit in [C II] emission and a low ratio of [C II] to total
far-infrared (FIR) emission. We developed a procedure to approximate the
missing [C II] flux and find a linear correlation between [C II] and FIR
without a [C II]-deficit. This demonstrates that at least some of the [C
II]-deficit found in Galactic H II bubbles can be attributed to
self-absorption.
~milliarcsecond
localization precision for the majority of detected FRBs. This paper
presents an overview of the design and implementation of the Outriggers,
covering their geographic distribution, structural design, and
observational capabilities. We detail the scientific objectives driving
the project, including the characterization of FRB populations, host
galaxy demographics, and the use of FRBs as cosmological probes. We also
discuss the calibration strategies available to mitigate ionospheric and
instrumental effects, ensuring high-precision localization. With two
stations currently in science operations, and the third in
commissioning, the CHIME/FRB Outriggers project is poised to become a
cornerstone of the FRB field, offering unprecedented insights into this
enigmatic cosmic phenomenon.
using COSMOS-Web, the largest-area JWST imaging survey to date, covering
$
^2
R_eM_*^α$) for star-forming and quiescent
galaxies. For star-forming galaxies, the slope
remains approximately 0.20 at
,
showing no significant evolution over this redshift range. At higher
redshifts, the slopes are
and
for
and
,
respectively. At fixed galaxy mass, the size evolution for star-forming
galaxies follows
, with
.
For quiescent galaxies, the slope is steeper
-
at
,
and
. We
find that the size-mass relation is consistent between UV and optical at
for star-forming
galaxies. However, we observe a decrease in the slope from UV to optical
at
, with a tentative
negative slope in the optical at
,
suggesting a complex interplay between intrinsic galaxy properties and
observational effects such as dust attenuation. We discuss the ratio
between galaxies’ half-light radius, and underlying halos’ virial
radius,
, and find the
median value of
. The star formation rate surface density evolves
as
, and the
-
relation remains flat at
. Lastly,
we identify a threshold in stellar mass surface density
-
marking the transition to compact, quenched
galaxies from extended, star-forming progenitors. In summary, our
findings show that the extensive COSMOS-Web dataset at
provides new
insights into galaxy size and related properties in the rest-frame
optical.
, this is the
closest known SN discovered following an Einstein Probe (EP) FXT. We
show that SN 2025kg’s optical spectra reveal the hallmark features of a
broad-lined Type Ic SN. Its light curve evolution and expansion
velocities are also comparable to those of GRB-SNe, including SN 1998bw,
and several past FXT SNe. We present JWST/NIRSpec spectroscopy taken
around SN 2025kg’s maximum light, and find weak absorption due to He I
m and a broad, unidentified feature at
4-4.5
m. Further, we observe clear evidence
for broadened H
in optical data at 42.5 days that is
not detected at other epochs, indicating interaction with hydrogen-rich
material. From its light curve, we derive a
Ni mass of 0.2 - 0.6
. Together with
our companion paper (Eyles-Ferris et al. 2025), our broadband data of EP
250108a/SN 2025kg are consistent with a trapped or low energy (
ergs) jet-driven explosion from a collapsar with a zero-age main
sequence mass of 15-30
. Finally, we
show that the sample of EP FXT SNe support past rate estimates that
low-luminosity jets seen through FXTs are more common than successful
(GRB) jets, and that similar FXT-like signatures are likely present in
at least a few percent of the brightest Ic-BL SNe.
and spans a
wide range, from the nuclei of nearby galaxies at
to quasars at
. 70 new
VLT/X-Shooter spectra of these sources covering UV to NIR wavelengths
are also presented, which will be used in future stacking experiments to
search for cold gas in the circumgalactic medium. Infrared magnitudes
from WISE indicate that the majority of the sources are consistent with
being quasars or blazars. After fitting the radio spectral energy
distributions of the calibrators, we find that most ALMA calibrators
exhibit peaked spectra or are re-triggered which is surprising given the
large number of blazars in the sample. The peak frequencies span three
orders of magnitude from 100 MHz to 170 GHz, corresponding to linear
sizes ranging from sub-pc to
10 kpc. In the future, when combined
with high-resolution radio imaging, these results will offer valuable
constraints on the molecular gas content of the CGM, as well as the ages
and duty cycles of AGN jets. The ever-growing ALMACAL data set will
remain an indispensable resource for studying the various aspects of
galaxy formation and evolution.
) of
the entire sample were obtained within a Bayesian framework to derive
robust estimates of these parameters along with their associated errors.
The analysis shows that stars along the extended main sequence turn-off
(eMSTO) cover a wide range of rotational velocities, from values
consistent with no/slow rotation up to
~ 250
km/s. The distribution of stellar rotation velocities appears to play a
crucial role in explaining the broadening of the eMSTO in this cluster,
and a correlation is observed between
and
the color of the eMSTO stars, with
increasing as the color becomes redder. Among the eMSTO stars, we
investigate the peculiar population of stars strongly dimmed in the UV
(so-called UV-dim stars), recently discovered in NGC 1783. UV-dim stars
show clear photometric evidence of self-extinction and mild
spectroscopic signatures typically observed in shell stars, thus
suggesting that they have likely a decretion disc observed nearly
equator-on. Interestingly, the study also shows that a significant
fraction of UV-dim stars are slow rotators. We discuss potential
implications these results may have on our understanding of the
formation and evolution of UV-dim stars and we propose that the
rotational properties of the UV-dim stars should vary with cluster
age.
distance calculations. For this reason, most widely adopted packages for
estimating correlations use clustering algorithms to approximate local
trends. However, methods for quantifying the error introduced by this
clustering have been understudied. In response, we present an algorithm
for estimating correlations that is probabilistic in the way that it
clusters objects, enabling us to quantify the uncertainty caused by
clustering simply through model inference. These soft clustering
assignments enable correlation estimators that are theoretically
differentiable with respect to their input catalogs. Thus, we also build
a theoretical framework for differentiable correlation functions and
describe their utility in comparison to existing surrogate models.
Notably, we find that repeated normalization and distance function calls
slow gradient calculations and that sparse Jacobians destabilize
precision, pointing towards either approximate or surrogate methods as a
necessary solution to exact gradients from correlation functions. To
that end, we close with a discussion of surrogate models as proxies for
correlation functions. We provide an example that demonstrates the
efficacy of surrogate models to enable gradient-based optimization of
astrophysical model parameters, successfully minimizing a correlation
function output. Our numerical experiments cover science cases across
cosmology, from point spread function (PSF) modeling efforts to
gravitational simulations to galaxy intrinsic alignment (IA).
from the first
10% data of the JWST Cycle 3 Treasury Program COSMOS-3D. These AGNs are
identified by their broad H
or H
emission lines through the NIRCam grism
wide-field slitless spectroscopy. One object at
with broad
H
emission has an F444W magnitude of 23.6
mag, making it one of the brightest
broad-line
AGNs yet known. Among the 13 AGNs, 10 objects have reddened optical
continua with slopes
.
The remaining three objects have their overall SEDs that resemble those
of UV-luminous quasars at similar redshifts, but their
, though
negative, are not as blue as those of unobscured quasars. We also obtain
MIRI photometry at 7.7-18
m for two AGNs and place strong
constraints on their rest-frame near-IR SED. We find no significant
variability in the rest-frame UV by comparing the COSMOS-3D and
COSMOS-Web F115W images taken apart by 60 days in the rest-frame. We
compute the H
luminosity functions (LFs) for the
broad H
emitters at
and
find a potential redshift evolution when compared with that of the
sample.
We also derive the H
LF at
for AGNs and galaxies
by combining our sample with those from the literature. The broad H
emitters in this work suggest a number
density two orders of magnitude higher than that predicted by the quasar
LF based on rest-frame UV-selected samples. As a preview, our work
showcases the ability of the COSMOS-3D grism survey to provide a
complete view of the properties, growth, and evolution of bright
broad-line AGNs at
.
and is surrounded by a He poor shell of dust and
gas. The abundances of He, C, N, O, and S determined by the model show
that the nebula has C/O=
and
N/O=
consistent with the progenitor mass found.
). The
combined requirement for optical detection and stringent signal-to-noise
ratio threshold ensure a high purity of the sample, but at the expense
of completeness, especially for T dwarfs. The detections range from
magnitudes 19 and 24 in the near-infrared bands, and extend down to 26
in the optical band. The average surface density of detected UCDs on the
sky is approximately 100 objects per
,
including 20 L and T dwarfs per
. This
leads to an expectation of at least 1.4 million ultracool dwarfs in the
final data release of the Euclid Wide Survey, including at least 300,000
L dwarfs, and more than 2,600 T dwarfs, using the strict selection
criteria from this work. We provide empirical Euclid colours as a
function of spectral type, and a probability that an object with a given
colour has a certain spectral type.
in the first
data release (Q1) of the
survey. We make use of the catalogues delivered by the
Science Ground Segment (SGS). After a galaxy selection on the
magnitude
and on the photometric redshift quality, we undertake the search using
the
algorithm, an overdensity finder based on
Delaunay tessellation that uses photometric redshift probability
distributions through Monte Carlo simulations. In this pilot study, we
conduct a search in the 11
tiles that contain previously known
high star-forming galaxy protocluster candidates and focus on the two
detections that coincide with these regions. These counterparts lie at
photometric redshifts
and
and
have both been confirmed by two other independent protocluster detection
algorithms. We study their colours, their derived stellar masses and
star-formation rates, and we estimate their halo mass lower limits. We
investigate whether we are intercepting these galaxy overdensities in
their `dying’ phase, such that the high star-formation rates would be
due to their last unsustainable starburst before transitioning to groups
or clusters of galaxies. Indeed, some galaxy members are found to lie
above the main sequence of galaxies (star-formation rate versus stellar
mass). These overdense regions occupy a specific position in the dark
matter halo mass / redshift plane where forming galaxy clusters are
expected to have experienced a transition between cold flows to shock
heating in the halo. Finally, we empirically update the potential for
galaxy protocluster discoveries at redshift up to
(wide survey)
and
(deep
survey) with
for
the next data release (DR1).
in the Euclid Deep Fields to the same depth as
the Euclid Wide Survey. This paper showcases, for the first time, the
performance of cluster finders on Euclid data and presents examples of
validated clusters in the Quick Release 1 (Q1) imaging data. We identify
clusters using two algorithms (AMICO and PZWav) implemented in the
Euclid cluster-detection pipeline. We explore the internal consistency
of detections from the two codes, and cross-match detections with known
clusters from other surveys using external multi-wavelength and
spectroscopic data sets. This enables assessment of the Euclid
photometric redshift accuracy and also of systematics such as
mis-centring between the optical cluster centre and centres based on
X-ray and/or Sunyaev–Zeldovich observations. We report 426 joint PZWav
and AMICO-detected clusters with high signal-to-noise ratios over the
full Q1 area in the redshift range
. The chosen redshift and signal-to-noise
thresholds are motivated by the photometric quality of the early Euclid
data. We provide richness estimates for each of the Euclid-detected
clusters and show its correlation with various external cluster mass
proxies. Out of the full sample, 77 systems are potentially new to the
literature. Overall, the Q1 cluster catalogue demonstrates a successful
validation of the workflow ahead of the Euclid Data Release 1, based on
the consistency of internal and external properties of Euclid-detected
clusters.
at
to match the gas
and weak lensing observables. The joint model retrieves a concentration
, which is
lower and more realistic than the high concentration retrieved from weak
lensing data alone under the assumption of spherical symmetry (
).
Application of our method to a larger sample will allow us to study at
the same time the shape of dark matter mass profiles and the level of
non-thermal pressure support in galaxy clusters.
z $<
<$ z $<$3.5, which can be followed up using
ground-based spectrographs to confirm their redshifts. Unlike previous
surveys, we use many independent fields to remove biases caused by
correlated absorption in the IGM. In this paper, we describe the survey
design, photometric measurements, and the use of mock galaxy samples to
optimize our color selection. With 3 filters, we can select a galaxy
sample of which $
<$ z $<$3.5 range for which we can detect
uncontaminated LyC emission in F336W. We also use mock IGM sightlines to
measure the expected transmission of the IGM, which will allow us to
determine escape fractions from our stacked galaxies. We color-select
$$1400 galaxies, and predict that this includes $$80 LyC-emitting
galaxies and $$500 that we can use in stacking. Finally, we present the
Keck/LRIS spectrum of a galaxy at z
2.99, demonstrating
that we can confirm the redshifts of z
3 galaxies from the
ground.
so that more
massive galaxies tend to grow their stellar mass and become enriched in
metals earlier than less massive ones. In addition, the current
gas-phase metallicity of a galaxy and its past evolution correlate with
the environment it inhabits. Galaxies in groups, especially massive
groups that have X-ray counterparts, tend to have higher gas-phase
metallicities and are enriched in metals earlier than field galaxies of
similar stellar mass. Galaxies in the highest stellar mass bin and
located in X-ray groups exhibit a more complex and varied chemical
composition. Strangulation due to interactions with the group
environment, leading to an early cessation of gas supply, may have
driven the faster mass growth and chemical enrichment observed in group
galaxies. Additionally, the removal of metal-enriched gas could play a
key role in the evolution of the most massive galaxies. Alternative
mechanisms other than environmental processes are also discussed.
arcsec
, tidal features and
stellar haloes contribute 2% and 10% of total galaxy luminosity,
respectively. Tidal features are detected in 36% of galaxies, with none
fainter than 27.8 mag
arcsec
. The most massive
galaxies are twice as likely to host tidal debris, and for early-type
galaxies their halos are twice as luminous as those in lower-mass
systems, a trend not observed in late-type galaxies. Although
small-scale interactions increase the frequency of tidal features, the
large-scale environment does not influence it. An anticorrelation
between this frequency and rotational support is found, but may reflect
the mass-driven effect. We release our database of annotated features
for deep learning applications. Our findings confirm that galaxy mass is
the dominant factor influencing tidal feature prevalence, consistent
with hierarchical formation models.
km/s)
reported by SDSS and DESI. We performed expert visual inspection and
classification of
images. We
discovered 38 grade A and 40 grade B candidate lenses, consistent with
an expected sample of $$32. Palomar spectroscopy confirmed 5 lens
systems, while DESI spectra confirmed one, provided ambiguous results
for another, and help to discard one. The automated lens modeler
modelled 53 candidates, confirming 38 as lenses, failing to model 9, and
ruling out 6 grade B candidates. For the remaining 25 candidates we
could not gather additional information. More importantly, our
expert-classified non-lenses provide an excellent training set for
machine learning lens classifiers. We create high-fidelity simulations
of lenses by painting realistic lensed sources behind the expert tagged
(non-lens) luminous red galaxies. This training set is the foundation
stone for the galaxy-galaxy strong lensing discovery engine.
). This catalogue is the result of the visual
inspection of 1260 cluster fields. Each galaxy cluster was ranked with a
probability,
, based on the number and plausibility of the
identified strong lensing features. Specifically, we identified 83
gravitational lenses with
, of
which 14 have
, and
clearly exhibiting secure strong lensing features, such as giant
tangential and radial arcs, and multiple images. Considering the
measured number density of lensing galaxy clusters, approximately
for
, we
predict that will likely see more than 4500 strong lensing clusters
over the course of the mission. Notably, only three of the identified
cluster-scale lenses had been previously observed from space. Thus, has
provided the first high-resolution imaging for the remaining
galaxy cluster lenses, including those
with the highest probability. The identified strong lensing features
will be used for training deep-learning models for identifying
gravitational arcs and multiple images automatically in observations.
This study confirms the huge potential of for finding new strong lensing
clusters, enabling exciting new discoveries on the nature of dark matter
and dark energy and the study of the high-redshift Universe.
) at
in
tomographic slices of 170 comoving
using photometric redshifts. Galaxy morphologies
are accurately retrieved thanks to the excellent resolution of VIS data.
The distribution of massive galaxies (
) in the projected cosmic web is analysed as a
function of morphology measured from VIS data. Specifically, the 2D
alignment of galaxy shapes with large-scale filaments is quantified as a
function of Sérsic indices and masses. We find the known trend that more
massive galaxies are closer to filament spines. At fixed stellar masses,
morphologies correlate both with densities and distances to large-scale
filaments. In addition, the large volume of this data set allows us to
detect a signal indicating that there is a preferential alignment of the
major axis of massive early-type galaxies along projected cosmic
filaments. Overall, these results demonstrate our capabilities to carry
out detailed studies of galaxy environments with Euclid, which will be
extended to higher redshift and lower stellar masses with the future
Euclid Deep Survey.
galaxy-galaxy
strong lenses across
deg
. The Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1) of
deg
Euclid images provides an excellent
opportunity to test our lens-finding ability, and to verify the
anticipated lens frequency in the EWS. Following the Q1 data release,
eight machine learning networks from five teams were applied to
approximately one million images. This was followed by a citizen science
inspection of a subset of around
images, of which
received high network
scores, with the remainder randomly selected. The top scoring outputs
were inspected by experts to establish confident (grade A), likely
(grade B), possible (grade C), and unlikely lenses. In this paper we
combine the citizen science and machine learning classifiers into an
ensemble, demonstrating that a combined approach can produce a purer and
more complete sample than the original individual classifiers. Using the
expert-graded subset as ground truth, we find that this ensemble can
provide a purity of
(grade A/B
lenses) with
completeness (for
context, due to the rarity of lenses a random classifier would have a
purity of
). We discuss future
lessons for the first major Euclid data release (DR1), where the
big-data challenges will become more significant and will require
analysing more than
million galaxies,
and thus time investment of both experts and citizens must be carefully
managed.
Quick Release (Q1)
fields. For each
source we collect
multi-wavelength photometry and spectroscopy information from Galaxy
Evolution Explorer (GALEX),
, Dark Energy Survey
(DES), Wise-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE),
, Dark Energy Survey
(DESI), and Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), including spectroscopic
redshift from public compilations. We investigate the AGN contents of
the Q1 fields by applying selection criteria using
colours and
WISE-AllWISE cuts finding respectively 292,222 and 65,131 candidates. We
also create a high-purity QSO catalogue based on
DR3 information
containing 1971 candidates. Furthermore, we utilise the collected
spectroscopic information from DESI to perform broad-line and
narrow-line AGN selections, leading to a total of 4392 AGN candidates in
the Q1 field. We investigate and refine the Q1 probabilistic random
forest QSO population, selecting a total of 180,666 candidates.
Additionally, we perform SED fitting on a subset of sources with
available
,
and by utilizing the derived AGN fraction, we identify a total of 7766
AGN candidates. We discuss purity and completeness of the selections and
define two new colour selection criteria (
and
) to improve on purity, finding 313,714
and 267,513 candidates respectively in the Q1 data. We find a total of
229,779 AGN candidates equivalent to an AGN surface density of 3641
deg
for
, and a subsample of 30,422 candidates
corresponding to an AGN surface density of 482 deg
when limiting the depth
to
. The surface density of AGN recovered from this
work is in line with predictions based on the AGN X-ray luminosity
functions.
,
,
, and
bands at various phases of the
transient light-curves, including before, during, and after the
observations of ground-based transient surveys. Approximately 70% of
known transients reported in the six months before the Euclid
observation date and with discovery magnitude brighter than 24 were
detected in Euclid
images. Our observations
include one of the earliest near-infrared detections of a Type~Ia
supernova (SN 2024pvw) 15 days prior to its peak brightness, and the
late-phase (435.9 days post peak) observations of the enigmatic
core-collapse SN 2023aew. Euclid deep photometry provides valuable
information on the nature of these transients such as their progenitor
systems and power sources, with late time observations being a uniquely
powerful contribution. In addition, Euclid is able to detect the host
galaxies of some transients that were previously classed as hostless.
The Q1 data demonstrate the power of the Euclid data even with only
single-epoch observations available, as will be the case for much larger
areas of sky in the Euclid Wide Survey.
in a magnitude-selected sample
spanning
. We measure a
mean bar fraction of
, consistent with
prior studies. At fixed redshift, massive galaxies exhibit higher bar
fractions, while lower-mass systems show a steeper decline with
redshift, suggesting earlier disc assembly in massive galaxies.
Comparisons with cosmological simulations (e.g., TNG50, Auriga) reveal a
broadly consistent bar fraction, but highlight overpredictions for
high-mass systems, pointing to potential over-efficiency in central
stellar mass build-up in simulations. These findings demonstrate
Euclid’s transformative potential for galaxy morphology studies and
underscore the importance of refining theoretical models to better
reproduce observed trends. Future work will explore finer mass bins,
environmental correlations, and additional morphological indicators.
, and absolute
astrometric accuracy compared to Gaia is
mas Image quality is stable over all Q1
images with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) of
. The stacked images (combining four nominal and
two short exposures) reach
(
, measured as the variance
of
diameter apertures). We also describe quality
control metrics provided with each image, and an appendix provides a
detailed description of the provided data products. The excellent
quality of these images demonstrates the immense potential of Euclid VIS
data for weak lensing. VIS data, covering most of the extragalactic sky,
will provide a lasting high-resolution atlas of the Universe.
with two instruments, the Visible Camera (VIS)
and the Near IR Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) down to
(
) in the Euclid Wide
Survey. Ground-based imaging data in the bands complement the data to
enable photo-
determination and VIS PSF modeling for
week lensing analysis. Euclid investigates the distance-redshift
relation and the evolution of cosmic structures by measuring shapes and
redshifts of galaxies and clusters of galaxies out to
. Generating the
multi-wavelength catalogues from and ground-based data is an essential
part of the data processing system. In the framework of the Science
Ground Segment (SGS), the aim of the MER Processing Function (PF)
pipeline is to detect objects in the imaging data, measure their
properties, and MERge them into a single multi-wavelength catalogue. The
MER PF pipeline performs source detection on both visible (VIS) and
near-infrared (NIR) images and offers four different photometric
measurements: Kron total flux, aperture photometry on PSF-matched
images, template fitting photometry, and Sérsic fitting photometry.
Furthermore, the MER PF pipeline measures a set of ancillary quantities,
spanning from morphology to quality flags, to better characterise all
detected sources. In this paper, we show how the MER PF pipeline is
designed, detailing its main steps, and we show that the pipeline
products meet the tight requirements that Euclid aims to achieve on
photometric accuracy. We also present the other measurements
(e.g. morphology) that are included in the OU-MER output catalogues and
we list all output products coming out of the MER PF pipeline.
galaxy
candidates using the deepest JWST/NIRCam data to date (5
depths
mag at
m), provided by the MIRI Deep Imaging
Survey (MIDIS) and the Next Generation Deep Extragalactic Exploratory
Public survey (NGDEEP). We estimate ultraviolet (UV) luminosity
functions and densities at
and
. The number density
of galaxies with absolute magnitudes
at
(
) is a factor of 4
(25) smaller than at
; the luminosity
density presents a similar evolution. Compared to state-of-the-art
galaxy simulations, we find the need for an enhanced UV-photon
production at
in
M
dark matter halos,
provided by an increase in the star formation efficiency at early times
and/or by intense compact starbursts with enhanced emissivity linked to
strong burstiness, low or primordial gas metallicities, and/or a
top-heavy initial mass function. There are few robust theoretical
predictions for the evolution of galaxies above
in the literature,
however, the continuing rapid drop in the halo mass function would
predict a more rapid evolution than we observe if photon production
efficiencies remained constant. Our
candidates present
mass-weighted ages around 30 Myr, and attenuations
mag. Their average stellar mass is
, implying a stellar-to-baryon mass fraction
around 10% if the emissivity increases with redshift, or significantly
higher otherwise. Three candidates present very blue UV spectral slopes
(
) compatible with
Pop III young (
Myr) stars
and/or high escape fractions of ionizing photons; the rest have
similar to
samples.
yr) to
categorise galaxies as
and
, we
obtain Euclid class fractions of 68-72%, 8-17%, and 14-19% for ageing,
quenched, and retired populations, respectively. Ageing and retired
galaxies dominate at the low- and high-mass end, respectively, while
quenched galaxies surpass the retired fraction for
. The
evolution with redshift shows increasing and decreasing fractions of
ageing and retired galaxies, respectively. More massive galaxies usually
undergo quenching episodes at earlier times than to their low-mass
counterparts. In terms of the mass-size-metallicity relation, ageing
galaxies generally exhibit disc morphologies and low metallicities.
Retired galaxies show compact structures and enhanced chemical
enrichment, while quenched galaxies form an intermediate population that
is more compact and chemically evolved than ageing systems. This work
demonstrates Euclid’s great potential for elucidating the physical
nature of the quenching mechanisms that govern galaxy evolution.
and a mass range of
,
from the Strong LensIng and Cluster Evolution (SLICE) JWST program.
These clusters represent a small subsample of the first clusters
observed in the SLICE program that are chosen based on the detection of
new multiple image constraints in the SLICE-JWST NIRCam/F150W2 and
F322W2 imaging. These constraints include new lensed dusty galaxies and
new substructures in previously identified lensed background galaxies.
Four clusters have never been modeled before. For the remaining 10
clusters, we present updated models based on JWST and HST imaging and,
where available, ground-based spectroscopy. We model the global mass
profile for each cluster and report the mass enclosed within 200 and 500
kpc. We report the number of new systems identified in the JWST imaging,
which in one cluster is as high as 19 new systems. The addition of new
lensing systems and constraints from substructure clumps in lensed
galaxies improves the ability of strong lensing models to accurately
reproduce the interior mass distribution of each cluster. We also report
the discovery of a candidate transient in a lensed image of the galaxy
cluster SPT-CL J0516-5755. All lens models and their associated products
are available for download at the Strong Lensing Cluster Atlas Data
Base, which is hosted at Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Marseille.
). In the initial 0.45% of Euclid’s
surveys, we double the total number of known lens candidates with
space-based imaging. Our catalogue includes 250 grade A candidates, the
vast majority of which (243) were previously unpublished. Euclid’s
resolution reveals rare lens configurations of scientific value
including double-source-plane lenses, edge-on lenses, complete Einstein
rings, and quadruply-imaged lenses. We resolve lenses with small
Einstein radii (
) in large numbers for the first time. These
lenses are found through an initial sweep by deep learning models,
followed by Space Warps citizen scientist inspection, expert vetting,
and system-by-system modelling. Our search approach scales
straightforwardly to Euclid Data Release 1 and, without changes, would
yield approximately 7000 high-confidence (grade A or B) lens candidates
by late 2026. Further extrapolating to the complete Euclid Wide Survey
implies a likely yield of over 100000 high-confidence candidates,
transforming strong lensing science.
of the
extragalactic sky and deliver high-quality imaging for many galaxies.
The depth and high spatial resolution of the data will enable a detailed
analysis of stellar population properties of local galaxies. In this
study, we test our pipeline for spatially resolved SED fitting using
synthetic images of Euclid, LSST, and GALEX generated from the TNG50
simulation. We apply our pipeline to 25 local simulated galaxies to
recover their resolved stellar population properties. We produce 3 types
of data cubes: GALEX + LSST + Euclid, LSST + Euclid, and Euclid-only. We
perform the SED fitting tests with two SPS models in a Bayesian
framework. Because the age, metallicity, and dust attenuation estimates
are biased when applying only classical formulations of flat priors, we
examine the effects of additional priors in the forms of mass-age-
relations, constructed using a
combination of empirical and simulated data. Stellar-mass surface
densities can be recovered well using any of the 3 data cubes,
regardless of the SPS model and prior variations. The new priors then
significantly improve the measurements of mass-weighted age and
compared to results obtained without
priors, but they may play an excessive role compared to the data in
determining the outcome when no UV data is available. The spatially
resolved SED fitting method is powerful for mapping the stellar
populations of galaxies with the current abundance of high-quality
imaging data. Our study re-emphasizes the gain added by including
multiwavelength data from ancillary surveys and the roles of priors in
Bayesian SED fitting. With the Euclid data alone, we will be able to
generate complete and deep stellar mass maps of galaxies in the local
Universe, thus exploiting the telescope’s wide field, NIR sensitivity,
and high spatial resolution.
. However, galaxy-scale
double-source-plane lenses (DSPLs) are extremely rare. In this paper, we
report the discovery of four new galaxy-scale double-source-plane lens
candidates in the Euclid Quick Release 1 (Q1) data. These systems were
initially identified through a combination of machine learning
lens-finding models and subsequent visual inspection from citizens and
experts. We apply the widely-used {} lens forecasting model to predict
that the full survey will discover 1700 DSPLs, which scales to
DSPLs in 63 deg
, the area of Q1. The number of
discoveries in this work is broadly consistent with this forecast. We
present lens models for each DSPL and infer their
values. Our initial Q1 sample
demonstrates the promise of to discover such rare objects.
completeness for mock red
QSOs with
contaminants. To refine
our selection function, we implement a probabilistic Random Forest
classifier, and use UMAP visualisation to disentangle non-linear
features in colour-space, reaching
completeness and
purity. A preliminary
analysis of the candidates in the Deep Field Fornax (EDF-F) shows that,
compared to VISTA+DECAm-based colour selection criteria, ’s superior
depth, resolution and optical-to-NIR coverage improves the
identification of the reddest, most obscured sources. Notably, the
exquisite resolution in the
filter unveils the presence of a
candidate dual quasar system, highlighting the potential for this
mission to contribute to future studies on the population of dual AGN.
The resulting catalogue of candidates, including more the 150 000
sources, provides a first census of red quasars in Q1 and sets the
groundwork for future studies in the Euclid Wide Survey (EWS), including
spectral follow-up analyses and host morphology characterisation.
and
. DESI’s
principle scientific objectives are to place precise constraints on the
equation of state of dark energy, the gravitationally driven growth of
large-scale structure, and the sum of the neutrino masses, and to
explore the observational signatures of primordial inflation. We present
DESI Data Release 1 (DR1), which consists of all data acquired during
the first 13 months of the DESI main survey, as well as a uniform
reprocessing of the DESI Survey Validation data which was previously
made public in the DESI Early Data Release. The DR1 main survey includes
high-confidence redshifts for 18.7M objects, of which 13.1M are
spectroscopically classified as galaxies, 1.6M as quasars, and 4M as
stars, making DR1 the largest sample of extragalactic redshifts ever
assembled. We summarize the DR1 observations, the spectroscopic
data-reduction pipeline and data products, large-scale structure
catalogs, value-added catalogs, and describe how to access and interact
with the data. In addition to fulfilling its core cosmological
objectives with unprecedented precision, we expect DR1 to enable a wide
range of transformational astrophysical studies and discoveries.
) and GC
half-number radii (
) around dwarf
galaxies, and their relations with host galaxy stellar masses (
), central surface
brightnesses (
), and effective radii (
).
Interestingly, we find that at a given stellar mass,
is almost
independent of the host galaxy
and
, while
depends on
and
; lower surface
brightness and diffuse dwarf galaxies show
while
higher surface brightness and compact dwarf galaxies show
-
. This means that for dwarf galaxies of
similar stellar mass, the GCs have a similar median extent; however,
their distribution is different from the field stars of their host.
Additionally, low surface brightness and diffuse dwarf galaxies on
average have a higher
than high
surface brightness and compact dwarf galaxies at any given stellar mass.
We also find that UDGs (ultra-diffuse galaxies) and non-UDGs have
similar
, while UDGs
have smaller
(typically less than 1) and 3-4 times higher
than
non-UDGs. Examining nucleated and not-nucleated dwarf galaxies, we find
that for
, nucleated dwarf galaxies seem to have smaller
and
, with no significant differences between their
, except at
where the nucleated dwarf galaxies tend to have a
higher
. Lastly, we
explore the stellar-to-halo mass ratio (SHMR) of dwarf galaxies and
conclude that the Perseus cluster dwarf galaxies follow the expected
SHMR at
extrapolated down to
.
galaxies within the
63.1 deg
area of the Euclid Quick Data Release
(Q1). The associated morphological catalogue includes two sets of
structural parameters fitted using : one for VIS images and one for a
combination of three NISP images in , and bands. We compare the
resulting Sérsic parameters to other morphological measurements provided
in the Q1 data release, and to the equivalent parameters based on
higher-resolution imaging. These comparisons confirm the consistency and
the reliability of the fits to Q1 data. Our analysis of colour gradients
shows that NISP profiles have systematically smaller effective radii
(
) and larger
Sérsic indices (
) than in VIS. In addition, we highlight
trends in NISP-to-VIS parameter ratios with both magnitude and
. From the
2D bimodality of the
colour-
plane, we define a
that separates early- and late-type galaxies
(ETGs and LTGs). We use the two subpopulations to examine the variations
of
across well-known scaling relations at
. ETGs display a
steeper size–stellar mass relation than LTGs, indicating a difference in
the main drivers of their mass assembly. Similarly, LTGs and ETGs occupy
different parts of the stellar mass–star-formation rate plane, with ETGs
at higher masses than LTGs, and further down below the Main Sequence of
star-forming galaxies. This clear separation highlights the link known
between the shutdown of star formation and morphological transformations
in the Euclid imaging data set. In conclusion, our analysis demonstrates
both the robustness of the Sérsic fits available in the Q1 morphological
catalogue and the wealth of information they provide for studies of
galaxy evolution with Euclid.
10% of multi-CTP cases
equally split between XMM-Newton and eROSITA. ML is then used to
distinguish between Galactic (8%) and extragalactic (92%) sources. We
computed photo-zs using deep learning for the 8617 sources detected in
the 10th data release of the DESI Legacy Survey, reaching an accuracy
and a fraction of outliers of about 5%. Based on their X-ray
luminosities, over 99% of CTPs identified as extragalactic are
classified as AGN, most of which appear unobscured given their hardness
ratios. With this paper, we release our catalogue, which includes
identifiers, basic X-ray properties, the details of the associations,
and additional features such as Galactic/extragalactic classifications
and photometric/spectroscopic redshifts. We also provide probabilities
for sub-selecting the sample based on purity and completeness, allowing
users to tailor the sample according to their specific needs.
-
M
), using an
observationally motivated model of the ICL. We identify a 50-200 kpc
circular annulus around the brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) in which the
signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of the ICL is maximised and use the S/N
within this aperture as our figure of merit for ICL detection. We
compare three state-of-the-art methods for ICL detection, and find that
a method that performs simple aperture photometry after high-surface
brightness source masking is able to detect ICL with minimal bias for
clusters more massive than
M
. The S/N of the ICL
detection is primarily limited by the redshift of the cluster, driven by
cosmological dimming, rather than the mass of the cluster. Assuming the
ICL in each cluster contains 15% of the stellar light, we forecast that
Euclid will be able to measure the presence of ICL in up to
clusters of
M
between
and 1.5 with a S/N
. Half of these clusters
will reside below
and the majority of
those below
will be detected with a
S/N
. A few thousand
clusters at
will have ICL detectable with a S/N greater than 3. The surface
brightness profile of the ICL model is strongly dependent on both the
mass of the cluster and the redshift at which it is observed so the
outer ICL is best observed in the most massive clusters of
M
. Euclid will detect
the ICL at more than 500 kpc distance from the BCG, up to
, in several hundred of
these massive clusters over its large survey volume.
), are analysed in the redshift range
. Due to the photometric redshift uncertainty, we
reconstruct the cosmic web skeleton, and measure cluster connectivity,
in 2-D projected slices with a thickness of 170 comoving
and centred on each cluster redshift, by using two different filament
finder algorithms on the most massive galaxies (
). In
agreement with previous measurements, we recover the mass-connectivity
relation independently of the filament detection algorithm, showing that
the most massive clusters are, on average, connected to a larger number
of cosmic filaments, consistent with hierarchical structure formation
models. Furthermore, we explore possible correlations between
connectivities and two cluster properties: the fraction of early-type
galaxies and the Sérsic index of galaxy members. Our result suggests
that the clusters populated by early-type galaxies exhibit higher
connectivity compared to clusters dominated by late-type galaxies. These
preliminary investigations highlight our ability to quantify the impact
of the cosmic web connectivity on cluster properties with Euclid.
galaxies with
,
giving a precise constraint of the SFMS at the high-mass end. We
investigated the SFMS, in a redshift interval between
and
, comparing our results with the
existing literature and fitting them with a parameterisation taking into
account the presence of a bending of the relation at the high-mass end,
depending on the bending mass,
. We find good agreement with previous
results in terms of
values, and an increasing trend for
the relation scatter at higher stellar masses. We also investigate the
distribution of physical (e.g. dust absorption,
, and formation age) and morphological
properties (e.g., Sérsic index and radius) in the SFR–stellar mass
plane, and their relation with the SFMS. These results highlight the
potential of Euclid in studying the fundamental scaling relations that
regulate galaxy formation and evolution in anticipation of the
forthcoming Data Release 1.
objects identified in the photometric survey. In
this paper, we present an overview of the SPE PF algorithm and assess
its performance by comparing its results with high-quality spectroscopic
redshifts from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) survey in
the Euclid Deep Field North. Our findings highlight remarkable accuracy
in successful redshift measurements, with a bias of less than
in
and a high precision of approximately
. The majority of
spectra have only a single spectral feature or none at all. To avoid
spurious detections, where noise features are misinterpreted as lines or
lines are misidentified, it is therefore essential to apply well-defined
criteria on quantities such as the redshift probability or the flux and
signal-to-noise ratio. Using a well-tuned quality selection, we achieve
an 89% redshift success rate in the target redshift range for cosmology
(
),
which is well covered by DESI for
. Outside this
range where the line is observable, redshift measurements are less
reliable, except for sources showing specific spectral features (e.g.,
two bright lines or strong continuum). Ongoing refinements along the
entire chain of PFs are expected to enhance both the redshift
measurements and the spectral classification, allowing us to define the
large and reliable sample required for cosmological analyses. Overall,
the Q1 SPE results are promising, demonstrating encouraging potential
for cosmology.
>1.3. With a total coverage of
63.1deg
, the Euclid Quick Data Release 1 (Q1)
is large enough to detect tens of clusters and hundreds of protoclusters
at these early epochs. The Q1 photometric redshift catalogue enables us
to detect clusters out to
< 1.5; however, infrared imaging
from Spitzer extends this limit to higher redshifts by using high local
projected densities of Spitzer-selected galaxies as signposts for
cluster and protocluster candidates. We use Spitzer imaging of the
Euclid Deep Fields (EDFs) to derive densities for a sample of
Spitzer-selected galaxies at redshifts
> 1.3, building Spitzer IRAC1 and
IRAC2 photometric catalogues that are 95% complete at a magnitude limit
of IRAC2=22.2, 22.6, and 22.8 for the EDF-S, EDF-F, and EDF-N,
respectively. We apply two complementary methods to calculate galaxy
densities: (1) aperture and surface density; and (2) the
Nth-nearest-neighbour method. When considering a sample selected at a
magnitude limit of IRAC2 < 22.2, at which all three EDFs are 95%
complete, our surface density distributions are consistent among the
three EDFs and with the SpUDS blank field survey. We also considered a
deeper sample (IRAC2 < 22.8), finding that 2% and 3% of the surface
densities in the North and Fornax fields are 3
higher than the average field
distribution and similar to densities found in the CARLA cluster survey.
Our surface densities are also consistent with predictions from the GAEA
semi-analytical model. Using combined Euclid and ground-based i-band
photometry we show that our highest Spitzer-selected galaxy overdense
regions, found at
~1.5, also host high densities of
passive galaxies. This means that we measure densities consistent with
those found in clusters and protoclusters at
>1.3.
used to largely rely
on rest-frame UV observations. However, these observations overlook
dusty and massive sources, resulting in an incomplete census of early
star-forming galaxies. Recently, infrared data from Spitzer and the
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have revealed a hidden population at
$z$3-6 with extreme red colours. Taking advantage of the overlap between
imaging in the Euclid Deep Fields (EDFs), covering
60 deg
, and ancillary Spitzer observations,
we identified 27000 extremely red objects with
(dubbed HIEROs) down to a
completeness magnitude
limit of IRAC2
22.5 AB. After a visual inspection to
discard artefacts and objects with troubling photometry, we ended up
with a final sample of 3900 candidates. We retrieved the physical
parameter estimates for these objects from the SED-fitting tool CIGALE.
Our results confirm that HIERO galaxies may populate the high-mass end
of the stellar mass function at
, with some reaching
extreme stellar masses (
) and exhibiting high dust attenuation (
). However, we
consider stellar mass estimates unreliable for
, favouring a
lower-z solution. The challenges faced by SED-fitting tools in
characterising these objects highlight the need for further studies,
incorporating shorter-wavelength and spectroscopic data. Euclid spectra
will help resolve degeneracies and better constrain the physical
properties of the brightest galaxies. Given the extreme nature of this
population, characterising these sources is crucial for understanding
galaxy evolution. This work demonstrates Euclid’s potential to provide
statistical samples of rare, massive, dust-obscured galaxies at
, which will be prime
targets for JWST, ALMA, and ELT.
, with a
mean difference between the predicted and true
of
and an overall root
mean square error (RMSE) of 0.051. This method moves beyond binary AGN
classification, enabling precise AGN contribution measurements. Applying
our model to a stellar-mass-limited sample (
,
) from the first quick data release (Q1), we
identify
AGN
over 63.1 deg
(
%) using a
threshold of
. We compare our DL-selected AGN with those
identified in X-ray, mid-infrared (MIR), and optical spectroscopy and
investigate their overlapping fractions depending on different
thresholds on the PSF contribution. We find that the overlap increases
with increasing X-ray or bolometric AGN luminosity. The AGN luminosity
in the
filter
correlates with host galaxy stellar mass, suggesting faster supermassive
black hole (SMBH) growth in more massive galaxies. Moreover, the mean
relative contribution of the AGN is higher in quiescent galaxies than in
star-forming ones. Starburst galaxies and the most massive galaxies
(across the star-formation main sequence) tend to host the most luminous
AGN, indicating concomitant assembly of the SMBH and the host
galaxy.
-1. We determine if a
galaxy is passive using the specific star-formation rate, and we
classify the morphologies of galaxies using the Sérsic index n and the
u-r colours. We measure the local environmental density of each galaxy
using the Nth-nearest neighbour method. We find that at fixed stellar
mass, the quenched fraction increases with increasing density up to
. This result shows
the separability of the effects from the stellar mass and the
environment, at least at
. At
, we observe
weak environmental effects, with most high mass galaxies being quenched
independently of environment. Up to
, the ETG fraction
increases with density at fixed stellar mass, meaning the environment
also transforms the morphology of the galaxy independently of stellar
mass, at low mass. For high mass galaxies, almost all galaxies are
early-types, with low impact from the environment. At
, the morphology
depends mostly on stellar mass, with only low-mass galaxies being
affected by the environment. Given that the morphology classifications
use u-r colours, these are correlated to the star-formation rate, and as
such our morphology results should be taken with caution; future
morphology classifications should verify these results. To summarise, we
identify the passive-density and morphology-density relations at
, but at
the relations
are less strong. At
, the
uncertainties are large, and future Euclid data releases are key to
confirm these trends.
covered by the quick
Euclid Quick Data Release (Q1) to extend the search for LRDs to brighter
magnitudes and to lower redshifts than what has been possible with JWST.
The selection is performed by fitting the available photometric data
(Euclid, the Spitzer Infrared Array Camera (IRAC), and ground-based
data) with two power
laws, to retrieve both the rest-frame optical and UV slopes consistently
over a large redshift range (i.e, z<7.6). We exclude extended objects
and possible line emitters, and perform a careful visual inspection to
remove any imaging artefacts. The final selection includes 3341 LRD
candidates at z=0.33-3.6, with 29 detected also in IRAC. The resulting
rest-frame UV luminosity function, in contrast with previous JWST
studies, shows that the number density of LRD candidates increases from
high-z down to z=1.5-2.5 and decreases at lower z. However, less
evolution is apparent focusing on the subsample of more robust LRD
candidates having IRAC detections, which however has low statistics and
limited by the IRAC resolution. The comparison with previous quasar
(QSO) UV luminosity functions shows that LRDs are not the dominant AGN
population at z<4 and
. Follow-up studies of these LRD candidates are
pivotal to confirm their nature, probe their physical properties and
check for their compatibility with JWST sources, given the different
spatial resolution and wavelength coverage of Euclid and JWST.
) or
extended (area
pixels)
galaxies in Q1. The catalogue was created by finetuning the Zoobot
galaxy foundation models on annotations from an intensive one month
campaign by Galaxy Zoo volunteers. Our measurements are fully automated
and hence fully scaleable. This catalogue is the first 0.4% of the
approximately 100 million galaxies where Euclid will ultimately resolve
detailed morphology.
) sample of galaxies from the first quick data
release (Q1), in the redshift range z=0.5-2. We selected AGN using X-ray
data, optical spectroscopy, mid-infrared colours, and processing
observations with an image decomposition algorithm. We used CNNs trained
on cosmological simulations to classify galaxies as mergers and
non-mergers. We found a larger fraction of AGN in mergers compared to
the non-merger controls for all AGN selections, with AGN excess factors
ranging from 2 to 6. Likewise, a generally larger merger fraction (
) is seen in
active galaxies than in the non-active controls. We analysed
as a function of
the AGN bolometric luminosity (
) and the
contribution of the point-source to the total galaxy light in the -band
(
) as a proxy for the
relative AGN contribution fraction. We uncovered a rising
, with increasing
up to
, after
which we observed a decreasing trend. We then derived the point-source
luminosity (
) and showed that
monotonically
increases as a function of
at z<0.9, with
$f_{merg}>$50% for
erg/s. At z>0.9,
rises as a
function of
, though mergers do
not dominate until
erg/s. For X-ray and spectroscopic AGN, we computed
, which has a
positive correlation with
for X-ray AGN,
while shows a less pronounced trend for spectroscopic AGN due to the
smaller sample size. At
erg/s, AGN mostly reside in mergers. We concluded
that mergers are strongly linked to the most powerful, dust-obscured
AGN, associated with rapid supermassive black hole growth.
,deg
COSMOS-Web survey, discovered using
exquisite James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) imaging across four
wavebands. Following two rounds of visual inspection, over 100
candidates were ranked as
of inspectors. The COWLS
sample has several notable properties: (i) magnified source galaxies
spanning redshifts
to
, which therefore
extend into the epoch of reionisation; (ii) the highest-redshift lens
galaxies known, pushing galaxy density profile evolution studies beyond
; (iii) all lenses
are distributed within a contiguous
,deg
region, allowing for joint strong and
weak lensing analyses; and (iv) a subset exhibits lensed source emission
ray-traced near the lens galaxy centers, enabling studies of
supermassive black holes and dust absorption. A key innovation of our
approach is the use of lens modelling to aid in identifying lenses that
may otherwise be missed. This paper is accompanied by the first COWLS
public release, providing JWST NIRCam imaging in four bands, lens
models, pixelized source reconstructions and lens redshift estimates :
https://github.com/Jammy2211/COWLS_COSMOS_Web_Lens_Survey
deg
survey of the COSMOS field using the
NIRCam and MIRI instruments aboard JWST, with the first catalogue of
strong lens candidates identified in the observed NIRCam data, COWLS. We
modify the lenspop package to produce a forecast for strong lensing in
COSMOS-Web. We add a new mock galaxy catalogue to use as the source
population, as well as the COSMOS-Web survey specifications, including
the transmission data for the four NIRCam filters used. We forecast 107
strong lenses can be detected in COSMOS-Web across all bands, assuming
complete subtraction of the lens galaxy light. The majority of the
lenses are forecast to have small Einstein radii (
arcsecond) and lie at redshifts between
,
whilst the source redshift distribution peaks at
and has a long tail
extending up to
, unambiguously
showing that strong lensing in JWST can probe the entirety of the epoch
of reionisation. We compare our forecast with the distributions of
Einstein radii, lens photometric redshifts, and lens and source
magnitudes in the observed lenses, finding that whilst the forecast and
observed Einstein radii distributions match, the redshifts and
magnitudes do not. The observed lens redshift distribution peaks at a
slightly lower redshift than the forecast one, whilst the lens
magnitudes are systematically brighter in the observed data than in the
forecast.
gain in spectroscopic
capability compared to the current state-of-the-art represented by the
Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument project (DESI). Spec-S5 will
provide a critical scientific capability in the post-Rubin and post-DESI
era for advancing cosmology, fundamental physics, and astrophysics in
the 2030s.
field. We subtracted a point–spread
function (PSF) model and removed the Galactic cirrus contribution in
each band after modelling it with the DAWIS software. We then applied
three methods to detect, characterise, and model the ICL and the
brightest cluster galaxy (BCG): the CICLE 2D multi-galaxy fitting; the
DAWIS wavelet-based multiscale software; and a mask-based 1D profile
fitting. We detect ICL out to 600 kpc. The ICL fractions derived by our
three methods range between 18% and 36% (average of 24%), while the
BCG+ICL fractions are between 21% and 41% (average of 29%), depending on
the band and method. A galaxy density map based on 219 selected cluster
members shows a strong cluster substructure to the south-east and a
smaller feature to the north-west. Based on colours, the ICL (out to
about 400 kpc) seems to be built by the accretion of small systems (M ~
solar mass), or
from stars coming from the outskirts of Milky Way-type galaxies (M ~
solar mass). Though
Abell 2390 does not seem to be undergoing a merger, it is not yet fully
relaxed, since it has accreted two groups that have not fully merged
with the cluster core. We estimate that the contributions to the inner
300 kpc of the ICL of the north-west and south-east subgroups are 21%
and 9% respectively.
G), together with its Early Type Galaxy
(ETG) extension, stand as the most extensive dataset of deep, uniform
mid-infrared (mid-IR; 3.6 and 4.5
m) imaging for a sample of
nearby (
Mpc) galaxies.
However, the velocity criterion used to select the original sample
results in an additional 422 galaxies without HI detection that ought to
have been included in the S
G on the basis of their optical
recession velocities. In order to create a complete magnitude-, size-
and volume-limited sample of nearby galaxies, we collect
m and
-band images using archival data from
different surveys and complement it with new observations for the
missing galaxies. We denote the sample of these additional galaxies as
Disc Galaxy (DG) extension. We present the Complete Spitzer Survey of
Stellar Structure in Galaxies (CS
G), encompassing a sample of
galaxies with consistent
imaging, surface brightness profiles, photometric parameters, and
revised morphological classification. Following the original strategy of
the S
G survey, we produce masks, surface
brightness profiles, and curves of growth using masked
m and
-band images. From these profiles, we
derive the integrated quantities: total magnitude, stellar mass,
concentration parameter, and galaxy size, converting to
m. We re-measure these
parameters also for the S
G and ETG to create a homogenous
sample. We present new morphological revised
-types, and we showcase mid-IR scaling
relations for the photometric parameters. We complete the S
G sample by incorporating 422 galaxies.
The CS
G includes at least 99.94% of the
complete sample of nearby galaxies, meeting the original selection
criteria, and it will enable a wide set of investigations into galaxy
structure and evolution.
deg
of
-band observations taken from the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope. We consider all sources with magnitudes
in the range
, without any colour preselection, yielding a
parent sample of seven million sources. We characterise our parent
sample via the visual inspection of
sources selected
at random. From it, we estimate, with a 68% confidence interval, that 1
in every
sources is an
edge-on lens candidate, with at least eight high-quality candidates in
the parent sample. This corresponds to 1 candidate per
edge-on late-type
galaxies. Our search relies on a convolutional neural network (CNN) to
select a reduced sample of candidates, followed by a visual inspection
to curate the final sample. The CNN is trained from scratch using
simulated
-band observations of edge-on lenses,
and real observations of non-lenses. We find 61 good edge-on lens
candidates using the CNN. Moreover, combining the CNN candidates with
those found serendipitously, and those identified while characterising
the parent sample, we discovered 4 grade A, 20 grade B, and 58 grade C
edge-on lens candidates; effectively doubling the known sample of these
systems. We also discovered 16 grade A, 16 grade B, and 18 grade C lens
candidates of other types. Finally, based on the characterisation of the
parent sample, we estimate that our search found around 60% of the
bright grade A and B edge-on lens candidates within the parent
sample.
. In this work, we use photometric redshifts to
extract the baryon acoustic oscillation signal (BAO) from the Flagship
galaxy mock catalogue with a tomographic approach to constrain the
evolution of the Universe and infer its cosmological parameters. We
measure the two-point angular correlation function in 13 redshift bins.
A template-fitting approach is applied to the measurement to extract the
shift of the BAO peak through the transverse Alcock–Paczynski parameter
. A joint analysis of all redshift bins
is performed to constrain
at the effective redshift
with MCMC and profile likelihood techniques. We
also extract one
parameter per redshift bin
to quantify its evolution as a function of time. From these 13
, which are directly
proportional to the ratio
, we
constrain
,
, and
. From
the joint analysis, we constrain
, which represents a three-fold improvement over
current constraints from the Dark Energy Survey. As expected, the
constraining power in the analysis of each redshift bin is lower, with
an uncertainty ranging from
to
. From these
results, we constrain
at 0.45 %,
at 0.91
%, and
at
7.7 %. We quantify the influence of analysis choices like the template,
scale cuts, redshift bins, and systematic effects like redshift-space
distortions over our constraints both at the level of the extracted
parameters and at the level
of cosmological inference.
. EP240801a
exhibits a burst duration of 148 s in X-rays and 22.3 s in gamma-rays,
with X-rays leading by 80.61 s. Spectral lag analysis indicates the
gamma-ray signal arrived 8.3 s earlier than the X-rays. Joint spectral
fitting of EP/WXT and Fermi/GBM data yields an isotropic energy
, a peak energy
, a fluence ratio
, classifying EP240801a as an X-ray flash (XRF).
The host-galaxy continuum spectrum, inferred using Prospector, was used
to correct its contribution for the observed outburst optical data.
Unusual early
-band behavior and EP/FXT observations
suggest multiple components in the afterglow. Three models are
considered: two-component jet model, forward-reverse shock model and
forward-shock model with energy injection. Both three provide reasonable
explanations. The two-component jet model and the energy injection model
imply a relatively small initial energy and velocity of the jet in the
line of sight, while the forward-reverse shock model remains typical.
Under the two-component jet model, EP240801a may resemble GRB 221009A
(BOAT) if the bright narrow beam is viewed on-axis. Therefore, EP240801a
can be interpreted as an off-beam (narrow) jet or an intrinsically weak
GRB jet. Our findings provide crucial clues for uncovering the origin of
XRFs.
200 km s
of the galaxy’s
systemic velocity. The galaxy seems to have a tail-like feature
extending away from it in the southern direction up to
41 kpc (in projection).
We also detect a cloud at anomalous velocities, but we did not find any
optical counterpart. We construct a detailed tilted ring model for this
edge-on galaxy to gain a deeper understanding of the vertical structure
of its neutral hydrogen. The model that best matches the data features a
thick disc with a scale height of
3$
%$ of the
total HI mass. This extraplanar gas is detected for the first time in
UGCA 250. Our analysis favours a mixed origin for the extraplanar gas in
UGCA 250, likely arising from a combination of internal stellar feedback
and external tidal interactions.
and
– we compute lensing observables to assess the
viability of the SFDM model. Our analysis establishes constraints on the
soliton core mass, directly probing the self-interaction parameter space
of scalar field dark matter. This work bridges semi-analytical
predictions with astrophysical observations, offering a lensing-based
framework to test ultralight dark matter scenarios in galaxy cluster
environments.
cm
) HI observations of 5
nearby galaxies with stellar mass of
M
, taken with the
MeerKAT radio telescope. Four of these were observed as part of the
MHONGOOSE survey. We characterise their main HI properties and compare
these with synthetic HI data from a sample of 25 similarly massive
star-forming galaxies from the TNG50 (20) and FIRE-2 (5) suites of
cosmological hydrodynamical simulations. Globally, the simulated systems
have HI and molecular hydrogen (H
) masses in good agreement with the
observations, but only when the H
recipe of Blitz & Rosolowsky
(2006) is employed. The other recipes that we tested overestimate the
H
-to-HI mass fraction by up to an order
of magnitude. On a local scale, we find two main discrepancies between
observed and simulated data. First, the simulated galaxies show a more
irregular HI morphology than the observed ones due to the presence of HI
with column density
cm
up to ~100 kpc from the
galaxy centre, in spite of the fact that they inhabit more isolated
environments than the observed targets. Second, the simulated galaxies
and in particular those from the FIRE-2 suite, feature more complex and
overall broader HI line profiles than the observed ones. We interpret
this as being due to the combined effect of stellar feedback and gas
accretion, which lead to a large-scale gas circulation that is more
vigorous than in the observed galaxies. Our results indicate that, with
respect to the simulations, gentler processes of gas inflows and
outflows are at work in the nearby Universe, leading to more regular and
less turbulent HI discs.
Jy; i.e. S/N
) and with faint
counterparts at NIR wavelengths (F150W
mag), we collect
a sample of 127 likely dusty star-forming galaxies (DSFGs). We estimate
their physical properties through SED fitting, compute the first radio
luminosity function for these types of sources, and their contribution
to the total cosmic star formation rate density. Our analysis confirms
that these sources represent a population of highly dust-obscured (
mag),
massive (
M
) and star-forming
galaxies (
M
yr
) located at
, representing the high-redshift tail of the full
distribution of radio sources. Our results also indicate that these
galaxies could dominate the bright end of the radio luminosity function
and reach a total contribution to the cosmic star formation rate density
equal to that estimated only considering NIR-bright sources at
. Finally, our
analysis further confirms that the radio selection can be employed to
collect statistically significant samples of DSFGs, representing a
complementary alternative to the other selections based on JWST colors
or detection at FIR/(sub)mm wavelengths.
from the
FEASTS program with a
(
) column density (
) depth
of
. We develop
two photometric methods to separate the extraplanar HI from the disk
component, based on existing interferometric data and parametric
modeling of the disk flux distribution respectively. With both methods,
the FEASTS data exhibit clear extended wings beyond the disk along the
minor axis. The extraplanar HI accounts for 5% to 20% of the total HI
mass and extends to
kpc at
. We
find a tight positive correlation between vertical extensions of the
extraplanar HI and total HI mass
. The
iso-density shape of HI at
has
an average axis ratio of
. The
off-disk
profiles of these edge-on galaxies well represent the lower envelop of
previous Lyman-
absorption measurements at
low-redshift. Our results suggest that at
, the HI extends considerably further than the
known thin and thick disks in the vertical direction, but still remains
much flattener than a spherical distribution, consistent with
theoretical expectations that outflow, circulation, and accretion should
have different impacts in these two directions. We show the tension of
our results with Illustris and TNG predictions, highlighting the
constraining power of our results for future simulations.
) and radio surface
brightness profile, and performed a comparison with observational
results. We obtained that properly accounting for the mass and redshift
dependence in the radio profile can reduce the overall scatter by a
factor of
, with an evident
residual dependence on the cluster dynamical status. We showed that
assuming no relation between the halo size (
) and the cluster mass
(
) allowed us to reconcile the observed
radio profile mass scaling and the one predicted starting from the
relation. We discuss
the implications of a lack of
relation, assessing
possible systematics and biases in the analyses, and interpreting it as
a natural consequence of the structure formation process. Finally, we
also considered the role of the magnetic field in the
relation, putting
constraints on its dependence upon the cluster mass and finding
consistent results with expectations from our radio power mass
scaling.
MJup, a
radius of
RJup, a
nearly circular orbit in spin-orbit alignment with the host star, a
relatively high metallicity, and a near-solar to super-solar C/O ratio.
However, key parameters such as the rotational velocity and radial
velocity could not be estimated as they require high-resolution
spectroscopic data that is impossible to obtain with classical
spectrographs. AF Lep b was recently observed with the new HiRISE
visitor instrument at the VLT, with the goal of obtaining
high-resolution (R~140,000) spectroscopic observations to better
constrain the orbital and atmospheric parameters of the young giant
exoplanet. We compare the extracted spectrum of AF Lep b to
self-consistent atmospheric models using ForMoSA. We then use our
measurements of the radial velocity of the planet to provide new
constraints on the orbit of the planet. From the forward modeling, we
find a C/O ratio that aligns with previous low-resolution analyses, and
we confirm the super-solar metallicity. We also confirm unambiguously
the presence of methane in the atmosphere of the companion. Based on all
available relative astrometry and radial velocity measurements of the
host star, we show that two distinct orbital populations are possible
for the companion. We derive the radial velocity of AF Lep b to be
km/s,
and show that this value agrees well with one of the two orbital
solutions, allowing us to rule out an entire family of orbits.
Additionally, assuming that the rotation and orbit are coplanar, the
derived planet’s rotation rate is consistent with the observed trend of
increasing spin velocity with higher planet mass.
, lensed by a massive
early-type galaxy at
. The redshift
is unambiguously identified with our NOEMA and Keck/MOSFIRE
spectroscopy, where the NOEMA observations reveal the CO(4-3) and
CO(5-4) lines at
, and the MOSFIRE
data detect [O] at
. Using
multi-wavelength photometry spanning near-infrared to radio bands, we
find that the lensed galaxy is a dust-obscured starburst (
,
) with high star-formation efficiency (gas
depletion time
Myr) as indicated by the C
non-detection. The redshift confirmation revalidates that the total lens
mass budget within the Einstein radius is fully accounted for by the
stellar and dark matter components, without the need of modifying the
initial mass function or dark matter distribution profile. This work
paves the way for detailed studies and future follow-ups of this unique
lensing system, providing an ideal laboratory for studying mass
distribution at
and physical
conditions of star formation at
.
area centered on the 2 deg
COSMOS legacy field. This compilation
contains 487,666 redshifts of 266,284 unique objects from 138 individual
observing programs up to
with median
stellar mass
to
M
(redshift dependent).
Rest-frame
colors and SFR –
stellar mass correlations show the compilation primarily contains low-
to intermediate-mass star-forming and massive, quiescent galaxies at
and mostly
low-mass bursty star-forming galaxies at
. Sources in the
compilation cover a diverse range of environments, including
protoclusters such as ``Hyperion’’. The full compilation is 50%
spectroscopically complete by
and
mag;
however, this is redshift dependent. Spatially, the compilation is
% (
%) complete within the
central (outer) region limited to
mag and
mag,
separately. We demonstrate how the compilation can be used to validate
photometric redshifts and investigate calibration metrics. By training
self-organizing maps on COSMOS2020/Classic and projecting the
compilation onto it, we find key galaxy subpopulations that currently
lack spectroscopic coverage including
intermediate-mass
quiescent galaxies and low-/intermediate-mass bursty star-forming
galaxies,
massive quiescent
galaxies, and
massive
star-forming galaxies. This highlights how combining self-organizing
maps with our compilation can provide guidance for future spectroscopic
observations to get a complete spectroscopic view of galaxy populations.
Lastly, the compilation will undergo periodic data releases that
incorporate new spectroscopic redshift measurements, providing a lasting
legacy resource for the community.
m. Then, we characterize the performance
of the setup by detailing the validation measurements obtained before
the campaign. In particular, the radiometric, geometric, and spectral
properties of the setup needed for the inversion of collected data and
the calculation of the instrument’s calibration functions are presented
and discussed. Finally, we provide an overview of conducted measurements
with MAJIS, and we discuss unforeseen events encountered during the
on-ground calibration campaign.
)
early-type galaxies (ETGs) in the Virgo cluster by analysing their
spatially resolved stellar population (SP), including their UV and H
emission. As part of the VESTIGE
survey, we used H
images to select ETGs that show no
signs of ongoing star formation. We combined VESTIGE with images from
Astrosat/UVIT, GALEX and CFHT from the NGVS to analyse radial spectral
energy distributions (SEDs) from the FUV to the NIR. The UV emission in
these galaxies is likely due to old, low mass stars in post main
sequence (PMS) phases, the UV upturn. We fit the radial SEDs with novel
SP models that include an old, hot stellar component of PMS stars with
various temperatures and energetics. This way, we explore the main
stellar parameters responsible for UV upturn stars irregardless of their
evolutionary path. Standard models are not able to reproduce the
galaxies’ central FUV emission (SMA/
),
while the new models well characterise it through PMS stars with
temperatures T$$25000 K. All galaxies are old (mass-weighted ages
Gyr) and the
most massive M49 and M87 are supersolar within SMA/
. Overall, we found flat age gradients (
Log(Age)
dex)
and shallow metallicity gradients (
Log(Z)
dex), except for
M87 (
Log(
)
dex). Our
results show that these ETGs formed with timescales
Myr,
having assembled between
of their
stellar mass at
. This is consistent
with recent JWST observations of quiescent massive galaxies at high
, which are likely the ancestors of the
largest ETGs in the nearby Universe. The derived flat/shallow gradients
indicate that major mergers might have contributed to the formation and
evolution of these galaxies.
area, 25.3 and 23.2 AB mag depth, as
well as 0.1” and 0.3” angular resolutions, in optical and near-IR bands,
respectively. Towards characterising the history of the Hubble sequence,
we perform a morphological analysis of 2445 and 12,786 galaxies with
and
,
respectively. We use single-Sérsic profiles and the sums of a Sérsic
bulge and an exponential disc to model these galaxies with
SourceXtractor++ and analyse their parameters in order to assess their
consistencies and discrepancies. The fitted galaxies to
span the
various Hubble types with ubiquitous bulge and disc components, and a
bulge-to-total light ratio B/T taking all values from 0 to 1. The
effective radius of the single-Sérsic profile is an intermediate
estimate of galaxy size, between the bulge and disc effective radii,
depending on B/T. The axis ratio of the single-Sérsic profile is higher
than the disc axis ratio, increasingly so with B/T. The model impacts
the photometry with -0.08 to 0.01 mag median systematic
offsets between single-Sérsic and
bulge+disc total magnitudes, and a 0.05 to 0.15 mag dispersion, from low
to high B/T. We measure a median 0.3 mag bulge-disk colour difference in
rest-frame
that originates
from the disc-dominated galaxies, whereas bulge-dominated galaxies have
similar median colours of their components. Remarkably, we also measure
redder-inside disc colour gradients, based on 5 to 10% systematic
variations of disc effective radii between the optical and near-IR
bands. This analysis demonstrates the usefulness and limitations of
single-Sérsic profile modelling, and the power of bulge-disc
decomposition for reliably characterising the morphology of lenticulars
and spirals in Euclid images.
, sets a
constraint on
.
). If its compactness is confirmed, it would be
the nearest known compact PRS at
. Our catalog
significantly increases the statistics of the Macquart relation at low
redshifts (
). In the near
future, the completed CHIME/FRB Outriggers array will produce hundreds
of FRBs localized with very long baseline interferometry (VLBI). This
will significantly expand the known sample and pave the way for future
telescopes relying on VLBI for FRB localization.
d and a minimum mass of
M
. Additionally, we
detect a tentative signal at 6.4 d, whose significance depends strongly
on the choice of Gaussian Process priors constrained by stellar activity
indicators and would require further observations for confirmation. In
contrast, no planetary signals are detected for Gl 382, where RV
variations are dominated by stellar activity.
with the complete resolution of the
[0.5-2] keV CXB.
. This is the first
strong gravitational lens discovered in Euclid and the first in an NGC
object from any survey. The combination of the low redshift of the lens
galaxy, the brightness of the source galaxy (
lensed,
unlensed), and the completeness of the ring make this an exceptionally
rare strong lens, unidentified until its observation by Euclid. We
present deep imaging data of the lens from the Euclid Visible Camera
(VIS) and Near-Infrared Spectrometer and Photometer (NISP) instruments,
as well as resolved spectroscopy from the Keck Cosmic Web Imager (KCWI).
The Euclid imaging in particular presents one of the highest
signal-to-noise ratio optical/near-infrared observations of a strong
gravitational lens to date. From the KCWI data we measure a source
redshift of
. Using data from
the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) we measure a velocity
dispersion for the lens galaxy of
. We
model the lens galaxy light in detail, revealing angular structure that
varies inside the Einstein ring. After subtracting this light model from
the VIS observation, we model the strongly lensed images, finding an
Einstein radius of 2.5 arcsec, corresponding to
at the redshift of the lens. This is small compared to the effective
radius of the galaxy,
.
Combining the strong lensing measurements with analysis of the
spectroscopic data we estimate a dark matter fraction inside the
Einstein radius of
and a stellar initial mass-function (IMF) mismatch parameter of
,
indicating a heavier-than-Chabrier IMF in the centre of the galaxy.
flux, the best-fit
single-flavour flux normalisation is
in the 90% energy range of the KM3NeT event.
Furthermore, the ultra-high-energy data are then fit together with the
IceCube measurements at lower energies, either with a single power law
or with a broken power law, allowing for the presence of a new component
in the spectrum. The joint fit including non-observations by other
experiments in the ultra-high-energy region shows a slight preference
for a break in the PeV regime if the ``High-Energy Starting Events’’
sample is included, and no such preference for the other two IceCube
samples investigated. A stronger preference for a break appears if only
the KM3NeT data is considered in the ultra-high-energy region, though
the flux resulting from such a fit would be inconsistent with null
observations from IceCube and Pierre Auger. In all cases, the observed
tension between KM3NeT and other datasets is of the order of
, and increased
statistics are required to resolve this apparent tension and better
characterise the neutrino landscape at ultra-high energies.
) back to
. The cosmic
molecular gas mass density increases with redshift, peaking around
, then slowly
declines towards higher redshifts by
dex. Our findings
confirm the key role of molecular gas in fuelling star formation. The
new
estimates allow us
to revisit the cosmic baryon cycle, showing that the ratio of molecular
gas-to-stellar mass density is consistent with the so-called ‘bathtub
model’ of baryons, which implies a continuous replenishment of gas. The
cosmic gas depletion timescale, estimated on a global scale, is shown to
be fairly constant at all redshifts. We emphasise the importance of
surveys using multiple small fields rather than a single contiguous area
to mitigate the effects of cosmic variance.
. We
search for systems with similar geometrical properties in the full-sky
mock galaxy catalogue of the MillenniumTNG simulations and find that
although such straight filaments are unusual and rare, they are
predicted by
CDM simulations (4% incidence). We study
the cold HI gas in a 1.3 Mpc section of the filament through HI-21cm
emission line observations and detect eleven HI sources, many more than
expected from the HI mass function in a similar volume. They have HI
masses
and are
mostly within ~120 kpc projected distance from the filament axis. None
of these HI sources has a confirmed optical counterpart. Their darkness
together with their large HI-21cm line-widths indicate that they contain
gas that might not yet be virialized. These clouds must be marking the
peaks of the dark matter and HI distributions over large scales within
the filament. The presence of such gas clouds around the filament spines
is predicted by simulations, but this is the first time that the
existence of such clouds in a filament is observationally confirmed.
new strong
gravitational lens candidates in the DESI Legacy Imaging Surveys using
residual neural networks (ResNet). We observed a subset (51) of our
candidates using the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). All of them were
confirmed to be strong lenses. We also briefly describe spectroscopic
follow-up observations by DESI and Keck NIRES programs. From this very
rich dataset, a number of studies will be carried out, including
evaluating the quality of the ResNet search candidates and lens
modeling. In this paper, we present our initial effort in these
directions. In particular, as a demonstration, we present the lens model
for DESI-165.4754-06.0423, with imaging data from HST, and lens and
source redshifts from DESI and Keck NIRES, respectively. In this effort,
we have applied a forward-modeling Bayesian approach (GIGA-Lens), using
GPUs, for the first time in both regards, to a strong lens with HST
data, or any high resolution imaging.
with unprecedented
statistics and establish robust constraints on the epoch of emergence of
the Hubble sequence. We measure the global (spheroids, disk-dominated,
bulge-dominated, peculiar) and resolved (stellar bars) morphologies for
about 400,000 galaxies down to F150W=27 using deep learning,
representing a two-orders-of-magnitude increase over previous studies.
We then provide reference Stellar Mass Functions (SMFs) of different
morphologies between
and
and best-fit
parameters to inform models of galaxy formation. All catalogs and data
are made publicly available. (a)At redshift z > 4.5, the massive
galaxy population (
) is dominated by disturbed morphologies (~70%) –
even in the optical rest frame – and very compact objects (~30%) with
effective radii smaller than ~500pc. This confirms that a significant
fraction of the star formation at cosmic dawn occurs in very dense
regions, although the stellar mass for these systems could be
overestimated.(b)Galaxies with Hubble-type morphologies – including
bulge and disk-dominated galaxies – arose rapidly around
and dominate the
morphological diversity of massive galaxies as early as
. (c)Using stellar
bars as a proxy, we speculate that stellar disks in massive galaxies
might have been common (>50%) among the star-forming population since
cosmic noon (
-2.5) and formed as
early as
(d)Massive quenched
galaxies are predominantly bulge-dominated from z~4 onward, suggesting
that morphological transformations briefly precede or are simultaneous
to quenching mechanisms at the high-mass end. (e) Low-mass (
) quenched galaxies are typically disk-dominated,
pointing to different quenching routes in the two ends of the stellar
mass spectrum from cosmic dawn.
, which
is steeper than self similarity in this mass regime. When comparing with
other measurements of the LM relation, we find evidence for a steepening
of the slope in the low mass regime, likely due to the impact of
non-gravitational processes. Our approach can be translated to eROSITA
data using multi-wavelength surveys to constrain the X-ray properties of
galaxy groups in the limits of high redshift and low mass.
. In this paper,
we identify F200W-dropout objects in the Cosmic Evolution Early Release
Science (CEERS) survey which are absent from existing catalogs. Our
selection method can effectively identify obscured low-mass (
) objects at
, massive
dust-rich sources up to
, and
ultra-high-redshift (
) candidates.
Primarily relying on NIRCam photometry from the latest CEERS data
release and supplementing with Mid-Infrared/(sub-)mm data when
available, our analysis pipeline combines multiple SED-fitting codes,
star formation histories, and CosMix - a novel tool for astronomical
stacking. Our work highlights three
dusty dwarf
galaxies which have larger masses compared to the typical dusty dwarfs
previously identified in CEERS. Additionally, we reveal five faint
sources with significant probability of lying above
, with best-fit
masses compatible with
CDM and a standard baryons-to-star
conversion efficiency. Their bi-modal redshift probability distributions
suggest they could also be
dwarf galaxies
with extreme dust extinction. We also identify a strong line emitter
galaxy at
mimicking the
near-infrared emission of a
galaxy. Our
sample holds promising candidates for future follow-ups. Confirming
ultra high-redshift galaxies or lower-z dusty dwarfs will offer valuable
insights into early galaxy formation, evolution with their central black
holes and the nature of dark matter, and/or cosmic dust production
mechanisms in low-mass galaxies, and will help us to understand
degeneracies and contamination in high-z object searches.
-emitting galaxies up to about redshift
two. This ambitious project seeks to elucidate the nature of dark energy
by mapping the 3-dimensional clustering of galaxies over a significant
portion of the sky. This paper presents the methodology and software
developed for estimating the 3-dimensional 2-point correlation function
within the Euclid Science Ground Segment. The software is designed to
overcome the significant challenges posed by the large and complex
Euclid data set, which involves millions of galaxies. Key challenges
include efficient pair counting, managing computational resources, and
ensuring the accuracy of the correlation function estimation. The
software leverages advanced algorithms, including kd-tree, octree, and
linked-list data partitioning strategies, to optimise the pair-counting
process. The implementation also includes parallel processing
capabilities using shared-memory open multi-processing to further
enhance performance and reduce computation times. Extensive validation
and performance testing of the software are presented. The results
indicate that the software is robust and can reliably estimate the
2-point correlation function, which is essential for deriving
cosmological parameters with high precision. Furthermore, the paper
discusses the expected performance of the software during different
stages of the Euclid Wide Survey observations and forecasts how the
precision of the correlation function measurements will improve over the
mission’s timeline, highlighting the software’s capability to handle
large data sets efficiently.
pixels, each
), high quantum
efficiency, high frame rates, and a correlated multi-sampling mode that
achieves low read noise. We performed a suite of bench-top and on-sky
tests to characterize this sensor and analyze its suitability for use in
astronomical instruments. This paper presents measurements of linearity,
conversion gain, read noise, dark current, quantum efficiency, image
lag, and crosstalk. We found that the sensor exhibits nonlinear response
below 5% of saturation. This nonlinearity is plausibly attributable to
the trapping of electrons in each pixel. We developed and implemented a
pixel-by-pixel nonlinearity correction, enabling accurate photometric
measurements across the dynamic range. After implementing this
correction, operating in the correlated multi-sampling mode, the sensor
achieved an effective read noise of
and dark current of
at
. The
quantum efficiency exceeded 50% from 250 nm to 800 nm, peaking at 89% at
600 nm. We observed significant optical crosstalk between the pixels,
likely caused by photoelectron diffusion. To demonstrate the sensor’s
astronomical performance, we mounted it on the WINTER 1m telescope at
Palomar Observatory. These tests confirmed that the linearity
calibration enables accurate stellar photometry and validated our
measured noise levels. Overall, the COSMOS-66 delivers similar noise
performance to large-format CCDs, with higher frame rates and relaxed
cooling requirements. If pixel design improvements are made to mitigate
the nonlinearity and crosstalk, then the camera may combine the
advantages of low-noise CMOS image sensors with the integration
simplicity of large-format CCDs, broadening its utility to a host of
astronomical science cases.
in at least one filter. This sample
includes 13, 3, and 2 AGN candidates at redshifts
, when the Universe
was
~Myr old.
After variability and luminosity function (down to
mag) completeness corrections, we estimate the
co-moving number density of SMBHs,
. At
,
. At low-
our observations are sensitive to AGN
fainter than
mag, and we estimate
. We discuss how these results place strong
constraints on a variety of SMBH seeding theories.
scatter. Conversely, stellar metallicity and age
estimates are, as expected, less robust, but still contain significant
information which originates from underlying correlations at a sub-kpc
scale between stellar mass surface density and stellar population
properties.
to
using
mass-limited angular clustering measurements in the 0.54 deg
of the COSMOS-Web survey. This study
provides the first measurements of the mass-limited two-point
correlation function at
and a consistent
analysis spanning 13.4 Gyr of cosmic history, setting new benchmarks for
future simulations and models. Using a halo occupation distribution
(HOD) framework, we derive characteristic halo masses and the
stellar-to-halo mass relationship (SHMR) across redshifts and stellar
mass bins. Our results first indicate that HOD models fit data at
best when
incorporating a non-linear scale-dependent halo bias, boosting
clustering at non-linear scales (r = 10-100 kpc). We find that galaxies
at z > 10.5 with
are
hosted by halos with
,
achieving a star formation efficiency (SFE) $M_/ (f_b M_{}) $ up to 1
dex higher than at
. The high galaxy
bias at
suggests that these
galaxies reside in massive halos with intrinsic high SFE. Our SHMR
evolves significantly with redshift, starting high at
, decreasing
until
, then
increasing again until the present. Current simulations fail to
reproduce both massive high-
galaxies and this evolution, while
semi-empirical models linking SFE to halo mass, accretion rates, and
redshift align with our findings. We propose that
galaxies
experience bursty star formation without significant feedback altering
their growth, driving the rapid growth of massive galaxies observed by
JWST. Over time, increasing feedback efficiency and exponential halo
growth suppress star formation. At
and
after, halo growth slows down while star formation continues, supported
by gas reservoirs in halos.
and up to a few
tens of members are the most common galaxy environment, marking the
transition between field and massive clusters. Identifying groups plays
a crucial role in understanding structure formation and galaxy
evolution. Modern deep surveys allow us to build well-characterized
samples of groups up to the regime where structures were taking shape.
We aimed to build the largest deep catalog of galaxy groups to date over
the COSMOS-Web field effective area of 0.45 deg
, leveraging the deep high quality data
of the new COSMOS-Web photometric catalog resulted from the James Webb
Space Telescope observations of the COSMOS-Web field. We performed the
group search with the AMICO algorithm, a linear matched filter based on
an analytical model for the group signal. AMICO has already been tested
in wide and deep field surveys, including COSMOS data up to
. In this work, we tested
the algorithm performances at even higher redshift and searched for
protocluster cores at
. We compiled a list
of known protoclusters in COSMOS at
, matched them with our detections and studied the
clustering of the detected cores. We estimated purity and completeness
of our sample by creating data-driven mocks with the SinFoniA code and
linked signal-to-noise to purity. We detected 1678 groups in the
COSMOS-Web field up to
, including lists of
members extending nearly two magnitudes deeper than the previous
AMICO-COSMOS catalog. 756 groups were detected with purity of 80%. More
than 500 groups have their redshift confirmed by assigning spectroscopic
counterparts. This group catalog offers a unique opportunity to explore
galaxy evolution in different environments spanning $$12 Gyr and to
study groups, from the least rich population to the formation of the
most massive clusters.
(w0, wa) contour, and
we conclude that the cosmic shear is relatively insensitive to the
binning methodology. We find that the information gain extracted on (w0,
wa) for any 3x2pt component starts to saturate at
7-8 bins. Any
marginal gains resulting from a greater number of bins is likely to be
limited by additional uncertainties present in a real measurement, and
the increasing demand for accuracy of the covariance matrix. Finally, we
consider a 5% contamination from catastrophic photometric redshift
outliers and find that, if these errors are not mitigated in the
analysis, the bias induced in the 3x2pt signal for 10 equipopulated bins
results in dark energy constraints that are inconsistent with the
fiducial LambdaCDM cosmology at
.
pseudo-color. We also derive metallicity
dispersions (
) for
the P1 and P2 stars of each GC. In all but three GCs, we measure a
significant correlation between the metallicity and the
pseudo-color of the P1 stars such that stars with
larger
have higher metallicities. We measure metallicity
spreads that range from 0.03 to 0.24 dex and correlate with the GC
masses. As for the intrinsic metallicity dispersions, when combining the
P1 and P2 stars, we measure values ranging from 0.02 dex to 0.08 dex
that correlate very well with the GC masses. We compared the metallicity
dispersion among the P1 and P2 stars and found that the P2 stars have
metallicity dispersions that are smaller or equal to that of the P1
stars. We find that both the metallicity spreads of the P1 stars (from
the
spread in the chromosome maps) and the
metallicity dispersions (
)
correlate with the GC masses, as predicted by some theoretical
self-enrichment models presented in the literature.
galaxies. Using
public data from JWST/NIRCam (COSMOS-Web) and ALMA (FMOS-COSMOS), we
study a sample of 32 massive (
) main-sequence galaxies at
with
resolution. We create composite morphological models consisting of
bulge, disk, and clumps to fully ‘deconstruct’ the galaxy images. With
the resulting measurements of the flux and size of these components, we
find the following: (I)The combined contribution of clumps is
towards the net star
formation rate (SFR) of the host while contributing
to its stellar mass.
The clumps show a correlation between their stellar mass and SFR, but
have an increased specific-SFR (sSFR) relative to the star-forming main
sequence, with offsets ranging from
. They
feature star formation surface densities of
,
consistent with values observed in local star-forming and starburst
galaxies. (II)The clumps span a large range of characteristic sizes
(
) and stellar masses (
). We
estimate a mass-size relation (
) along with a stellar mass function (slope,
),
both suggesting a hierarchical nature similar to that expected in
star-forming regions in local galaxies. (III)Our measurements agree with
the properties of stellar clumps in
lensed systems,
bridging the gap between lensed and unlensed studies by detecting
structures at sub-kpc scales.(IV)Clumps are found to be preferentially
located along spiral features visible primarily in the residual
rest-frame near-IR images. In conclusion, we present an
observation-based, coherent picture of star-forming clumps at
.
and a mass of
. TOI-5786 b is
similar to Saturn with a radius of
and a mass of
. The host star
for TOI-5108 b is a moderately bright (Vmag 9.75) G-type star. TOI-5786
is a slightly dimmer (Vmag 10.2) F-type star. Both planets are close to
their host stars with periods of 6.75 days and 12.78 days respectively.
This puts TOI-5108 b just inside the bounds of the Neptune desert while
TOI-5786 b is right above the upper edge. We estimate hydrogen-helium
envelope mass fractions of
for TOI-5108 b and $74
% $ for TOI-5786 b. However, using a model for the interior structure
that includes tidal effects the envelope fraction of TOI-5108 b could be
much lower (
) depending
on the obliquity. We estimate mass-loss rates between 1.0 *
g/s and 9.8 *
g/s for TOI-5108 b and
between 3.6 *
g/s and 3.5 *
g/s for TOI-5786 b. Given
their masses, this means that both planets are stable against
photoevaporation. We also detect a transit signal for a second planet
candidate in the TESS data of TOI-5786 with a period of 6.998 days and a
radius of
. Using our RV
data and photodynamical modeling, we are able to provide a 3-
upper limit of 26.5
for the mass of
the potential inner companion to TOI-5786 b.
of the sky in visible and
near-infrared wavelengths, mapping the extra-galactic sky to constrain
our cosmological model of the Universe. Although the survey focusses on
regions further than 15 deg from the ecliptic, it should allow for the
detection of more than about
Solar System objects
(SSOs). After simulating the expected signal from SSOs in Euclid images
acquired with the visible camera (VIS), we describe an automated
pipeline developed to detect moving objects with an apparent velocity in
the range of 0.1-10 arcsec/h, typically corresponding to sources in the
outer Solar System (from Centaurs to Kuiper-belt objects). In
particular, the proposed detection scheme is based on Sourcextractor
software and on applying a new algorithm capable of associating moving
objects amongst different catalogues. After applying a suite of filters
to improve the detection quality, we study the expected purity and
completeness of the SSO detections. We also show how a Kohonen
self-organising neural network can be successfully trained (in an
unsupervised fashion) to classify stars, galaxies, and SSOs. By
implementing an early-stopping method in the training scheme, we show
that the network can be used in a predictive way, allowing one to assign
the probability of each detected object being a member of each
considered class.
. Unlike in the
local Universe, the origin and the consequence of spirals at this epoch
remain unexplored. We use public JWST/NIRCam data from the COSMOS-Web
survey to map spiral structures in eight massive (
)
star-forming galaxies at
. We present a method for systematically
quantifying spiral arms at
, enabling direct
measurements of flux distributions. Using rest-frame near-IR images, we
construct morphological models accurately tracing spiral arms. We detect
offsets (
) between the rest-frame optical and near-IR flux
distributions across most arms. Drawing parallels to the local Universe,
we conclude that these offsets reflect the presence of density waves.
For nine out of eighteen arms, the offsets indicate spiral shocks
triggered by density waves. Five arms have offsets in the opposite
direction and are likely associated with tidal interactions. For the
remaining cases with no detected offsets, we suggest that stochastic
‘clumpy’ star formation is the primary driver of their formation. In
conclusion, we find a multi-faceted nature of spiral arms at
, similar to that
in the local Universe.
for the young energetic pulsar J0537-6910, while
the lowest constraint on the ellipticity is
for the bright nearby millisecond pulsar
J0437-4715. Additionally, for a subset of 16 targets we performed a
narrowband search that is more robust regarding the emission model, with
no evidence of a signal. We also found no evidence of non-standard
polarizations as predicted by the Brans-Dicke theory.
) radial
distributions based on total-power HI images obtained by FAST in the
FEASTS program, for 35 galaxies with inclinations lower than 72 degree.
We derive the HI radius
, which is the
radius for the 0.01
(
) iso-density level, 100 times deeper than the 1
level previously commonly used to measure
. The profile shapes show a large
diversity at a given radius in units of kpc, group virial radius, and
, but align more tightly with radius
normalized by
. The universal HI
profile has a scatter of
dex, and a
scale-length of
in
the outer region. We derive a new
-
relation,
which has a scatter of 0.02 dex, and similar slope of $$0.5 as the
previously known
-
relation.
Excluding strongly tidal-interacting galaxies, the ratio
(anti-)correlate strongly and significantly with the HI-to-stellar mass
ratio and sSFR, but not with the stellar mass,
, dark matter
mass, or SFR. The strongly tidal-interacting galaxies tend to show
deviations from these trends, and have the most flattened profiles.
These results imply that in absence of major tidal interactions,
physical processes must cooperate so that
distributes
in a self-similar way in the outer region down to the 0.01
level. Moreover, they may drive gas flows in such
a way, that HI-richer galaxies have HI disks not only extend further,
but also transport HI inward more efficiently from
to
.